Preparation and Evaluation of 64Cu-Radiolabled Dual-Ligand Multifunctional Gold Nanoparticles for Tumor Theragnosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Synthesis of AuNP Conjugates
2.2. Cellular Uptake of AuNP Conjugates Labeled with Iodine-125
2.3. Chelator-Free Cu-64 Labeling
2.4. Small-Animal PET Imaging and Biodistribution
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals and Materials
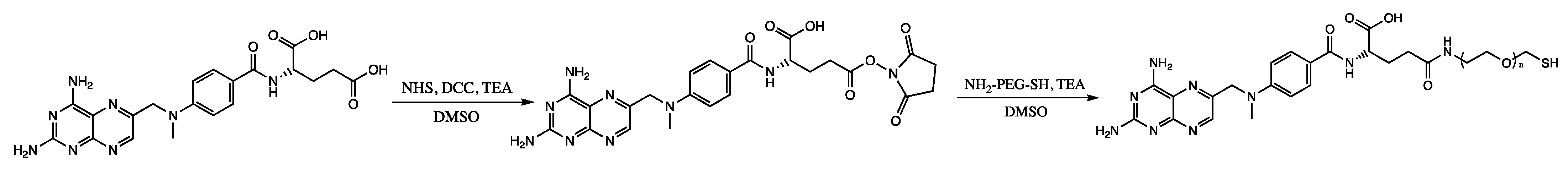
3.2. Synthesis of MTX-PEG-SH
3.3. Synthesis of Glucose-PEG-SH
3.4. Physical Production of Colloidal AuNPs
3.5. Quantitatively Controlled Conjugation of AuMPs
3.6. Preparation of 64Cu-Labeled AuNP Conjugates
3.7. Cellular Uptake of AuNPs
3.8. Small-Animal PET Imaging and Biodistributions
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Beik, J.; Khademi, S.; Attaran, N.; Sarkar, S.; Shakeri-Zadeh, A.; Ghaznavi, H.; Ghadiri, H. A Nanotechnology-based Strategy to Increase the Efficiency of Cancer Diagnosis and Therapy: Folate-conjugated Gold Nanoparticles. Curr. Med. Chem. 2017, 24, 4399–4416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, P.B.; Machado, R.; Pironi, A.M.; Alves, R.C.; de Araújo, P.R.; Dragalzew, A.C.; Dalberto, I.; Chorilli, M. Recent Advances in the Use of Metallic Nanoparticles with Antitumoral Action—Review. Curr. Med. Chem. 2019, 26, 2108–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambasta, R.K.; Gupta, R.; Kumar, D.; Bhattacharya, S.; Sarkar, A.; Kumar, P. Can luteolin be a therapeutic molecule for both colon cancer and diabetes? Brief. Funct. Genom. 2018, 18, 230–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization [Internet]. Available online: http/www.who.int (accessed on 14 October 2022).
- Sen, S.; Koyyalamudi, V.; Smith, D.D.; Weis, R.A.; Molloy, M.; Spence, A.L.; Kaye, A.J.; Labrie-Brown, C.C.; Hall, M.O.; Cornett, E.M.; et al. The role of regional anesthesia in the propagation of cancer: A comprehensive review. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Anaesthesiol. 2019, 33, 507–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keyhanian, K.; Mansoori, G.A.; Rahimpour, M. Prospects for cancer nanotechnology treatment by azurin. Dyn. Biochem. Proc. Biotech. Mol. Biol. 2010, 4, 48–66. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, J.; Chen, X.; Huang, P. Graphene-based nanomaterials for bioimaging. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 105 Pt B, 242–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, H.; Peng, R.; Liu, Z. Carbon nanotubes for biomedi- cal imaging: The recent advances. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 1951–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beik, J.; Abed, Z.; Ghoreishi, F.S.; Hosseini-Nami, S.; Mehrzadi, S.; Shakeri-Zadeh, A.; Kamrava, S.K. Nanotech- nology in hyperthermia cancer therapy: From fundamental principles to advanced applications. J. Control. Release 2016, 235, 205–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Her, S.; Jaffray, D.A.; Allen, C. Gold nanoparticles for applications in cancer radiotherapy: Mechanisms and recent advancements. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2017, 109, 84–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neal, D.P.; Hirsch, L.R.; Halas, N.J.; Payne, J.D.; West, J.L. Photo-thermal tumor ablation in mice using near infrared-absorbing nanoparticles. Cancer Lett. 2004, 209, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, C.-H.; Chen, C.D.; Wang, C.R.C. Highly efficient, wavelength-tunable, gold nanoparticle based optothermal nanoconvertors. J. Phys. Chem. 2005, 109, 11135–11138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wust, P.; Hildebrandt, B.; Sreenivasa, G.; Rau, B.; Gellerman, J.; Riess, H.; Felix, R.; Schlag, P.M. Hyperthermia in combined treatment of cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2002, 3, 487–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, C.J.; Gole, A.M.; Stone, J.W.; Sisco, P.N.; Akliany, A.M.; Goldsmith, E.C.; Baxter, S.C. Gold nanoparticles in biology: Beyond toxicity to cellular imaging. Acc. Chem. Res. 2008, 41, 1721–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Pang, Y.; Ku, G.; Xie, X.; Stoica, G.; Wang, L.V. Three-dimensional laser-induced photoacoustic tomography of mouse brain with the skin and skull intact. Opt. Lett. 2003, 28, 1739–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Pang, Y.; Ku, G.; Xie, X.; Stoica, G.; Wang, L.V. Noninvasive laser-induced photoacoustic tomography for structure and functional in vivo imaging of the brain. Nat. Biotechnol. 2003, 21, 803–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, A.; Shao, X.; Rajian, J.R.; Zhang, H.; Chamberland, D.L.; Kotov, N.A.; Wang, X.D. Dual-mode imaging with radiolabeled gold nanorod. J. Biomed. Opt. 2011, 16, 0513071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, C.; Qian, W.; Shao, X.; Xie, Z.; Cheng, X.; Liu, S.; Cheng, Q.; Liu, B.; Wang, X. Plasmonic Nanoparticles with Quantitatively Controlled Bioconjugation for Photoacoustic Imaging of Live Cancer Cells. Adv. Sci. 2016, 3, 1600237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, C.C.; Miranda, O.R.; Gider, B.; Ghosh, P.S.; Kim, I.B.; Erdogan, B.; Krovi, S.A.; Bunz, U.H.; Rotello, V.M. Detection and identification of proteins using nanoparticle-fluorescent polymer ‘chemical nose’ sensors. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2007, 2, 318–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, J.C.; Estroff, L.A.; Kriebel, J.K.; Nuzzo, R.G.; Whitesides, G.M. Self-assembled monolayers of thiolates on metals as a form of nanotechnology. Chem. Rev. 2005, 105, 1103–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, X.; Peng, X.H.; Ansari, D.O.; Yin-Goen, Q.; Chen, G.Z.; Shin, D.M.; Yang, L.; Young, A.N.; Wang, M.D.; Nie, S. In vivo tumor targeting and spectroscopic detection with surface-enhanced Raman nanoparticle tags. Nat. Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mullen, D.G.; Fang, M.; Desai, A.; Baker, J.R.; Orr, B.G.; Banaszak Holl, M.M. A quantitative assessment of nanoparticle-ligand distributions: Implications for targeted drug and imaging delivery in dendrimer conjugates. ACS Nano. 2010, 4, 657–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, W.; Murakami, M.; Ichikawa, Y.; Che, Y. Highly Efficient and Controllable PEGylation of Gold Nanoparticles Prepared by Femtosecond Laser Ablation in Water. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 23293–23298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, X.; Agarwal, A.; Rajian, J.R.; Kotov, N.A.; Wang, X. Synthesis and bioevaluation of ¹²⁵I-labeled gold nanorods. Nanotechnology 2011, 22, 1351021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Agarwal, A.; Shao, X.; Rajian, J.R.; Chamberland, D.L.; Kotov, N.A.; Wang, X.D. Photoacoustic and Nuclear Imaging of [125I]-labeled Gold Nanorod Contrast Agent. Proc. SPIE 2011, 7899, 789924. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, X.; Zhang, H.; Rajian, J.R.; Chamberland, D.L.; Sherman, P.S.; Quesada, C.A.; Koch, A.E.; Kotov, N.A.; Wang, X. 125I-labeled gold nanorods for targeted imaging of inflammation. ACS Nano. 2011, 11, 8967–8973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, X.; Schnau, P.; Qian, W.; Wang, X. Quantitatively Understanding Cellular Uptake of Gold Nanoparticles via Radioactivity Analysis. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2015, 15, 3834–3838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papachristou, M.; Kastis, G.A.; Stavrou, P.Z.; Xanthopoulos, S.; Furenlid, L.R.; Datseris, I.E.; Bouziotis, P. Radiolabeled methotrexate as a diagnostic agent of inflammatory target sites: A proof-of-concept study. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 17, 2442–2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tielens, F.; Santos, E. AuS and SH Bond Formation/Breaking during the Formation of Alkanethiol SAMs on Au(111): A Theoretical Study. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 9444–9452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirkin, C.A.; Letsinger, R.L.; Mucic, R.C.; Storhoff, J.J. A DNA-based method for rationally assembling nanoparticles into macroscopic materials. Nature 1996, 382, 607–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rang, H.P.; Dale, M.M.; Ritter, J.M.; Flower, R.H.; Henderson, G. Anticancer drugs. In Pharmacology, 7th ed.; Rang, H.P., Dale, M.M., Eds.; Churchill Livingstone Elsevier: London, UK, 2011; pp. 673–688. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Lin, J.; Ma, J.; Song, L.; Lin, H.; Tang, B.; Chen, D.; Su, G.; Ye, S.; Zhu, X.; et al. Methotrexate-Camptothecin Prodrug Nanoassemblies as a Versatile Nanoplatform for Biomodal Imaging-Guided Self-Active Targeted and Synergistic Chemotherapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 34650–34665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Chen, S.; Hua, L.; Zhang, C.; Chen, M.; Chen, D.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, M.; Song, X.; et al. Self-targeted salinomycin-loaded DSPE-PEG-methotrexate nanomicelles for targeting both head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cancer cells and cancer stem cells. Nanomedicine 2017, 12, 295–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, J.; Pope, L.E.; VitoIs, K.S.; Huennekens, F.M. Affinity labelling of folate transport proteins with the N’-hydroxysuccinimide ester of the γ-isomer of fluorescein-methotrexate. Biochemistry 1991, 30, 4573–4580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, A.S.; Love, W.G.; Williams, B.D. Synthesis of methotrexate-dimyristoylphpsphatidylethanolamine analogs and characterization of methotrexate release in vitro. Int. J. Pharm. 1992, 85, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauwels, E.K.; McCready, V.R.; Stoot, J.H.; van Deurzen, D.F. The mechanism of accumulation of tumour-localising radiopharmaceuticals. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. 1998, 25, 277–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irure, A.; Marradi, M.; Arnáiz, B.; Genicio, N.; Padro, D.; Penadés, S. Sugar/gadolinium-loaded gold nanoparticles for labelling and imaging cells by magnetic resonance imaging. Biomater. Sci. 2013, 1, 658–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marradi, M.; Alcántara, D.; de la Fuente, J.M.; García-Martín, M.L.; Cerdán, S.; Penadés, S. Paramagnetic Gd-based gold glyconanoparticles as probes for MRI: Tuning relaxivities with sugars. Chem. Commun. 2009, 26, 3922–3924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Hu, Z.; Murakami, M.; Che, Y. Production of Metal and Metal-Alloy Nanoparticles with High Repetition Rate Ultrafast Pulsed Laser Ablation in Liquids. U.S. Patent 8,246,714, 21 August 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.; Hu, Z.; Che, Y.; Chen, Y.; Pan, X. Nanoparticle generation in ultrafast pulsed laser ablation of nickel. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 90, 044103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biesso, A.; Qian, W.; Huang, X.; El-Sayed, M.A. Gold Nanoparticles Surface Plasmon Field Effects on the Proton Pump Process of the Bacteriorhodopsin Photosynthesis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 2442–2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niidome, T.; Yamagata, M.; Okamoto, Y.; Akiyama, Y.; Takahashi, H.; Kawan, T.; Katayama, Y.; Niidome, Y. PEG—Modified Gold Nanorods with a Stealth Character for In Vivo Applications. J. Control. Release 2006, 114, 343–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahbari, R.; Sheahan, T.; Modes, V.; Collier, P.; Macfarlane, C.; Badge, R.M. A novel L1 retrotransposon marker for HeLa cell line identification. BioTechniques 2009, 46, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuire, J.J. Anticancer antifolates: Current status and future directions. Curr. Pharm. Design. 2003, 9, 2593–2613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pretze, M.; van der Meulen, N.P.; Wängler, C.; Schibli, R.; Wängler, B. Targeted 64Cu-labeled gold nanoparticles for dual imaging with positron emission tomography and optical imaging. J. Label. Compd. Radiopharm. 2019, 62, 471–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Huang, X.; Yan, X.; Wang, Y.; Guo, J.; Jacobson, O.; Liu, D.; Szajek, L.P.; Zhu, W.; Niu, G.; et al. Chelator-Free 64Cu-Intergrated Gold Nanomaterials for Positron Emission Tomography Imaging Guided Photothermal Cancer Therapy. ACS Nano. 2014, 8, 8438–8446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| AuNP Conjugate | 1st Ligand | 2nd Ligand |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | PEG | RGD |
| 2 | PEG | MTX |
| 3 | PEG | Glucose |
| 4 | MTX | RGD |
| 5 | Glucose | RGD |
| 6 | Glucose | MTX |
| AuNP Conjugate | After 1st Ligand Conjugation (nm) | After 2nd Ligand Conjugation (nm) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 5.1 | 1.8 |
| 2 | 5.1 | 2.5 |
| 3 | 5.1 | 4.2 |
| 4 | 4.5 | 2.1 |
| 5 | 8.2 | 2.2 |
| 6 | 8.2 | 3.1 |
| AuNP Conjugate | Time Post-Injection | Figure | Tumor to Muscle Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|
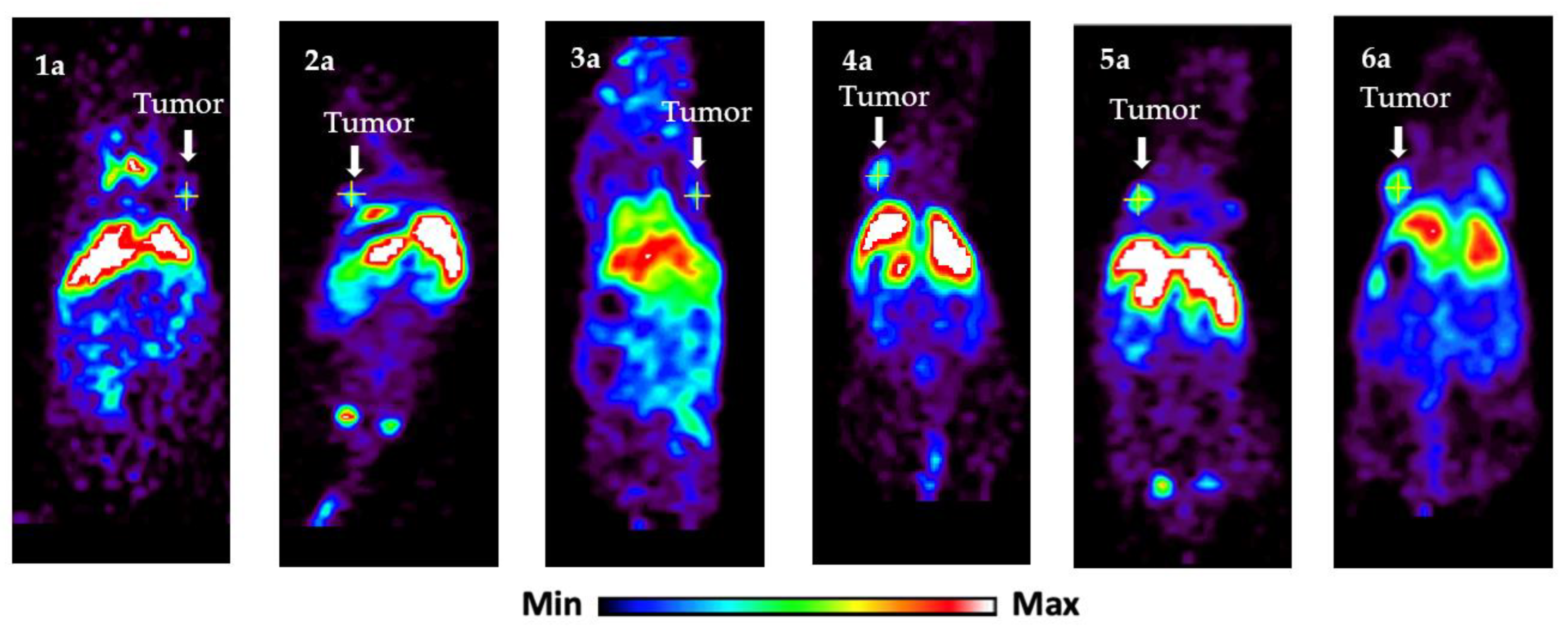
| 1 | 22 h | Figure 2, panel 1a | 4.8 ± 2.0 |
| 2 | 22 h | Figure 2, panel 2a | 5.0 ± 2.5 |
| 3 | 22 h | Figure 2, panel 3a | 3.9 ± 2.4 |
| 4 | 22 h | Figure 2, panel 4a | 5.3 ± 2.0 |
| 5 | 22 h | Figure 2, panel 5a | 5.5 ± 2.1 |
| 6 | 22 h | Figure 2, panel 6a | 5.4 ± 2.1 |
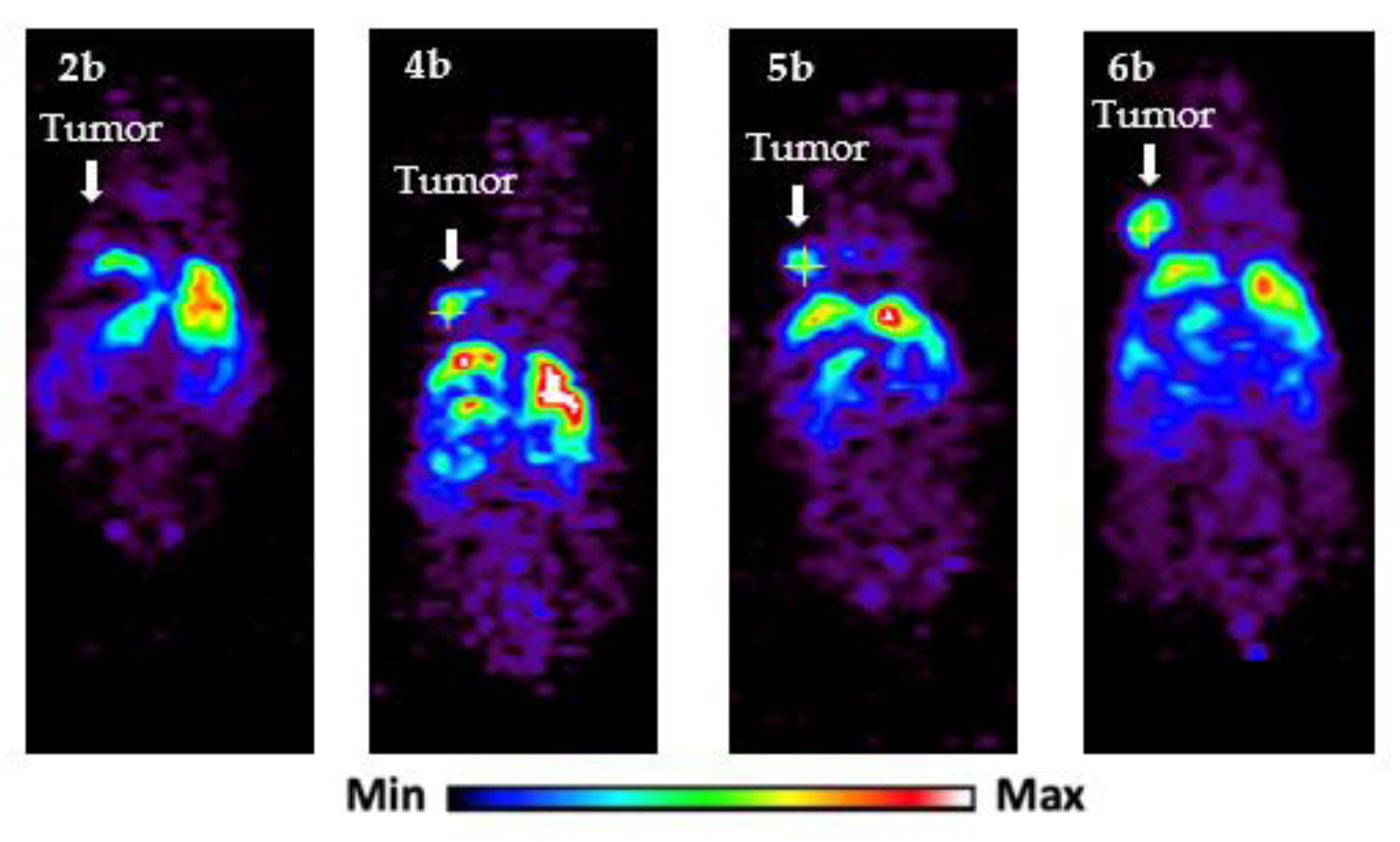
| 2 | 45 h | Figure 3, panel 2b | 3.3 ± 2.1 |
| 4 | 45 h | Figure 3, panel 4b | 3.0 ± 2.4 |
| 5 | 45 h | Figure 3, panel 5b | 4.9 ± 1.6 |
| 6 | 45 h | Figure 3, panel 6b | 7.9 ± 2.1 |
| AuNP Conjugate | Time Post-Injection | Figure | Tumor SUV Max |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 22 h | Figure 2, panel 1a | 1.7 ± 1.1 |
| 2 | 22 h | Figure 2, panel 2a | 1.4 ± 0.7 |
| 3 | 22 h | Figure 2, panel 3a | 2.0 ± 1.0 |
| 4 | 22 h | Figure 2, panel 4a | 1.9 ± 0.4 |
| 5 | 22 h | Figure 2, panel 5a | 2.6 ± 0.9 |
| 6 | 22 h | Figure 2, panel 6a | 2.6 ± 0.5 |
| 2 | 45 h | Figure 3, panel 2b | 2.8 ± 2.0 |
| 4 | 45 h | Figure 3, panel 4b | 3.5 ± 2.3 |
| 5 | 45 h | Figure 3, panel 5b | 5.3 ± 2.8 |
| 6 | 45 h | Figure 3, panel 6b | 5.0 ± 2.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mhanna, K.; Qian, W.; Zhong, Z.; Brooks, A.F.; Ouchi, E.; Stauff, J.; Arteaga, J.; Papachristou, M.; Datseris, I.E.; Liu, B.; et al. Preparation and Evaluation of 64Cu-Radiolabled Dual-Ligand Multifunctional Gold Nanoparticles for Tumor Theragnosis. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16010071
Mhanna K, Qian W, Zhong Z, Brooks AF, Ouchi E, Stauff J, Arteaga J, Papachristou M, Datseris IE, Liu B, et al. Preparation and Evaluation of 64Cu-Radiolabled Dual-Ligand Multifunctional Gold Nanoparticles for Tumor Theragnosis. Pharmaceuticals. 2023; 16(1):71. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16010071
Chicago/Turabian StyleMhanna, Karim, Wei Qian, Ziyun Zhong, Allen F. Brooks, Erika Ouchi, Jenelle Stauff, Janna Arteaga, Maria Papachristou, Ioannis E. Datseris, Bing Liu, and et al. 2023. "Preparation and Evaluation of 64Cu-Radiolabled Dual-Ligand Multifunctional Gold Nanoparticles for Tumor Theragnosis" Pharmaceuticals 16, no. 1: 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16010071
APA StyleMhanna, K., Qian, W., Zhong, Z., Brooks, A. F., Ouchi, E., Stauff, J., Arteaga, J., Papachristou, M., Datseris, I. E., Liu, B., Shao, X., & Scott, P. J. H. (2023). Preparation and Evaluation of 64Cu-Radiolabled Dual-Ligand Multifunctional Gold Nanoparticles for Tumor Theragnosis. Pharmaceuticals, 16(1), 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16010071






