In Vivo Anti-Leukemia, Quantum Chemical Calculations and ADMET Investigations of Some Quaternary and Isothiouronium Surfactants
Abstract
:1. Introduction
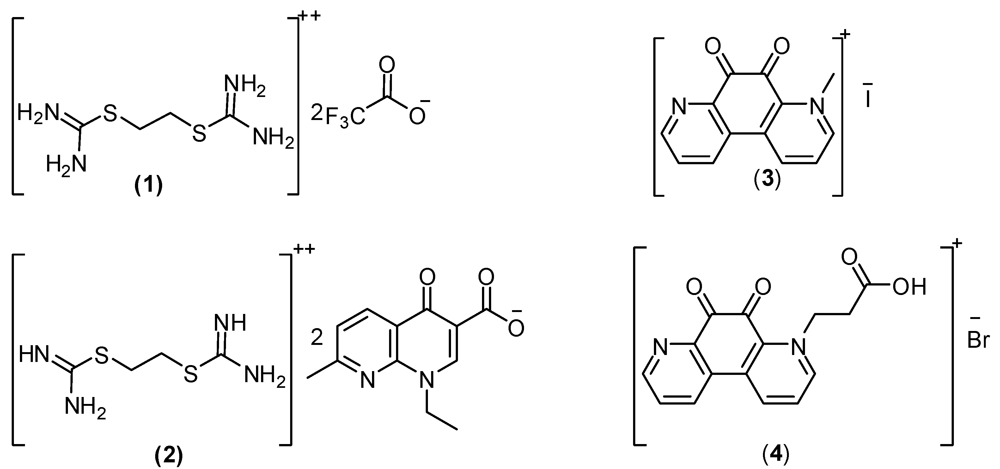
2. Result and Discussion
2.1. Surface Parameter Results for the Prepared Isothornium Salts Surfactants
2.1.1. CMC of the Prepared Surfactants
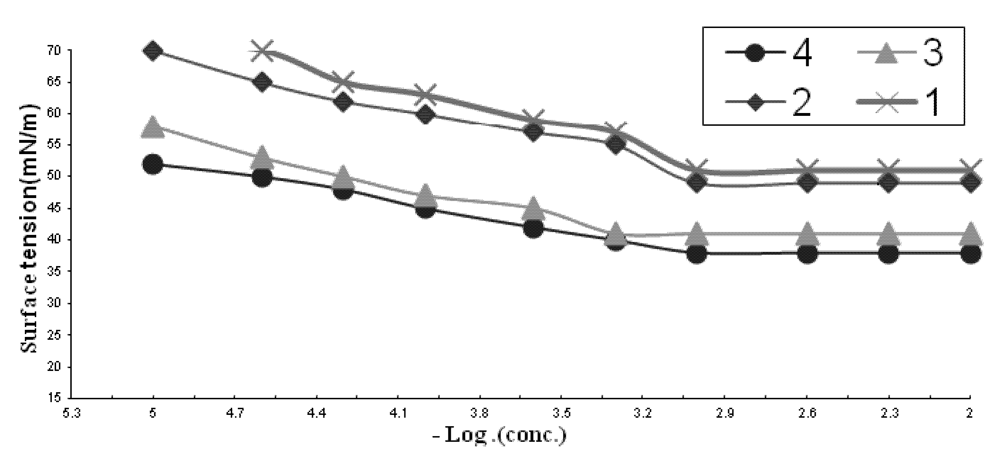
| Comp. | CMC X 10−3 | γCMC (mN/m) | ΠCMC (mN/m) | PC20 (Mole/L) | Γmax X 10−11 (Mole/cm2) | A min (nm2) | Δ Gads | Δ Gmic |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.3 | 51 | 21 | 3.0 | 6.9 | 2.3 | −36 | −33 |
| 2 | 1.05 | 49 | 23 | 3.2 | 6.5 | 2.5 | −37.5 | −33.9 |
| 3 | 0.9 | 41 | 31 | 4.5 | 4.9 | 3.3 | −41 | −34.7 |
| 4 | 0.6 | 38 | 34 | 5.0 | 4.5 | 3.6 | −44 | −36.4 |
2.1.2. Effectiveness (Πcmc)
2.1.3. Efficiency (PC20)
2.1.4. Maximum Surface Excess (Γmax)
2.1.5. Minimum Area per Molecule (Amin)
2.1.6. The Standard Free Energies of Micellization (ΔGomic) and Adsorption (ΔGoads)
2.2. Anti-Cancer Screening
| Compds. | Dose (µg/kg.) | ILS % * |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 400 | 0 |
| 200 | 100 | |
| 100 | 100 | |
| 2 | 400 | 0 |
| 200 | 91 | |
| 100 | 99 | |
| 3 | 400 | 0 |
| 200 | 105 | |
| 100 | 120 | |
| 4 | 400 | 61 |
| 200 | 107 | |
| 100 | 114 |
2.3. Molecular Modeling
| CPD | HF | E | Es | ZPE | S° | CV° | H° | G° |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | −458.26 | −407.84 | −43.58 | 1601.57 | 462.36 | 236.63 | 0.155427819 | −0.207933 |
| 2 | −376.38 | −446.96 | −70.57 | 628.37 | 516.22 | 296.04 | 0.112537693 | 0.0539166 |
| 3 | −1835.03 | −1914.11 | −79.08 | 514.11 | 606.16 | 385.66 | −0.436475908 | −0.505311 |
| 4 | −508.01 | −628.05 | −45.80 | 602.05 | 857.66 | 697.30 | 0.452964763 | 0.3555698 |
| CPD | HOMO | LUMO | HLG | IP | ESP | µ | χ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | −10.21 | −2.31 | 7.9 | 299.90 | 77.90 | 6.04 | 3.95 |
| 2 | −8.66 | −1.32 | 7.34 | 51.61 | −285.32 | 5.74 | 3.67 |
| 3 | −8.03 | −1.95 | 6.08 | 43.46 | −448.58 | 9.84 | 3.04 |
| 4 | −8.77 | −1.51 | 7.26 | 42.94 | −279.41 | 7.97 | 3.63 |
2.3.1. Energy Features
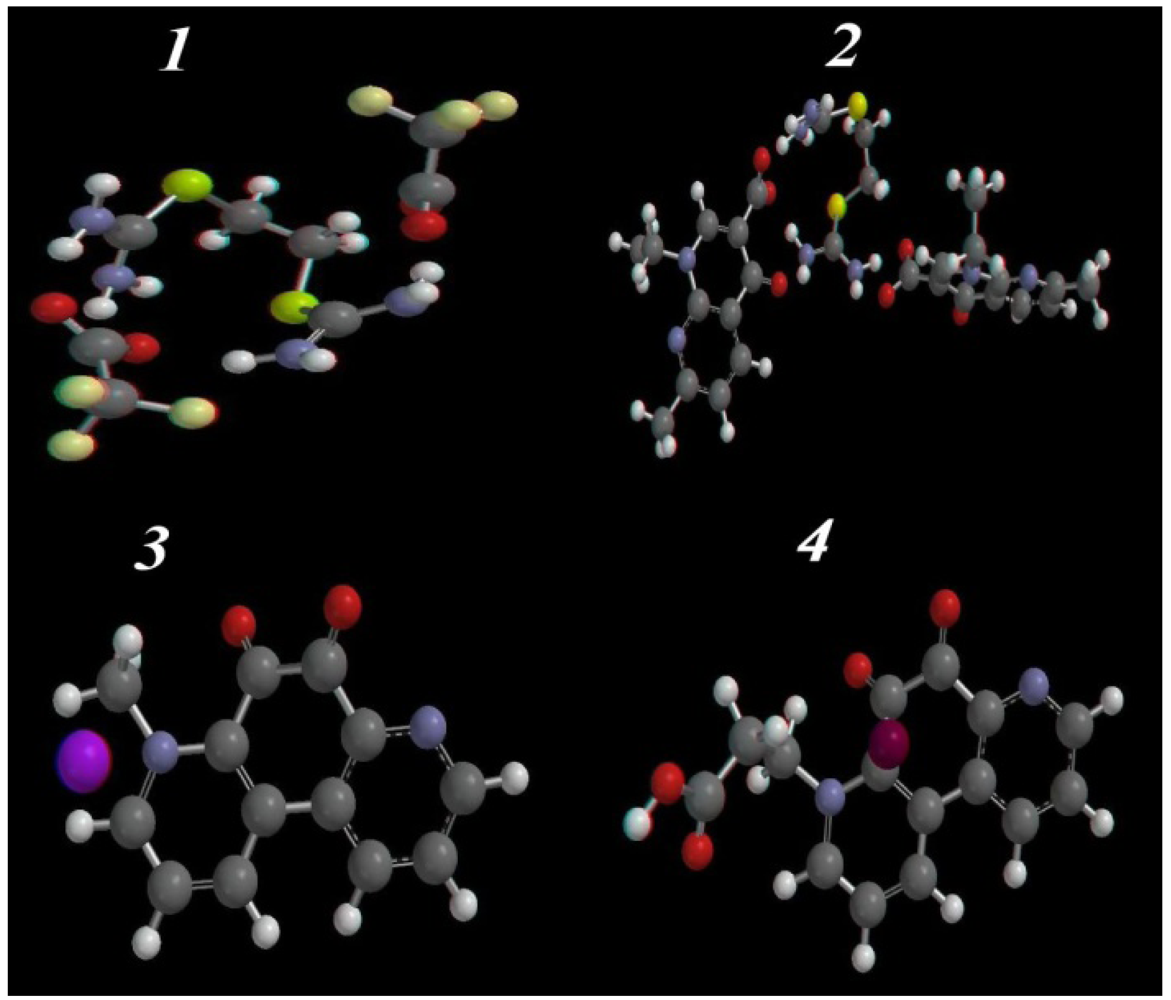
2.3.2. Optimized Geometry
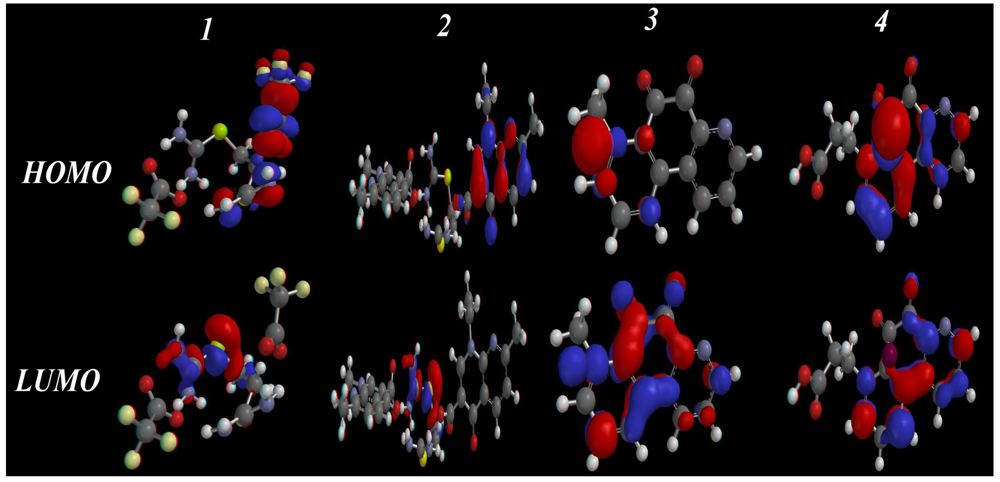
2.3.3. HOMO-LUMO and Dipole Moments Analysis
2.3.4. Flexible Alignment

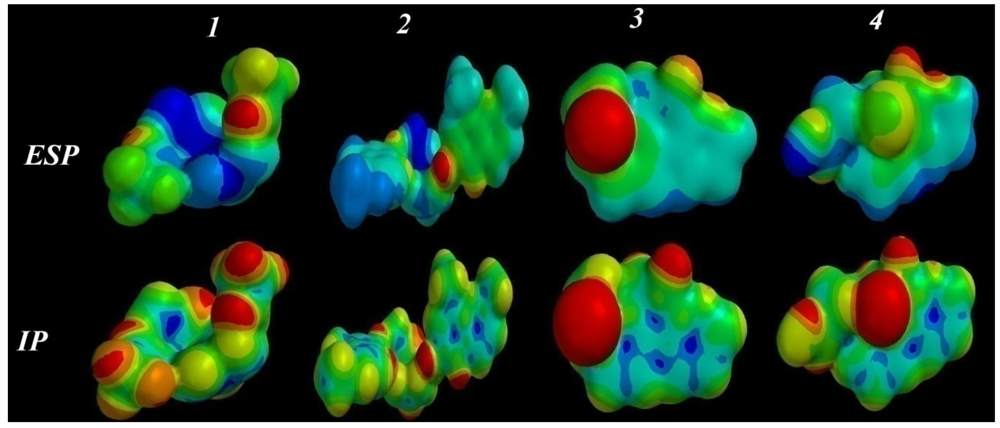
2.3.5. Electrostatic (ESP) and Ionization Potential (IP) Map
2.4. ADMET Factor Profiling
| CPD | Mwt | TPSA | %ABS | V | LogP | HBD | HBA | Lip-V |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 408.344 | 187.58 | 44.2849 | 255.875 | 1.58 | 4 | 8 | 0 |
| 2 | 642.76 | 249.88 | 22.7914 | 658.961 | 2.27 | 4 | 14 | 2 |
| 3 | 352.13 | 50.88 | 91.4464 | 265.068 | 2.83 | 0 | 4 | 0 |
| 4 | 363.16 | 88.50 | 78.4675 | 307.261 | 2.035 | 1 | 6 | 0 |
2.5. Pharmacophore Prediction
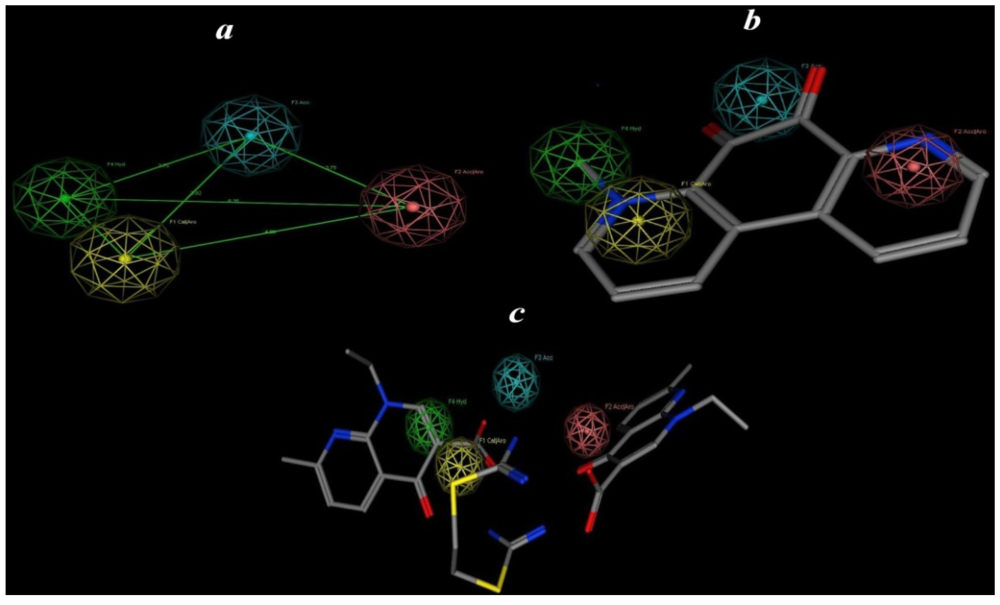
| Pharmacophoric features | Structure features |
|---|---|
| F1: Aro/Cat | Pyridinyl |
| F2: Aro/Acc | Alkyl pyridinyl |
| F3: Acc | CO |
| F4: Hydro | Alkyl |
3. Experimental
3.1. Surface Active Properties Evaluation Methods
3.1.1. Surface Tension Measurements
3.1.2. Efficiency (PC20)
3.1.3. Effectiveness (Πcmc)
3.1.4. Determination of Critical Micelle Concentration
3.1.5. Maximum Surface Excess Γmax

3.1.6. Minimum Surface Area (Amin)

3.1.7. The Standard Free Energies of Micellization ΔGomic and Adsorption ΔGoads
3.2. Anticancer Screening against Leukemia L-1210
3.3. Molecular Modeling
3.3.1. Computational Details
3.3.2. Conformational Search and Flexible Alignment
4. Conclusions
References
- Balunas, M.J.; Kinghorn, A.D. Drug Discovery from medicinal plants. Life Sci. 2005, 78, 431–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkin, D.M. Global cancer statistics in the year 2000. Lancet Oncol. 2001, 2, 533–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tait, A.; Gamberini, G.; Giovannini, M.G.; di Bella, M. S-aryl (tetramethyl) isothiouronium salts as possible antimicrobial agents, IV. Farmaco 1989, 44, 1129–1140. [Google Scholar]
- Tait, A.; Gamberini, G.; Giovannini, M.G.; di Bella, M. S-aryl (tetramethyl) isothiouronium salts as possible antimicrobial agents, III. Farmaco 1988, 43, 979–988. [Google Scholar]
- Trani, A.; Ferrari, P.; Pallanza, R.; Ciabatti, R. Thioureas and isothiouronium salts of the aglycone of teicoplanin. I. Synthesis and biological activity. J. Antibiot. (Tokyo) 1989, 42, 1268–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manez, R.M.; Sancenon, F. Fluorogenic and chromogenic chemosensors and reagents for anions. Chem. Rev. 2003, 103, 4419–4476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manez, R.M.; Sancenon, F. New advances in fluorogenic anion chemosensors. J. Fluoresc. 2005, 15, 267–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatachalam, T.K.; Vassilev, A.O.; Benyunov, A.; Grigoriants, O.; Tibbles, H.E.; Uckun, F.M. Stereochemistry as a Determinant of the Anti-Leukemic Potency of Halopyridyl and Thiazolyl Thiourea Compounds. Lett. Drug Des. Discov. 2007, 4, 318–326. [Google Scholar]
- Manjula, S.N.; Noolvi, N.M.; Parihar, K.V. Synthesis and antitumor activity of optically active thiourea and their 2-aminobenzothiazole derivatives: A novel class of anticancer agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 44, 2923–2929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatachalam, T.K.; Mao, C.; Uckun, F.M. Effect of stereochemistry on the anti-HIV activity of chiral thiourea compounds. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2004, 12, 4275–4284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, R.; Kaschula, C.H.; Parker, I.M.; Caira, M.R.; Richards, P.; Travis, S.; Taute, F.; Qwebani, T. Substituted ajoenes as novel anti-cancer agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2008, 18, 5277–5279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubo, Y.; Ishihara, S.; Tsukahara, M.; Tokita, S. Isothiouronium-derived simple fluorescent chemosensors of anions. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 2 2002, 2002, 1455–1460. [Google Scholar]
- Kubo, Y.; Kato, M.; Misawa, Y.; Tokita, S. A fluorescence-active 1,3-bis(isothiouronium)-derived naphthalene exhibiting versatile binding modes toward oxoanions in aqueous MeCN solution: New methodology for sensing oxoanions. Tetrahedron Lett. 2004, 45, 3769–3773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubo, Y.; Tsukahara, M.; Ishihara, S.; Tokita, S. A simple anion chemosensor based on a naphthalene-thiouronium dyad. Chem. Commun. 2000, 2000, 653–654. [Google Scholar]
- Nishizawa, S.; Cui, Y.Y.; Minagawa, M.; Morita, K.; Kato, Y.; Taniguchi, S.; Kato, R.; Teramae, N. Conversion of thioureas to fluorescent isothiouronium-based photoinduced electron transfer sensors for oxoanion sensing. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 2 2002, 2002, 866–870. [Google Scholar]
- Yeo, W.S.; Hong, J.I. Thiouronium-thymine conjugate as a new carrier for selective transport of 5'-AMP. Tetrahedron Lett. 1998, 22, 3769–3772. [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava, S. Electrodeposition of Copper Metal in Presence of Organic Solvents. Ph.D. Thesis, Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi, India, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Yeo, W.S.; Hong, J.I. Oxoanion recognition by a thiouronium receptor. Tetrahedron Lett. 1998, 39, 8137–8140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badawi, A.M.; Seliem, V.R.; Haroun, B.; Solima, H. Isothironium salts of potential biological activity. Oriental J.Chem. 1988, 4, 107–118. [Google Scholar]
- Profeta, S.; Allinger, N.L. Molecular mechanics calculations on aliphatic amines. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1985, 107, 1907–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halgren, T.A. Merck molecular force field I. Basis, form, scope, parameterization, and performance of MMFF94. J. Comput. Chem. 1996, 17, 490–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spartan 08, Software; Wavefunction Inc.: Irvine, CA, USA, 2008.
- Stewart, J.J.P. MOPAC Manual. J. Comput. Chem. 1989, 10, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauk, A. Orbital Interaction Theory of Organic Chemistry, 2nd ed; Wiley Interscience: New York, NY, USA, 2001; p. 86. [Google Scholar]
- Streitwieser, A., Jr. Molecular Orbital Theory for Organic Chemists; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1961. [Google Scholar]
- Fleming, I. Frontier Orbitals and Organic Chemical Reactions; John Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Fukui, K. Role of Frontier Orbitals in Chemical Reactions. Science 1982, 218, 747–754. [Google Scholar]
- Computational Chemistry (MOE 2009.10). Computing Group Inc: Montreal, Canada, 2009.
- Sjoberg, P.; Murray, J.S.; Brinck, T.; Politzer, P. Average local ionization energies on the molecular surfaces of aromatic systems as guides to chemical reactivity. Can. J. Chem. 1990, 68, 1440–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Politzer, P.; Murray, J.S.; Concha, M.C. The complementary roles of molecular surface electrostatic potentials and average local ionization energies with respect to electrophilic processes. Int. J. Quant. Chem. 2002, 88, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Abraham, M.H.; Lee, J.; Hersey, A.; Luscombe, N.C.; Beck, G.; Sherborne, B.; Cooper, I. Rate-limited steps of human oral absorption and QSAR studies. Pharm. Res. 2002, 19, 1446–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipinski, C.A.; Lombardo, F.; Dominy, B.W.; Feeney, P.J. Experimental and computational approaches to estimate solubility and permeability in drug discovery and development settings. Adv. Drug. Delivery Rev. 1997, 23, 3–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, D.E.; Pickett, S.D. Computational methods for the prediction of drug-likeness. Drug Discov. Today 2000, 5, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wildman, S.A.; Crippen, G.M. Prediction of Physicochemical Parameters by Atomic Contribution. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 1999, 39, 868–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Findlay, A. Practical Physical Chemistry, 6th ed; Longmans: New York, NY, USA, 1963; pp. 92–101. [Google Scholar]
- Hampson, J.W.; Cosnell, D.G. Surface-tension Properties of Some Poly dispersed Alkyl-Substituted polyoxy-ethylated Phenyl Sulfonamides. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1996, 73, 891–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeshita, T.I.; Shimohara, W.; Maeda, S. Surface-tension Properties of Some Poly dispersed Alkyl-Substituted. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1980, 57, 9430–9435. [Google Scholar]
- Takeshita, T.I.; Shimohara, W.; Maeda, S. A Rapid Synthesis of Fatty Acyl Urea Derivatives. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1982, 59, 90–94. [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharyya, D.N.; Kelkar, R.Y.; Almeida, M.R.; Das, A.K.; Chikhale, S.V. Tenside Surfactants Detergents; Carl Hanser Publisher: Munich, Germany, 1994; Volume 31, p. 260. [Google Scholar]
- Rosen, M.J. Surfactants and Interfacial Phenomena; Johm Wiley and Sons Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Hikota, T.; Merguro, K.J. Surfactants and interfacial phenomena. Jpn. Chem. Soc. 1970, 47, 158. [Google Scholar]
Supplementary Files
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
El-Henawy, A.A.; Khowdiary, M.M.; Badawi, A.B.; Soliman, H.M. In Vivo Anti-Leukemia, Quantum Chemical Calculations and ADMET Investigations of Some Quaternary and Isothiouronium Surfactants. Pharmaceuticals 2013, 6, 634-649. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph6050634
El-Henawy AA, Khowdiary MM, Badawi AB, Soliman HM. In Vivo Anti-Leukemia, Quantum Chemical Calculations and ADMET Investigations of Some Quaternary and Isothiouronium Surfactants. Pharmaceuticals. 2013; 6(5):634-649. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph6050634
Chicago/Turabian StyleEl-Henawy, Ahmed A., Manal M. Khowdiary, Abdelfattah B. Badawi, and Hussein M. Soliman. 2013. "In Vivo Anti-Leukemia, Quantum Chemical Calculations and ADMET Investigations of Some Quaternary and Isothiouronium Surfactants" Pharmaceuticals 6, no. 5: 634-649. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph6050634
APA StyleEl-Henawy, A. A., Khowdiary, M. M., Badawi, A. B., & Soliman, H. M. (2013). In Vivo Anti-Leukemia, Quantum Chemical Calculations and ADMET Investigations of Some Quaternary and Isothiouronium Surfactants. Pharmaceuticals, 6(5), 634-649. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph6050634





