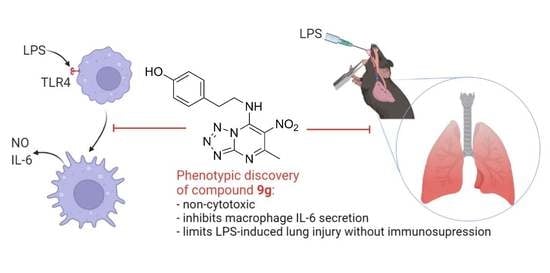
Discovery of Nitro-azolo[1,5-a]pyrimidines with Anti-Inflammatory and Protective Activity against LPS-Induced Acute Lung Injury
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
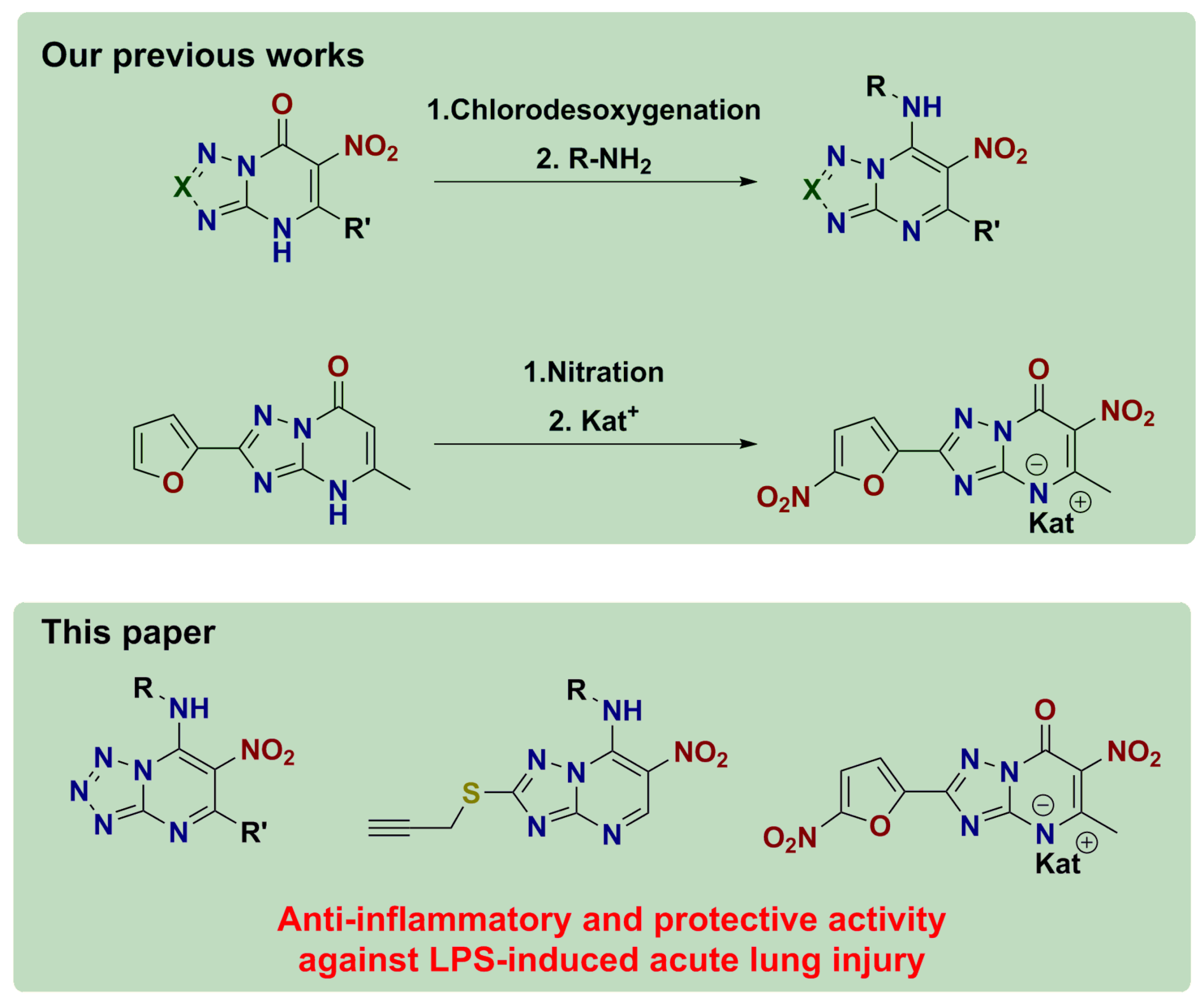
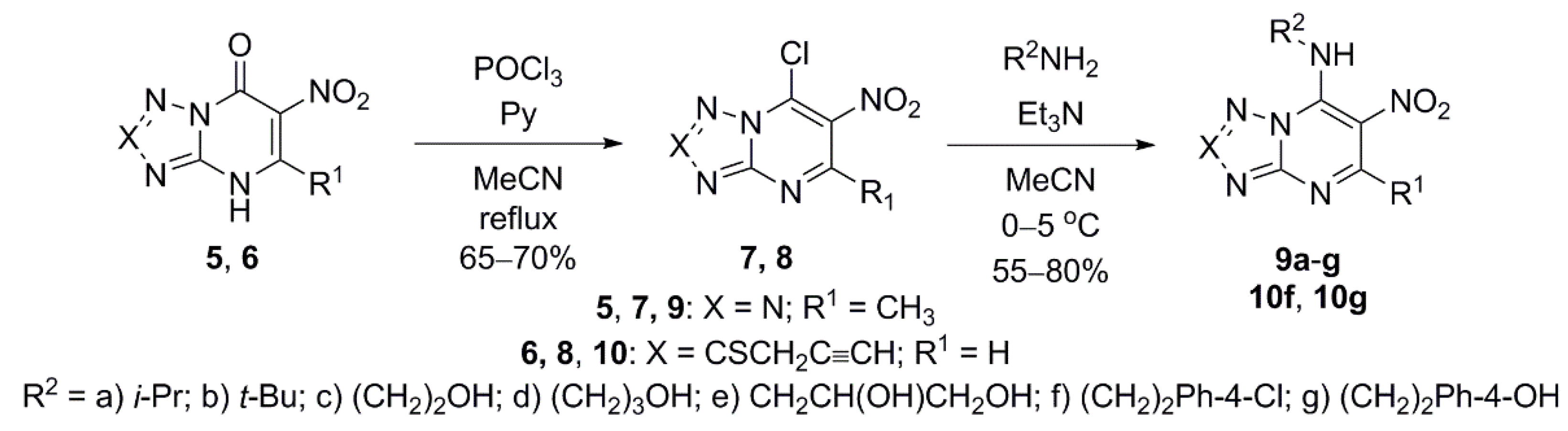
2.1. Chemistry
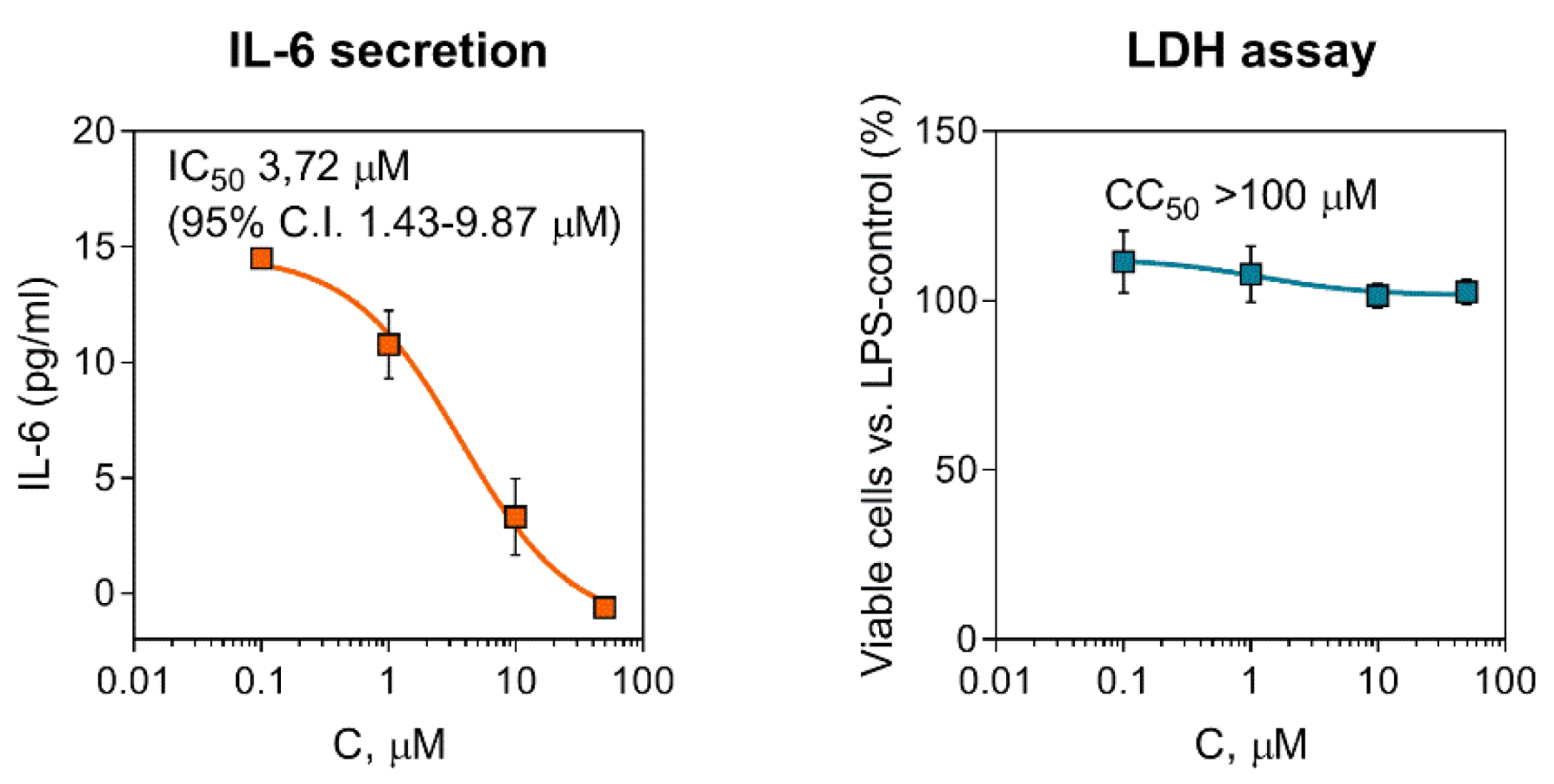
2.2. Effect of Compounds on Pro-Inflammatory Activation of Macrophages
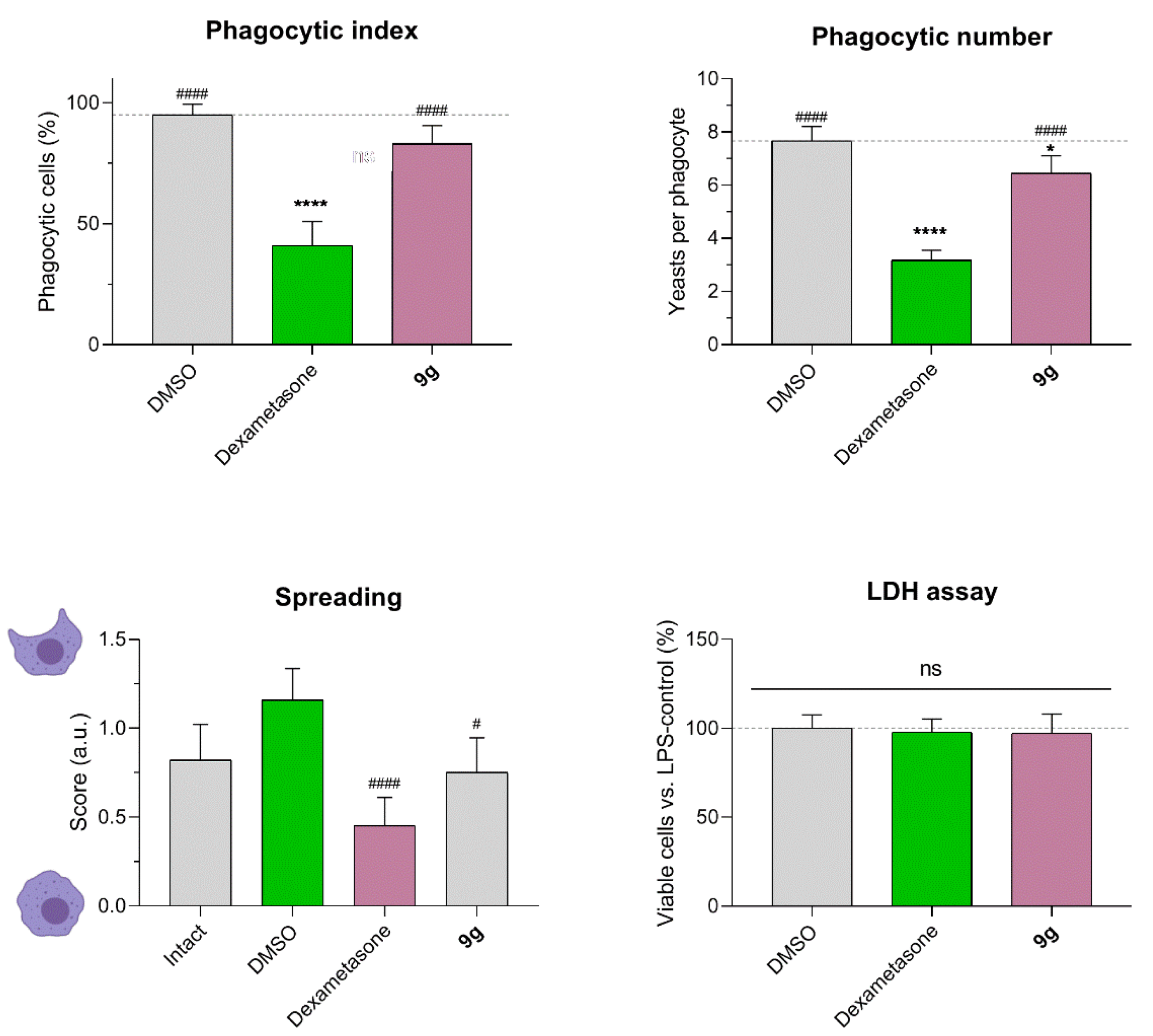
2.3. Effect of Compound 9g on Macrophage Phagocytosis
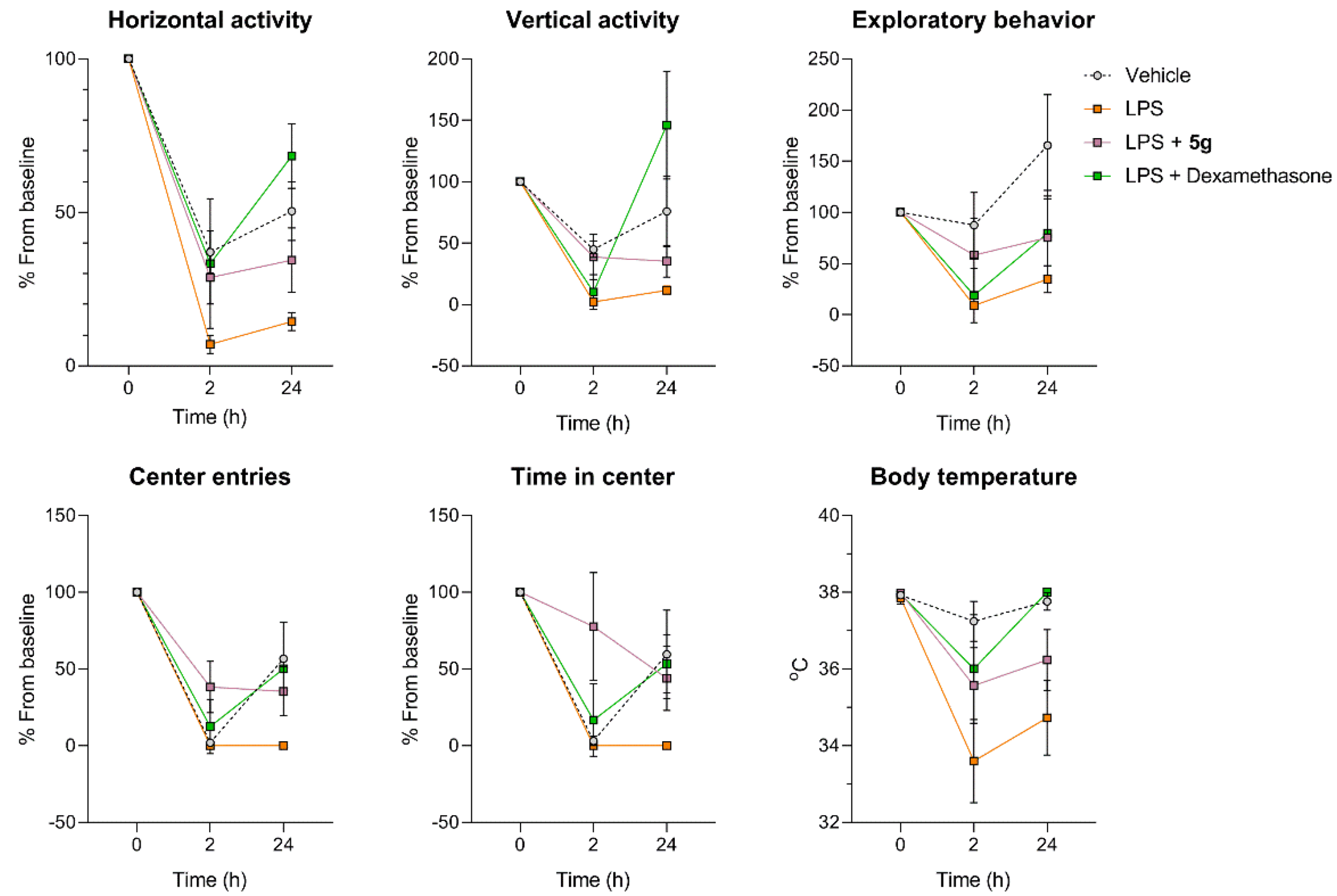
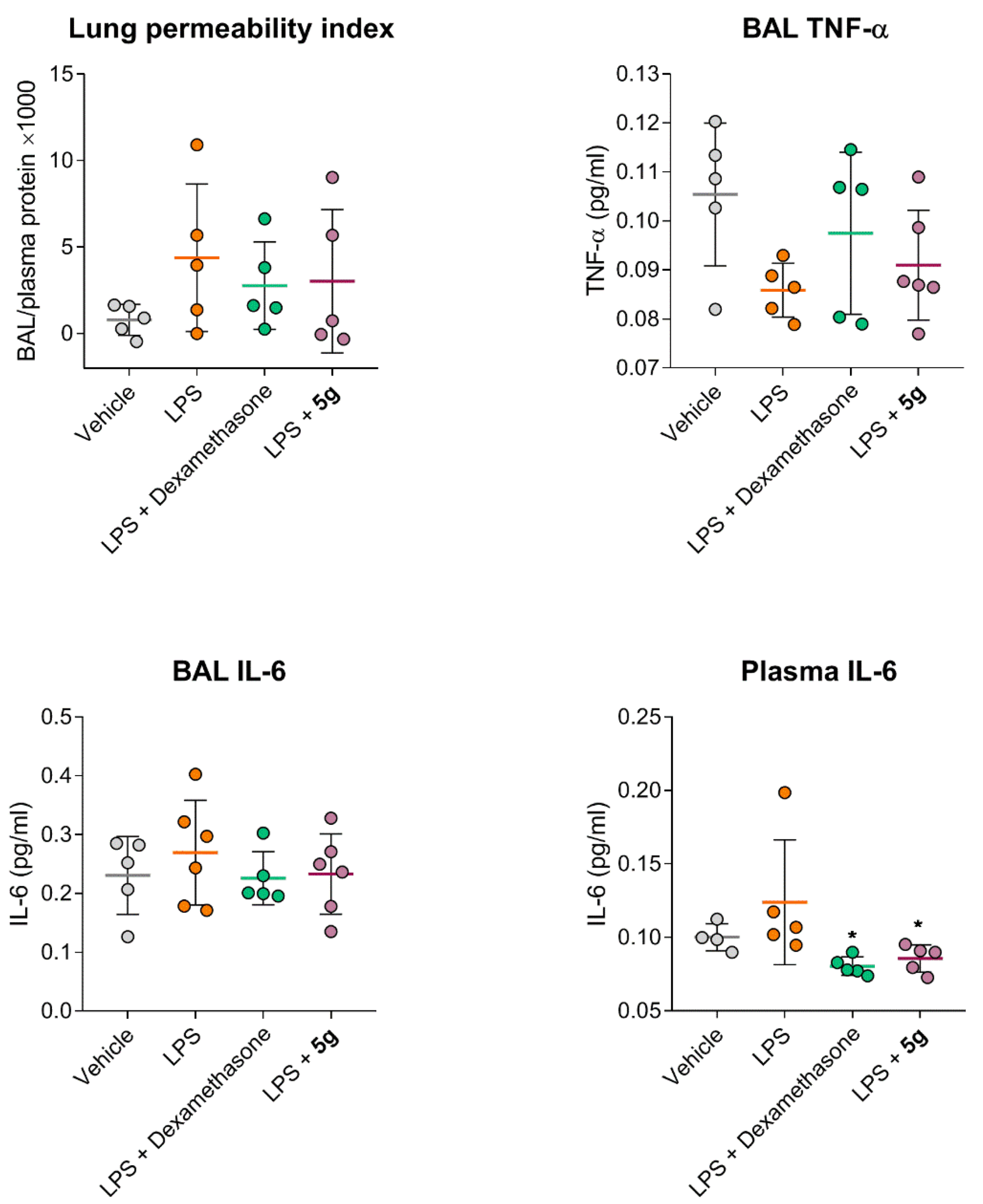
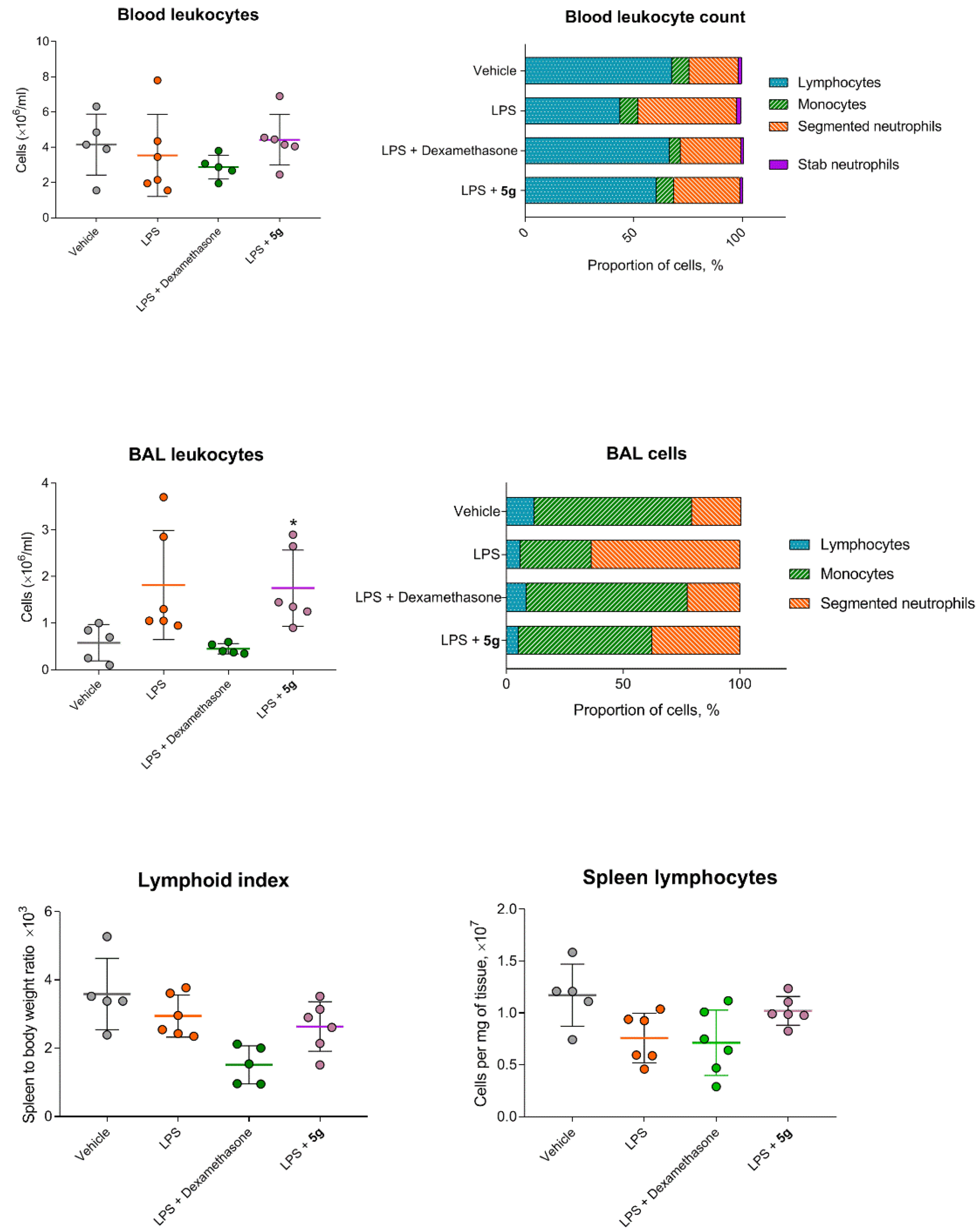
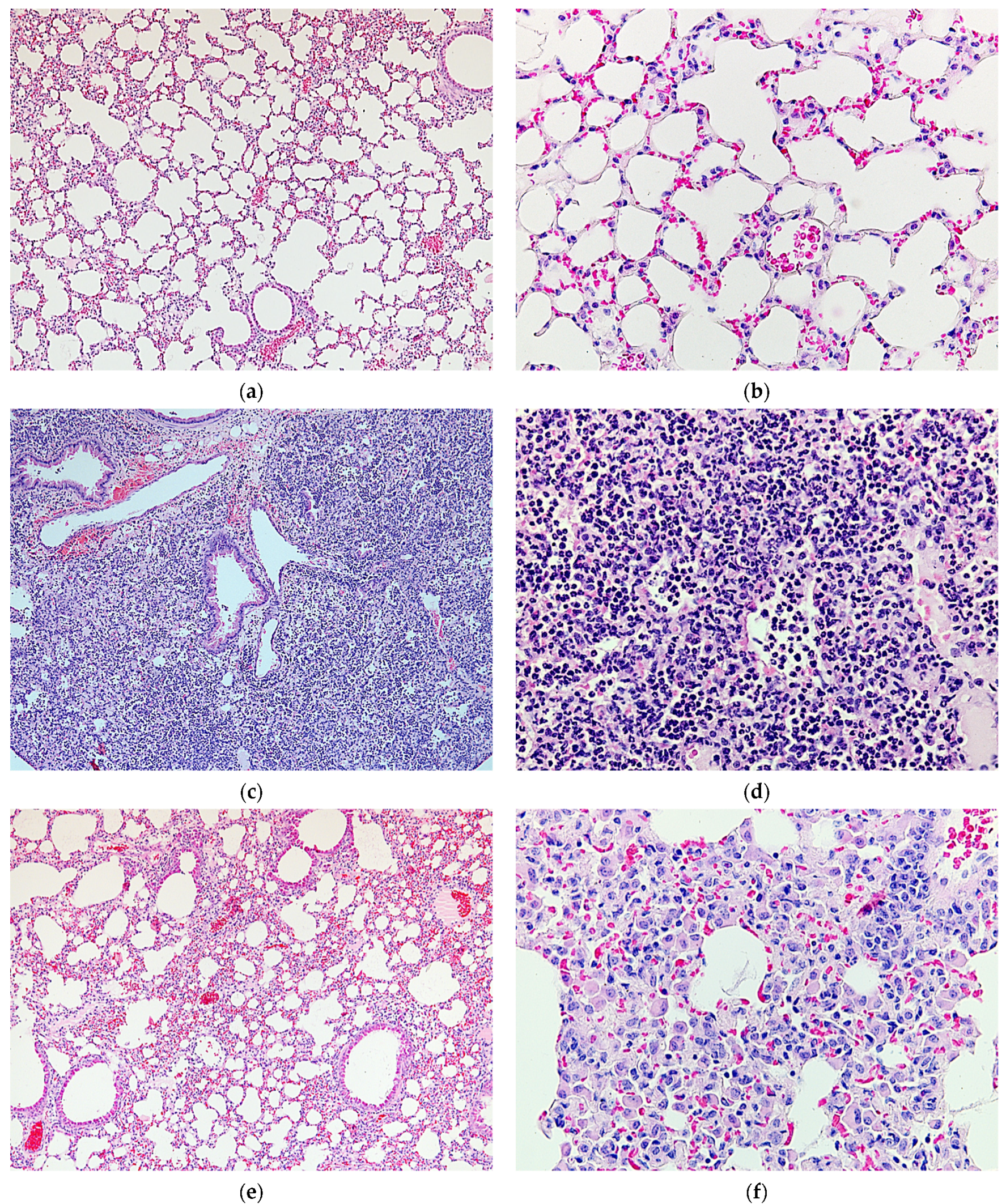
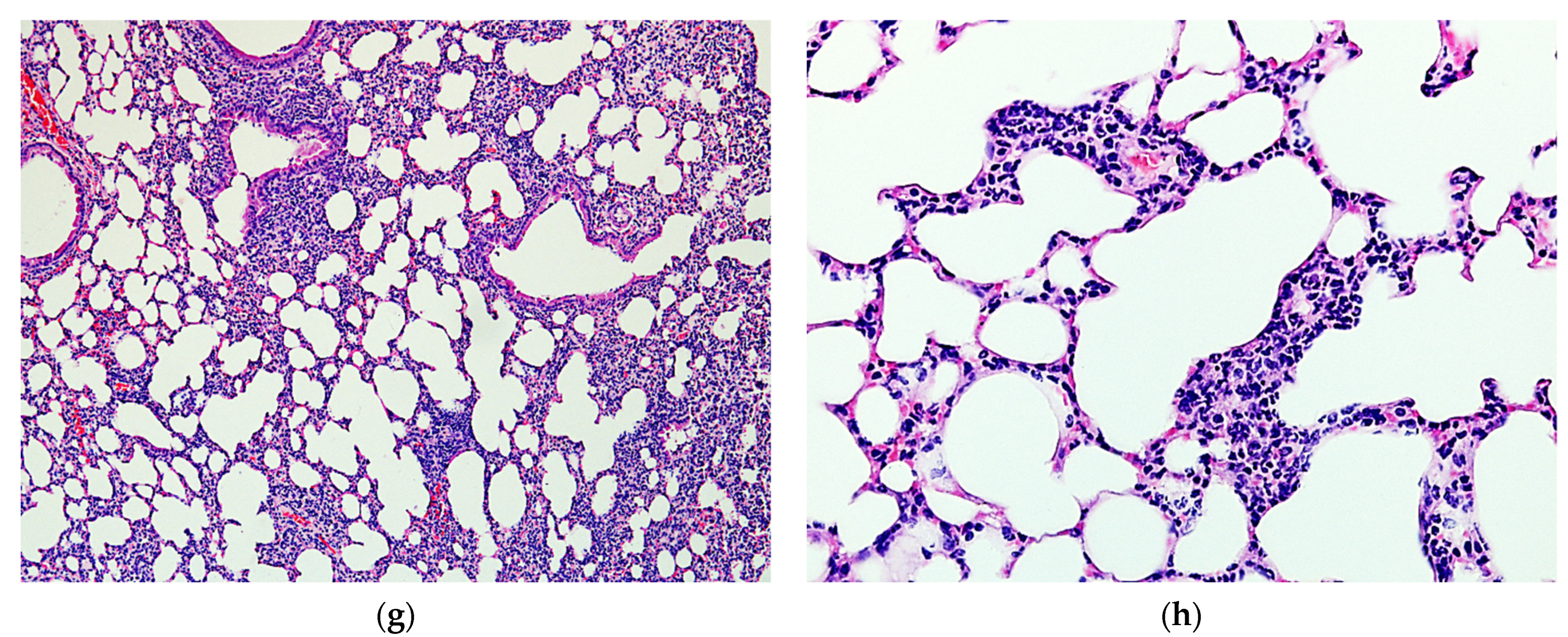
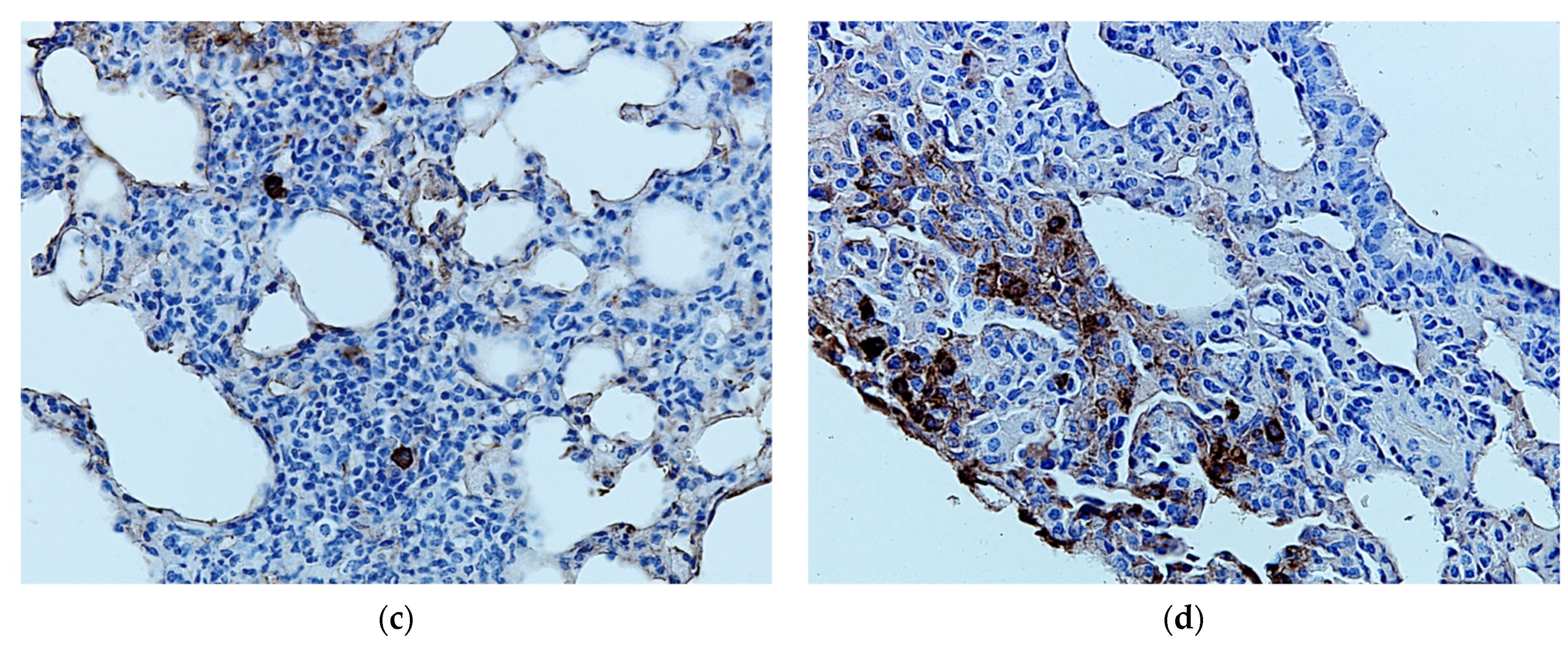
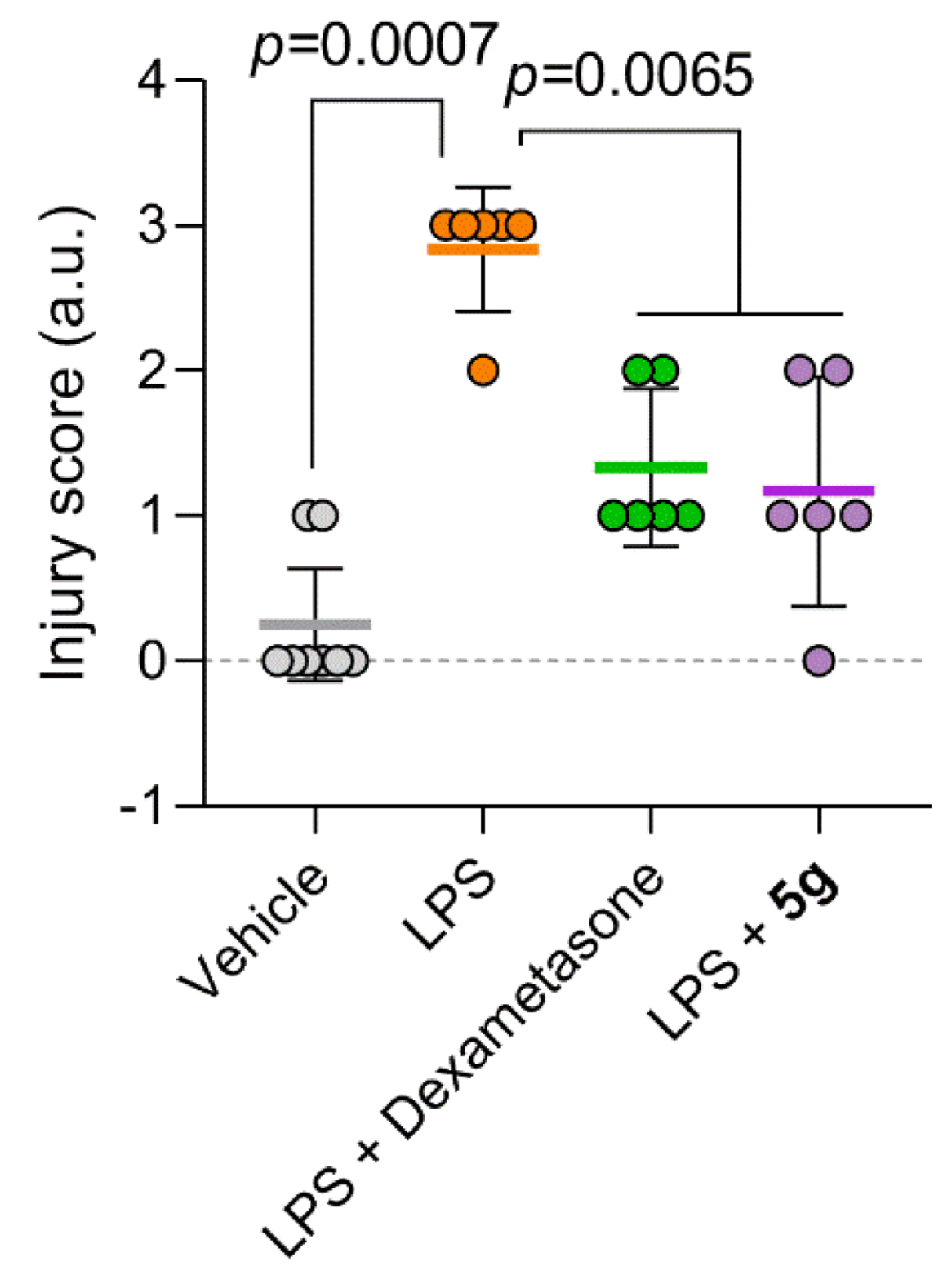
2.4. Protective Activity of 9g in LPS-Induced Acute Lung Injury
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
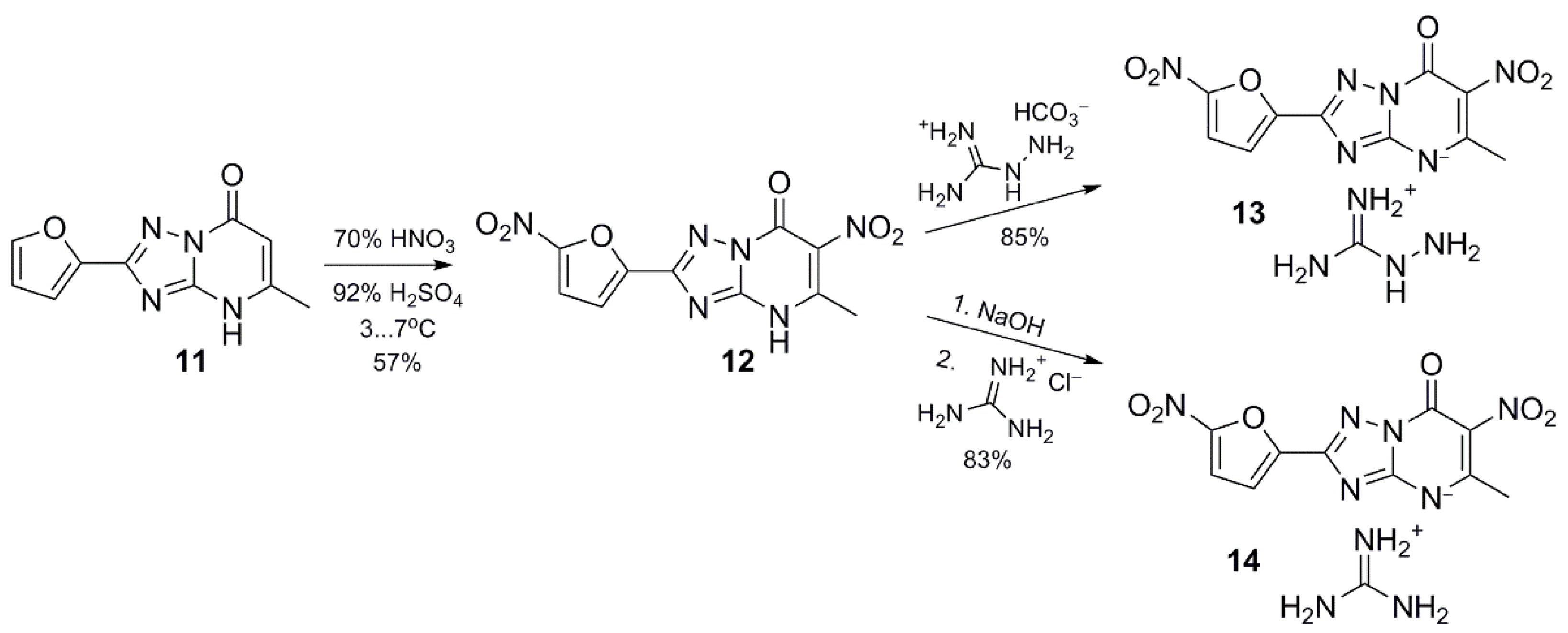
4.1. Synthesis
4.1.1. Preparation of 7-Alkylamino-5-methyl-6-nitrotetrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidines 9a–f (General Method)
4.1.2. N-Isopropyl-5-methyl-6-nitrotetrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidin-7-amine (9a)
4.1.3. N-Tert-Butyl-5-methyl-6-nitrotetrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidin-7-amine (9b)
4.1.4. 2-[(5-Methyl-6-nitrotetrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidin-7-yl)-amino]ethanol (9c)
4.1.5. 3-[(5-Methyl-6-nitrotetrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidin-7-yl)-amino]propanol (9d)
4.1.6. 3-[(5-Methyl-6-nitrotetrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidin-7-yl)-amino]propane-1,2-diol (9e)
4.1.7. N-[2-(4-Chlorophenyl)ethyl]-5-methyl-6-nitrotetrazolo-[1,5-a]pyrimidin-7-amine (9f)
4.1.8. N-[2-(4-Hydroxyphenyl)ethyl]-5-methyl-6-nitrotetrazolo-[1,5-a]pyrimidin-7-amine (9g)
4.1.9. Synthesis of 6-nitro-2-(prop-2-yn-1-ylsulfanyl)[1,2,4]triazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidin-7-amines 10f, 10g (General Method)
4.1.10. N-(4-Chlorophenethyl)-6-nitro-2-(prop-2-yn-1-yl-sulfanyl)[1,2,4]triazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidin-7-amine (10f)
4.1.11. 4-{2-[(6-Nitro-2-(prop-2-yn-1-ylsulfanyl)[1,2,4]triazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidin-7-yl)amino]ethyl}phenol (10g)
4.1.12. 2-(5-Nitrofur-2-yl)-5-methyl-6-nitro-1,2,4-triazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidin-7-one aminoguanidinium salt (13)
4.1.13. 2-(5-Nitrofur-2-yl)-5-methyl-6-nitro-1,2,4-triazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidin-7-one guanidinium salt (14)
4.2. Animals
4.3. Isolation and Treatment of Peritoneal Macrophages
4.4. Assay of Nitric Oxide (NO)
4.5. Assay of Cytokines
4.6. Cytotoxicity Study
4.7. Phagocytosis Assay
4.8. LPS-Induced Acute Lung Injury
4.9. Open Field Test
4.10. Bronchoalveolar Lavage and Plasma Preparation
4.11. Leukocyte Count in Blood and BAL
4.12. Lung Permeability Index
4.13. Histological Study
4.14. Data Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rubenfeld, G.D.; Herridge, M.S. Epidemiology and Outcomes of Acute Lung Injury. Chest 2007, 131, 554–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, G.; Shi, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Ju, M.; He, H.; Ma, G.; Hao, G.; Luo, Z. Glucocorticoid Attenuates Acute Lung Injury through Induction of Type 2 Macrophage. J. Transl. Med. 2017, 15, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.-Q.; Zhou, X.; Zhou, Y.; Rong, L.; Gao, L.; Xu, W. Low-Dose Dexamethasone Alleviates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Acute Lung Injury in Rats and Upregulates Pulmonary Glucocorticoid Receptors. Respirology 2008, 13, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Jiang, W.; He, Q.; Wang, C.; Wang, B.; Zhou, P.; Dong, N.; Tong, Q. A Retrospective Cohort Study of Methylprednisolone Therapy in Severe Patients with COVID-19 Pneumonia. Sig. Transduct. Target Ther. 2020, 5, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinzón, M.A.; Ortiz, S.; Holguín, H.; Betancur, J.F.; Arango, D.C.; Laniado, H.; Arias, C.A.; Muñoz, B.; Quiceno, J.; Jaramillo, D.; et al. Dexamethasone vs Methylprednisolone High Dose for Covid-19 Pneumonia. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0252057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zheng, X.; Huang, Y.; Shan, H.; Huang, J. Successful Use of Methylprednisolone for Treating Severe COVID-19. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2020, 146, 325–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marik, P.E.; Meduri, G.U.; Rocco, P.R.M.; Annane, D. Glucocorticoid Treatment in Acute Lung Injury and Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Crit. Care Clin. 2011, 27, 589–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontali, E.; Volpi, S.; Signori, A.; Antonucci, G.; Castellaneta, M.; Buzzi, D.; Montale, A.; Bustaffa, M.; Angelelli, A.; Caorsi, R.; et al. Efficacy of Early Anti-Inflammatory Treatment with High Doses of Intravenous Anakinra with or without Glucocorticoids in Patients with Severe COVID-19 Pneumonia. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2021, 147, 1217–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barkas, F.; Christaki, E.; Liberopoulos, E.; Kosmidou, M.; Milionis, H. Anakinra in COVID-19: A Step Closer to the Cure. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2022, 96, 113–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, S.-H.; Lai, C.-C.; Huang, H.-T.; Chang, S.-P.; Lu, L.-C.; Hsueh, P.-R. Tocilizumab for Severe COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2020, 56, 106103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Huang, Q.; Wang, D.C.; Ingbar, D.H.; Wang, X. Acute Lung Injury in Patients with COVID-19 Infection. Clin. Transl. Med. 2020, 10, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdellatif, K.R.A.; Bakr, R.B. Pyrimidine and Fused Pyrimidine Derivatives as Promising Protein Kinase Inhibitors for Cancer Treatment. Med. Chem. Res. 2021, 30, 31–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Chen, C.-J.; Yu, R.-N.; Shu, L.; Wang, Z.-J.; Zhang, T.-T.; Zhang, D.-Y. Novel 1H-Pyrazolo[3,4-d]Pyrimidin-6-Amino Derivatives as Potent Selective Janus Kinase 3 (JAK3) Inhibitors. Evaluation of Their Improved Effect for the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Bioorg. Chem. 2020, 98, 103720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, N.; Pan, J.; Hao, Q.; Li, Y.; Zhou, W. Design, Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Novel 3-Substituted Pyrazolopyrimidine Derivatives as Potent Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase (BTK) Inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2018, 26, 2165–2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McElroy, W.T. Interleukin-1 Receptor-Associated Kinase 4 (IRAK4) Inhibitors: An Updated Patent Review (2016–2018). Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2019, 29, 243–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.S.; Huang, X.; Chen, L.Z.; Liu, M.M.; Shi, J.B. Design and Synthesis of Novel Pyrazolo[4,3-d]Pyrimidines as Potential Therapeutic Agents for Acute Lung Injury. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2019, 34, 1121–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusinov, V.L.; Charushin, V.N.; Chupakhin, O.N. Biologically active azolo-1,2,4-triazines and azolopyrimidines. Russ. Chem. B 2018, 67, 573–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpenko, I.; Deev, S.; Kiselev, O.; Charushin, V.; Rusinov, V.; Ulomsky, E.; Deeva, E.; Yanvarev, D.; Ivanov, A.; Smirnova, O.; et al. Antiviral Properties, Metabolism, and Pharmacokinetics of a Novel Azolo-1,2,4-Triazine-Derived Inhibitor of Influenza A and B Virus Replication. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 2017–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chupakhin, O.N.; Charushin, V.N.; Rusinov, V.L. Scientific Foundations for the Creation of Antiviral and Antibacterial Preparations. Herald Russ. Acad. Sci. 2016, 86, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savateev, K.V.; Ulomsky, E.N.; Butorin, I.I.; Charushin, V.N.; Rusinov, V.L.; Chupakhin, O.N. Azoloazines as A2a receptor antagonists. Structure—activity relationship. Russ. Chem. Rev. 2018, 87, 636–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savateev, K.V.; Ulomsky, E.N.; Fedotov, V.V.; Rusinov, V.L.; Sivak, K.V.; Lyubishin, M.M.; Kuzmich, N.N.; Aleksandrov, A.G. 6-Nitrotriazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidines as Promising Structures for Pharmacotherapy of Septic Conditions. Russ. J. Bioorg. Chem. 2017, 43, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spasov, A.A.; Babkov, D.A.; Sysoeva, V.A.; Litvinov, R.A.; Shamshina, D.D.; Ulomsky, E.N.; Savateev, K.V.; Fedotov, V.V.; Slepukhin, P.A.; Chupakhin, O.N.; et al. 6-Nitroazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidin-7(4H)-ones as Antidiabetic Agents. Arch. Pharm. 2017, 350, 1700226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusinov, V.L.; Sapozhnikova, I.M.; Bliznik, A.M.; Chupakhin, O.N.; Charushin, V.N.; Spasov, A.A.; Vassiliev, P.M.; Kuznetsova, V.A.; Rashchenko, A.I.; Babkov, D.A. Synthesis and Evaluation of Novel [1,2,4]Triazolo[5,1-c][1,2,4]-triazines and Pyrazolo[5,1-c][1,2,4]triazines as Potential Antidiabetic Agents. Arch. Pharm. 2017, 350, 1600361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savateev, K.V.; Slepukhin, P.A.; Kotovskaya, S.K.; Charushin, V.N.; Rusinov, V.L.; Chupakhin, O.N. Atom-Efficient Synthesis of Hybrid Molecules Combining Fragments of Triazolopyrimidines and 3-Ethoxycarbonyl-1-Ethyl-6-Fluoroquinolin-4(1H)-One through 1,2,3-Triazole Linker. Chem. Heterocycl. Comp. 2021, 57, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savateev, K.V.; Fedotov, V.V.; Ulomskiy, E.N.; Rusinov, V.L. 7-Alkylamino-6-Nitrotetrazolo[1,5-a]Pyrimidines as Precursors of Anomalous Nucleosides and Heterocycles with Potential Antiseptic Activity. Chem. Heterocycl. Comp. 2018, 54, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chupakhin, O.N.; Charushin, V.N.; Rusinov, V.L.; Savateev, K.V.; Ulomskii, E.N.; Fedoto, V.V.; Petrov, V.I.; Spasov, A.A.; Babkova, V.A.; Babkov, D.A. 2-(5-Nitronylfuran-2-yl)-5-methyl-6-nitro-1,2,4-triazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidin-7(4H)-one and salts thereof. RU Patent 2716715 C2, 30 January 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Farhad, A.R.; Razavi, S.; Jahadi, S.; Saatchi, M. Use of Aminoguanidine, a Selective Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase Inhibitor, to Evaluate the Role of Nitric Oxide in Periapical Inflammation. J. Oral Sci. 2011, 53, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Becker, J.; Grasso, R.J. Suppression of Phagocytosis by Dexamethasone in Macrophage Cultures: Inability of Arachidonic Acid, Indomethacin, and Nordihydroguaiaretic Acid to Reverse the Inhibitory Response Mediated by a Steroid-Inducible Factor. Int. J. Immunopharmacol. 1985, 7, 839–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasso, R.J.; West, L.A.; Guay, R.C.; Klein, T.W. Inhibition of Yeast Phagocytosis by Dexamethasone in Macrophage Cultures: Reversibility of the Effect and Enhanced Suppression in Cultures of Stimulated Macrophages. J. Immunopharmacol. 1982, 4, 265–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannon, G.J.; Swanson, J.A. The Macrophage Capacity for Phagocytosis. J. Cell Sci. 1992, 101, 907–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donaldson, K.; Bolton, R.E.; Brown, D.; Douglas, A. AN Improved Macrophage Spreading Assay—A Simple and Effective Measure of Activation. Immunol. Commun. 1984, 13, 229–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chistiakov, D.A.; Killingsworth, M.C.; Myasoedova, V.A.; Orekhov, A.N.; Bobryshev, Y.V. CD68/Macrosialin: Not Just a Histochemical Marker. Lab. Investig. 2017, 97, 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Zuo, Z.; Chen, K.; Fang, J.; Cui, H.; Shu, G.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Z.; Huang, C.; Liu, W. Histopathological Changes Caused by Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in Diet-Induced-Obese Mouse Following Experimental Lung Injury. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 14250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrne, A.J.; Mathie, S.A.; Gregory, L.G.; Lloyd, C.M. Pulmonary Macrophages: Key Players in the Innate Defence of the Airways. Thorax 2015, 70, 1189–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, D.; Chow, A.; Noizat, C.; Teo, P.; Beasley, M.B.; Leboeuf, M.; Becker, C.D.; See, P.; Price, J.; Lucas, D.; et al. Tissue-Resident Macrophages Self-Maintain Locally throughout Adult Life with Minimal Contribution from Circulating Monocytes. Immunity 2013, 38, 792–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guilliams, M.; De Kleer, I.; Henri, S.; Post, S.; Vanhoutte, L.; De Prijck, S.; Deswarte, K.; Malissen, B.; Hammad, H.; Lambrecht, B.N. Alveolar Macrophages Develop from Fetal Monocytes That Differentiate into Long-Lived Cells in the First Week of Life via GM-CSF. J. Exp. Med. 2013, 210, 1977–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamacher, M. Kinase Inhibitors in Signal Transduction Therapy. In Protein Kinases as Drug Targets; John Wiley & Son: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarrin, A.A.; Bao, K.; Lupardus, P.; Vucic, D. Kinase Inhibition in Autoimmunity and Inflammation. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2020, 20, 39–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Li, M.; Zhou, Z.; Guan, X.; Xiang, Y. Can We Use Interleukin-6 (IL-6) Blockade for Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)-Induced Cytokine Release Syndrome (CRS)? J. Autoimmun. 2020, 111, 102452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coomes, E.A.; Haghbayan, H. Interleukin-6 in Covid-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Rev. Med. Virol. 2020, 30, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Li, L.; Xu, M.; Wu, J.; Luo, D.; Zhu, Y.; Li, B.; Song, X.; Zhou, X. Prognostic Value of Interleukin-6, C-Reactive Protein, and Procalcitonin in Patients with COVID-19. J. Clin. Virol. 2020, 127, 104370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobb, D.A.; Lee, D.W. Cytokine Release Syndrome Biology and Management. Cancer J. 2021, 27, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.R.; Cho, Y.C.; Cho, S. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of a Novel Compound, MPQP, through the Inhibition of IRAK1 Signaling Pathways in LPS-Stimulated RAW 264.7 Macrophages. BMB Rep. 2018, 51, 308–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bassi, G.S.; Kanashiro, A.; Santin, F.M.; de Souza, G.E.P.; Nobre, M.J.; Coimbra, N.C. Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Sickness Behaviour Evaluated in Different Models of Anxiety and Innate Fear in Rats. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2012, 110, 359–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochalski, S.J.; Hartman, D.A.; Belfast, M.T.; Walter, T.L.; Glaser, K.B.; Carlson, R.P. Inhibition of Endotoxin-Induced Hypothermia and Serum TNF-α Levels in CD-1 Mice by Various Pharmacological Agents. Agents Actions 1993, 39, C52–C54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simons, R.K.; Junger, W.G.; Loomis, W.H.; Hoyt, D.B. Acute Lung Injury in Endotoxemic Rats Is Associated with Sustained Circulating IL-6 Levels and in-Trapulmonary CINC Activity and Neutrophil Recruitment—Role of Circulating TNF-α and IL-β? Shock 1996, 6, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faffe, D.S.; Seidl, V.R.; Chagas, P.S.; Gonçalves de Moraes, V.L.; Capelozzi, V.L.; Rocco, P.R.; Zin, W.A. Respiratory Effects of Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammatory Lung Injury in Mice. Eur. Respir. J. 2000, 15, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sert, N.P.D.; Ahluwalia, A.; Alam, S.; Avey, M.T.; Baker, M.; Browne, W.J.; Clark, A.; Cuthill, I.C.; Dirnagl, U.; Emerson, M.; et al. Reporting Animal Research: Explanation and Elaboration for the ARRIVE Guidelines 2.0. PLoS Biol. 2020, 18, e3000411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Alessio, F.R. Mouse Models of Acute Lung Injury and ARDS. Methods Mol. Biol. 2018, 1809, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Compound | Structure | Inhibition of NO Synthesis vs. LPS Control (%, m ± SD) | Cell Viability vs. LPS Control, MTT Test, (%, m ± SD) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 9a | 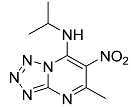 | 47.73 ± 6.98 * | 73.47 ± 12.07 |
| 9b | 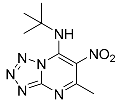 | 36.99 ± 3.25 * | 104.9 ± 5.87 |
| 9c |  | 54.21 ± 11.50 | 109.0 ± 2.00 |
| 9d |  | 40.28 ± 5.14 * | 116.6 ± 8.97 |
| 9e | 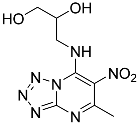 | 21.53 ± 2.74 | 94.98 ± 12.48 |
| 9f | 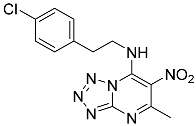 | 35.80 ± 4.45 * | 102.67 ± 6.35 |
| 9g | 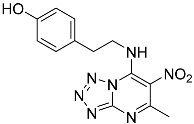 | 58.51 ± 5.93 * | 84.65 ± 5.83 |
| 10f | 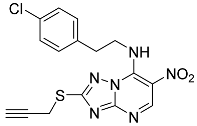 | 50.62 ± 1.27 * | 38.37 ± 6.89 * |
| 10g |  | 28.49 ± 3.21 | 30.9 ± 7.7 * |
| 13 | 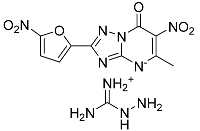 | 58.97 ± 7.07 * | 96.97 ± 7.18 |
| 14 | 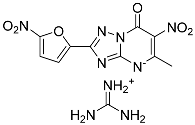 | 16.09 ± 5.78 | 111.95 ± 8.67 |
| Dexamethasone | − | 90.91 ± 5.53 * | 104.21 ± 2.18 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Spasov, A.; Kosolapov, V.; Babkov, D.; Klochkov, V.; Sokolova, E.; Miroshnikov, M.; Borisov, A.; Velikorodnaya, Y.; Smirnov, A.; Savateev, K.; et al. Discovery of Nitro-azolo[1,5-a]pyrimidines with Anti-Inflammatory and Protective Activity against LPS-Induced Acute Lung Injury. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 537. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15050537
Spasov A, Kosolapov V, Babkov D, Klochkov V, Sokolova E, Miroshnikov M, Borisov A, Velikorodnaya Y, Smirnov A, Savateev K, et al. Discovery of Nitro-azolo[1,5-a]pyrimidines with Anti-Inflammatory and Protective Activity against LPS-Induced Acute Lung Injury. Pharmaceuticals. 2022; 15(5):537. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15050537
Chicago/Turabian StyleSpasov, Alexander, Vadim Kosolapov, Denis Babkov, Vladlen Klochkov, Elena Sokolova, Mikhail Miroshnikov, Alexander Borisov, Yulia Velikorodnaya, Alexey Smirnov, Konstantin Savateev, and et al. 2022. "Discovery of Nitro-azolo[1,5-a]pyrimidines with Anti-Inflammatory and Protective Activity against LPS-Induced Acute Lung Injury" Pharmaceuticals 15, no. 5: 537. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15050537
APA StyleSpasov, A., Kosolapov, V., Babkov, D., Klochkov, V., Sokolova, E., Miroshnikov, M., Borisov, A., Velikorodnaya, Y., Smirnov, A., Savateev, K., Fedotov, V., Kotovskaya, S., & Rusinov, V. (2022). Discovery of Nitro-azolo[1,5-a]pyrimidines with Anti-Inflammatory and Protective Activity against LPS-Induced Acute Lung Injury. Pharmaceuticals, 15(5), 537. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15050537