Therapeutic Potential of Bioactive Compounds in Edible Mushroom-Derived Extracellular Vesicles: Isolation and Characterization of EVs from Pleurotus eryngii
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
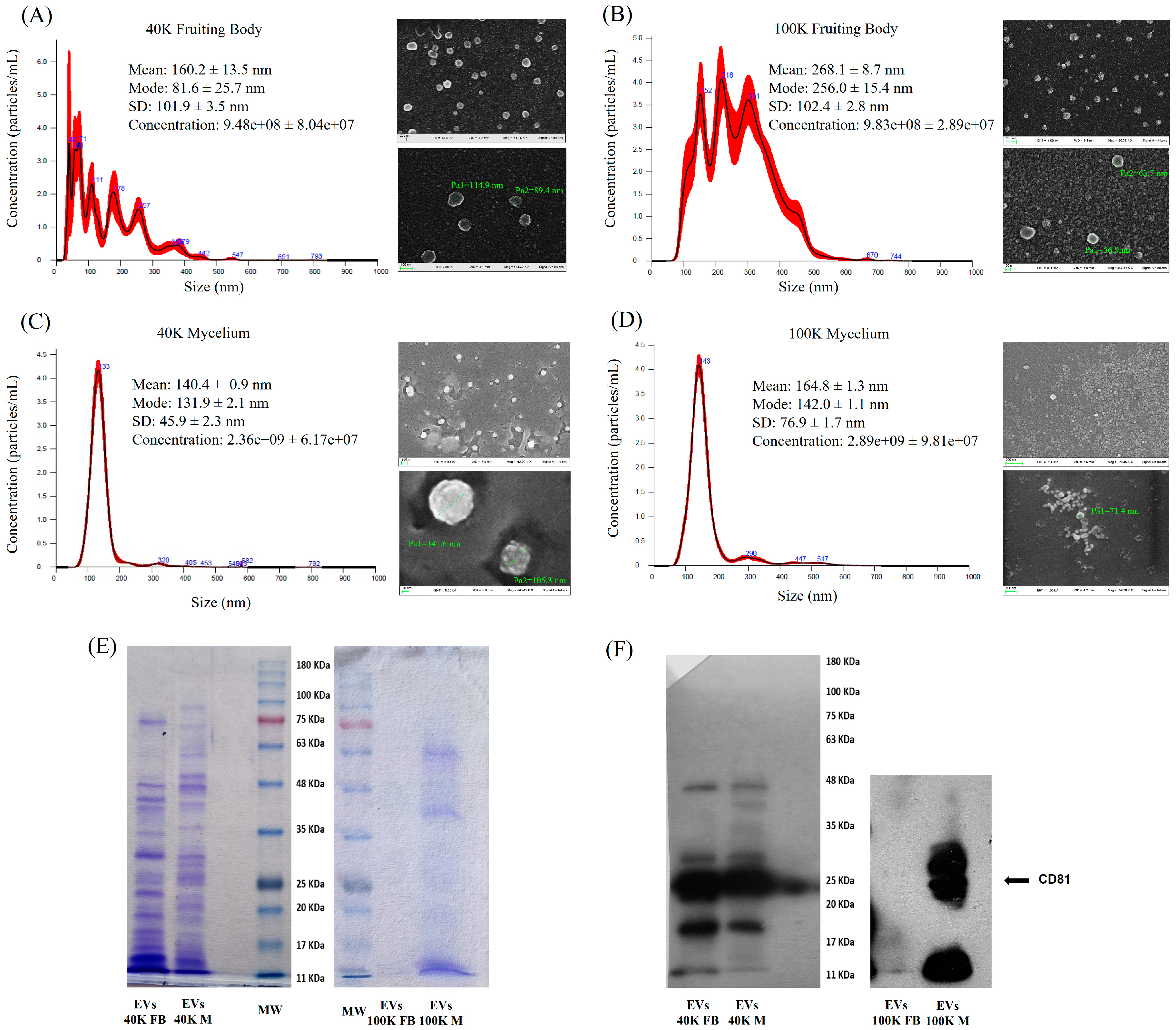
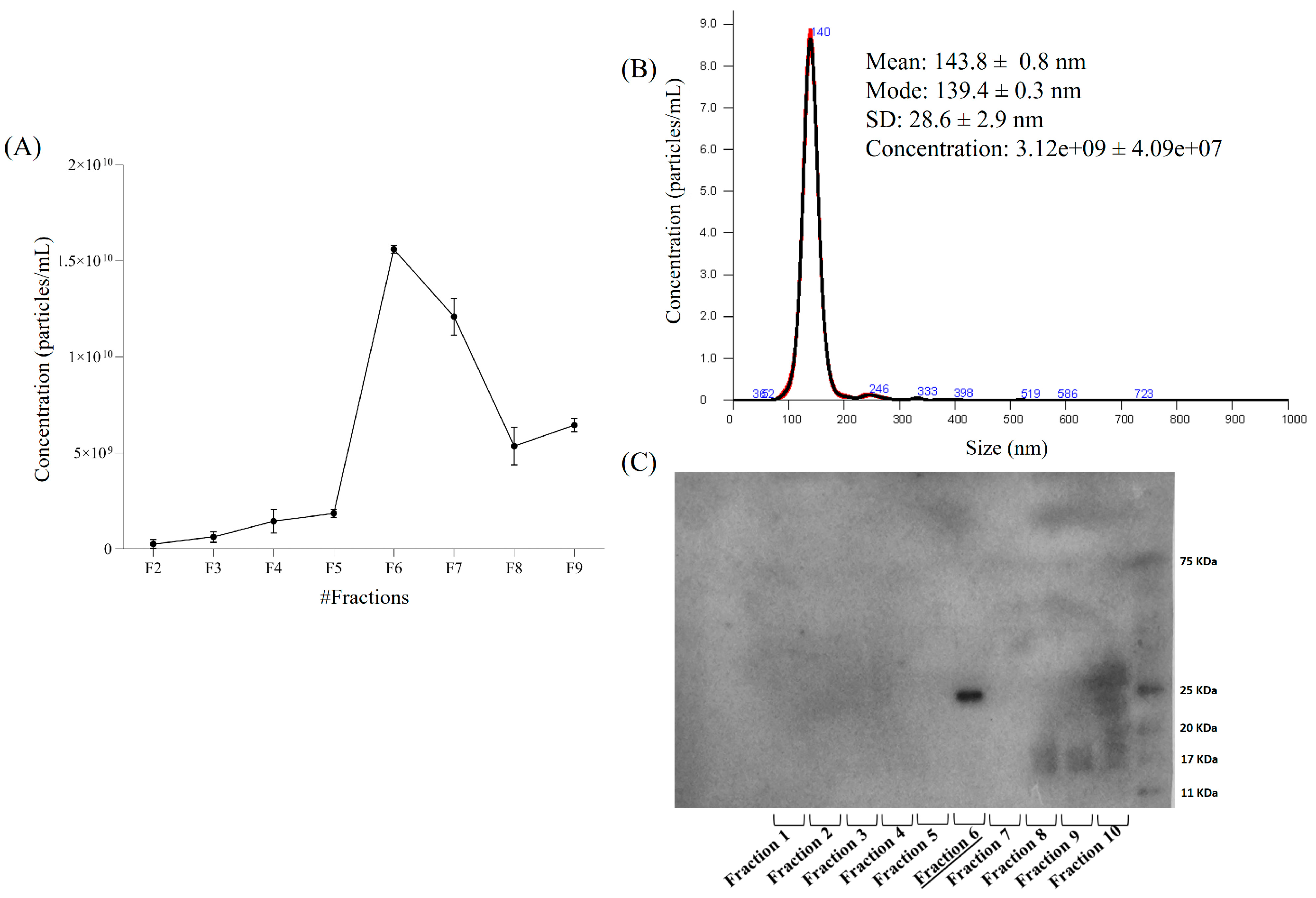
2.1. Characterization of Mushroom-Derived Extracellular Vesicles
Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM), Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis (NTA) and Immunoblotting Analysis
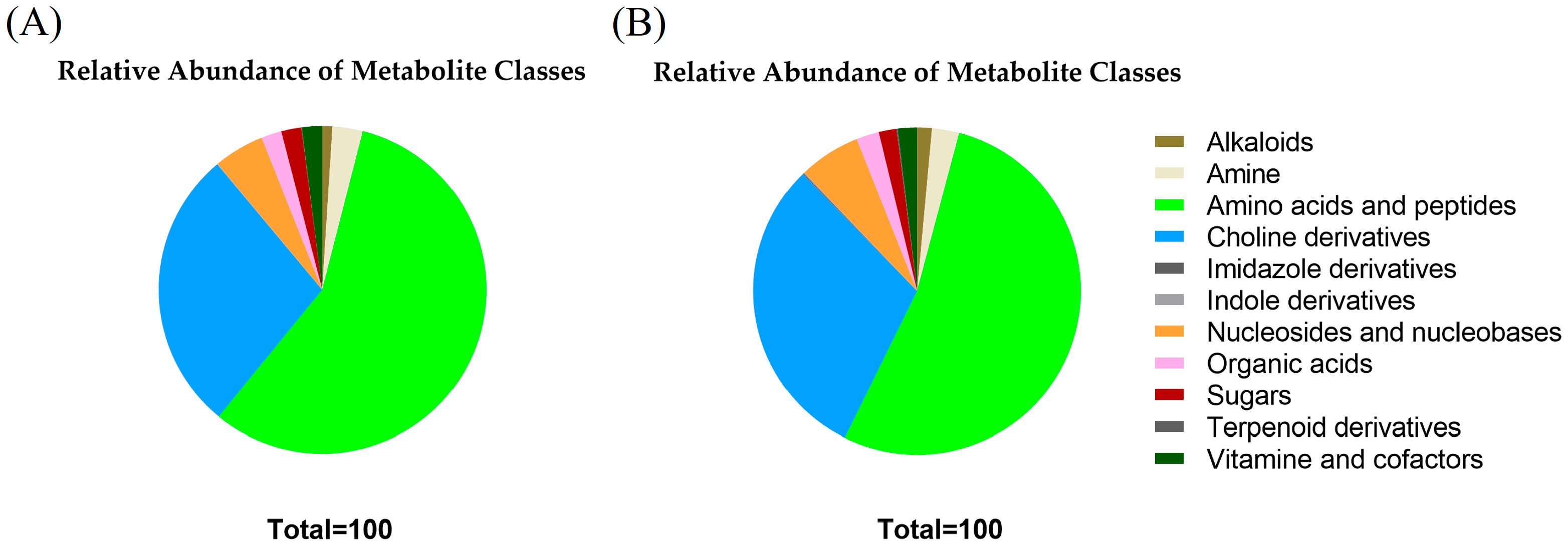
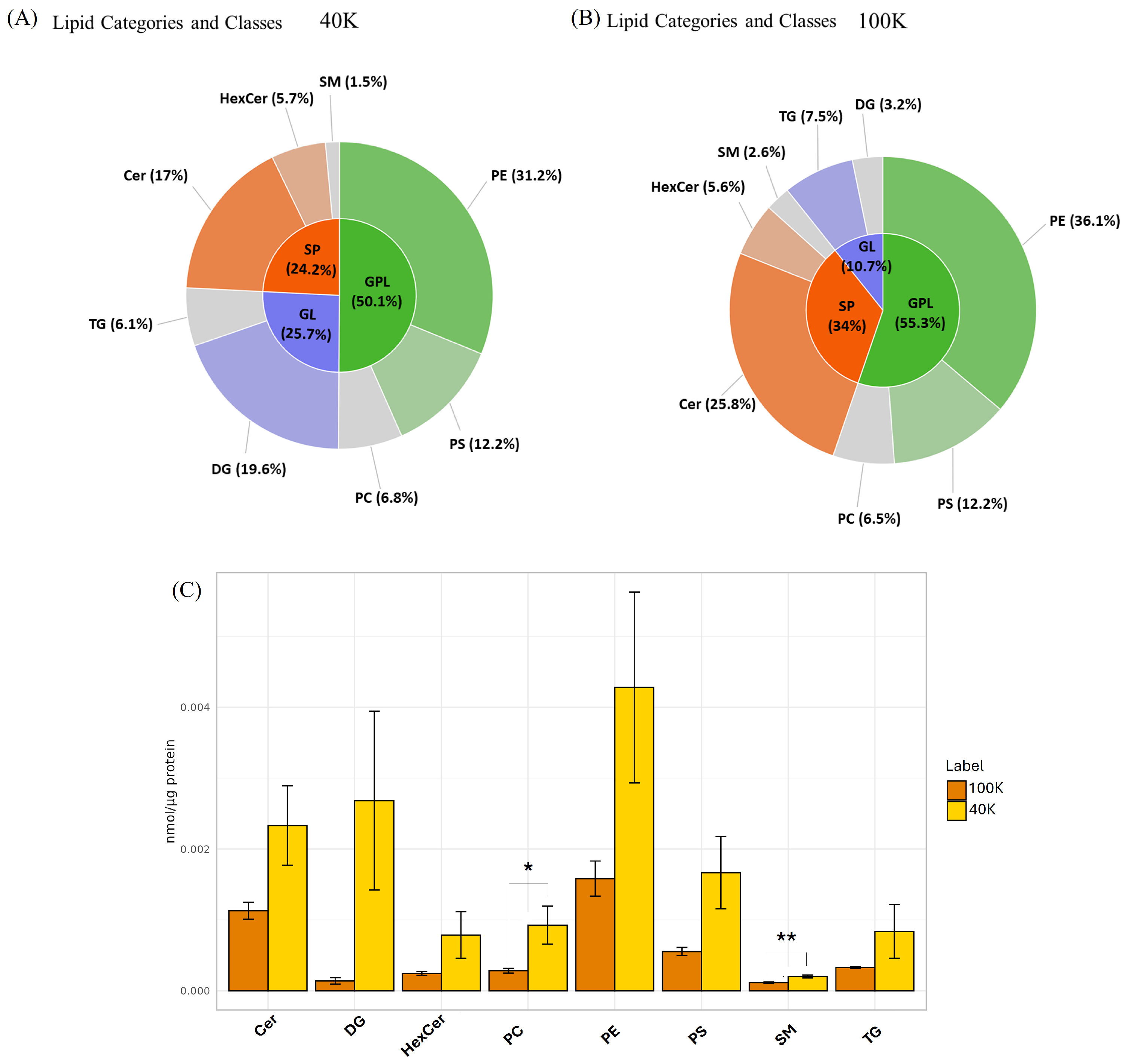
2.2. Untargeted LC-MS/MS-Based Metabolomics Analysis of MDEVs
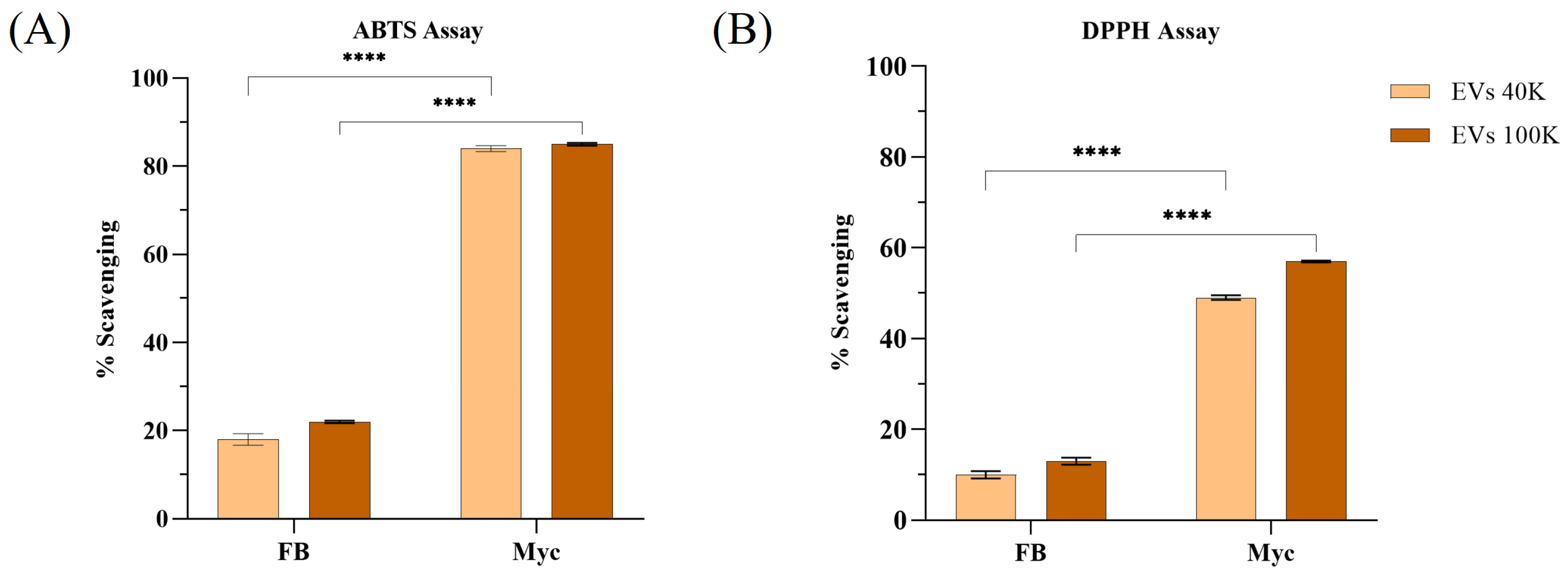
2.3. Antioxidant Activity of Mushroom-Derived Extracellular Vesicles
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Mushroom Material
4.2. Purification of Mushroom-Derived Extracellular Vesicles and P. eryngii Crude Extract
4.3. Characterization of Mushroom-Derived Extracellular Vesicles
4.3.1. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) and Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis (NTA)
4.3.2. Immunoblotting Analysis
4.4. Scavenging Activity
4.5. Determination of Total Phenolic Content (TPC)
4.6. Untargeted LC-MS/MS-Based Metabolomics Analysis of MDEVs
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ABTS | 2,2′-Azino-bis(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid) |
| ACN | Acetonitrile |
| Cer | Ceramide |
| CUPRAC | Cupric Ion Reducing Antioxidant Capacity |
| DG | Diacylglycerol |
| DPPH | 2,2-Diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl |
| ECL | Enhanced Chemiluminescence |
| EVs | Extracellular Vesicles |
| FB | Fruiting Body |
| FRAP | Ferric Reducing Antioxidant Power |
| GAE | Gallic Acid Equivalent |
| IPA | Isopropanol |
| LC-MS/MS | Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry |
| MDEVs | Mushroom Derived Extracellular Vesicles |
| ME | Malt Extract |
| MTBE | Methyl tert-butyl ether |
| Myc | Mycelium |
| NTA | Nano-Particle Tracking Analysis |
| PBS | Phosphate-Buffered Saline |
| PC | Phosphatidylcholine |
| PE | Phosphatidylethanolamine |
| PS | Phosphatidylserine |
| PVDF | Polyvinylidene Difluoride |
| QTOF | Quadrupole Time-of-Flight |
| SD | Standard Deviation |
| SE | Standard Error |
| SEM | Scanning Electron Microscopy |
| TE | Trolox Equivalent |
| TG | Triacylglycerol |
| TPC | Total Phenolic Content |
| TPTZ | 2,4,6-Tripyridyl-s-triazine |
| UPLC | Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography |
References
- Cerrotti, G.; Buratta, S.; Latella, R.; Calzoni, E.; Cusumano, G.; Bertoldi, A.; Porcellati, S.; Emiliani, C.; Urbanelli, L. Hitting the Target: Cell Signaling Pathways Modulation by Extracellular Vesicles. Extracell. Vesicles Circ. Nucleic Acids 2024, 5, 527–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalluri, R.; LeBleu, V.S. The Biology, Function, and Biomedical Applications of Exosomes. Science 2020, 367, eaau6977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calzoni, E.; Bertoldi, A.; Cusumano, G.; Buratta, S.; Urbanelli, L.; Emiliani, C. Plant-Derived Extracellular Vesicles: Natural Nanocarriers for Biotechnological Drugs. Processes 2024, 12, 2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calzoni, E.; Bertoldi, A.; Cesaretti, A.; Alabed, H.B.R.; Cerrotti, G.; Pellegrino, R.M.; Buratta, S.; Urbanelli, L.; Emiliani, C. Aloe Extracellular Vesicles as Carriers of Photoinducible Metabolites Exhibiting Cellular Phototoxicity. Cells 2024, 13, 1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Saini, R.K.; Kumar, A.; Chawla, P.; Kaushik, R. Mushrooms as Nutritional Powerhouses: A Review of Their Bioactive Compounds, Health Benefits, and Value-Added Products. Foods 2025, 14, 741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zong, Z.; Niu, B.; Chen, H.; Wu, W.; Fang, X.; Liu, R.; Gao, H.; Mu, H. Shiitake Mushroom-Derived Extracellular Nanovesicles: Preparation, Characterization, and Inhibition of Caco-2 Cells. Food Chem. 2025, 463, 141339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, X.; Li, W.; Li, W.; Chen, W.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, D.; Yang, Y. Quality Characteristics and Non-Volatile Taste Formation Mechanism of Lentinula Edodes during Hot Air Drying. Food Chem. 2022, 393, 133378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelini, P.; Pellegrino, R.M.; Tirillini, B.; Flores, G.A.; Alabed, H.B.R.; Ianni, F.; Blasi, F.; Cossignani, L.; Venanzoni, R.; Orlando, G.; et al. Metabolomic Profiling and Biological Activities of Pleurotus columbinus Quél. Cultivated on Different Agri-Food Byproducts. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ianni, F.; Blasi, F.; Angelini, P.; Simone, S.C.; Angeles Flores, G.; Cossignani, L.; Venanzoni, R. Extraction Optimization by Experimental Design of Bioactives from Pleurotus ostreatus and Evaluation of Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Activities. Processes 2021, 9, 743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrino, R.; Ianni, F.; Blasi, F.; Angelini, P.; Emiliani, C.; Venanzoni, R.; Cossignani, L. Lipidomic Profiling of Pleurotus ostreatus by LC/MS Q-TOF Analysis. Food Res. Int. 2022, 156, 111335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angeles Flores, G.; Girometta, C.E.; Cusumano, G.; Pellegrino, R.M.; Silviani, S.; Bistocchi, G.; Arcangeli, A.; Ianni, F.; Blasi, F.; Cossignani, L.; et al. Diversity of Pleurotus spp. (Agaricomycetes) and Their Metabolites of Nutraceutical and Therapeutic Importance. Int. J. Med. Mushrooms 2023, 25, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calabretti, A.; Mang, S.M.; Becce, A.; Castronuovo, D.; Cardone, L.; Candido, V.; Camele, I. Comparison of Bioactive Substances Content between Commercial and Wild-Type Isolates of Pleurotus eryngii. Sustainability 2021, 13, 3777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akyüz, M.; Kirbag, S.; Kırbağ, S.; Karatepe, M.; Karatepe, M.; Güvenç, M.; Zengin, F. Vitamin and Fatty Acid Composition of P. eryngii Var. eryngii. Bitlis Eren Univ. J. Sci. Technol. 2011, 1, 16–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cardwell, G.; Bornman, J.F.; James, A.P.; Black, L.J. A Review of Mushrooms as a Potential Source of Dietary Vitamin D. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angeles Flores, G.; Girometta, C.E.; Cusumano, G.; Angelini, P.; Tirillini, B.; Ianni, F.; Blasi, F.; Cossignani, L.; Pellegrino, R.M.; Emiliani, C.; et al. Untargeted Metabolomics Used to Describe the Chemical Composition, Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Effects of Extracts from Pleurotus spp. Mycelium Grown in Different Culture Media. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlassopoulou, M.; Paschalidis, N.; Savvides, A.L.; Saxami, G.; Mitsou, E.K.; Kerezoudi, E.N.; Koutrotsios, G.; Zervakis, G.I.; Georgiadis, P.; Kyriacou, A.; et al. Immunomodulating Activity of Pleurotus eryngii Mushrooms Following Their In Vitro Fermentation by Human Fecal Microbiota. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Shah, N.P. Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Proliferative Activities of Natural and Sulphonated Polysaccharides from Pleurotus eryngii. J. Funct. Foods 2016, 23, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassi, S.; Benvenuti, M.; Mirata, S.; Piazza, S.; Salis, A.; Damonte, G.; Zotti, M.; Scarfì, S. Enhanced Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Activity of the Extracts of Pleurotus ostreatus Edible Mushroom Grown on Lavandula Angustifolia Residues. Food Biosci. 2024, 60, 104382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentharavithana, J.; Islam, T.; Xu, B. Medicinal Mushrooms in Colon Cancer Therapy: Mechanisms of Action of Bioactive Compounds and Therapeutic Potential. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Yuan, B.; Xiao, H.; Zhao, L.; Wu, X.; Rakariyatham, K.; Zhong, L.; Han, Y.; Muinde Kimatu, B.; Yang, W. Polyphenols-Rich Extract from Pleurotus eryngii with Growth Inhibitory of HCT116 Colon Cancer Cells and Anti-Inflammatory Function in RAW264.7 Cells. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 1601–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutter, B.D.; Innes, R.W. Extracellular Vesicles in Phytopathogenic Fungi. Extracell. Vesicles Circ. Nucleic Acids 2023, 4, 90–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.; Jiang, B.; Hou, F.; Huang, X.; Ling, B.; Lu, H.; Zhong, T.; Huang, J. The Emerging Role of Extracellular Vesicles in Fungi: A Double-Edged Sword. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1216895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, M.; Jin, X.; Chen, S.; Yang, N.; Feng, G. Plant-Derived Extracellular Vesicles -a Novel Clinical Anti-Inflammatory Drug Carrier Worthy of Investigation. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 169, 115904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lian, M.Q.; Chng, W.H.; Liang, J.; Yeo, H.Q.; Lee, C.K.; Belaid, M.; Tollemeto, M.; Wacker, M.G.; Czarny, B.; Pastorin, G. Plant-Derived Extracellular Vesicles: Recent Advancements and Current Challenges on Their Use for Biomedical Applications. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2022, 11, 12283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bleackley, M.R.; Dawson, C.S.; Anderson, M.A. Fungal Extracellular Vesicles with a Focus on Proteomic Analysis. PROTEOMICS 2019, 19, 1800232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Che, C.; Yang, S.; Ding, P.; Si, M.; Yang, G. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Extracellular Vesicles from Morchella on LPS-Stimulated RAW264.7 Cells via the ROS-Mediated P38 MAPK Signaling Pathway. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2023, 478, 317–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Wu, T.; Jin, J.; Li, Z.; Cheng, W.; Dai, X.; Yang, K.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, H.; et al. Exosome-like Nanovesicles Derived from Phellinus Linteus Inhibit Mical2 Expression through Cross-Kingdom Regulation and Inhibit Ultraviolet-Induced Skin Aging. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2022, 20, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lerussi, G.; Villagrasa-Araya, V.; Moltó-Abad, M.; del Toro, M.; Pintos-Morell, G.; Seras-Franzoso, J.; Abasolo, I. Extracellular Vesicles as Tools for Crossing the Blood–Brain Barrier to Treat Lysosomal Storage Diseases. Life 2025, 15, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.; Liu, K. Plant-Derived Extracellular Vesicles as Oral Drug Delivery Carriers. J. Control. Release 2022, 350, 389–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buratta, S.; Latella, R.; Chiaradia, E.; Salzano, A.M.; Tancini, B.; Pellegrino, R.M.; Urbanelli, L.; Cerrotti, G.; Calzoni, E.; Alabed, H.B.R.; et al. Characterization of Nanovesicles Isolated from Olive Vegetation Water. Foods 2024, 13, 835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, H.C.; Kato, A.F.; Sena, B.A.G.; Duarte, I.; Jozefowicz, L.J.; Castelli, R.F.; Kuczera, D.; Reis, F.C.G.; Alves, L.R.; Rodrigues, M.L. Biogenesis of Fungal Extracellular Vesicles: What Do We Know? In Fungal Extracellular Vesicles: Biological Roles; Rodrigues, M., Janbon, G., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 1–11. ISBN 978-3-030-83391-6. [Google Scholar]
- Buendia, M.E.; González-Gómez, G.H.; Maciel-Cerda, A.; González-Torres, M. Epicatechin Derivatives in Tissue Engineering: Antioxidant, Anti-Inflammatory, Regenerative Use. Tissue Eng. Part B Rev. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Li, F.; Zhang, X.; Xu, W.; Wang, Y.; Yao, Y.; Han, Z.; Xia, D. (−)-Epicatechin Ameliorates Monosodium Urate-Induced Acute Gouty Arthritis Through Inhibiting NLRP3 Inflammasome and the NF-κB Signaling Pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 799552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, X.; Guo, J.; You, Y.; Zhan, J.; Huang, W. P-Coumaric Acid Prevents Obesity via Activating Thermogenesis in Brown Adipose Tissue Mediated by mTORC1-RPS6. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 7810–7824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadidi, M.; Liñán-Atero, R.; Tarahi, M.; Christodoulou, M.C.; Aghababaei, F. The Potential Health Benefits of Gallic Acid: Therapeutic and Food Applications. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Sun, W.; Jin, L. Caffeic Acid Alleviates Inflammatory Response in Rheumatoid Arthritis Fibroblast-like Synoviocytes by Inhibiting Phosphorylation of IκB Kinase α/β and IκBα. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2017, 48, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrino, R.M.; Di Veroli, A.; Valeri, A.; Goracci, L.; Cruciani, G. LC/MS Lipid Profiling from Human Serum: A New Method for Global Lipid Extraction. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2014, 406, 7937–7948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.B.; Lee, G.B.; Moon, M.H. Size Separation of Exosomes and Microvesicles Using Flow Field-Flow Fractionation/Multiangle Light Scattering and Lipidomic Comparison. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 8958–8965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitencourt, T.A.; Hatanaka, O.; Pessoni, A.M.; Freitas, M.S.; Trentin, G.; Santos, P.; Rossi, A.; Martinez-Rossi, N.M.; Alves, L.L.; Casadevall, A.; et al. Fungal Extracellular Vesicles Are Involved in Intraspecies Intracellular Communication. mBio 2022, 13, e03272-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, J.C.; Oprea, O.B.; Gaceu, L.; Más Diego, S.M.; Morris Quevedo, H.J.; Galindo Alonso, L.; Rivero Ramírez, L.; Badea, M. Edible Mushroom Cultivation in Liquid Medium: Impact of Microparticles and Advances in Control Systems. Processes 2025, 13, 2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobhani, M.; Farzaei, M.H.; Kiani, S.; Khodarahmi, R. Immunomodulatory; Anti-Inflammatory/Antioxidant Effects of Polyphenols: A Comparative Review on the Parental Compounds and Their Metabolites. Food Rev. Int. 2020, 37, 759–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mileo, A.M.; Miccadei, S. Polyphenols as Modulator of Oxidative Stress in Cancer Disease: New Therapeutic Strategies. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 6475624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozkan, G.; Ceyhan, T.; Çatalkaya, G.; Rajan, L.; Ullah, H.; Daglia, M.; Capanoglu, E. Encapsulated Phenolic Compounds: Clinical Efficacy of a Novel Delivery Method. Phytochem. Rev. 2024, 23, 781–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akuma, P.; Okagu, O.D.; Udenigwe, C.C. Naturally Occurring Exosome Vesicles as Potential Delivery Vehicle for Bioactive Compounds. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2019, 3, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, A.E.; Sneider, A.; Witwer, K.W.; Bergese, P.; Bhattacharyya, S.N.; Cocks, A.; Cocucci, E.; Erdbrügger, U.; Falcon-Perez, J.M.; Freeman, D.W.; et al. Biological Membranes in EV Biogenesis, Stability, Uptake, and Cargo Transfer: An ISEV Position Paper Arising from the ISEV Membranes and EVs Workshop. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2019, 8, 1684862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Dai, S.; Zhu, N.; Meng, Q.; Fan, S.; Zhao, W.; Yuan, X. Fungal Extracellular Vesicle Proteins with Potential in Biological Interaction. Molecules 2024, 29, 4012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullah, A.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, K.; Hua, Y.; Ullah, S.; Rahman, M.u.; Wang, J.; Wang, Q.; Hu, X.; Zheng, L. Characteristics and Potential Clinical Applications of the Extracellular Vesicles of Human Pathogenic Fungi. BMC Microbiol. 2023, 23, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A Rapid and Sensitive Method for the Quantitation of Microgram Quantities of Protein Utilizing the Principle of Protein-Dye Binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buratta, S.; Shimanaka, Y.; Costanzi, E.; Ni, S.; Urbanelli, L.; Kono, N.; Morena, F.; Sagini, K.; Giovagnoli, S.; Romani, R.; et al. Lipotoxic Stress Alters the Membrane Lipid Profile of Extracellular Vesicles Released by Huh-7 Hepatocarcinoma Cells. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 4613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buratta, S.; Urbanelli, L.; Sagini, K.; Giovagnoli, S.; Caponi, S.; Fioretto, D.; Mitro, N.; Caruso, D.; Emiliani, C. Extracellular Vesicles Released by Fibroblasts Undergoing H-Ras Induced Senescence Show Changes in Lipid Profile. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0188840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiaradia, E.; Sansone, A.; Ferreri, C.; Tancini, B.; Latella, R.; Tognoloni, A.; Gambelunghe, A.; dell’Omo, M.; Urbanelli, L.; Giovagnoli, S.; et al. Phospholipid Fatty Acid Remodeling and Carbonylated Protein Increase in Extracellular Vesicles Released by Airway Epithelial Cells Exposed to Cigarette Smoke Extract. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2023, 102, 151285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zengin, G.; Sarikurkcu, C.; Uyar, P.; Aktumsek, A.; Uysal, S.; Kocak, M.S.; Ceylan, R. Crepis foetida L. subsp. rhoeadifolia (Bieb.) Celak. as a Source of Multifunctional Agents: Cytotoxic and Phytochemical Evaluation. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 17, 698–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buanong, M.; Khunmuang, S.; Promboon, J.; Penchaiya, P.; Promyos, N.; Thepouyporn, A. Low Storage Temperature Maintains the Quality, Antioxidant Activity, and Nutraceutical Properties of Edible Flowers and Their Anti-Inflammatory Effects on RAW 264.7 Cells. J. Agric. Food Res. 2025, 21, 101938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aktumsek, A.; Zengin, G.; Guler, G.O.; Cakmak, Y.S.; Duran, A. Screening for in Vitro Antioxidant Properties and Fatty Acid Profiles of Five Centaurea L. Species from Turkey Flora. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2011, 49, 2914–2920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cajka, T.; Hricko, J.; Rudl Kulhava, L.; Paucova, M.; Novakova, M.; Kuda, O. Optimization of Mobile Phase Modifiers for Fast LC-MS-Based Untargeted Metabolomics and Lipidomics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsugawa, H.; Ikeda, K.; Takahashi, M.; Satoh, A.; Mori, Y.; Uchino, H.; Okahashi, N.; Yamada, Y.; Tada, I.; Bonini, P.; et al. A Lipidome Atlas in MS-DIAL 4. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 1159–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gertner, D.S.; Violi, J.P.; Bishop, D.P.; Padula, M.P. Lipid Spectrum Generator: A Simple Script for the Generation of Accurate In Silico Lipid Fragmentation Spectra. Anal. Chem. 2023, 95, 2909–2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alabed, H.B.R.; Mancini, D.F.; Buratta, S.; Calzoni, E.; Giacomo, D.D.; Emiliani, C.; Martino, S.; Urbanelli, L.; Pellegrino, R.M. LipidOne 2.0: A Web Tool for Discovering Biological Meanings Hidden in Lipidomic Data. Curr. Protoc. 2024, 4, e70009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Polyphenols | P. eryngii Mycelium-Derived EVs | P. eryngii Extract | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Caffeic acid | 6.290 ± 0.126 | 1.269 ± 0.115 | *** |
| epicatechin gallate | 22.352 ± 0.303 | 32.198 ± 2.153 | ** |
| (−)-epicatechin | 41.141 ± 0.461 | 27.256 ± 4.569 | ** |
| Rutin | 6.389 ± 0.075 | 3.677 ± 0.093 | ** |
| Chlorogenic acid | 2.041 ± 0.034 | 2.031 ± 0.011 | ns |
| Gallic acid | 1.307 ± 0.032 | 0.251 ± 0.037 | *** |
| Salicylic acid | 7.312 ± 0.077 | 31.874 ± 0.678 | *** |
| trans-4-Coumaric acid | 13.166 ± 0.107 | 1.441 ± 0.144 | *** |
| 40 K | p | 100 K | p | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FB | Myc | FB | Myc | |||
| DPPH (µg TE/µg EVs) | 25.96 ± 1.27 | 56.27 ± 0.48 | **** | 17.68 ± 2.75 | 64.73 ± 1.84 | **** |
| ABTS (µg TE/µg EVs) | 14.18 ± 1.51 | 89.61 ± 0.32 | **** | 11.17 ± 0.18 | 117.15 ± 0.66 | **** |
| FRAP (µg TE/µg EVs) | 15.92 ± 1.12 | 113.34 ± 5.04 | **** | 17.99 ± 5.86 | 64.32 ± 1.77 | *** |
| CUPRAC (µg TE/µg EVs) | 14.72 ± 0.83 | 196.5 ± 2.76 | **** | 9.01 ± 0.36 | 76.73 ± 7.38 | **** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cusumano, G.; Bertoldi, A.; Calzoni, E.; Alabed, H.B.R.; Pellegrino, R.M.; Urbanelli, L.; Zengin, G.; Angeles Flores, G.; Venanzoni, R.; Angelini, P.; et al. Therapeutic Potential of Bioactive Compounds in Edible Mushroom-Derived Extracellular Vesicles: Isolation and Characterization of EVs from Pleurotus eryngii. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 1362. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18091362
Cusumano G, Bertoldi A, Calzoni E, Alabed HBR, Pellegrino RM, Urbanelli L, Zengin G, Angeles Flores G, Venanzoni R, Angelini P, et al. Therapeutic Potential of Bioactive Compounds in Edible Mushroom-Derived Extracellular Vesicles: Isolation and Characterization of EVs from Pleurotus eryngii. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(9):1362. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18091362
Chicago/Turabian StyleCusumano, Gaia, Agnese Bertoldi, Eleonora Calzoni, Husam B. R. Alabed, Roberto Maria Pellegrino, Lorena Urbanelli, Gokhan Zengin, Giancarlo Angeles Flores, Roberto Venanzoni, Paola Angelini, and et al. 2025. "Therapeutic Potential of Bioactive Compounds in Edible Mushroom-Derived Extracellular Vesicles: Isolation and Characterization of EVs from Pleurotus eryngii" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 9: 1362. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18091362
APA StyleCusumano, G., Bertoldi, A., Calzoni, E., Alabed, H. B. R., Pellegrino, R. M., Urbanelli, L., Zengin, G., Angeles Flores, G., Venanzoni, R., Angelini, P., & Emiliani, C. (2025). Therapeutic Potential of Bioactive Compounds in Edible Mushroom-Derived Extracellular Vesicles: Isolation and Characterization of EVs from Pleurotus eryngii. Pharmaceuticals, 18(9), 1362. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18091362













