Mangifera indica ‘Namdokmai’ Prevents Neuronal Cells from Amyloid Peptide Toxicity and Inhibits BACE-1 Activities in a Drosophila Model of Alzheimer’s Amyloidosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. In Vitro Screening on Enzyme Inhibition
2.2. Phytochemical Profile
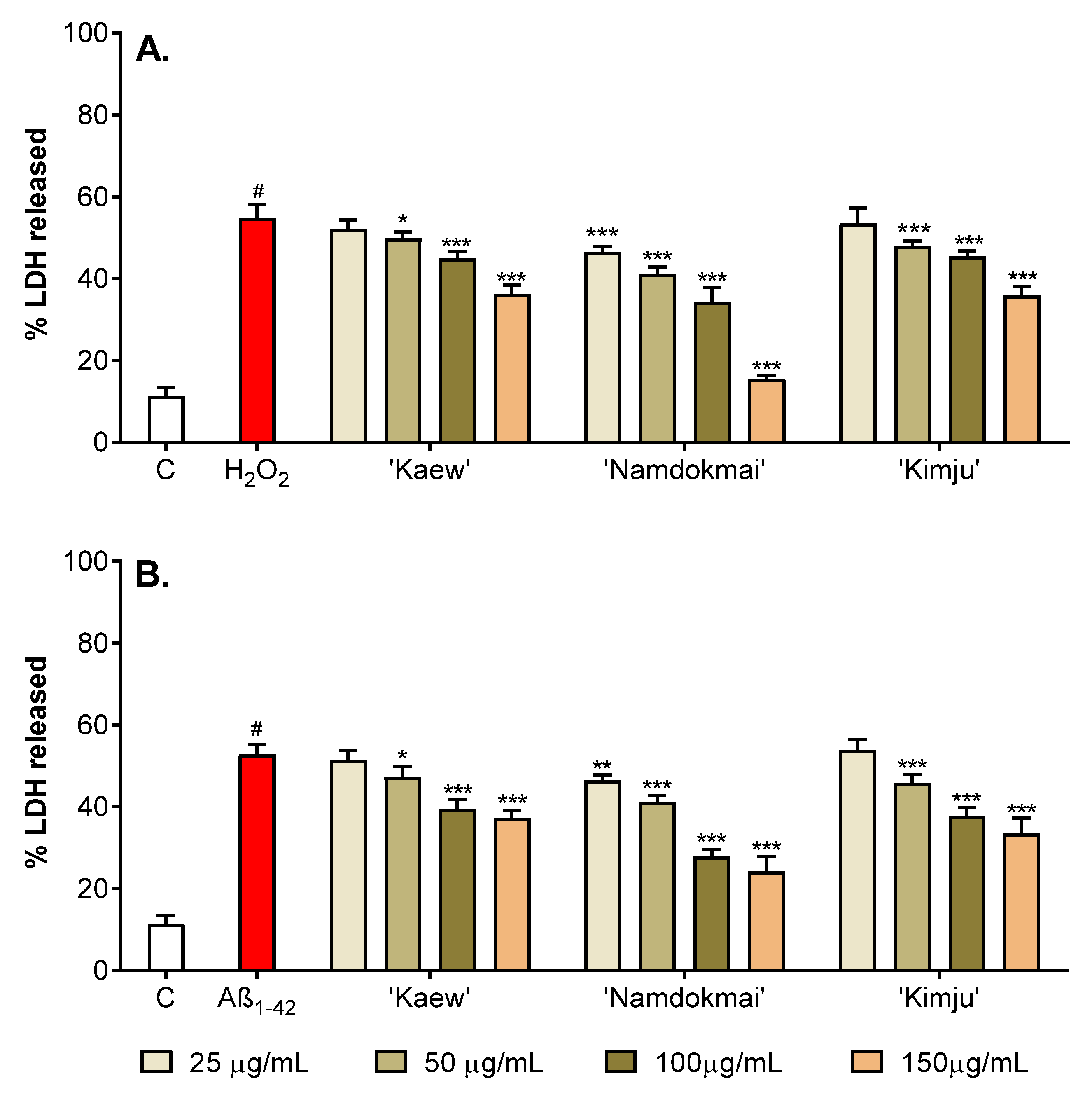
2.3. Neurotoxicity of the Selected Fruit Extracts
2.4. Neuroprotective Effects of the Selected Fruit Extracts
2.5. Anti-Alzheimer’s Disease Activities in Drosophila Model
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Sample Preparation and Extraction
4.2. Determination of Enzyme Inhibitory Activities
4.3. Determination of Phytochemical Profiles
4.4. Cell Culture Preparation
4.5. Preparation of Aβ Peptides
4.6. Cytotoxicity of the Selected Fruit Exacts
4.7. Neuroprotective Effects against H2O2- and Aβ1–42-Induced Cytotoxicity
4.7.1. Cell Viability Assay
4.7.2. Lactate Dehydrogenase (LDH) Assay
4.7.3. Glutathione (GSH) Assay
4.8. Drosophila Stock, Culture and Treatment
4.9. Drosophila Locomotor Assay
4.10. Determination of Aβ1–42 Peptide by Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) and BACE-1 Activity in Drosophila Brain
4.11. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- James, B.D.; Leurgans, S.E.; Hebert, L.E.; Scherr, P.A.; Yaffe, K.; Bennett, D.A. Contribution of Alzheimer disease to mortality in the United States. Neurology 2014, 82, 1045–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, C.; Kivipelto, M.; von Strauss, E. Epidemiology of Alzheimer’s disease: Occurrence, determinants, and strategies toward intervention. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 2009, 11, 111–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.F.; Xu, T.H.; Yan, Y.; Zhou, Y.R.; Jiang, Y.; Melcher, K.; Xu, H.E. Amyloid beta: Structure, biology and structure-based therapeutic development. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2017, 38, 1205–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehmann, S.; Delaby, C.; Boursier, G.; Catteau, C.; Ginestet, N.; Tiers, L.; Maceski, A.; Navucet, S.; Paquet, C.; Dumurgier, J.; et al. Relevance of Aβ42/40 Ratio for Detection of Alzheimer Disease Pathology in Clinical Routine: The PLM(R) Scale. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2018, 10, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moussa-Pacha, N.M.; Abdin, S.M.; Omar, H.A.; Alniss, H.; Al-Tel, T.H. BACE1 inhibitors: Current status and future directions in treating Alzheimer’s disease. Med. Res. Rev. 2020, 40, 339–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoval, H.; Lichtenberg, D.; Gazit, E. The molecular mechanisms of the anti-amyloid effects of phenols. Amyloid 2007, 14, 73–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mufson, E.J.; Counts, S.E.; Perez, S.E.; Ginsberg, S.D. Cholinergic system during the progression of Alzheimer’s disease: Therapeutic implications. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2008, 8, 1703–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atri, A. Current and Future Treatments in Alzheimer’s Disease. Semin. Neurol. 2019, 39, 227–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancuso, C.; Bates, T.E.; Butterfield, D.A.; Calafato, S.; Cornelius, C.; De Lorenzo, A.; Dinkova Kostova, A.T.; Calabrese, V. Natural antioxidants in Alzheimer’s disease. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2007, 16, 1921–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, M.R.; Lee, S.H.; Choi, S.H.; Bae, K.H.; Seong, Y.H.; Lee, K.B.; Song, K.S. Plant Phenolics as β-Secretase (BACE1) Inhibitors. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2006, 15, 617–624. [Google Scholar]
- Hajipour, S.; Sarkaki, A.; Farbood, Y.; Eidi, A.; Mortazavi, P.; Valizadeh, Z. Effect of Gallic Acid on Dementia Type of Alzheimer Disease in Rats: Electrophysiological and Histological Studies. Basic Clin. Neurosci. 2016, 7, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hole, K.L.; Williams, R.J. Flavonoids as an Intervention for Alzheimer’s Disease: Progress and Hurdles Towards Defining a Mechanism of Action. Brain Plast. 2021, 6, 167–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spencer, J.P. Flavonoids and brain health: Multiple effects underpinned by common mechanisms. Genes Nutr. 2009, 4, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramezani, M.; Meymand, A.Z.; Khodagholi, F.; Kamsorkh, H.M.; Asadi, E.; Noori, M.; Rahimian, K.; Shahrbabaki, A.S.; Talebi, A.; Parsaiyan, H.; et al. A role for flavonoids in the prevention and/or treatment of cognitive dysfunction, learning, and memory deficits: A review of preclinical and clinical studies. Nutr. Neurosci. 2022, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temviriyanukul, P.; Kittibunchakul, S.; Trisonthi, P.; Inthachat, W.; Siriwan, D.; Suttisansanee, U. Analysis of Phytonutrients, Anti-Mutagenic and Chemopreventive Effects of Tropical Fruit Extracts. Foods 2021, 10, 2600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suttisansanee, U.; Charoenkiatkul, S.; Jongruaysup, B.; Tabtimsri, S.; Siriwan, D.; Temviriyanukul, P. Mulberry Fruit Cultivar ‘Chiang Mai’ Prevents Beta-Amyloid Toxicity in PC12 Neuronal Cells and in a Drosophila Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Molecules 2020, 25, 1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temviriyanukul, P.; Sritalahareuthai, V.; Jom, K.N.; Jongruaysup, B.; Tabtimsri, S.; Pruesapan, K.; Thangsiri, S.; Inthachat, W.; Siriwan, D.; Charoenkiatkul, S.; et al. Comparison of Phytochemicals, Antioxidant, and In Vitro Anti-Alzheimer Properties of Twenty-Seven Morus spp. Cultivated in Thailand. Molecules 2020, 25, 2600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momtazi-Borojeni, A.A.; Sadeghi-Aliabadi, H.; Rabbani, M.; Ghannadi, A.; Abdollahi, E. Cognitive enhancing of pineapple extract and juice in scopolamine-induced amnesia in mice. Res. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 12, 257–264. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, Y.R.; Jong, Y.X.; Balakrishnan, M.; Bok, Z.K.; Weng, J.K.K.; Tay, K.C.; Goh, B.H.; Ong, Y.S.; Chan, K.G.; Lee, L.H.; et al. Beneficial Role of Carica papaya Extracts and Phytochemicals on Oxidative Stress and Related Diseases: A Mini Review. Biology 2021, 10, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, C.; Jeong, H.; Choi, G.; Kwak, J.; Kim, J.; Park, S.; Kim, D.; Shim, K.; Choi, S.; Heo, H. Neuronal cell protective effects of hot water extracts from Guava (Psidium guajava L.) fruit and leaf. Korean J. Food Preserv. 2011, 18, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Plekratoke, K.; Waiwut, P.; Suchaichit, N.P.; Bunyapraphatsara, N.; Reubroycharoen, P.; Boonyarat, C. Neuroprotective Effect of Durio zibithinus against Beta Amyloid. Thai J. Pharmacol. 2018, 40, 14–25. [Google Scholar]
- Wattanathorn, J.; Muchimapura, S.; Thukham-Mee, W.; Ingkaninan, K.; Wittaya-Areekul, S. Mangifera indica fruit extract improves memory impairment, cholinergic dysfunction, and oxidative stress damage in animal model of mild cognitive impairment. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2014, 2014, 132097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirichai, P.; Kittibunchakul, S.; Thangsiri, S.; On-Nom, N.; Chupeerach, C.; Temviriyanukul, P.; Inthachat, W.; Nuchuchua, O.; Aursalung, A.; Sahasakul, Y.; et al. Impact of Drying Processes on Phenolics and In Vitro Health-Related Activities of Indigenous Plants in Thailand. Plants 2022, 11, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.H.; Lane, H.Y. Plasma Glutathione Levels Decreased with Cognitive Decline among People with Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI): A Two-Year Prospective Study. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, Y.P.; Rai, H.; Singh, G.; Singh, G.K.; Mishra, S.; Kumar, S.; Srikrishna, S.; Modi, G. A review on ferulic acid and analogs based scaffolds for the management of Alzheimer’s disease. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 215, 113278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajialyani, M.; Hosein Farzaei, M.; Echeverría, J.; Nabavi, S.M.; Uriarte, E.; Sobarzo-Sánchez, E. Hesperidin as a Neuroprotective Agent: A Review of Animal and Clinical Evidence. Molecules 2019, 24, 648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oboh, G.; Agunloye, O.M.; Akinyemi, A.J.; Ademiluyi, A.O.; Adefegha, S.A. Comparative study on the inhibitory effect of caffeic and chlorogenic acids on key enzymes linked to Alzheimer’s disease and some pro-oxidant induced oxidative stress in rats’ brain-in vitro. Neurochem. Res. 2013, 38, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Mori, A.; Chen, Q.; Zhao, B. Fermented papaya preparation attenuates beta-amyloid precursor protein: Beta-amyloid-mediated copper neurotoxicity in beta-amyloid precursor protein and beta-amyloid precursor protein Swedish mutation overexpressing SH-SY5Y cells. Neuroscience 2006, 143, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.E.; Kim, D.H.; Park, S.J.; Kim, J.M.; Lee, Y.W.; Jung, J.M.; Lee, C.H.; Hong, J.G.; Liu, X.; Cai, M.; et al. Neuroprotective effect of sinapic acid in a mouse model of amyloid β(1-42) protein-induced Alzheimer’s disease. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2012, 103, 260–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ademosun, A.O.; Oboh, G.; Bello, F.; Ayeni, P.O. Antioxidative Properties and Effect of Quercetin and Its Glycosylated Form (Rutin) on Acetylcholinesterase and Butyrylcholinesterase Activities. J. Evid. Based. Complem. Altern. Med. 2016, 21, Np11-7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szwajgier, D.; Borowiec, K. Phenolic acids from malt are efficient acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase inhibitors. J. Inst. Brew. 2012, 118, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penido, A.B.; De Morais, S.M.; Ribeiro, A.B.; Alves, D.R.; Rodrigues, A.L.; Dos Santos, L.H.; de Menezes, J.E. Medicinal Plants from Northeastern Brazil against Alzheimer’s Disease. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 2017, 1753673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palafox-Carlos, H.; Yahia, E.M.; González-Aguilar, G.A. Identification and quantification of major phenolic compounds from mango (Mangifera indica, cv. Ataulfo) fruit by HPLC–DAD–MS/MS-ESI and their individual contribution to the antioxidant activity during ripening. Food Chem. 2012, 135, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, S.M.R.; Barbosa, L.C.A.; Queiroz, J.H.; Knödler, M.; Schieber, A. Phenolic compounds and antioxidant capacity of Brazilian mango (Mangifera indica L.) varieties. Food Chem. 2008, 110, 620–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Chen, X.; Liu, J.; Ma, Q.; Zhuo, Z.; Chen, H.; Zhou, L.; Yang, S.; Zheng, L.; Ning, C.; et al. Gallic acid disruption of Aβ(1-42) aggregation rescues cognitive decline of APP/PS1 double transgenic mouse. Neurobiol. Dis. 2019, 124, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimmyo, Y.; Kihara, T.; Akaike, A.; Niidome, T.; Sugimoto, H. Flavonols and flavones as BACE-1 inhibitors: Structure–activity relationship in cell-free, cell-based and in silico studies reveal novel pharmacophore features. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Gen. Subj. 2008, 1780, 819–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Aliaga, K.; Bermejo-Bescós, P.; Benedí, J.; Martín-Aragón, S. Quercetin and rutin exhibit antiamyloidogenic and fibril-disaggregating effects in vitro and potent antioxidant activity in APPswe cells. Life Sci. 2011, 89, 939–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinutha, B.; Prashanth, D.; Salma, K.; Sreeja, S.L.; Pratiti, D.; Padmaja, R.; Radhika, S.; Amit, A.; Venkateshwarlu, K.; Deepak, M. Screening of selected Indian medicinal plants for acetylcholinesterase inhibitory activity. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2007, 109, 359–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begum, S.; Banerjee, A.; De, B. Antioxidant and Enzyme Inhibitory Properties of Mangifera indica leaf Extract. Nat. Prod. J. 2020, 10, 384–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchoukh, I.; Hazmoune, T.; Boudelaa, M.; Bensouici, C.; Zellagui, A. Anticholinesterase and antioxidant activities of foliar extract from a tropical species: L. (Myrtaceae) grown in Algeria. Curr. Issues Pharm. Med. Sci. 2019, 32, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, W.N.L.d.; da Silva Sauthier, M.C.; dos Santos, A.M.P.; de Andrade Santana, D.; Almeida Azevedo, R.S.; da Cruz Caldas, J. Simultaneous determination of 13 phenolic bioactive compounds in guava (Psidium guajava L.) by HPLC-PAD with evaluation using PCA and Neural Network Analysis (NNA). Microchem. J. 2017, 133, 583–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrachaianan, T.; Chaiyasirisuwan, S.; Athikomkulchai, S.; Sareedenchai, V. Screening of acetylcholinesterase inhibitory activity in essential oil from Myrtaceae. Thai J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 43, 63–68. [Google Scholar]
- Song, N.; Yang, H.; Pang, W.; Qie, Z.; Lu, H.; Tan, L.; Li, H.; Sun, S.; Lian, F.; Qin, C.; et al. Mulberry extracts alleviate aβ 25-35-induced injury and change the gene expression profile in PC12 cells. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2014, 2014, 150617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, H.; Liu, G.Q. Protection against hydrogen peroxide-induced cytotoxicity in PC12 cells by scutellarin. Life Sci. 2004, 74, 2959–2973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.-Y.; Jeong, W.-S.; Jun, M. Protective Effects of the Key Compounds Isolated from Corni fructus against β-Amyloid-Induced Neurotoxicity in PC12 Cells. Molecules 2012, 17, 10831–10845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Li, Y.; Mu, X. Effect of quercetin on PC12 Alzheimer’s disease cell model induced by Aβ25-35 and its mechanism based on Sirtuin1/Nrf2/HO-1 pathway. BioMed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 8210578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iskusnykh, I.Y.; Zakharova, A.A.; Pathak, D. Glutathione in Brain Disorders and Aging. Molecules 2022, 27, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubos, E.; Loscalzo, J.; Handy, D.E. Glutathione peroxidase-1 in health and disease: From molecular mechanisms to therapeutic opportunities. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2011, 15, 1957–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Townsend, D.M.; Tew, K.D. The role of glutathione-S-transferase in anti-cancer drug resistance. Oncogene 2003, 22, 7369–7375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunkeaw, T.; Suttisansanee, U.; Trachootham, D.; Karinchai, J.; Chantong, B.; Potikanond, S.; Inthachat, W.; Pitchakarn, P.; Temviriyanukul, P. Diplazium esculentum (Retz.) Sw. reduces BACE-1 activities and amyloid peptides accumulation in Drosophila models of Alzheimer’s disease. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 23796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Kim, J.R.; Lee, S.B.; Kim, Y.J.; Jung, M.Y.; Kwon, H.W.; Ahn, Y.J. Effects of curcuminoids identified in rhizomes of Curcuma longa on BACE-1 inhibitory and behavioral activity and lifespan of Alzheimer’s disease Drosophila models. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2014, 14, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Perumalsamy, H.; Kwon, H.W.; Na, Y.E.; Ahn, Y.J. Effects and possible mechanisms of action of acacetin on the behavior and eye morphology of Drosophila models of Alzheimer’s disease. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duffy, J.B. GAL4 system in Drosophila: A fly geneticist’s Swiss army knife. Genesis 2002, 34, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuda, L.; Lim, Y.-M. Alzheimer’s Disease Model System Using Drosophila. In Drosophila Models for Human Diseases; Yamaguchi, M., Ed.; Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp. 25–40. [Google Scholar]
- Youn, K.; Jun, M. Inhibitory Effects of Key Compounds Isolated from Corni fructus on BACE1 Activity. Phytother. Res. 2012, 26, 1714–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.T.; Wang, Z.Z.; Yuan, Y.H.; Sun, H.M.; Chen, N.H.; Zhang, Y. Mangiferin: A multipotent natural product preventing neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease models. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 146, 104336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Infante-Garcia, C.; Ramos-Rodriguez, J.J.; Delgado-Olmos, I.; Gamero-Carrasco, C.; Fernandez-Ponce, M.T.; Casas, L.; Mantell, C.; Garcia-Alloza, M. Long-Term Mangiferin Extract Treatment Improves Central Pathology and Cognitive Deficits in APP/PS1 Mice. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 54, 4696–4704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, H.F.; Yong, H.S. Malaysian Fruits in Color; Tropical Press: Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 1980; p. 130. [Google Scholar]
- Tinggal, H.S.D.S.H. Brunei Darussalam Fruits in Colour; Universiti Brunei Darussalam: Bandar Seri Begawan, Brunei, 1992; p. 148. [Google Scholar]
- Suttisansanee, U.; Kunkeaw, T.; Thatsanasuwan, N.; Tonglim, J.; Temviriyanukul, P. The Investigation on Cholinesterases and BACE1 Inhibitory Activities in Various Tea Infusions. Walailak J. Sci. Technol. (WJST) 2019, 16, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jantrapirom, S.; Lo Piccolo, L.; Yoshida, H.; Yamaguchi, M. A new Drosophila model of Ubiquilin knockdown shows the effect of impaired proteostasis on locomotive and learning abilities. Exp. Cell Res. 2018, 362, 461–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Fruit Extracts | Enzyme Inhibitory Activities (%Inhibition) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AChE 1 | BChE 1 | BACE-1 2 | ||
| Ananas comosus | ‘Pattavia’ | 84.67 ± 1.99 a | 18.94 ± 0.97 d | 58.56 ± 4.26 a |
| ‘Phulae’ | 55.81 ± 1.51 c | 24.48 ± 0.65 c | 39.29 ± 1.98 c | |
| Carica papaya | ‘Khaekdum’ | 54.89 ± 0.36 c | 32.05 ± 1.46 a | 41.11 ± 3.31 c |
| ‘Khaeknuan’ | 49.19 ± 0.80 d | 27.35 ± 2.09 b | 41.34 ± 1.02 c | |
| Durio zibethinus | ‘Chanee’ | 58.68 ± 0.70 b | 21.39 ± 2.04 d | 51.58 ± 2.67 b |
| ‘Monthong’ | 38.36 ± 0.25 e | 13.34 ± 0.51 e | 27.34 ± 1.50 d | |
| Mangifera indica | ‘Namdokmai’ | 83.14 ± 0.4 A | 84.14 ± 0.64 A | 48.88 ± 2.57 A |
| ‘Keaw’ | 69.12 ± 0.21 C | 54.72 ± 1.61 C | 36.89 ± 1.65 B | |
| Psidium guajava | ‘Kimju’ | 69.69 ± 0.41 C | 70.31 ± 2.50 B | 32.09 ± 1.13 C |
| ‘Keenok’ | 70.69 ± 0.83 B | 68.95 ± 0.55 B | 28.59 ± 0.90 D | |
| Donepezil (IC50) (µM) | 3.12 ± 0.37 | 2.14 ± 0.43 | 1.31 ± 0.07 | |
| Phenolics (µg/g Extract) | Mangifera indica | Psidium guajava | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ‘Kaew’ | ‘Namdokmai’ | ‘Kimju’ | |
| Gallic acid | 7802.07 ± 199.68 aA | 4790.75 ± 36.74 aB | 596.80 ± 12.98 bC |
| Quercetin | 6.59 ± 0.44 bB | 52.65 ± 5.23 bB | 1867.27 ± 138.86 aA |
| Naringenin | ND | ND | 3.50 ± 0.34 c |
| Kaempferol | ND | ND | <LOD |
| Isorhamnetin | ND | ND | 53.73 ± 2.27 c |
| Assay | Enzyme (100 μL) | Substrate (40 μL) | Indicator (10 µL) | Extract (40 µL) | Detection Wavelength |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AChE | 20 ng Electrophorus electricus AChE (1000 units/mg) | 0.8 mM acetylthiocholine | 16 mM 5,5′-dithiobis(2-nitrobenzoic acid) | 0.25–0.5 mg/mL | 412 nm |
| BChE | 50 ng equine serum BChE (≥10 units/mg) | 0.4 mM butyrylthiocholine |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Temviriyanukul, P.; Kittibunchakul, S.; Trisonthi, P.; Kunkeaw, T.; Inthachat, W.; Siriwan, D.; Suttisansanee, U. Mangifera indica ‘Namdokmai’ Prevents Neuronal Cells from Amyloid Peptide Toxicity and Inhibits BACE-1 Activities in a Drosophila Model of Alzheimer’s Amyloidosis. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 591. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15050591
Temviriyanukul P, Kittibunchakul S, Trisonthi P, Kunkeaw T, Inthachat W, Siriwan D, Suttisansanee U. Mangifera indica ‘Namdokmai’ Prevents Neuronal Cells from Amyloid Peptide Toxicity and Inhibits BACE-1 Activities in a Drosophila Model of Alzheimer’s Amyloidosis. Pharmaceuticals. 2022; 15(5):591. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15050591
Chicago/Turabian StyleTemviriyanukul, Piya, Suwapat Kittibunchakul, Piyapat Trisonthi, Thanit Kunkeaw, Woorawee Inthachat, Dalad Siriwan, and Uthaiwan Suttisansanee. 2022. "Mangifera indica ‘Namdokmai’ Prevents Neuronal Cells from Amyloid Peptide Toxicity and Inhibits BACE-1 Activities in a Drosophila Model of Alzheimer’s Amyloidosis" Pharmaceuticals 15, no. 5: 591. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15050591
APA StyleTemviriyanukul, P., Kittibunchakul, S., Trisonthi, P., Kunkeaw, T., Inthachat, W., Siriwan, D., & Suttisansanee, U. (2022). Mangifera indica ‘Namdokmai’ Prevents Neuronal Cells from Amyloid Peptide Toxicity and Inhibits BACE-1 Activities in a Drosophila Model of Alzheimer’s Amyloidosis. Pharmaceuticals, 15(5), 591. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15050591







