Beyond Traditional Use: The Scientific Evidence for the Role of Astragali radix in Organ Protection via Modulating Oxidative Stress, Cell Death, and Immune Responses
Abstract
1. Introduction
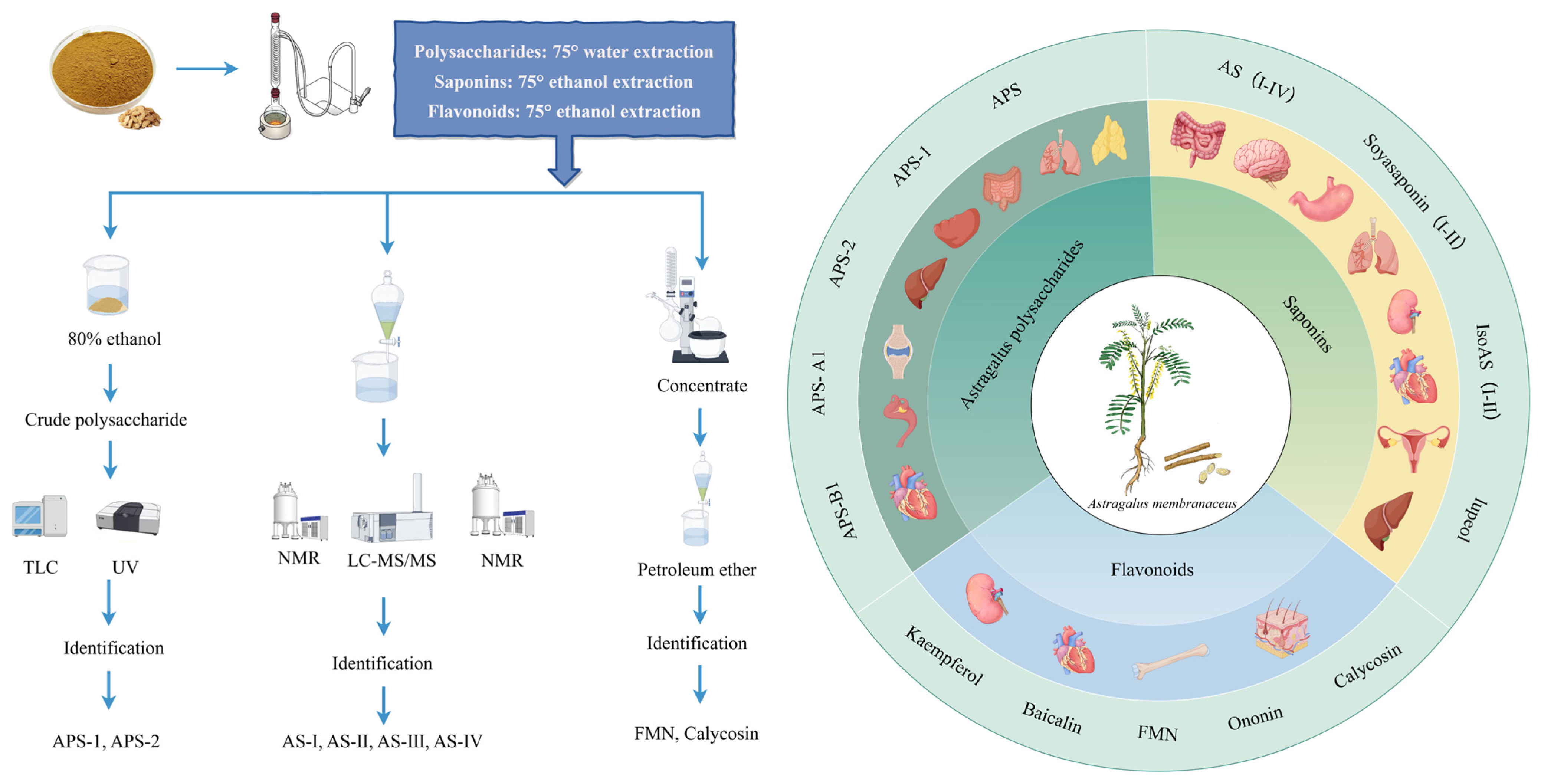
2. AR Extracts and Chemical Properties
2.1. Polysaccharides
2.2. Triterpenoid Saponins
2.3. Flavonoids
3. AR and Its Active Ingredients with Protective Effects on Multiple Organs and Tissues
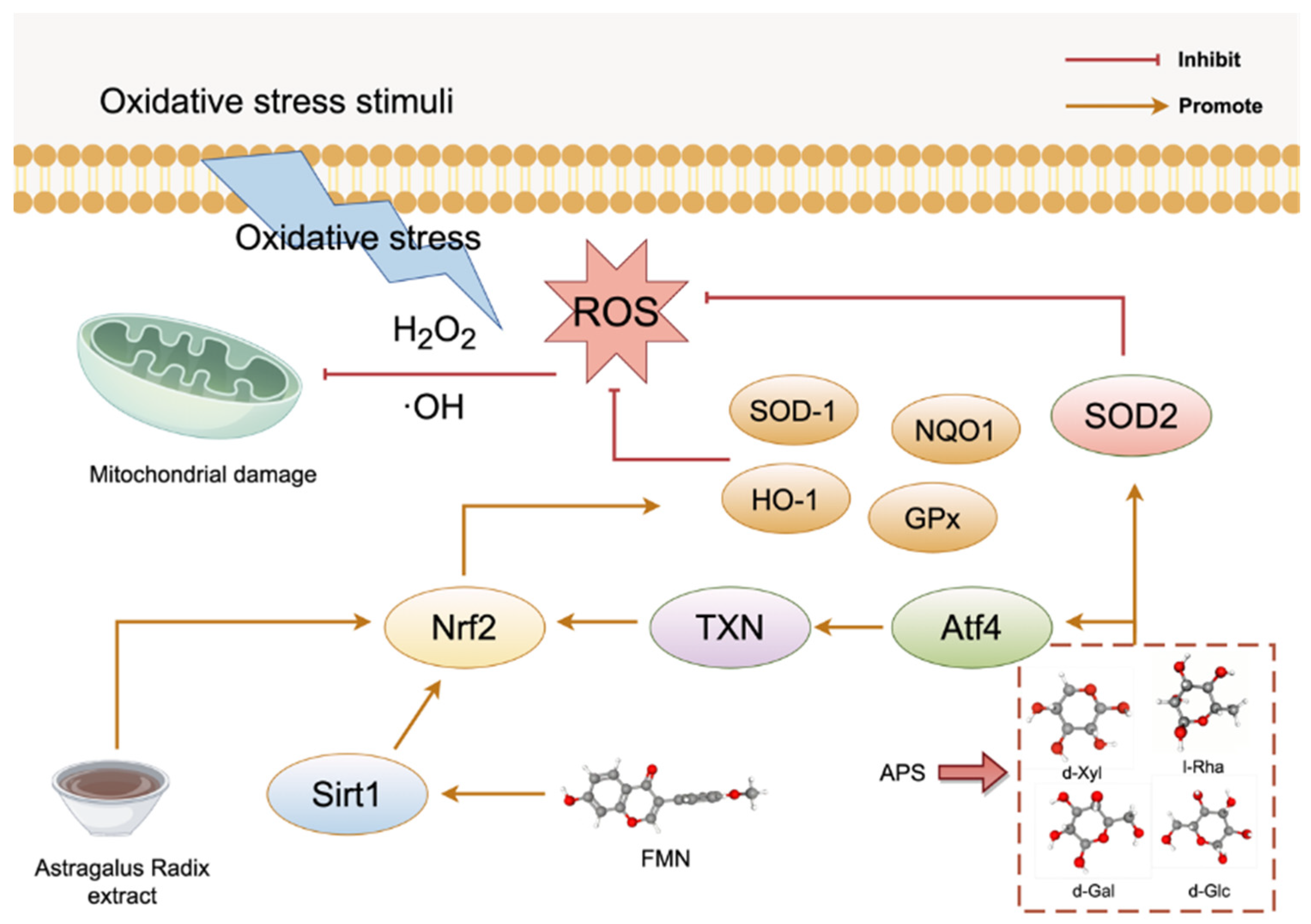
3.1. Oxidative Stress
3.2. Antiapoptotic Effects
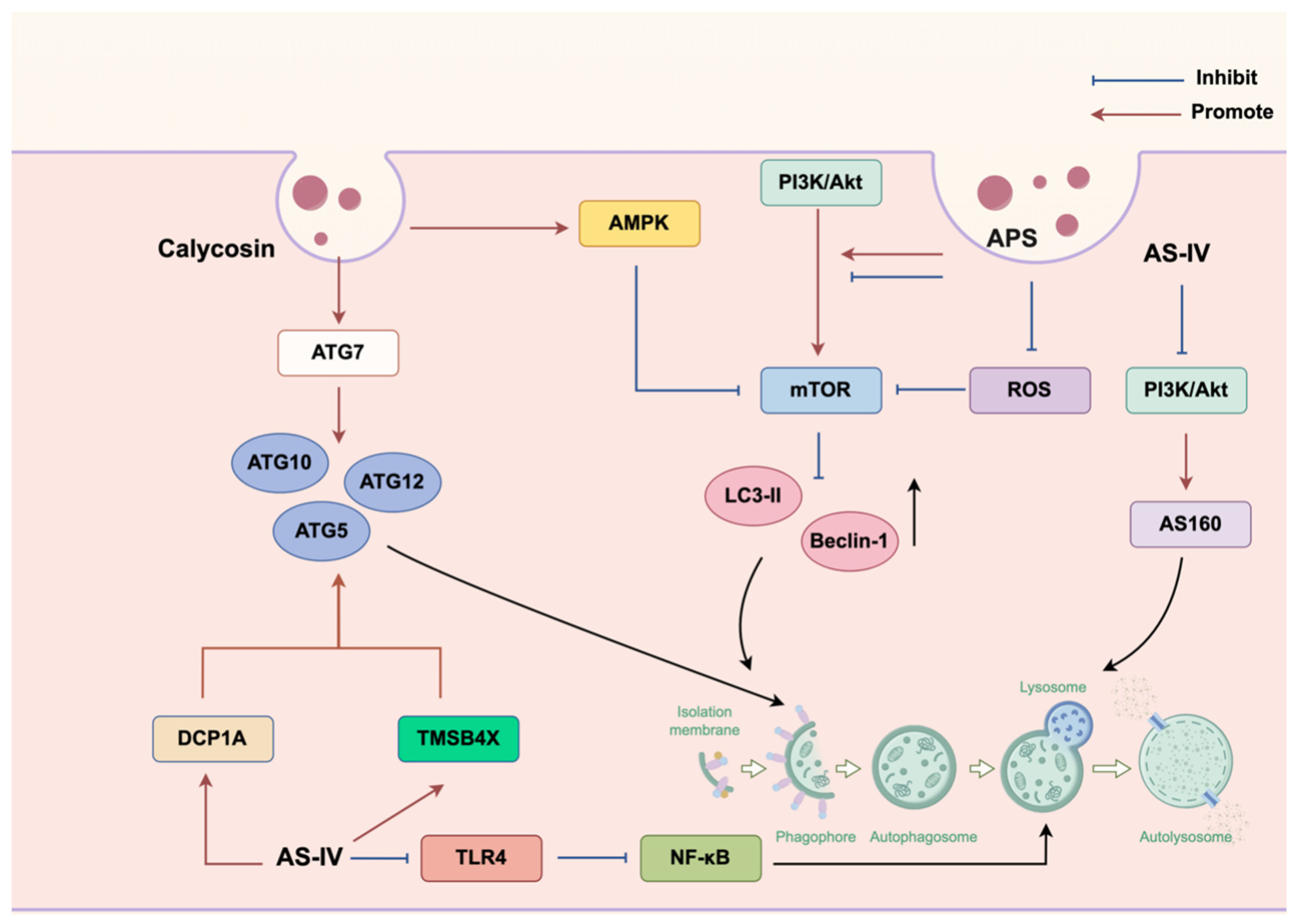
3.3. Autophagy
3.4. Immunoregulatory Effects
3.5. Anti-Inflammatory Effects
3.6. Other Functions
3.7. Multipathway Synergistic Effects
4. Safety Evaluation of AR Extract Components
5. Pharmacokinetic Study of AR
6. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AR | Astragali radix |
| APS | astragalus polysaccharides |
| FMN | formononetin |
| CA | Calycosin |
| ROS | reactive oxygen species |
| AS | astragalosides; astragalus saponins |
| AS-IV | astragaloside IV |
| IsoAS | isoastragalosides |
| SOD | superoxide dismutase |
| ATF4 | transcription factor 4 |
| TXN | thioredoxin |
| CSPCs | cardiac stem/progenitor cells |
| OGT | O-GlcNAc transferase |
| OGA | O-GlcNAcase |
| CHOP | C/EBP homologous protein |
| ER | endoplasmic reticulum |
| ATG | autophagy-related genes |
| DOX | doxorubicin |
| ASMCs | airway smooth muscle cells |
| CAG | Cycloastragenol |
| HIBD | hypoxic–ischemic brain damage |
| NOAEL | no-observed-adverse-effect level |
| PK | Pharmacokinetics |
| DDIs | drug–drug interactions |
References
- Xu, L.I.; Yu, X.; Chen, Q. Exploratory review on the effect of Astragalus mongholicus on signaling pathways. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1510307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Zhang, F.; Sun, C.; E, X.; He, Y. Investigation of Substance-Based Differences Among Mongolian Astragalus, Astragalus membranaceus, and Their Honey-Fried Varieties Based on Chemical Composition. Shizhen Guoji Guoyao 2021, 32, 2681–2684. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J.; Ji, H.Y.; Liu, A.J. Alcohol-soluble polysaccharide from Astragalus membranaceus: Preparation, characteristics and antitumor activity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 118 Pt B, 2057–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.; Yang, S.; Zhang, N.; Yu, C.; Liu, J.; Feng, W.; Xu, W.; Mao, Y. Astragalus polysaccharides alleviates cardiac hypertrophy in diabetic cardiomyopathy via inhibiting the BMP10-mediated signaling pathway. Phytomedicine 2023, 109, 154543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Wen, F.; Zhong, X.; Du, W.; Chen, M.; Wang, J. Astragaloside IV ameliorate acute alcohol-induced liver injury in mice via modulating gut microbiota and regulating NLRP3/caspase-1 signaling pathway. Ann. Med. 2023, 55, 2216942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.; Yu, J.Y.; Li, J.; Li, M.; Peng, L.Y.; Yi, P.F. Astragaloside IV Regulates cGAS-STING Signaling Pathway to Alleviate Immunosuppression Caused by PRRSV Infection. Viruses 2023, 15, 1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Cui, T.; Liu, Y.; Wu, S.; Han, C.; Li, J. Astragalus membranaceus and Salvia miltiorrhiza ameliorate diabetic kidney disease via the “gut-kidney axis”. Phytomedicine 2023, 121, 155129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.; Li, W.; Wang, G.; Fang, S.; Cai, J.; Wang, T.; Zhang, H.; Liu, P.; Wu, J.; Ma, Y. Hepatoprotective effects of Huangqi decoction (Astragali Radix and Glycyrrhizae Radix et Rhizoma) on cholestatic liver injury in mice: Involvement of alleviating intestinal microbiota dysbiosis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 267, 113544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Ren, J.; Yang, L.; Sun, H.; Yan, G.; Han, Y.; Wang, X. Elucidation for the pharmacological effects and mechanism of Shen Bai formula in treating myocardial injury based on energy metabolism and serum metabolomic approaches. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 323, 117670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, S.S.; Aday, A.W.; Allen, N.B.; Almarzooq, Z.I.; Anderson, C.A.M.; Arora, P.; Avery, C.L.; Baker-Smith, C.M.; Bansal, N.; Beaton, A.Z.; et al. 2025 Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics: A Report of US and Global Data From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2025, 151, e41–e660. [Google Scholar]
- Han, X.; Hu, S.; Yang, Q.; Sang, X.; Tang, D.; Cao, G. Paeoniflorin ameliorates airway inflammation and immune response in ovalbumin induced asthmatic mice: From oxidative stress to autophagy. Phytomedicine 2022, 96, 153835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muro, P.; Zhang, L.; Li, S.; Zhao, Z.; Jin, T.; Mao, F.; Mao, Z. The emerging role of oxidative stress in inflammatory bowel disease. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1390351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wimmer, R.A.; Leopoldi, A.; Aichinger, M.; Wick, N.; Hantusch, B.; Novatchkova, M.; Taubenschmid, J.; Hämmerle, M.; Esk, C.; Bagley, J.A.; et al. Human blood vessel organoids as a model of diabetic vasculopathy. Nature 2019, 565, 505–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beydag-Tasöz, B.S.; Yennek, S.; Grapin-Botton, A. Towards a better understanding of diabetes mellitus using organoid models. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2023, 19, 232–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, P.; Long, H.; Yang, Q.; Zhou, R.; Yang, W.J.; Chen, F.X.; Xie, J.W.; Zhao, Y.N.; Xu, H.B. Astragaloside IV alleviates diabetic nephropathy by modulating the gut-kidney axis and AMPK/PI3K/AKT pathway. Food Biosci. 2024, 62, 105448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Yu, H.; Liu, P.; Yang, Q.; Chen, Y.; Luo, P.; Zhang, C.; Gao, Y. Calycosin modulates inflammation via suppressing TLR4/NF-κB pathway and promotes bone formation to ameliorate glucocorticoid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head in rat. Phytother. Res. 2021, 35, 2824–2835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Yao, Y.; Ding, H.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Cai, T. Rapid classification and identification of chemical components of Astragali radix by UPLC-Q-TOF-M.S. Phytochem. Anal. 2022, 33, 943–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Yang, M.; Ma, L.; Liu, X.; Ding, Q.; Chai, G.; Lu, Y.; Wei, H.; Zhang, S.; Ding, C. Structural Modification and Biological Activity of Polysaccharides. Molecules 2023, 28, 5416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, H.; Wang, M.; Li, R.; Duan, M.; Wu, H.; Zhou, H. Extraction condition optimization and effects of drying methods on physicochemical properties and antioxidant activities of polysaccharides from Astragalus cicer L. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Huang, L.; Zhang, H.; Yang, S.; Chen, S. Structural features of a polysaccharide from Astragalus membranaceus (Fisch.) Bge. var. mongholicus (Bge.) Hsiao. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2013, 15, 687–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Jiang, N.; Zheng, J.; Hu, H.; Yang, H.; Lin, A.; Hu, B.; Liu, H. Structural characterization and anti-inflammatory activity of polysaccharides from Astragalus membranaceus. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 241, 124386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.C.; Shan, J.J.; Wang, Z.T.; Hu, Z.B. Isolation and Structural Analysis of an Acidic Polysaccharide from Astragalus membranaceus (Fisch.) Bunge. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2006, 48, 1379–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajimura, K.; Takagi, Y.; Miyano, K.; Sawabe, Y.; Mimura, M.; Sakagami, Y.; Yokoyama, H.; Yoneda, K. Polysaccharide of Astragali radix enhances IgM antibody production in aged mice. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 1997, 20, 1178–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Yu, X.; Xu, J.; Zhan, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, L. Separation, structural characterization, and bioactivity study of Astragalus polysaccharides. Food Ferment. Ind. 2020, 46, 50–56. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Q.; Lv, G.; Li, Y.; Guo, J.; Wang, R. Research on Astragalus polysaccharides. Acta Pharm. Sin. 1982, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Peng, Y.; Zhuang, Y.; Wang, N.; Jin, J.; Zhan, Z. Purification, Structural Analysis and Cardio-Protective Activity of Polysaccharides from Radix Astragali. Molecules 2023, 28, 4167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Ji, H.; Dong, X.; Feng, Y.; Liu, A. Apoptosis of human gastric carcinoma MGC-803 cells induced by a novel Astragalus membranaceus polysaccharide via intrinsic mitochondrial pathways. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 126, 811–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, A.J.; Yu, J.; Ji, H.Y.; Zhang, H.C.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, H.P. Extraction of a Novel Cold-Water-Soluble Polysaccharide from Astragalus membranaceus and Its Antitumor and Immunological Activities. Molecules 2017, 23, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, X.; Ma, X.; Liu, L.; Ren, J.; Li, H.; Li, X.; Yu, S.; Zhang, W.; Fan, W. Structural characterization and antioxidant activity in vitro of polysaccharides from angelica and astragalus. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 137, 154–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, W.; Li, J.; Tang, S.; Wang, M.; Huang, W.; Yao, W.; Gao, X. A polysaccharide extracted from Astragalus membranaceus residue improves cognitive dysfunction by altering gut microbiota in diabetic mice. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 205, 500–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, F.; Yang, S.; Li, M.; Wang, J.; Liu, L.; Zhang, L. Research Progress on the Anti-Cancer Effects of Astragalus membranaceus Saponins and Their Mechanisms of Action. Molecules 2024, 29, 3388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abd Elrahim Abd Elkader, H.T.; Essawy, A.E.; Al-Shami, A.S. Astragalus species: Phytochemistry, biological actions and molecular mechanisms underlying their potential neuroprotective effects on neurological diseases. Phytochemistry 2022, 202, 113293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, W.; Zhang, Z. Characterization of astragaloside I-IV based on the separation of HPTLC from Pleurotus ostreatus cultivated with Astragalus. J. Food Sci. 2020, 85, 3183–3190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, C.; Cai, H.X.; Ren, M.T.; Liu, E.H.; Li, B.; Qi, L.W.; Li, P. Characterization of novel astragaloside malonates from Radix Astragali by HPLC with ESI quadrupole TOF MS. J. Sep. Sci. 2010, 33, 570–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.D.; Su, Q.X.; Wang, N.L.; Pei, D.; Huang, X.Y. Separation of astragaloside IV from Astragalus membranaceus based on high-speed countercurrent chromatography in continuous injection mode. Phytochem. Anal. 2025, 36, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Jiang, X.; Shi, J.; Zhang, J.; Shi, X.; Xie, Z.; Chen, G.; Zhang, H.; Mu, Y.; Chen, J.; et al. Isoastragaloside I attenuates cholestatic liver diseases by ameliorating liver injury, regulating bile acid metabolism and restoring intestinal barrier. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 335, 118649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Zhao, H.; Luo, Y. Anti-Aging Implications of Astragalus Membranaceus (Huangqi): A Well-Known Chinese Tonic. Aging Dis. 2017, 8, 868–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Chen, B.; Liang, D.; Quan, X.; Gu, R.; Meng, Z.; Gan, H.; Wu, Z.; Sun, Y.; Liu, S.; et al. Pharmacological Effects of Astragaloside IV: A Review. Molecules 2023, 28, 6118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.F.; Qin, L.Y.; Wang, J.X.; Guan, P.; Wang, N.; Ji, E.S. Astragaloside IV Attenuates the Myocardial Injury Caused by Adriamycin by Inhibiting Autophagy. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 669782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Zhang, X.; Xie, L.; Deng, M.; Chen, H.; Song, J.; Long, J.; Li, X.; Luo, J. Lupeol and its derivatives as anticancer and anti-inflammatory agents: Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic efficacy. Pharmacol. Res. 2021, 164, 105373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, X.; Chen, X.; Guo, Y.; Gong, P.; Pei, S.; Wang, D.; Wang, P.; Wang, M.; Chen, F. Advances in Chemical Composition, Extraction Techniques, Analytical Methods, and Biological Activity of Astragali Radix. Molecules 2022, 27, 1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Q.T.; Qi, L.W.; Li, P.; Yi, L.; Zhao, J.; Bi, Z. Determination of seventeen main flavonoids and saponins in the medicinal plant Huang-qi (Radix astragali) by HPLC-DAD-ELSD. J. Sep. Sci. 2007, 30, 1292–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitagawa, I.; Wang, H.; Yoshikawa, M. Saponin and Sapogenol. XXXVII. Chemical constituents of Astragali Radix, the root of Astragalus membranaceus Bunge. (4) Astragalosides VII and VIII. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1983, 31, 716–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, N.; Wang, T.; Gan, Q.; Liu, S.; Wang, L.; Jin, B. Plant flavonoids: Classification, distribution, biosynthesis, and antioxidant activity. Food Chem. 2022, 383, 132531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasteva, I.; Platikanov, S.; Nikolov, S.; Kaloga, M. Flavonoids from Astragalus hamosus. Nat. Prod. Res. 2007, 21, 392–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, J.; Yang, B. UHPLC-MS/MS Analysis on Flavonoids Composition in Astragalus membranaceus and Their Antioxidant Activity. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gencer, G.; Sarikurkcu, C.; Tepe, B. Unveiling the Phytochemical Diversity and Bioactivity of Astragalus melanophrurius: A First Report Integrating Experimental and In Silico Approaches. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altemimi, A.B.; Mohammed, M.J.; Yi-Chen, L.; Watson, D.G.; Lakhssassi, N.; Cacciola, F.; Ibrahim, S.A. Optimization of Ultrasonicated Kaempferol Extraction from Ocimum basilicum Using a Box-Behnken Design and Its Densitometric Validation. Foods 2020, 9, 1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Ma, X.; Cheng, Q.; Wang, L.; Zhang, L. Deep Eutectic Solvent-Based Ultrahigh Pressure Extraction of Baicalin from Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi. Molecules 2018, 23, 3233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, C.; Cui, W.Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zou, X.S.; Hao, J.Y.; Zheng, S.D.; Wang, T.T.; Wang, X.Z.; Wu, T.; Liu, Y.Y.; et al. Ultrasound-assisted deep eutectic solvents extraction of glabridin and isoliquiritigenin from Glycyrrhiza glabra: Optimization, extraction mechanism and in vitro bioactivities. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2022, 83, 105946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.; Wang, H.; Shan, H.; Lü, H. Preparative Isolation and Purification of Calycosin and Formononetin from Astragali Radix using Hydrolytic Extraction Combined with High Speed Countercurrent Chromatography. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2021, 59, 412–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, K.; Jiang, X.; Liu, R.; Ye, C.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Quan, S.; Huang, H. Formononetin Activates the Nrf2/ARE Signaling Pathway Via Sirt1 to Improve Diabetic Renal Fibrosis. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 616378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, X.; Quan, S.; Guo, R.; Li, Z.; Bai, M.; Wang, B.; Su, P.; Xu, E.; Li, Y. Calycosin-7-O-β-D-glucoside downregulates mitophagy by mitigating mitochondrial fission to protect HT22 cells from oxygen-glucose deprivation/reperfusion-induced injury. Mol. Med. Rep. 2025, 31, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, W.; Kan, H.; Li, P.; Liu, S.; Liu, Z. Screening and structural characterization of potential α-glucosidase inhibitors from Radix Astragali flavonoids extract by ultrafiltration LC-DAD-ESI-MSn. Anal. Methods 2014, 7, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.Y.; Li, J.Y.; Zhang, M.; Yang, L.; Wang, Y.Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, J. Pharmacokinetic investigation on the mechanism of interaction of anti-breast cancer calycosin with albumin: In vitro. Arab. J. Chem. 2023, 16, 105175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.D.; Qi, L.W.; Li, P.; Bao, K.D.; Yan, X.W.; Yi, L.; Li, C.Y. Simultaneous determination of calycosin-7-O-beta-D-glucoside, ononin, astragaloside IV, astragaloside I and ferulic acid in rat plasma after oral administration of Danggui Buxue Tang extract for their pharmacokinetic studies by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2008, 865, 99–105. [Google Scholar]
- Vesnina, A.; Milentyeva, I.; Minina, V.; Kozlova, O.; Asyakina, L. Evaluation of the In Vivo Anti-Atherosclerotic Activity of Quercetin Isolated from the Hairy Roots of Hedysarum neglectum Ledeb. Life 2023, 13, 1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Wang, J.; Sun, L.; Ba, B.; Shen, D. Mechanism of Astragalus membranaceus (Huangqi, HQ) for treatment of heart failure based on network pharmacology and molecular docking. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2024, 28, e18331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Chen, L.; Dong, Q.; Yang, D.H.; Zhang, Q.; Zeng, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Cui, Y.; et al. Astragali radix (Huangqi): A time-honored nourishing herbal medicine. Chin. Med. 2024, 19, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahara, S.; Kohjyouma, M.; Kohoda, H. Flavonoid glycosides and saponins from Astragalus shikokianus. Phytochemistry 2000, 53, 469–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sies, H. Oxidative stress: A concept in redox biology and medicine. Redox Biol. 2015, 4, 180–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahzad, M.; Shabbir, A.; Wojcikowski, K.; Wohlmuth, H.; Gobe, G.C. The Antioxidant Effects of Radix Astragali (Astragalus membranaceus and Related Species) in Protecting Tissues from Injury and Disease. Curr. Drug Targets 2016, 17, 1331–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaganjac, M.; Milkovic, L.; Zarkovic, N.; Zarkovic, K. Oxidative stress and regeneration. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2022, 181, 154–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adesso, S.; Russo, R.; Quaroni, A.; Autore, G.; Marzocco, S. Astragalus membranaceus Extract Attenuates Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in Intestinal Epithelial Cells via NF-κB Activation and Nrf2 Response. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Wang, J.; Guo, W.; Liu, Y.; Guo, Z.; Miao, Y.; Wang, D. Studies on characteristics and anti-diabetic and -nephritic effects of polysaccharides isolated from Paecilomyces hepiali fermentation mycelium in db/db mice. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 232, 115766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Qin, C.; Ji, C.; Yu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Xu, L.; Jiang, Y.; Zou, G. Astragalus polysaccharide alleviates oxidative stress and senescence in chondrocytes in osteoarthritis via GCN2/ATF4/TXN axis. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 310 Pt 3, 143285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.J.; Kang, M.H.; Han, S.H.; Kim, G.S.; Kim, H.D.; Jang, G.Y. Roasted Astragalus membranaceus Inhibits Aβ25-35-Induced Oxidative Stress in Neuronal Cells by Activating the Nrf2/HO-1 and AKT/CREB/BDNF Pathways. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacco, F.; Brownlee, M. Oxidative stress and diabetic complications. Circ. Res. 2010, 107, 1058–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Ju, J.; Yang, Y.; Wang, H.; Chen, W.; Zhao, X.; Ye, H.; Zhang, Y. Astragalus polysaccharides protect cardiac stem and progenitor cells by the inhibition of oxidative stress-mediated apoptosis in diabetic hearts. Drug Des. Devel Ther. 2018, 12, 943–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coolen, S.A.; Daykin, C.A.; van Duynhoven, J.P.; van Dorsten, F.A.; Wulfert, F.; Mathot, J.; Scheltinga, M.R.; Stroosma, O.; Vader, H.; Wijnen, M.H. Measurement of ischaemia-reperfusion in patients with intermittent claudication using NMR-based metabonomics. NMR Biomed. 2008, 21, 686–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Ni, J.; Cao, Y.; Xing, X.; Wu, Q.; Fan, G. Astragaloside IV Attenuates Myocardial Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury from Oxidative Stress by Regulating Succinate, Lysophospholipid Metabolism, and ROS Scavenging System. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 9137654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Shen, H.; Jiang, M.; Huang, L.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, Q. Calycosin reduces infarct size, oxidative stress and preserve heart function in isoproterenol-induced myocardial infarction model. Pak. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 33, 1341–1347. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, Y.; Liu, W.; Xiong, Y.; Li, Y.; Wan, Q.; Zhou, W.; Zhao, H.; Xiao, Q.; Liu, D. Astragaloside IV alleviates ulcerative colitis by regulating the balance of Th17/Treg cells. Phytomedicine 2022, 104, 154287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Xu, W.Y.; Gu, Y.; Tang, Y.X.; Xu, X.W.; Li, X.N.; Li, J.L. Inhibition of mtDNA-PRRs pathway-mediated sterile inflammation by astragalus polysaccharide protects against transport stress-induced cardiac injury in chicks. Poult. Sci. 2024, 103, 103638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, X.; Xin, J.; Chen, W.; Wang, J.; Lv, Y.; Wei, Y.; Li, Z.; Ding, Q.; Shen, Y.; Xu, X.; et al. Astragalus polysaccharide ameliorated complex factor-induced chronic fatigue syndrome by modulating the gut microbiota and metabolites in mice. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 163, 114862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, K.; Shang, T.; Cai, Z.; Lu, C.; Shen, M.; Yu, S.; Yao, X.; Shen, Y.; Chen, X.; et al. Astragaloside IV Improves Muscle Atrophy by Modulating the Activity of UPS and ALP via Suppressing Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Denervated Mice. Mol. Neurobiol. 2025, 62, 4689–4704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Mao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Xu, Y.; An, J.; Huang, Z. The chemical biology of apoptosis: Revisited after 17 years. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 177, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyer, A.; Tanaka, K.; Cheng, E.H. Apoptosis in Cancer Biology and Therapy. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2025, 20, 303–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grilo, A.L.; Mantalaris, A. Apoptosis: A mammalian cell bioprocessing perspective. Biotechnol. Adv. 2019, 37, 459–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, M.S.; Schmezer, P.; Breuer, R.; Haas, S.F.; Essers, M.A.; Krammer, P.H.; Li-Weber, M. The traditional Chinese medical compound Rocaglamide protects nonmalignant primary cells from DNA damage-induced toxicity by inhibition of p53 expression. Cell Death Dis. 2014, 5, e1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.Y.; Zeng, L.J.; Huang, Y.; Huang, Y.Q.; Zhu, Q.F.; Liao, Z.H. 8-60hIPP5(m)-induced G2/M cell cycle arrest involves activation of ATM/p53/p21(cip1/waf1) pathways and delayed cyclin B1 nuclear translocation. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2014, 15, 4101–4107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, W.R.; Li, Z.P.; Zhang, Q.W.; Li, L.F.; Liu, H.B.; Ma, D.L.; Leung, C.H.; Lu, A.P.; Bian, Z.X.; Han, Q.B. Astragalus polysaccharide RAP Selectively Attenuates Paclitaxel-Induced Cytotoxicity Toward RAW 264.7 Cells by Reversing Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, B.; Sun, Y.; Jia, Y.; Xu, Z. Astragalus root extract inhibits retinal cell apoptosis and repairs damaged retinal neovascularization in retinopathy of prematurity. Cell Cycle 2019, 18, 3147–3159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, A.; Bello, D.; Fernández-Tejada, A. Advances in chemical probing of protein O-GlcNAc glycosylation: Structural role and molecular mechanisms. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 10451–10485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahie, K.; Papanicolaou, K.N.; Zachara, N.E. Integration of O-GlcNAc into Stress Response Pathways. Cells. 2022, 11, 3509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Queiroz, R.M.; Carvalho, E.; Dias, W.B. O-GlcNAcylation: The Sweet Side of the Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2014, 4, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.J.; Lee, D.E.; Choi, S.Y.; Kwon, O.S. OSMI-1 Enhances TRAIL-Induced Apoptosis through ER Stress and NF-κB Signaling in Colon Cancer Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Duan, F.; Pan, Z.; Liu, X.; Lu, W.; Liang, C.; Fang, Z.; Peng, P.; Jia, D. Astragalus polysaccharide Promotes Doxorubicin-Induced Apoptosis by Reducing O-GlcNAcylation in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cells 2023, 12, 866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Yang, S.; An, N.; Wang, G.; Xu, Q.; Liu, J.; Mao, Y. Astragalus polysaccharides inhibits cardiomyocyte apoptosis during diabetic cardiomyopathy via the endoplasmic reticulum stress pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2019, 238, 111857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Chen, H.; Yin, K.; Shen, Y.; Lin, K.; Guo, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, N.; Xin, W.; Xu, Y.; et al. Formononetin Attenuates Renal Tubular Injury and Mitochondrial Damage in Diabetic Nephropathy Partly via Regulating Sirt1/PGC-1α Pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 901234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, P.F.; Mahendran, R.; Tsai, B.C.; Lu, C.Y.; Kuo, C.H.; Lin, K.H.; Lu, S.Y.; Wu, Y.L.; Chang, Y.M.; Kuo, W.W.; et al. Calycosin Enhances Heat Shock Related-Proteins in H9c2 Cells to Modulate Survival and Apoptosis against Heat Shock. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2024, 52, 1173–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, S.T.; Kim, C.; Lee, J.H.; Chinnathambi, A.; Alharbi, S.A.; Shair, O.H.M.; Sethi, G.; Ahn, K.S. Cycloastragenol can negate constitutive STAT3 activation and promote paclitaxel-induced apoptosis in human gastric cancer cells. Phytomedicine 2019, 59, 152907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Yu, Y.; Chen, K.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Zou, X.; Xu, X.; Jiang, Y. Astragalus polysaccharides ameliorate osteoarthritis via inhibiting apoptosis by regulating ROS-mediated ASK1/p38 MAPK signaling pathway targeting on TXN. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 258 Pt 2, 129004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Ye, Z.; Zheng, G.; Su, Z. Polysaccharides targeting autophagy to alleviate metabolic syndrome. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 283 Pt 1, 137393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, S.; Yoshimori, T. New insights into autophagosome-lysosome fusion. J. Cell Sci. 2017, 130, 1209–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.C.; Guan, K.-L. mTOR: Apharmacologic target for autophagy regulation. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 125, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Spina, M.; Contreras, P.S.; Rissone, A.; Meena, N.K.; Jeong, E.; Martina, J.A. MiT/TFE Family of Transcription Factors: An Evolutionary Perspective. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 609683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, A.; Koh, H.C. NF-κB/mTOR-mediated autophagy can regulate diquat-induced apoptosis. Arch Toxicol. 2019, 93, 1239–1253. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30848314/ (accessed on 23 September 2025). [CrossRef]
- Vanhoutte, D.; Schips, T.G.; Vo, A.; Grimes, K.M.; Molkentin, J.D. Thbs1 induces lethal cardiac atrophy through PERK-ATF4 regulated autophagy. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Yin, L.; Sun, Z.; Shao, S.; Chen, W.; Man, X.; Du, Y.; Chen, Y. Astragalus polysaccharide exerts anti-Parkinson via activating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway to increase cellular autophagy level in vitro. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 153, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, S.; Luo, Y.; Liu, W.; Tang, C.; Zhu, T.; Tian, L.; Zheng, T.; Ling, L.; Jia, M.; Li, X. Calycosin alleviates ovariectomy-induced osteoporosis by promoting BMSCs autophagy via the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025, 398, 11963–11974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Qu, Q.; Zhao, C.; Liu, X.; Yang, P.; Li, Z.; Han, L.; Shi, X. Paecilomyces cicadae-fermented Radix astragali activates podocyte autophagy by attenuating PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathways to protect against diabetic nephropathy in mice. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 129, 110479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ying, Y.; Sun, C.B.; Zhang, S.Q.; Chen, B.J.; Yu, J.Z.; Liu, F.Y.; Wen, J.; Hou, J.; Han, S.S.; Yan, J.Y. Induction of autophagy via the TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway by astragaloside IV contributes to the amelioration of inflammation in RAW264.7 cells. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 137, 111271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, X.; Tang, Z.; Bai, Y.; Wan, M.; Yu, M.; Chen, J.; Li, G.; Zhang, R.; Ge, M. Astragalus Polysaccharide Protects Against Cadmium-Induced Autophagy Injury Through Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Pathway in Chicken Embryo Fibroblast. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2022, 200, 318–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mauvezin, C.; Neufeld, T.P. Autophagosomes take the Klp98-A train. Small GTPases. 2017, 8, 16–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lu, R.; Chen, J.; Liu, B.; Lin, H.; Bai, L.; Zhang, P.; Chen, D.; Li, H.; Li, J.; Zhou, Y.; et al. Protective role of Astragaloside IV in chronic glomerulonephritis by activating autophagy through PI3K/AKT/AS160 pathway. Phytother. Res. 2020, 34, 3236–3248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Lu, L.; Gao, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, W. Calycosin attenuates doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity via autophagy regulation in zebrafish models. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 137, 111375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Li, Y.; Jiang, W.; Wang, Z. Molecular Mechanism of Calycosin Inhibited Vascular Calcification. Nutrients 2023, 16, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, C.; He, Z.; Cai, Y. Quantitative proteomics analysis of differentially expressed proteins induced by astragaloside IV in cervical cancer cell invasion. Cell Mol. Biol. Lett. 2020, 25, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, J.I.; Farber, D.L. Tissue-Resident Immune Cells in Humans. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2022, 40, 195–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.O.; Zhang, J.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Li, P.; Cornish, A.E. Multilayered Immunity by Tissue-Resident Lymphocytes in Cancer. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2024, 42, 647–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Han, X.; Yuan, J.; Xing, F.; Hu, Z.; Huang, F.; Wu, H.; Shi, H.; Zhang, T.; Wu, X. Early astragaloside IV administration attenuates experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in mice by suppressing the maturation and function of dendritic cells. Life Sci. 2020, 249, 117448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Hu, X.; Wang, S.; Jiao, Z.; Sun, T.; Liu, T.; Song, K. Characterization and anti-tumor bioactivity of astragalus polysaccharides by immunomodulation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 145, 985–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dou, B.; Li, S.; Wei, L.; Wang, L.; Zhu, S.; Wang, Z.; Ke, Z.; Chen, K.; Wang, Z. Astragaloside IV suppresses post-ischemic natural killer cell infiltration and activation in the brain: Involvement of histone deacetylase inhibition. Front. Med. 2021, 15, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.Y.; Yang, Y.H.; Lin, Y.S.; Shu, L.H.; Liu, H.T.; Lu, C.K.; Wu, Y.H.; Wu, Y.H. The effect and mechanism of astragalus polysaccharides on T cells and macrophages in inhibiting prostate cancer. Biomed. J. 2025, 48, 100741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Li, S.; Chen, T.; Li, Z.; Gao, X.; Wang, Z. Astragaloside IV ameliorates peripheral immunosuppression induced by cerebral ischemia through inhibiting HPA axis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2022, 105, 108569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Tao, Y.; Wang, M.; Chen, Y.; Han, X.; Wu, H.; Shi, H.; Huang, F.; Wu, X. Astragaloside II, a natural saponin, facilitates remyelination in demyelination neurological diseases via p75NTR receptor mediated β-catenin/Id2/MBP signaling axis in oligodendrocyte precursor cells. J. Adv. Res. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Song, L.; Huang, J.; Zhou, W.; Liu, Y.; Lu, X.; Zhao, H.; Liu, D. Astragalus polysaccharides ameliorates experimental colitis by regulating memory B cells metabolism. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2024, 394, 110969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.T.; Zheng, Q.; Tai, Z.G.; Jiang, W.C.; Xie, S.Q.; Luo, Y.; Fei, X.Y.; Luo, Y.; Ma, X.; Kuai, L. Formononetin attenuates psoriasiform inflammation by regulating interferon signaling pathway. Phytomedicine 2024, 128, 155412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lassmann, H. Classification of demyelinating diseases at the interface between etiology and pathogenesis. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2001, 14, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin, R.; Simons, M. CNS remyelination and inflammation: From basic mechanisms to therapeutic opportunities. Neuron 2022, 110, 3549–3565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emery, B.; Wood, T.L. Regulators of Oligodendrocyte Differentiation. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2024, 16, a041358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritala, J.F.; Lyne, S.B.; Sajanti, A.; Girard, R.; Koskimäki, J. Towards a comprehensive understanding of p75 neurotrophin receptor functions and interactions in the brain. Neural Regen. Res. 2022, 17, 701–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Cheng, B.; Xu, X.; Yan, W.; Meng, Q.; Liu, J.; Yao, R.; Dong, F.; Liu, Y. High-intensity interval training stimulates remyelination via the Wnt/β-catenin pathway in cuprizone-induced demyelination mouse model. Neurol. Res. 2024, 46, 996–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bianconi, V.; Sahebkar, A.; Atkin, S.L.; Pirro, M. The regulation and importance of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 2018, 25, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, N.; Li, X.; Xue, C.; Zhang, L.; Wang, C.; Xu, X.; Shan, A. Astragalus polysaccharides alleviates LPS-induced inflammation via the NF-κB/MAPK signaling pathway. J. Cell Physiol. 2020, 235, 5525–5540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Qi, M.; Liu, C.; Li, L. Astragalus polysaccharide attenuates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis by inhibiting TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway and regulating gut microbiota. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2023, 944, 175594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, E.K.; Kim, J.K.; Shin, D.M.; Sasakawa, C. Molecular mechanisms regulating NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2016, 13, 148–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Hu, M.; Yuan, C.; Ren, B.; Zhong, M.; Zhou, S.; Wang, X.; Gao, Q.; Zeng, M.; Cai, X.; et al. Astragaloside IV ameliorates indomethacin-induced intestinal inflammation in rats through inhibiting the activation of NLRP3 inflammasome. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 135, 112281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapouri-Moghaddam, A.; Mohammadian, S.; Vazini, H.; Taghadosi, M.; Esmaeili, S.A.; Mardani, F.; Seifi, B.; Mohammadi, A.; Afshari, J.T.; Sahebkar, A. Macrophage plasticity, polarization, and function in health and disease. J. Cell Physiol. 2018, 233, 6425–6440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, W.; Zhao, B.; Wei, H.; Yang, Y.; Yin, H.; Gao, J.; Zhao, W.; Kong, W.; Ge, G.; Lei, T. Astragalus polysaccharide ameliorates vascular endothelial dysfunction by stimulating macrophage M2 polarization via potentiating Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway. Phytomedicine 2023, 112, 154667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alblihed, M.A. Astragalin attenuates oxidative stress and acute inflammatory responses in carrageenan-induced paw edema in mice. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2020, 47, 6611–6620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Lai, Y.; Peng, H.; Tong, C. Role of Lymphadenectomy During Interval Debulking Surgery Performed After Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Patients with Advanced Ovarian Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 646135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Liu, G.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H. Astragalus polysaccharides inhibit ovarian cancer cell growth via microRNA-27a/FBXW7 signaling pathway. Biosci. Rep. 2020, 40, BSR20193396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Q.; Yu, Y.; Ye, L.; Zhang, S.; Li, Y.; Hua, X.; Shen, S.; Hu, D.; Lu, W. Astragalus polysaccharides sensitize ovarian cancer stem cells to PARPi by inhibiting mitophagy via PINK1/Parkin signaling. iScience 2024, 27, 110376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Stockwell, B.R.; Conrad, M. Ferroptosis: Mechanisms, biology and role in disease. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2021, 22, 266–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Zhao, J.; Li, C.; Wang, R.; Jiang, X.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, Q.; Xiao, M. Total Astragalus saponins promote ferroptosis in gastric cancer cells by upregulating SIRT3. Transl. Cancer Res. 2025, 14, 1311–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Le, Y.; Yuan, A.; Liu, J.; Chen, H.; Qiu, J.; Wang, C.; Dou, X.; Yuan, X.; Lu, D. Astragaloside IV ameliorates cisplatin-induced liver injury by modulating ferroptosis-dependent pathways. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 328, 118080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Han, Y.; Wang, Y. Yanghe Pingchuan Granules Alleviate Airway Inflammation in Bronchial Asthma and Inhibit Pyroptosis by Blocking the TLR4/NF-κB/NRLP3 Signaling Pathway. Mediat. Inflamm. 2022, 2022, 6561048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, J.; Pan, H.; Yang, K.; Hu, C. Astragaloside IV promotes the pyroptosis of airway smooth muscle cells in childhood asthma by suppressing HMGB1/RAGE axis to inactivate NF-κb pathway. Autoimmunity 2024, 57, 2387100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Shi, J.; Shen, Q.; Fu, Y.; Qi, S.; Wu, J.; Chen, J.; Zhang, H.; Mu, Y.; Chen, G.; et al. Astragalus saponins protect against extrahepatic and intrahepatic cholestatic liver fibrosis models by activation of farnesoid X receptor. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 318 Pt A, 116833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Zhang, N.; Zhao, L.; Wu, W.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, F.; Li, J. Astragalus Polysaccharides and Saponins Alleviate Liver Injury and Regulate Gut Microbiota in Alcohol Liver Disease Mice. Foods 2021, 10, 2688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamel, R.; El Morsy, E.M. Hepatoprotective effect of methylsulfonylmethane against carbon tetrachloride-induced acute liver injury in rats. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2013, 36, 1140–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, L.; Lo, H.; Zheng, J.; Weng, W.; Sun, Y.; Pan, X. Cycloastragenol reduces microglial NLRP3 inflammasome activation in Parkinson’s disease models by promoting autophagy and reducing Scrib-driven ROS. Phytomedicine 2024, 135, 156210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Di, Y.M.; May, B.; Zhang, A.L.; Zhang, L.; Chen, J.; Wang, R.; Liu, X.; Xue, C.C. Renal protective effects and mechanisms of Astragalus membranaceus for diabetic kidney disease in animal models: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Phytomedicine 2024, 129, 155646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Ding, W.; Yang, X.; Lu, T.; Liu, Y. Isoliquiritigenin, a potential therapeutic agent for treatment of inflammation-associated diseases. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 318 Pt B, 117059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Ding, Y.P.; Shao, B.P.; Yang, J.; Wu, J.G. Interaction between homologous functional food Astragali Radix and intestinal flora. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 2020, 45, 2486–2492. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, M.; Hu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Jiang, J.; Qi, R.; Chen, S.; Li, Y.; Zheng, H.; Liu, R.; Guo, Q.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Astragalus-Containing Traditional Chinese Medicine Combined with Platinum-Based Chemotherapy in Advanced Gastric Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 632168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Fang, Z.; Shi, J.; Feng, Y.; Liu, H.; Chen, H. Neuroprotection and safety profile of Astragalus membranaceus extract TA-65 in neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain damage by activating mitochondrial telomerase reverse transcriptase: Evidence from in vitro and in vivo studies. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2025, 351, 120073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murbach, T.S.; Glávits, R.; Endres, J.R.; Hirka, G.; Vértesi, A.; Béres, E.; Szakonyiné, I.P. Toxicological Evaluation of a Mixture of Astragalus membranaceus and Panax notoginseng Root Extracts (InnoSlim®). J. Toxicol. 2019, 2019, 5723851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Lee, D.; Min, B.; Bae, J.S.; Chang, G.T.; Kim, H. Safety evaluation of Astragalus extract mixture HT042 and its constituent herbs in Sprague-Dawley rats. Phytomedicine 2017, 32, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacevic, K.D.; Gilbert, J.C.; Jilma, B. Pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics and safety of aptamers. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2018, 134, 36–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Xia, K.; Wu, S.; Wang, Q.; Cheng, W.; Ji, C.; Yang, W.; Kang, C.; Yuan, Z.; Li, Y. Simultaneous determination and pharmacokinetic study of six components in beagle dog plasma by UPLC-MS/MS after oral administration of Astragalus membranaceus aqueous extract. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2022, 36, e5488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Zheng, L.; Lin, Z.; Hou, C.; Liu, W.; Yan, T.; Zhu, L.; Wang, Y.; Lu, L.; Liu, Z. Study of pharmacokinetic profiles and characteristics of active components and their metabolites in rat plasma following oral administration of the water extract of Astragali radix using UPLC-MS/MS. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 169, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, Y.; Huang, S.; Yang, G.; Li, W.; Cai, B. A simple and sensitive LC-MS/MS approach for simultaneous quantification of six bioactive compounds in rats following oral administration of aqueous extract and ultrafine powder of Astragalus propinquus: Application to a comparative pharmacokinetic study. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2018, 1096, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinder, M. Pharmacodynamic Drug–Drug Interactions; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, M.K.; Song, I.S. Pharmacokinetic Drug-Drug Interactions and Herb-Drug Interactions. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.; Liu, L.; Song, H.; Li, H. Pharmacokinetic study on the co-administration of abemaciclib and astragaloside IV in rats. Pharm. Biol. 2022, 60, 1944–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Wang, C.; Kong, Q.; Wu, X.; Lu, J.J.; Chen, X. Recent progress in doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity and protective potential of natural products. Phytomedicine 2018, 40, 125–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.H.; Shao, L.Q.; Xuan, L.Y.; Wang, C.G.; Wei, C.X.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, M. Effects of Astragalus membranaceus injection on cardiomyocyte apoptosis, endoplasmic reticulum stress and expression of connexin in cardiomyopathy rats induced by adriamycin. Chin. J. Appl. Physiol. 2018, 34, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, W.; Liu, T.; Wang, K.; Mu, L.; Ji, L.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, Q. Astragalus Injection Modulates the Pharmacokinetics of Doxorubicin and CYP450 Enzymes. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2025, 31, 3234–3246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, W.; Hu, J.; Liang, J.; Yang, X.; Fang, B.; Ma, G. Effect of Astragali radix extract on pharmacokinetic behavior of dapagliflozin in healthy and type 2 diabetic rats. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1214658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Wei, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, D.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, J.; Wu, X. Pharmacokinetics and hepatic uptake of gliquidone affected by Huangqi injection. Eur. J. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 2014, 39, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, F.; Zhou, H.; Fang, Y.; Li, C.; He, Y.; Yu, L.; Wan, H.; Yang, J. Astragaloside IV alleviates ischemia reperfusion-induced apoptosis by inhibiting the activation of key factors in death receptor pathway and mitochondrial pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 248, 112319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.G.; Li, J.L.; Li, P.; Yang, S.Q.; Zang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yu, Y.T.; Xie, X.; Li, H.F.; Hao, X.L.; et al. Neuroprotective triterpenoids from Astragalus membranaceus stems and leaves: Anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic mechanisms for memory improvement via in vivo and in vitro models. Bioorg. Chem. 2025, 160, 108492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Source | Chemical Name | Composition | Quality Ratio | Molecular Weight (Da) | Classification | Ref. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Astragalus polysaccharides (APS) | APS | l-Rha:d-Xyl:d-Glc:d-Gal | 1:4:5:1.5 | 3.01 × 105 | Heteropolysaccharides | Water-alcohol extraction | [20] |
| APSID3 | Ara:Rha:Gal:Glc | 2:2:5:6 | 5.79 × 105 | — | [22] | ||
| F-8 | Rha:Rib:Fuc:Ara:Xyl:Man:Gal:Glc | 2:2:1: 2:6:2: 3:100 | 2.2 × 104 | Neutral polysaccharide | [23] | ||
| F-9 | Fuc:Xyl:Glc | 1:2:100 | 1.2 × 104 | — | [23] | ||
| APS-1 | Gal:Glc | 1:49.76 | 3.84 × 104 | Heteropolysaccharides | [24] | ||
| APS-2 | Rha:Gal:Glc | 1:2.99:16.26 | 5.2 × 103 | Heteropolysaccharides | [24] | ||
| AH-1 | Gly:Glc:Rha:Ara | 1:0.04:0.02:0.01 | — | Acidic polysaccharide | [25] | ||
| AH-2 | Glc:Ara | 1:0.15 | — | — | [25] | ||
| APS-A1 | Glc:Gal:Ara | 52.3:1.0:1.3 | 2.62 × 106 | Neutral polysaccharide | [21] | ||
| APS-B1 | Glc:Gal:Arae:Man:Rha:GalA | 75.2:17.3:19.4:1.0:1.1:1.3 | 4.95 × 106 | Acidic polysaccharide | [21] | ||
| APS2-I | Man:Rha:GlcA:GalA:Glc:Gal:Xyl:Ara | 2.3:4.8:1.7:14.0:5.8:11.7:2.8:12.6 | 1.96 × 106 | Dextran | [26] | ||
| APS3-I | Rha:GlcA:Glc:Gal:Ara | 0.8:2.3:0.8:2.3:4.1 | 3.91 × 106 | Dextran | [26] | ||
| APS4 | Rha:Ara:Xyl:Man:Gal | 12.1:0.3:0.6:1.0:1.0:1.7 | 1.5 × 106 | — | [27] | ||
| cAMPs-1A | Fuc:Ara:Gal:Glc:Xyl | 0.01:0.06:0.20:1.00:0.06 | 1.23 × 104 | Water-soluble polysaccharides | [28] | ||
| AAP-2A | Rha:Gal:Ara:Glc | 1:2.13:3.22:6.18 | 2.252 × 103 | Neutral polysaccharide | [29] | ||
| AERP1 | Man:Rha:GalA:Glc:Gal:Ara | 1.00:2.59:12.15:2.60:3.07:4.54 | 2.01 × 106 | Acidic polysaccharide | [30] | ||
| AERP2 | — | — | 2.11 × 103 | Dextran | [30] |
| Source | Chemical Names | Chemical Structure or Composition | Molecular Formula | Molecular Weight (Da) | Classification | Extraction Methods | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Astragalus saponins (AS) | AS-I | 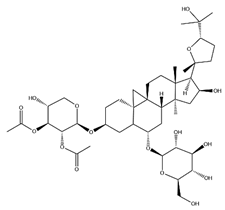 | C41H68O14 | 869.04 | Triterpenoid saponins | 70% methanol extraction | [33,34] |
| IsoAS-I | 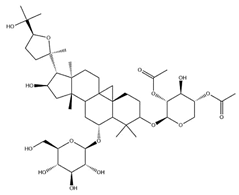 | C45H72O16 | 869.02 | Triterpenoid saponins | 70% methanol extraction | [33,34,36] | |
| AS-II | 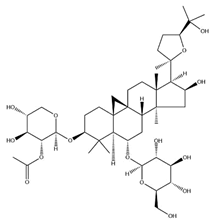 | C45H72O16 | 827.13 | Triterpenoid saponins | 70% methanol extraction | [33,37] | |
| AS-III | 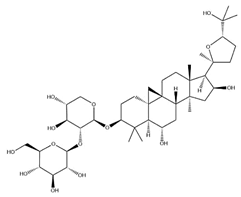 | C41H68O14 | 784.98 | Triterpenoid saponins | 70% methanol extraction | [33,37] | |
| AS-IV |  | C41H68O14 | 784.98 | Triterpenoid saponins | 70% methanol extraction | [32,38,39] | |
| lupeol | 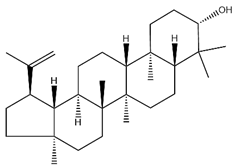 | C30H50O | 426.73 | Triterpenoid saponins | Supercritical CO2 extraction | [40] | |
| Soyasaponin I | 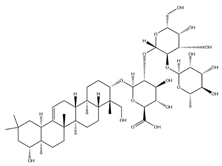 | C48H78O18 | 943.26 | Triterpenoid saponins | 45% methanol solid phase extraction | [41] | |
| Soyasaponin II |  | C47H76O17 | 913.11 | Triterpenoid saponins | 45% methanol solid phase extraction | [41] | |
| Agroastragaloside III | 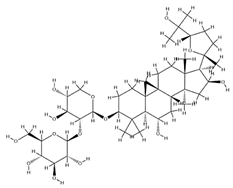 | C51H82O21 | 1031.18 | Triterpenoid saponins | Methanol extraction | [42] | |
| Agroastragaloside IV |  | C49H80O20 | 989.14 | Triterpenoid saponins | Methanol extraction | [42] | |
| Acetylastragaloside I | 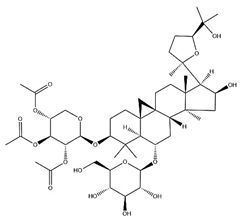 | C47H74O17 | 911.10 | Triterpenoid saponins | Methanol extraction | [43] | |
| IsoAS-II | 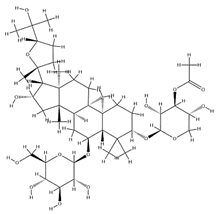 | C43H70O15 | 827.02 | Triterpenoid saponins | Methanol extraction | [43] | |
| AS-VII |  | C47H78O19 | 947.1 | Triterpenoid saponins | Methanol extraction | [43] |
| Source | Chemical Names | Chemical Structure or Composition | Molecular Formula | Molecular Weight (Da) | Classification | Extraction Methods | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flavonoids | Kaempferol | 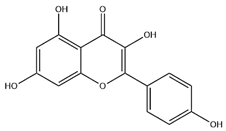 | C15H10O6 | 286.24 | flavonol | Ultrasound-assisted extraction (UAE) | [48] |
| Baicalin | 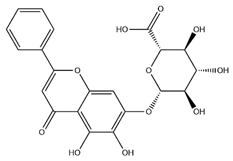 | C21H18O11 | 446.36 | Flavonoid glycosides | Microwave-assisted extraction (MAE) | [49] | |
| Isoliquiritigenin |  | C15H12O4 | 256.28 | Chalcone | UAE | [50] | |
| FMN | 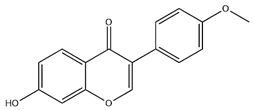 | C16H12O4 | 268.26 | isoflavone | Hexane-ethyl acetate-ethanol-water two-phase solvent extraction system | [51,52] | |
| Calycosin-7-O-β-d glucoside | 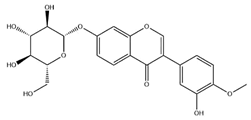 | C22H22O10 | 446.40 | isoflavone | 70% ethanol extraction | [53,54] | |
| CA |  | C16H12O5 | 284.28 | isoflavone | 70% ethanol extraction | [55] | |
| Ononin | 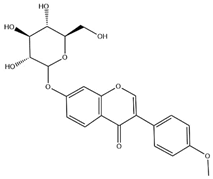 | C22H22O9 | 430.40 | isoflavone | Solid phase extraction (SPE) | [56] | |
| Quercetin | 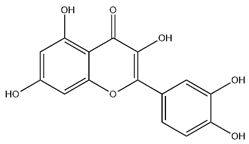 | C15H10O7 | 302.24 | flavonol | 50% ethanol extraction | [57] | |
| Licochalcone B | 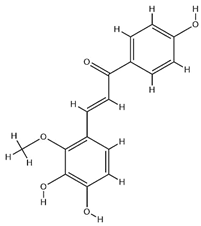 | C16H14O5 | 286.28 | Chalcone | Ethanol extraction | [58] | |
| Pendulone | 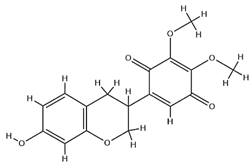 | C17H16O6 | 316.31 | Isoflavone | Ethanol extraction | [59,60] | |
| Astrasikokioside I | 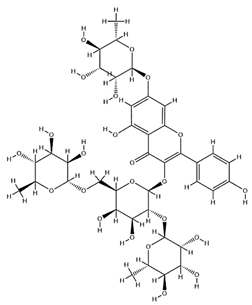 | C39H50O23 | 886.80 | Flavonoid glycosides | Ethanol extraction | [60] | |
| Isoquercitrin |  | C21H20O12 | 464.38 | Flavonoid glycosides | 90% ethanol extraction | [45] | |
| Astragalin | 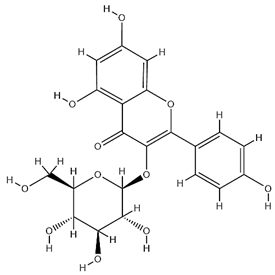 | C21H20O11 | 448.38 | Flavonoid glycosides | 90% ethanol extraction | [45] |
| Components | Models | Maximum Dose and Treatment Duration (In Vivo) | Organs | Effects | Mechanisms | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| APS | Aβ25-35-induced HT22 mouse hippocampal neurons; Streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetic mouse model; and SOD-2+/− gene knockout mouse model | 2.0 g/kg; 10 weeks | Heart | Anti-oxidative stress; and apoptosis | ↑SOD-2 enzyme activity; ↓ROS production, and ↓apoptosis in CSPCs. | [69] |
| APS | Chick transport stress (TS) model | 100 μL/animal; 8 h (oral) | Heart | Anti-oxidative stress; and immunoregulation | ↓mtDNA-PRRs pathway; ↑GSH, GPX, GST, SOD-2, and ↓MDA. | [74] |
| APS | Diabetic cardiomyopathy (DCM) rat model | 1 g/kg; 16 weeks | Heart | Apoptosis | ↓PERK and ATF6 pathways in ER stress. | [89] |
| CA | H9c2 cardiomyocytes subjected to thermal shock | — | Heart | Apoptosis | ↓p-JNK pathway, Fas/FasL apoptosis pathway, and ↑PI3K/Akt pathway. | [91] |
| AS | Zebrafish | — | Heart | Autophagy | ↑atg7, LC3-II, and ↓p62. | [107] |
| FMN | High-glucose-induced glomerular mesangial cells (GMCs); and db/db diabetic mice | 25–50 mg/kg; 8 weeks | Kidneys | Anti-oxidative stress; anti-inflammation; and anti-fibrosis | ↑Sirt1, and Nrf2/ARE pathway. | [146] |
| FMN | High-glucose-induced HK-2 human proximal tubule epithelial cell model; and STZ-induced diabetic nephropathy rat model | 20 mg/kg; 8 weeks | Kidneys | Apoptosis | Regulation of Bcl-2/Bax balance, ↓caspase-3; as well as regulation of Sirt1/PGC-1α pathway and ↓ROS. | [90] |
| Fermentation of AR with P. cicadae | High-glucose-induced podocytes; and STZ-induced mouse diabetic nephropathy model | 4.5 g/kg; 6 weeks | Kidneys | Autophagy | ↓PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. | [102] |
| AS | LPS-induced human mesangial cell (HMC) model; and C-BSA-induced chronic glomerulonephritis (CGN) rat model | 20 mg/kg; 6 weeks | Kidneys | Autophagy | ↓PI3K/AKT/AS160, ↑C3-II, Beclin1, and ↓p62. | [106] |
| Astragalus injection/decoction | STZ-induced T1D, spontaneous GK rat model (T2D) | 3–10 g/kg; 4–12 weeks | Kidneys | Anti-oxidative stress; and anti-fibrosis | ↑NRF2/KEAP1 pathway, ↓TGF-β/Smad signaling, NF-κB activation, and regulation of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway to protect podocytes. | [145] |
| APS | Hep3B liver cancer cells; and Hep3B cell-bearing nude mouse model | 50 mg/kg; 28 days | Liver | Apoptosis | ↓O-GlcNAc synthesis, ↑Dox-induced ER stress, ↓Bcl-2, and ↑activated CHOP and Caspase-3. | [88] |
| AS | AML-12 cell ferroptosis model; and cisplatin-induced mouse liver injury model | 80 mg/kg; 9 days | Liver | Ferroptosis; anti-oxidative stress; and anti-inflammation | ↓Ferroptosis; ↑PPARα/FSP1 signaling pathway, ↓key markers of ferroptosis, and regulation of lipid peroxidation. | [138] |
| ATS | Biliary duct ligation (BDL) rat cholestatic liver fibrosis model; and DDC diet-induced mouse liver fibrosis model | 56 mg/kg; 4 weeks | Liver | Anti-fibrosis | ↑FXR, SHP, BSEP, NTCP expression, ↓Cyp7a1, and reduce serum/liver taurine-conjugated bile acids (BAs). | [141] |
| APS, AS | Alcoholic liver disease (ALD) mouse model | APS: 600 mg/kg AS: 100 mg/kg; 4 weeks | Liver | Anti-oxidative stress; and anti-inflammation | ↑KEAP1/NRF2 antioxidant pathway, and ↓TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB inflammatory pathway. | [142] |
| AS | Middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) mouse model | 40 mg/kg; 3 days | Spleen | Immunoregulation | Reduction of spleen atrophy and restoration of spleen NK/T/B-cell counts. | [116] |
| APS | 4T1 breast cancer-bearing BALB/c mouse model | 200 mg/kg; 14 days | Spleen, thymus | Immunoregulation; and apoptosis | Improvement of thymus index and spleen index, and enhancement of macrophage phagocytic ability. | [113] |
| AS | Cigarette smoke extract (CSE)-induced inflammatory model in RAW264.7 macrophages | — | Lungs | Autophagy; and anti-inflammation | ↓TLR4/NF-Κb pathway, ↑LC3-II, ↑ATG5, ATG7, Beclin1; and ↓p62. | [103] |
| APS | Bleomycin (BLM)-induced model | 100 mg/kg; 28 days | Lungs | Anti-inflammation | ↓TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway, TLR4/NF-κB pathway, TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β, and TGF-β1. | [127] |
| Cycloastragenol (CAG) | Human gastric cancer SNU-1 and SNU-16 cells | — | Stomach | Apoptosis | ↓STAT3 phosphorylation, JAK1/2, and Src kinase activity. | [92] |
| ATS | Gastric cancer cells (SGC-7901) | — | Stomach | Ferroptosis; and apoptosis | ↑SIRT3 expression, ferroptosis, ↓SLC7A11/GPX4, and ↑ACSL4 protein. | [137] |
| AR water extract | IEC-6 intestinal epithelial cells; and mouse IBD model | — | Intestines | Anti-oxidative stress; and anti-inflammation | ↓NF-κB pathway, and ↑Nrf2 pathway. | [64] |
| AS | DSS-induced mouse model of ulcerative colitis | 100 mg/kg; 14 days | Intestines | Anti-oxidative stress; and immunoregulation | Regulation of Th17/Treg immune balance, ↓MDA, and ↑SOD/GSH-Px. | [73] |
| APS | LPS-induced RAW264.7 macrophages; and collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) rat model | 200 mg/kg; 7 days | Intestines | Anti-inflammation | ↓TLR4/NF-κB pathway, p-p65, p-IκB levels, MAPK pathway, IL-6, IL-1β, and TNF-α. | [126] |
| AS | Rat middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) model | 20 mg/kg; 7 days | Brain | Immunoregulation | Reduction of NK cell activation receptor NKG2D expression and IFN-γ production, and reversal of NK cell deficiency in the spleen and blood. | [114] |
| APS | BV2 microglia; and chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS) mouse model | 800 mg/kg; 5 weeks | Gut; Brain | Anti-oxidative stress; and anti-inflammation | ↑Nrf2 pathway; and ↓NF-κB pathway. | [75] |
| APS | 6-OHDA-induced PC12 cells | — | Brain neurons | Autophagy | ↑PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. | [100] |
| CAG | α-Synuclein (α-Syn)-induced Parkinson’s disease (PD) mouse model and primary microglia | 125 mg/kg; 16 weeks | Central nervous system (Brain) | Anti-oxidative stress; and autophagy; Anti-inflammation; and immunoregulation | ↓Scrib/NOX-ROS axis, inhibition of NLRP3, and ROS. | [144] |
| Processed AR water extract | Aβ25-35-induced HT22 mouse hippocampal neurons | — | Nervous system | Anti-oxidative stress; and apoptosis | ↑Nrf2 pathway, and AKT/CREB/BDNF pathway. | [67] |
| APS | tBHP-induced mouse chondrocytes; and DMM surgery-induced osteoarthritis mouse model | — | Joint cartilage | Anti-oxidative stress | ↑GCN2/ATF4/TXN axis. | [66] |
| APS | TBHP-induced chondrocyte apoptotic model; and DMM surgery-induced osteoarthritis mouse model | 200 mg/kg; 6 weeks | Joint cartilage | Apoptosis | ↓Mitochondrial apoptosis pathway; and ↓ROS. | [93] |
| AS | Sciatic nerve transection mouse model of muscle atrophy | 20 mg/kg; 14 days | Skeletal muscle | Anti-oxidative stress; and anti-inflammation | ↑SOD1/GPX1, ↓ROS/NOX2/4, ↓NLRP3/IL-1β/IL-6/TNF-α, and ↓LC3II/BNIP3 | [76] |
| CA | Ovariectomized mice | 50 mg/kg; 12 weeks | Bone tissue | Autophagy | ↑PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. | [101] |
| AS | Experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis model (EAE) | 20 mg/kg; 10 days | Bone marrow | Immunoregulation | ↓Maturation of splenic, bone marrow-derived DCs; ↓Th1/Th17 cell differentiation; ↓IL-6, and IL-12. | [112] |
| APS | Taxol-induced cytotoxicity in RAW 264.7 macrophages; and 4T1 tumor-bearing mouse model | 40 mg/kg; 6 weeks | Immune system | Immunoregulation; and apoptosis | ↓G2/M phase arrest, P-H2A.X, PARP, ↑Bcl-XL, and Mcl-1. | [82] |
| APS | LPS-induced RAW264.7 macrophages | — | Immune system | Anti-inflammation | ↓NF-Κb, MAPK pathways; ↓ROS production (immune regulation); ↓NLRP3, iNOS, and COX-2 expression. | [21] |
| AS | Rat vascular smooth muscle cells | — | Vascular system | Autophagy | ↑AMPK/mTOR pathway, and STX17-SNAP29-VAMP8. | [108] |
| APS | LPS/high-glucose-induced THP-1 macrophages and HUVECs coculture; and STZ-induced T2DM rat model | 800 mg/kg; 8 weeks | Vascular endothelium | Anti-inflammation | ↑macrophage M2 polarization, Nrf2/HO-1 pathway, ↓ROS, VCAM-1, MCP-1, and ↓Bax/Bcl-2. | [131] |
| APS | Ovarian cancer stem cells (OCSCs, 3AO/SKOV3 cells) | — | Ovaries | Autophagy | ↓PINK1/Parkin pathway-mediated mitochondrial autophagy, and ↑TOMM20/COX IV, ↓PINK1 protein. | [135] |
| APS | OC cells (OV-90/SKOV3 cells) | — | Ovaries | Apoptosis | ↓EMT; ↓miR-27a expression; ↑FBXW7 protein, and ↑E-cadherin. | [134] |
| AS | SiHa cell nude mouse xenograft model | 50 mg/kg; 35 days | Cervix | Autophagy | Regulation of the DCP1A/WDFY3/Atg12 and TMSB4X/Akt/Atg5/Atg12 pathways. | [110] |
| AS | PDGF-BB-induced human airway smooth muscle cells (ASMCs); and OVA-induced asthma mouse model | 100 mg/kg; 4 weeks | Respiratory tract | Pyroptosis | Alleviation of pulmonary inflammation; inhibition of HMGB1 cytoplasmic translocation, blockage of the HMGB1/RAG axis, inactivation of the NF-κB pathway, reduction of inflammatory factors, and ↑pyroptosis markers. | [140] |
| APS | Mouse macrophages (RAW 264.7), and mouse spleen-derived CD4+/CD8+ T cells | — | Prostate | Immunoregulation | Regulation of the PD-1/PD-L1 pathway, ↑T-cell secretion of IFN-γ, CXCL2, CCL5, TNF-α, IL-6, and CCL5. | [115] |
| APS | DSS-induced colitis mouse model | 200 mg/kg; 14 days | Colon | Immunoregulation | ↑Mitochondrial metabolism; ↑IgA+ MBCs, and ↓IgG+ MBCs. | [118] |
| AS | Indomethacin-induced SD rat enteritis model | 80 mg/kg; 3 days | Small intestine | Anti-inflammation | ↓NLRP3 inflammasome activation; ↓NF-κB4; ↓IL-1β, and IL-18. | [129] |
| FMN | HaCaT cells (psoriasis-like inflammation); and IMQ-induced psoriasis mouse model | — | Skin | Anti-inflammation | ↓IFN-α/β/γ signaling pathway, CXCL9/10/11 and other chemokines, p-STAT1/3, IRF1 expression, TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-17 levels. | [119] |
| APS | Cadmium (CdCl2) induced chicken embryo fibroblast (CEF) damage model | — | Fibroblasts | Autophagy; and anti-oxidative stress | ↓ROS, LC3-II, Beclin1, ↑SOD, and GSH-Px. | [104] |
| AS | Oligodendrocyte precursor cells; Cuprizone (CPZ)-induced mouse demyelination model, and experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) mouse model | 50 mg/kg; 7 days | Myelin tissue | Immunoregulation | Targeting and binding to the p75NTR receptor, and ↓Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. | [117] |
| Medicines | Interacting Drugs | Animal Models | Routes of Administration and Dosages | PK Parameters of Ingredients | Ref. | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cmax (ng/mL) | AUC(0−t) (ng/mL·h) | AUC(0−inf) (ng/mL·h) | t1/2 (h) | tmax (h) | CL ((mL/h)/kg) | MRT(0−t) (h) | |||||
| Astragali radix extract (ARE) | Dapagliflozin | Male SD rats | With ARE (300 mg/kg for seven days, intragastrically administered) | 426.67 ± 58.92 | 4051.27 ± 952.61 | 4865.13 ± 1307.11 | 9.69 ± 3.47 | 1.50 ± 0.77 | 228.25 ± 56.10 | 7.64 ± 0.70 | [162] |
| Astragalus Injection | DOX | Male SD rats | With Astragalus injection (4.25 mL/kg/day for 14 days, intraperitoneal injection) | 5262.77 ± 111.15 | 3777.27 ± 130.55 | 7141.76 ± 177.96 | 0.14 ± 0.04 | 11.72 ± 1.22 | 1.09 ± 0.37 | — | [161] |
| AS-IV | Abemaciclib | Male Sprague Dawley rats | With AS IV (50 mg/kg for 7d, orally administered | 163,000 ± 147,850 | 36,380 ± 4230 | — | 38.24 ± 7.53 | 3.24 ± 1.15 | 0.49 ± 0.107 | 20.57 ± 0.92 | [158] |
| With AS IV (100 mg/kg for 7d, orally administered | 1,698,170 ± 104,430 | 43,810 ± 1850 | — | 51.59 ± 17.08 | 2.65 ± 0.77 | 0.34 ± 0.059 | 20.87 ± 0.40 | [158] | |||
| With AS IV (150 mg/kg for 7d, orally administered | 23,080,500 ± 55,290 | 66,140 ± 1170 | — | 66.17 ± 28.73 | 2.12 ± 0.84 | 0.19 ± 0.042 | 21.76 ± 0.32 | [158] | |||
| Radix astragali | Pioglitazone | Male Wistar rats | With RA (28.35 g/kg for 7 days, orally administered) | 2334.0 ± 87,369.92 | 9945.3 ± 871,556.29 | — | 2.787 ± 0.08 | 1.17 ± 0.42 | 36.55 ± 75.73 | — | [162] |
| Huangqi injection (HI) | Gliquidone | Male Wistar rats | With HI (8 mL/kg for 5 min, intravenously) | 22.46 ± 3.61 | 281.9 ± 12.4 | — | 2.46 ± 0.76 | — | 0.18 ± 0.04 | — | [163] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, C.; Liu, H.; Dong, S.; Yang, L.; Kong, L.; Guan, Y.; Sun, H.; Yan, G.; Sun, Y.; Han, Y.; et al. Beyond Traditional Use: The Scientific Evidence for the Role of Astragali radix in Organ Protection via Modulating Oxidative Stress, Cell Death, and Immune Responses. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 1448. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18101448
Lin C, Liu H, Dong S, Yang L, Kong L, Guan Y, Sun H, Yan G, Sun Y, Han Y, et al. Beyond Traditional Use: The Scientific Evidence for the Role of Astragali radix in Organ Protection via Modulating Oxidative Stress, Cell Death, and Immune Responses. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(10):1448. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18101448
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Chuan, Huiqiang Liu, Siyi Dong, Le Yang, Ling Kong, Yu Guan, Hui Sun, Guangli Yan, Ye Sun, Ying Han, and et al. 2025. "Beyond Traditional Use: The Scientific Evidence for the Role of Astragali radix in Organ Protection via Modulating Oxidative Stress, Cell Death, and Immune Responses" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 10: 1448. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18101448
APA StyleLin, C., Liu, H., Dong, S., Yang, L., Kong, L., Guan, Y., Sun, H., Yan, G., Sun, Y., Han, Y., & Wang, X. (2025). Beyond Traditional Use: The Scientific Evidence for the Role of Astragali radix in Organ Protection via Modulating Oxidative Stress, Cell Death, and Immune Responses. Pharmaceuticals, 18(10), 1448. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18101448






