Gut Microbiota-Targeted Intervention of Hyperlipidemia Using Monascus-Fermented Ginseng
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
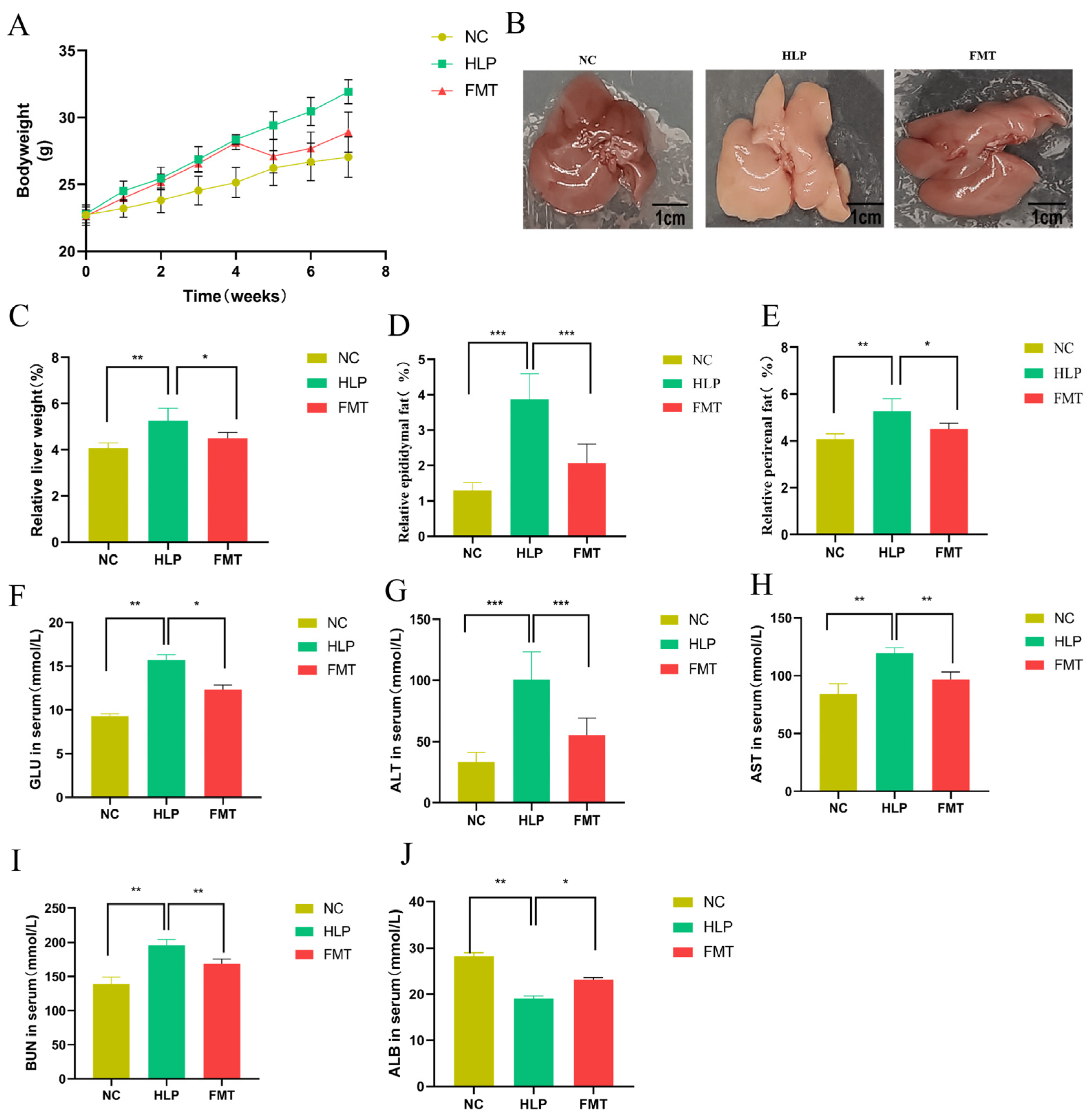
2.1. Effects of FMT on Phenotype and Biochemical Indicator Alterations in Mice
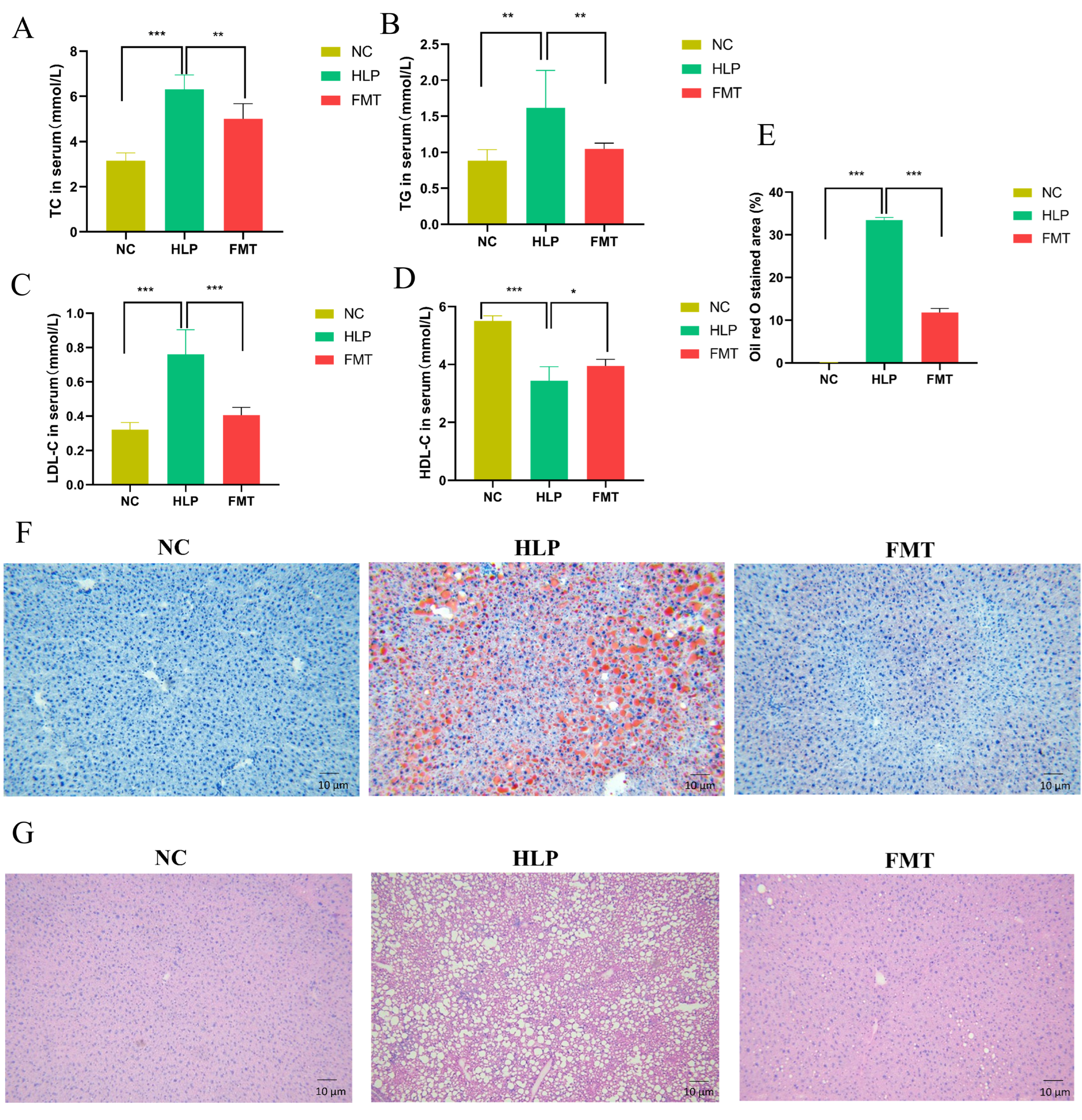
2.2. Effects of FMT on Lipid Accumulation in Mice
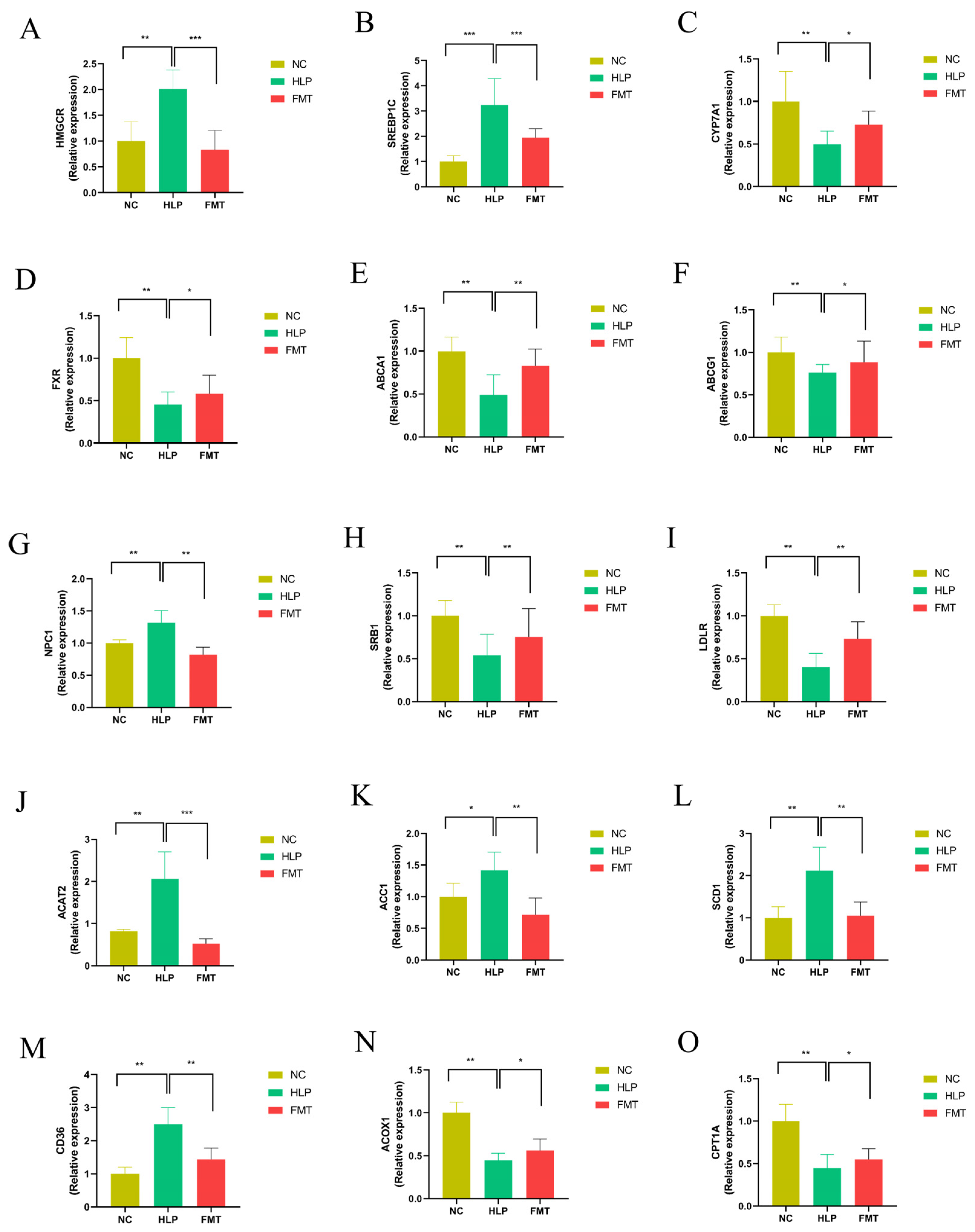
2.3. Effects of FMT on Hepatic Gene Expression Profiles in Mice
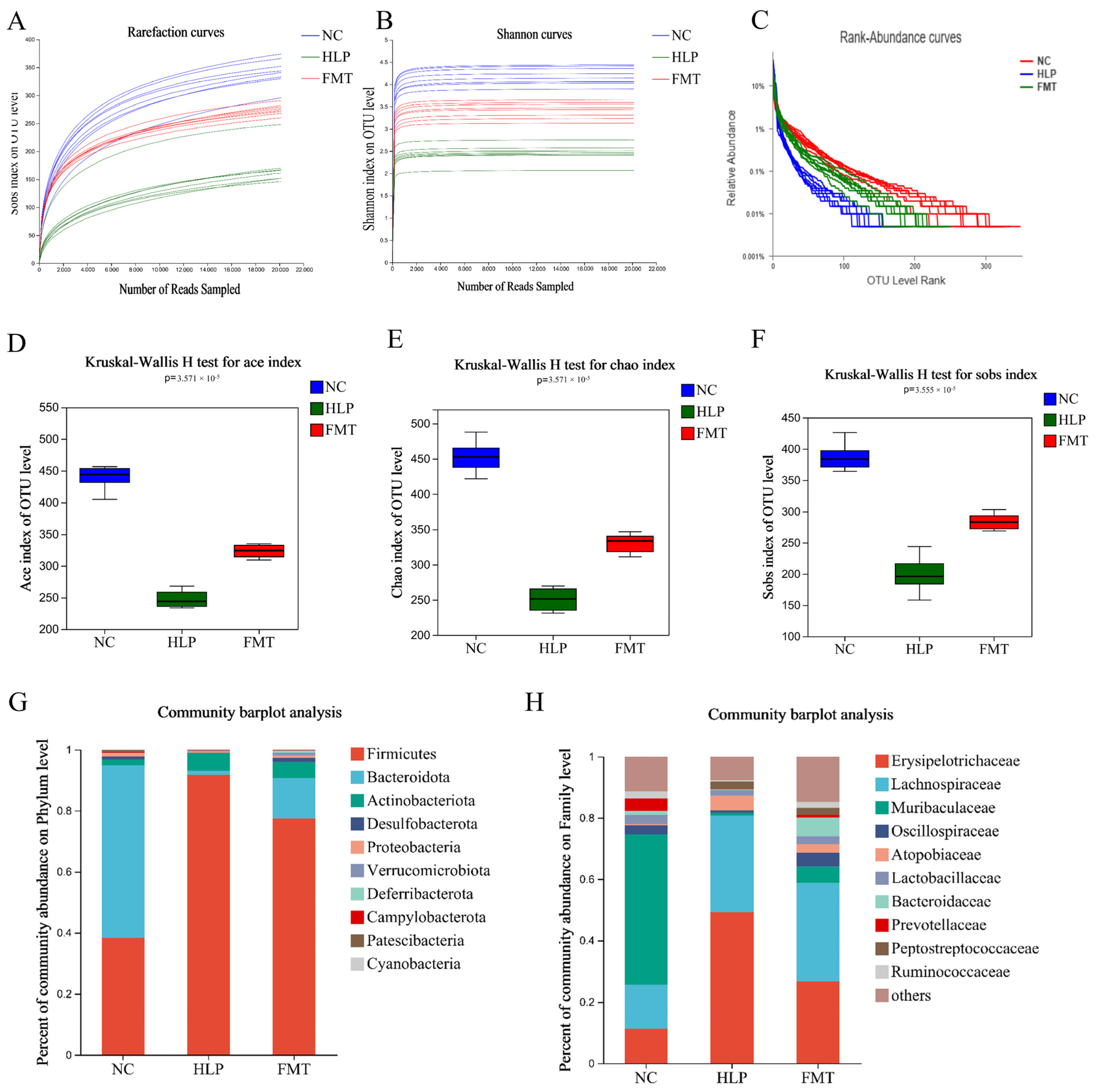
2.4. Effects of FMT on Altered Gut Microbiota in Mice
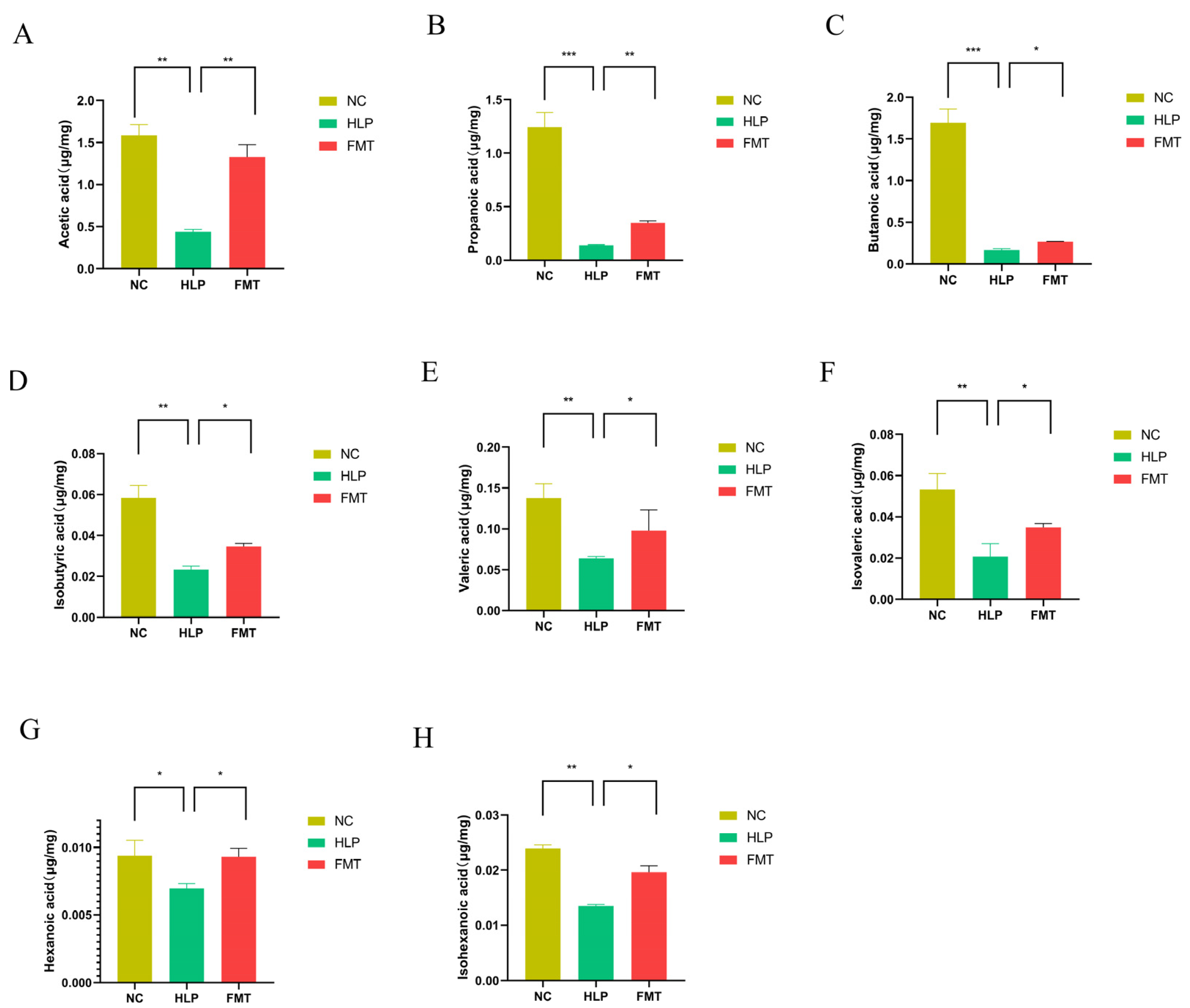
2.5. Effects of FMT on SCFAs Contents in Mice
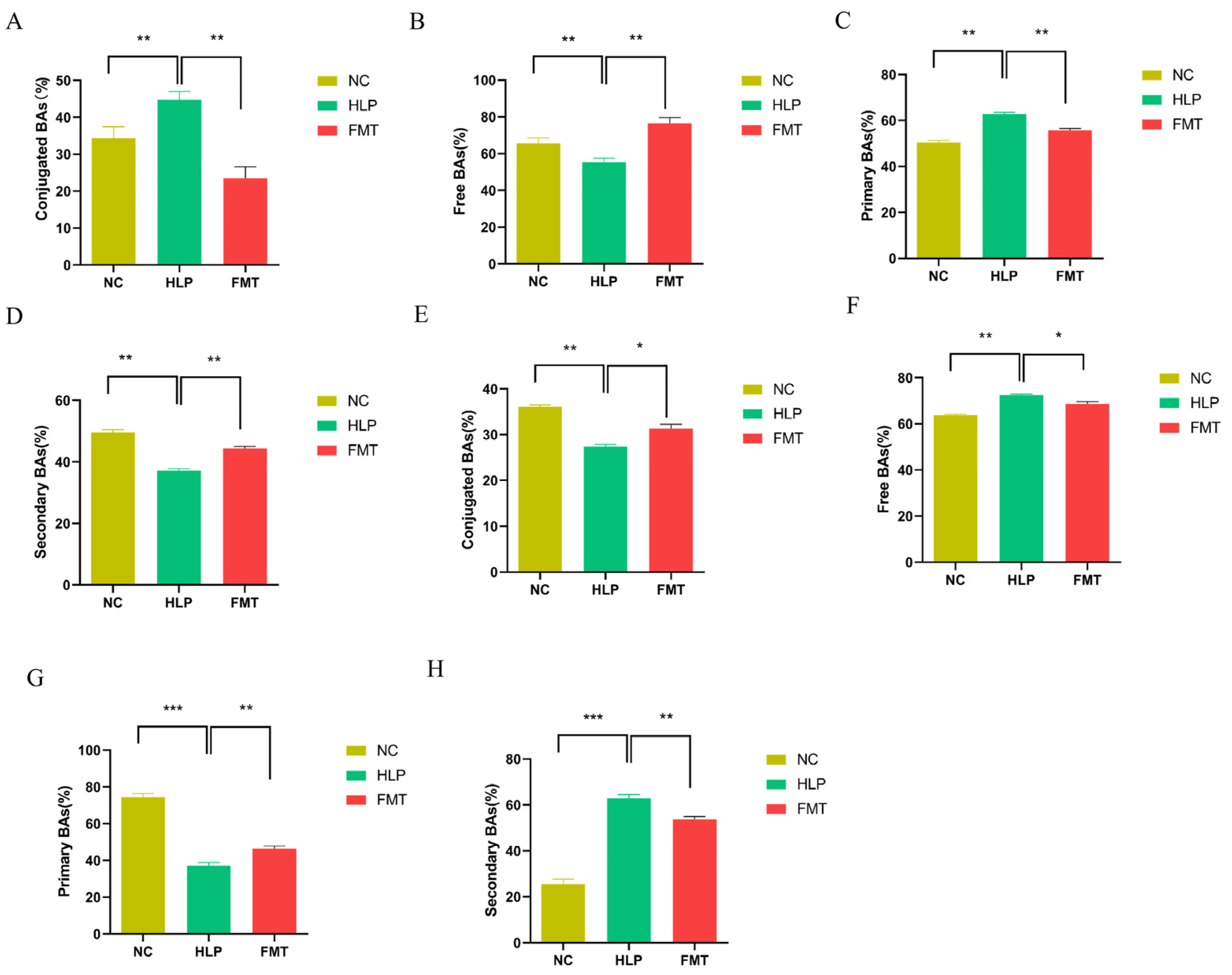
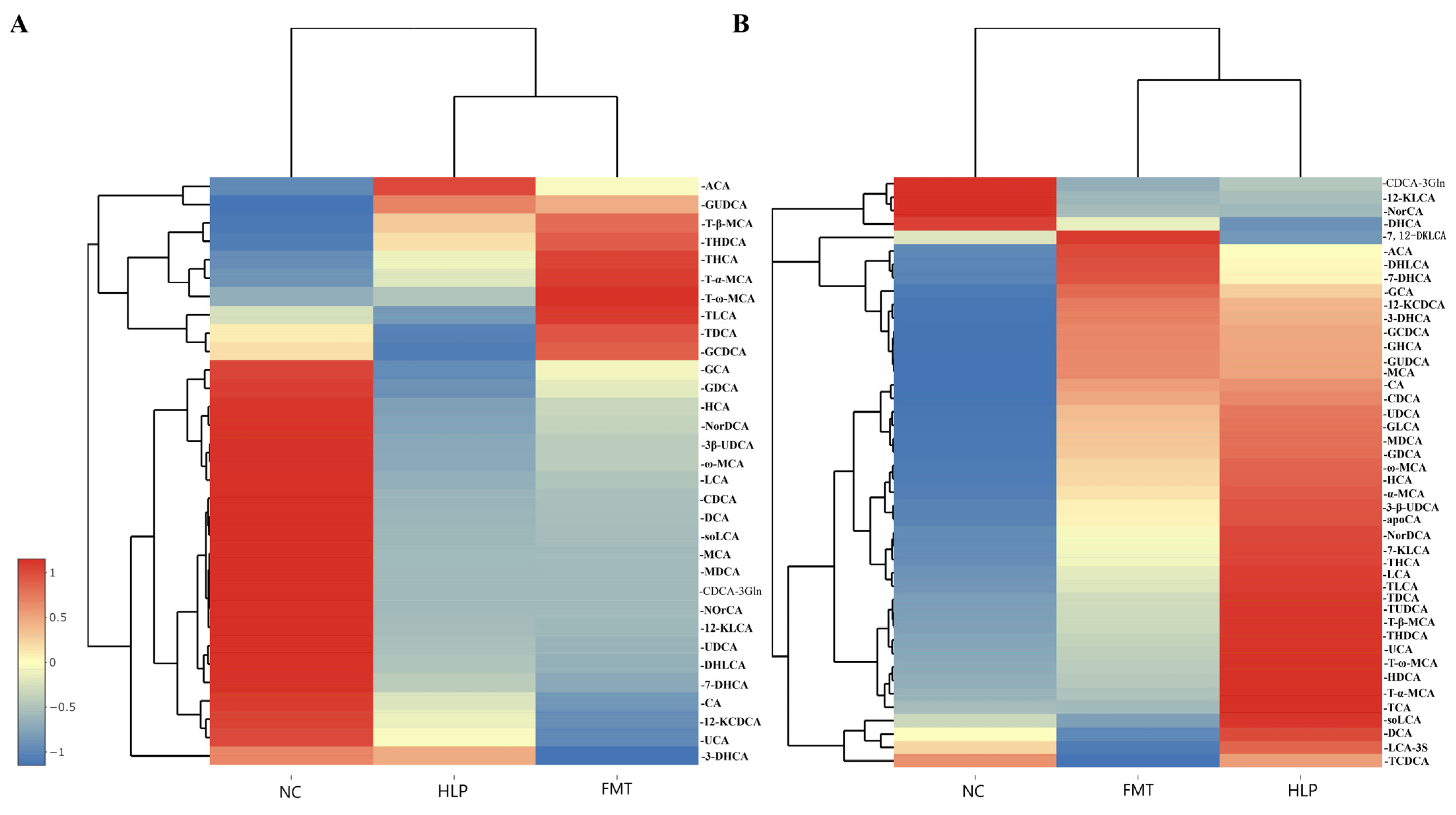
2.6. Effects of FMT on the Regulation of BAs Metabolism in Mice
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
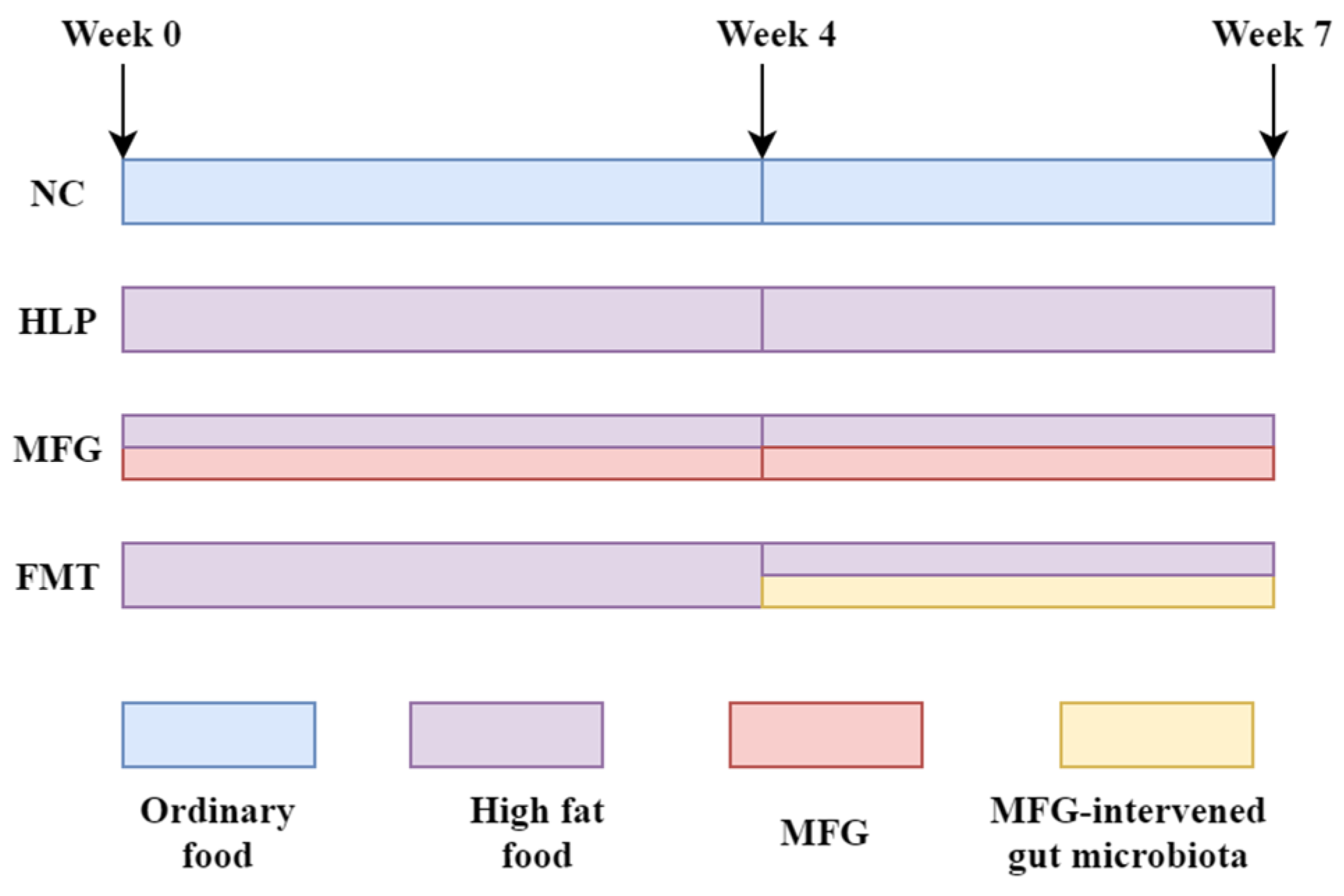
4.2. Animal Experiments
- (1)
- NC group: normal chow diet.
- (2)
- HLP group: HFD (4.2% fat, 20% protein, 52% carbohydrate, 2.3% fiber).
- (3)
- MFG group: HFD + MFG (2 g·kg−1·d−1, oral gavage).
- (4)
- FMT group: HFD + treated with the feces from the mice in the MFG group (daily from week 4).
4.3. Fecal Microbiota Transplantation
4.4. Serum Biochemical Indicators and Staining Analysis
4.5. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (RT-qPCR)
4.6. BAs Analysis
4.7. SCFAs Analysis
4.8. 16S rRNA Sequencing
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HLP | hyperlipidemia |
| MFG | Monascus-fermented ginseng |
| FMT | fecal microbiota transplantation |
| TCM | Traditional Chinese Medicine |
| TC | total cholesterol |
| TG | triglycerides |
| LDL-C | low-density lipoprotein cholesterol |
| HDL-C | high-density lipoprotein cholesterol |
| ALT | alanine aminotransferase |
| AST | aspartate aminotransferase |
| BUN | blood urea nitrogen |
| ALB | albumin |
| GLU | glucose |
| BAs | bile acids |
| SCFAs | short-chain fatty acids |
| HFD | high-fat diet |
| RT-qPCR | Quantitative real-time PCR |
| Hmgcr | hydroxymethylglutarate monoacyl coenzyme A reductase |
| Srebp1c | sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1C |
| Cyp7a1 | 7α-hydroxylase |
| Fxr | farnesol-derived X receptor |
| Abca1 | ATP-binding cassette transporter protein A1 |
| Abcg1 | ATP-binding cassette transporter protein G1 |
| Npc1 | Niemann–Pick type C1 |
| Srb1 | scavenger receptor type B1 |
| Ldlr | low-density lipoprotein receptor |
| Acat2 | acyl coenzyme A–cholesterol acyltransferase 2 |
| Acc1 | acetyl-CoA carboxylase 1 |
| Scd1 | stearoyl-CoA desaturase 1 |
| Cd36 | cluster of differentiation 36 |
| Acox1 | Acyl-CoA oxidase 1 |
| Cpt1a | carnitine palmitoyl transferase 1 |
| F/B | Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes |
| OTUs | operational taxonomic units |
References
- Yanai, H.; Adachi, H.; Hakoshima, M.; Katsuyama, H. Postprandial Hyperlipidemia: Its Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, Atherogenesis, and Treatments. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Zuo, P. Obesity-hyperlipidemia, Hypertension, and Left Atrial Enlargement During Stroke in Young Adults. Neurologist 2023, 28, 386–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Dong, Z.; Wu, H.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, S.; Zhang, Y.; Qi, X.; Wei, L. The triglyceride-glucose index is associated with atherosclerosis in patients with symptomatic coronary artery disease, regardless of diabetes mellitus and hyperlipidaemia. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2023, 22, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandaglio-Collados, D.; Marín, F.; Rivera-Caravaca, J.M. Peripheral artery disease: Update on etiology, pathophysiology, diagnosis and treatment. Med. Clin. 2023, 161, 344–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaeli, D.T.; Michaeli, J.C.; Albers, S.; Boch, T.; Michaeli, T. Established and Emerging Lipid-Lowering Drugs for Primary and Secondary Cardiovascular Prevention. Am. J. Cardiovasc. Drugs 2023, 23, 477–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Li, J.; Zhou, B.; Ji, X.; Yuan, J.; Yan, J.; Nan, X.; Guo, D. Efficacy and safety of oral Chinese patent medicines in the treatment of coronary heart disease combined with hyperlipidemia: A systematic review and network meta-analysis of 78 trials. Chin. Med. 2023, 18, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Guo, Z.; Wang, J.; Yue, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wen, Y.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, X. Qinlian hongqu decoction ameliorates hyperlipidemia via the IRE1-α/IKKB-β/NF-κb signaling pathway: Network pharmacology and experimental validation. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 318, 116856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Luo, J.; Lin, S.; Wang, Y.; Yan, Z.; Ren, Q.; Liu, X.; Li, X. Efficacy of Poria cocos and Alismatis rhizoma against diet-induced hyperlipidemia in rats based on transcriptome sequencing analysis. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 17493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Li, Y.; Dong, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Xi, Z.; Yuan, M.; Xu, H. Korean red ginseng formula attenuates non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in oleic acid-induced HepG2 cells and high-fat diet-induced rats. Heliyon 2023, 9, e21846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.K.; Lin, X.R.; Lin, Y.L.; Fang, W.H.; Lin, S.W.; Chang, S.Y.; Kao, J.T. Magnolol-mediated regulation of plasma triglyceride through affecting lipoprotein lipase activity in apolipoprotein A5 knock-in mice. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0192740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Jiang, Y.; Zeng, J.; Li, X.; Xie, H.; Yang, R.; Qi, H.; Zeng, N. Phytochemistry, pharmacological properties and pharmacokinetics of Citri Reticulatae Pericarpium: A systematic review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 333, 118503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Ouyang, Q.; Li, X.; Alolgal, R.N.; Fan, Y.; Sun, Y.; Gong, H.; Xiao, P.; Ma, G. The Role of Gynostemma pentaphyllum in Regulating Hyperlipidemia. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2023, 51, 953–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, S.; Ding, X.; Ji, G.; Huang, C. Extracts of Rhizoma polygonati odorati prevent high-fat diet-induced metabolic disorders in C57BL/6 mice. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e81724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awasthi, V.K.; Mahdi, F.; Chander, R.; Khanna, A.K.; Saxena, J.K.; Singh, R.; Mahdi, A.A.; Singh, R.K. Hypolipidemic Activity of Cassia tora Seeds in Hyperlipidemic Rats. Indian J. Clin. Biochem. IJCB 2015, 30, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.Y.; Han, L.; Lin, Y.Q.; Li, T.; Wei, Y.; Zhao, L.H.; Tong, X.L. Probiotic Fermentation of Herbal Medicine: Progress, Challenges, and Opportunities. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2023, 51, 1105–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Guo, F.; Li, C.; Xiang, D.; Gong, M.; Yi, H.; Chen, L.; Yan, L.; Zhang, D.; Dai, L.; et al. Aqueous extract of fermented Eucommia ulmoides leaves alleviates hyperlipidemia by maintaining gut homeostasis and modulating metabolism in high-fat diet fed rats. Phytomedicine 2024, 128, 155291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Qu, Q.; Yang, F.; Li, Z.; Yang, P.; Han, L.; Shi, X. Monascus ruber fermented Panax ginseng ameliorates lipid metabolism disorders and modulate gut microbiota in rats fed a high-fat diet. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 278, 114300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Q.; Chen, H.; Hu, J.; Fan, S.; Nie, S. Dietary compounds and traditional Chinese medicine ameliorate type 2 diabetes by modulating gut microbiota. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 59, 848–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Xia, Y.; Wang, Y.; Han, D.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Fu, J.; Wang, L.; Gan, Z.; Liu, B.; et al. Gut microbiota bridges dietary nutrients and host immunity. Sci. China. Life Sci. 2023, 66, 2466–2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vos, W.M.; Tilg, H.; Van Hul, M.; Cani, P.D. Gut microbiome and health: Mechanistic insights. Gut 2022, 71, 1020–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francescangeli, F.; De Angelis, M.L.; Zeuner, A. Dietary Factors in the Control of Gut Homeostasis, Intestinal Stem Cells, and Colorectal Cancer. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoeler, M.; Caesar, R. Dietary lipids, gut microbiota and lipid metabolism. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2019, 20, 461–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gargari, G.; Deon, V.; Taverniti, V.; Gardana, C.; Denina, M.; Riso, P.; Guardamagna, O.; Guglielmetti, S. Evidence of dysbiosis in the intestinal microbial ecosystem of children and adolescents with primary hyperlipidemia and the potential role of regular hazelnut intake. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2018, 94, fiy045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, F.; Yu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Du, T.; Yu, L.; Tian, F.; Chen, W.; Zhai, Q. A High-Fat, High-Cholesterol Diet Promotes Intestinal Inflammation by Exacerbating Gut Microbiome Dysbiosis and Bile Acid Disorders in Cholecystectomy. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, W.; Yang, B.; Wang, Y.; Sun, M.; Yang, W.; Cui, H.; Jin, J.; Zhao, Z. Rotundic acid alleviates hyperlipidemia in rats by regulating lipid metabolism and gut microbiota. Phytother. Res. PTR 2023, 37, 5958–5973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.Y.; Huang, C.K.; Hong, W.S.; Liu, Y.H.; Shih, M.C.; Lin, J.C. Influence of Symbiotic Fermentation Broth on Regulating Metabolism with Gut Microbiota and Metabolite Profiles Is Estimated Using a Third-Generation Sequencing Platform. Metabolites 2023, 13, 999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, W.; Li, Y.; Cheung, K.C.P.; Zheng, X. Bile acid signaling in the regulation of whole body metabolic and immunological homeostasis. Sci. China Life Sci. 2024, 67, 865–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, E.R.; Lam, Y.K.; Uhlig, H.H. Short-chain fatty acids: Linking diet, the microbiome and immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2024, 24, 577–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhang, F. The Next Generation Fecal Microbiota Transplantation: To Transplant Bacteria or Virome. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, e2301097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Liu, J.; Xia, Q. Role of gut microbiome in cancer immunotherapy: From predictive biomarker to therapeutic target. Exp. Hematol. Oncol. 2023, 12, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Li, D.; Ke, W.; Liang, D.; Hu, X.; Chen, F. Resveratrol-induced gut microbiota reduces obesity in high-fat diet-fed mice. Int. J. Obes. 2020, 44, 213–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mocanu, V.; Zhang, Z.; Deehan, E.C.; Kao, D.H.; Hotte, N.; Karmali, S.; Birch, D.W.; Samarasinghe, K.K.; Walter, J.; Madsen, K.L. Fecal microbial transplantation and fiber supplementation in patients with severe obesity and metabolic syndrome: A randomized double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 2 trial. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 1272–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grover, M.; Kashyap, P.C. Germ-free mice as a model to study effect of gut microbiota on host physiology. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2014, 26, 745–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wang, S.; Zhang, T.; Lv, B.; Jin, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; Li, N.; Han, N.; Wu, Y.; et al. Walnut peptide alleviates obesity, inflammation and dyslipidemia in mice fed a high-fat diet by modulating the intestinal flora and metabolites. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1305656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Liu, L.; Deng, J.; Jiang, Y.; Yan, X.; Liu, W. Analysis of the mechanism of action of quercetin in the treatment of hyperlipidemia based on metabolomics and intestinal flora. Food Funct. 2023, 14, 2112–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; Huws, S.A.; Xu, G.; Li, J.; Ren, J.; Xu, J.; Guan, L.L.; Yao, J.; Wu, S. Ileal microbial microbiome and its secondary bile acids modulate susceptibility to nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in dairy goats. Microbiome 2024, 12, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascual, J.; Hahnke, S.; Abendroth, C.; Langer, T.; Ramm, P.; Klocke, M.; Luschnig, O.; Porcar, M. Draft Genome Sequence of a New Oscillospiraceae Bacterium Isolated from Anaerobic Digestion of Biomass. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2020, 9, 10-1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cignarella, F.; Cantoni, C.; Ghezzi, L.; Salter, A.; Dorsett, Y.; Chen, L.; Phillips, D.; Weinstock, G.M.; Fontana, L.; Cross, A.H.; et al. Intermittent Fasting Confers Protection in CNS Autoimmunity by Altering the Gut Microbiota. Cell Metab. 2018, 27, 1222-1235.e1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.M.; Rao, J.H.; Wei, Z.Y.; Xia, S.Y.; Huang, L.; Tang, M.T.; Hide, G.; Zheng, T.T.; Li, J.H.; Zhao, G.A.; et al. Transplantation of Gut Microbiota From High-Fat-Diet-Tolerant Cynomolgus Monkeys Alleviates Hyperlipidemia and Hepatic Steatosis in Rats. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 876043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Alm, E.J.; Kelley, J.M.; Cheng, V.; Smith, M.; Kassam, Z.; Nee, J.; Iturrino, J.; Lembo, A. Effect of antibiotic pretreatment on bacterial engraftment after Fecal Microbiota Transplant (FMT) in IBS-D. Gut Microbes 2022, 14, 2020067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.; Shen, G.; Wang, Y.; Hong, F.; Tang, X.; Zeng, Y.; Zhang, T.; Liu, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; et al. Elevated Kallistatin promotes the occurrence and progression of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Qiu, W.; Sun, X.; Gao, M.; Zhao, Y.; Li, M.; Fan, Z.; Lv, G. Novel insights into causal effects of serum lipids and lipid-modifying targets on cholelithiasis. Gut 2024, 73, 521–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosmas, C.E.; Rodriguez Polanco, S.; Bousvarou, M.D.; Papakonstantinou, E.J.; Peña Genao, E.; Guzman, E.; Kostara, C.E. The Triglyceride/High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol (TG/HDL-C) Ratio as a Risk Marker for Metabolic Syndrome and Cardiovascular Disease. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Yao, H.; Wang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Thorne, R.F.; Zhu, Y.; Wu, M.; Liu, L. circPRKAA1 activates a Ku80/Ku70/SREBP-1 axis driving de novo fatty acid synthesis in cancer cells. Cell Rep. 2022, 41, 111707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Cai, Q.; Guo, W.; Su, Q.; Qin, H.; Wang, T.; Xian, Y.; Zeng, L.; Cai, M.; Guan, H.; et al. Malonylation of Acetyl-CoA carboxylase 1 promotes hepatic steatosis and is attenuated by ketogenic diet in NAFLD. Cell Rep. 2023, 42, 112319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.S.; Song, J.W.; Park, J.H.; Lim, B.K.; Moon, O.S.; Son, H.Y.; Lee, J.H.; Gao, B.; Won, Y.S.; Kwon, H.J. TXNIP/VDUP1 attenuates steatohepatitis via autophagy and fatty acid oxidation. Autophagy 2021, 17, 2549–2564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, H.; Peng, Y.; Hang, W.; Nie, J.; Zhou, N.; Wang, D.W. The role of CD36 in cardiovascular disease. Cardiovasc. Res. 2022, 118, 115–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, J.; Li, X.; Liu, C.; Lu, D.; Ouyang, J.; Zhou, F.; Liu, Q.; Huang, J.; Liu, Z. Junshanyinzhen tea extract prevents obesity by regulating gut microbiota and metabolic endotoxemia in high-fat diet fed rats. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2024, 13, 2036–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, N.R.; Kwon, T.J.; Chung, E.C.; Bae, J.; Soung, S.H.; Tak, H.J.; Choi, J.Y.; Lee, Y.E.; Won Hwang, N.; Lee, J.S.; et al. Combination of Lacticaseibacillus paracasei BEPC22 and Lactiplantibacillus plantarum BELP53 attenuates fat accumulation and alters the metabolome and gut microbiota in mice with high-fat diet-induced obesity. Food Funct. 2024, 15, 647–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Z.; Yang, Y.; Chen, S.; Wu, Z. Long-Term Exposure to Polystyrene Microspheres and High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity in Mice: Evaluating a Role for Microbiota Dysbiosis. Environ. Health Perspect. 2024, 132, 97002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.X.; Huang, W.J.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, D.D.; Mu, G.H.; Nan, H.; Ni, B.R.; Huang, X.Q.; Wang, H.C.; Liu, Y.F.; et al. Shenlian (SL) Decoction, a Traditional Chinese Medicine Compound, May Ameliorate Blood Glucose via Mediating the Gut Microbiota in db/db Mice. J. Diabetes Res. 2022, 2022, 7802107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, X.; Xu, W.; Zhang, L.; Li, X.; Wang, R.; Wu, S. Impact of Gut Microbiota and Microbiota-Related Metabolites on Hyperlipidemia. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 634780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, M.; Man, S.; Liang, Y.; Ma, L.; Guo, L.; Huang, L.; Gao, W. Diosgenin alleviates nonalcoholic steatohepatitis through affecting liver-gut circulation. Pharmacol. Res. 2023, 187, 106621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzolo, D.; Kong, B.; Taylor, R.E.; Brinker, A.; Goedken, M.; Buckley, B.; Guo, G.L. Bile acid homeostasis in female mice deficient in Cyp7a1 and Cyp27a1. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2021, 11, 3847–3856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Feng, X.; Liu, X.; Huo, X.; Sun, J.; Hao, J. TRIM21-mediated Sohlh2 ubiquitination suppresses M2 macrophage polarization and progression of triple-negative breast cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2023, 14, 850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Liu, M.; Han, Y.; Li, S.; Zhu, X.; Li, D.; Shi, Y.; Liu, B. Effects of Saponins on Lipid Metabolism: The Gut-Liver Axis Plays a Key Role. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, N.H.T.; Joglekar, M.V.; Wong, W.K.M.; Nassif, N.T.; Simpson, A.M.; Hardikar, A.A. Short-chain fatty acids and insulin sensitivity: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutr. Rev. 2024, 82, 193–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, K.; Zhao, H.; Hao, Z.; Yang, Y.; Gao, M.; Zhao, D. Integrated lipidomics and network pharmacology analysis to reveal the mechanisms of berberine in the treatment of hyperlipidemia. J. Transl. Med. 2022, 20, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, X.K.; Tang, M.; Lei, L.; Li, J.R.; Sun, H.; Jiang, J.; Dong, B.; Li, H.Y.; Jiang, J.D.; et al. Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron ameliorates mouse hepatic steatosis through regulating gut microbial composition, gut-liver folate and unsaturated fatty acids metabolism. Gut Microbes 2024, 16, 2304159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.X.; Cheng, S.L.; Liu, Y.H.; Li, Y.; Zhang, R.; Li, N.N.; Li, Z. Fecal microbiota transplantation for treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Mechanism, clinical evidence, and prospect. World J. Gastroenterol. 2024, 30, 833–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Lezana, T.; Raurell, I.; Bravo, M.; Torres-Arauz, M.; Salcedo, M.T.; Santiago, A.; Schoenenberger, A.; Manichanh, C.; Genescà, J.; Martell, M.; et al. Restoration of a healthy intestinal microbiota normalizes portal hypertension in a rat model of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology 2018, 67, 1485–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, E.W.; Gao, L.; Stastka, P.; Cheney, M.C.; Mahabamunuge, J.; Torres Soto, M.; Ford, C.B.; Bryant, J.A.; Henn, M.R.; Hohmann, E.L. Fecal microbiota transplantation for the improvement of metabolism in obesity: The FMT-TRIM double-blind placebo-controlled pilot trial. PLoS Med. 2020, 17, e1003051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, Q.; Yang, C.; Jia, M.; Qu, Q.; Peng, X.; Ren, W.; Li, G.; Xie, Y.; Li, B.; Shi, X. Gut Microbiota-Targeted Intervention of Hyperlipidemia Using Monascus-Fermented Ginseng. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 661. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18050661
Zhou Q, Yang C, Jia M, Qu Q, Peng X, Ren W, Li G, Xie Y, Li B, Shi X. Gut Microbiota-Targeted Intervention of Hyperlipidemia Using Monascus-Fermented Ginseng. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(5):661. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18050661
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Qing, Cuiting Yang, Mingyue Jia, Qingsong Qu, Xinhui Peng, Weishuo Ren, Guoqing Li, Yueyang Xie, Bingxuan Li, and Xinyuan Shi. 2025. "Gut Microbiota-Targeted Intervention of Hyperlipidemia Using Monascus-Fermented Ginseng" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 5: 661. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18050661
APA StyleZhou, Q., Yang, C., Jia, M., Qu, Q., Peng, X., Ren, W., Li, G., Xie, Y., Li, B., & Shi, X. (2025). Gut Microbiota-Targeted Intervention of Hyperlipidemia Using Monascus-Fermented Ginseng. Pharmaceuticals, 18(5), 661. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18050661





