Generation of a Transgenic Zebrafish Line for In Vivo Assessment of Hepatic Apoptosis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
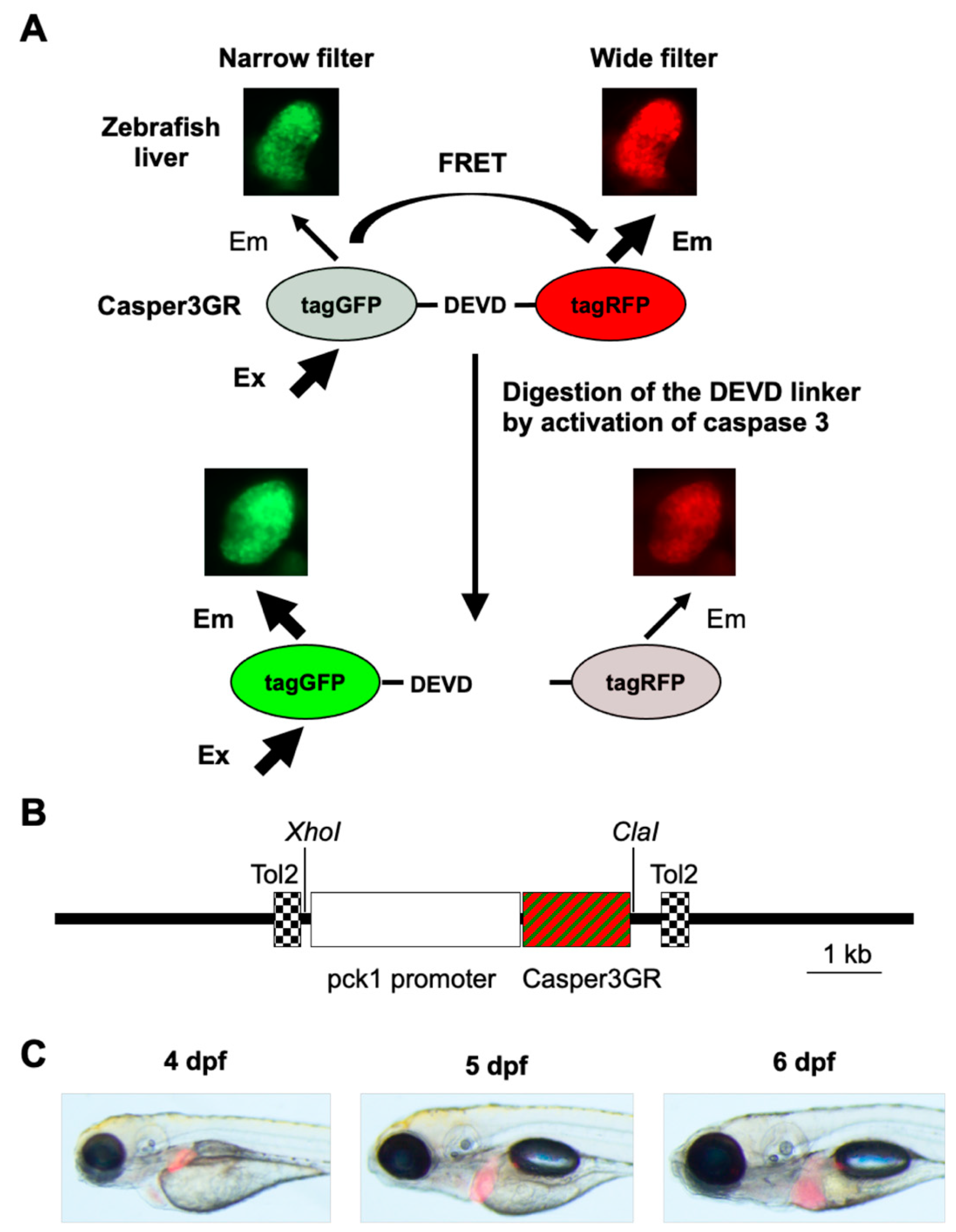
2.1. Generation of a Transgenic Zebrafish Expressing Casper3GR in Hepatocytes
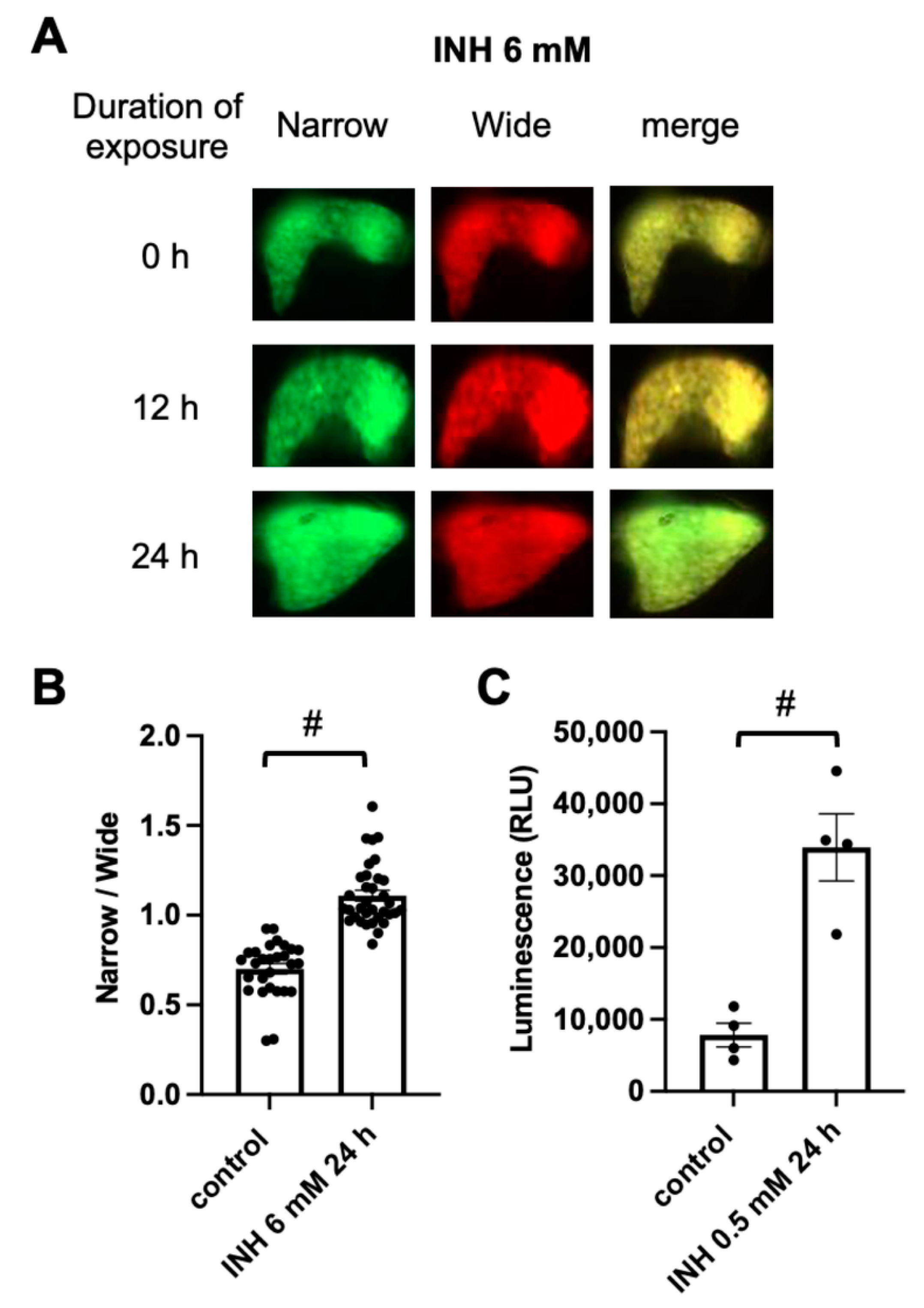
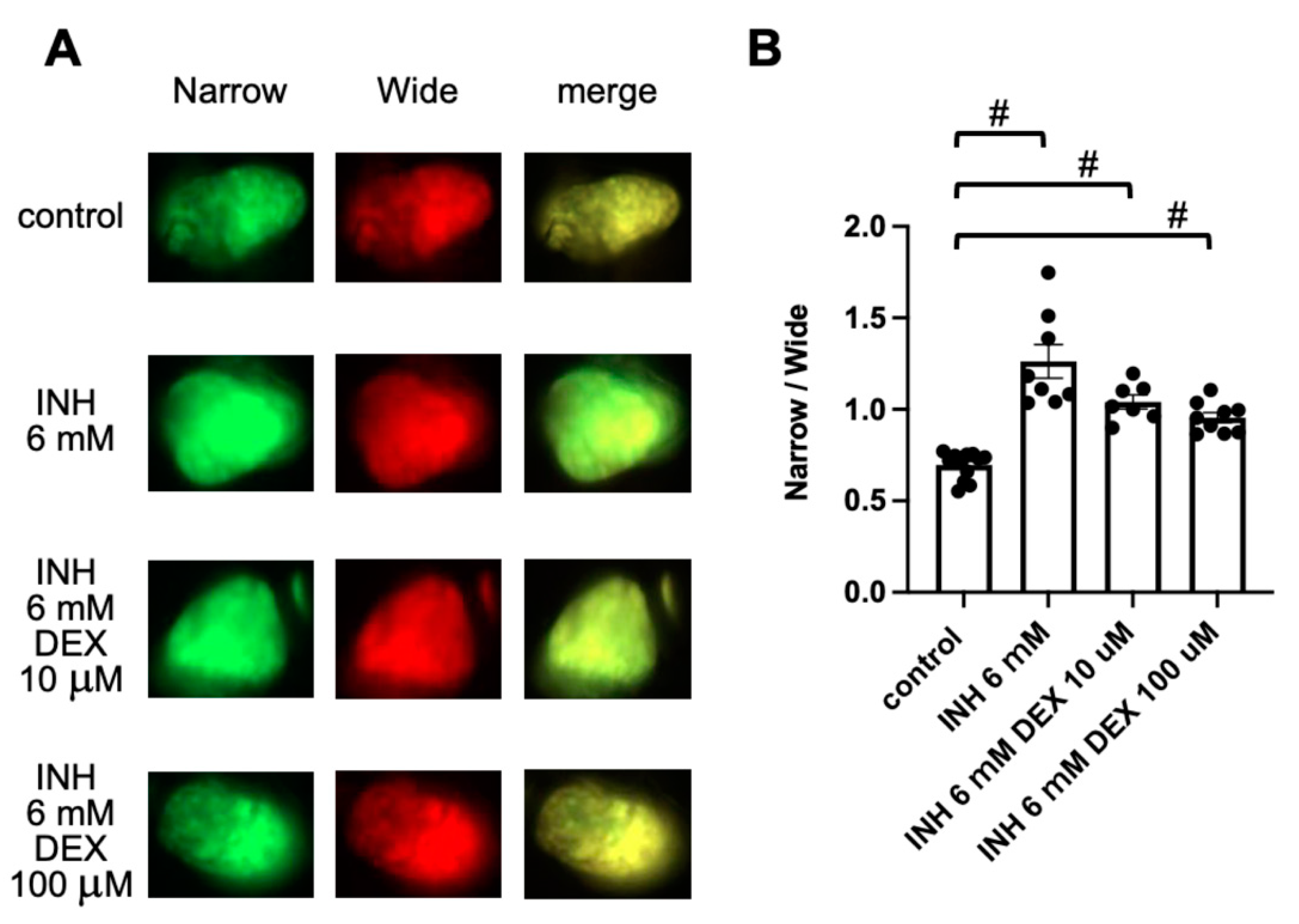
2.2. FRET-Based Imaging of Tg (pck1:Casper3GR) Detects Isoniazid (INH)-Induced Hepatocyte Apoptosis
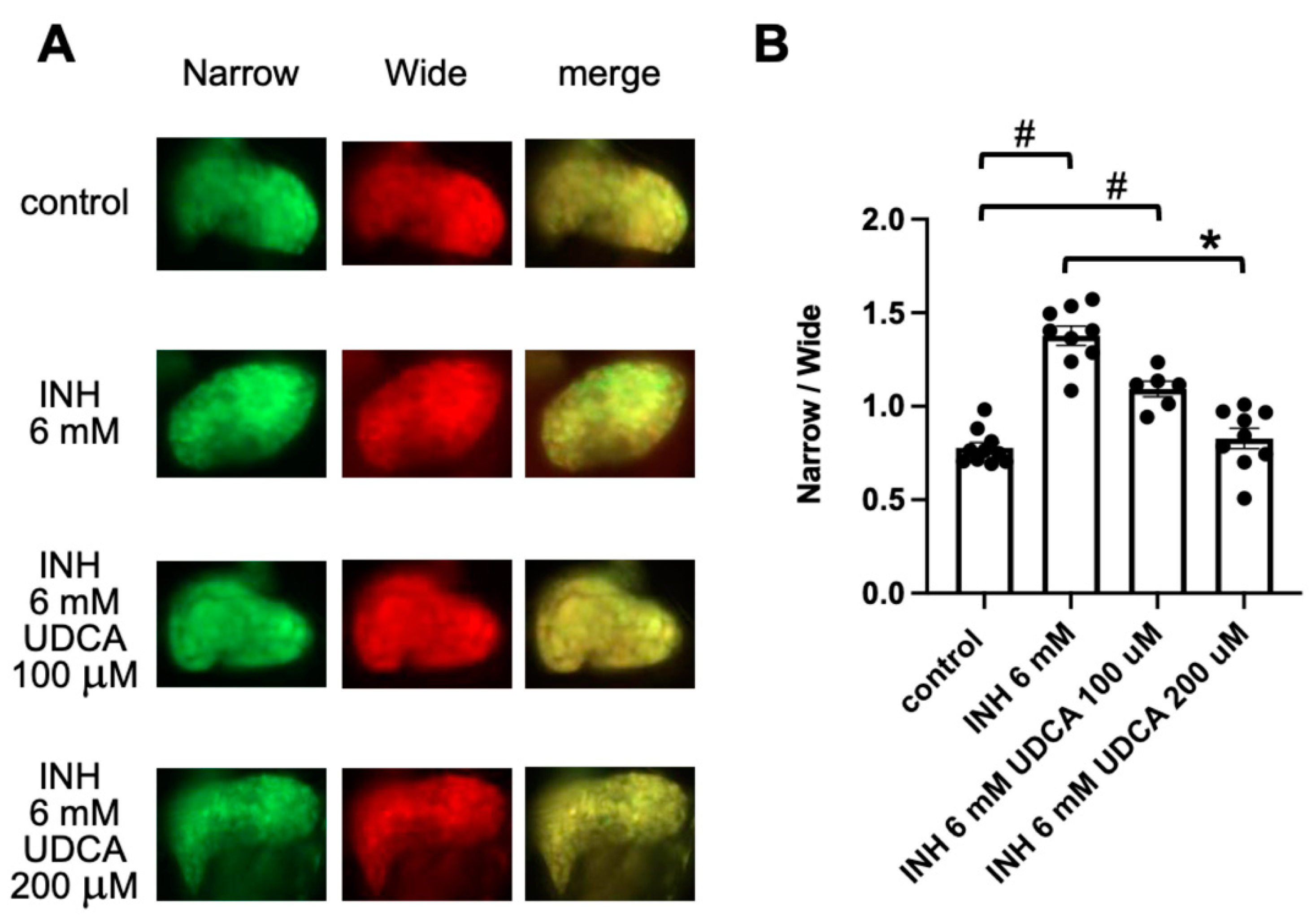
2.3. Detection of Ursodeoxycholic Acid (UDCA)-Associated Hepatoprotection Using FRET-Based Imaging of Tg (pck1:Casper3GR)
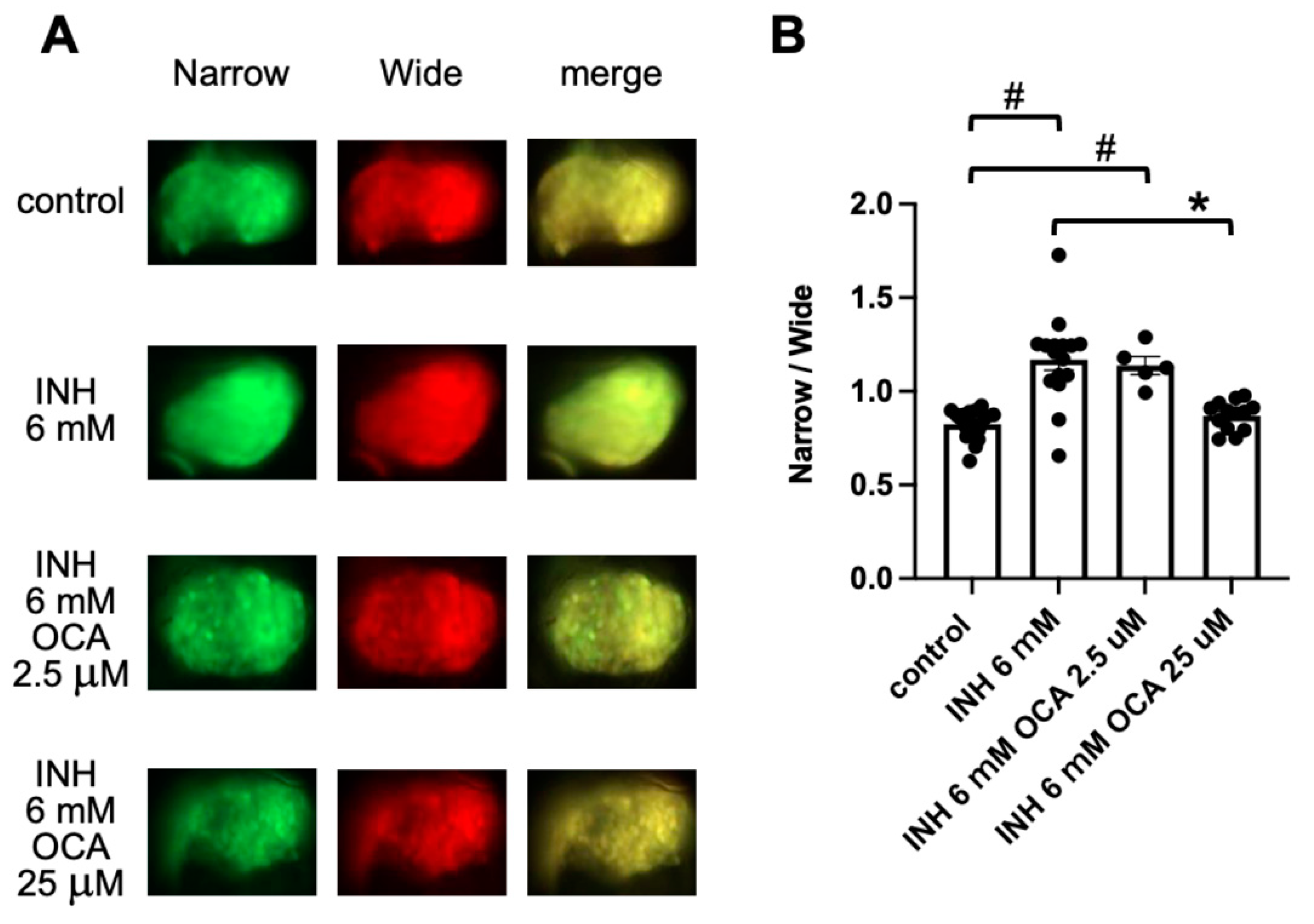
2.4. Detection of Obeticholic Acid (OCA)-Associated Hepatoprotection Using FRET-Based Imaging of Tg (pck1:Casper3GR)
2.5. Detection of DEX-Induced Hepatotoxicity Using FRET-Based Imaging of Tg (pck1:Casper3GR)
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Ethics Statement
4.2. Compounds
4.3. Zebrafish Husbandry
4.4. Generation of Tg (pck1:Casper3GR) Zebrafish
4.5. Exposure of Tg (pck1:Casper3GR) to Chemicals and In Vivo Fluorescence Imaging
4.6. Caspase 3/7 Assay
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, K. Molecular mechanisms of hepatic apoptosis. Cell Death Dis. 2014, 5, e996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwabe, R.F.; Luedde, T. Apoptosis and necroptosis in the liver: A matter of life and death. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 15, 738–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shojaie, L.; Iorga, A.; Dara, L. Cell Death in Liver Diseases: A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Pacher, P.; De Lisle, R.C.; Huang, H.; Ding, W.X. A Mechanistic Review of Cell Death in Alcohol-Induced Liver Injury. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2016, 40, 1215–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vernetti, L.A.; Vogt, A.; Gough, A.; Taylor, D.L. Evolution of Experimental Models of the Liver to Predict Human Drug Hepatotoxicity and Efficacy. Clin. Liver Dis. 2017, 21, 197–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poloznikov, A.; Gazaryan, I.; Shkurnikov, M.; Nikulin, S.; Drapkina, O.; Baranova, A.; Tonevitsky, A. In vitro and in silico liver models: Current trends, challenges and opportunities. Altex 2018, 35, 397–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, P.A.; Ryder, S.; Lavado, A.; Dilworth, C.; Riley, R.J. The evolution of strategies to minimise the risk of human drug-induced liver injury (DILI) in drug discovery and development. Arch. Toxicol. 2020, 94, 2559–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevzorova, Y.A.; Boyer-Diaz, Z.; Cubero, F.J.; Gracia-Sancho, J. Animal models for liver disease—A practical approach for translational research. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 423–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maes, M.; Vinken, M.; Jaeschke, H. Experimental models of hepatotoxicity related to acute liver failure. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2016, 290, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ozaki, M.; Haga, S.; Ozawa, T. In vivo monitoring of liver damage using caspase-3 probe. Theranostics 2012, 2, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fu, Q.; Duan, X.; Yan, S.; Wang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Jia, S.; Du, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhan, L. Bioluminescence imaging of caspase-3 activity in mouse liver. Apoptosis Int. J. Program. Cell Death 2013, 18, 998–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vliegenthart, A.D.; Tucker, C.S.; Del Pozo, J.; Dear, J.W. Zebrafish as model organisms for studying drug-induced liver injury. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2014, 78, 1217–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goessling, W.; Sadler, K.C. Zebrafish: An important tool for liver disease research. Gastroenterology 2015, 149, 1361–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Katoch, S.; Patial, V. Zebrafish: An emerging model system to study liver diseases and related drug discovery. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2021, 41, 33–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Souza Anselmo, C.; Sardela, V.F.; de Sousa, V.P.; Pereira, H.M.G. Zebrafish (Danio rerio): A valuable tool for predicting the metabolism of xenobiotics in humans? Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2018, 212, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaji, T.; Yamashita, N.; Umeda, H.; Zhang, S.; Mizoguchi, N.; Seki, M.; Kitazawa, T.; Teraoka, H. Cytochrome P450 Expression and Chemical Metabolic Activity before Full Liver Development in Zebrafish. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verstraelen, S.; Peers, B.; Maho, W.; Hollanders, K.; Remy, S.; Berckmans, P.; Covaci, A.; Witters, H. Phenotypic and biomarker evaluation of zebrafish larvae as an alternative model to predict mammalian hepatotoxicity. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2016, 36, 1194–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, B.; Zheng, Y.-M.; Zhang, J.-P. Comparative Study of Different Diets-Induced NAFLD Models of Zebrafish. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, G.; Cao, L.; Du, J.; Jia, R.; Kitazawa, T.; Kubota, A.; Teraoka, H. Dexamethasone-induced hepatomegaly and steatosis in larval zebrafish. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2017, 42, 455–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- North, T.E.; Goessling, W.; Walkley, C.R.; Lengerke, C.; Kopani, K.R.; Lord, A.M.; Weber, G.J.; Bowman, T.V.; Jang, I.H.; Grosser, T.; et al. Prostaglandin E2 regulates vertebrate haematopoietic stem cell homeostasis. Nature 2007, 447, 1007–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashita, A.; Deguchi, J.; Honda, Y.; Yamada, T.; Miyawaki, I.; Nishimura, Y.; Tanaka, T. Increased susceptibility to oxidative stress-induced toxicological evaluation by genetically modified nrf2a-deficient zebrafish. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods 2019, 96, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.; Luo, K.Q. Fluorescence resonance energy transfer-based sensor zebrafish for detecting toxic agents with single-cell sensitivity. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 408, 124826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shcherbo, D.; Souslova, E.A.; Goedhart, J.; Chepurnykh, T.V.; Gaintzeva, A.; Shemiakina, I.I.; Gadella, T.W.; Lukyanov, S.; Chudakov, D.M. Practical and reliable FRET/FLIM pair of fluorescent proteins. BMC Biotechnol. 2009, 9, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xia, N.S.; Luo, W.X.; Zhang, J.; Xie, X.Y.; Yang, H.J.; Li, S.W.; Chen, M.; Ng, M.H. Bioluminescence of Aequorea macrodactyla, a common jellyfish species in the East China Sea. Mar. Biotechnol. 2002, 4, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Merzlyak, E.M.; Goedhart, J.; Shcherbo, D.; Bulina, M.E.; Shcheglov, A.S.; Fradkov, A.F.; Gaintzeva, A.; Lukyanov, K.A.; Lukyanov, S.; Gadella, T.W.; et al. Bright monomeric red fluorescent protein with an extended fluorescence lifetime. Nat. Methods 2007, 4, 555–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong, K.; Ikura, M. The use of FRET imaging microscopy to detect protein–protein interactions and protein conformational changes in vivo. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2001, 11, 573–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, N.; Ramel, M.C.; Kumar, S.; Alexandrov, Y.; Kelly, D.J.; Warren, S.C.; Kerry, L.; Lockwood, N.; Frolov, A.; Frankel, P.; et al. Visualising apoptosis in live zebrafish using fluorescence lifetime imaging with optical projection tomography to map FRET biosensor activity in space and time. J. Biophotonics 2016, 9, 414–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jia, H.; Song, Y.; Huang, B.; Ge, W.; Luo, K.Q. Engineered Sensor Zebrafish for Fast Detection and Real-Time Tracking of Apoptosis at Single-Cell Resolution in Live Animals. ACS Sens. 2020, 5, 823–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gut, P.; Baeza-Raja, B.; Andersson, O.; Hasenkamp, L.; Hsiao, J.; Hesselson, D.; Akassoglou, K.; Verdin, E.; Hirschey, M.D.; Stainier, D.Y. Whole-organism screening for gluconeogenesis identifies activators of fasting metabolism. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2013, 9, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jia, Z.L.; Cen, J.; Wang, J.B.; Zhang, F.; Xia, Q.; Wang, X.; Chen, X.Q.; Wang, R.C.; Hsiao, C.D.; Liu, K.C.; et al. Mechanism of isoniazid-induced hepatotoxicity in zebrafish larvae: Activation of ROS-mediated ERS, apoptosis and the Nrf2 pathway. Chemosphere 2019, 227, 541–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sefried, S.; Häring, H.-U.; Weigert, C.; Eckstein, S.S. Suitability of hepatocyte cell lines HepG2, AML12 and THLE-2 for investigation of insulin signalling and hepatokine gene expression. Open Biol. 2018, 8, 180147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Promega. Caspase-Glo® 3/7 Assay Technical Bulletin. Available online: https://www.promega.com/resources/protocols/technical-bulletins/101/caspase-glo-37-assay-protocol/?cs=y (accessed on 28 October 2021).
- Roma, M.G.; Toledo, F.D.; Boaglio, A.C.; Basiglio, C.L.; Crocenzi, F.A.; Sánchez Pozzi, E.J. Ursodeoxycholic acid in cholestasis: Linking action mechanisms to therapeutic applications. Clin. Sci. 2011, 121, 523–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beuers, U.; Trauner, M.; Jansen, P.; Poupon, R. New paradigms in the treatment of hepatic cholestasis: From UDCA to FXR, PXR and beyond. J. Hepatol. 2015, 62, S25–S37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, X.; Xu, J.; Zhang, C.; Yu, T.; Wang, H.; Zhao, M.; Duan, Z.H.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, J.M.; Xu, D.X. The protective effects of ursodeoxycholic acid on isoniazid plus rifampicin induced liver injury in mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 659, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.G.; Zhang, C.; Wang, J.X.; Wang, B.W.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Z.H.; Chen, Y.H.; Lu, Y.; Tao, L.; Wang, J.Q.; et al. Obeticholic acid protects against carbon tetrachloride-induced acute liver injury and inflammation. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2017, 314, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Chen, L.; Wen, Y.; Rao, Z.; Wei, Y.; Wu, X. Pyridoxal isonicotinoyl hydrazone inhibition of FXR is involved in the pathogenesis of isoniazid-induced liver injury. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2020, 402, 115134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, P.F.; Xie, W.F. Corticosteroid therapy in drug-induced liver injury: Pros and cons. J. Dig. Dis. 2019, 20, 122–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polianskyte-Prause, Z.; Tolvanen, T.A.; Lindfors, S.; Dumont, V.; Van, M.; Wang, H.; Dash, S.N.; Berg, M.; Naams, J.B.; Hautala, L.C.; et al. Metformin increases glucose uptake and acts renoprotectively by reducing SHIP2 activity. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 2858–2869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hughes, C.B.; Mussman, G.M.; Ray, P.; Bunn, R.C.; Cornea, V.; Thrailkill, K.M.; Fowlkes, J.L.; Popescu, I. Impact of an SGLT2-loss of function mutation on renal architecture, histology, and glucose homeostasis. Cell Tissue Res. 2021, 384, 527–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inyushin, M.; Meshalkina, D.; Zueva, L.; Zayas-Santiago, A. Tissue Transparency In Vivo. Molecules 2019, 24, 2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Owen, J.P.; Kelsh, R.N.; Yates, C.A. A quantitative modelling approach to zebrafish pigment pattern formation. eLife 2020, 9, e52998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.Y.; Fox, C.S.; North, T.E.; Goessling, W. Functional validation of GWAS gene candidates for abnormal liver function during zebrafish liver development. Dis. Models Mech. 2013, 6, 1271–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- White, R.M.; Sessa, A.; Burke, C.; Bowman, T.; LeBlanc, J.; Ceol, C.; Bourque, C.; Dovey, M.; Goessling, W.; Burns, C.E.; et al. Transparent adult zebrafish as a tool for in vivo transplantation analysis. Cell Stem Cell 2008, 2, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoofnagle, J.H.; Björnsson, E.S. Drug-Induced Liver Injury—Types and Phenotypes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 264–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boelsterli, U.A.; Lee, K.K. Mechanisms of isoniazid-induced idiosyncratic liver injury: Emerging role of mitochondrial stress. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 29, 678–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, H.M.; Guo, H.L.; Yousef, B.A.; Luyong, Z.; Zhenzhou, J. Hepatotoxicity mechanisms of isoniazid: A mini-review. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2015, 35, 1427–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Pradhan, K.; Zhong, X.B.; Ma, X. Isoniazid metabolism and hepatotoxicity. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2016, 6, 384–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Erwin, E.R.; Addison, A.P.; John, S.F.; Olaleye, O.A.; Rosell, R.C. Pharmacokinetics of isoniazid: The good, the bad, and the alternatives. Tuberculosis 2019, 116s, S66–S70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Ikejima, T.; Li, L.; Wu, R.; Yuan, X.; Zhao, J.; Wang, Y.; Peng, S. Impairment of Mitochondrial Biogenesis and Dynamics Involved in Isoniazid-Induced Apoptosis of HepG2 Cells Was Alleviated by p38 MAPK Pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Verma, A.K.; Yadav, A.; Singh, S.V.; Mishra, P.; Rath, S.K. Isoniazid induces apoptosis: Role of oxidative stress and inhibition of nuclear translocation of nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2 (Nrf2). Life Sci. 2018, 199, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Qu, X.; Gao, H.; Zhai, J.; Tao, L.; Sun, J.; Song, Y.; Zhang, J. Quercetin attenuates NLRP3 inflammasome activation and apoptosis to protect INH-induced liver injury via regulating SIRT1 pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 85, 106634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orbach, S.M.; Ehrich, M.F.; Rajagopalan, P. High-throughput toxicity testing of chemicals and mixtures in organotypic multi-cellular cultures of primary human hepatic cells. Toxicol. Vitr. Int. J. Publ. Assoc. BIBRA 2018, 51, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramappa, V.; Aithal, G.P. Hepatotoxicity Related to Anti-tuberculosis Drugs: Mechanisms and Management. J. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2013, 3, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suzuki, A.; Yuen, N.A.; Ilic, K.; Miller, R.T.; Reese, M.J.; Brown, H.R.; Ambroso, J.I.; Falls, J.G.; Hunt, C.M. Comedications alter drug-induced liver injury reporting frequency: Data mining in the WHO VigiBase™. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2015, 72, 481–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Niu, H.; Sanabria-Cabrera, J.; Alvarez-Alvarez, I.; Robles-Diaz, M.; Stankevičiūtė, S.; Aithal, G.P.; Björnsson, E.S.; Andrade, R.J.; Lucena, M.I. Prevention and management of idiosyncratic drug-induced liver injury: Systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised clinical trials. Pharmacol. Res. 2021, 164, 105404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral, J.D.; Castro, R.E.; Solá, S.; Steer, C.J.; Rodrigues, C.M. p53 is a key molecular target of ursodeoxycholic acid in regulating apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 34250–34259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhai, J.; Gao, H.; Tao, L.; Song, Y. Dysregulation of BSEP and MRP2 May Play an Important Role in Isoniazid-Induced Liver Injury via the SIRT1/FXR Pathway in Rats and HepG2 Cells. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2018, 41, 1211–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hassan, H.M.; Guo, H.; Yousef, B.A.; Ping-Ping, D.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, Z. Dexamethasone Pretreatment Alleviates Isoniazid/Lipopolysaccharide Hepatotoxicity: Inhibition of Inflammatory and Oxidative Stress. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Xiong, X.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Shi, G.; Yang, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, H.; Hong, J.; et al. Glucocorticoids promote hepatic cholestasis in mice by inhibiting the transcriptional activity of the farnesoid X receptor. Gastroenterology 2012, 143, 1630–1640.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakai, E.; Suzumura, Y.; Ikemura, K.; Mizuno, T.; Watanabe, M.; Takeuchi, K.; Nishimura, Y. An Integrated In Silico and In Vivo Approach to Identify Protective Effects of Palonosetron in Cisplatin-Induced Nephrotoxicity. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westerfield, M. A Guide for the Laboratory Use of Zebrafish (Danio rerio); University of Oregon Press: Eugene, OR, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Nishimura, Y.; Inoue, A.; Sasagawa, S.; Koiwa, J.; Kawaguchi, K.; Kawase, R.; Maruyama, T.; Kim, S.; Tanaka, T. Using zebrafish in systems toxicology for developmental toxicity testing. Congenit. Anom. 2016, 56, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelsh, R.N.; Brand, M.; Jiang, Y.J.; Heisenberg, C.P.; Lin, S.; Haffter, P.; Odenthal, J.; Mullins, M.C.; van Eeden, F.J.; Furutani-Seiki, M.; et al. Zebrafish pigmentation mutations and the processes of neural crest development. Development 1996, 123, 369–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urasaki, A.; Morvan, G.; Kawakami, K. Functional dissection of the Tol2 transposable element identified the minimal cis-sequence and a highly repetitive sequence in the subterminal region essential for transposition. Genetics 2006, 174, 639–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suster, M.L.; Abe, G.; Schouw, A.; Kawakami, K. Transposon-mediated BAC transgenesis in zebrafish. Nat. Protoc. 2011, 6, 1998–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawakami, K. Tol2: A versatile gene transfer vector in vertebrates. Genome Biol. 2007, 8 (Suppl. 1), S7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schindelin, J.; Arganda-Carreras, I.; Frise, E.; Kaynig, V.; Longair, M.; Pietzsch, T.; Preibisch, S.; Rueden, C.; Saalfeld, S.; Schmid, B.; et al. Fiji: An open-source platform for biological-image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Higuchi, A.; Wakai, E.; Tada, T.; Koiwa, J.; Adachi, Y.; Shiromizu, T.; Goto, H.; Tanaka, T.; Nishimura, Y. Generation of a Transgenic Zebrafish Line for In Vivo Assessment of Hepatic Apoptosis. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 1117. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14111117
Higuchi A, Wakai E, Tada T, Koiwa J, Adachi Y, Shiromizu T, Goto H, Tanaka T, Nishimura Y. Generation of a Transgenic Zebrafish Line for In Vivo Assessment of Hepatic Apoptosis. Pharmaceuticals. 2021; 14(11):1117. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14111117
Chicago/Turabian StyleHiguchi, Aina, Eri Wakai, Tomoko Tada, Junko Koiwa, Yuka Adachi, Takashi Shiromizu, Hidemasa Goto, Toshio Tanaka, and Yuhei Nishimura. 2021. "Generation of a Transgenic Zebrafish Line for In Vivo Assessment of Hepatic Apoptosis" Pharmaceuticals 14, no. 11: 1117. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14111117
APA StyleHiguchi, A., Wakai, E., Tada, T., Koiwa, J., Adachi, Y., Shiromizu, T., Goto, H., Tanaka, T., & Nishimura, Y. (2021). Generation of a Transgenic Zebrafish Line for In Vivo Assessment of Hepatic Apoptosis. Pharmaceuticals, 14(11), 1117. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14111117







