Cytostatics in Indoor Environment: An Update of Analytical Methods
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Search
3. Cytostatics Included in the Studies
4. Surface Contamination
4.1. Sampling
4.1.1. Surface Type and Area
4.1.2. Sampling Devices
4.1.3. Wetting Solution
4.1.4. Wiping Procedure
4.1.5. Wiping Personnel
4.1.6. Stability of Cytostatics on Surfaces
4.1.7. Storage and Shipping
4.2. Sample Preparation
4.2.1. Extraction Solution
4.2.2. Extraction Procedure
4.2.3. Stability of Sampling Extracts
5. Air Contamination
5.1. Sampling
5.2. Sample Preparation
6. Instrumental Method of Analysis
6.1. Separation of Critical Cytostatics
6.2. Validation Parameters
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- IARC. IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans: Volume 50—Pharmaceutical Drugs; International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon, France, 1990; ISBN 978-92-832-1250-8. [Google Scholar]
- Agents Classified by the IARC Monographs, Volumes 1–129. Available online: https://monographs.iarc.fr/agents-classified-by-the-iarc/ (accessed on 12 April 2021).
- Bernabeu-Martínez, M.A.; Merino, M.R.; Gago, J.M.S.; Sabucedo, L.M.A.; Wanden-Berghe, C.; Sanz-Valero, J. Guidelines for safe handling of hazardous drugs: A systematic review. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0197172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vyas, N.; Yiannakis, D.; Turner, A.; Sewell, G.J. Occupational exposure to anti-cancer drugs: A review of effects of new technology. J. Oncol. Pharm. Pract. 2014, 20, 278–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit, M.; Curti, C.; Roche, M.; Montana, M.; Bornet, C.; Vanelle, P. Environmental monitoring by surface sampling for cytotoxics: A review. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2017, 189, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roussel, C.; Witt, K.L.; Shaw, P.B.; Connor, T.H. Meta-analysis of chromosomal aberrations as a biomarker of exposure in healthcare workers occupationally exposed to antineoplastic drugs. Mutat. Res. Rev. Mutat. Res. 2019, 781, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turci, R.; Sottani, C.; Spagnoli, G.; Minoia, C. Biological and environmental monitoring of hospital personnel exposed to antineoplastic agents: A review of analytical methods. J. Chromatogr. B 2003, 789, 169–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiffmeyer, T.K.; Kube, C.; Opiolka, S.; Schmidt, K.G.; Schöppe, G.; Sessink, P.J.M. Vapour pressures, evaporation behaviour and airborne concentrations of hazardous drugs: Implications for occupational safety. Pharm. J. 2002, 268, 331–337. [Google Scholar]
- Connor, T.H.; Zock, M.D.; Snow, A.H. Surface wipe sampling for antineoplastic (chemotherapy) and other hazardous drug residue in healthcare settings: Methodology and recommendations. J. Occup. Environ. Hyg. 2016, 13, 658–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller-Ramírez, C.; Squibb, K.; McDiarmid, M. Accessible analytical methodology for assessing workplace contamination of antineoplastic drugs in limited-resource oncology health-care settings. J. Anal. Sci. Technol. 2016, 7, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Da Silva, C.B.P.; Julio, I.P.; Donadel, G.E.; Martins, I. UPLC-MS/MS method for simultaneous determination of cyclophosphamide, docetaxel, doxorubicin and 5-fluorouracil in surface samples. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods 2016, 82, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guichard, N.; Rudaz, S.; Bonnabry, P.; Fleury-Souverain, S. Validation and uncertainty estimation for trace amounts determination of 25 drugs used in hospital chemotherapy compounding units. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2019, 172, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guichard, N.; Fekete, S.; Guillarme, D.; Bonnabry, P.; Fleury-Souverain, S. Computer-assisted UHPLC–MS method development and optimization for the determination of 24 antineoplastic drugs used in hospital pharmacy. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2019, 164, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guichard, N.; Boccard, J.; Rudaz, S.; Bonnabry, P.; Fleury Souverain, S. Wipe-sampling procedure optimisation for the determination of 23 antineoplastic drugs used in the hospital pharmacy. Eur. J. Hosp. Pharm. 2021, 28, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dugheri, S.; Bonari, A.; Pompilio, I.; Boccalon, P.; Tognoni, D.; Cecchi, M.; Ughi, M.; Mucci, N.; Arcangeli, G. Analytical strategies for assessing occupational exposure to antineoplastic drugs in healthcare workplaces. Med. Pr. 2018, 69, 589–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dugheri, S.; Bonari, A.; Pompilio, I.; Boccalon, P.; Mucci, N.; Arcangeli, G. A new approach to assessing occupational exposure to antineoplastic drugs in hospital environments. Arch. Ind. Hyg. Toxicol. 2018, 69, 226–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, M.; Jeronimo, M.; Astrakianakis, G.; Apte, C.; Hon, C.-Y. Wipe sampling method and evaluation of environmental variables for assessing surface contamination of 10 antineoplastic drugs by liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry. Ann. Work Expo. Health 2017, 61, 1003–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hetzel, T.; vom Eyser, C.; Tuerk, J.; Teutenberg, T.; Schmidt, T.C. Micro-liquid chromatography mass spectrometry for the analysis of antineoplastic drugs from wipe samples. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 8221–8229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bobin-Dubigeon, C.; Amiand, M.; Percheron, C.; Audeval, C.; Rochard, S.; Leynia, P.; Bard, J.-M. A New, validated wipe-sampling procedure coupled to LC–MS analysis for the simultaneous determination of 5-fluorouracil, doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide in surface contamination. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2013, 37, 433–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeda, S.; Miwa, Y. Multicomponent high-performance liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry analysis of ten chemotherapeutic drugs in wipe samples. J. Chromatogr. B 2013, 921–922, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dal Bello, F.; Santoro, V.; Scarpino, V.; Martano, C.; Aigotti, R.; Chiappa, A.; Davoli, E.; Medana, C. Antineoplastic drugs determination by HPLC-HRMSn to monitor occupational exposure. Drug Test. Anal. 2016, 8, 730–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- B’Hymer, C.; Connor, T.; Stinson, D.; Pretty, J. Validation of an HPLC-MS/MS and wipe procedure for mitomycin C contamination. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2015, 53, 619–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeronimo, M.; Colombo, M.; Astrakianakis, G.; Hon, C.Y. A surface wipe sampling and LC-MS/MS method for the simultaneous detection of six antineoplastic drugs commonly handled by healthcare workers. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 7083–7092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acramel, A.; Chouquet, T.; Plé, A.; Sauvageon, H.; Mourah, S.; Jouenne, F.; Goldwirt, L. Development and validation of a liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry quantification method for 14 cytotoxic drugs in environmental samples. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2020, 34, e8594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossignol, E.; Amiand, M.B.; Sorrieul, J.; Bard, J.M.; Bobin-Dubigeon, C. A fully validated simple new method for environmental monitoring by surface sampling for cytotoxics. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods 2020, 101, 106652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panahi, D.; Azari, M.; Akbari, M.E.; Zendehdel, R.; Mirzaei, H.R.; Hatami, H.; Mehrabi, Y. Development of a new method for sampling and monitoring oncology staff exposed to cyclophosphamide drug. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakui, N.; Ookubo, T.; Iwasaki, Y.; Ito, R.; Mitui, M.; Yano, Y.; Saito, K.; Nakazawa, H. Determination of exposure of dispensary drug preparers to cyclophosphamide by passive sampling and liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry. J. Oncol. Pharm. Pract. 2013, 19, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, J.P.; Sammons, D.L.; Robertson, S.A.; Pretty, J.R.; DeBord, D.G.; Connor, T.H.; Snawder, J.E. Detection and measurement of surface contamination by multiple antineoplastic drugs using multiplex bead assay. J. Oncol. Pharm. Pract. 2016, 22, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.P.; Sammons, D.L.; Pretty, J.R.; Kurtz, K.S.; Robertson, S.A.; Debord, D.G.; Connor, T.H.; Snawder, J.E. Detection of 5-fluorouracil surface contamination in near real time. J. Oncol. Pharm. Pract. 2016, 22, 396–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pałaszewska-Tkacz, A.; Czerczak, S.; Konieczko, K.; Kupczewska-Dobecka, M. Cytostatics as hazardous chemicals in healthcare workers’ environment. Int. J. Occup. Med. Environ. Health 2019, 32, 141–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DrugBank Database Version 5.1.8. Available online: https://www.drugbank.ca/ (accessed on 1 June 2021).
- ChemSpider. Available online: http://www.chemspider.com/ (accessed on 1 June 2021).
- Connor, T.H.; Anderson, R.W.; Sessink, P.J.; Spivey, S.M. Effectiveness of a closed-system device in containing surface contamination with cyclophosphamide and ifosfamide in an i.v. admixture area. Am. J. Health-Syst. Pharm. 2002, 59, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedmer, M.; Tinnerberg, H.; Axmon, A.; Jönsson, B.A.G. Environmental and biological monitoring of antineoplastic drugs in four workplaces in a Swedish hospital. Int. Arch. Occup. Environ. Health. 2008, 81, 899–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuerk, J.; Kiffmeyer, T.K.; Hadtstein, C.; Heinemann, A.; Hahn, M.; Stuetzer, H.; Kuss, H.-M.; Eickmann, U. Development and validation of an LC-MS/MS procedure for environmental monitoring of eight cytostatic drugs in pharmacies. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2011, 91, 1178–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA). Evaluation Guidelines for Surface Sampling Methods; OSHA Salt Lake Technical Center: Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 2001.
- Larson, R.R.; Khazaeli, M.B.; Dillon, H.K. A new monitoring method using solid sorbent media for evaluation of airborne cyclophosphamide and other antineoplastic agents. Appl. Occup. Environ. Hyg. 2003, 18, 120–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odraska, P.; Dolezalova, L.; Piler, P.; Oravec, M.; Blaha, L. Utilization of the solid sorbent media in monitoring of airborne cyclophosphamide concentrations and the implications for occupational hygiene. J. Environ. Monit. 2011, 13, 1480–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiffmeyer, T.K.; Tuerk, J.; Hahn, M.; Stuetzer, H.; Hadtstein, C.; Heinemann, A.; Eickmann, U. Application and assessment of a regular environmental monitoring of the antineoplastic drug contamination level in pharmacies—The MEWIP project. Ann. Occup. Hyg. 2013, 57, 444–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]

| Cytostatic | Abbreviation | Chemical Structure | Studied by |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5-Fluorouracil | 5FU | 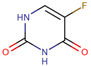 | [11,12,13,14,15,16,17,19,21,23,24,25] |
| Busulfan | BUS |  | [12,13,14] |
| Carboplatin | CPt | 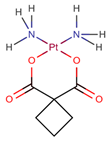 | [21] |
| Cyclophosphamide | CYC |  | [10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,23,24,25,26,27] |
| Cytarabine | CYT | 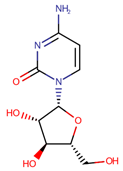 | [12,13,14,15,16,21,24] |
| Dacarbazine | DAC |  | [12,13,14,15,16,24] |
| Daunorubicin | DAU | 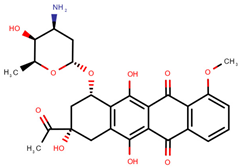 | [12,13,14] |
| Docetaxel | DOC | 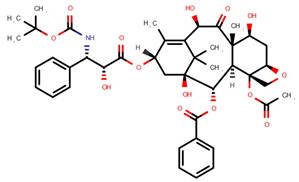 | [11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,20,24] |
| Doxorubicin | DOX |  | [11,12,13,14,15,16,18,19,20,21,24,25] |
| Epirubicin | EPI | 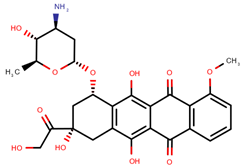 | [12,13,14,15,16,18,20,24,25] |
| Etoposide | ETO |  | [12,13,14,15,16,18,24] |
| Etoposide phosphate | ETP |  | [12,13,14] |
| Fludarabine phosphate | FLU | 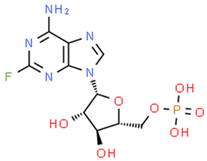 | [12,13,14] |
| Fotemustine | FOT |  | [15,16] |
| Ganciclovir | GAN |  | [12,14] |
| Gemcitabine | GEM |  | [12,13,14,15,16,18,21,24,25] |
| Idarubicin | IDA | 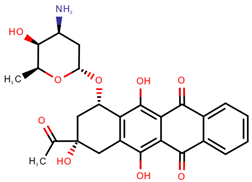 | [12,13,14,15,16] |
| Ifosfamide | IFO |  | [10,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,20,21,24,25] |
| Irinotecan | IRI |  | [12,13,14,15,16,18,20,24] |
| Melphalan | MEL | 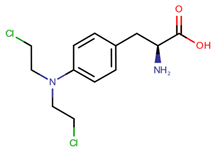 | [15,16] |
| Methotrexate | MET |  | [12,13,14,15,16,17,18,21,23,24] |
| Mitomycin C | MIT | 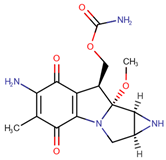 | [15,16,21,22] |
| Oxaliplatin | OPt | 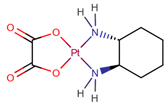 | [17,23] |
| Paclitaxel | PAC | 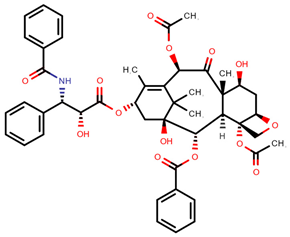 | [10,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,20,23,24] |
| Pemetrexed | PEM |  | [12,13,14,24] |
| Raltitrexed | RAL | 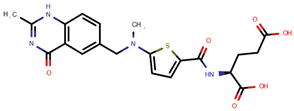 | [12,13,14] |
| Topotecan | TOP |  | [12,13,14,15,16,18] |
| Vinblastine | VBL |  | [12,13,14,15,16,17] |
| Vincristine | VCR | 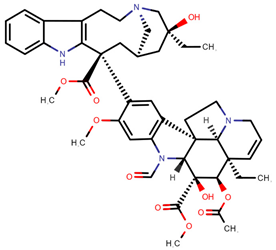 | [12,13,14,15,16,17,20,23] |
| Vindesine | VDE |  | [17,20] |
| Vinorelbine | VOR | 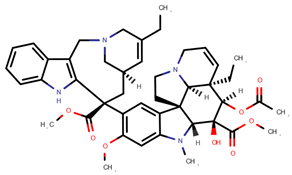 | [12,13] |
| Sampling | Sample Preparation | Recovery (%) | Cytostatic | References | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Surface Type | Sampling Area (cm2) | Sampling Device | Wetting Solution | Wiping Procedure | Extraction Solution | Extraction Procedure | Removal of Suspended Solids | From Surfaces | From Sampling Devices | ||
| N/S | 400 | Cellulose filter paper (Whatman 42, 55 mm) | MeOH:ACN:potassium phosphate buffer (25:10:65; 0.25 mL) | 2 wetted wipes | 9.75 mL MeOH:ACN: potassium phosphate buffer (25:10:65) | Sonication, 10 min | Filtration (0.22 µm); SPE; evaporate under nitrogen; reconstitute | N/S | 94 96 89 | CYC IFO PAC | [10] |
| Formica® Gloves Door locks | N/S | Wipe (Kleenex tissues) | MeOH:ethyl acetate (1:2; 1 mL) | 1 wetted wipe; vertical and horizontal wiping | 4 mL MeOH:ethyl acetate (1:2) | Ultrasonication, 30 min | N/S | 105 103 102 61 | N/S | 5FU CYC DOC DOX | [11] |
| Stainless steel | 100 | Polyester swab (Texwipe® TX716) | ISO:H2O (75:25) | 1 wetted swab | 10 mM acetic acid (pH 5.1, with 2% ACN) | Vortex, 5 min | N/S | N/S | 95 (mean value) | 5FU BUS CYC CYT DAC DAU DOC DOX EPI ETO ETP FLU GAN GEM IDA IFO IRI MET PAC PEM RAL TOP VCR | [12,13,14] |
| Stainless steel | 100 | Polyester swab (Texwipe® TX716) | ISO:H2O 75:25) | 1 wetted swab | 10 mM acetic acid (pH 5.1, with 2% ACN) | Sonication, 5 min | N/S | N/S | 95 (mean value) | ||
| Stainless steel | 100 | Polyester swab (Texwipe® TX714) | ISO:H2O (75:25) | 1 wetted swab | 10 mM acetic acid (pH 5.1, with 2% ACN) | Vortex, 5 min | N/S | N/S | 90 (mean value) | ||
| Stainless steel | 100 | Polyester swab (Texwipe® TX714) | ISO:H2O (75:25) | 1 wetted swab | 10 mM acetic acid (pH 5.1, with 2% ACN) | Sonication, 5 min | N/S | N/S | 90 (mean value) | ||
| Stainless steel | 100 | Polyurethane swab (Texwipe® TX712) | ISO:H2O (75:25) | 1 wetted swab | 10 mM acetic acid (pH 5.1, with 2% ACN) | Vortex, 5 min | N/S | N/S | 84 (mean value) | ||
| Stainless steel | 100 | Polyurethane swab (Texwipe® TX712) | ISO:H2O (75:25) | 1 wetted swab | 10 mM acetic acid (pH 5.1, with 2% ACN) | Sonication, 5 min | N/S | N/S | 74 (mean value) | ||
| Stainless steel | 100 | Cellulose filter paper (Whatman, 3mm) | ISO:H2O (75:25) | 1 wetted filter | 10 mM acetic acid (pH 5.1, with 2% ACN) | Vortex, 5 min | N/S | N/S | 69 (mean value) | ||
| Stainless steel | 100 | Cellulose filter paper (Whatman, 3mm) | ISO:H2O (75:25) | 1 wetted filter | 10 mM acetic acid (pH 5.1, with 2% ACN) | Sonication, 5 min | N/S | N/S | 69 (mean value) | ||
| Stainless steel | 100 | Cellulose filter paper (Whatman, 3mm) | ISO:H2O (75:25) | 1 wetted filter | 2 mL diluent | Vortex, few seconds | N/S | N/S | N/S | ||
| Stainless steel Non-porous polycarbonate Polyvinyl chloride flooring | 400 | Wipe (3-layer nonwoven, STS Medical Group Luigi Salvadori) | H2O:MeOH (equimolar; 0.5 mL/filter) | 1 wetted wipe; right, down and left wiping | 1.8 mL H2O:MeOH (equimolar) | Automated wipe desorption (Chromline) | N/S | N/S | 70–77 85–94 83–91 81–89 82–89 83–91 86–96 79–94 85–88 75–81 76–88 84–95 86–92 83–90 87–91 87–93 78–91 84–93 87–94 79–89 75–84 | 5FU CYC CYT DAC DOC DOX EPI ETO FOT GEM IDA IFO IRI MEL MET MIT PAC Pt TOP VBL VCR | [15,16] |
| Stainless steel Non-porous polycarbonate Polyvinyl chloride flooring | 400 | Wipe (3-layer nonwoven, STS Medical Group Luigi Salvadori) | H2O:MeOH (equimolar; 0.5 mL/filter) | 1 wetted wipe; right, down and left wiping | 2 mL H2O:MeOH (equimolar) | Filtered in-line (0.2 µm filters; manually or in automated mode) | N/S | ||||
| Stainless steel 304 (new) | 100 | Cellulose filter paper (Whatman 42, 70 mm) | H2O:MeOH (20:80, 0.1% HCOOH; 0.5 mL/filter) | 1 wetted filter; vertical and horizontal wiping | 5 mL H2O:MeOH (50:50, 0.1% HCOOH) | Ultrasonication, 35 min | Centrifugation (4500 rpm, 15 min) | ~40 | 44 | 5FU | [17] |
| ~95 | 101 | CYC | |||||||||
| ~100 | 113 | DOC | |||||||||
| ~100 | 101 | IFO | |||||||||
| ~70 | 100 | MET | |||||||||
| ~60 | 73 | OPt | |||||||||
| ~95 | 98 | PAC | |||||||||
| ~80 | 98 | VBL | |||||||||
| ~85 | 95 | VCR | |||||||||
| ~70 | 97 | VDE | |||||||||
| N/S | 900 | Wipe (Kimwipe®) | H2O:ISO (30:70; 1 mL/wipe) | 3 wetted wipes; each in a different direction (right, down, left) | 30 mL H2O:ISO (70:30, 0.1% HCOOH) | Ultrasonication, 15 min | Filtration (cellulose, 0.45 µm; 1 mL extract) | N/S | ~110 | CYC | [18] |
| ~110 | DOC | ||||||||||
| ~85 | DOX | ||||||||||
| ~90 | EPI | ||||||||||
| ~120 | ETO | ||||||||||
| ~105 | GEM | ||||||||||
| ~115 | IFO | ||||||||||
| ~105 | IRI | ||||||||||
| ~120 | MET | ||||||||||
| ~110 | PAC | ||||||||||
| ~100 | TOP | ||||||||||
| N/S | 900 | Wipe (Kimwipe®) | H2O:ISO (30:70; 1 mL/wipe) | 3 wetted wipes; each in a different direction | 30 mL H2O:ISO (80:20, 0.1% HCOOH) | Ultrasonication, 15 min | Filtration (cellulose, 0.45 µm; 1 mL extract) | N/S | 55 (DOX, EPI) –100 (DOC, IFO) | CYC DOC DOX EPI ETO GEM IFO IRI MET PAC TOP | [18] |
| N/S | 900 | Wipe (Kimwipe®) | H2O:ISO (30:70; 1 mL/wipe) | 3 wetted wipes; each in a different direction | 30 mL H2O:ISO (85:15, 0.1% HCOOH) | Ultrasonication, 15 min | Filtration (cellulose, 0.45 µm; 1 mL extract) | N/S | 40 (DOX, EPI) –95 (IFO) | ||
| N/S | 900 | Wipe (Kimwipe®) | H2O:ISO (30:70; 1 mL/wipe) | 3 wetted wipes; each in a different direction | 30 mL H2O:ISO (90:10, 0.1% HCOOH) | Ultrasonication, 15 min | Filtration (cellulose, 0.45 µm; 1 mL extract) | N/S | 35 (DOX, EPI) –105 (IFO) | ||
| N/S | 900 | Wipe (Kimwipe®) | H2O:ISO (30:70; 1 mL/wipe) | 3 wetted wipes; each in a different direction | 30 mL H2O:ISO (95:5, 0.1% HCOOH) | Ultrasonication, 15 min | Filtration (cellulose, 0.45 µm; 1 mL extract) | N/S | 25 (DOX, EPI)– 100 (DOC, ETO) | ||
| N/S | 900 | Wipe (Kimwipe®) | H2O:ISO (30:70; 1 mL/wipe) | 3 wetted wipes; each in a different direction | 30 mL H2O:ACN (80:20, 0.1% HCOOH) | Ultrasonication, 15 min | Filtration (cellulose, 0.45 µm; 1 mL extract) | N/S | 70 (EPI) –100 (PAC) | ||
| N/S | 900 | Wipe (Kimwipe®) | H2O:ISO (30:70; 1 mL/wipe) | 3 wetted wipes; each in a different direction | 30 mL H2O:ACN (85:15, 0.1% HCOOH) | Ultrasonication, 15 min | Filtration (cellulose, 0.45 µm; 1 mL extract) | N/S | 55 (EPI)– 90 (IFO, CYC) | ||
| N/S | 900 | Wipe (Kimwipe®) | H2O:ISO (30:70; 1 mL/wipe) | 3 wetted wipes; each in a different direction | 30 mL H2O:ACN (90:10, 0.1% HCOOH) | Ultrasonication, 15 min | Filtration (cellulose, 0.45 µm; 1 mL extract) | N/S | 40 (EPI) –105 (ETO) | ||
| N/S | 900 | Wipe (Kimwipe®) | H2O:ISO (30:70; 1 mL/wipe) | 3 wetted wipes; each in a different direction | 30 mL H2O:ACN (95:5, 0.1% HCOOH) | Ultrasonication, 15 min | Filtration (cellulose, 0.45 µm; 1 mL extract) | N/S | 30 (EPI) –105 (ETO) | ||
| N/S | 900 | Wipe (Kimwipe®) | H2O:ISO (30:70; 1 mL/wipe) | 3 wetted wipes; each in a different direction | 30 mL H2O:DMSO (80:20, 0.1% HCOOH) | Ultrasonication, 15 min | Filtration (cellulose, 0.45 µm; 1 mL extract) | N/S | 45 (EPI) –105 (DOC) | ||
| N/S | 900 | Wipe (Kimwipe®) | H2O:ISO (30:70; 1 mL/wipe) | 3 wetted wipes; each in a different direction | 30 mL H2O:DMSO (85:15, 0.1% HCOOH) | Ultrasonication, 15 min | Filtration (cellulose, 0.45 µm; 1 mL extract) | N/S | 35 (EPI) –115 (ETO) | ||
| N/S | 900 | Wipe (Kimwipe®) | H2O:ISO (30:70; 1 mL/wipe) | 3 wetted wipes; each in a different direction | 30 mL H2O:DMSO (90:10, 0.1% HCOOH) | Ultrasonication, 15 min | Filtration (cellulose, 0.45 µm; 1 mL extract) | N/S | 25 (EPI)– 95 (CYC, IFO) | ||
| N/S | 900 | Wipe (Kimwipe®) | H2O:ISO (30:70; 1 mL/wipe) | 3 wetted wipes; each in a different direction | 30 mL H2O:DMSO (95:5, 0.1% HCOOH) | Ultrasonication, 15 min | Filtration (cellulose, 0.45 µm; 1 mL extract) | N/S | 25 (EPI) –100 (CYC) | ||
| Stainless steel | 100 | Cellulose filter paper (Whatman 42, 55 mm) | Sterile water (10 mL) | 1 wetted filter, then 1 dry filter | 15 mL acetic acid 1% | Mix 10 min; SPE | Centrifugation (10,000 rpm, 4 °C; 50 mL acetic acid 1%) | N/S | 76.3 76.3 70.0 | 5FU CYC DOX | [19] |
| N/S | 800 | Wipe (Kimwipe® S-200) | MeOH (70%, 0.1% HCOOH; 1 mL/wipe) | 3 wetted wipes | 8 mL MeOH (70%, 0.1% HCOOH) | Shaker, 30 min, 2000 rpm | N/S | N/S | N/S | CYC, DOC, DOX, EPI, IFO, IRI, PAC, VBL, VCR, VDE | [20] |
| N/S | 2000 | Swab (sterile, non-woven) | MeOH:(0.05% HCOOH) (8:2; 4 mL) | 1 wetted swab (wipe twice) | 40 mL H2O (0.05% HCOOH) | Ultrasonication, 15 min | N/S | N/S | 97 | 5FU | [21] |
| 99 | CPt | ||||||||||
| 101 | CYC | ||||||||||
| 93 | CYT | ||||||||||
| 82 | DOX | ||||||||||
| 82 | GEM | ||||||||||
| 92 | IFO | ||||||||||
| 87 | MET | ||||||||||
| 64 | MIT | ||||||||||
| Stainless steel 304 | 100 | Cellulose filter paper (Whatman 42, 55 mm) | ACN:ISO:H2O (20:45:35; 0.2 mL/filter) | 3 dry filters (sampling area wetted each time) | 9 mL ACN:ISO:H2O (20:45:35) | Orbital shaker, 30 min | Filtration (PVDF, 0.22 µm) | 62–98 | N/S | MIT | [22] |
| Stainless steel 304 | 100 | Polyester swab (Texwipe® TX714A) | ACN:ISO:H2O (20:45:35; 0.2 mL/filter) | 3 dry filters (sampling area wetted each time) | 9 mL ACN:ISO:H2O (20:45:35) | Orbital shaker, 30 min | Filtration (PVDF, 0.22 µm) | 61–98 | N/S | ||
| Vinyl | 100 | Cellulose filter paper (Whatman 42, 55 mm) | ACN:ISO:H2O (20:45:35; 0.2 mL/filter) | 3 dry filters (sampling area wetted each time) | 9 mL ACN:ISO:H2O (20:45:35) | Orbital shaker, 30 min | Filtration (PVDF, 0.22 µm) | 51–63 | N/S | ||
| Vinyl | 100 | Polyester swab (Texwipe® TX714A) | ACN:ISO:H2O (20:45:35; 0.2 mL/filter) | 3 dry filters (sampling area wetted each time) | 9 mL ACN:ISO:H2O (20:45:35) | Orbital shaker, 30 min | Filtration (PVDF, 0.22 µm) | 53–62 | N/S | ||
| Formica® | 100 | Cellulose filter paper (What-man 42, 55 mm) | ACN:ISO:H2O (20:45:35; 0.2 mL/filter) | 3 dry filters (sampling area wetted each time) | 9 mL ACN:ISO:H2O (20:45:35) | Orbital shaker, 30 min | Filtration (PVDF, 0.22 µm) | 30–96 | N/S | ||
| Formica® | 100 | Polyester swab (Texwipe® TX714A) | ACN:ISO:H2O (20:45:35; 0.2 mL/filter) | 3 dry filters (sampling area wetted each time) | 9 mL ACN:ISO:H2O (20:45:35) | Orbital shaker, 30 min | Filtration (PVDF, 0.22 µm) | 63–97 | N/S | ||
| Stainless steel (new and worn) | 100 | Cellulose filter paper (Whatman 42, 70 mm) | H2O:MeOH (20:80, 0.1% HCOOH; 0.5 mL) | 1 wetted filter; vertical and horizontal wiping | 5 mL H2O:MeOH (50:50, 0.1% HCOOH) | Ultrasonication, 35 min | Centrifugation (4500 rpm, 15 min); filtration | ~60 ~80 ~20 ~40 ~85 ~60 | 63 99 102 80 101 103 | 5FU CYC MET OPt PAC VCR | [23] |
| Stainless steel (new and worn) | 100 | Cellulose filter paper (Whatman 42, 70 mm) | H2O:MeOH (20:80, 0.1% HCOOH; 0.5 mL) | 1 wetted filter; vertical and horizontal wiping | 5 mL H2O:MeOH (20:80, 0.1% HCOOH) | Ultrasonication, 35 min | Centrifugation (4500 rpm, 15 min); filtration | - | 65 (5FU) – 120 (PAC) | 5FU CYC MET OPt PAC VCR | |
| Stainless steel (new and worn) | 100 | Cellulose filter paper (Whatman 42, 70 mm) | H2O:MeOH (20:80, 0.1% HCOOH; 0.5 mL) | 1 wetted filter; vertical and horizontal wiping | 5 mL H2O:MeOH (50:50, 0.1% HCOOH) | Ultrasonication, 20 min | Centrifugation (4500 rpm, 15 min); filtration | - | 63 (5FU) – 99 (VCR) | ||
| Stainless steel (new and worn) | 100 | Cellulose filter paper (Whatman 42, 70 mm) | H2O:MeOH (80:20, 0.1% HCOOH; 0.5 mL) | 1 wetted filter; vertical and horizontal wiping | 5 mL H2O:MeOH (50:50, 0.1% HCOOH) | Ultrasonication, 35 min | Centrifugation (4500 rpm, 15 min); filtration | 25 (VCR) –95 (CYC) | N/S | ||
| Stainless steel (new and worn) | 100 | Cellulose filter paper (Whatman 42, 70 mm) | H2O:MeOH (50:50, 0.1% HCOOH; 0.5 mL) | 1 wetted filter; vertical and horizontal wiping | 5 mL H2O:MeOH (50:50, 0.1% HCOOH) | Ultrasonication, 35 min | Centrifugation (4500 rpm, 15 min); filtration | 20 (MET) –70 (CYC) | N/S | ||
| Stainless steel (new and worn) | 100 | Cellulose filter paper (Whatman 42, 70 mm) | H2O (0.1% HCOOH; 0.5 mL) | 1 wetted filter; vertical and horizontal wiping | 5 mL H2O:MeOH (50:50, 0.1% HCOOH) | Ultrasonication, 35 min | Centrifugation (4500 rpm, 15 min); filtration | 10 (PAC, VCR)– 70 (CYC) | N/S | ||
| Stainless steel (new and worn) | 100 | Cellulose filter paper (Whatman 42, 70 mm) | MeOH (0.1% HCOOH; 0.5 mL) | 1 wetted filter; vertical and horizontal wiping | 5 mL H2O:MeOH (50:50, 0.1% HCOOH) | Ultrasonication, 35 min | Centrifugation (4500 rpm, 15 min); filtration | 5 (MET)–80 (CYC, PAC) | N/S | ||
| Stainless steel (new and worn) | 100 | Cellulose filter paper (Whatman 42, 70 mm) | H2O:MeOH:ACN (65:25:10, 0.1% HCOOH; 0.5 mL) | 1 wetted filter; vertical and horizontal wiping | 5 mL H2O:MeOH (50:50, 0.1% HCOOH) | Ultrasonication, 35 min | Centrifugation (4500 rpm, 15 min); filtration | 30 (VCR)–95 (CYC) | N/S | ||
| N/S | 225 | Viscose swab (DeltalaB) | Sterile water (0.05 mL) | 1 wetted swab, then 1 dry swab; both in 3 different directions (vertical, horizontal, diagonal) | 2 mL MeOH | Vortex, 30 s; ultrasonication, 10 min | Centrifugation (19,000 g, 5 min) | N/S | 75–114 | 5FU, CYC, CYT, DAC, DOC, DOX, EPI, ETO, GEM, IFO, IRI, MET, PAC, PEM | [24] |
| N/S | 100 | Cellulose filter paper (Whatman, 55mm) | Sterile water (0.4 mL) | 1 wetted filter, then 1 dry filter | 15 mL acetic acid 1% | Mix 20 min; SPE | N/S | N/S | 21 | 5FU | [25] |
| 75 | CYC | ||||||||||
| 18 | DOX | ||||||||||
| 14 | EPI | ||||||||||
| 54 | GEM | ||||||||||
| 81 | IFO | ||||||||||
| Cytostatic | Instrumentation | Stationary Phase | Mobile Phase | Run Time | Linearity | Precision (%) | Accuracy (%) 1 | IDL | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CYC, IFO, PAC | LC–UV | Symmetry® C18 (150 × 4.6 mm, 5 µm) | (A) H2O + 10 mM phosphate buffer (pH 6) (B) ACN | 25 min | 0.3–38 ng/cm2—PAC 0.6–38 ng/cm2—CYC 0.8–38 ng/cm2—IFO | Within-run: 1.5–1.7 Between-run: 1.7–2.3 | N/S | 20 pg/cm2—IFO 30 pg/cm2—PAC 100 pg/cm2—CYC | [10] |
| 5FU, CYC, DOC, DOX | UPLC–MS/MS | SHIM-PACK XR-ODC-C18 (100 × 3 mm, 2.2 µm) | (A) H2O + 0.1% HCOOH (B) ACN | 15 min | 0.1–15 ng/cm2—5FU 2 0.2–15 ng/cm2—CYC, DOC, DOX 2 | Within-run: 1.2–14.2 Between-run: 1.3–13.2 | N/S | 25 pg/cm2—5FU 2 50 pg/cm2—CYC, DOC, DOX 2 | [11] |
| 5FU, BUS, CYC, CYT, DAC, DAU, DOC, DOX, EPI, ETO, ETP, FLU, GAN, GEM, IDA, IFO, IRI, MET, PAC, PEM, RAL, TOP, VCR | UPLC–MS/MS | CORTECS UPLC T3 (100 × 2.1 mm, 1.6 µm) | (A) H2O + 10 mM ammonium acetate (pH 5.1) (B) ACN | 17.5 min | N/S | N/S | N/S | N/S | [12,13] |
| 5FU, CYC, CYT, DAC, DOC, DOX, EPI, ETO, FOT, GEM, IDA, IFO, IRI, MEL, MET, MIT, PAC, Pt, TOP, VBL, VCR | LC–MS/MS (all except Pt) | For 5FU, CYT, DAC, GEM: SeQuant ZIC-HILIC (100 × 2.1 mm, 5 µm) | For 5FU, CYT, DAC, GEM: (A) H2O + 0.1 M ammonium formate (B) ACN | 15 min | 0.003–0.1 ng/cm2 (all) | Within-run: 1.4–5.4 Between-run: 3.3–6.7 | N/S | 0.05 pg/cm2—Pt 0.2 pg/cm2—IFO 0.3 pg/cm2—CYC, EPI, MEL, PAC 0.4 pg/cm2—5FU, DOC, IRI, MET, TOP, VCR 0.5 pg/cm2—FOT 1.1 pg/cm2—IDA 1.2 pg/cm2—MIT 2.2 pg/cm2—GEM 2.3 pg/cm2—DOX, VBL 2.6 pg/cm2—CYT, DAC 3.0 pg/cm2—ETO | [15,16] |
| For others: Atlantis T3 (100 × 2.1 mm, 3 µm) | For others: (A) H2O + 0.1% HCOOH (B) ACN:MeOH (60:40) + 0.1% HCOOH | 20.5 min | |||||||
| For all (except Pt): YMC-Pack ODS-AQ (250 × 2.1 mm, 5 µm) | For all (except Pt): (A) H2O (B) ACN:MeOH (60:40) + 0.1% HCOOH | 23 min | |||||||
| ICP–MS (Pt) | - | - | - | ||||||
| 5FU, CYC, DOC, IFO, MET, OPt, PAC, VBL, VCR, VDE | LC–MS/MS | Kinetex Biphenyl (50 × 4.6 mm, 2.6 µm) | (A) H2O (+formic acid + ammonium formate; pH 2.3) (B) MeOH | 8 min | 0.06–11 ng/cm2—5FU, OXP 0.01–11 ng/cm2—others | Within-run: 1–13 Between-run: 1–8 | 92–105 | 0.01 pg/cm2—VCR 0.04 pg/cm2—VBL 0.05 pg/cm2—PAC 0.4 pg/cm2—DOC 0.8 pg/cm2—VDE 1.8 pg/cm2—CYC 3.9 pg/cm2—MET 10.7 pg/cm2—IFO 86.9 pg/cm2—OPt 176.4 pg/cm2—5FU | [17] |
| CYC, DOC, DOX, EPI, ETO, GEM, IFO, IRI, MET, PAC, TOP | Micro-LC–MS/MS | YMC Triart C18 (50 × 0.3 mm, 1.9 µm) | (A) H2O + 0.1% HCOOH (B) ACN + 0.1% HCOOH | 2.25 min | 0.0004–0.4 ng/cm2—IFO 0.0004–1.8 ng/cm2—PAC 0.0004–4 ng/cm2—DOX 0.0004–0.9 ng/cm2—others | Within-run: 2.7–13.5 Between-run: 3.3–16.2 | N/S | 1.9 pg/cm2—DOX 2.2 pg/cm2—TOP 2.5 pg/cm2—CYC, GEM 3.5 pg/cm2—EPI 3.9 pg/cm2—IFO 4.0 pg/cm2—ETO 4.5 pg/cm2—MET 4.6 pg/cm2—IRI 7.6 pg/cm2—PAC 17.9 pg/cm2—DOC | [18] |
| 5FU, CYC, DOX | LC–MS | Pursuit XRs Ultra (100 × 2 mm, 2.8 µm) | (A) H2O + 0.1% acetic acid (B) water ACN | 30 min | 0.01–1 ng/cm2—CYC 0.1–5—5FU, DOX | Within-run: 2.5–8.4 Between-run: 2.1–9.4 | 82–104 | 5 pg/cm2—CYC 50 pg/cm2—5FU, DOX | [19] |
| CYC, DOC, DOX, EPI, IFO, IRI, PAC, VBL, VCR, VDE | LC–MS/MS | Inertsil® ODS-3 (50 × 2.1 mm, 3 µm) | (A) H2O + 0.1% HCOOH (B) ACN + 0.1% HCOOH | 22 min | 0.06–13 ng/cm2—VBL, VCR, VDE 0.06–1.3 ng/cm2—others | Within-run: 1.0–11.5 Between-run: 3.6–14.4 | Within-run: 89–113 Between-run: 85–112 | 19 pg/cm2—VBL, VCR, VDE 3 1.9 pg/cm2—others 3 | [20] |
| 5FU, CPt, CYC, CYT, DOX, GEM, IFO, MET, MIT | LC–HRMS/MS | Varian Pursuit C18 (150 × 2 mm, 3 µm) | Positive ion mode: (A) H2O + 0.05% HCOOH (B) MeOH Negative ion mode: (A) H2O + 0.1 mM ammonium acetate (B) MeOH | 25 min | 0.02–2 ng/cm2 (all) | Within-run: 5.0–12.2 (except MIT—99.9) Between-run: 3.0–7.5 (except MIT—19.9) | N/S | 7 pg/cm2 (all) 3 | [21] |
| MIT | LC–MS/MS | Zorbax Rx C18 (250 × 3.0 mm, 3.5 µm) | (A) ACN:H2O (10:90) + 0.1% acetic acid (B) ACN:H2O (75:25) + 0.1% acetic acid | 24 min | 0.2–50 ng/cm2 | Stainless steel 304: 1.0–10.8 Vinyl: 2.3–12.6 Formica®: 0.7–8.5 | Stainless steel 304: 93–104 Vinyl: 95–105 Formica®: 94–103 | 20 pg/cm2 | [22] |
| 5FU, CYC, MET, OPt, PAC, VCR | LC–MS/MS | Kinetex Biphenyl (50 × 4.6 mm, 2.6 µm) | (A) H2O (+ formic acid + ammonium formate; pH 2.3) (B) MeOH | 7 min | 0.01–11 ng/cm2—CYC, MET, PAC, VCR 0.6–11 ng/cm2—5FU, OPt | Within-run: 0.9–8.9 Between-run: 3.8–11.0 | 89–106 | 1 pg/cm2—PAC 4 pg/cm2—CYC, MET 5 pg/cm2—VCR 127 pg/cm2—OPt 832 pg/cm2—5FU | [23] |
| 5FU, CYC, CYT, DAC, DOC, DOX, EPI, ETO, GEM, IFO, IRI, MET, PAC, PEM | LC–MS/MS | For 5FU: Hypercarb™ (100 × 2.1 mm, 5µm) For others: Acquity UPLC® BEH C18 (50 × 2.1 mm, 1.9 µm) | For 5FU: (A) H2O (B) MeOH For others: (A) H2O (B) ACN + 0.1% HCOOH | 8 min | 0.0004–0.2 ng/cm2—CYC, DOX, EPI 0.0009–0.2 ng/cm2—5FU, DAC, GEM, IFO, IRI, MET, PAC, PEM 0.004–0.2 ng/cm2—CYT, DOC, ETO | 1.5–13.5 | 61–133 | 0.1 pg/cm2—CYC, DOX, EPI 3 1 pg/cm2—CYT, DOC, ETO 3 0.3—others 3 | [24] |
| 5FU, CYC, DOX, EPI, GEM, IFO | UPLC–MS/MS | HSS T3 (50 × 2.1 mm, 1.8 µm) | (A) H2O + 0.5% acetic acid (B) ACN + 0.5% acetic acid | 6.5 min | 0.002–0.4 ng/cm2—CYC, GEM, IFO 0.025–2 ng/cm2—5FU, DOX, EPI | N/S | 98–108 | 0.2 pg/cm2—CYC, GEM 0.4 pg/cm2—IFO 1.25 pg/cm2—5FU, DOX 5 pg/cm2—EPI | [25] |
| CYC | GC–ECD | BP5 (30 m) | Nitrogen (99.9995%) | 25 min | 212–1062 µg/m3 | Within-run: 4.8 Between-run: 8.9 | Within-run: 95–109 Between-run: 97–104 | 100 µg/m3 | [26] |
| CYC | LC–UV | Inertsil® ODS-3 (150 × 4.6 mm, 5 µm) | (A) H2O (B) ACN | N/S | 0.05–500 µg/mL | N/S | N/S | 0.01 µg/mL | [27] |
| CYC | LC–MS/MS | L-column 2 ODS (150 × 2.1 mm, 5 µm) | (A) H2O (B) ACN | N/S | 0.00001–0.3 µg/mL | N/S | N/S | 0.000005 µg/mL |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Portilha-Cunha, M.F.; Alves, A.; Santos, M.S.F. Cytostatics in Indoor Environment: An Update of Analytical Methods. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 574. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14060574
Portilha-Cunha MF, Alves A, Santos MSF. Cytostatics in Indoor Environment: An Update of Analytical Methods. Pharmaceuticals. 2021; 14(6):574. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14060574
Chicago/Turabian StylePortilha-Cunha, M. Francisca, A. Alves, and Mónica S. F. Santos. 2021. "Cytostatics in Indoor Environment: An Update of Analytical Methods" Pharmaceuticals 14, no. 6: 574. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14060574
APA StylePortilha-Cunha, M. F., Alves, A., & Santos, M. S. F. (2021). Cytostatics in Indoor Environment: An Update of Analytical Methods. Pharmaceuticals, 14(6), 574. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14060574







