The Chemoprevention Effects of Two Herbal Mixtures on Chemically Induced Lung Tumorigenesis in Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Inhibitory Efficacy of RHF and RHT on BP-Induced Lung Tumorigenesis
2.2. Tissue Concentrations of Rosmarinic Acid and Cucurbitacin B after Feeding Mice RHT or RHF
2.3. Effects of RHF and RHT on Ki67 Expression
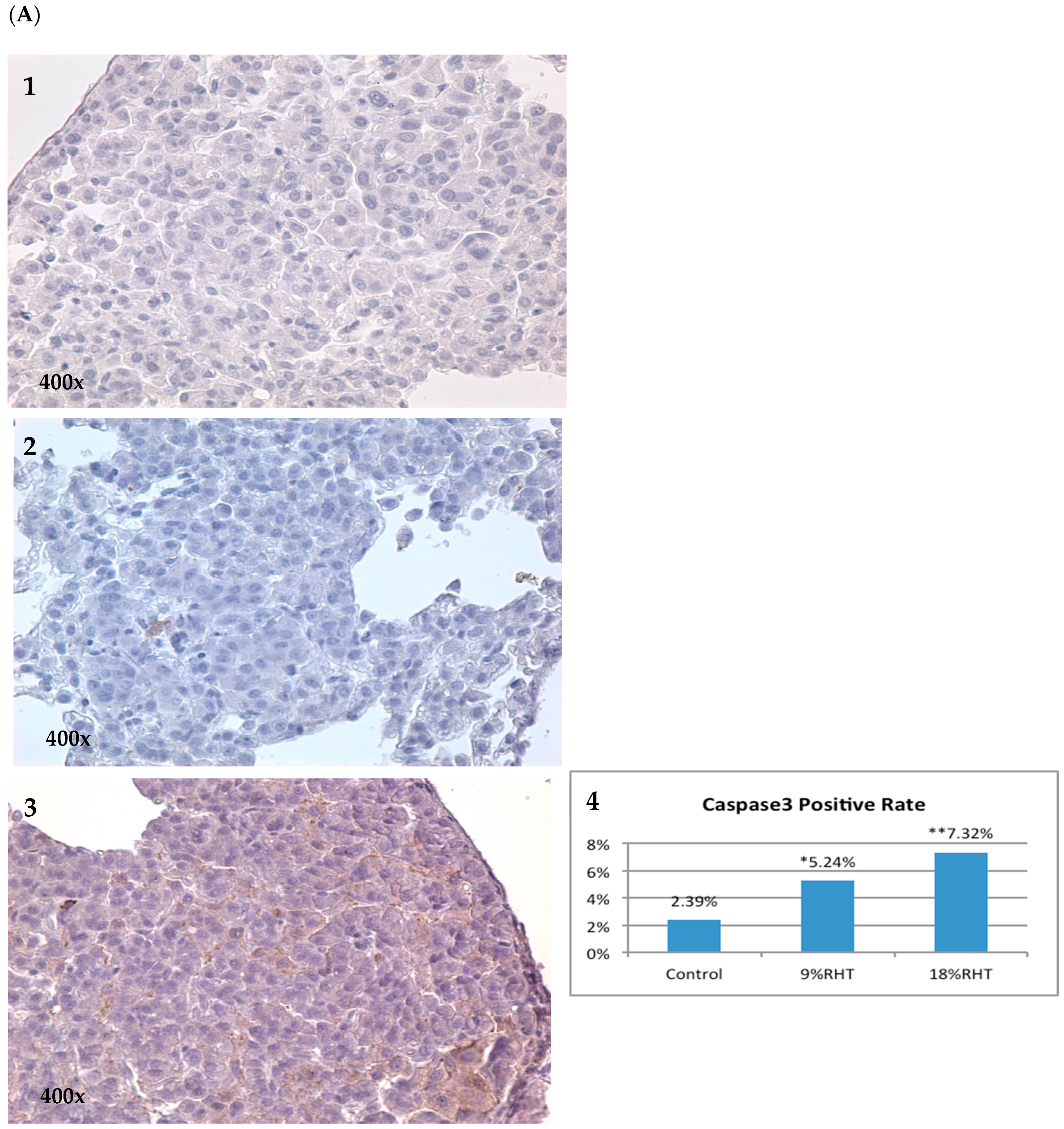
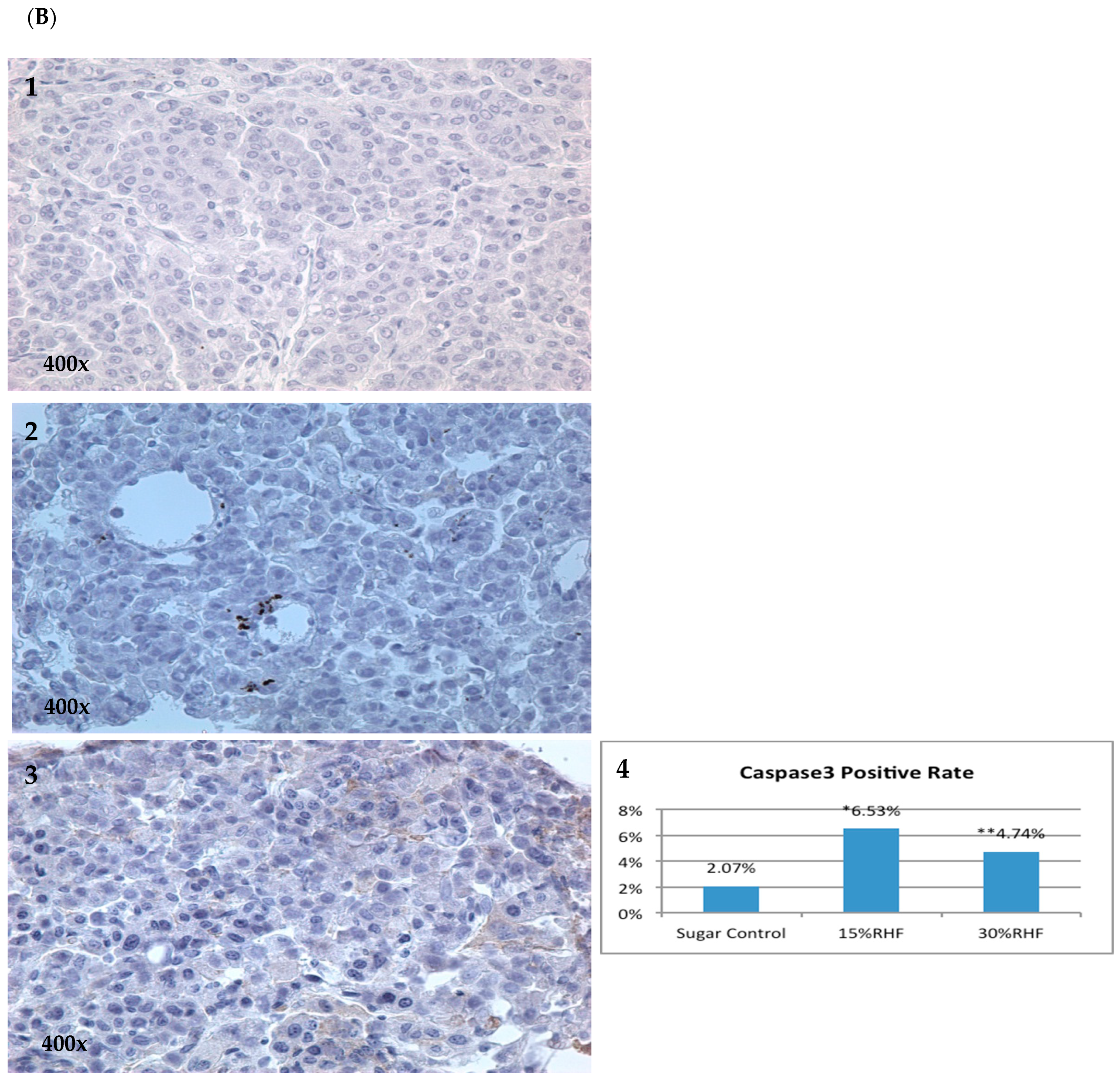
2.4. Effects of RHF and RHT on Caspase 3 Expression
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents and Animals
4.2. Animal Bioassays Using the BP-Induced Lung Tumorigenesis Model
4.3. Tissue Collection and Processing
4.4. Immunohistochemical (IHC) Analysis
4.5. Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography (UPLC) Conditions for Analysis
4.6. Mass Spectrometry (MS) Conditions for Analysis
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jemal, A.; Siegel, R.; Ward, E.; Hao, Y.; Xu, J.; Thun, M.J. Cancer statistics, 2009. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2009, 59, 225–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shopland, D.R.; Fyre, J.I.I.; Pechacek, T.F. Smoking attributable cancer mortality in 1991: Is lung cancer now the leading cause of death among smokers in the United States? J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1993, 83, 1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patterson, S.L.; Maresso, K.C.; Hawk, E. Cancer chemoprevention: Successes and failures. Clin. Chem. 2013, 59, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hennekens, C.H.; Buring, J.E.; Manson, J.E.; Stampfer, M.; Rosner, B.; Cook, N.R.; Belanger, C.; LaMotte, F.; Gaziano, J.M.; Ridker, P.M.; et al. Lack of effect of long-term supplementation with β carotene on the incidence of malignant neoplasms and cardiovascular disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 1996, 334, 1145–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, A.M.; Browman, G.P.; Levine, M.N.; D’Souza, T.; Johnstone, B.; Skingley, P.; Turner-Smith, L.; Cayco, R.; Booker, L.; Newhouse, M.; et al. The effect of the synthetic retinoid etretinate on sputum cytology: Results from a randomized trial. Br. J. Cancer 1992, 65, 737–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastorino, U.; Infante, M.; Maioli, M.; Chiesa, G.; Buyse, M.; Firket, P.; Rosmentz, N.; Clerici, M.; Soresi, E.; Valente, M.; et al. Adjuvant treatment of stage I Lung cancer with high-dose vitamin A. J. Clin. Oncol. 1993, 11, 1216–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omenn, G.S.; Goodman, G.E.; Thornquist, M.D.; Balmes, J.; Cullen, M.R.; Glass, A.; Keogh, J.P.; Meyskens, F.L., Jr.; Valanis, B.; Williams, J.H., Jr.; et al. Risk factors for lung cancer and for intervention effects in CARET, the β-Carotene and Retinol Efficacy Trial. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1996, 88, 1550–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Lippman, S.M.; Benner, S.E.; Lee, J.J.; Ro, J.Y.; Lukeman, J.M.; Morice, R.C.; Peters, E.J.; Pang, A.C.; Fritsche, H.A., Jr. Randomized placebo-controlled trial of isotretinoin in chemoprevention of bronchial squamous metaplasia. J. Clin. Oncol. 1994, 12, 937–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Zandwijk, N.; Dalesio, O.; Pastorino, U.; de Vries, N.; van Tinteren, H. EUROSCAN, a randomized trial of vitamin A and N-acetylcysteine in patients with head and neck cancer or lung cancer. For the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer Head and Neck and Lung Cancer Cooperative Group. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2000, 92, 977–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, S.; MacAulay, C.; Le Riche, J.C.; Dyachkova, Y.; Coldman, A.; Guillaud, M.; Hawk, E.; Christen, M.O.; Gazdar, A.F. A randomized phase IIb trial of anethole dithiolethione in smokers with bronchial dysplasia. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2002, 94, 1001–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabo, E. Selecting targets for cancer prevention: Where do we go from here? Nat. Rev. Cancer 2006, 6, 867–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Garbow, J.R.; Rowland, D.J.; Lubet, R.A.; Sit, D.; Law, F.; You, M. Chemoprevention of lung squamous cell carcinoma in mice by a mixture of Chinese herbs. Cancer Prev. Res. 2009, 2, 634–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, P.; Zhang, J.; Rong, Z.; Han, R.; Xu, S.; Gao, R.; Ding, Z.; Wang, J.; Feng, H.; Cao, S. Studies on medicamentous inhibitory therapy for esophageal precancerous lesions 3- and 5-year inhibitory effects of antitumor-B, retinamide and riboflavin. Proc. Chin. Acad. Med. Sci. Peking Union Med. Coll. 1990, 5, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Yao, R.; Li, J.; Yan, Y.; La Regina, M.; Lemon, W.L.; Grubbs, C.J.; Lubet, R.A.; You, M. Cancer chemopreventive activity of a mixture of Chinese herbs (antitumor B) in mouse lung tumor models. Oncogene 2004, 23, 3841–3850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bullwinkel, J.; Baron-Lühr, B.; Lüdemann, A.; Wohlenberg, C.; Gerdes, J.; Scholzen, T. Ki-67 protein is associated with ribosomal RNA transcription in quiescent and proliferating cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 2006, 3, 624–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahmanzadeh, R.; Hüttmann, G.; Gerdes, J.; Scholzen, T. Chromophore-assisted light inactivation of pKi-67 leads to inhibition of ribosomal RNA synthesis. Cell Prolif. 2007, 3, 422–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, F.; Li, G. Traditional Chinese medicine and lung cancer—From theory to practice. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 137, 11381. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, L.; Jia, Y.; Ji, K.; Sanders, A.J.; Xue, K.; Ji, J.; Mason, M.D.; Jiang, W.G. Traditional Chinese medicine in the prevention and treatment of cancer and cancer metastasis. Oncol. Lett. 2015, 10, 1240–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhuang, Z.; Guo, M.; Wu, K.; Yang, Q.; Min, X.; Cui, W.; Xu, F. Ze-Qi decoction inhibits non-small lung cancer growth and metastasis by modulating the PI3K/Akt/p53 signaling pathway. J. Tradit. Complement. Med. 2023, 13, 417–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholzen, T.; Gerdes, J. The Ki-67 protein: From the known and the unknown. J. Cell. Physiol. 2000, 3, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alnemri, E.S.; Livingston, D.J.; Nicholson, D.W.; Salvesen, G.; Thornberry, N.A.; Wong, W.W.; Yuan, J. Human ICE/CED-3 protease nomenclature. Cell 1996, 2, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.H.; Wang, F.T.; Chan, W.H. Role of caspase-3-cleaved/activated PAK2 in brusatol-triggered apoptosis of human lung cancer A549 cells. Toxicol. Res. 2022, 11, 791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Xiong, D.; Pan, J.; Wang, Y.; Hardy, M.; Kalyanaraman, B.; You, M. Chemoprevention of Lung Cancer with a Combination of Mitochondria-Targeted Compounds. Cancer 2022, 14, 2538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

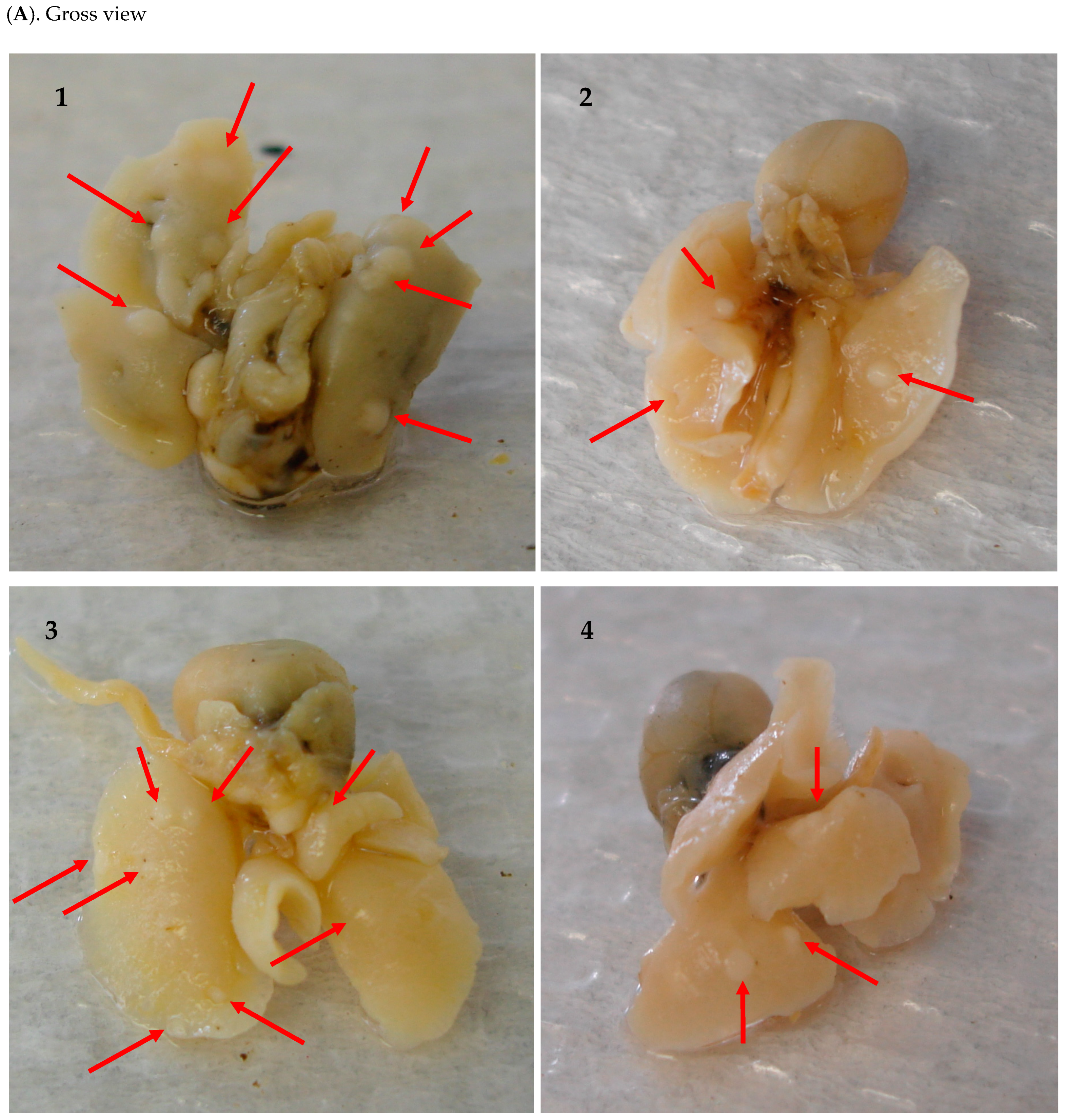
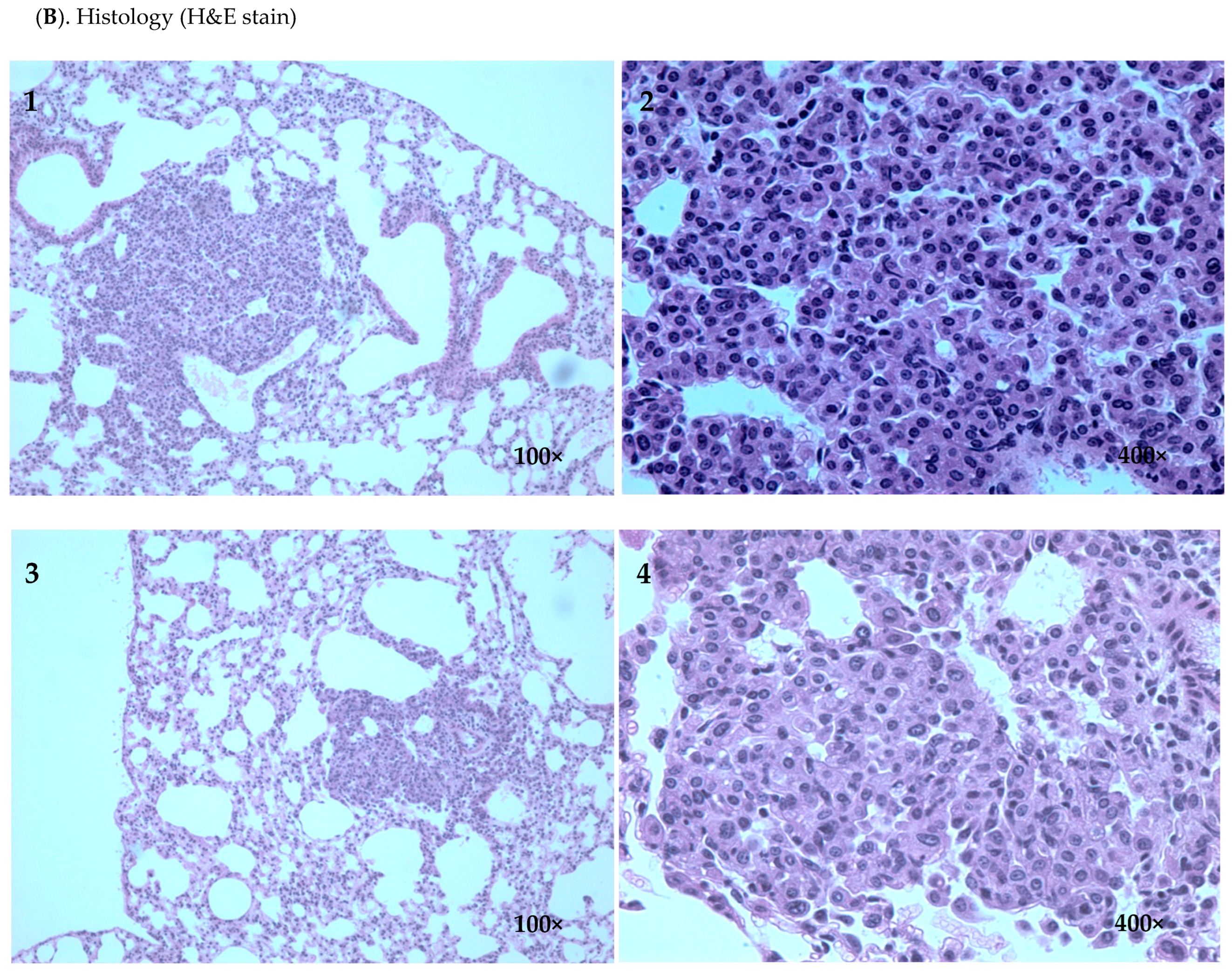

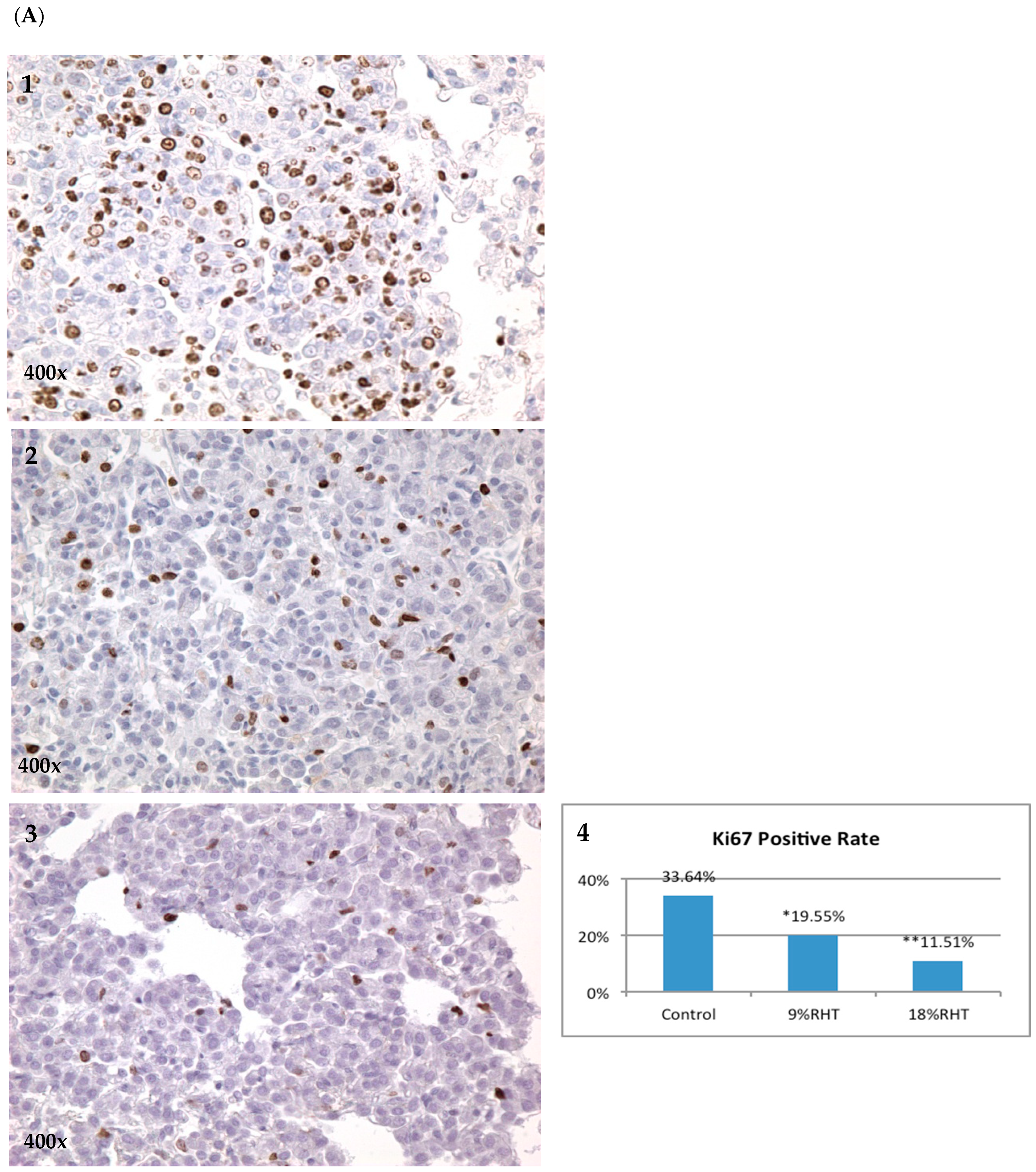
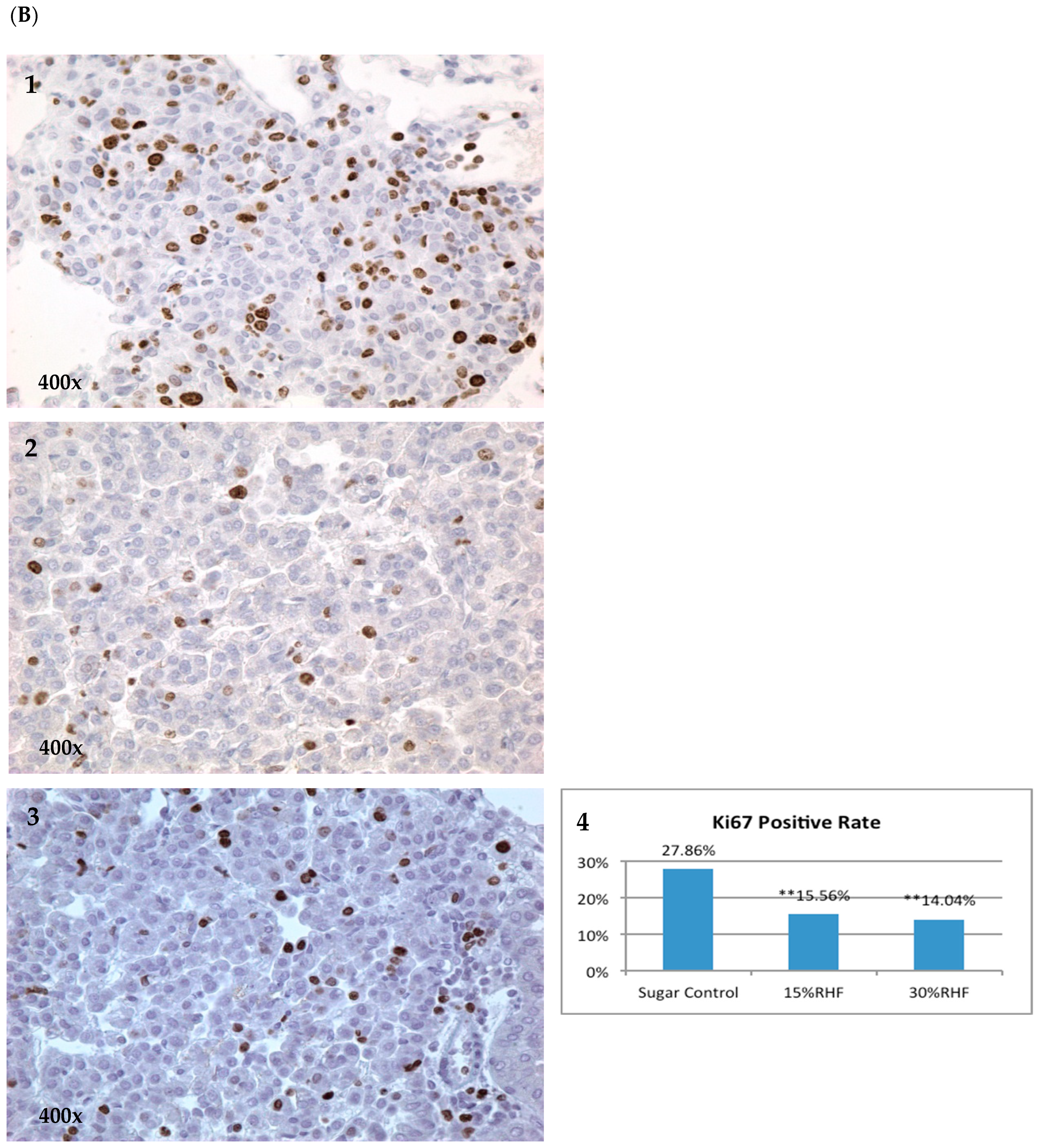
| Group | Number of Mice | Mice with Tumor | Incidence | Group | Number of Mice | Mice with Tumor | Incidence |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 17 | 17 | 100% | Control | 15 | 15 | 100% |
| 9% RHT | 15 | 13 | 87% | 15% RHF | 14 | 14 | 100% |
| 18% RHT | 14 | 14 | 100% | 30% RHF | 15 | 14 | 93% |
| Group | Number of Tumors | SD | p Value | Inhibition | Group | Tumor Load | SD | p Value | Inhibition |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 6.88 (n = 17) | 2.85 | Control | 7.74 (n = 17) | 5.09 | ||||
| 9%RHT | 4.40 (n = 15) | 3.24 | <0.05 | 36.05% | 9%RHT | 5.64 (n = 15) | 5.79 | 27.13% | |
| 18%RHT | 4.21 (n = 14) | 2.35 | <0.05 | 38.81% | 18%RHT | 3.41 (n = 14) | 4.79 | <0.05 | 55.94% |
| Group | Number of Tumors | SD | p Value | Inhibition | Group | Tumor Load | SD | p Value | Inhibition |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 7.53 (n = 15) | 3.74 | Control | 13.44 (n = 15) | 12.23 | ||||
| 15%RHF | 6.57 (n = 14) | 2.47 | 12.75% | 15%RHF | 10.97 (n = 14) | 6.83 | 18.38% | ||
| 30%RHF | 4.53 (n = 15) | 2.72 | <0.01 | 39.84% | 30%RHF | 5.15 (n = 15) | 5.54 | 0.013 | 61.68% |
| Compound | Q1 | Q3 | DP | CEP | CE | CXP |
| Rosmarinic acid | 359 | 161 | −51 | −26 | −23 | −1 |
| Cucurbitacin b | 557 | 497 | −48 | −27 | −16 | −3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, C.; Wang, Y.; Gao, S.; Hu, M.; You, M. The Chemoprevention Effects of Two Herbal Mixtures on Chemically Induced Lung Tumorigenesis in Mice. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1666. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16121666
Li C, Wang Y, Gao S, Hu M, You M. The Chemoprevention Effects of Two Herbal Mixtures on Chemically Induced Lung Tumorigenesis in Mice. Pharmaceuticals. 2023; 16(12):1666. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16121666
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Chunjie, Yian Wang, Song Gao, Ming Hu, and Ming You. 2023. "The Chemoprevention Effects of Two Herbal Mixtures on Chemically Induced Lung Tumorigenesis in Mice" Pharmaceuticals 16, no. 12: 1666. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16121666
APA StyleLi, C., Wang, Y., Gao, S., Hu, M., & You, M. (2023). The Chemoprevention Effects of Two Herbal Mixtures on Chemically Induced Lung Tumorigenesis in Mice. Pharmaceuticals, 16(12), 1666. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16121666







