Evaluation of the Pharmaceutical Activities of Chuanxiong, a Key Medicinal Material in Traditional Chinese Medicine
Abstract
1. Introduction
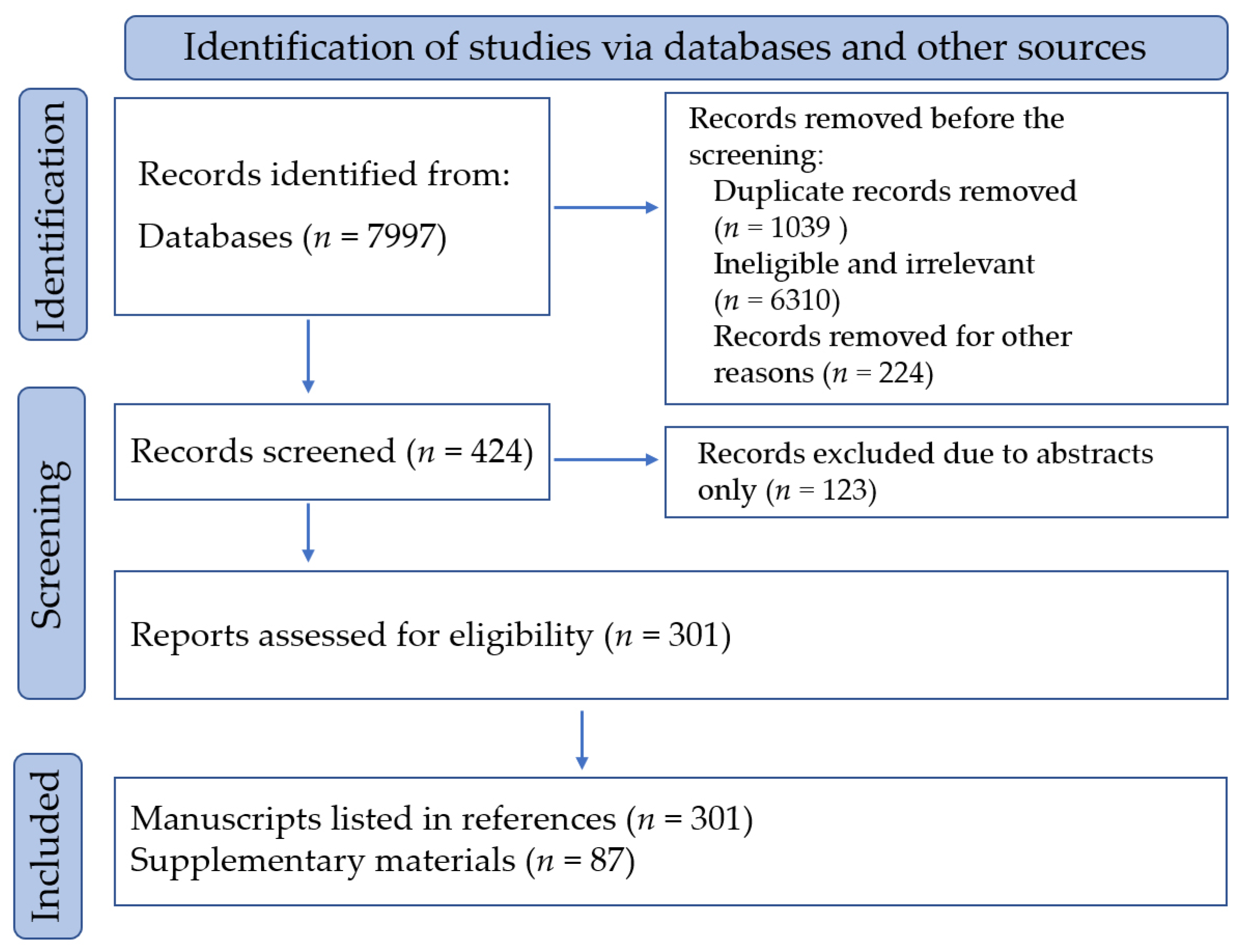
2. Materials and Methods
3. Chemical Constituents
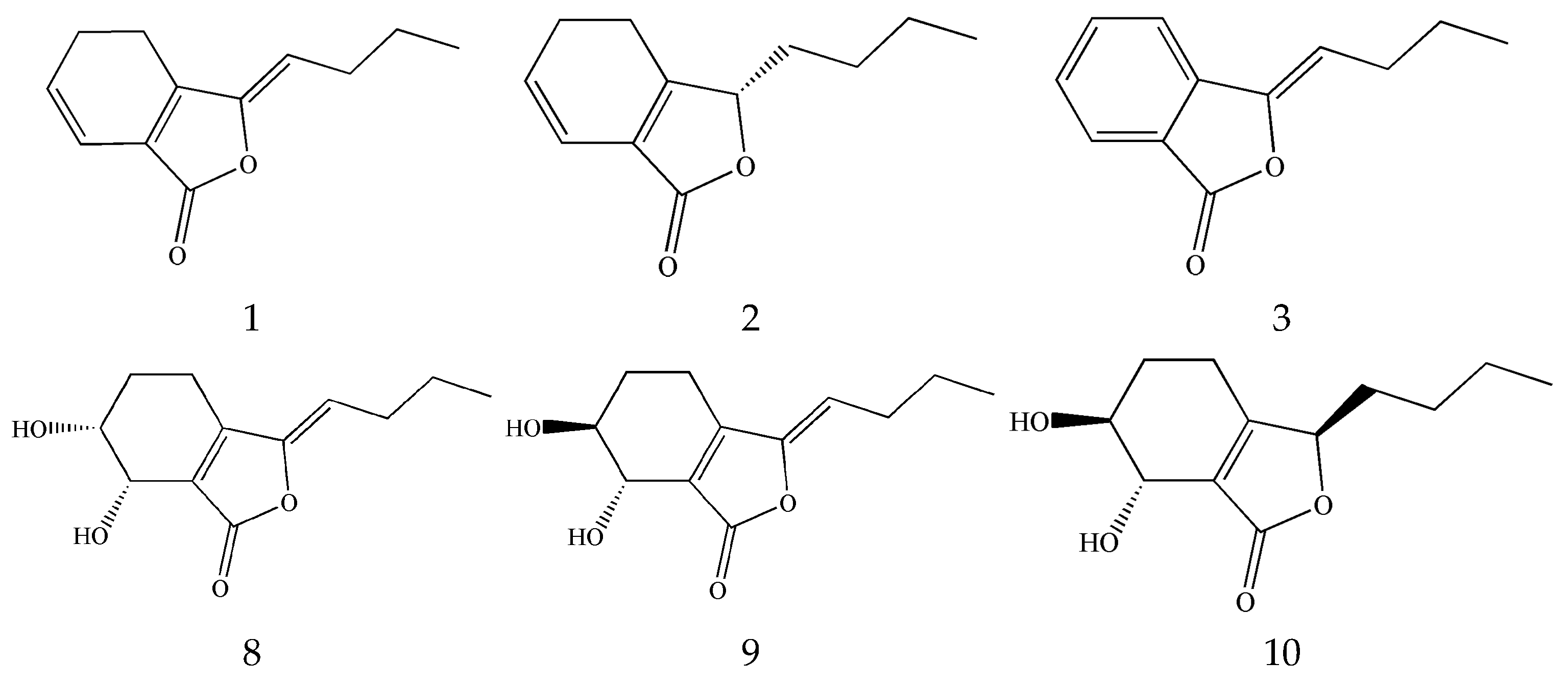
3.1. Phthalides
3.1.1. Monomeric Phthalides
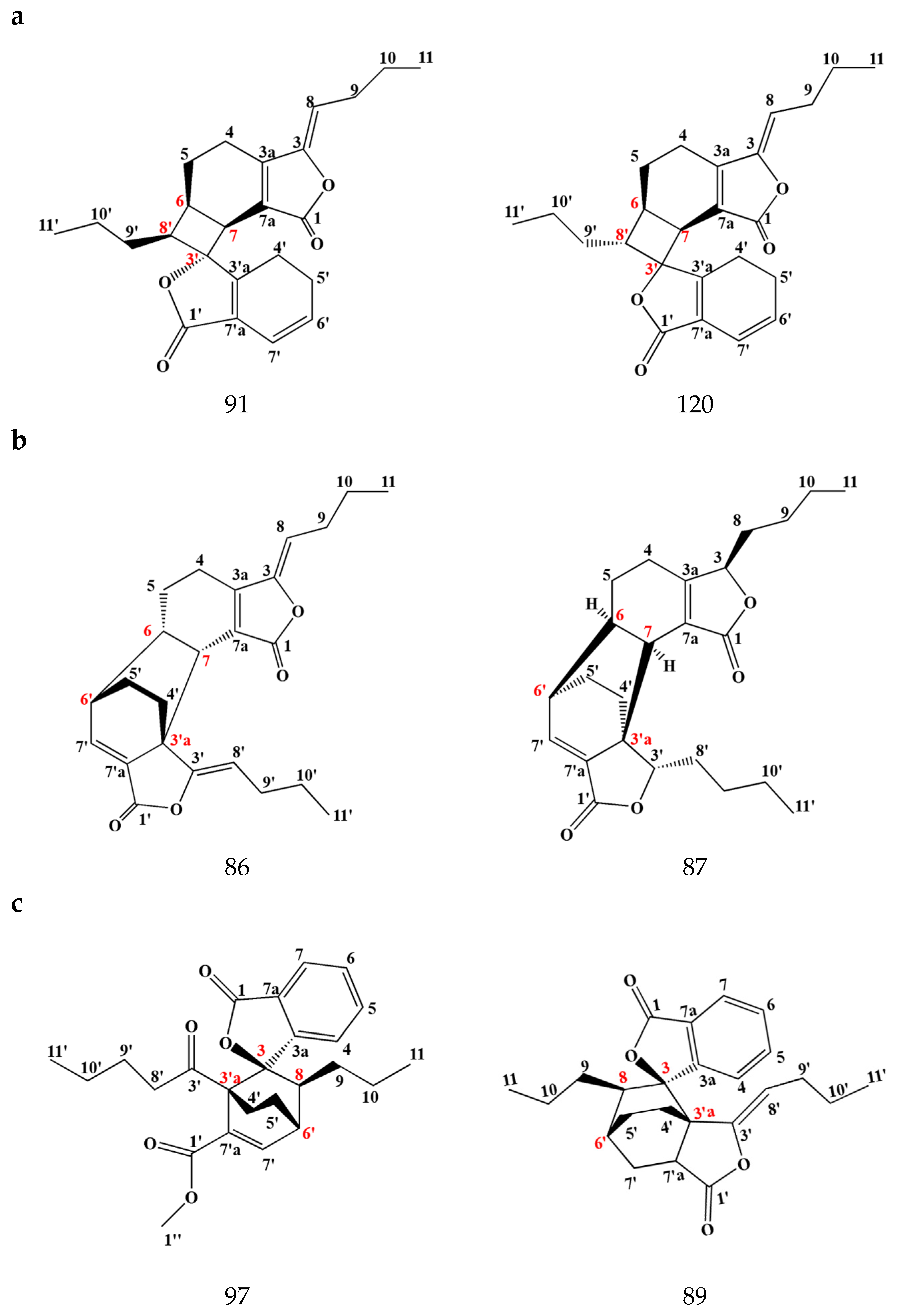
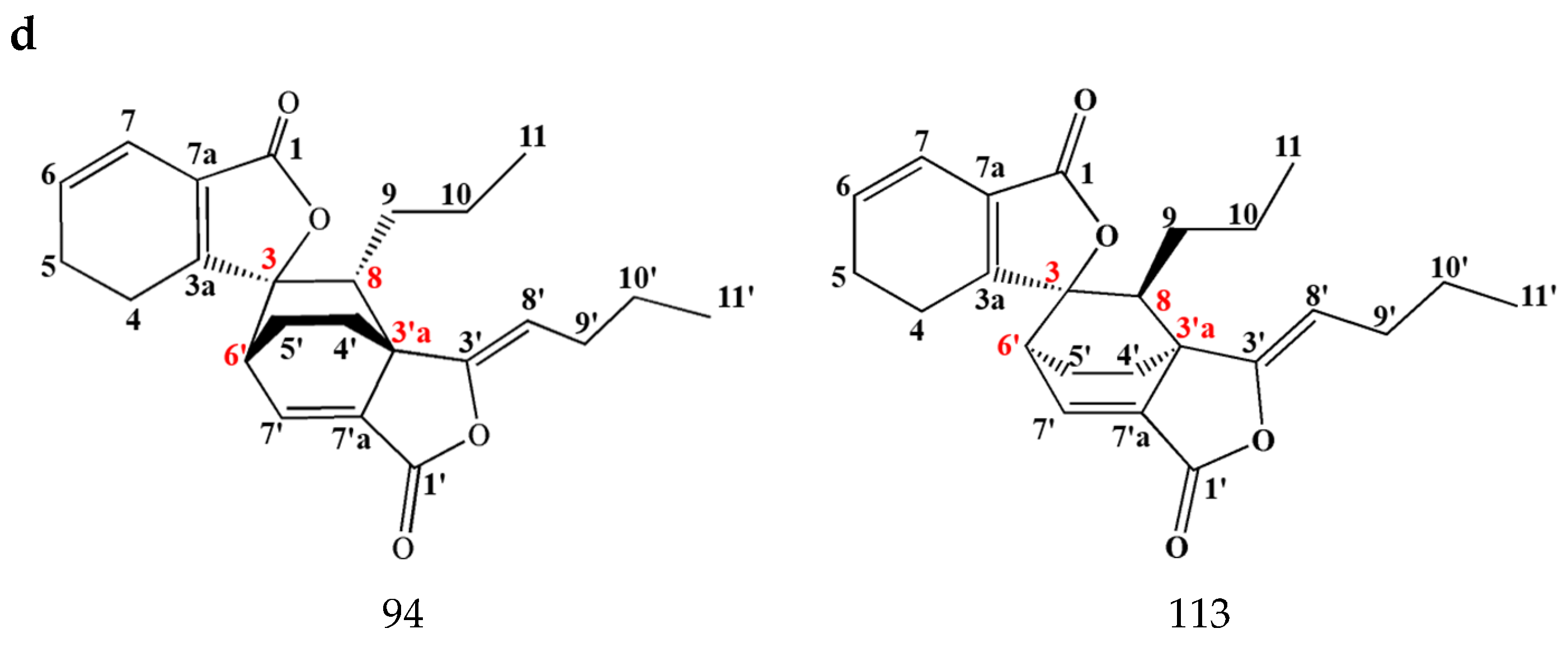
3.1.2. Dimeric Phthalides
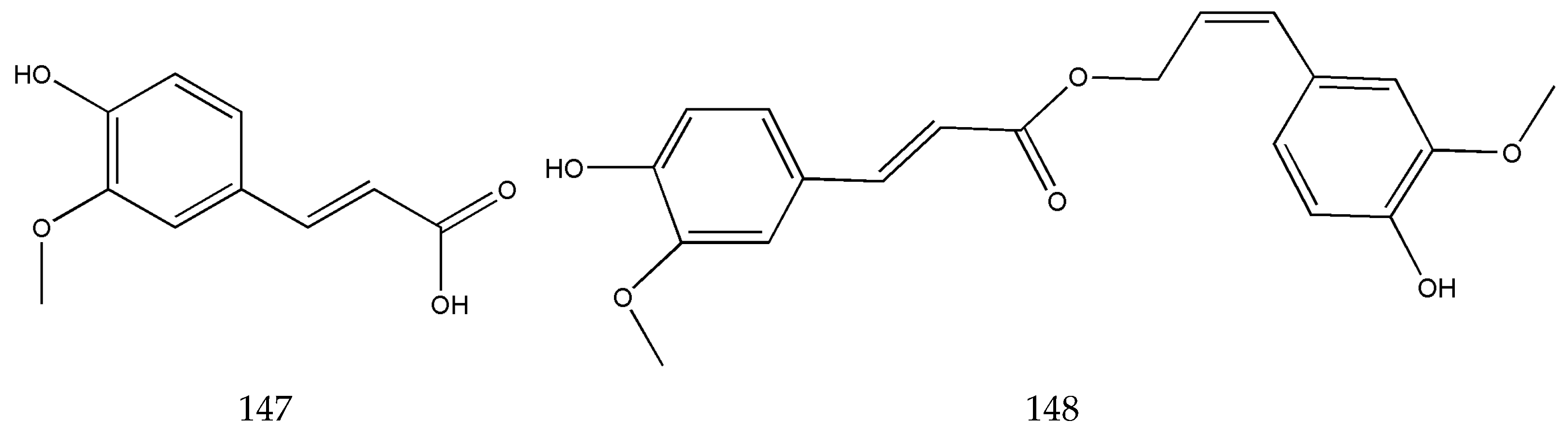
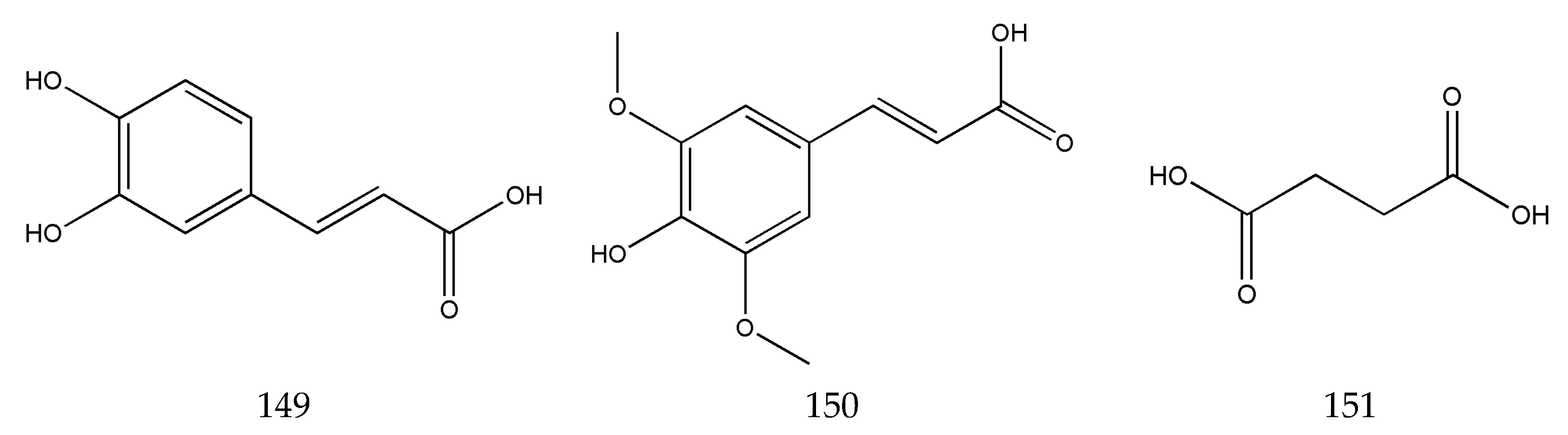
3.2. Organic Phenolic Acids and Their Esters
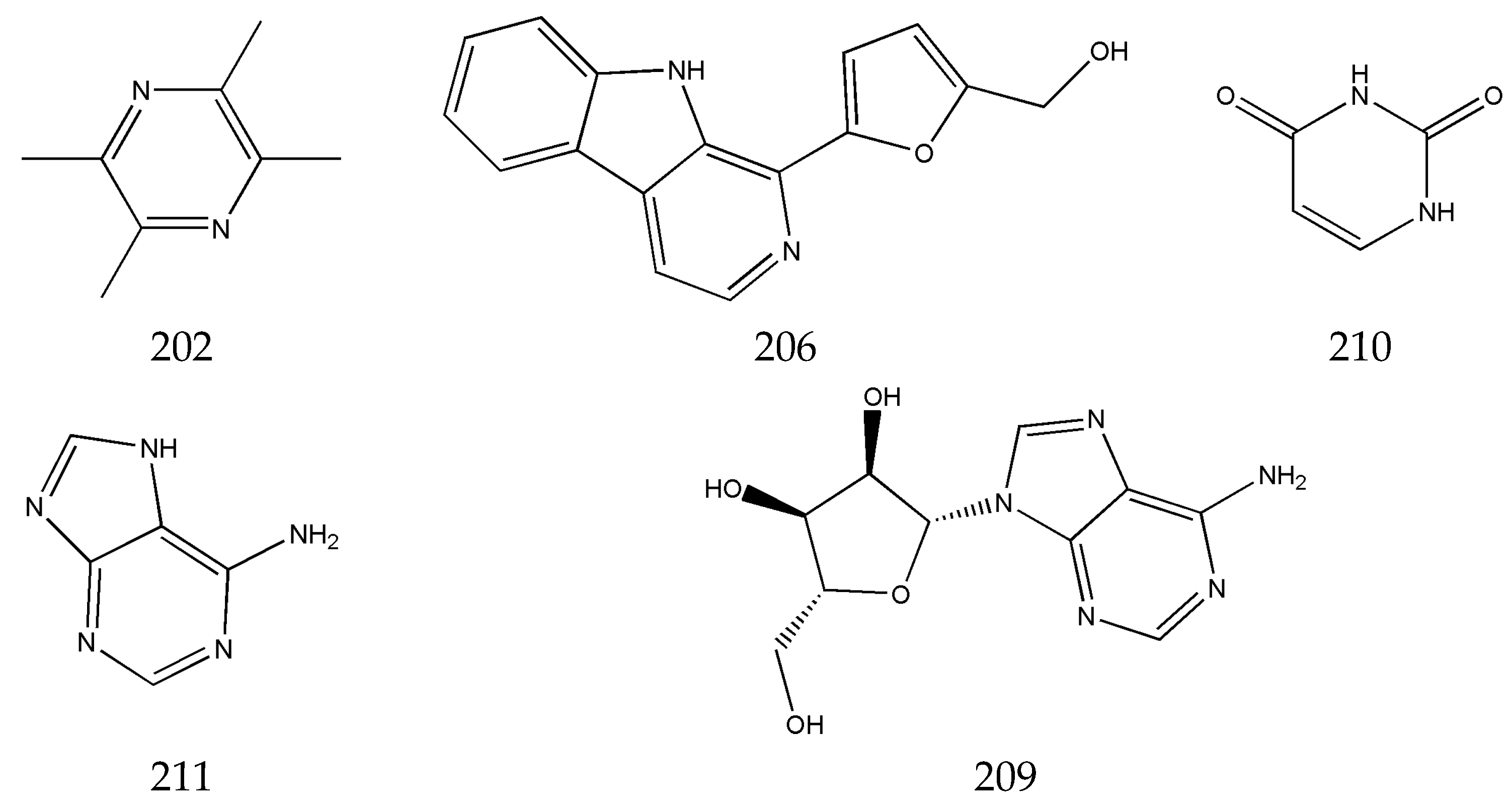
3.3. Alkaloids
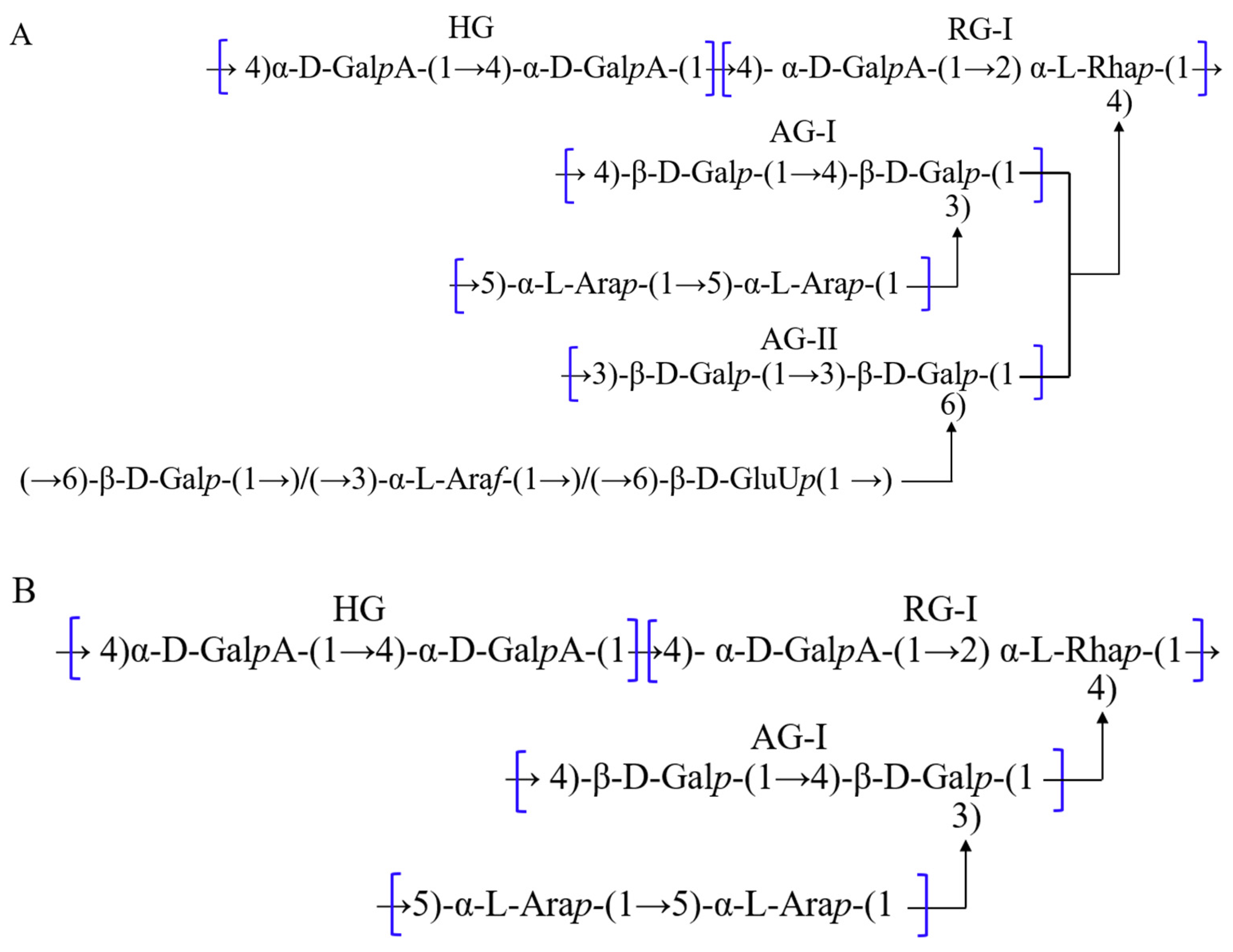
3.4. Polysaccharides
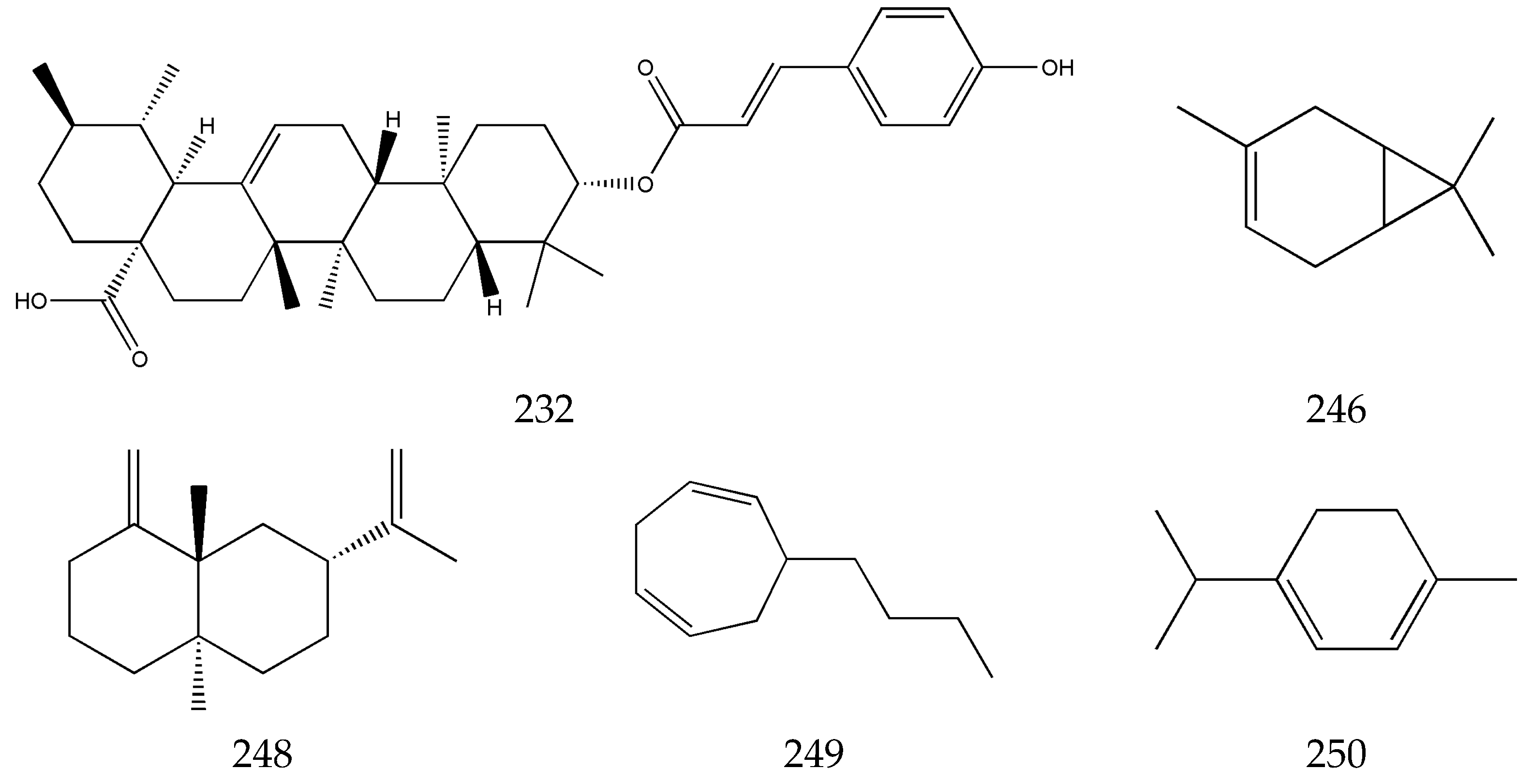
3.5. Terpenes
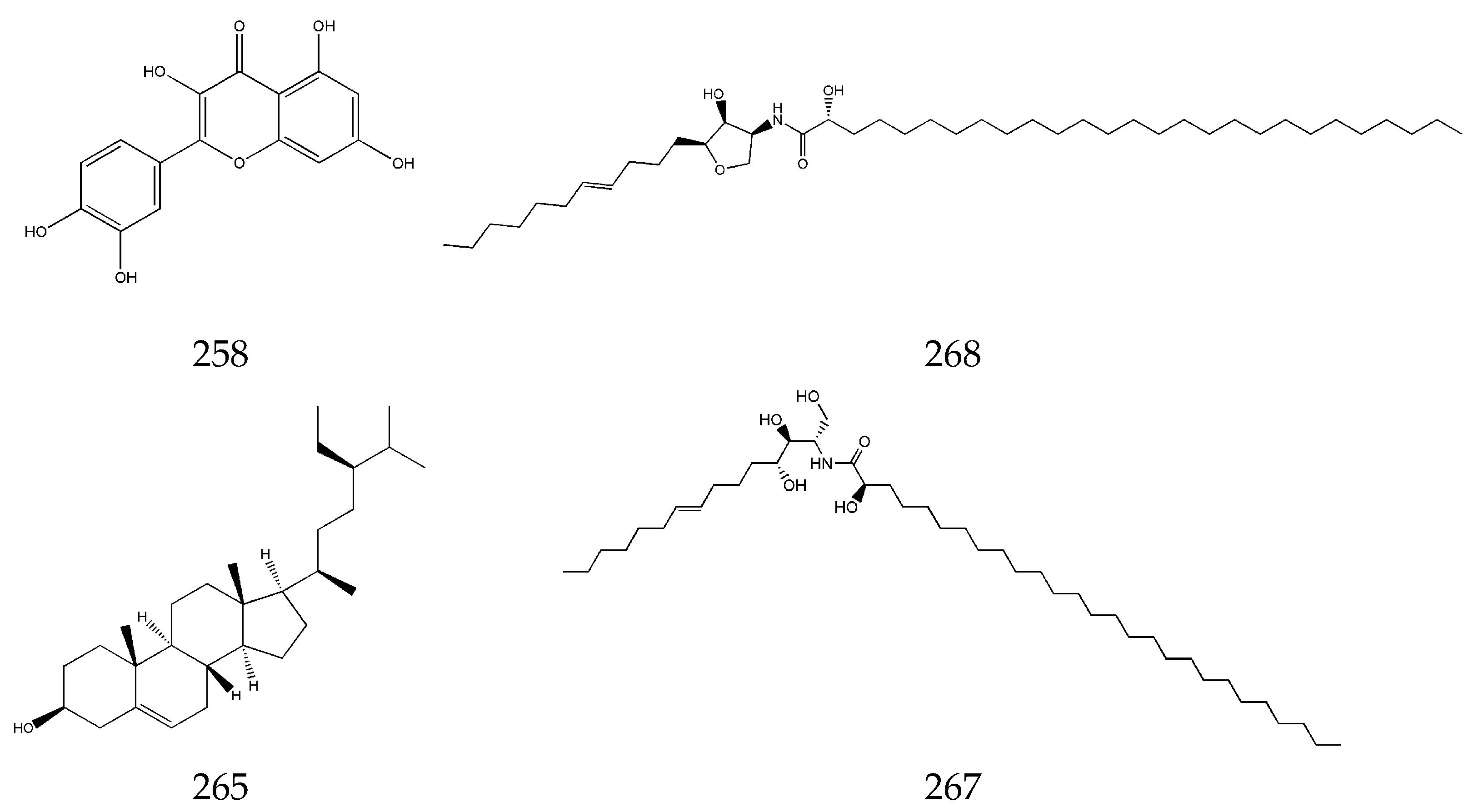
3.6. Others
4. Pharmaceutical Activities
4.1. The Cardiocerebrovascular System
4.1.1. Coronary Heart Disease
4.1.2. Cerebral Hemorrhage
4.1.3. Atherosclerosis
4.1.4. Hypertension
4.2. The Nervous System
4.3. The Respiratory System
4.4. The Digestive System
4.5. The Urinary System
4.6. Other Pharmacological Activities
| Region of Action | Components/Extracts of SLR | Model Types | Targets/Signal Pathways/Genes | Function | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coronary heart disease | SLR and Chishao | Myocardial infarction model in mice | Notch pathway | Reduce infarct size and improve cardiac function | [70,72,73] |
| Atherosclerosis model in rabbits | TC, FC | Protect the anti-inflammatory function of high-density lipoprotein, maintaining normal lipid transport function | |||
| SLR extract | Cardiovascular disease model in mice | NO3-NO2-NO | Relaxes the blood vessels and treats coronary heart disease | ||
| Cerebral hemorrhage | Z-ligustilide | Thromboembolic stroke model in mice | Nurr1, BDNF, CXCR4, SDF1αβ | Short-term incubation with low ligustilide concentrations is neuroprotective and can promote neurogenesis | [86,87] |
| MCAO model in rats | Nrf 2, HSP 70 | Prevents cerebral ischemia | |||
| Atherosclerosis | SLR extract | Atherosclerosis model in rabbits | TG, HDL-C, TC | Reduces serum cholesterol and LDL levels and improves erythrocyte deformability | [98,99,100,101,102,103] |
| SLR extract | Rat vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation model | NO | Inhibits the proliferation of the vascular smooth muscle cells | ||
| SLR lactone | Mouse atherosclerosis model | NF-κB | Reduces serum triglycerides, total cholesterol, and LDL cholesterol | ||
| Senkyunolide A Z-ligustilide | AP-1, NF-κB | Ameliorates atherosclerosis and modulates autoimmunity | |||
| Ferulic acid | AMPK α, SREBP1, ACC1 | Alleviates atherosclerosis and regulates lipid levels in mice | |||
| Ferulic acid | Vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation model | NO, p21 | Increases the level of NO and induces the migration and proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) | ||
| Hypertensive | Ferulic acid | Atherosclerotic and spontaneously hypertensive model in rats | ROS, ALT, AST, ALP | Improves the structure and function of the heart, blood vessels, liver, and kidneys | [108,110] |
| Ligustilide | Hypertensive model in rats | c-Myc, MMP2, ROCK1 | Reduces blood pressure and lipid levels | ||
| Nervous system | SLR | Microsphere-embolized (ME) cerebral ischemia model in rats | DCX, NeuroD1, GAP-43, GFAP, IL-1β, and TNF-α | Protects the neurons, anti-neuroinflammation | [116,118,119,120,121,122,123] |
| Ligustilide, senkyunolide I, and senkyunolide H | Glucose deprivation (OGD) model in mice, intracerebral hemorrhage model cells | MAPK pathway, PI3K-AKT-CREB pathway | Protect the nerve cells | ||
| SLR extract | Parkinson’s syndrome model in rats | DA, miR-23a-3p/SNCA | Potential efficacy in Parkinson’s disease | ||
| Volatile oil of SLR | Chronic unpredictable mild stress (CUMS) depression model in rats | DA, NE | Antidepressant | ||
| Respiratory system | SLR–Danshen–Danggui | Lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury model in mice | TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β, iNOS, COX-2, CRP, IL-6, MCP-1 | Inhibit the production of inflammatory factors and treat acute lung injury | [125,129,130,131,132,133] |
| SLR | Pulmonary fibrosis model in rats | Tumor necrosis factor-α, interleukin (IL)-1β, and IL-6 | Improves pulmonary fibrosis and attenuates oxidative stress and inflammation | ||
| TGF-β1/Smad pathway | Improves lung function and inhibits pulmonary fibrosis | ||||
| Z-ligustilide | Human NSCLC cell lines H1299 and A549 | PTEN/AKT pathway | Regulates the proliferation, apoptosis, and aerobic glycolysis of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cells | ||
| Cisplatin-resistant lung cancer cells | PLPP1, AKT, PIP3 | Reduces cell viability, induces cell cycle arrest, and promotes apoptosis of cisplatin-resistant lung cancer cells | |||
| Digestive system | SLR | Gastric ulcer model and gastric mucosal injury model in rats | Prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) | Anti-ulcer and anti-gastric mucosal damage effects | [134,135,136,137] |
| SLR–Orange Fruit (Zhiqiao) | CUMS model in rats | AMPAR/BDNF/mTOR/synapsin I pathway | Reduce depression-like behavior and improve gastrointestinal activity | ||
| SLR–Kudzuvine Root (Gegen) | Middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) model in rats | Claudin-5, ZO-1 | Regulate the intestinal barrier | ||
| SLR decoctions | Gastric mucosal injury model rats | Specific viscosity in the blood and plasma cortisol levels | Protect from gastric mucosal injury and protect microcirculation in the gastric mucosa | ||
| Urinary system | Ethanolic extract of SLR | A streptozotocin (STZ)-induced DN C57BL/6 mice model | Nrf2, NF-κB | Attenuates structural and functional renal damage | [140,141,142,143,144,148,149,150] |
| Phthalides in SLR | Improve hyperglycemia-induced diabetic renal dysfunction | ||||
| SLR | Renal fibrosis model in rats | Nrf2/HO-1 pathway | Relieves the degree of renal fibrosis | ||
| Senkyunolide A | Unilateral ureteral obstruction model in rats | Wnt4/β-catenin signaling pathway | Inhibit extracellular matrix deposition in renal tissues and improves renal function | ||
| Senkyunolide I | Renal ischemia–reperfusion model in mice | TNF-α, IL-6, Nrf2, HO-1, NQO1, GRP78, CHOP | Alleviates ischemia–reperfusion-induced renal injury | ||
| SLR and rhubarb | Acute kidney injury in rats | p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK)/p53 signaling | Inhibit renal tubular epithelial cell apoptosis and ameliorate acute kidney injury and renal fibrosis | ||
| SLR | Renal inflammatory model in rats | miR-103a-3p | Inhibits the renal inflammatory response | ||
| Acute pyelonephritis (APN) model in rats | IL-6/STAT3 axis | Improves renal function and suppresses inflammatory response |
5. Evaluation of Pharmaceutical Activities Based on SLR’s Action in Activating Blood Circulation and Removing Blood Stasis
5.1. Quantification of Improved Blood Rheology
5.2. Quantification of Improved Hemodynamics
5.3. Quantification of Improved Vascular Microcirculation
5.4. Quantification of Anti-Platelet Aggregation
5.5. Quantification of an Anticoagulant Effect
5.6. Calculation of a Comprehensive Index of Pharmaceutical Activities
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AngII | Angiotensin II |
| AP-1 | Activating protein-1 |
| CGMP-PKG | Cyclic guanosine monophosphate-protein kinase G |
| CHD | Coronary heart disease |
| CMM | Chinese materia medica |
| CUMS | Chronic unpredictable mild stress |
| CVDs | Cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases |
| HUVEC | Human umbilical vein endothelial cell vessels |
| ICAM-1 | Intercellular adhesion molecule-1 |
| NF-κB | Nuclear factor-kappa B |
| LDL | Low-density lipoprotein |
| MCP-1 | Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 |
| MOVAS | Mouse aortic smooth muscle cells |
| MAPK | Mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| NSCLC | Non-small cell lung cancer |
| PDGF | Platelet-derived growth factor |
| PGC-1α | Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator-1alpha |
| PGE2 | Prostaglandin E2 |
| PI3K | Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase |
| PIP3 | Phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate |
| SLR | Szechwan lovage rhizome |
| TGF-β1 | Transforming growth factor-β |
| TNF-α | Tumor necrosis factor-α |
| VCAM-1 | Vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 |
| VEGF | Vascular endothelial growth factor |
| VSMCs | Vascular smooth muscle cells |
References
- Pharmacopoeia Committee of Chinese. Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China; Medical Science Press: Beijing, China, 2020; Volume 1, p. 42. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.-H.; Zhao, J.-C.; Jin, Y.; Liu, H.-H.; Chen, S.-B.; Zhang, W.; Peng, H.-S.; Cai, Q.-J.; Li, B.; Yang, H.-J.; et al. Herbal Textual Research on Chuanxiong Rhizoma in Famous Classical Formulas. Chin. J. Exp. Tradit. Med. Formulae 2022, 28, 262–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, S.-P.; Ma, X.; Zhang, B.-C.; Wang, Q.-Z. Herbal Textual Research and Historical Evolution of Rhizoma Ligusticum Chuanxiong. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2000, 25, 434–436. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; He, P.-Y.; Zhang, D.-K.; Pei, Z.-G.; Chen, Y.-P.; Li, Z.; Zheng, C. Current situation and development strategy of Chuanxiong Rhizoma industry. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 2024, 55, 2771–2783. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, J.-W.; Fu, F.-H.; Jiang, W.-L.; Chao-Yun, W.; Sun, F.; Zhang, T.-P. Protective effect of ligusticum chuanxiong phthalides on local cerebral ischemia in rats and its related mechanism of action. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2005, 30, 466–468. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, Y.-M.; Jiang, C.; Zang, Z.-Z.; Wu, W.-T.; Zhu, W.-F.; Jin, C.; Wu, X.; Chen, L.-H. Advances in chemical composition, pharmacological effects and clinical application of volatile oil of Rhizoma Ligusticum Chuanxiong. Chin. Tradit. Pat. Med. 2024, 46, 873–880. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, K.; Geng, Y. Research Progress on Anti-Tumor Effects of Common Blood-activating and Pain-relieving Medicine. Chin. Arch. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2014, 32, 252–253. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, N.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Tong, Y.-P.; Kong, H.-W.; Xu, G.-W. Analysis of volatile oils of Ligusticum chuanxiong Hort. from different geographical origins by comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography/time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Chin. J. Chromatogr. 2010, 28, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, C.; Lim, S.; Moon, S.-J.; Cho, S. Neuroprotective effects of methanolic extract from Chuanxiong Rhizoma in mice with middle cerebral artery occlusion-induced ischemic stroke: Suppression of astrocyte- and microglia-related inflammatory response. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2024, 24, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. World Health Statistics; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 28–31. [Google Scholar]
- Nie, B.; Chen, X.-Q.; Hou, Z.-W.; Guo, M.-X.; Li, C.; Sun, W.-K.; Ji, J.-J.; Zang, L.-L.; Yang, S.; Fan, P.-X.; et al. Haplotype-phased genome unveils the butylphthalide biosynthesis and homoploid hybrid origin of Ligusticum chuanxiong. Sci. Adv. 2024, 10, eadj6547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Long, Y.; Yu, S.; Shi, A.; Wan, J.; Wen, J.; Li, X.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Li, N.; et al. Research Advances in Cardio-Cerebrovascular Diseases of Ligusticum chuanxiong Hort. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 832673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyisai, N.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Subin, B.H.C.; Li, W.; Zhang, J. Optimization of the preparation process of Chuanxiong extract and study on itsimmunomodulatory effect. Glob. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2024, 17, 785–793. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, X.L.; Yu, W.X.; Li, C.M.; Zhou, L.P.; Wong, M.S. Chuanxiong (Rhizome of Ligusticum chuanxiong) Protects Ovariectomized Hyperlipidemic Rats from Bone Loss. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2020, 48, 463–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.-P. Extraction and Separation Skin-Whitening Agent from Rhizoma Chuanxiong and Its Application in Cosmetics. Master’s Thesis, Guangdong Pharmaceutical University, Guangzhou, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.-L. Study on Quality Evaluation of the Overground Parts of Chuanxiong and Preparation of Tea Bags. Master’s Thesis, Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chengdu, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, Y.-H.; Wang, C.-S. Analysis of production and marketing trend of chuanxiong rhizome. Mod. Chin. Med. 2014, 16, 769–784. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 8071:2024; Traditional Chinese Medicine—Ligusticum Chuanxiong Rhizome. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2024.
- Chen, Z.; Zhang, C.; Gao, F.; Fu, Q.; Fu, C.; He, Y.; Zhang, J. A systematic review on the rhizome of Ligusticum chuanxiong Hort. (Chuanxiong). Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 119, 309–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathew, S.; Abraham, T.E. Ferulic acid: An antioxidant found naturally in plant cell walls and feruloyl esterases involved in its release and their applications. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2004, 24, 59–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.-L.; Jin, Y.-Q.; Yao, Y.-X.; Lin, M.-Y.; Wei, B.-P.; Jiang, W.-D.; Lu, G.-H. Assay of Tetramethylpyrazine in Szechwan Lovage Rhizome and Cnidium Rhizome by HPLC-DAD-MS. J. Chin. Med. Mater. 2015, 38, 36–40. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, Y.-X.; Hong, Y.-L.; Hua, F.; Jin, Y.-Q.; Liang, S.; Chen, Z.-M.; Lu, G.-H. Assay of Total Alkaloids in Szechwan Lovage Rhizome and Cnidium Rhizome for Quality Assessment. Asia-Pac. Trad. Med. 2017, 13, 20–23. [Google Scholar]
- Ku, Y.-T.; Tseng, K.-F. Chemical Studies on Chinese Drug Chuanxiong (Ligusticum Wallichii Fr.). Acta. Chim. Sin. (Chin. Ed.) 1957, 23, 246–249. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, Y.-Z.; Yan, H.-L.; Liu, Y.-Y.; Yan, Y.-M.; Wang, L.; Qiao, J.-X.; Wu, J.; Tian, Y.; Peng, C. Structurally diverse phthalides from fibrous roots of Ligusticum chuanxiong Hort. and their biological activities. Fitoterapia 2024, 175, 105882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- León, A.; Del-Ángel, M.; Ávila, J.L.; Delgado, G. Phthalides: Distribution in Nature, Chemical Reactivity, Synthesis, and Biological Activity. In Progress in the Chemistry of Organic Natural Products 104; Progress in the Chemistry of Organic Natural Products; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 127–246. [Google Scholar]
- Du, J.-C.; Xie, X.-F.; Xiong, L.; Sun, C.; Peng, C. Research progress of chemical constituents and pharmacological activities of essential oil of Ligusticum chuanxiong. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2016, 41, 4328–4333. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.-L. The Isolation and Identification of Anti-Tumor Active Phthalides Targeting Nuclear Receptor TR3 from Chuanxiong Rhizoma. Master’s Thesis, Xiameng University, Xiameng, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.S.; Ma, C.j.; Li, X.y.; Liu, K. Studies on the Stability of Ligustilide and the Analysis of lts lsomerized Products by GC-MS. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 2000, 6, 7–9. [Google Scholar]
- Zuo, A.-H.; Cheng, M.-C.; Zhuo, R.-J.; Wang, L.; Xiao, H.-B. Structure elucidation of degradation products of Z-ligustilide by UPLC-QTOF-MS and NMR spectroscopy. Acta Pharm. Sin. 2013, 48, 911–916. [Google Scholar]
- Duric, K.; Liu, Y.; Chen, S.-N.; Lankin, D.C.; Nikolic, D.; McAlpine, J.B.; Friesen, J.B.; Pauli, G.F. Studying Mass Balance and the Stability of (Z)-Ligustilide from Angelica sinensis Helps to Bridge a Botanical Instability–Bioactivity Chasm. J. Nat. Prod. 2019, 82, 2400–2408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.-S.; Gao, X.-L.; Aiho, F.; Michiharu, K. Studies on the chemical composition of the Chinese medicine chuanxiong ligusticum. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 1985, 16, 45. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, F.; Tan, Y.-Z.; AO, H.; Yan, H.-L.; Luo, W.; Yang, Q.; Hu, C.-J.; Peng, C. Discovery of phthalides with vasodilating activity in stems and leaves of Ligusticum chuanxiong. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 2020, 51, 1190–1195. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, L.; Peng, C.; Guo, L.; Feng, R.; Shu, H.Z.; Tian, Y.C.; Zhou, Q.M.; Xiong, L. Six pairs of enantiomeric phthalide dimers from the rhizomes of Ligusticum chuanxiong and their absolute configurations and anti-inflammatory activities. Bioorg. Chem. 2022, 127, 105970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, X.; Yin, Y.; Ding, G.; Tang, X.; Hou, P.; Sun, S.; Wang, W. Identification of coniferyl ferulate as the bioactive compound behind the xanthine oxidase inhibitory activity of Chuanxiong Rhizome. J. Funct. Foods 2023, 100, 105378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.-H.; Xie, X.-Q.; Wan, L.; Wang, S.-B.; Zhan, K. Chemical Constituents from Ligusticum chuanxiong. Lishizhen Med. Mater. Med. Res. 2007, 18, 1576–1577. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, S.-J.; Zhang, Z.-X.; Tian, Y.; Ma, Y.-P.; Peng, Q.; Shen, S.; Zhang, L.; Wang, J.-H. Study on chemical constituents of Ligusticum chuanxiong Hort. Mod. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2010, 12, 22–25. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.; Lin, L.-B.; Zhang, Q.-L.; Li, L.; Liu, S.-Y.; Li, Y.-B.; Zhang, L. Dynam ic Changes of Ferulic Acid and Coniferyl Ferulate in Chuanxiong Rhizom a during the Sun-drying Process. Plant Sci. J. 2015, 33, 259–263. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, G.H.; Chan, K.; Leung, K.; Chan, C.L.; Zhao, Z.Z.; Jiang, Z.H. Assay of free ferulic acid and total ferulic acid for quality assessment of Angelica sinensis. J. Chromatogr. A 2005, 1068, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Yang, C.; Liu, Y.; Qin, M.; Sun, J.; Liu, G. Effects of sodium ferulate for injection on anticoagulation of warfarin in rats in vivo. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2024, 24, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.H.; Ou-Yang, J.P. Pharmacological actions of sodium ferulate in cardiovascular system. Cardiovasc. Drug Rev. 2005, 23, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, Y.; Yao, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, T.; Zuo, X.; Zhang, G. Exploring the quality markers of the production region of Ligusticum chuanxiong through antiplatelet aggregation bioactivity and multiple active components, and correlation analysis of the quality markers and geographical factors. Ind. Crops Prod. 2023, 200, 116845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Department of Internal Medicine, Xiyuan Hospital, Chinese Medicine Research Institute. Observation on the efficacy of Chuanxiong alkaline injection in the treatment of angina pectoris in coronary heart disease. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 1977, 1, 15–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.L.; Yan, R.; Tam, Y.K.; Lin, G. Post-harvest alteration of the main chemical ingredients in Ligusticum chuanxiong Hort. (Rhizoma Chuanxiong). Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2007, 55, 140–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Han, B.; Feng, Z.M.; Jiang, J.S.; Yang, Y.N.; Zhang, P.C. Chemical constituents of Ligusticum chuanxiong and their anti-inflammation and hepatoprotective activities. Bioorg. Chem. 2020, 101, 104016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Li, J.; Lu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Wan, H. Synergistic protective effect of astragaloside IV–tetramethylpyrazine against cerebral ischemic-reperfusion injury induced by transient focal ischemia. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2012, 140, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bader, M.; Cai, X.; Chen, Z.; Pan, X.; Xia, L.; Chen, P.; Yang, Y.; Hu, H.; Zhang, J.; Li, K.; et al. Inhibition of Angiogenesis, Fibrosis and Thrombosis by Tetramethylpyrazine: Mechanisms Contributing to the SDF-1/CXCR4 Axis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, Z.-H.; Liu, J.; Peng, C.; Luo, M.; Zhou, Q.-M.; Xie, X.-F.; Chen, M.-H.; Xiong, L. Nucleoside alkaloids with anti-platelet aggregation activity from the rhizomes of Ligusticum striatum. Nat. Prod. Res. 2017, 33, 1399–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Wu, S.; Dai, W.; Pang, L.; Xie, Y.; Ren, T.; Zhang, X.; Bi, S.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, J.; et al. Tetramethylpyrazine: A Review of Its Antitumor Potential and Mechanisms. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 764331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, B.; Zheng, C.; Cao, J.; Luo, F.; Li, H.; Hu, S.; Lee, S.M.; Yang, X.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Tetramethylpyrazine nitrone exerts neuroprotection via activation of PGC-1α/Nrf2 pathway in Parkinson’s disease models. J. Adv. Res. 2023, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.-Z.; Yang, M.-G.; Pang, L. Preliminary observations on the cardiovascular effects of chuanxiongxizine in anesthetized dogs. Acta Pharm. Sin. 1979, 10, 624–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, F.; Jiao, L. Ligustrazine, allicin and shear-induced platelet aggregation. Clin. Hemorheol. Microcirc. 2000, 22, 167–168. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.; Wang, T.; Wang, Y. Determination of chuanxiongxizine in chuanxiongxiong from different origins by HPLC. Chin. J. Pharm. Anal. 2005, 25, 278–280. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, K.; Guo, D.; Lou, Q.; Lu, X.; Cheng, J.; Qiao, J.; Lu, L.; Cai, T.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, H. Synthesis of Ligustrazine from Acetaldehyde by a Combined Biological-Chemical Approach. ACS Synth. Biol. 2020, 9, 2902–2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, K.; Wang, P.; Xu, X.; Chu, F.; Lin, J.; Zhang, Y.; Lei, H. An overview on structural modifications of ligustrazine and biological evaluation of its synthetic derivatives. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2015, 41, 1385–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Liu, Y.; Cao, B.; Lin, M.; Wang, S.; Dong, B.; Zhang, M.; Li, G. Improving Chuanxiong Rhizoma quality standards using an effect-constituent index based bioassay. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2023, 233, 115455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.Y.; Peng, R.Q.; Wang, X.; Zuo, H.L.; Lyu, L.Y.; Yang, F.Q.; Hu, Y.J. A network pharmacology-based study on the quality control markers of antithrombotic herbs: Using Salvia miltiorrhiza—Ligusticum chuanxiong as an example. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 292, 115197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L. Bioactivities, isolation and purification methods of polysaccharides from natural products: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 92, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Zhang, Z. Extraction, Purification and Anti-oxidative Activities of Polysaccharidesfrom Liqusticum chuanxiong Hort. Nat. Prod. Res. Dev. 2005, 17, 561–563. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Wang, L.; Zhou, H.; Liang, X.D.; Zhang, M.T.; Tang, Y.X.; Wang, J.H.; Mao, J.L. The isolation, structural features and biological activities of polysaccharide from Ligusticum chuanxiong: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 285, 118971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.; Cao, X.; Chen, X.; Fu, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Luo, Q.; Li, L.; Song, X.; Jia, R.; et al. A pectic polysaccharide from Ligusticum chuanxiong promotes intestine antioxidant defense in aged mice. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 174, 915–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, C.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Pu, Y.; Yang, Z.; Bao, Y. Physicochemical properties of polysaccharides from Ligusticum chuanxiong and analysis of their anti-tumor potential through immunoregulation. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 1719–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P. The Research on Squid Skin Collagen/Chuanxiong Polysaccharide Composite Biomaterial. Master’s Thesis, Lanzhou University ofTechnology, Lanzhou, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Ruan, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, Y.-Y.; He, X.-X. The effect of different preparation methods on the chemical composition of the volatile oil of Rhizoma Ligusticum Chuanxiong. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2003, 6, 572–574. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, X.-L.; Ma, Y.-B.; Zhang, X.-M.; Jiang, Z.-Y.; Chen, Z.-J. Studies on chemical constituents of rhizomes of Ligusticum chuanxiong. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2007, 15, 1533–1536. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, Y.-Q.; Li, L.; You, X.-L.; Masayan, T.; Kimie, B. Studies on Chemical Constituents of the Rhizomae of Ligusticum chuanxiong. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2002, 7, 519–522. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Q.-Q. Exploring the Effect and Mechanism of Qingli Huoxue Method in Treating Chronic Kidney Disease Based on “Adriamycin Nephropathy” Model. Ph.D. Thesis, Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Nanjing, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Dou, L.L.; Duan, L.; Guo, L.; Liu, L.L.; Zhang, Y.D.; Li, P.; Liu, E.H. An UHPLC-MS/MS method for simultaneous determination of quercetin 3-O-rutinoside, kaempferol 3-O-rutinoside, isorhamnetin 3-O-rutinoside, bilobalide and ligustrazine in rat plasma, and its application to pharmacokinetic study of Xingxiong injection. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2017, 15, 710–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.-W. Expert Consensus on the Management of Coronary Heart Disease with Ischemie Stroke in Community. Chin. J. Cardiovasc. Res. 2022, 20, 772–793. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, J.-Y.; Wu, Y.-J.; Shi, D.-Z. Guidelines on the Clinical Application of Proprietary Chinese Medicines in the Treatment of Coronary Heart Disease (2020). Chin. J. Integr. Med. Cardio-Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2021, 19, 1409–1435. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.-W.; Xu, W.-H.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, Y.-H.; Luo, W.; Zheng, J.-H.; Zhu, Z.-M. Action mechanisms of Chuanxiong Rhizoma in treating coronary heart diseasebased on network pharmacology. Chin. Tradit. Pat. Med. 2019, 41, 2096–2101. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, W.L.; Zhao, J.; Yuan, R.; Lu, Y.; Xin, Q.Q.; Liu, Y.; Cong, W.H.; Chen, K.J. Combination of Ligusticum Chuanxiong and Radix Paeonia Promotes Angiogenesis in Ischemic Myocardium through Notch Signalling and Mobilization of Stem Cells. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2019, 2019, 7912402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.H.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Tong, W.X.; Xu, F.Q. Protective effects of Xiongshao Capsule (XSC) on anti-inflammatory function of high-density lipoprotein in an atherosclerosis rabbit model. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 2017, 23, 357–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, B.Q.; Guo, Y.H.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Huang, S.M.; Wei, X.W.; Wang, H.S.; Liu, R.Y.; Liu, Y.; Tang, Y.P. Molecular mechanism of Chuanxiong Rhizoma in treating coronary artery diseases. Chin. Herb. Med. 2021, 13, 396–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Yang, W.; Li, W.; Wu, T. Unveiling differential mechanisms of chuanxiong cortex and pith in the treatment of coronary heart disease using SPME-GC×GC-MS and network pharmacology. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2023, 234, 115540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Z.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, L.; Wang, Q.; Tang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zheng, F.; Li, Y. The efficacy of sodium ferulate combination therapy in coronary heart disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Phytomedicine 2023, 115, 154829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, W.; Ni, J.; Xia, X.; Jiang, M.; Bai, G. Searching for synergistic calcium antagonists and novel therapeutic regimens for coronary heart disease therapy from a Traditional Chinese Medicine, Suxiao Jiuxin Pill. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2018, 1092, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Hu, F.-Y.; Wu, B. Interpretation of “Chinese classification of cerebrovascular diseases (2015)”. Chin. J. Contemp. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2017, 17, 865–868. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, X.; Chen, H.; Shi, H.; Fu, K.; Li, J.; Tian, L.; Teng, W. Lipid levels and the risk of hemorrhagic stroke: A dose-response meta-analysis. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2021, 31, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Stefano, V.; De Angelis, M.V.; Montemitro, C.; Russo, M.; Carrarini, C.; di Giannantonio, M.; Brighina, F.; Onofrj, M.; Werring, D.J.; Simister, R. Clinical presentation of strokes confined to the insula: A systematic review of literature. Neurol. Sci. 2021, 42, 1697–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.-H. Present Status and Prospect Using Ligusticum Chuanxiong to Prevent and Treat Stroke. Chin. J. Integr. Med. Cardio-Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2006, 4, 339–341. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.-Y. Study on Dosage and Compatibility of Chinese Medical Masters in Treating Stroke Based on Data Mining Technology. Master’s Thesis, Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medcine, Chengdu, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Cai, C.; Luo, Y.; Wu, Y.; Qiu, F. The Diagnostic Model of Ligusticum Chuanxiong Hort. Against Cerebral Stroke Using Network Pharmacology and Transcriptomics Analyses. J. Integr. Neurosci. 2023, 22, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Zeng, L.; Ge, A.; Shi, Y.; Zhu, X.; Liu, W.; Ge, J. The Effect of Hedysarum multijugum Maxim.-Chuanxiong rhizoma Compound on Ischemic Stroke: A Research Based on Network and Experimental Pharmacology. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2020, 6072380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, P.; Yi, Y.; Su, H.F.; Ye, C.Y.; Sun, Y.W.; Zhou, X.W.; Lu, Y.; Shi, A.; Tian, Q. Key Phytochemicals and Biological Functions of Chuanxiong Rhizoma Against Ischemic Stroke: A Network Pharmacology and Experimental Assessment. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 758049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, H.Q.; Guo, J.X.; Yang, Y.; Xu, L.; Wang, J.; Yang, F.; Xu, Z.B.; Huang, Y.F.; Shi, W.; Lu, X.; et al. Elucidating the chemical interaction effects of herb pair Danshen-Chuanxiong and its anti-ischemic stroke activities evaluation. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 318, 117058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, K.; Fu, R.H.; Huang, Y.C.; Chen, S.Y.; Lin, S.Z.; Huang, P.C.; Lin, P.C.; Chang, F.K.; Liu, S.P. Therapeutic Effect of Ligustilide-Stimulated Adipose-Derived Stem Cells in a Mouse Thromboembolic Stroke Model. Cell Transplant. 2016, 25, 899–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Yu, J.; Ma, H.; Yang, N.; Li, L.; Zheng, D.D.; Wu, M.X.; Zhao, Z.L.; Qi, H.Y. Intranasal Pretreatment with Z-Ligustilide, the Main Volatile Component of Rhizoma Chuanxiong, Confers Prophylaxis against Cerebral Ischemia via Nrf2 and HSP70 Signaling Pathways. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2017, 65, 1533–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.M.; Chiu, J.H.; Wu, I.H.; Wang, B.W.; Pan, C.M.; Chen, Y.H. Ferulic acid augments angiogenesis via VEGF, PDGF and HIF-1 alpha. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2010, 21, 627–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Tang, M.; Xie, X.; Xu, Y.; Su, P.; Jin, Z. Efficacy of ferulic acid in the treatment of acute ischemic stroke injury in rats: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1278036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Wang, X.; Liu, X.-R.; Li, K.-X.; Liu, Y. Effects of ferulic acid on regulating the neurovascular unit: Implications for ischemic stroke treatment. World J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2022, 8, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayguru, W. Study on the distribution pattern of Chinese medicine symptoms in atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases in the literature. Master’s Thesis, Beijing University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Beijing, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.; Cui, X.; Zhang, L.; Wang, X.; Xu, Y.; Qin, Z.; Liu, G.; Wang, Q.; Tian, K.; Lim, K.S.; et al. The Functional Role of Lipoproteins in Atherosclerosis: Novel Directions for Diagnosis and Targeting Therapy. Aging Dis. 2022, 13, 491–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Packard, R.R.; Lichtman, A.H.; Libby, P. Innate and adaptive immunity in atherosclerosis. Semin. Immunopathol. 2009, 31, 5–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, C.; Noels, H. Atherosclerosis: Current pathogenesis and therapeutic options. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 1410–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, D.; Ley, K. Immunity and Inflammation in Atherosclerosis. Circ. Res. 2019, 124, 315–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nègre-Salvayre, A.; Augé, N.; Camaré, C.; Bacchetti, T.; Ferretti, G.; Salvayre, R. Dual signaling evoked by oxidized LDLs in vascular cells. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2017, 106, 118–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, T.; Jiang, N.; Yang, X.; Li, C.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; Chang, H. Network pharmacology and molecular docking technology research on the mechanismof Chuanxiong in the treatment of atherosclerosis. Chin. J. Arterioscler. 2021, 29, 761–769. [Google Scholar]
- Mei, J.-J.; Cai, D.-Y.; Chen, Z.-F.; Ye, G.-M.; Tian, W.-H. The mechanism of prevention of atherosclerotic lesions in rabbits by chuanxiong. Chin. J. Pathophysiol. 2001, 17, 816. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, Y.Z.; Zhao, G.R.; Yuan, Y.J.; Zhu, G.G.; Hiltunen, R. Inhibition of rat vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation by extract of Ligusticum chuanxiong and Angelica sinensis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2005, 100, 140–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Wang, Y.C.; Li, L.L.; Jin, Y.C.; Sironi, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y. Lactones from Ligusticum chuanxiong Hort. reduces atherosclerotic lesions in apoE-deficient mice via inhibiting over expression of NF-kB-dependent adhesion molecules. Fitoterapia 2014, 95, 240–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, W.; Deng, Y.F.; Hu, X.Y.; Ni, J.N.; Jiang, M.; Bai, G. Phthalides, senkyunolide A and ligustilide, show immunomodulatory effect in improving atherosclerosis, through inhibiting AP-1 and NF-κB expression. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 117, 109074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, M.; Huang, Z.; Jiang, J.; Chen, Y.; Chen, J.; Jia, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, F. Ferulic Acid Ameliorates Atherosclerotic Injury by Modulating Gut Microbiota and Lipid Metabolism. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 621339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Hu, Z.; Zhou, J.; Liu, J.; Ren, P.; Huang, X. Ferulic Acid Alleviates Atherosclerotic Plaques by Inhibiting VSMC Proliferation Through the NO/p21 Signaling pathway. J. Cardiovasc. Transl. Res. 2022, 15, 865–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doyle, A.E. Hypertension and vascular disease. Am. J. Hypertens. 1991, 4, 103s–106s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Global Report on Hypertension: The Race Against a Silent Killer; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2023; p. 8. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, S.-S. Research on the law of Medication for hypertension differentiationin Ancient and Modern Medical Cases Based on Data Mining. Master’s Thesis, Jiangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanchang, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, X.; Ding, Y.; Li, S.; Yang, D.; He, X.; Jiang, W. Study on Mechanism reating Hypertension of Ligusticum chuanxiong Based on Network Pharmacology. Chin. J. Ethnomed. Ethnopharm. 2020, 29, 18–24. [Google Scholar]
- Alam, M.A.; Sernia, C.; Brown, L. Ferulic acid improves cardiovascular and kidney structure and function in hypertensive rats. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2013, 61, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Z.-F. Clinical observation on 55 cases of hypertensive nephropathy treated by injectable sodium ferulate therapy. Cardiovasc. Dis. Electron. J. Integr. Tradit. Chin. West. Med. 2015, 3, 50–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Deng, H.; Fang, Z.; Zeng, A.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, W.; Lu, Q. Ligustilide Inhibited Rat Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells Migration via c-Myc/MMP2 and ROCK/JNK Signaling Pathway. J. Food Sci. 2019, 84, 3573–3583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, T.; Zhang, H.; Yang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Ma, J.; Yan, Y. Research progress on Chuanxiong Rhizoma and its prescription compatibility in treatment of migraine. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 2024, 55, 1004–1013. [Google Scholar]
- Zuo, A.-H.; Cheng, M.-C.; Wang, L.; Xiao, H.-B. Analysis of chemical constituents of Chuanxiong Rhizoma absorbed into rat brain tissues by UPLC-Q-TOF-MS. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2012, 37, 3647–3650. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Yao, M.-J.; Liu, J.-X.; Wu, Y.-J.; Wang, P.; Ren, J.-G.; Fan, X.-D. Study on the Active Components of Ligusticum Chuanxiong for Neuroprotection. World J. Integr. Tradit. West. Med. 2021, 16, 793–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.; Yu, X.; Lin, L. Protective effect of Ligusticum chuanxiong hort extract on hypoxia microglia cells. Chin. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 34, 1967–1970. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, W.; Zhao, W.; Yu, L.; Bao, Y. Study on effects and mechanism of extract of Rhizoma Chuanxiong on radicular neuralgia in rats with cervical spondylotic radiculopathy. J. Guangdong Pharm. Univ. 2008, 24, 496–499. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, Y.; Chen, F.; Tang, Z.; Ren, H.; Wang, Q.; Shen, N.; Lin, W.; Xiao, Y.; Yuan, M.; Chen, H.; et al. Ligusticum chuanxiong Hort as a medicinal and edible plant foods: Antioxidant, anti-aging and neuroprotective properties in Caenorhabditis elegans. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 1049890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Yao, M.; Liu, J.; Takagi, N.; Yang, B.; Zhang, M.; Xu, L.; Ren, J.; Fan, X.; Tian, F. Ligusticum chuanxiong exerts neuroprotection by promoting adult neurogenesis and inhibiting inflammation in the hippocampus of ME cerebral ischemia rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 249, 112385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.-Y. Neuroprotective Effect of Senkyunolide H and Preparation and Characterization of Its Nanoparticle. Master’s Thesis, Tianjin University of Science & Technology, Tianjin, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, Y.; Wang, R.; Wang, Q.; Sun, Y.; Xie, S.; Yang, Z.; Li, M.; Jin, Y.; Yang, S. Design and synthesis of novel senkyunolide analogues as neuroprotective agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2018, 28, 668–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, L.; Liu, D.L.; Zeng, Q.K.; Shi, M.Q.; Zhao, L.X.; He, Q.; Kuang, X.; Du, J.R. The neuroprotective effects and probable mechanisms of Ligustilide and its degradative products on intracerebral hemorrhage in mice. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2018, 63, 43–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, D.; He, J.-C.; Chen, J.-F. Neuroprotective effects and mechanisms of Chuanxiong Chatiao pulvis against MPTP-induced dopam inergic neurotoxicity in mice model of parkinson’s disease. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2009, 34, 2494–2497. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, P.; Liao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Du, C.; Chen, H. Effects of Ligusticum Chuanxiong extract on MPp+-induced SH-SY5Ycells in Parkinson’s syndrome model via miR-23a-3p/SNCA axis. J. Xi’an Jiaotong Univ., Med. Sci. 2023, 44, 626–633. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, L.; Tang, Y.; Zheng, Q.; Wu, H.; Hu, P.; Guo, Y.; Yang, T.; Wang, M.; Yang, M. Study on Antidepressant Effects of Rhizoma Ligusticum Chuanxiong Volatile Oil Based on CUMS Rats. World Chin. Med. 2019, 14, 1643–1648. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.-N.; Yong, Q.; Zhang, M.; Yao, W.; Wang, J.; Feng, Q.; Wang, N.; Wang, J.; Cui, L. Experimental Research on the Antidepressant Activity of Gardeniajasminoides Ellis processed Ligusticum Based on Network Pharmacology. Chin. J. Comp. Med. 2020, 30, 47–53. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Yan, Q.; Zhang, W.; Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Du, S.; Hua, X.; Lin, J.; Shu, G.; Peng, G.; et al. Enhancement of the functionality of attenuating acute lung injury by a microemulsion formulation with volatile oil of Angelicae Sinensis Radix and Ligusticum Chuanxiong Rhizoma encapsulated. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 156, 113888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Y.; Xu, M.; Chen, X. Clinical Study of Danshen Chuanxiong Injection Combined with Naloxone Injection in the Treatment of Copd Complicated with Respiratory Failure. Chin. J. Coal Ind. Med. 2019, 22, 532–535. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.-Q.; Zhao, W.-J.; Han, N.-P.; Chen, J. Progress of research on activating blood circulation and removing blood stasis in single-flavored Chinese medicines against bronchial asthma. Chin. J. Ethnomed. Ethnopharm. 2015, 24, 33–34. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Li, W.; Luo, Z.; Chen, Y. The molecular mechanism of Ligusticum wallichii for improving idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: A network pharmacology and molecular docking study. Medicine 2022, 101, e28787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, W.; Feng, B.; Xu, S.; Shen, X.; Zhang, T. Inhibitory effect of compound Chuanxiong Kangxian granules on bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 96, 1179–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.-J.; Dong, X.-P.; Du, T. Effect of combination therapy of Angelica sinensis and Ligusticum chuanxiong on TGF-β1/Smad signaling pathway in rat models of pulmonary fibrosis. Chin. Tradit. Pat. Med. 2021, 43, 1451–1456. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, L.; Huang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Niu, W.; Pang, J.; Li, S.; Li, X. Chuanxiong Rhizoma inhibits brain metastasis of lung cancer through multiple activeingredients acting on multiple targets, pathways and biological functions. J. South. Med. Univ. 2021, 41, 1319–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Zhao, W.; Zhu, F.; Wu, H.; Ding, X.; Bai, J.; Zhang, X.; Qian, M. Ligustilide inhibits the proliferation of non-small cell lung cancer via glycolytic metabolism. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2021, 410, 115336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, P.; Zhao, J.; Li, Q.; Wang, X.; Qin, W.; Wang, T.; Shi, X.; Liu, X.; Chen, J.; Qiu, H.; et al. Z-Ligustilide Combined with Cisplatin Reduces PLPP1-Mediated Phospholipid Synthesis to Impair Cisplatin Resistance in Lung Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 17046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Wang, J.-H.; Lao, S.-X. Studies on the Pharmacological Effects and Mechanisms of Codonopsis Pilosula(CP), Ligusticum Chuanxiong(LC), Taraxacum Mongolican(TM) and Their Formula on Preventing Gastric Mucosa from Ulceration and injury. Pharmacol. Clin. Chin. Mater. Med. 1991, 7, 10–11. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Luo, M.; Wang, Z.; Yang, S.J.; Su, M.; Wang, Y.; Wang, W.; Sun, Z.; Cai, Y.; Wu, L.; et al. Mind shift I: Fructus Aurantii–Rhizoma Chuanxiong synergistically anchors stress-induced depression-like behaviours and gastrointestinal dysmotility cluster by regulating psycho-immune-neuroendocrine network. Phytomedicine 2024, 128, 155324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.; Wu, P.; Cai, Z.; Tang, L.; Ye, L.; Hou, C.; Yang, N.; Zhao, J. The combination of Puerariae Lobatae Radix and Chuanxiong Rhizoma enhanced the absorption and pharmacokinetics of puerarin by modulating the intestinal barrier and influenced gut microbiota. J. Funct. Foods 2018, 47, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.-Q.; Ma, L.-T.; Zhou, Y.-F.; Li, M.-Z.; Yu, L.-L. Effect of decoction of ligusticum wallichii franch on gastric mucosal injury induced by lesion of hypothalamus in rats. Chin. J. Pathophysiol. 1989, 5, 307–311. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.-R.; Chai, K.-F. Prevention and treatment of diabetic nephropathy by activating blood circulation and removing blood stasis: A review. Henan Tradit. Chin. Med. 2011, 31, 1355–1356. [Google Scholar]
- Zuo, W.; Song, B.; Li, K.; Zhang, L.; Liang, X.; Qi, J.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Wang, H. Exploration of the Compatibility of Ligusticum Wallichii in the Prevention and Treatment of Diabetic Nephropathy. Acta Chin. Med. 2012, 27, 196–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.J.; Li, Y.R.; Gao, H.; Wu, X.Y.; Wang, X.L.; Wang, X.N.; Xiang, L.; Ren, D.M.; Lou, H.X.; Shen, T. Protective effect of the ethanol extract from Ligusticum chuanxiong rhizome against streptozotocin-induced diabetic nephropathy in mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018, 227, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.Y.; Peng, G.C.; Han, Q.T.; Yan, J.; Chen, L.Z.; Wang, T.; Xu, L.T.; Liu, M.J.; Xu, Z.P.; Wang, X.N.; et al. Phthalides from the rhizome of Ligusticum chuanxiong Hort. attenuate diabetic nephropathy in mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 319, 117247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Huang, W.; Han, X.; Ma, Q. Ligusticum chuanxiong Effects on Oxidative Stress and Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling Using Nano-Magnetic Beads in Bleomycin-Induced Renal Fibrosis Rats. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. Lett. 2020, 12, 1185–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Chen, X.; Yin, B.-W.; Chen, D.-K.; Hu, M.-Z. Effect and Mechanism of Senkyunolide A on Renal Interstitial Fibrosis in Unilateral Ureteral Obstruction Rats. Chin. J. Surg. Integr. Tradit. West. Med. 2020, 26, 237–242. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.L.; Huang, J.; Chen, X.Y.; Xie, J.; Yang, Q.; Wang, J.F.; Deng, X.M. Senkyunolide I alleviates renal Ischemia-Reperfusion injury by inhibiting oxidative stress, endoplasmic reticulum stress and apoptosis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2022, 102, 108393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B. Therapeutic effect of sodium ferulate on renal vein thrombosis. Chronic Pathematology J. 2006, 5, 125–126. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.; Zheng, J.; Qian, S.; Qu, C.; Zhu, S.; Zhao, J.-X.; Chen, S.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Y. Chuanxiong on the Prevention of Acute Renal Failure: Experimental Results and Preliminary Clinical Observations. Med. J. Chin. People’s Lib. Army 1986, 11, 172–174. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, W.-L.; Ma, Y.-J.; Zheng, J.-F.; Wu, H. The Effect of ligusticum Wallichii on Renal Tissue TXB2, 6-keto-PGF,. and 6-keto-PGF, /TXB2, in Rabbits with Glycerol Induced Acute Renal Failure. Chin. J. Integr. Tradit. West. Med. 1996, 16, 283–285. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Li, T.; Li, Z.; Song, Z.; Gong, X. Nephroprotective mechanisms of Rhizoma Chuanxiong and Radix et Rhizoma Rhei against acute renal injury and renal fibrosis based on network pharmacology and experimental validation. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1154743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, H.; Zhou, E.-C.; Luo, J.-P. Effect of Chuanxiong extract on renal inflammation induced by angiotensin lI. Chin. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2021, 37, 3111–3114. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, J.; Bi, Z.; Tian, L.; Hou, S.; Zhang, Q.; Li, S. Szechwan Lovage Rhizome Extract Improves Renal Function and Alleviates Inflammatory Responses in Pyelonephritis Rats Infected with Escherichia Coli via IL-6/STAT3 Axis. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2023, 69, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Zou, Q.; Zhou, Y.; He, H.; Yu, W.; Yan, H.; Yi, Y.; Zhao, Z. Water extract from Ligusticum chuanxiong delays the aging of Saccharomyces cerevisiae via improving antioxidant activity. Heliyon 2023, 9, e19027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.-B.; Ye, Q.-C. The efficacy of external application of chuanxiong rhizome in the treatment of costochondritis in 30 cases. Mil. Med. Jt. Logist. 1994, 8, 306. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.-H.; Liang, Y.-H.; Sun, P.-D. Study on the whitening dual-targeting activity of Chuanxiong rhizome extract. China Surfactant Deterg. Cosmet. 2020, 50, 249–254. [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.; Li, Q.; Bi, K. Simultaneous determination of six active components by a single standard to determine multicomponents combined with fingerprint analysis for the quality control of Rhizoma Chuanxiong. J. Sep. Sci. 2015, 38, 1090–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.-H.; Gu, J.-F.; Feng, L.; Jia, X.-B. Research strategy and practice of “multi-dimensional structure and process dynamics qualitycontrol system” of traditional Chinese medicines. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2013, 38, 3608–3612. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Q. The Methodology of Pharmacological Research in Chinese Medicine; People’s Health Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2006; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- World Federation of Chinese Medicine Societies. International Diagnostic Guidelines for Blood-Stasis Syndrome. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 2022, 17, 297–303. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, N.; Ren, D.; Duan, J.; Xu, X.; Xie, N.; Tian, L. Ceramides and Cerebrosides from Ligusticum Chuanxiong Hort. Helv. Chim. Acta 2009, 92, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, M.; Peng, S.; Li, J.; Cao, Y.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Qiao, Y. Comparison of the clinical effect features of Han-Ku-Gan and Wen-Xin-Gan based on the efficacy of promoting blood circulation and removing blood stasis. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. Sci. 2022, 9, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; He, X.; Pan, S.; Jiang, W. Exploring the Mechanism of Chuanxiong Rhizoma against Thrombosis Based on Network Pharmacology, Molecular Docking and Experimental Verification. Molecules 2023, 28, 6702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-J.; Peng, C. Experimental Study of the Extract of Chuanxiong in Promoting Blood Circulation. J. Hubei Univ. Natl. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2011, 29, 456–459. [Google Scholar]
- Goldsmith, H.L.; Cokelet, G.R.; Gaehtgens, P. Robin Fåhraeus: Evolution of his concepts in cardiovascular physiology. Am. J. Physiol. 1989, 257, H1005–H1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baskurt, O.K.; Meiselman, H.J. Blood rheology and hemodynamics. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2003, 29, 435–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, M.; Rajagopal, K.R. A Short Review of Advances in the Modelling of Blood Rheology and Clot Formation. Fluids 2017, 2, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drenjancevic, I.; Koller, A.; Selthofer-Relatic, K.; Grizelj, I.; Cavka, A. Assessment of coronary hemodynamics and vascular function. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2015, 57, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popel, A.S.; Johnson, P.C. Microcirculation and Hemorheology. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2005, 37, 43–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipowsky, H.H. Microvascular rheology and hemodynamics. Microcirculation 2005, 12, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dintenfass, L. The clinical impact of the newer research in blood rheology: An overview. Angiology 1981, 32, 217–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, Z.S.; Jackson, S.P. The role of platelets in atherothrombosis. Hematology 2011, 2011, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, M.-M.; Yang, K.; Wang, Y.-T. Evaluation of the synergistic effect of Chuanxiong Tianma in the formula of Dachuanxiong Wan in the treatment of migraine from blood rheology and blood flow velocity. Pharmacol. Clin. Chin. Mater. Med. 2008, 24, 6–8. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.-X.; Tang, Y.-P.; Guo, J.-M.; Huang, M.-Y.; Qian, D.-W.; Duan, J.A. Comparative Assessing the Effects of Angelica Root and Chuanxiong on the Hemorheology and the Blood Coagulation Function in Acute Blood Stasls Rats. Chin. J. Integr. Tradit. West. Med. 2012, 32, 806–811. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, D.-P.; Wu, Y.; Tang, Q.; Wu, D.-K. Effects of the combination of Angelica sinensis and Rhizoma Ligustici Chuanxiong on blood rheology in rats with acute blood stasis syndrome. Jiangsu J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2014, 46, 85–86. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.-H.; Wang, S.-J. Effects of Angelica combined with Chuanxiong on hemorheology and coagulation function in acute blood stasis rats. Mod. J. Integr. Tradit. Chin. West. Med. 2014, 23, 1833–1835. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.; Liu, W. Effects of Compound Ligusticum chuanxiong Drop Pill on Hemorheology and Blood Gas in Model Rats with Diabetic Nephropathy. China Pharm. 2017, 28, 909–912. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.-G.; Xu, F.-Q.; Shi, D.-Z.; Dong, G.-J. Effect of the Extracts from Rhizoma Chuanxiong and Radix Paeoniae Rubra in Different Proportions on Promoting Blood Circulation and Removing Blood Stasis. Tradit. Chin. Drug Res. Clin. Pharmacol.Y 2005, 16, 315–317. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, J.-X.; Yan, Y.-Q.; Jiang, Y. Effects of the Combination of Astragalus membranaceus (Fisch), Bge. (AM), Tail of Angelica sinensis (Oliv), Diels (TAS), Cyperus rotundus L. (CR), Ligusticum chuanxiong Hort. (LC) and Peaonia veitchii lynch(PV) on the Hemorrheological Changes in “Blood Stagnating” Rats. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 1994, 19, 108–110. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B. Effect of Danxiong Yiningyin in Comparsion with Warfarin on Hemorrheological Paramters and Anticoagalation in Rabbit. Master’s Thesis, Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang, China, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Du, h.; Niu, X.; Feng, Q.-J.; Dong, X.-Y.; Xu, R.-Y. Effects of microemulsion of Chuanxiong Rhizoma based on hemorheological indexes. J. Beijing Univ. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2007, 30, 681–683. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Z.-M.; Xu, Z.-H.; Zhang, Y.-L.; Liu, B.-M. The effect of Rhizoma Ligustici on the changes of hemorheology under intraosseous hypertension. China J. Orthop. Traumatol. 1996, 9, 12–14. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, M.; Li, Y.; He, W.; Lu, G.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Q. Effects of Levistilide A on Hemorheology and Endothelial Cell Injury in Rats with Blood Stasis. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. Ecam 2021, 2021, 6595383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Z.-L.; Chang, J. Effects of combined use of sodium ferulate and astragalus injection on changes of hemorrheology and renal function in patients with early diabetic nephropathy. Chin. J. Integr. Tradit. West. Med. Intensive Crit. Care 2006, 13, 41–43. [Google Scholar]
- Pop, G.A.; Duncker, D.J.; Gardien, M.; Vranckx, P.; Versluis, S.; Hasan, D.; Slager, C.J. The clinical significance of whole blood viscosity in (cardio)vascular medicine. Neth. Heart J. 2002, 10, 512–516. [Google Scholar]
- Cushman, M.; Wang, W.; Parikh, R.; Lutsey, P.L.; Beckman, J.D.; Folsom, A.R. Hematocrit and Incidence of Venous Thromboembolism. Blood 2019, 134, 1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natali, A.; L’Abbate, A.; Ferrannini, E. Erythrocyte sedimentation rate, coronary atherosclerosis, and cardiac mortality. Eur. Heart J. 2003, 24, 639–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, K.; Lamoureux, E.S.; Myrand-Lapierre, M.E.; Duffy, S.P.; Ma, H. Technologies for measuring red blood cell deformability. Lab. Chip. 2022, 22, 1254–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, F.; Li, X.-Y. Fluid-structure interaction study on blood flow and arterial wall. J. Med. Biomech. 2008, 23, 405–409. [Google Scholar]
- O’Rourke, M.F. Vascular mechanics in the clinic. J. Biomech. 2003, 36, 623–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Shi, Y.-M.; Zheng, H.-M. Experimental Study of Ligusticum Wallichii on Cerebrovascular Hemodynamiec Parameters. Chin. J. Integr. Tradit. West. Med. 1993, 13, 417–419. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, J.-G.; Zhen, Z.-W.; Yang, K.; Huang, L.-Z.; Tang, Y.-L.; Li, S.-Y.; Shi, B.; Liu, L.; Wang, X.-Q.; Feng, Q.-Y. Study on Herbs with Neutral Nature and Blood Circulation Promoting and Blood Stasis Removing Action on the Hemodynamic Indexes of Rats. Chin. Arch. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2012, 30, 1447–1449. [Google Scholar]
- Ruan, Q.; He, X.-X.; Hu, Y.-Y.; Sun, H.-Y. Hemodynamic Effects of Aqua Decoction and Volatile Oil of Ligusticum Chuanxiong in Isolated Rat Hearts. Chin. Pharm. J. 2004, 39, 906–909. [Google Scholar]
- Ruan, Q.; Hu, Y.-Y.; He, X.-X.; Xu, Q.; Yu, C.-Z. Effect of Tetramethylpyrazine on Hemodynamics in Anesthetized Rabbits. J. Shaoxing Univ. 2003, 23, 19–21. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Gao, F.; Cao, Y.; Wang, H.; Duan, H. Effects of the Supercritical Fluid Extraction of Dahurian Angelica Root and Szechwan Lovage Rhizome on Spontaneous Hypertension Rats. Chin. Med. 2012, 03, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ren, P.; Jiao, K.; Li, Y.-C.; Huang, X.; Zang, Y.-M.; Wang, Y.-M. Different effects of tetramethylpyrazine and/or ferulate on hemodynamics in anesthetized dogs. J. Air Force Med. 1999, 20, 797–799. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.-Y.; Ruan, Q.; He, X.-X.; Xu, Y.-F. Effects of tetramethylpyrazine and ferulic acid on hemodynamics in isolated rat heart. J. Hangzhou Norm. Univ. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2004, 27, 382–385. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.; Wei, W.; Zhong, Q. Effect of Sodium Ferulate on Hemodynamics in Hepatic Cirrhosis Patients with Portal Hypertension. Chin. J. Integr. Tradit. West. Med. 2008, 28, 640–642. [Google Scholar]
- Patterson, T.; Rivolo, S.; Burkhoff, D.; Schreuder, J.; Briceno, N.; Allen, C.; Williams, R.; Arri, S.; Asrress, K.N.; Joseph, J.; et al. Physiological Impact of Afterload Reduction on Cardiac Mechanics and Coronary Hemodynamics Following Isosorbide Dinitrate Administration in Ischemic Heart Disease. J. Cardiovasc. Transl. Res. 2021, 14, 962–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calviello, L.A.; Zeiler, F.A.; Donnelly, J.; Uryga, A.; de Riva, N.; Smielewski, P.; Czosnyka, M. Estimation of pulsatile cerebral arterial blood volume based on transcranial doppler signals. Med. Eng. Phys. 2019, 74, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyajima, T.; Yokoyama, H.; Taira, H.; Tsuji, Y. Quantitative estimation of renal blood flow by power Doppler ultrasonography in renovascular hypertensive dogs. Kidney Int. 2005, 68, 2781–2786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Z.-Z.; Zhou, L.-H.; Xiao, S.-D.; Jiang, S.-J. Advances in hepatic blood flow measurement. Int. J. Dig. Dis. 1987, 1, 4–7. [Google Scholar]
- Saldanha, C. Hemorheology, microcirculation and macrocirculation. Rev. Port. Cardiol. 2020, 39, 25–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pretolani, E. Hemorheology and microcirculation. G. Clin. Med. 1988, 69, 601–604. [Google Scholar]
- Tibiriçá, E.; Lorenzo, A.; Oliveira, G.M.M. Microcirculation and Cardiovascular Diseases. Arq. Bras. Cardiol. 2018, 111, 120–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, W.-Y. Hemorheology and Microcirculation. J. Chin. Microcirc. 2000, 10, 19–22. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Y.-M.; Zhang, Y.-L.; Zhen, H.-M.; Chen, D.-R.; Jin, K.-J.; Du, R.-J.; Tian, G.-Q. Experimental study and clinical application of the action of Chuanxiong in activating blood circulation and removing blood stasis. Med. J. Chin. People’s Lib. Army 1979, 4, 98–103. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, L.-F.; Zheng, X.-M.; Cai, Z.; Wu, B.-S. Comparison of influence of essential oil from Ligusticum chuanxiong Hort. on microcirculation in rabbit conjunctiva bulbar before and after decomposition of ligustilide. Chin. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 1995, 9, 157–158. [Google Scholar]
- Larsson, M.; Strömberg, T. Toward a velocity-resolved microvascular blood flow measure by decomposition of the laser Doppler spectrum. J. Biomed. Opt. 2006, 11, 014024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, J.M.; Kaneko, S.; Joels, C.; Tobin, G.R.; Banis, J.C., Jr.; Barker, J.H. Microcirculation research, angiogenesis, and microsurgery. Microsurgery 1994, 15, 399–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, L.-L.; Li, L.-M.; Huang, L.; Ning, N.; Qi, S.-B.; Liu, Y.-L.; Qiao, M. Study on the effects of Chuanxiong extracts on the aortic rings of rats and the microcirculation disturbance of mice. Pharmacol. Clin. Chin. Mater. Med. 2013, 29, 105–108. [Google Scholar]
- Furie, B.; Furie, B.C. Mechanisms of thrombus formation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 938–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamon, M. Mechanism of thrombosis: Physiopathology, role of thrombin and its inhibition by modern therapies. Arch. Mal. Coeur Vaiss. 2006, 99, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hou, Y.; Carrim, N.; Wang, Y.; Gallant, R.C.; Marshall, A.; Ni, H. Platelets in hemostasis and thrombosis: Novel mechanisms of fibrinogen-independent platelet aggregation and fibronectin-mediated protein wave of hemostasis. J. Biomed. Res. 2015, 29, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rana, A.; Westein, E.; Niego, B.; Hagemeyer, C.E. Shear-Dependent Platelet Aggregation: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Opportunities. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2019, 6, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Du, J.R.; Wang, J.; Yu, D.K.; Chen, Y.S.; He, Y.; Wang, C.Y. Z-ligustilide extracted from Radix Angelica Sinensis decreased platelet aggregation induced by ADP ex vivo and arterio-venous shunt thrombosis in vivo in rats. Yakugaku Zasshi J. Pharm. Soc. Jpn. 2009, 129, 855–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, J.-J.; Weng, Y.-P.; Luo, L.-B.; Wang, J.-Q.; Lin, H.-Z.; Zhang, G.-M.; Yue, L.; Yao, Y.-X. The study of different markers among Chuanxiong Chatiao dosage forms based on bioactive components and antiplatelet aggregation biopotency integrated with chemometrics. Arab. J. Chem. 2024, 17, 105421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Chen, L.; Wang, X.; Chen, J.; Xu, S.; Ye, L.; Yao, Y. Simultaneous Determination of Night Effective Constituents and Correlation Analysis of Multiconstituents and Antiplatelet Aggregation Bioactivity In Vitro in Chuanxiong Rhizoma Subjected to Different Decoction Times. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2019, 2019, 8970624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsoupras, A.; Zabetakis, I.; Lordan, R. Platelet aggregometry assay for evaluating the effects of platelet agonists and antiplatelet compounds on platelet function in vitro. MethodsX 2019, 6, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardinal, D.C.; Flower, R.J. The electronic aggregometer: A novel device for assessing platelet behavior in blood. J. Pharmacol. Methods 1980, 3, 135–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DiChiara, J.; Bliden, K.P.; Tantry, U.S.; Hamed, M.S.; Antonino, M.J.; Suarez, T.A.; Bailon, O.; Singla, A.; Gurbel, P.A. The effect of aspirin dosing on platelet function in diabetic and nondiabetic patients: An analysis from the aspirin-induced platelet effect (ASPECT) study. Diabetes 2007, 56, 3014–3019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, S.; Li, L.; Yuan, Z.; Xu, G. Screening of anti-thrombin active components from Ligusticum chuanxiong by affinity-ultrafiltration coupled with HPLC-Q-Orbitrap-MS(n). Phytochem. Anal. 2023, 34, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.-H.; Yang, J.; Wu, S.-H.; Li, H.-B.; Tang, J.-F. Quality evaluation of Danhong Injection based on anticoagulant biological potency. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 2022, 53, 2348–2355. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, S.; Chen, J.; Liu, X.; Xing, C.; Zhao, L.; Chan, K.; Lu, G. Evaluation of the Pharmaceutical Activities of Chuanxiong, a Key Medicinal Material in Traditional Chinese Medicine. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 1157. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17091157
Huang S, Chen J, Liu X, Xing C, Zhao L, Chan K, Lu G. Evaluation of the Pharmaceutical Activities of Chuanxiong, a Key Medicinal Material in Traditional Chinese Medicine. Pharmaceuticals. 2024; 17(9):1157. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17091157
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Shiwei, Jiamei Chen, Xiaohua Liu, Chunxin Xing, Lu Zhao, Kelvin Chan, and Guanghua Lu. 2024. "Evaluation of the Pharmaceutical Activities of Chuanxiong, a Key Medicinal Material in Traditional Chinese Medicine" Pharmaceuticals 17, no. 9: 1157. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17091157
APA StyleHuang, S., Chen, J., Liu, X., Xing, C., Zhao, L., Chan, K., & Lu, G. (2024). Evaluation of the Pharmaceutical Activities of Chuanxiong, a Key Medicinal Material in Traditional Chinese Medicine. Pharmaceuticals, 17(9), 1157. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17091157








