Rational Function-Based Approach for Integrating Tableting Reduced-Order Models with Upstream Unit Operations: Dry Granulation Case Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation and Characterization of Granules
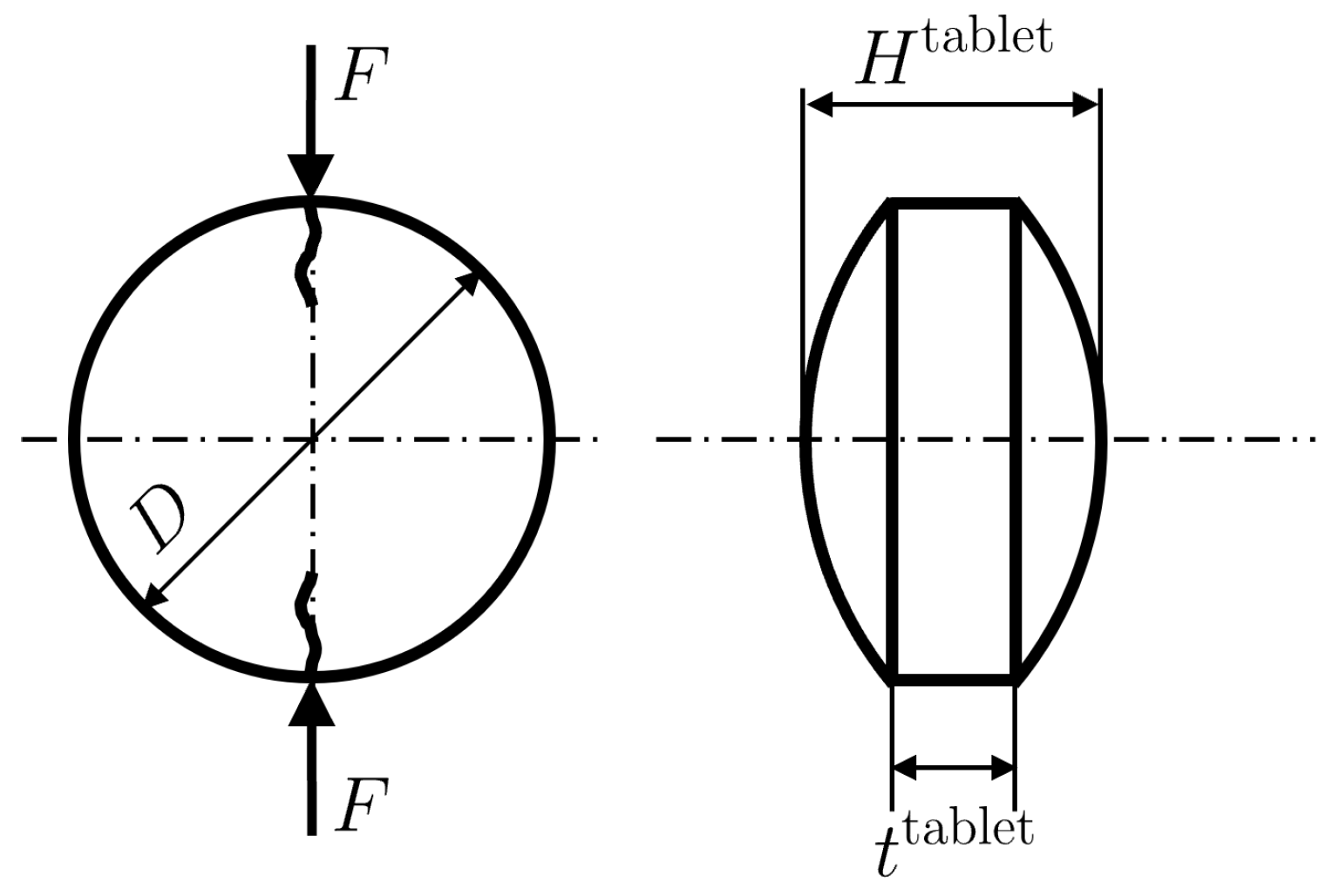
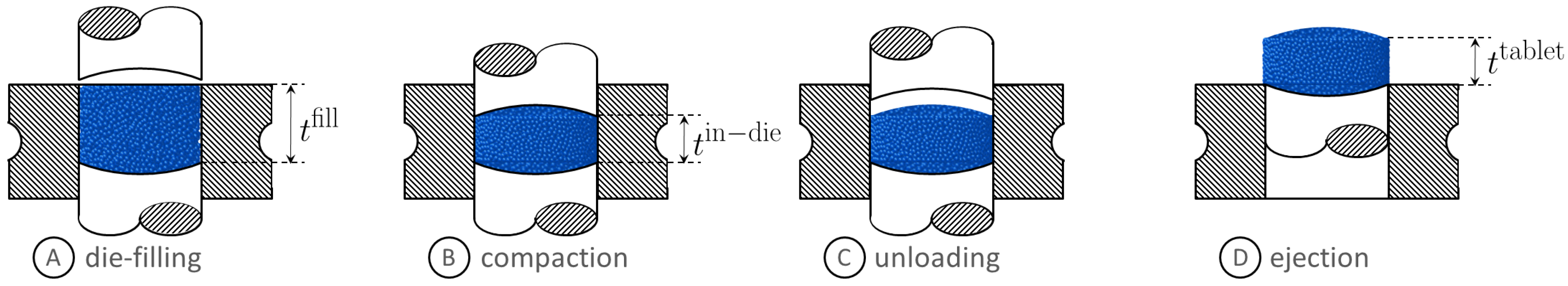
2.2. Preparation and Characterization of Tablets
3. Tableting Reduced-Order Models
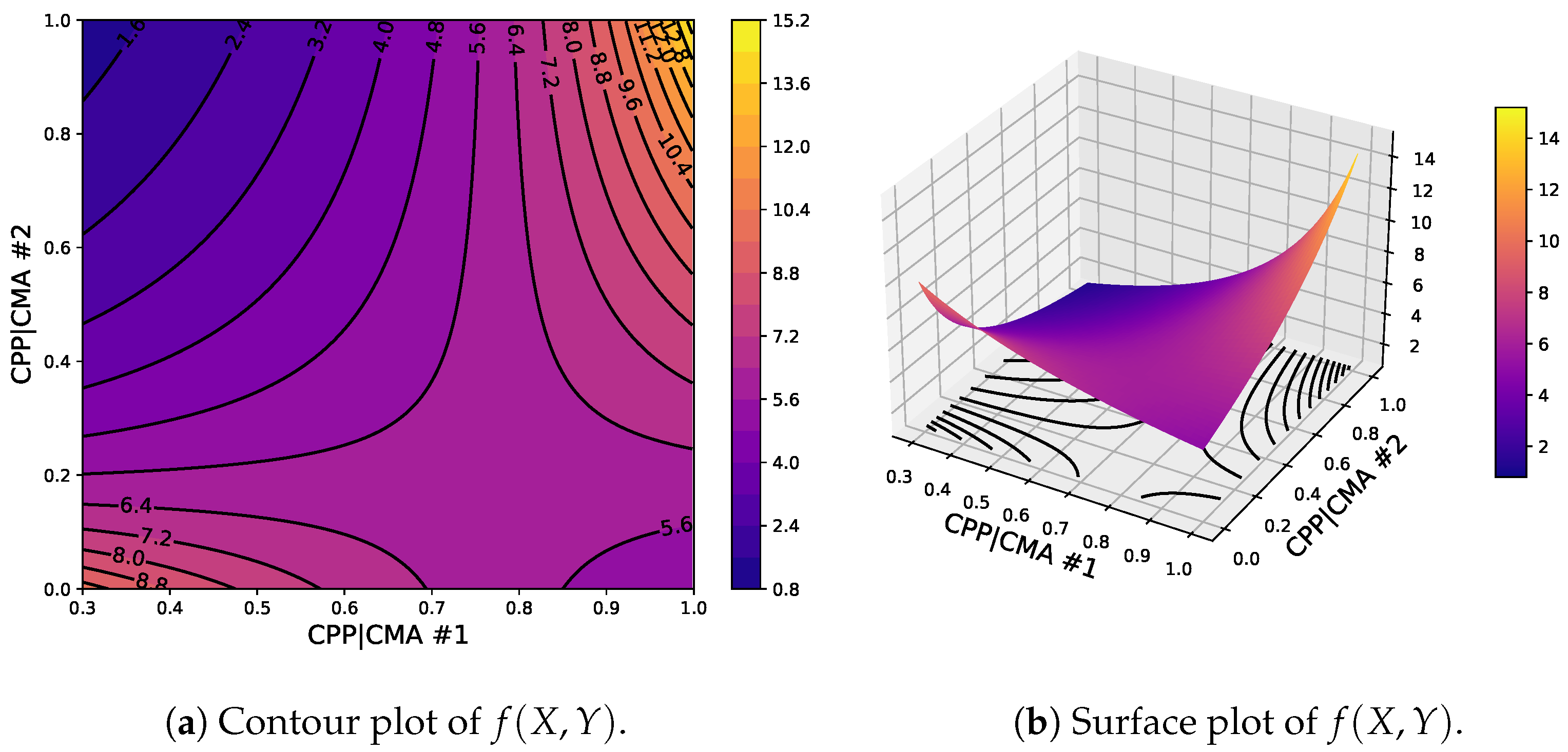
4. Model Selection and Parameter Estimation
5. Reduced-Order Models to Integrate Dry Granulation and Tableting Processes
6. Results and Discussion
6.1. Tablet Weight
6.2. Compaction Force
6.3. Elastic Recovery and Tablet Density
6.4. Tensile Strength
6.5. Discussion
| Granule Properties | Tablet Weight | Compaction Force | Elastic Recovery | Tensile Strength |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| — | 2 | 2 | — | |
| 1 | — | — | 2 | |
| 2 | — | — | — |
| Weight | |
| , | |
| ; ; | |
| , | |
| ; | |
| Compaction force | |
| ; | |
| ; | |
| ; | |
| Elastic recovery | |
| ; | |
| ; ; | |
| Tensile strength | |
| ; | |
| ; ; ; | |
| ; ; ; |
7. Conclusions
8. Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| QbD | Quality by Design |
| FDA | Food and Drug Administration |
| QbC | Quality by Control |
| API | Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients |
| CPP | Critical Process Parameters |
| CQA | Critical Quality Attributes |
| ROMs | Reduced-Order Models |
| NMPC | Nonlinear Model Predictive Control |
| CMAs | Critical Material Attributes |
| MCC | Microcrystalline Cellulose Avicel PH-102 |
| APAP | Acetaminophen Grade 0048 |
| GSD | Granule Size Distributions |
| ML | Machine-learning |
| NIR | Near-infrared |
References
- Su, Q.; Bommireddy, Y.; Shah, Y.; Ganesh, S.; Moreno, M.; Liu, J.; Gonzalez, M.; Yazdanpanah, N.; O’Connor, T.; Reklaitis, G.V.; et al. Data reconciliation in the Quality-by-Design (QbD) implementation of pharmaceutical continuous tablet manufacturing. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 563, 259–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.X.; Amidon, G.; Khan, M.A.; Hoag, S.W.; Polli, J.; Raju, G.; Woodcock, J. Understanding pharmaceutical quality by design. AAPS J. 2014, 16, 771–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Q.; Ganesh, S.; Moreno, M.; Bommireddy, Y.; Gonzalez, M.; Reklaitis, G.V.; Nagy, Z.K. A perspective on Quality-by-Control (QbC) in pharmaceutical continuous manufacturing. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2019, 125, 216–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.S.; Sheriff, M.Z.; Bachawala, S.; Gonzalez, M.; Nagy, Z.K.; Reklaitis, G.V. Evaluation of a Combined MHE-NMPC Approach to Handle Plant-Model Mismatch in a Rotary Tablet Press. Processes 2021, 9, 1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, M. Generalized loading-unloading contact laws for elasto-plastic spheres with bonding strength. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2019, 122, 633–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachawala, S.; Gonzalez, M. Development of mechanistic reduced order models (ROMs) for glidant and lubricant effects in continuous manufacturing of pharmaceutical solid-dosage forms. In 32nd European Symposium on Computer Aided Process Engineering; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; Computer Aided Chemical Engineering; Volume 51, pp. 1129–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferdoush, S.; Gonzalez, M. Semi-mechanistic reduced order model of pharmaceutical tablet dissolution for enabling Industry 4.0 manufacturing systems. Int. J. Pharm. 2023, 631, 122502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.S.; Sheriff, M.Z.; Bachawala, S.; Gonzalez, M.; Nagy, Z.K.; Reklaitis, G.V. Application of MHE-based NMPC on a Rotary Tablet Press under Plant-Model Mismatch. In Computer Aided Chemical Engineering; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; Volume 49, pp. 2149–2154. [Google Scholar]
- Herting, M.G.; Kleinebudde, P. Studies on the reduction of tensile strength of tablets after roll compaction/dry granulation. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2008, 70, 372–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavi, E.; Reynolds, G.K. System model of a tablet manufacturing process. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2014, 71, 130–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.-S.; Lagare, R.B.; Bailey, P.; Sixon, D.; Gonzalez, M.; Nagy, Z.K.; Reklaitis, G.V. Hybrid model development and nonlinear model predictive control implementation for continuous dry granulation process. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2024, 183, 108586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razavi, S.M.; Gonzalez, M.; Cuitino, A.M. General and mechanistic optimal relationships for tensile strength of doubly convex tablets under diametrical compression. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 484, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pishnamazi, M.; Casilagan, S.; Clancy, C.; Shirazian, S.; Iqbal, J.; Egan, D.; Edlin, C.; Croker, D.M.; Walker, G.M.; Collins, M.N. Microcrystalline cellulose, lactose and lignin blends: Process mapping of dry granulation via roll compaction. Powder Technol. 2019, 341, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matji, A.; Donato, N.; Gagol, A.; Morales, E.; Carvajal, L.; Serrano, D.R.; Worku, Z.A.; Healy, A.M.; Torrado, J.J. Predicting the critical quality attributes of ibuprofen tablets via modelling of process parameters for roller compaction and tabletting. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 565, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.S.; Sixon, D.; Bailey, P.; Lagare, R.B.; Gonzalez, M.; Nagy, Z.K.; Reklaitis, G.V. A Machine Learning-assisted Hybrid Model to Predict Ribbon Solid Fraction, Granule Size Distribution and Throughput in a Dry Granulation Process. In 33rd European Symposium on Computer Aided Process Engineering; Kokossis, A.C., Georgiadis, M.C., Pistikopoulos, E., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; Computer Aided Chemical Engineering; Volume 52, pp. 813–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johanson, J.R. A Rolling Theory for Granular Solids. J. Appl. Mech. 1965, 32, 842–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Peck, G.E.; Miller, R.W.; Morris, K.R. Real-time near-infrared monitoring of content uniformity, moisture content, compact density, tensile strength, and young’s modulus of roller compacted powder blends. J. Pharm. Sci. 2005, 94, 1589–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowley, M.E.; Hegarty, A.; McAuliffe, M.A.; O’Mahony, G.E.; Kiernan, L.; Hayes, K.; Crean, A.M. Near-infrared monitoring of roller compacted ribbon density: Investigating sources of variation contributing to noisy spectral data. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 102, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilari, J.L.; Martens, H.; Isaksson, T. Determination of particle size in powders by scatter correction in diffuse near-infrared reflectance. Appl. Spectrosc. 1988, 42, 722–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Hagrasy, A.; Cruise, P.; Jones, I.; Litster, J. In-line size monitoring of a twin screw granulation process using high-speed imaging. J. Pharm. Innov. 2013, 8, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitt, K.; Newton, J.; Stanley, P. Stress distributions in doubly convex cylindrical discs under diametral loading. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 1989, 22, 1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Román-Ospino, A.D.; Romañach, R.J.; Ierapetritou, M.; Ramachandran, R. Real time monitoring of powder blend bulk density for coupled feed-forward/feed-back control of a continuous direct compaction tablet manufacturing process. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 495, 612–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawakita, K.; Lüdde, K.H. Some considerations on powder compression equations. Powder Technol. 1971, 4, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leuenberger, H.; Rohera, B.D. Fundamentals of powder compression. I. The compactibility and compressibility of pharmaceutical powders. Pharm. Res. 1986, 3, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuyt, A.A.; Verdonk, B.M. Multivariate rationale Interpolation. Computing 1985, 34, 41–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmensiek, R.; Meyer, P. An efficient adaptive frequency sampling algorithm for model-based parameter estimation as applied to aggressive space mapping. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 2000, 24, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akaike, H. A new look at the statistical model identification. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 1974, 19, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HURVICH, C.M.; TSAI, C.L. Regression and time series model selection in small samples. Biometrika 1989, 76, 297–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brouwers, H.J.H. Packing fraction of crystalline structures of binary hard spheres: A general equation and application to amorphization. Phys. Rev. E 2008, 78, 011303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brouwers, H.J.H. Random packing fraction of bimodal spheres: An analytical expression. Phys. Rev. E 2013, 87, 032202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Lu, P.; Li, S. Packing properties of binary mixtures in disordered sphere systems. Particuology 2014, 16, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Zhang, Y. Simulation of random packing of spherical particles with different size distributions. Appl. Phys. A 2008, 92, 621–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordström, J.; Welch, K.; Frenning, G.; Alderborn, G. On the physical interpretation of the Kawakita and Adams parameters derived from confined compression of granular solids. Powder Technol. 2008, 182, 424–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, B.; Hilden, J.; Litster, J. Assessment of intragranular and extragranular fracture in the development of tablet tensile strength. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 107, 2581–2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitra, B.; Hilden, J.; Litster, J.D. Effects of the granule composition on the compaction behavior of deformable dry granules. Powder Technol. 2016, 291, 487–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordström, J.; Alderborn, G.; Frenning, G. Compressibility and tablet forming ability of bimodal granule mixtures: Experiments and DEM simulations. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 540, 120–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, B.; Alderborn, G. The effect of shape and porosity on the compression behaviour and tablet forming ability of granular materials formed from microcrystalline cellulose. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2001, 52, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordström, J.; Alderborn, G. The Granule Porosity Controls the Loss of Compactibility for Both Dry- and Wet-Processed Cellulose Granules but at Different Rate. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 104, 2029–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitag, F.; Kleinebudde, P. How do roll compaction/dry granulation affect the tableting behaviour of inorganic materials? Comparison of four magnesium carbonates. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2003, 19, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farber, L.; Hapgood, K.P.; Michaels, J.N.; Fu, X.Y.; Meyer, R.; Johnson, M.A.; Li, F. Unified compaction curve model for tensile strength of tablets made by roller compaction and direct compression. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 346, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yohannes, B.; Gonzalez, M.; Abebe, A.; Sprockel, O.; Nikfar, F.; Kang, S.; Cuitino, A. The role of fine particles on compaction and tensile strength of pharmaceutical powders. Powder Technol. 2015, 274, 372–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Gandarillas, L.; Perez-Gago, A.; Mazor, A.; Kleinebudde, P.; Lecoq, O.; Michrafy, A. Effect of roll-compaction and milling conditions on granules and tablet properties. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2016, 106, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kása, P.; Bajdik, J.; Zsigmond, Z.; Pintye-Hódi, K. Study of the compaction behaviour and compressibility of binary mixtures of some pharmaceutical excipients during direct compression. Chem. Eng. Process. Process. Intensif. 2009, 48, 859–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilić, I.; Kása, P., Jr.; Dreu, R.; Pintye-Hódi, K.; Srčič, S. The compressibility and compactibility of different types of lactose. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2009, 35, 1271–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonnergaard, J.M. A critical evaluation of the Heckel equation. Int. J. Pharm. 1999, 193, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heckel, R.W. Density-pressure relationships in powder compaction. Trans. Metal. Soc. AIME 1961, 221, 671–675. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, S.; Kaushal, A.M.; Bansal, A.K. Compression physics in the formulation development of tablets. Crit. Rev. Ther. Drug Carr. Syst. 2006, 23, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

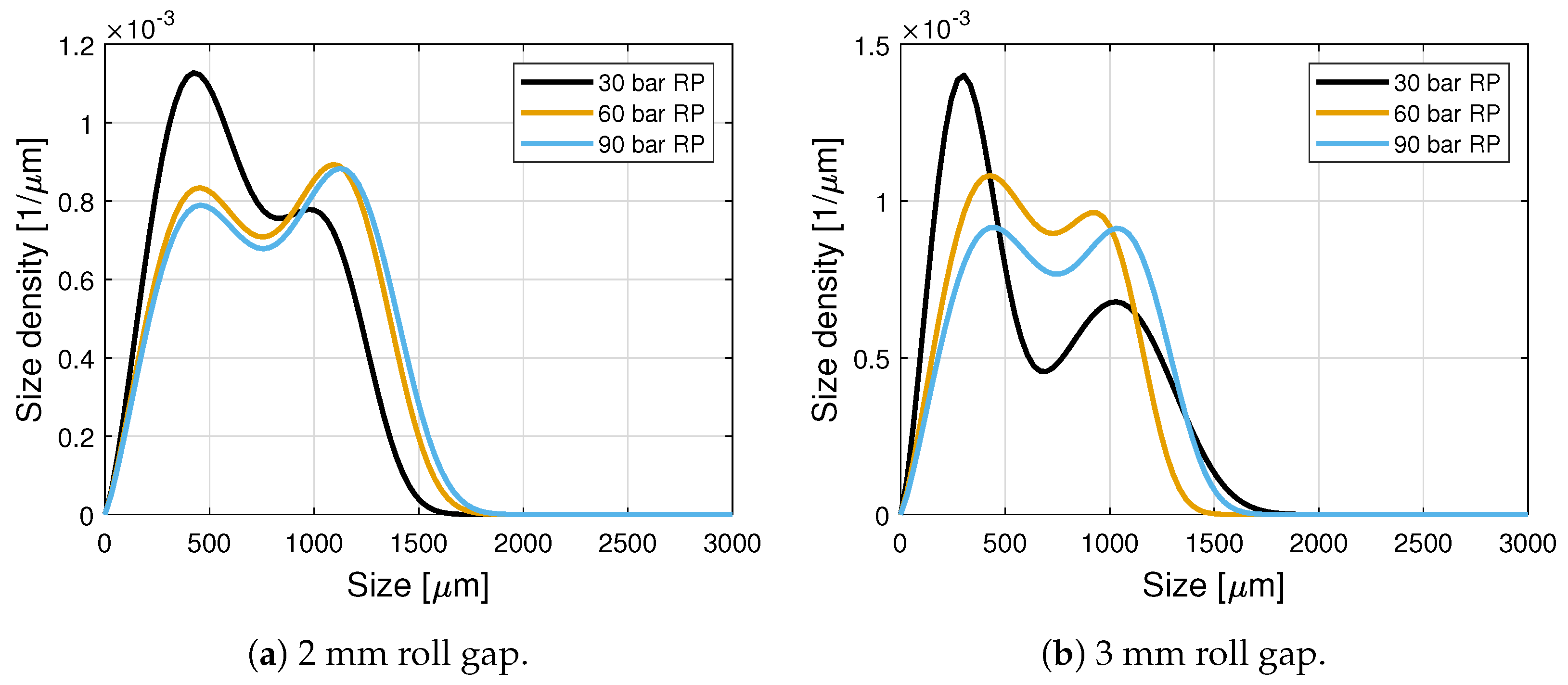
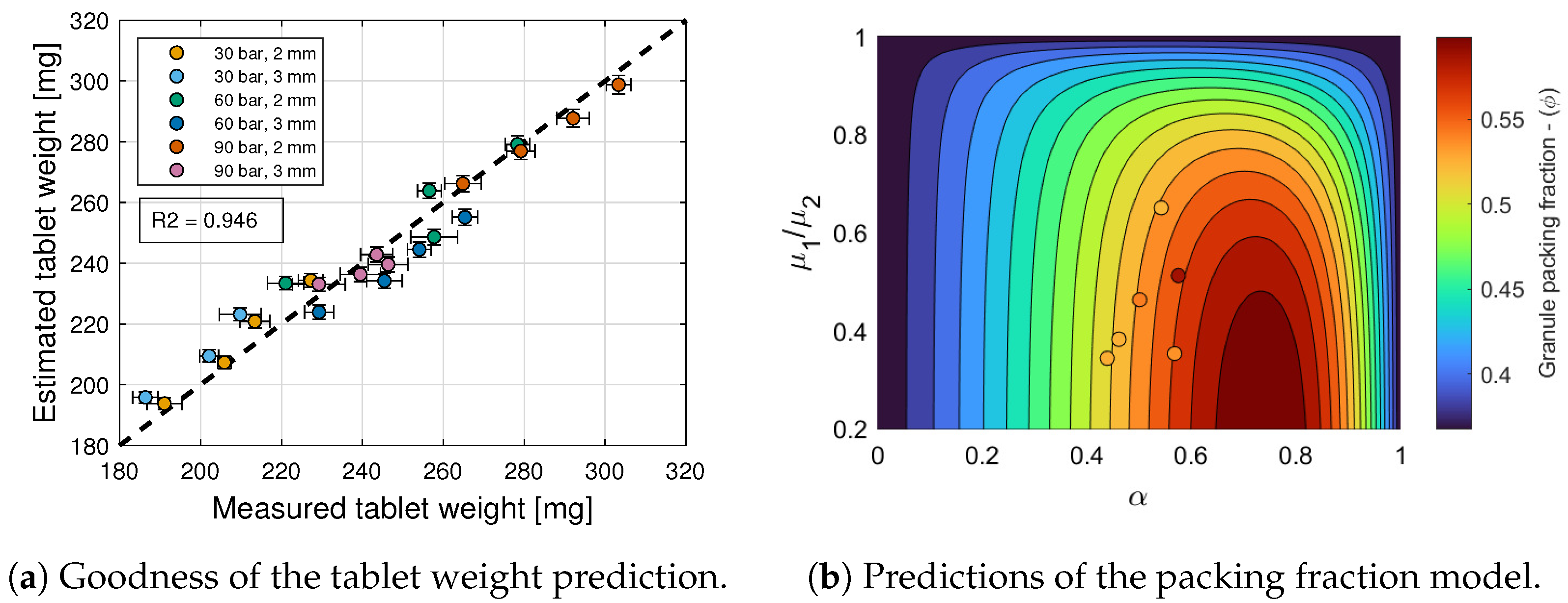
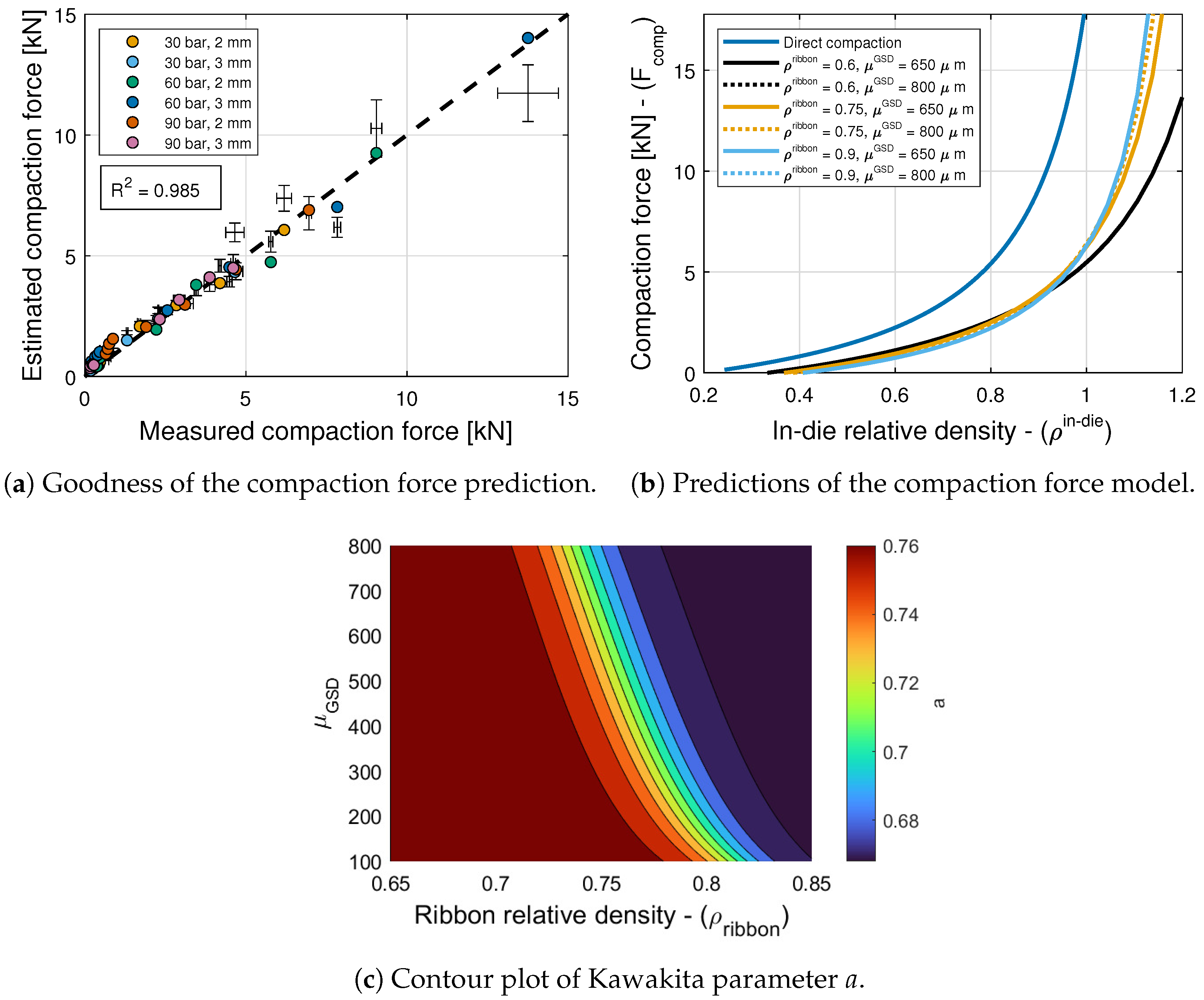
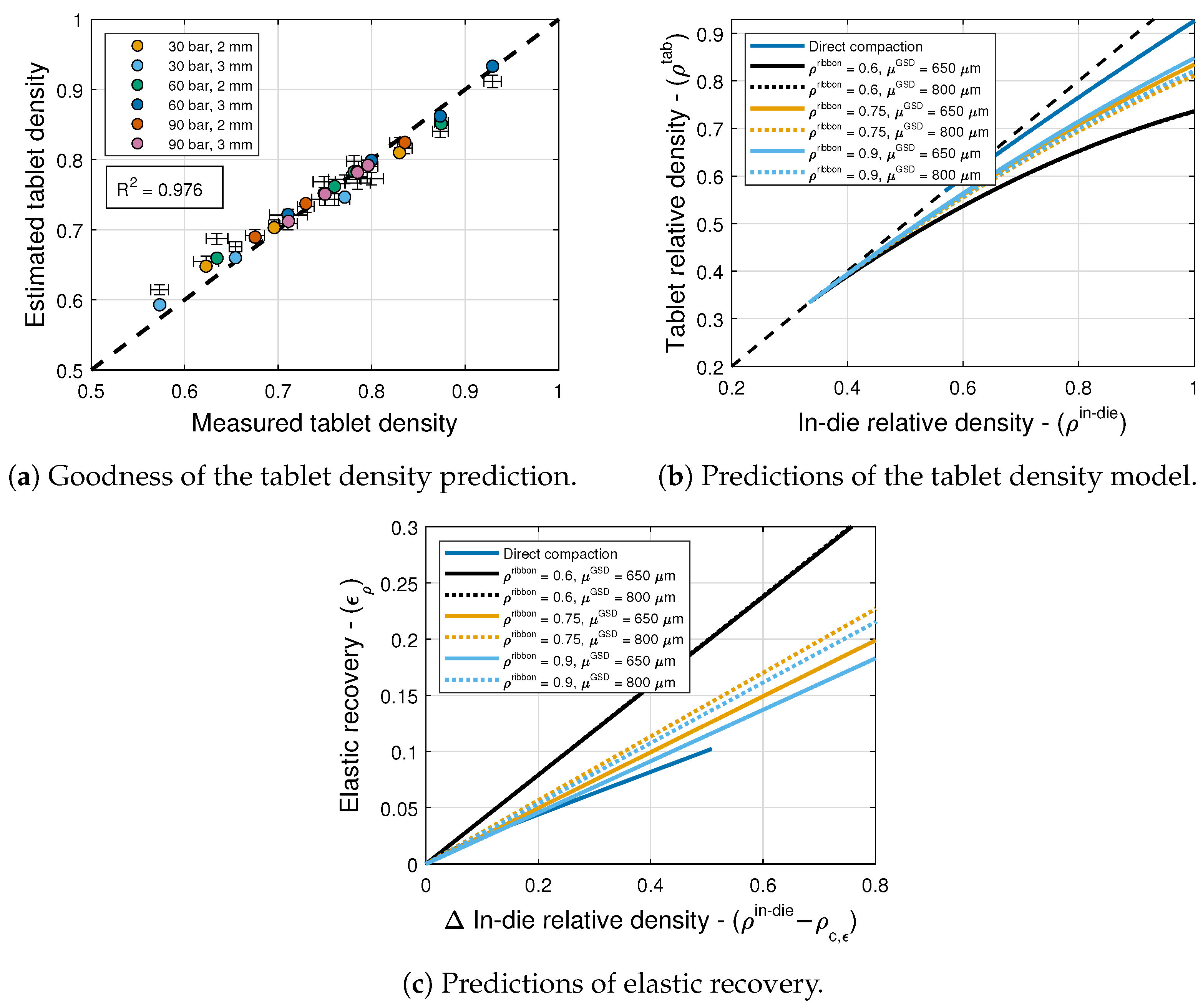

| Roll Pressure [bar] | Roll Gap [mm] | [m] | [m] | [m] | [m] | [m] | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30 | 2 | 0.54 | 524 | 1055 | 2.25 | 5.32 | 457 | 991 | 696 | 0.640 |
| 30 | 3 | 0.57 | 518 | 1019 | 2.25 | 5.43 | 325 | 999 | 667 | 0.613 |
| 60 | 2 | 0.46 | 541 | 1170 | 2.24 | 4.98 | 479 | 1074 | 800 | 0.739 |
| 60 | 3 | 0.58 | 517 | 1009 | 2.26 | 5.46 | 458 | 931 | 658 | 0.708 |
| 90 | 2 | 0.44 | 546 | 1202 | 2.23 | 4.89 | 484 | 1102 | 830 | 0.803 |
| 90 | 3 | 0.50 | 533 | 1114 | 2.24 | 5.15 | 472 | 1024 | 747 | 0.770 |
| Roller Compactor Settings | Tablet Press Settings | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Batch | Roll Pressure [bar] | Roll Gap [mm] | Dosing Position [mm] | Main Compression Thickness [mm] |
| 1 | 30 | 2 | 7.0–8.5 | 2.5–3.0 |
| 2 | 30 | 3 | 7.0–8.0 | 2.5–3.2 |
| 3 | 60 | 2 | 7.5–9.0 | 2.5–3.0 |
| 4 | 60 | 3 | 7.0–8.0 | 2.5–3.2 |
| 5 | 90 | 2 | 8.0–9.0 | 3.5–4.0 |
| 6 | 90 | 3 | 7.0–7.3 | 3.0–3.3 |
| Lower Bound () | Upper Bound () | Normalized | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ribbon relative density: | 1 | ||
| Mean granule size: | 0 |
| Compaction Force | Elastic Recovery | Tensile Strength | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Model Number | Rational Function | No. of Parameters |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 9 | |
| 2 | 7 | |
| 3 | 7 | |
| 4 | 5 | |
| 5 | 7 | |
| 6 | 5 | |
| 7 | 5 | |
| 8 | 3 | |
| 9 | Constant − | 1 |
| Function Variant | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ✓ | ✓ | |||||||
| 2 | ✓ | ✓ | |||||||
| 3 | ✓ | ✓ | |||||||
| 4 | ✓ | ✓ | |||||||
| 5 | ✓ | ✓ | |||||||
| 6 | ✓ | ✓ | |||||||
| 7 | ✓ | ✓ | |||||||
| 8 | ✓ | ✓ | |||||||
| 9 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| SSE | AIC | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7 | 7 | 9 | 5.539 | 0.985 | −79.37 |
| 6 | 9 | 7 | 6.707 | 0.982 | −74.57 |
| 4 | 9 | 7 | 6.79 | 0.982 | −74.00 |
| 4 | 4 | 11 | 5.903 | 0.984 | −72.44 |
| 8 | 8 | 7 | 7.053 | 0.981 | −72.26 |
| SSE | AIC | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | 9 | 7 | 0.004 | 0.976 | −185.5 |
| 8 | 9 | 5 | 0.005 | 0.968 | −182.6 |
| 2 | 9 | 9 | 0.004 | 0.977 | −181.6 |
| 3 | 9 | 9 | 0.004 | 0.976 | −181.5 |
| 6 | 9 | 7 | 0.005 | 0.970 | −180.3 |
| SSE | AIC | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 0.913 | 177 | 16 | −5302 | ||
| 1 | 1 | 0.906 | 193 | 16 | −5123 | ||
| 3 | 3 | 0.903 | 197 | 12 | −5082 | ||
| 3 | 3 | 0.900 | 205 | 12 | −5004 | ||
| 7 | 7 | 0.881 | 243 | 8 | −4639 | ||
| 2 | 2 | 0.873 | 259 | 14 | −4497 | ||
| 5 | 5 | 0.873 | 260 | 12 | −4491 | ||
| 1 | 9 | 0.862 | 281 | 10 | −4327 | ||
| 2 | 2 | 0.856 | 293 | 14 | −4229 | ||
| 4 | 4 | 0.848 | 309 | 10 | −4122 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bachawala, S.; Lagare, R.B.; Delaney, A.B.; Nagy, Z.K.; Reklaitis, G.V.; Gonzalez, M. Rational Function-Based Approach for Integrating Tableting Reduced-Order Models with Upstream Unit Operations: Dry Granulation Case Study. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 1158. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17091158
Bachawala S, Lagare RB, Delaney AB, Nagy ZK, Reklaitis GV, Gonzalez M. Rational Function-Based Approach for Integrating Tableting Reduced-Order Models with Upstream Unit Operations: Dry Granulation Case Study. Pharmaceuticals. 2024; 17(9):1158. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17091158
Chicago/Turabian StyleBachawala, Sunidhi, Rexonni B. Lagare, Abigail B. Delaney, Zoltan K. Nagy, Gintaras V. Reklaitis, and Marcial Gonzalez. 2024. "Rational Function-Based Approach for Integrating Tableting Reduced-Order Models with Upstream Unit Operations: Dry Granulation Case Study" Pharmaceuticals 17, no. 9: 1158. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17091158
APA StyleBachawala, S., Lagare, R. B., Delaney, A. B., Nagy, Z. K., Reklaitis, G. V., & Gonzalez, M. (2024). Rational Function-Based Approach for Integrating Tableting Reduced-Order Models with Upstream Unit Operations: Dry Granulation Case Study. Pharmaceuticals, 17(9), 1158. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17091158








