Comparative Risk of Complications Following Intestinal Surgery After Infliximab, Vedolizumab, or Ustekinumab Treatment: Systematic Review & Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Eligibility Criteria
2.2. Literature Screening and Data Extraction
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Main Analysis
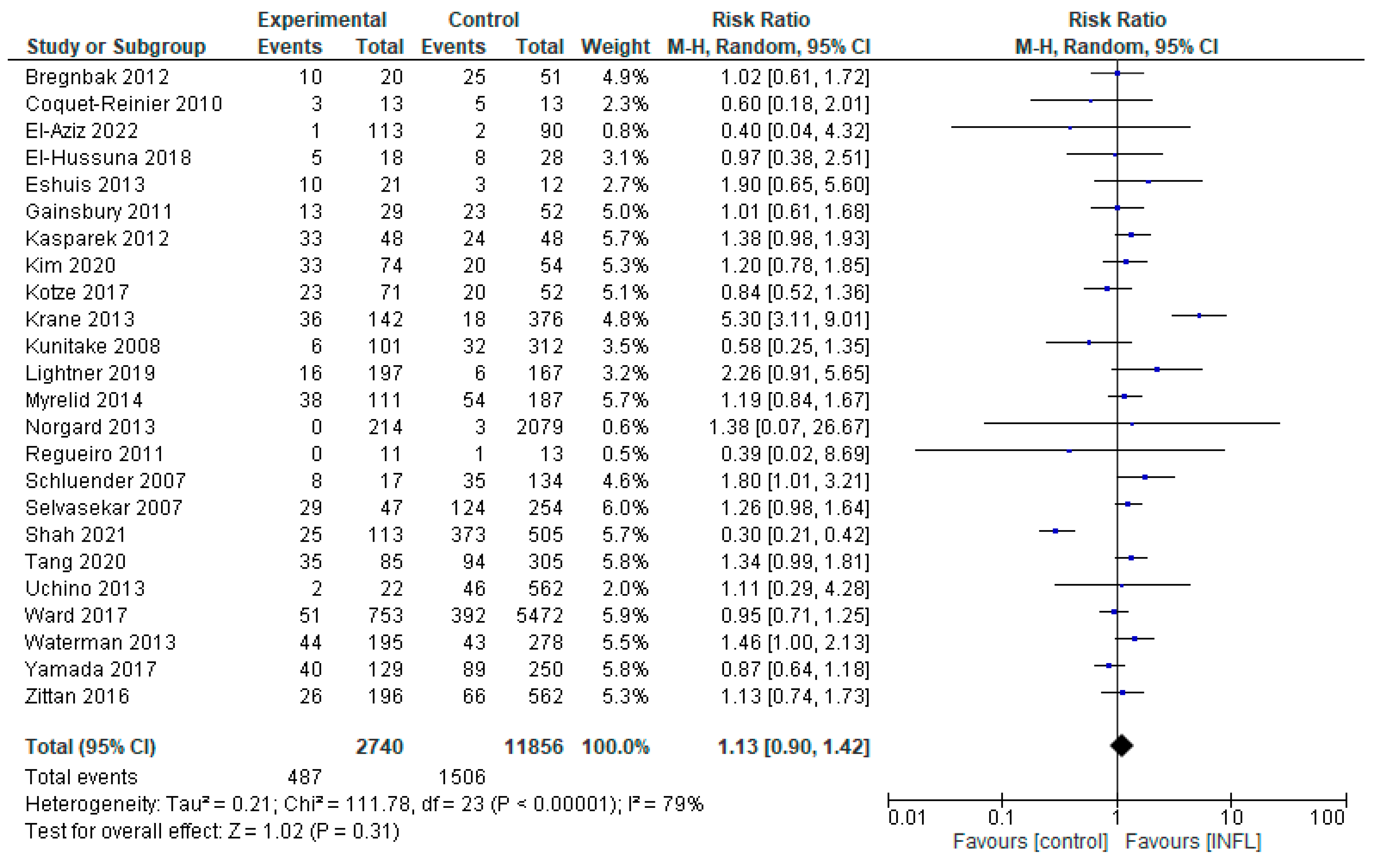
3.1.1. INFL vs. Controls
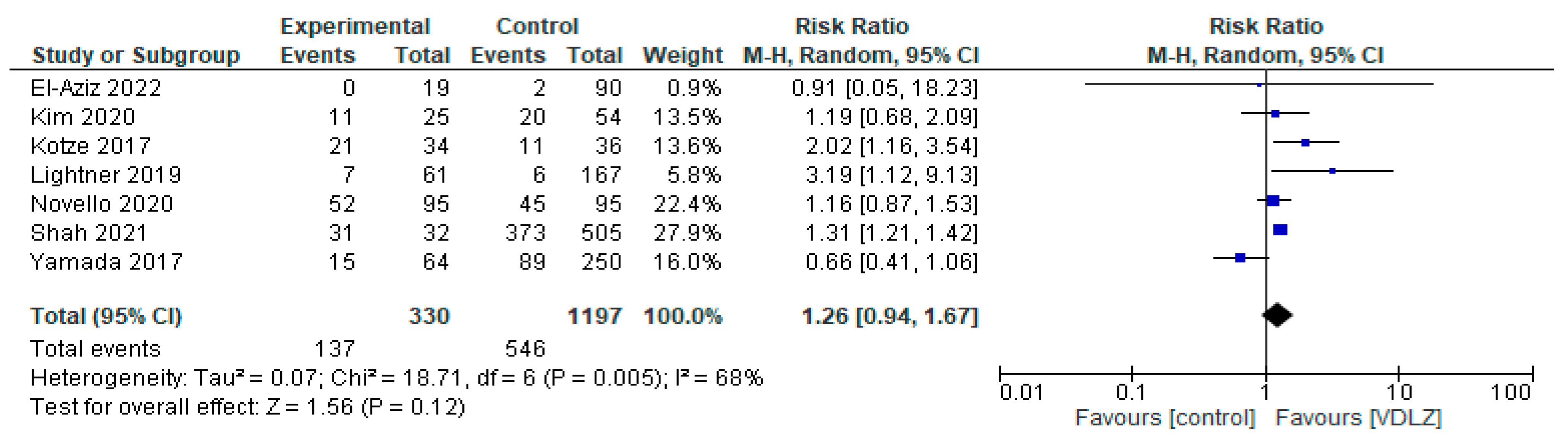
3.1.2. VDLZ vs. Controls
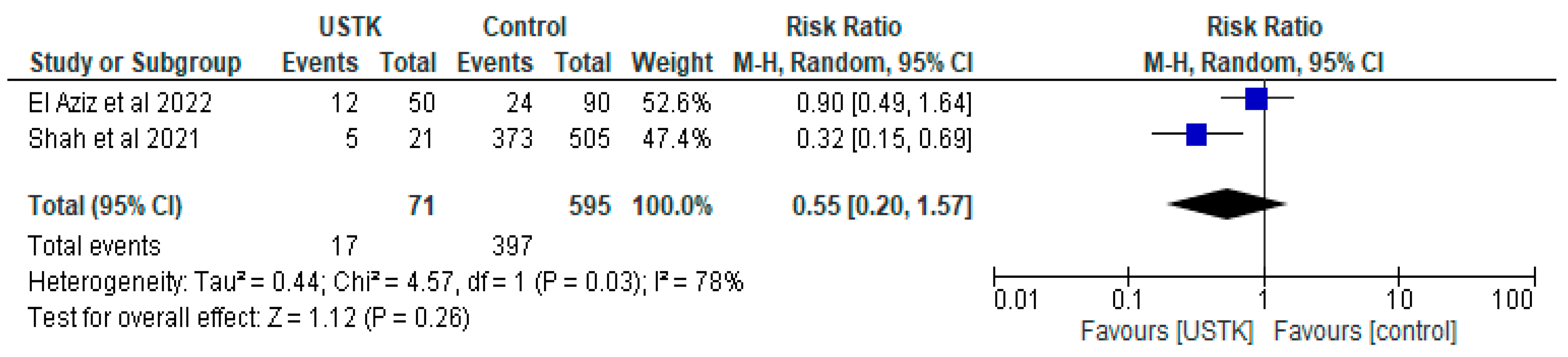
3.1.3. USTK vs. Controls
3.2. Head-to-Head Analysis in Between the Biological Groups
3.2.1. USTK vs. INFL
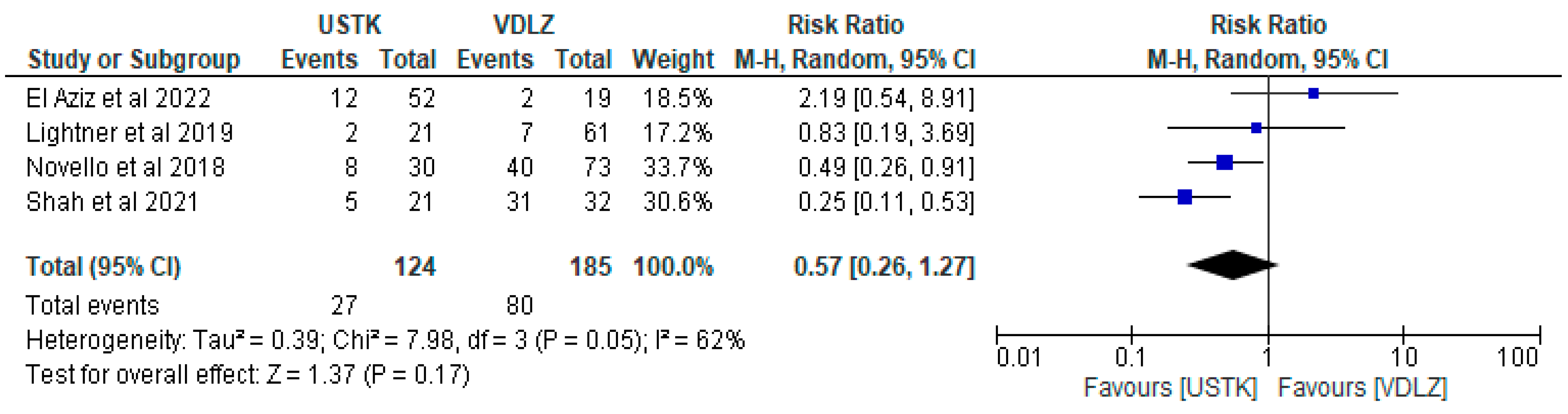
3.2.2. USTK vs. VDLZ
3.2.3. INFL vs. VDLZ
4. Discussion
4.1. Inflammatory Bowel Diseases and Biological Therapies
4.2. Infliximab
4.3. Vedolizumab
4.4. Ustekinumab
4.5. Summary and Clinical Implications
4.6. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| IBDs | Inflammatory Bowel Diseases |
| CD | Crohn’s Disease |
| UC | Ulcerative Colitis |
| INFL | INFL |
| VDLZ | VDLZ |
| USTK | USTK |
| GI | Gastrointestinal |
References
- Anto, V.P.; Dawes, A.J.; Vrees, M.; Watson, A.R.; Lightner, A.L. Surgical Management of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. R. I. Med. J. (2013) 2022, 105, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tsai, L.; Ma, C.; Dulai, P.S.; Prokop, L.J.; Eisenstein, S.; Ramamoorthy, S.L.; Feagan, B.G.; Jairath, V.; Sandborn, W.J.; Singh, S. Contemporary Risk of Surgery in Patients with Ulcerative Colitis and Crohn’s Disease: A Meta-Analysis of Population-Based Cohorts. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 19, 2031–2045.e2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saur, N.M.; Paulson, E.C. Operative Management of Anastomotic Leaks after Colorectal Surgery. Clin. Colon Rectal Surg. 2019, 32, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toh, J.W.T.; Cecire, J.; Hitos, K.; Shedden, K.; Gavegan, F.; Pathmanathan, N.; El Khoury, T.; Di Re, A.; Cocco, A.; Limmer, A.; et al. The impact of variations in care and complications within a colorectal Enhanced Recovery After Surgery program on length of stay. Ann. Coloproctol. 2022, 38, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutiérrez, A.; Rivero, M.; Martín-Arranz, M.D.; García Sánchez, V.; Castro, M.; Barrio, J.; de Francisco, R.; Barreiro-de Acosta, M.; Juliá, B.; Cea-Calvo, L.; et al. Perioperative management and early complications after intestinal resection with ileocolonic anastomosis in Crohn’s disease: Analysis from the PRACTICROHN study. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2019, 7, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baelum, J.K.; Qvist, N.; Ellebaek, M.B. Ileorectal anastomosis in patients with Crohn’s disease. Postoperative complications and functional outcome-a systematic review. Color. Dis. 2021, 23, 2501–2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atıcı, A.E.; Özocak, A.B.; Karpuz, G.F.; Sevindi, H.I.; Dağancı, Ş.F.; Yeğen, Ş.C. Risk factors for anastomotic complications after elective intestinal resection in Crohn’s disease. Turk. J. Surg. 2024, 40, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, L.; Krane, M.K.; Fichera, A. Inflammatory bowel disease surgery in the biologic era. World J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2016, 8, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menni, A.E.; Kyriazopoulou, E.; Karakike, E.; Tzikos, G.; Filidou, E.; Kotzampassi, K. Interplay of Gut Microbiota, Biologic Agents, and Postoperative Anastomotic Leakage in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Narrative Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 7066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, M.I.; Cohen, B.L.; Greenstein, A.J. A review of the impact of biologics on surgical complications in Crohn’s disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2015, 21, 1472–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menni, A.; Tzikos, G.; Goulas, P.; Chatziantoniou, G.; Vouchara, A.; Apostolidis, A.S.; Ioannidis, A.; Germanidis, G.; Papazoglou, L.G.; Giouleme, O.; et al. The Effects of the Biological Agents INFL, VDLZ, and USTK on Intestinal Anastomosis: An Experimental Study in Rats. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parums, D.V. Editorial: Review Articles, Systematic Reviews, Meta-Analysis, and the Updated Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) 2020 Guidelines. Med. Sci. Monit. 2021, 27, e934475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, S.; Dong, X.; Liu, W.; Qi, W.; Ye, L.; Yang, X.; Cao, Q.; Ge, X.; Zhou, W. Compare risk factors associated with postoperative infectious complication in Crohn’s disease with and without preoperative INFL therapy: A cohort study. Int. J. Color. Dis. 2020, 35, 727–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Hussuna, A.; Qvist, N.; Zangenberg, M.S.; Langkilde, A.; Siersma, V.; Hjort, S.; Gögenur, I. No effect of anti-TNF-α agents on the surgical stress response in patients with inflammatory bowel disease undergoing bowel resections: A prospective multi-center pilot study. BMC Surg. 2018, 18, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, S.T.; Mytton, J.; Henderson, L.; Amin, V.; Tanner, J.R.; Evison, F.; Radley, S. Anti-TNF therapy is not associated with an increased risk of post-colectomy complications, a population-based study. Color. Dis. 2018, 20, 416–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zittan, E.; Milgrom, R.; Ma, G.W.; Wong-Chong, N.; O’Connor, B.; McLeod, R.S.; MacRae, H.M.; Greenberg, G.R.; Nguyen, G.C.; Croitoru, K.; et al. Preoperative Anti-tumor Necrosis Factor Therapy in Patients with Ulcerative Colitis Is Not Associated with an Increased Risk of Infectious and Noninfectious Complications After Ileal Pouch-anal Anastomosis. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2016, 22, 2442–2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myrelid, P.; Marti-Gallostra, M.; Ashraf, S.; Sunde, M.L.; Tholin, M.; Oresland, T.; Lovegrove, R.E.; Tøttrup, A.; Kjaer, D.W.; George, B.D. Complications in surgery for Crohn’s disease after preoperative antitumour necrosis factor therapy. Br. J. Surg. 2014, 101, 539–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchino, M.; Ikeuchi, H.; Matsuoka, H.; Bando, T.; Ichiki, K.; Nakajima, K.; Tomita, N.; Takesue, Y. Risk factors for surgical site infection and association with INFL administration during surgery for Crohn’s disease. Dis. Colon Rectum 2013, 56, 1156–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchino, M.; Ikeuchi, H.; Matsuoka, H.; Bando, T.; Ichiki, K.; Nakajima, K.; Tomita, N.; Takesue, Y. INFL administration prior to surgery does not increase surgical site infections in patients with ulcerative colitis. Int. J. Color. Dis. 2013, 28, 1295–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krane, M.K.; Allaix, M.E.; Zoccali, M.; Umanskiy, K.; Rubin, M.A.; Villa, A.; Hurst, R.D.; Fichera, A. Preoperative INFL therapy does not increase morbidity and mortality after laparoscopic resection for inflammatory bowel disease. Dis. Colon Rectum 2013, 56, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waterman, M.; Xu, W.; Dinani, A.; Steinhart, A.H.; Croitoru, K.; Nguyen, G.C.; McLeod, R.S.; Greenberg, G.R.; Cohen, Z.; Silverberg, M.S. Preoperative biological therapy and short-term outcomes of abdominal surgery in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Gut 2013, 62, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eshuis, E.J.; Al Saady, R.L.; Stokkers, P.C.; Ponsioen, C.Y.; Tanis, P.J.; Bemelman, W.A. Previous INFL therapy and postoperative complications after proctocolectomy with ileum pouch anal anastomosis. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2013, 7, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nørgård, B.M.; Nielsen, J.; Qvist, N.; Gradel, K.O.; de Muckadell, O.B.; Kjeldsen, J. Pre-operative use of anti-TNF-α agents and the risk of post-operative complications in patients with Crohn’s disease—A nationwide cohort study. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 37, 214–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasparek, M.S.; Bruckmeier, A.; Beigel, F.; Müller, M.H.; Brand, S.; Mansmann, U.; Jauch, K.W.; Ochsenkühn, T.; Kreis, M.E. INFL does not affect postoperative complication rates in Crohn’s patients undergoing abdominal surgery. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2012, 18, 1207–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nørgård, B.M.; Nielsen, J.; Qvist, N.; Gradel, K.O.; de Muckadell, O.B.; Kjeldsen, J. Pre-operative use of anti-TNF-α agents and the risk of post-operative complications in patients with ulcerative colitis—A nationwide cohort study. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2012, 35, 1301–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bregnbak, D.; Mortensen, C.; Bendtsen, F. INFL and complications after colectomy in patients with ulcerative colitis. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2012, 6, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regueiro, M.; El-Hachem, S.; Kip, K.E.; Schraut, W.; Baidoo, L.; Watson, A.; Swoger, J.; Schwartz, M.; Barrie, A.; Pesci, M.; et al. Postoperative INFL is not associated with an increase in adverse events in Crohn’s disease. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2011, 56, 3610–3615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gainsbury, M.L.; Chu, D.I.; Howard, L.A.; Coukos, J.A.; Farraye, F.A.; Stucchi, A.F.; Becker, J.M. Preoperative INFL is not associated with an increased risk of short-term postoperative complications after restorative proctocolectomy and ileal pouch-anal anastomosis. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2011, 15, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coquet-Reinier, B.; Berdah, S.V.; Grimaud, J.C.; Birnbaum, D.; Cougard, P.A.; Barthet, M.; Desjeux, A.; Moutardier, V.; Brunet, C. Preoperative INFL treatment and postoperative complications after laparoscopic restorative proctocolectomy with ileal pouch-anal anastomosis: A case-matched study. Surg. Endosc. 2010, 24, 1866–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunitake, H.; Hodin, R.; Shellito, P.C.; Sands, B.E.; Korzenik, J.; Bordeianou, L. Perioperative treatment with INFL in patients with Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis is not associated with an increased rate of postoperative complications. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2008, 12, 1730–1736; discussion 1736–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schluender, S.J.; Ippoliti, A.; Dubinsky, M.; Vasiliauskas, E.A.; Papadakis, K.A.; Mei, L.; Targan, S.R.; Fleshner, P.R. Does INFL influence surgical morbidity of ileal pouch-anal anastomosis in patients with ulcerative colitis? Dis. Colon Rectum 2007, 50, 1747–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selvasekar, C.R.; Cima, R.R.; Larson, D.W.; Dozois, E.J.; Harrington, J.R.; Harmsen, W.S.; Loftus, E.V., Jr.; Sandborn, W.J.; Wolff, B.G.; Pemberton, J.H. Effect of INFL on short-term complications in patients undergoing operation for chronic ulcerative colitis. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2007, 204, 956–962, discussion 962–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poylin, V.Y.; Serrato, J.C.; Pastrana Del Valle, J.; Feuerstein, J.D. VDLZ does not increase perioperative surgical complications in patients with inflammatory bowel disease, cohort study. Intest. Res. 2022, 20, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.Y.; Zaghiyan, K.; Lightner, A.; Fleshner, P. Risk of postoperative complications among ulcerative colitis patients treated preoperatively with VDLZ: A matched case-control study. BMC Surg. 2020, 20, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novello, M.; Stocchi, L.; Steele, S.R.; Holubar, S.D.; Duraes, L.C.; Kessler, H.; Shawki, S.; Hull, L.T. Case-matched Comparison of Postoperative Outcomes Following Surgery for Inflammatory Bowel Disease After Exposure to VDLZ vs Other Biologics. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2020, 14, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.T.; Sceats, L.; Dehghan, M.; Trickey, A.W.; Wren, A.; Wong, J.J.; Bensen, R.; Limketkai, B.N.; Keyashian, K.; Kin, C. Risk of post-operative surgical site infections after VDLZ vs anti-tumour necrosis factor therapy: A propensity score matching analysis in inflammatory bowel disease. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 48, 340–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotze, P.G.; Saab, M.P.; Saab, B.; da Silva Kotze, L.M.; Olandoski, M.; Pinheiro, L.V.; Martinez, C.A.; Ayrizono, M.L.; Magro, D.O.; Coy, C.S. Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha Inhibitors Did Not Influence Postoperative Morbidity After Elective Surgical Resections in Crohn’s Disease. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2017, 62, 456–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lightner, A.L.; Mathis, K.L.; Tse, C.S.; Pemberton, J.H.; Shen, B.; Kochhar, G.; Singh, A.; Dulai, P.S.; Eisenstein, S.; Sandborn, W.J.; et al. Postoperative Outcomes in VDLZ-Treated Patients Undergoing Major Abdominal Operations for Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Retrospective Multicenter Cohort Study. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2018, 24, 871–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lightner, A.L.; McKenna, N.P.; Tse, C.S.; Raffals, L.E.; Loftus, E.V., Jr.; Mathis, K.L. Postoperative outcomes in VDLZ-treated Crohn’s disease patients undergoing major abdominal operations. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 47, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lightner, A.L.; McKenna, N.P.; Moncrief, S.; Pemberton, J.H.; Raffals, L.E.; Mathis, K.L. Surgical Outcomes in VDLZ-Treated Patients with Ulcerative Colitis. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2017, 23, 2197–2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lightner, A.L.; Raffals, L.E.; Mathis, K.L.; Cima, R.R.; Tse, C.S.; Pemberton, J.H.; Dozois, E.J.; Loftus, E.V. Postoperative Outcomes in VDLZ-Treated Patients Undergoing Abdominal Operations for Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2017, 11, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrante, M.; de Buck van Overstraeten, A.; Schils, N.; Moens, A.; Van Assche, G.; Wolthuis, A.; Vermeire, S.; D’Hoore, A. Perioperative Use of VDLZ is not Associated with Postoperative Infectious Complications in Patients with Ulcerative Colitis Undergoing Colectomy. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2017, 11, 1353–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, A.; Komaki, Y.; Patel, N.; Komaki, F.; Aelvoet, A.S.; Tran, A.L.; Pekow, J.; Dalal, S.; Cohen, R.D.; Cannon, L.; et al. Risk of Postoperative Complications Among Inflammatory Bowel Disease Patients Treated Preoperatively With VDLZ. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 112, 1423–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, R.S.; Bachour, S.; Jia, X.; Holubar, S.D.; Hull, T.L.; Achkar, J.P.; Philpott, J.; Qazi, T.; Rieder, F.; Cohen, B.L.; et al. Hypoalbuminaemia, Not Biologic Exposure, Is Associated with Postoperative Complications in Crohn’s Disease Patients Undergoing Ileocolic Resection. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2021, 15, 1142–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lightner, A.L.; McKenna, N.P.; Alsughayer, A.; Harmsen, W.S.; Taparra, K.; Parker, M.E.; Raffals, L.E.; Loftus, E.V., Jr. Biologics and 30-Day Postoperative Complications After Abdominal Operations for Crohn’s Disease: Are There Differences in the Safety Profiles? Dis. Colon Rectum 2019, 62, 1352–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shim, H.H.; Ma, C.; Kotze, P.G.; Seow, C.H.; Al-Farhan, H.; Al-Darmaki, A.K.; Pang, J.X.Q.; Fedorak, R.N.; Devlin, S.M.; Dieleman, L.A.; et al. Preoperative USTK Treatment Is Not Associated with Increased Postoperative Complications in Crohn’s Disease: A Canadian Multi-Centre Observational Cohort Study. J. Can. Assoc. Gastroenterol. 2018, 1, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El Aziz, M.A.; Abdalla, S.; Calini, G.; Saeed, H.; Stocchi, L.; Merchea, A.; Colibaseanu, D.T.; Shawki, S.; Larson, D.W. Postoperative Safety Profile of Minimally Invasive Ileocolonic Resections for Crohn’s Disease in the Era of Biologic Therapy. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2022, 16, 1079–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ioannidis, J.P.; Trikalinos, T.A. The appropriateness of asymmetry tests for publication bias in meta-analyses: A large survey. Can. Med Assoc. J. 2007, 176, 1091–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novello, M.; Stocchi, L.; Holubar, S.; Shawki, S.; Lipman, J.; Gorgun, E.; Hull, T.; Steele, S.R. Surgical outcomes of patients treated with USTK vs. VDLZ in inflammatory bowel disease: A matched case analysis. Int. J. Color. Dis. 2019, 34, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, D.; Rukkannagari, S.; Kethu, S. Pathogenesis and clinical approach to extraintestinal manifestations of inflammatory bowel disease. Minerva Gastroenterol. Dietol. 2007, 53, 233–248. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rioux, J.D.; Xavier, R.J.; Taylor, K.D.; Silverberg, M.S.; Goyette, P.; Huett, A.; Green, T.; Kuballa, P.; Barmada, M.M.; Datta, L.W.; et al. Genome-wide association study identifies new susceptibility loci for Crohn disease and implicates autophagy in disease pathogenesis. Nat. Genet. 2007, 39, 596–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsianos, E.V.; Katsanos, K.H.; Tsianos, V.E. Role of genetics in the diagnosis and prognosis of Crohn’s disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 18, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lashner, B. Inflammatory Bowel Disease. In Cleveland Clinic: Current Clinical Medicine, 2nd ed.; Carey, W.D., Ed.; Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Amre, D.K.; D’Souza, S.; Morgan, K.; Seidman, G.; Lambrette, P.; Grimard, G.; Israel, D.; Mack, D.; Ghadirian, P.; Deslandres, C.; et al. Imbalances in dietary consumption of fatty acids, vegetables, and fruits are associated with risk for Crohn’s disease in children. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 102, 2016–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawson, M.M.; Thomas, A.G.; Akobeng, A.K. Tumour necrosis factor alpha blocking agents for induction of remission in ulcerative colitis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2006, 3, Cd005112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mor, I.J.; Vogel, J.D.; da Luz Moreira, A.; Shen, B.; Hammel, J.; Remzi, F.H. INFL in ulcerative colitis is associated with an increased risk of postoperative complications after restorative proctocolectomy. Dis. Colon Rectum 2008, 51, 1202–1207; discussion 1207–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poritz, L.S.; Rowe, W.A.; Koltun, W.A. Remicade does not abolish the need for surgery in fistulizing Crohn’s disease. Dis. Colon Rectum 2002, 45, 771–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhofstad, M.H.; Lange, W.P.; van der Laak, J.A.; Verhofstad, A.A.; Hendriks, T. Microscopic analysis of anastomotic healing in the intestine of normal and diabetic rats. Dis. Colon Rectum 2001, 44, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inan, A.; Koca, C.; Sen, M. Effects of diclofenac sodium on bursting pressures of anastomoses and hydroxyproline contents of perianastomotic tissues in a laboratory study. Int. J. Surg. 2006, 4, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grundmann, S.; Hoefer, I.; Ulusans, S.; van Royen, N.; Schirmer, S.H.; Ozaki, C.K.; Bode, C.; Piek, J.J.; Buschmann, I. Anti-tumor necrosis factor-{alpha} therapies attenuate adaptive arteriogenesis in the rabbit. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2005, 289, H1497–H1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. INFL, INFL-dyyb MONOGRAPH for Professionals. Available online: https://www.drugs.com/monograph/infliximab.html (accessed on 15 July 2019).
- Parrish, A.B.; Lopez, N.E.; Truong, A.; Zaghiyan, K.; Melmed, G.Y.; McGovern, D.P.B.; Ha, C.; Syal, G.; Bonthala, N.; Jain, A.; et al. Preoperative Serum VDLZ Levels Do Not Impact Postoperative Outcomes in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Dis. Colon Rectum 2021, 64, 1259–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotze, P.G.; Ma, C.; McKenna, N.; Almutairdi, A.; Kaplan, G.G.; Raffals, L.E.; Loftus, E.V., Jr.; Panaccione, R.; Lightner, A.L. VDLZ and early postoperative complications in nonintestinal surgery: A case-matched analysis. Therap Adv. Gastroenterol. 2018, 11, 1756284818783614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, B.; Jin, X.; Fan, L.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, B.; Yang, T. Treatment efficacy and patient satisfaction of USTK compared with tumor necrosis factor-alpha inhibitors in Chinese patients with moderate-to-severe psoriasis: A real-world study. J. Dermatolog Treat. 2024, 35, 2405554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Study | Study Design | Type of IBD | Patients (n) | Time from Last Biologic Infusion to Surgery, Days [Median (IQR)] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Tang, Shasha et al. (2020) [13] | Retrospective | CD | 390 | 8 weeks |
| 2 | El-Hussuna, Alaa et al. (2018) [14] | Prospective Multi-Center Pilot Study | CD/UC | 46 | 12 weeks |
| 3 | Ward, S. T et al. (2017) [15] | Population Study | UC | 753 | 12 weeks (4 weeks_418 pts) |
| 4 | Zittan, Eran et al. (2016) [16] | Retrospective | UC | 773 | <15 or 15–30 or 30–180 days |
| 5 | Myrelid, P. et al. (2014) [17] | Multicenter Study | CD | 298 | 2 months |
| 6 | Uchino, Motoi et al. (2013) [18] | Prospective | CD | 405 | 43 days |
| 7 | Uchino, Motoi et al. (2013) [19] | Clinical Trial | UC | 196 | 12 weeks |
| 8 | Krane, Mukta K et al. (2013) [20] | Retrospective | IBDs | 142 | |
| 9 | Waterman, Matti et al. (2013) [21] | Retrospective | IBDs | 195 | <14 or 15–30 or 31–180 days |
| 10 | Eshuis, Emma J et al. (2013) [22] | Retrospective | UC | 72 | 7 months |
| 11 | Norgard, B M et al. (2013) [23] | Cohort | CD | 2293 | 12 weeks |
| 12 | Kasparek, M. S et al. (2012) [24] | Prospective | CD | 48 | 3 months |
| 13 | Norgard, B M et al. (2012) [25] | Cohort | UC | 1226 | 12 weeks |
| 14 | Bregnbak, D. et al. (2012) [26] | Retrospective | UC | 71 | 90 days |
| 15 | Regueiro, Miguel et al. (2011) [27] | Double Blinded Controlled Study | CD | 24 | 4 weeks |
| 16 | Gainsbury, M. L et al. (2011) [28] | Retrospective | UC | 81 | 12 weeks |
| 17 | Coquet-Reinier, B. et al. (2010) [29] | Retrospective | UC | 26 | 44 days |
| 18 | Kunitake, Hiroko et al. (2008) [30] | Retrospective | CD/UC | 413 | 12 weeks |
| 19 | Schluender, Stefanie J et al. (2007) [31] | Prospective | UC | 151 | 2 months |
| 20 | Selvasekar, C. R et al. (2007) [32] | Retrospective | UC | 301 | 2 months |
| 21 | Poylin, Vitaliy Y et al. (2022) [33] | Retrospective | CD/UC | 199 | 4 weeks |
| 22 | Kim, Jeong Yeon et al. (2020) [34] | Matched Case–Control Study | UC | 153 | 12 weeks |
| 23 | Novello, M et al. (2020) [35] | Matched Case–Control Study | CD/UC | 980 | 12 weeks |
| 24 | Park, K T et al. (2018) [36] | Retrospective Cohort | CD/UC | 186 | 30 days |
| 25 | Kotze, P.G. et al. (2017) [37] | Case-Matched Study | CD/UC | 68 | 12 weeks |
| 26 | Lightner, Amy L et al. (2018) [38] | Retrospective Cohort | UC | 435 | 12 weeks |
| 27 | Lightner, A L et al. (2018) [39] | Retrospective | CD | 100 | 12 weeks |
| 28 | Lightner, Amy L et al. (2017) [40,41] | Retrospective | UC | 150 | 12 weeks |
| 29 | Ferrante, Marc et al. (2017) [42] | Retrospective | UC | 170 | 8–16 weeks |
| 30 | Yamada, Akihiro et al. (2017) [43] | Retrospective | CD/UC | 443 | 4 weeks |
| 31 | Shah, Ravi S et al. (2021) [44] | Retrospective | CD | 815 | 12 weeks |
| 32 | Lightner, Amy L et al. (2019) [45] | Retrospective | CD | 712 | 12 weeks |
| 33 | Shim, Hang Hocj et al. (2018) [46] | Cohort | CD | 60 | 4 months |
| 34 | Abd El Aziz, Mohamed A et al. (2022) [47] | Retrospective | CD | 274 | 4 weeks |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Menni, A.-E.; Tzikos, G.; Petrakis, G.; Goulas, P.; Karathanasis, P.V.; Apostolidis, S. Comparative Risk of Complications Following Intestinal Surgery After Infliximab, Vedolizumab, or Ustekinumab Treatment: Systematic Review & Meta-Analysis. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 1466. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18101466
Menni A-E, Tzikos G, Petrakis G, Goulas P, Karathanasis PV, Apostolidis S. Comparative Risk of Complications Following Intestinal Surgery After Infliximab, Vedolizumab, or Ustekinumab Treatment: Systematic Review & Meta-Analysis. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(10):1466. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18101466
Chicago/Turabian StyleMenni, Alexandra-Eleftheria, Georgios Tzikos, George Petrakis, Patroklos Goulas, Panagiotis V. Karathanasis, and Stylianos Apostolidis. 2025. "Comparative Risk of Complications Following Intestinal Surgery After Infliximab, Vedolizumab, or Ustekinumab Treatment: Systematic Review & Meta-Analysis" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 10: 1466. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18101466
APA StyleMenni, A.-E., Tzikos, G., Petrakis, G., Goulas, P., Karathanasis, P. V., & Apostolidis, S. (2025). Comparative Risk of Complications Following Intestinal Surgery After Infliximab, Vedolizumab, or Ustekinumab Treatment: Systematic Review & Meta-Analysis. Pharmaceuticals, 18(10), 1466. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18101466