Evolutionary Trend Analysis of Research on Immunotherapy for Brain Metastasis Based on Machine-Learning Scientometrics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Literature Selection Strategy and Conceptual Design of the Entire Study
2.2. Distribution and Cooperation of the Contributing Countries/Regions
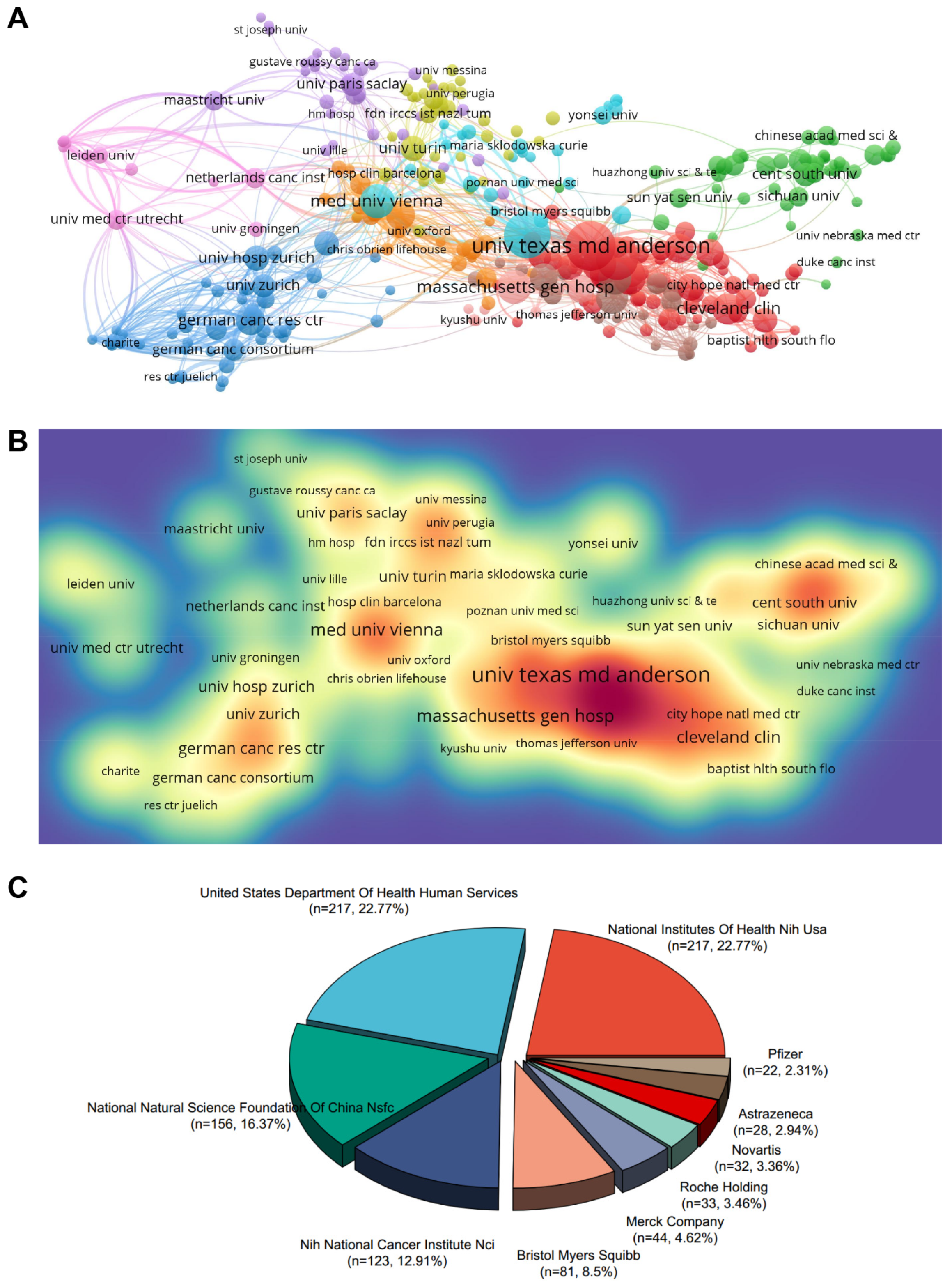
2.3. Contributing Institutions and Funding Agencies
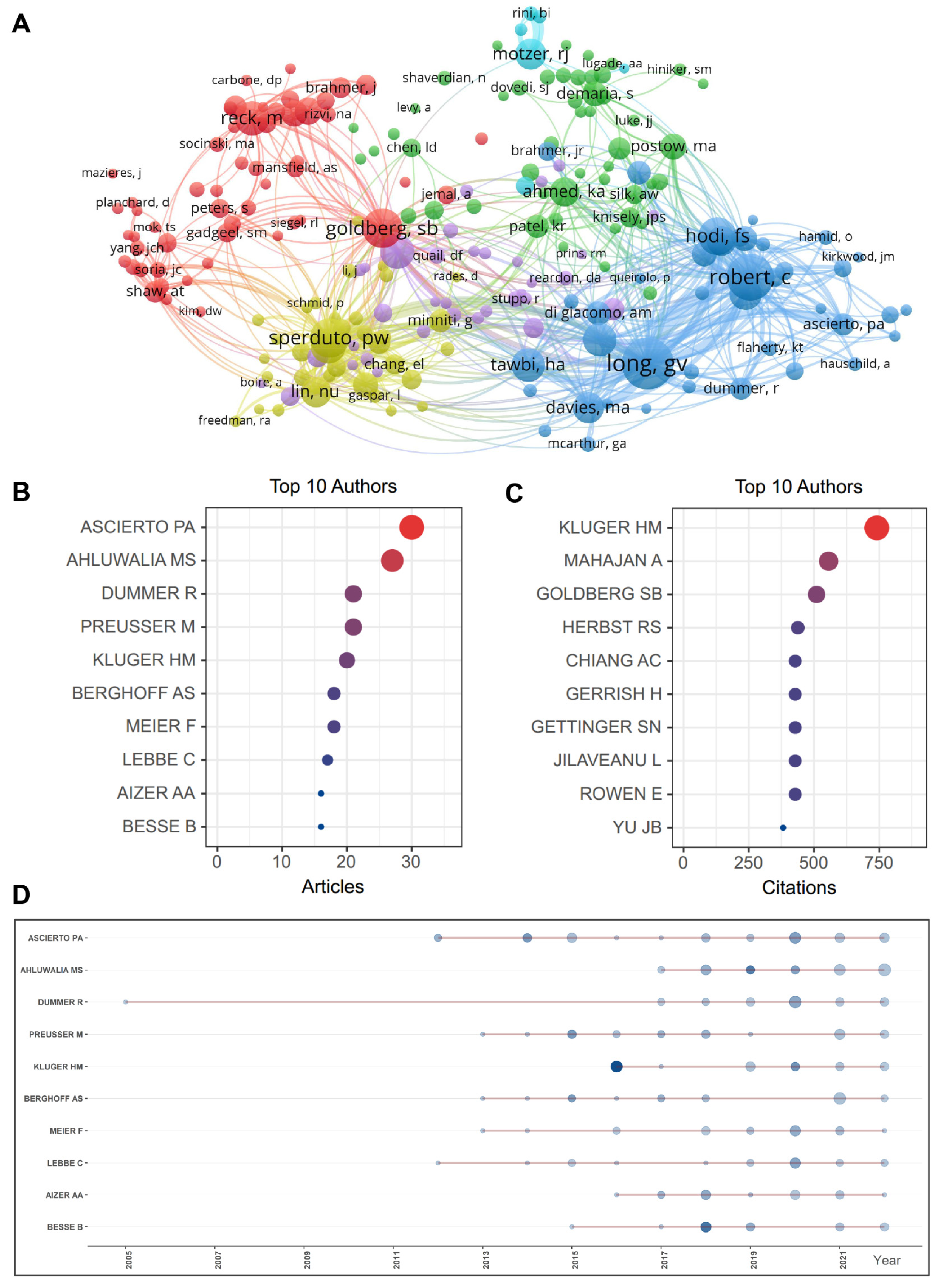
2.4. Active Authors and Co-Citation Analysis
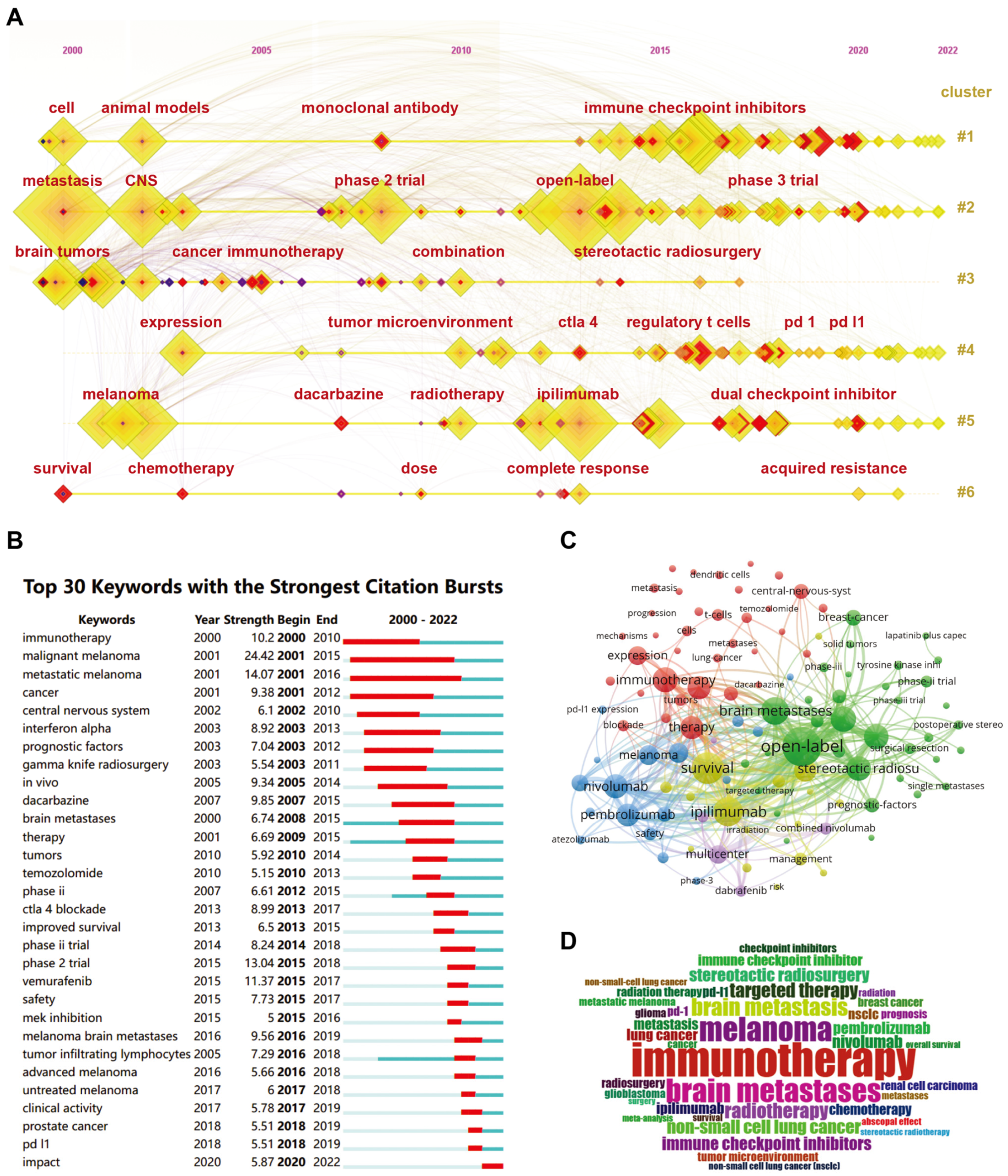
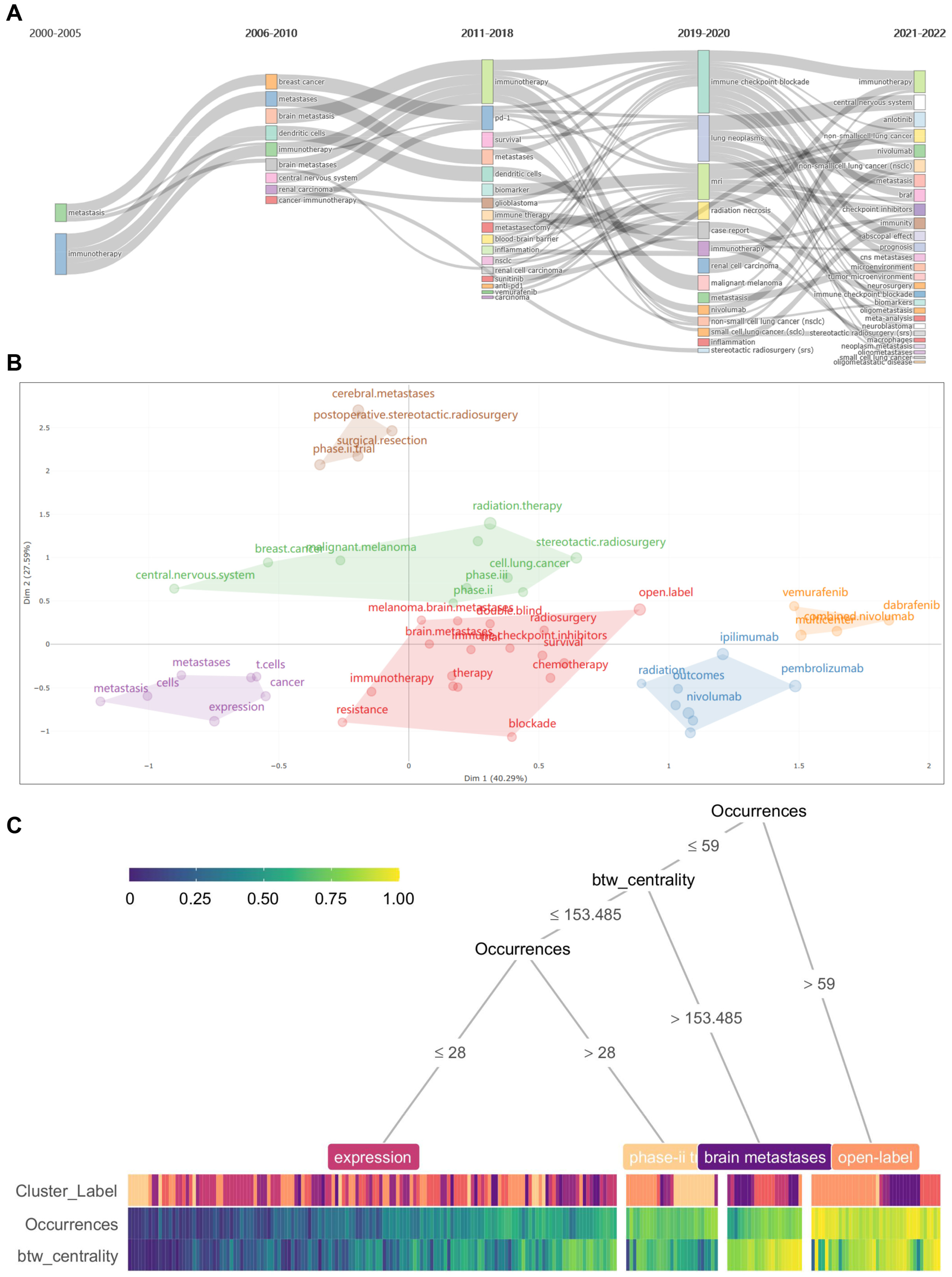
2.5. Keywords Analysis Regarding Co-Occurrence, Burstiness, Vicissitude, and Clustering
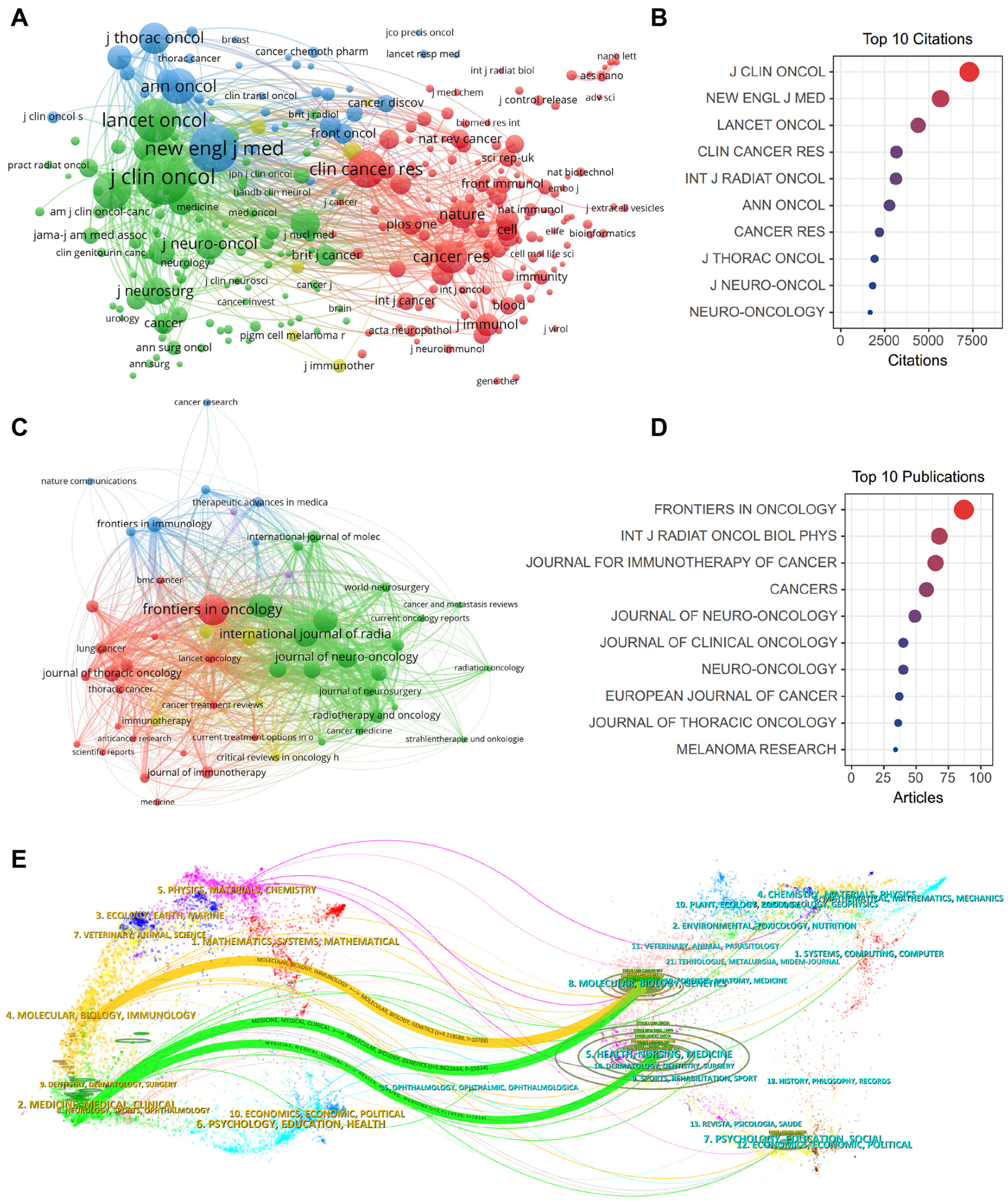
2.6. Impactful Journals and Co-Citation Analysis
2.7. Influential References and Co-Citation Analysis
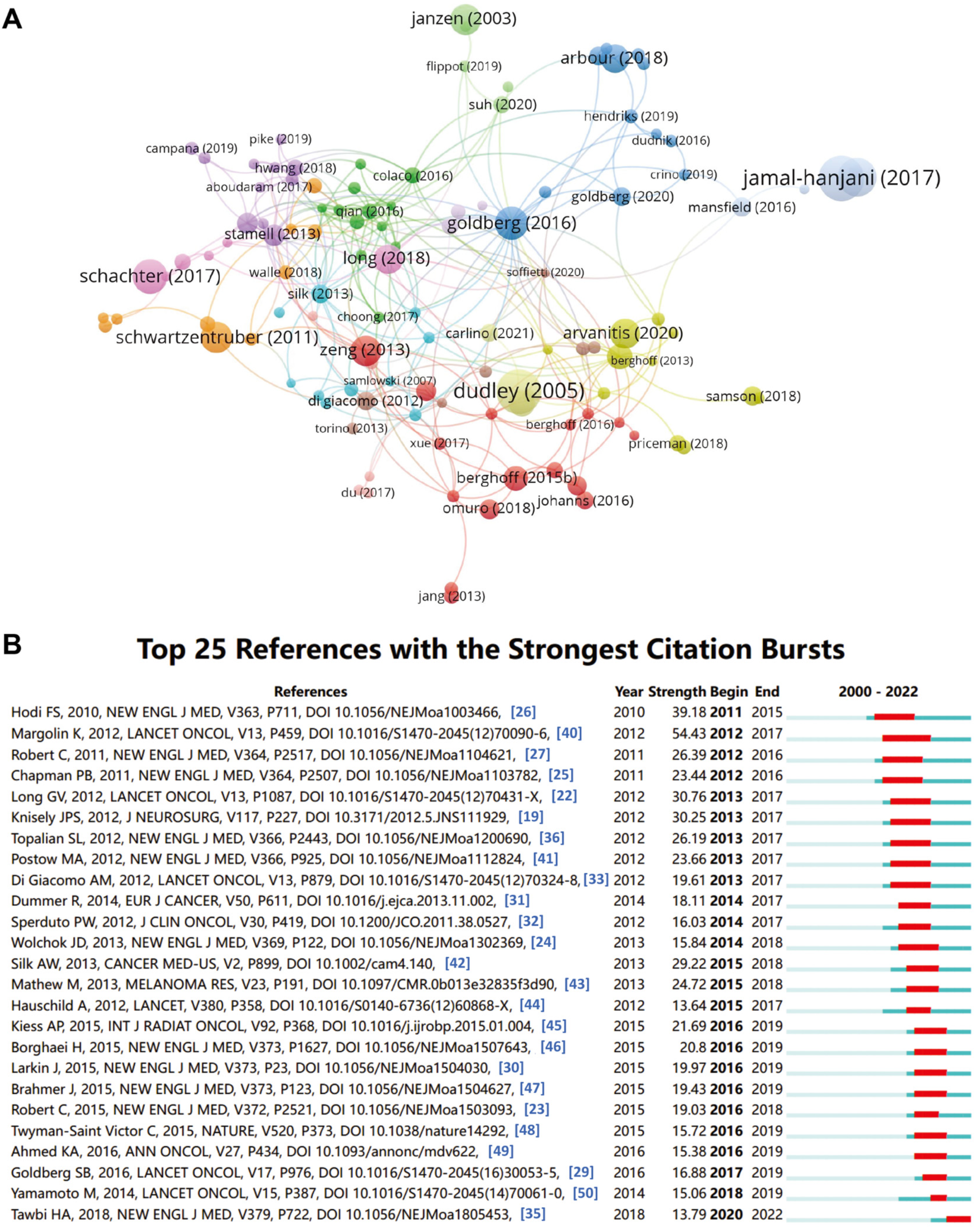
| Rank | Title | First Author | Institute (Country) | Year | Journal | IF (2023) | TLS | Citations (Ref.) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Pembrolizumab for patients with melanoma or non-small-cell lung cancer and untreated brain metastases: early analysis of a non-randomized, open-label, phase 2 trial | Sarah B Goldberg | Yale School of Medicine (USA) | 2016 | Lancet Oncol | 51.1 | 4142 | 342 [29] |
| 2 | Ipilimumab in patients with melanoma and brain metastases: an open-label, phase 2 trial | Kim Margolin | Providence Saint John’s Health Center (USA) | 2012 | Lancet Oncol | 51.1 | 4061 | 327 [40] |
| 3 | Combined Nivolumab and Ipilimumab in Melanoma Metastatic to the Brain | Hussein A Tawbi | University of Texas, MD Anderson Cancer Center (USA) | 2018 | N Engl J Med | 158.5 | 3309 | 291 [35] |
| 4 | Improved survival with ipilimumab in patients with metastatic melanoma | F Stephen Hodi | Dana–Farber Cancer Institute (USA) | 2010 | N Engl J Med | 158.5 | 2972 | 264 [26] |
| 5 | Combination nivolumab and ipilimumab or nivolumab alone in melanoma brain metastases: a multicentre randomized phase 2 study | Georgina V Long | University of Sydney (Australia) | 2018 | Lancet Oncol | 51.1 | 3005 | 246 [20] |
| 6 | Nivolumab versus Docetaxel in Advanced Nonsquamous Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer | Hossein Borghaei | Fox Chase Cancer Center (USA) | 2015 | N Engl J Med | 158.5 | 2260 | 226 [46] |
| 7 | Pembrolizumab versus Chemotherapy for PD-L1-Positive Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer | Martin Reck | German Center of Lung Research (Germany) | 2016 | N Engl J Med | 158.5 | 2111 | 196 [38] |
| 8 | Stereotactic radiosurgery for melanoma brain metastases in patients receiving ipilimumab: safety profile and efficacy of combined treatment | Kiess A.P | Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center (USA) | 2015 | Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys | 7.0 | 2633 | 178 [45] |
| 9 | Combined Nivolumab and Ipilimumab or Monotherapy in Untreated Melanoma | Larkin J. | Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center (USA) | 2015 | N Engl J Med | 158.5 | 1839 | 161 [30] |
| 10 | Nivolumab versus Docetaxel in Advanced Squamous-Cell Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer | Brahmer Julie | Sidney Kimmel Comprehensive Cancer Center at Johns Hopkins (USA) | 2015 | N Engl J Med | 158.5 | 1628 | 157 [47] |
3. Discussion
3.1. General Information
3.2. Keywords and Emerging Hotpots
3.3. Limitations and Future Direction
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Database and Study Collection
4.2. Visualization and Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Scoccianti, S.; Ricardi, U. Treatment of brain metastases: Review of phase III randomized controlled trials. Radiother. Oncol. 2012, 102, 168–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cagney, D.N.; Martin, A.M.; Catalano, P.J.; Redig, A.J.; Lin, N.U.; Lee, E.Q.; Wen, P.Y.; Dunn, I.F.; Bi, W.L.; Weiss, S.E. Incidence and prognosis of patients with brain metastases at diagnosis of systemic malignancy: A population-based study. Neuro-Oncology 2017, 19, 1511–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Achrol, A.S.; Rennert, R.C.; Anders, C.; Soffietti, R.; Ahluwalia, M.S.; Nayak, L.; Peters, S.; Arvold, N.D.; Harsh, G.R.; Steeg, P.S. Brain metastases. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2019, 5, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guérin, A.; Sasane, M.; Dea, K.; Zhang, J.; Culver, K.; Nitulescu, R.; Wu, E.Q.; Macalalad, A.R. The economic burden of brain metastasis among lung cancer patients in the United States. J. Med. Econ. 2016, 19, 526–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamba, N.; Wen, P.Y.; Aizer, A.A. Epidemiology of brain metastases and leptomeningeal disease. Neuro-Oncology 2021, 23, 1447–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suh, J.H.; Kotecha, R.; Chao, S.T.; Ahluwalia, M.S.; Sahgal, A.; Chang, E.L. Current approaches to the management of brain metastases. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 17, 279–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogelbaum, M.A.; Brown, P.D.; Messersmith, H.; Brastianos, P.K.; Burri, S.; Cahill, D.; Dunn, I.F.; Gaspar, L.E.; Gatson, N.T.N.; Gondi, V. Treatment for brain metastases: ASCO-SNO-ASTRO guideline. Neuro-Oncology 2022, 24, 331–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampson, J.H.; Maus, M.V.; June, C.H. Immunotherapy for brain tumors. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 2450–2456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubli, S.P.; Berger, T.; Araujo, D.V.; Siu, L.L.; Mak, T.W. Beyond immune checkpoint blockade: Emerging immunological strategies. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2021, 20, 899–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Ye, F.; Deng, X.; Tang, Y.; Liang, J.Y.; Huang, X.; Sun, Y.; Tang, H.; Lei, J.; Zheng, S.; et al. Circular RNA: A promising new star of vaccine. J. Transl. Intern. Med. 2023, 11, 372–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Harrison, E.B.; Li, H.; Hirabayashi, K.; Chen, J.; Li, Q.-X.; Gunn, J.; Weiss, J.; Savoldo, B.; Parker, J.S. Targeting brain lesions of non-small cell lung cancer by enhancing CCL2-mediated CAR-T cell migration. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quail, D.F.; Joyce, J.A. The microenvironmental landscape of brain tumors. Cancer Cell 2017, 31, 326–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kienast, Y.; Von Baumgarten, L.; Fuhrmann, M.; Klinkert, W.E.F.; Goldbrunner, R.; Herms, J.; Winkler, F. Real-time imaging reveals the single steps of brain metastasis formation. Nat. Med. 2010, 16, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valiente, M.; Obenauf, A.C.; Jin, X.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, X.H.F.; Lee, D.J.; Chaft, J.E.; Kris, M.G.; Huse, J.T.; Brogi, E. Serpins promote cancer cell survival and vascular co-option in brain metastasis. Cell 2014, 156, 1002–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Giacomo, A.M.; Valente, M.; Cerase, A.; Lofiego, M.F.; Piazzini, F.; Calabrò, L.; Gambale, E.; Covre, A.; Maio, M. Immunotherapy of brain metastases: Breaking a “dogma”. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valiente, M.; Ahluwalia, M.S.; Boire, A.; Brastianos, P.K.; Goldberg, S.B.; Lee, E.Q.; Le Rhun, E.; Preusser, M.; Winkler, F.; Soffietti, R. The evolving landscape of brain metastasis. Trends Cancer 2018, 4, 176–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerstberger, S.; Jiang, Q.; Ganesh, K. Metastasis. Cell 2023, 186, 1564–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldberg, S.B.; Schalper, K.A.; Gettinger, S.N.; Mahajan, A.; Herbst, R.S.; Chiang, A.C.; Lilenbaum, R.; Wilson, F.H.; Omay, S.B.; Yu, J.B.; et al. Pembrolizumab for management of patients with NSCLC and brain metastases: Long-term results and biomarker analysis from a non-randomised, open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 655–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knisely, J.P.S.; Yu, J.B.; Flanigan, J.; Sznol, M.; Kluger, H.M.; Chiang, V.L.S. Radiosurgery for melanoma brain metastases in the ipilimumab era and the possibility of longer survival: Clinical article. J. Neurosurg. JNS 2012, 117, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, G.V.; Atkinson, V.; Lo, S.; Sandhu, S.; Guminski, A.D.; Brown, M.P.; Wilmott, J.S.; Edwards, J.; Gonzalez, M.; Scolyer, R.A. Combination nivolumab and ipilimumab or nivolumab alone in melanoma brain metastases: A multicentre randomised phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2018, 19, 672–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, G.V.; Atkinson, V.; Menzies, A.M.; Lo, S.; Guminski, A.D.; Brown, M.P.; Gonzalez, M.M.; Diamante, K.; Sandhu, S.K.; Scolyer, R.A.; et al. A randomized phase II study of nivolumab or nivolumab combined with ipilimumab in patients (pts) with melanoma brain metastases (mets): The Anti-PD1 Brain Collaboration (ABC). J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 9508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, G.V.; Trefzer, U.; Davies, M.A.; Kefford, R.F.; Ascierto, P.A.; Chapman, P.B.; Puzanov, I.; Hauschild, A.; Robert, C.; Algazi, A.; et al. Dabrafenib in patients with Val600Glu or Val600Lys BRAF-mutant melanoma metastatic to the brain (BREAK-MB): A multicentre, open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2012, 13, 1087–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robert, C.; Schachter, J.; Long, G.V.; Arance, A.; Grob, J.J.; Mortier, L.; Daud, A.; Carlino, M.S.; McNeil, C.; Lotem, M.; et al. Pembrolizumab versus Ipilimumab in Advanced Melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 2521–2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolchok, J.D.; Kluger, H.; Callahan, M.K.; Postow, M.A.; Rizvi, N.A.; Lesokhin, A.M.; Segal, N.H.; Ariyan, C.E.; Gordon, R.A.; Reed, K.; et al. Nivolumab plus ipilimumab in advanced melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 122–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapman, P.B.; Hauschild, A.; Robert, C.; Haanen, J.B.; Ascierto, P.; Larkin, J.; Dummer, R.; Garbe, C.; Testori, A.; Maio, M.; et al. Improved survival with vemurafenib in melanoma with BRAF V600E mutation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 2507–2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodi, F.S.; O’Day, S.J.; McDermott, D.F.; Weber, R.W.; Sosman, J.A.; Haanen, J.B.; Gonzalez, R.; Robert, C.; Schadendorf, D.; Hassel, J.C. Improved survival with ipilimumab in patients with metastatic melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 711–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, C.; Thomas, L.; Bondarenko, I.; O’Day, S.; Weber, J.; Garbe, C.; Lebbe, C.; Baurain, J.F.; Testori, A.; Grob, J.J.; et al. Ipilimumab plus dacarbazine for previously untreated metastatic melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 2517–2526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berghoff, A.S.; Ricken, G.; Wilhelm, D.; Rajky, O.; Widhalm, G.; Dieckmann, K.; Birner, P.; Bartsch, R.; Preusser, M. Tumor infiltrating lymphocytes and PD-L1 expression in brain metastases of small cell lung cancer (SCLC). J. Neuro-Oncol. 2016, 130, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, S.B.; Gettinger, S.N.; Mahajan, A.; Chiang, A.C.; Herbst, R.S.; Sznol, M.; Tsiouris, A.J.; Cohen, J.; Vortmeyer, A.; Jilaveanu, L. Pembrolizumab for patients with melanoma or non-small-cell lung cancer and untreated brain metastases: Early analysis of a non-randomised, open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 976–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larkin, J.; Chiarion-Sileni, V.; Gonzalez, R.; Grob, J.J.; Cowey, C.L.; Lao, C.D.; Schadendorf, D.; Dummer, R.; Smylie, M.; Rutkowski, P. Combined nivolumab and ipilimumab or monotherapy in untreated melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dummer, R.; Goldinger, S.M.; Turtschi, C.P.; Eggmann, N.B.; Michielin, O.; Mitchell, L.; Veronese, L.; Hilfiker, P.R.; Felderer, L.; Rinderknecht, J.D. Vemurafenib in patients with BRAF(V600) mutation-positive melanoma with symptomatic brain metastases: Final results of an open-label pilot study. Eur. J. Cancer 2014, 50, 611–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sperduto, P.W.; Kased, N.; Roberge, D.; Xu, Z.; Shanley, R.; Luo, X.; Sneed, P.K.; Chao, S.T.; Weil, R.J.; Suh, J.; et al. Summary report on the graded prognostic assessment: An accurate and facile diagnosis-specific tool to estimate survival for patients with brain metastases. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Giacomo, A.M.; Ascierto, P.A.; Pilla, L.; Santinami, M.; Ferrucci, P.F.; Giannarelli, D.; Marasco, A.; Rivoltini, L.; Simeone, E.; Nicoletti, S.V.; et al. Ipilimumab and fotemustine in patients with advanced melanoma (NIBIT-M1): An open-label, single-arm phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2012, 13, 879–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Giacomo, A.M.; Ascierto, P.A.; Queirolo, P.; Pilla, L.; Ridolfi, R.; Santinami, M.; Testori, A.; Simeone, E.; Guidoboni, M.; Maurichi, A.; et al. Three-year follow-up of advanced melanoma patients who received ipilimumab plus fotemustine in the Italian Network for Tumor Biotherapy (NIBIT)-M1 phase II study. Ann. Oncol. 2015, 26, 798–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tawbi, H.A.; Forsyth, P.A.; Algazi, A.; Hamid, O.; Hodi, F.S.; Moschos, S.J.; Khushalani, N.I.; Lewis, K.; Lao, C.D.; Postow, M.A.; et al. Combined Nivolumab and Ipilimumab in Melanoma Metastatic to the Brain. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 722–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Topalian, S.L.; Hodi, F.S.; Brahmer, J.R.; Gettinger, S.N.; Smith, D.C.; McDermott, D.F.; Powderly, J.D.; Carvajal, R.D.; Sosman, J.A.; Atkins, M.B.; et al. Safety, activity, and immune correlates of anti-PD-1 antibody in cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 2443–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauko, A.; Thapa, B.; Venur, V.A.; Ahluwalia, M.S. Management of Brain Metastases in the New Era of Checkpoint Inhibition. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2018, 18, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reck, M.; Rodríguez-Abreu, D.; Robinson, A.G.; Hui, R.; Csőszi, T.; Fülöp, A.; Gottfried, M.; Peled, N.; Tafreshi, A.; Cuffe, S. Pembrolizumab versus chemotherapy for PD-L1–positive non–small-cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1823–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brastianos, P.K.; Lee, E.Q.; Cohen, J.V.; Tolaney, S.M.; Lin, N.U.; Wang, N.; Chukwueke, U.; White, M.D.; Nayyar, N.; Kim, A.; et al. Single-arm, open-label phase 2 trial of pembrolizumab in patients with leptomeningeal carcinomatosis. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 1280–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margolin, K.; Ernstoff, M.S.; Hamid, O.; Lawrence, D.; McDermott, D.; Puzanov, I.; Wolchok, J.D.; Clark, J.I.; Sznol, M.; Logan, T.F. Ipilimumab in patients with melanoma and brain metastases: An open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2012, 13, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postow, M.A.; Callahan, M.K.; Barker, C.A.; Yamada, Y.; Yuan, J.; Kitano, S.; Mu, Z.; Rasalan, T.; Adamow, M.; Ritter, E.; et al. Immunologic correlates of the abscopal effect in a patient with melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 925–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silk, A.W.; Bassetti, M.F.; West, B.T.; Tsien, C.I.; Lao, C.D. Ipilimumab and radiation therapy for melanoma brain metastases. Cancer Med. 2013, 2, 899–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathew, M.; Tam, M.; Ott, P.A.; Pavlick, A.C.; Rush, S.C.; Donahue, B.R.; Golfinos, J.G.; Parker, E.C.; Huang, P.P.; Narayana, A. Ipilimumab in melanoma with limited brain metastases treated with stereotactic radiosurgery. Melanoma Res. 2013, 23, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hauschild, A.; Grob, J.J.; Demidov, L.V.; Jouary, T.; Gutzmer, R.; Millward, M.; Rutkowski, P.; Blank, C.U.; Miller, W.H., Jr.; Kaempgen, E.; et al. Dabrafenib in BRAF-mutated metastatic melanoma: A multicentre, open-label, phase 3 randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2012, 380, 358–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiess, A.P.; Wolchok, J.D.; Barker, C.A.; Postow, M.A.; Tabar, V.; Huse, J.T.; Chan, T.A.; Yamada, Y.; Beal, K. Stereotactic radiosurgery for melanoma brain metastases in patients receiving ipilimumab: Safety profile and efficacy of combined treatment. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2015, 92, 368–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borghaei, H.; Paz-Ares, L.; Horn, L.; Spigel, D.R.; Steins, M.; Ready, N.E.; Chow, L.Q.; Vokes, E.E.; Felip, E.; Holgado, E. Nivolumab versus docetaxel in advanced nonsquamous non–small-cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 1627–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brahmer, J.; Reckamp, K.L.; Baas, P.; Crinò, L.; Eberhardt, W.E.E.; Poddubskaya, E.; Antonia, S.; Pluzanski, A.; Vokes, E.E.; Holgado, E. Nivolumab versus docetaxel in advanced squamous-cell non–small-cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Twyman-Saint Victor, C.; Rech, A.J.; Maity, A.; Rengan, R.; Pauken, K.E.; Stelekati, E.; Benci, J.L.; Xu, B.; Dada, H.; Odorizzi, P.M.; et al. Radiation and dual checkpoint blockade activate non-redundant immune mechanisms in cancer. Nature 2015, 520, 373–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, K.A.; Stallworth, D.G.; Kim, Y.; Johnstone, P.A.; Harrison, L.B.; Caudell, J.J.; Yu, H.H.; Etame, A.B.; Weber, J.S.; Gibney, G.T. Clinical outcomes of melanoma brain metastases treated with stereotactic radiation and anti-PD-1 therapy. Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27, 434–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, M.; Serizawa, T.; Shuto, T.; Akabane, A.; Higuchi, Y.; Kawagishi, J.; Yamanaka, K.; Sato, Y.; Jokura, H.; Yomo, S.; et al. Stereotactic radiosurgery for patients with multiple brain metastases (JLGK0901): A multi-institutional prospective observational study. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Yuan, C.; Chen, L.; Guo, L.; Chen, Y.; Peng, Z.; Lu, L. Survival benefits of anti-PD-1 therapy in combination with radiotherapy in chinese melanoma patients with brain metastasis. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 646328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, P.; Masucci, L.; Florescu, M.; Plourde, M.E.; Panet-Raymond, V.; Pavic, M.; Owen, S.; Masson-Coté, L.; Ménard, C.; Routy, B.; et al. Phase II multicenter trial combining nivolumab and radiosurgery for NSCLC and RCC brain metastases. Neurooncol. Adv. 2023, 5, vdad018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, K.A.; Kim, Y.; Arrington, J.A.; Kim, S.; DeJesus, M.; Soyano, A.E.; Armaghani, A.J.; Costa, R.L.B.; Khong, H.T.; Loftus, L.S.; et al. Nivolumab and Stereotactic Radiosurgery for Patients With Breast Cancer Brain Metastases: A Nonrandomized, Open-Label Phase 1b Study. Adv. Radiat. Oncol. 2021, 6, 100798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, W.J.; Baghai, T.; Ong, M.; Lo, B.; Ibrahim, A.M.; Smith, T.K.T.; Song, X. A Contemporary Report of Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Melanoma Brain Metastases. Curr. Oncol. 2021, 28, 428–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, L.; Rodríguez-Abreu, D.; Gadgeel, S.; Esteban, E.; Felip, E.; De Angelis, F.; Domine, M.; Clingan, P.; Hochmair, M.J.; Powell, S.F.; et al. Pembrolizumab plus Chemotherapy in Metastatic Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 2078–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadgeel, S.M.; Lukas, R.V.; Goldschmidt, J.; Conkling, P.; Park, K.; Cortinovis, D.; de Marinis, F.; Rittmeyer, A.; Patel, J.D.; von Pawel, J.; et al. Atezolizumab in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer and history of asymptomatic, treated brain metastases: Exploratory analyses of the phase III OAK study. Lung Cancer 2019, 128, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louveau, A.; Smirnov, I.; Keyes, T.J.; Eccles, J.D.; Rouhani, S.J.; Peske, J.D.; Derecki, N.C.; Castle, D.; Mandell, J.W.; Lee, K.S. Structural and functional features of central nervous system lymphatic vessels. Nature 2015, 523, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aspelund, A.; Antila, S.; Proulx, S.T.; Karlsen, T.V.; Karaman, S.; Detmar, M.; Wiig, H.; Alitalo, K. A dural lymphatic vascular system that drains brain interstitial fluid and macromolecules. J. Exp. Med. 2015, 212, 991–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wyler, L.; Napoli, C.U.; Ingold, B.; Sulser, T.; Heikenwälder, M.; Schraml, P.; Moch, H. Brain metastasis in renal cancer patients: Metastatic pattern, tumour-associated macrophages and chemokine/chemoreceptor expression. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 110, 686–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duchnowska, R.; Pęksa, R.; Radecka, B.; Mandat, T.; Trojanowski, T.; Jarosz, B.; Czartoryska-Arłukowicz, B.; Olszewski, W.P.; Och, W.; Kalinka-Warzocha, E. Immune response in breast cancer brain metastases and their microenvironment: The role of the PD-1/PD-L axis. Breast Cancer Res. 2016, 18, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Placke, J.M.; Kimmig, M.; Griewank, K.; Herbst, R.; Terheyden, P.; Utikal, J.; Pföhler, C.; Ulrich, J.; Kreuter, A.; Mohr, P.; et al. Correlation of tumor PD-L1 expression in different tissue types and outcome of PD-1-based immunotherapy in metastatic melanoma—Analysis of the DeCOG prospective multicenter cohort study ADOREG/TRIM. EBioMedicine 2023, 96, 104774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Deng, X.; Xie, J.; Tang, H.; Zou, Y. Heterogeneous PD-L1 expression in metastases impacts immunotherapy response. EBioMedicine 2023, 97, 104816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansfield, A.S.; Aubry, M.C.; Moser, J.C.; Harrington, S.M.; Dronca, R.S.; Park, S.S.; Dong, H. Temporal and spatial discordance of programmed cell death-ligand 1 expression and lymphocyte tumor infiltration between paired primary lesions and brain metastases in lung cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27, 1953–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldman, J.W.; Crino, L.; Vokes, E.E.; Holgado, E.; Reckamp, K.; Pluzanski, A.; Spigel, D.; Kohlhaeufl, M.; Garassino, M.; Chow, L.Q. P2. 36: Nivolumab (nivo) in patients (pts) with advanced (adv) NSCLC and central nervous system (CNS) metastases (mets): Track: Immunotherapy. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2016, 11, S238–S239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klemm, F.; Maas, R.R.; Bowman, R.L.; Kornete, M.; Soukup, K.; Nassiri, S.; Brouland, J.-P.; Iacobuzio-Donahue, C.A.; Brennan, C.; Tabar, V. Interrogation of the microenvironmental landscape in brain tumors reveals disease-specific alterations of immune cells. Cell 2020, 181, 1643–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biermann, J.; Melms, J.C.; Amin, A.D.; Wang, Y.; Caprio, L.A.; Karz, A.; Tagore, S.; Barrera, I.; Ibarra-Arellano, M.A.; Andreatta, M. Dissecting the treatment-naive ecosystem of human melanoma brain metastasis. Cell 2022, 185, 2591–2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez, H.; Mei, W.; Robles, I.; Hagerling, C.; Allen, B.M.; Okholm, T.L.H.; Nanjaraj, A.; Verbeek, T.; Kalavacherla, S.; van Gogh, M. Cellular architecture of human brain metastases. Cell 2022, 185, 729–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, C.; Winkler, F. Insights and opportunities at the crossroads of cancer and neuroscience. Nat. Cell Biol. 2022, 24, 1454–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, J.; Liu, M.; Deng, X.; Tang, Y.; Zheng, S.; Ou, X.; Tang, H.; Xie, X.; Wu, M.; Zou, Y. Gut microbiota reshapes cancer immunotherapy efficacy: Mechanisms and therapeutic strategies. iMeta 2024, 3, e156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seferbekova, Z.; Lomakin, A.; Yates, L.R.; Gerstung, M. Spatial biology of cancer evolution. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2023, 24, 295–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, A.S.; Chaligne, R.; Landau, D.A. Integrating genetic and non-genetic determinants of cancer evolution by single-cell multi-omics. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2021, 22, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.; Jones, M.G.; Naranjo, S.; Rideout, W.M.; Min, K.H.J.; Ho, R.; Wu, W.; Replogle, J.M.; Page, J.L.; Quinn, J.J. Lineage tracing reveals the phylodynamics, plasticity, and paths of tumor evolution. Cell 2022, 185, 1905–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.; Chen, W.; Minkina, A.; Chardon, F.M.; Suiter, C.C.; Regalado, S.G.; Domcke, S.; Hamazaki, N.; Lee, C.; Martin, B. A time-resolved, multi-symbol molecular recorder via sequential genome editing. Nature 2022, 608, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludwig, L.S.; Lareau, C.A.; Ulirsch, J.C.; Christian, E.; Muus, C.; Li, L.H.; Pelka, K.; Ge, W.; Oren, Y.; Brack, A. Lineage tracing in humans enabled by mitochondrial mutations and single-cell genomics. Cell 2019, 176, 1325–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veninga, V.; Voest, E.E. Tumor organoids: Opportunities and challenges to guide precision medicine. Cancer Cell 2021, 39, 1190–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subbiah, V. The next generation of evidence-based medicine. Nat. Med. 2023, 39, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bloch, O.; Crane, C.A.; Kaur, R.; Safaee, M.; Rutkowski, M.J.; Parsa, A.T. Gliomas Promote Immunosuppression through Induction of B7-H1 Expression in Tumor-Associated MacrophagesB7-H1 in Glioma TAM. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 3165–3175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pham, C.D.; Flores, C.; Yang, C.; Pinheiro, E.M.; Yearley, J.H.; Sayour, E.J.; Pei, Y.; Moore, C.; McLendon, R.E.; Huang, J. Differential Immune Microenvironments and Response to Immune Checkpoint Blockade among Molecular Subtypes of Murine MedulloblastomaImmune Characterization of Murine Medulloblastoma Subtypes. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 582–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, S.; Repic, M.; Guo, Z.; Kavirayani, A.; Burkard, T.; Bagley, J.A.; Krauditsch, C.; Knoblich, J.A. Genetically engineered cerebral organoids model brain tumor formation. Nat. Methods 2018, 15, 631–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Eck, N.J.; Waltman, L. Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping. Scientometrics 2010, 84, 523–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Synnestvedt, M.B.; Chen, C.; Holmes, J.H. CiteSpace II: Visualization and knowledge discovery in bibliographic databases. MIA Annu. Symp. Proc. AMIA Symp. 2005, 2005, 724–728. [Google Scholar]

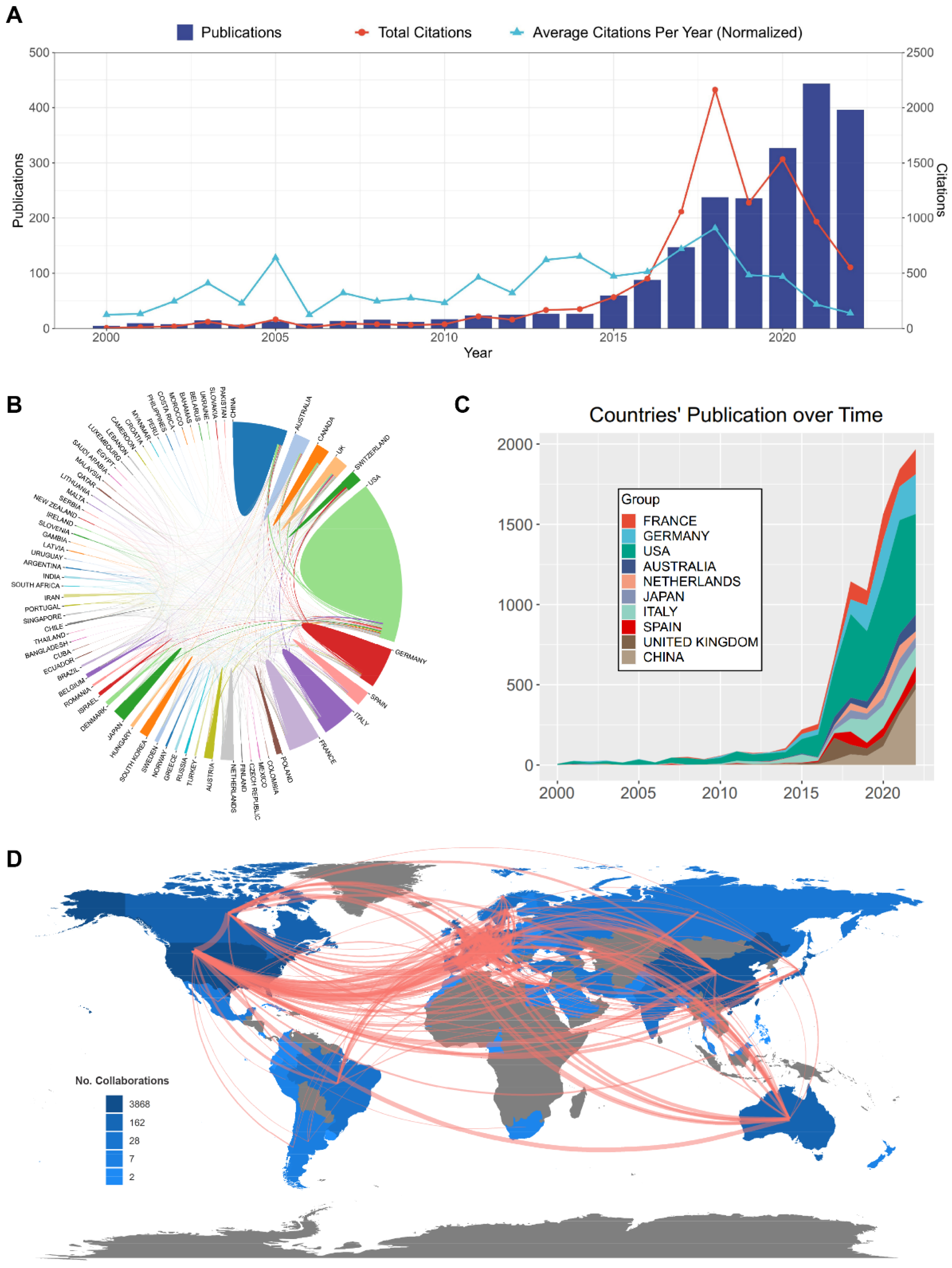
| Rank | Country | Counts | Total (%) | CAF (%) | ACI | Total Citations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | USA | 1017 | 47.0 | 15.7 | 32.32 | 32,868 |
| 2 | China | 340 | 15.7 | 16.0 | 11.20 | 3808 |
| 3 | Germany | 217 | 10.0 | 22.0 | 35.57 | 7719 |
| 4 | Italy | 209 | 9.7 | 19.3 | 26.19 | 5474 |
| 5 | France | 158 | 7.3 | 24.7 | 25.07 | 3962 |
| 6 | Canada | 110 | 5.1 | 23.4 | 38.60 | 4246 |
| 7 | Japan | 104 | 4.8 | 2.7 | 17.91 | 1863 |
| 8 | UK | 102 | 4.7 | 22.0 | 62.05 | 6329 |
| 9 | Spain | 99 | 4.6 | 30.0 | 37.70 | 3732 |
| 10 | Australia | 97 | 4.5 | 22.0 | 47.51 | 4608 |
| Rank | Institutes | Country | Counts | TLS | ACI | Total Citations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Univ Texas Md Anderson Canc Ctr | USA | 90 | 62,170 | 31.31 | 2818 |
| 2 | Harvard Med Sch | USA | 79 | 48,859 | 33.35 | 2635 |
| 3 | Mem Sloan Kettering Canc Ctr | USA | 67 | 32,713 | 51.59 | 3457 |
| 4 | Med Univ Vienna | Austria | 47 | 28,921 | 32.63 | 1534 |
| 5 | Dana Farber Canc Inst | USA | 45 | 32,743 | 58.17 | 2618 |
| 6 | Massachusetts Gen Hosp | USA | 45 | 24,676 | 34.04 | 1532 |
| 7 | Mayo Clin | USA | 43 | 26,405 | 53.04 | 2281 |
| 8 | Emory Univ | USA | 40 | 22,998 | 45.65 | 1826 |
| 9 | Univ Pittsburgh | Germany | 40 | 17,970 | 32.25 | 1290 |
| 10 | Cleveland Clin | USA | 39 | 27,931 | 32.94 | 1285 |
| Rank | Author [Ref.] | Institute (Country) | Counts | Total Citations | H- Index | TLS | Co-Cited Author [Ref.] | Institute (Country) | Total Citations | TLS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Ahluwalia, Manmeet S. [3,6,16] | Florida International University (USA) | 24 | 881 | 44 | 15,704 | Long, GV [18,19,20,21,22,23] | University of Sydney (Australia) | 769 | 12,794 |
| 2 | Kluger, Harriet M. [19,24] | Yale School of Medicine (USA) | 19 | 1522 | 59 | 9712 | Robert, C [23,25,26,27] | Gustave Roussy and Paris-Saclay University (France) | 638 | 10,264 |
| 3 | Preusser, Matthias [16,28] | Medical University of Vienna (Austria) | 19 | 1091 | 72 | 9900 | Goldberg, SB [16,18,29] | Yale School of Medicine (USA) | 498 | 7585 |
| 4 | Dummer, Reinhard [30,31] | University Hospital Zurich (Switzerland) | 16 | 132 | 123 | 4799 | Sperduto, PW [32] | Duke University Medical Center (USA) | 483 | 8658 |
| 5 | Ascierto, Paolo A. [22,25,33,34] | Istituto Nazionale Tumori IRCCS (Italy) | 15 | 965 | 96 | 5369 | Hodi, FS [26,35,36] | Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Harvard Medical School (USA) | 453 | 7332 |
| 6 | Chiang, Veronica L. [18,19,29] | Yale School of Medicine (USA) | 15 | 618 | 31 | 6122 | Brown, PD [7,20,21,32] | Mayo Clinic (USA) | 405 | 7305 |
| 7 | Lauko, Adam [37] | Lerner Research Institute, Cleveland Clinic (USA) | 14 | 58 | 9 | 4069 | Reck, M [38] | German Center for Lung Research (Germany) | 381 | 4638 |
| 8 | Aizer, Ayal A. [5] | Dana-Farber Cancer Institute (USA) | 13 | 494 | 39 | 8629 | Berghoff, AS [28] | Medical University of Vienna (Austria) | 376 | 5521 |
| 9 | Brastianos, Priscilla K. [7,16,39] | Harvard Medical School (USA) | 13 | 332 | 49 | 9979 | Tawbi, HA [35] | University of Texas, MD Anderson Cancer Center (USA) | 366 | 5635 |
| 10 | Heimberger, Amy B. | Northwestern University (USA) | 13 | 255 | 66 | 4509 | Margolin, K [40] | Providence Saint John’s Health Center (USA) | 364 | 6182 |
| Rank | Keywords | Occurrences | TLS | Rank | Keywords | Occurrences | TLS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Immunotherapy | 742 | 1450 | 11 | Pembrolizumab | 87 | 232 |
| 2 | Brain Metastases | 358 | 770 | 12 | Lung Cancer | 81 | 182 |
| 3 | Melanoma | 348 | 706 | 13 | Ipilimumab | 78 | 234 |
| 4 | Brain Metastasis | 200 | 420 | 14 | Metastasis | 77 | 119 |
| 5 | Radiotherapy | 149 | 352 | 15 | Chemotherapy | 73 | 172 |
| 6 | Targeted Therapy | 132 | 315 | 16 | Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor | 72 | 125 |
| 7 | Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer | 122 | 241 | 17 | NSCLC | 72 | 140 |
| 8 | Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors | 112 | 223 | 18 | PD-L1 | 65 | 160 |
| 9 | Stereotactic Radiosurgery | 112 | 292 | 19 | PD-1 | 58 | 172 |
| 10 | Nivolumab | 98 | 272 | 20 | Tumor Microenvironment | 57 | 84 |
| Rank | Journals | Counts | IF (2023) | JCR (2023) | H-Index | Total Citations | Co-Cited Journals | IF (2023) | JCR (2023) | Total Citations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Front Oncol | 97 | 4.7 | Q2 | 56 | 987 | J Clin Oncol | 45.3 | Q1 | 7780 |
| 2 | Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys | 68 | 7.0 | Q1 | 34 | 1732 | New Engl J Med | 158.5 | Q1 | 5935 |
| 3 | J Immunother Cancer | 67 | 10.9 | Q1 | 50 | 1175 | Lancet Oncol | 51.1 | Q1 | 4676 |
| 4 | Cancers | 65 | 5.2 | Q2 | 54 | 611 | Clin Cancer Res | 11.5 | Q1 | 3359 |
| 5 | J Neuro-Oncol | 52 | 3.9 | Q2 | 22 | 853 | Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys | 7.0 | Q1 | 3319 |
| 6 | J Clin Oncol | 41 | 45.3 | Q1 | 84 | 2432 | Ann Oncol | 50.5 | Q1 | 2991 |
| 7 | Neuro-Oncology | 41 | 15.9 | Q1 | 37 | 1215 | Cancer Res | 11.2 | Q1 | 2365 |
| 8 | Eur J Cancer | 40 | 8.4 | Q1 | 42 | 865 | J Thorac Oncol | 20.4 | Q1 | 2158 |
| 9 | J Thorac Oncol | 37 | 20.4 | Q1 | 51 | 907 | J Neuro-Oncol | 3.9 | Q2 | 1960 |
| 10 | Melanoma Res | 35 | 2.2 | Q3 | 13 | 598 | Neuro-Oncology | 15.9 | Q1 | 1843 |
| Tumor Type | Phase | Drugs (Target) | n | Trial arm | Intracranial RR (%) | Median PFS | Median OS | Trial No. (Ref.) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Melanoma | I | Ipilimumab (CTLA-4) | 17 | Ipilimumab + SRS/WBRT | 65 | 2.5 mos | 8.0 mos | NCT 01703507 [45] |
| Melanoma | I | Nivolumab (PD-1) | 17 | Nivolumab + SRS | 60 | / | / | NCT 02716948 [51] |
| Melanoma | II | Ipilimumab (CTLA-4) | 72 | (1) Asymptomatic: Ipilimumab; (2) Symptomatic: Ipilimumab | (1) 25 (2) 10 | (1) 1.9 mos (2) 1.2 mos | (1) 7.0 mos (2) 3.7 mos | NCT 00623766 [40] |
| Melanoma | II | Nivolumab Ipilimumab (PD-1/CTLA-4) | 90 | Nivolumab + Ipilimumab induction followed by Nivolumab maintenance | 57 | 59% at 9 mos | 82% at 9 mos | NCT 02320058 [35] |
| Melanoma | II | Ipilimumab (CTLA-4) | 86 | Ipilimumab + Fotemustine | 35 | 3.0 mos | 12.7 mos | NCT 01654692 [33,34] |
| Melanoma | II | Nivolumab Ipilimumab (PD-1/CTLA-4) | 76 | (1) Asymptomatic: Nivolumab + Ipilimumab; (2) Asymptomatic: Nivolumab; (3) Symptomatic: Nivolumab | (1) 44 (2) 20 (3) 6 | (1) 50% (2) 29% (3) 0% at 6 mos | (1) 75% (2) 59% (3) 44% at 6 mos | NCT 02374242 [21] |
| Melanoma/NSCLC | II | Pembrolizumab (PD-1) | 65 | Pembrolizumab | 22 33 | 2.0 mos | 17.0 mos | NCT 02085070 [18] |
| NSCLC/RCC | II | Nivolumab (PD-1) | 26 | Nivolumab + SRS | 42 | 6.1 mos | 21.4 mos | NCT 02978404 [52] |
| Breast Cancer | I | Nivolumab (PD-1) | 14 | Nivolumab + SRS | 55 | / | / | NCT 03807765 [53] |
| Melanoma | II | Nivolumab Ipilimumab (PD-1/CTLA-4) | 128 a | Nivolumab + Ipilimumab followed by Nivolumab or Nivolumab + SRS | / | / | / | NCT03340129 [54] |
| NSCLC | III | Pembrolizumab (PD-1) | 108 | Pembrolizumab + Chemotherapy | / | / | / | NCT 02578680 [55] |
| NSCLC | III | Atezolizumab (PD-L1) | 124 | Atezolizumab | / | / | 16.0 mos | NCT 02008227 [56] |
| Solid Tumors | II | Pembrolizumab (PD-1) | 101 | Pembrolizumab ± SRS | 40 | / | / | NCT 02886585 [39] |
| Trial No. | Tumor Type | Phase | Drugs | n | Trial Arm | Country | Principle Institute | Duration |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT 02460068 | Melanoma | III | Nivolumab Ipilimumab | 168 | (1) Ipilimumab + Fotemustine; (2) Ipilimumab + Nivolumab; (3) Bevaczumab + Pembrolizumab; (4) Fortemustine | USA | University Hospital of Siena | 2012–2020 |
| NCT 02681549 | Melanoma NSCLC | II | Pembrolizumab | 53 | Pembrolizumab + Bevacizumab | USA | Yale University | 2016–2024 |
| NCT 02696993 | NSCLC | II | Nivolumab Ipilimumab | 88 | Nivolumab ± Ipilimumab + SRS or WBRT | USA | M.D. Anderson Cancer Center | 2016–2023 |
| NCT 02978404 | NSCLC RCC | II | Nivolumab | 60 | Nivolumab + SRS | Canada | University of Montreal Health Centre | 2017–2023 |
| NCT 03340129 | Melanoma | II | Nivolumab Ipilimumab | 218 | Nivolumab + Ipilimumab ± SRS | Australia | Melanoma Institute Australia | 2017–2025 |
| NCT 03955198 | Melanoma | II | Durvalumab | 100 | Radiotherapy ± Durvalumab | France | Institut Claudius Regaud | 2021–2025 |
| NCT 03175432 | Melanoma | II | Atezolizumab bevacizumab | 60 | Atezolizumab + Bevacizumab ± Cobimetinib | USA | M.D. Anderson Cancer Center | 2017–2023 |
| NCT 03873818 | Melanoma | I | Ipilimumab Pembrolizumab | 30 | Ipilimumab + Pembrolizumab | USA | M.D. Anderson Cancer Center | 2019–2023 |
| NCT 03696030 | Breast Cancer | I | / | 39 | HER2-CAR T cells | USA | City of Hope Medical Center | 2018–2023 |
| NCT 02442297 | Breast Cancer | I | / | 28 | HER2-specific T cells | USA | Baylor College of Medicine | 2016–2036 |
| NCT 03449238 | Breast Cancer | I/II | Pembrolizumab | 41 | Pembrolizumab + SRS | USA | Weill Medical College of Cornell University | 2018–2026 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, X.; Deng, X.; Xie, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, H.; Feng, B.; Zou, Y.; Wang, C. Evolutionary Trend Analysis of Research on Immunotherapy for Brain Metastasis Based on Machine-Learning Scientometrics. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 850. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17070850
Hu X, Deng X, Xie J, Zhang H, Zhang H, Feng B, Zou Y, Wang C. Evolutionary Trend Analysis of Research on Immunotherapy for Brain Metastasis Based on Machine-Learning Scientometrics. Pharmaceuticals. 2024; 17(7):850. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17070850
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Xiaoqian, Xinpei Deng, Jindong Xie, Hanqi Zhang, Huiting Zhang, Beibei Feng, Yutian Zou, and Chuhuai Wang. 2024. "Evolutionary Trend Analysis of Research on Immunotherapy for Brain Metastasis Based on Machine-Learning Scientometrics" Pharmaceuticals 17, no. 7: 850. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17070850
APA StyleHu, X., Deng, X., Xie, J., Zhang, H., Zhang, H., Feng, B., Zou, Y., & Wang, C. (2024). Evolutionary Trend Analysis of Research on Immunotherapy for Brain Metastasis Based on Machine-Learning Scientometrics. Pharmaceuticals, 17(7), 850. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17070850






