Abstract
Snakebite envenomings are a global public health issue. The therapy based on the administration of animal-derived antivenoms has limited efficacy against the venom-induced local tissue damage, which often leads to permanent disability. Therefore, there is a need to find inhibitors against toxins responsible for local damage. This work aimed to synthesize thioesters derived from 2-sulfenyl ethylacetate and to evaluate the inhibitory effects on two snake venom toxins. Ethyl 2-((4-chlorobenzoyl)thio)acetate (I), Ethyl 2-((3-nitrobenzoyl)thio)acetate (II) and Ethyl 2-((4-nitrobenzoyl)thio)acetate (III) were synthesized and spectroscopically characterized. Computational calculations were performed to support the study. The inhibitory capacity of compounds (I–III) was evaluated on a phospholipase A2 (Cdcum6) isolated from the venom of the Colombian rattlesnake Crotalus durissus cumanensis and the P-I type metalloproteinase Batx-I isolated from Bothrops atrox. I–III inhibited PLA2 with IC50 values of 193.2, 305.4 and 132.7 µM, respectively. Otherwise, compounds II and III inhibited the proteolytic activity of Batx-I with IC50 of 2774 and 1879 µM. Molecular docking studies show that inhibition of PLA2 may be due to interactions of the studied compounds with amino acids in the catalytic site and the cofactor Ca2+. Probably, a blockage of the hydrophobic channel and some amino acids of the interfacial binding surface of PLA2 may occur.
1. Introduction
The World Health Organization (WHO) recognized snakebites as one of the most important Neglected Tropical Diseases in 2017. Nearly 5.4 million snakebites occur each year, and more than 95% of cases occur in tropical or developing countries, mostly in rural areas [1]. There are between 81,410 and 137,880 deaths per year and around three times as many cases of permanent disabilities including amputations [2]. A total of 4978 ophidian accidents were reported in Colombia in 2017 [3].
Pathophysiological effects observed in snakebite envenomations combine the action of several enzymes, proteins and peptides, such as phospholipases A2 (PLA2), hemorrhagic metalloproteinases, and other proteolytic enzymes, coagulant components, neurotoxins, cytotoxins and cardiotoxins, among others [4]. Snake venom metalloproteinases (SVMPs) have been shown to participate in the hemorrhagic process by proteolytic degradation of endothelial cell surface proteins and extracellular matrix components, involved in the maintenance of capillary structure and integrity, leading to capillary network disruption, edema and hemorrhage [5]. Phospholipases A2 (PLA2) are calcium-depending enzymes that hydrolyze the sn2 ester bond of glycerophospholipids, inducing systemic and local myotoxicity, myonecrosis, neurotoxicity hemolytic activity, among others [6,7].
Nowadays, the only available and accepted therapy for the treatment of snakebites is the intravenous administration of equine or ovine antivenoms [8]. Nevertheless, several reports demonstrated the limited efficacy of antivenom therapy against the local tissue damage caused by venoms [9]. Therefore, there is a need for specific inhibitors of enzymes responsible for local damage to complement conventional parenteral antivenom therapy.
As usual in drug discovery, inhibitors could be found in natural sources or obtained by chemical synthesis, and in some cases in combination with in silico methodologies. This strategy was used for synthesizing naringenin derivatives which have structural similarity with quercetin, a flavonoid that binds to the active site of a PLA2 [10].
There are reports of natural and synthetic inhibitors of PLA2 from snake venoms including substituted thiobenzoic acid S-benzyl esters [11], Aiplai from leaves of Azadirachta indica [12] and cholic and ursodeoxycholic acids [13]. Some of the inhibitors have reported IC50 with the same methodology that we use; Pinostrobin, a flavonone isolated from Renealmia alpinia, with an IC50 of 1.85 mM [14]; and Morelloflavone, a biflavonoid from Garcinia madruno, with IC50 of 0.38 mM [15].
In a previous study we found that substituted thiobenzoic acid S-benzyl esters are inhibitors of an Asp49-PLA2 enzyme isolated from the venom of the Colombian Crotalus durissus cumanensis rattlesnake, but they have solubility drawbacks [11]. Looking for increasing the polarity and maintaining the biological activity, thioesters derived from 2-sulfenyl ethyl acetate were synthesized changing a phenyl group for an ethyl ester (Figure 1, Table 1). The present study aims to evaluate the inhibitory capacity of these compounds on the PLA2 from C. d. cumanensis rattlesnake and a PI type SVMP from Bothrops atrox venom.
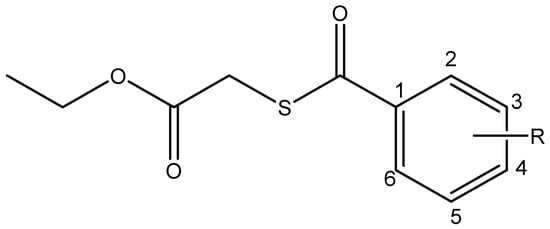
Figure 1.
General structure of studied compounds: Ethyl 2-((4-chlorobenzoyl)thio)acetate (I), Ethyl 2-((3-nitrobenzoyl)thio)acetate (II) and Ethyl 2-((4-nitrobenzoyl)thio)acetate (III).

Table 1.
Studied compounds and physicochemical properties.
2. Results
2.1. Synthesis and Spectroscopical Characterization
We report the synthesis and characterization by GC-MS, IR and NMR of thioesters derived from 2-sulfenyl ethylacetate. Spectra are available as Supplementary Material.
2.1.1. Ethyl 2-((4-chlorobenzoyl)thio)acetate (I)
Colorless crystals; m.p. 55.6 °C; 97% yield; FT-IR (KBr) ν 1734 and 1662 cm−1 (C=O); 1H NMR (CDCl3, 250 MHz) δ (ppm) 7.90 (2H, dt, J = 8, 2 and <1 Hz, H2 and H6); 7.43 (2H, dt, J = 8, 2 y < 1 Hz, H3 and H5); 4.22 (2H, q, J = 7 Hz, O-CH2); 3.87 (2H, s, S-CH2); 1.29 (3H, t, J = 7 Hz, CH3); 13C NMR (CDCl3, 62.98 MHz) δ (ppm) 189.0 (S-C=O); 168.6 (O-C=O); 140.2 (C4); 134.5 (C1); 129.1 (C2 and C6); 128.8 (C3 and C5); 62.0 (O-CH2); 31.5 (S-CH2); 14.1 (CH3); MS m/z 258 (2%) [M]+; 139 (100%) [C7H435ClO]+.
2.1.2. Ethyl 2-((3-nitrobenzoyl)thio)acetate (II)
Colorless crystals; m.p. 44.5 °C; 97% yield; FT-IR (KBr) ν 1738 and 1670 cm−1 (C=O); 1H NMR (CDCl3, 250 MHz) δ (ppm) 8.80 (1H, s, H2); 8.46 (1H, br.d, J = 8 Hz, H4); 8.30 (1H, br.d, J = 8 Hz, H6); 7.70 (1H, t, J = 8 Hz, H5); 4.26 (2H, q, J = 7 Hz, O-CH2); 3.94 (2H, s, S-CH2); 1.32 (3H, t, J = 7 Hz, CH3); 13C NMR (CDCl3, 62.98 MHz) δ (ppm) 188.4 (S-C=O); 168.2 (O-C=O); 147.3 (C3); 138.4 (C1); 132.9 (C6); 130.0 (C5); 129.7 (C4); 122.4 (C2); 62.2 (O-CH2); 31.7 (S-CH2); 14.1 (CH3); MS m/z 269 (2%) [M]+; 150 (100%) [C7H4O3N]+.
2.1.3. Ethyl 2-((4-nitrobenzoyl)thio)acetate (III)
Colorless crystals; m.p. 56.2 °C; 97% yield; FT-IR (KBr) ν 1730 and 1668 cm−1 (C=O); 1H NMR (CDCl3, 250 MHz) δ (ppm) 8.34 (2H, dt, J = 8, 2 y < 1 Hz, H3 and H5); 8.15 (2H, dt, J = 8, 2 y <1 Hz, H2 and H6); 4.27 (2H, q, J = 7 Hz, O-CH2); 3.95 (2H, s, S-CH2); 1.33 (3H, t, J =7 Hz, CH3); 13C NMR (CDCl3, 62.98 MHz) δ (ppm) 188.7 (S-C=O); 168.0 (O-C=O); 150.7 (C4); 140.6 (C1); 128.4 (C2 and C6); 123.9 (C3 and C5); 59.9 (O-CH2); 31.7 (S-CH2); 14.0 (CH3); MS m/z 269 (2%) [M]+; 150 (100%) [C7H4O3N]+.
2.2. Biological Activity
2.2.1. Inhibition of PLA2 activity
The synthetized compounds inhibited the PLA2 activity in a dose dependent way. IC50 values were 193.2, 305.4 and 132.7 μM for compounds I, II and III respectively. The results and confidence interval values are shown in Table 2. The determination of IC50 value was determined from a logistic-dose response curve (Figure 2).

Table 2.
IC50 and confidence interval values for inhibition of phospholipases A2 (PLA2) and proteolytic activity.
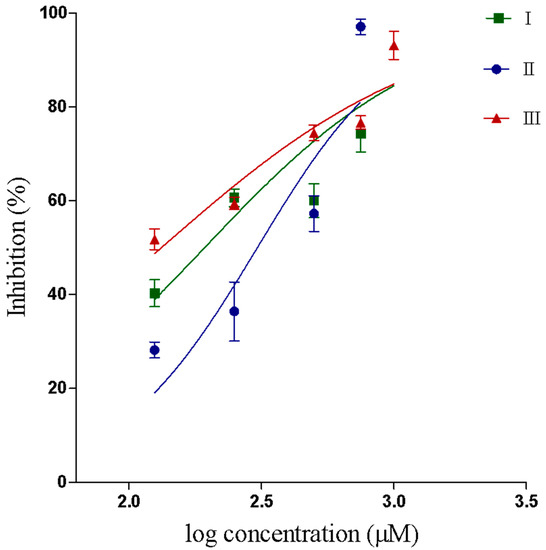
Figure 2.
IC50 curve showing inhibition of the PLA2 enzymatic activity by compounds I, II and III.
2.2.2. Inhibition of Proteolytic Activity
Compounds II and III inhibited the proteolytic activity of Baxt-I on gelatin, in a concentration-dependent manner (Figure 3). Proteolytic IC50 and confidence intervals values are shown in Table 2. The concentrations of compounds I–III used in this assay did not induce proteolytic activity on gelatin. However, for compound I the proteolytic IC50 could not be determined because 70% of Batx-I proteolytic activity was still observed even at a concentration of 2000 µM.
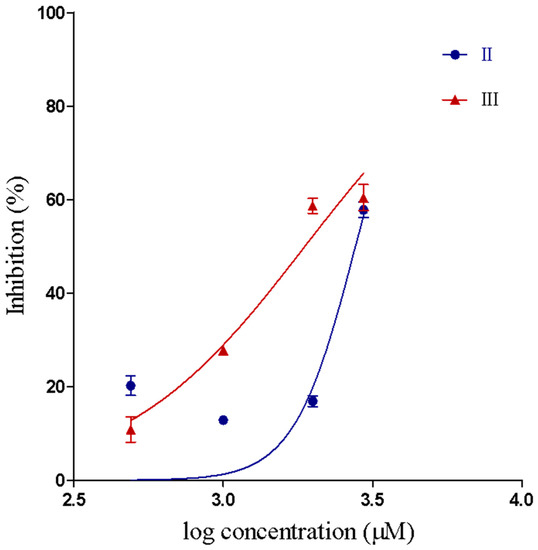
Figure 3.
IC50 curve showing inhibition of the metalloproteinase proteolytic activity by compounds II and III.
2.3. Computational Studies
2.3.1. Quantum Chemical Calculations
The bridge that connect thioester and ester moieties was explored through a potential energy curve around the dihedral angle δ S-C-C=O using a B3LYP/6-31++G(d,p) approximation. We found two minima at 0° and at 120° with a small energy difference (1 kJ/mol) that indicate the coexistence of both conformers (Figure 4).
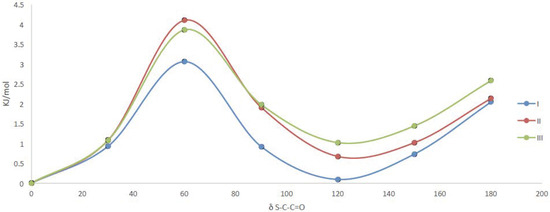
Figure 4.
Potential energy curve around the dihedral angle δ S-C-C=O for compounds I, II and III at B3LYP/6-31++G(d,p) level of approximation.
The geometric parameters and vibrational frequencies for both conformers were calculated at the same level of theory. The dihedral angle values calculated for the thioester and ester moieties are presented in Table 3.

Table 3.
Dihedral angle values for stable conformers.
2.3.2. Molecular Docking
To suggest the mechanism of inhibition of the PLA2, docking studies with the active compounds were performed using the available protein structure (PDB code 2QOG).
Docking conformations with the lowest binding energy were selected and described. The observed binding free energies with the enzyme PLA2 were −23.0; −24.7 and −23.9 kJ/mol for compounds I, II and III, respectively.
Docking results suggested that compounds I–III could form interactions with the residues His 48, Asp 49 and the cofactor Ca2+, belonging to the PLA2’s active site. In addition, these compounds may interact with amino acids located at the enzyme’s hydrophobic channel and interfacial binding surface, blocking the free access of glycerophospholipids to the active site of the enzyme (Figure 5 and Figure 6).

Figure 5.
Docking results PLA2 with compounds I (A), II (B) and III (C).

Figure 6.
Binding of compounds I, II and III to the substrate binding cleft of the PLA2. The red areas of the surface represent the acid regions; the white areas represent the neutral and the blue areas the basic regions. The blue sphere represents Ca2+. Compound I (yellow), II (green) and III (red).
3. Discussion
Several PLA2s and SVMPs inhibitors with IC50 values in the nano and micromolar range for the neutralization of different activities of these toxins have been reported [11,12,13,14]. However, some inhibitors have poor water solubility and low specificity that make their clinical applications difficult. Thus, the aim of this work was to synthesize thioester compounds with improved water solubility with respect to substituted thiobenzoic acid S-benzyl esters reported in a previous work [11], while maintaining the expected biological activity as PLA2 inhibitors. The condensation reaction is a high-yielding synthesis (97%) and the strategy was to utilize the same benzoyl chlorides used in the previous study, with a different thiol. The new selected reactant gives us the possibility to obtain the thioester moiety, and also an additional ester moiety in its structure. This change allows the increase in the number of hydrogen acceptors, improving the solubility (lower values of calculated partition coefficient Log P). The calculated Log P for the previous reported thiobenzoic acid S-benzyl esters were between 3.84 and 4.58, and for compounds I–II were between 2.48 and 3.23.
Compounds I–III have both thioester and ester moiety in their structure. Thioester (X=S) and ester (X=O) moieties usually present a synperiplanar configuration around the δO=C-X-C dihedral angle as the more stable conformer. The results obtained for compounds I, II and III are in agreement with previous reports [11,16,17].
Envenomations induced by viperid snakebites are characterized by local and systemic bleeding. Local effects are associated with a pronounced local tissue damage, while hemodynamic alterations predominate in the systemic effects [18,19]. Both enzymes studied in this work, PLA2s and SVMPs contribute to this pathogenesis inducing hemorrhage, myonecrosis, dermonecrosis, blister formation and edema [5,7,20]. The described effects are difficult to neutralize by antibodies due to their rapid symptoms after envenomation [21]. Therefore, it is important to find SVMPs and PLA2s inhibitors, like synthetic compounds I–III, that can be administered at the bite site.
The enzymatic activity of a PLA2 is determined by three principal factors: the integrity of the active site (residues His48, Asp49, Tyr52, Asp99), coordination of Ca2+ cofactor (residues Tyr28, Gly30, Gly32 and Asp49) and the adsorption of the enzyme onto the lipid–water interface of the phospholipids membrane bilayer (interfacial binding surface) [22], hence they are crucial to study the inhibition mechanism. The molecular docking study suggests that both stable conformations of the studied compounds may interact by either van der Waals or H-bond with amino acids His48 and Asp49 blocking catalytic cycle of PLA2. The catalytic mechanism implies water activation by His48 for the subsequent nucleophilic attack of sn2 ligation of the glycerophospholipids that will be hydrolyzed, and carboxylate of the Asp49 side chain stabilizes the oxyanion formed after the nucleophilic attack [22]. Catalytic activity and substrate binding of snake venom phospholipases need submicromolar concentrations of calcium ions. Recently, molecular dynamic studies have demonstrated that calcium induces atomistic movements and conformational changes in snake venom PLA2 which led to the formation of a widened cleft at the active site of calcium bound PLA2 when compared with free PLA2 [23]. This ion is also available for binding the substrate phosphate group [22]. Molecular docking also suggested van der Waals interactions between compounds I, II and III with Gly30 and coordination with Ca2+ that could destabilize metal coordination and block enzymatic catalysis.
The interfacial binding surface of the PLA2s mediates the adsorption of the enzyme onto the lipid–water interface of the phospholipid membrane bilayer. Residues Trp31 and Lys69 are part of this structure. Our molecular docking results suggested that all compounds may form van der Waals or π-alkyl interactions with the mentioned residues, thus, the binding of the substrate to the PLA2 active site may be blocked. Similar findings were reported in substituted thiobenzoic acid S-benzyl esters at 50 μM and obtained inhibition percentages higher than 50% for three of the four assayed compounds [11].
There is a type of snake venom PLA2s catalytically inactive (PLA2-like myotoxins) due to lack of Ca2+ coordination by a natural mutation in which the residue aspartate at position 49 is substituted with a lysine generating the loss of the catalytic activity. However, these toxins are able to induce local mionecrosis by a mechanism dependent of two different sites forming a putative membrane-docking site (MDoS) and a putative membrane disruption site (MDiS) [24]. Different small molecules inhibitors have been described by their inhibition against PLA2-like myotoxins through the binding at just one critical region related to the myotoxic mechanism: the MDoS, MDiS or hydrophobic channel. Recently was demonstrated that chicoric acid binds at the entrance of the hydrophobic channel and clusters of a PLA2-like myotoxin that participate in membrane disruption [25]. We hypothesized that thioester compounds could inhibit PLA2-like myotoxic activity interacting with amino acids located at the hydrophobic channel, since some amino acids of this structure (Leu2 and Phe5) are involved in the interaction with the Asp49-PLA2 tested in this study (Figure 5). Nevertheless, this must be confirmed in future studies.
Compounds I–III have IC50s between 132.7 and 305.4 μM against PLA2 enzymatic activity (p > 0.05) and are much more active than inhibitors like Pinostrobin and Moreloflavone with IC50s determined by the same method of 1.85 and 0.38 mM, respectively [14,15]. Compounds I and III have an electronegative substitution in the para position of the aromatic ring and comparable IC50s, whereas compound II is substituted in the meta position. Besides these subtle differences, our docking results suggested that compounds I and III may interact in a similar position with the benzoyl ring at the beginning of the hydrophobic channel and thioester moiety at the middle of the hydrophobic pocket, near to the active site of the enzyme. Instead, compound II was located in an opposite way with phenyl ring near to the active site of the PLA2, which may explain the difference in its inhibition capacity. In order to improve the inhibitory potency of compounds, some structural modifications, such as the substitution with a metal binding group can be done with the aim to improve their interaction with catalytically active PLA2 Asp49.
Synthesized compounds were also tested to inhibit the enzymatic activity of a SVMP, however, only II and III showed some ability to inhibit the enzyme with IC50 values about 10 times higher than those found for PLA2. This talk about their specificity for PLA2s, however these compounds may give the possibility to partially also inhibit SVMPs present in snake venoms. Nevertheless, this hypothesis should be addressed in future studies with whole venom and in vivo assays.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. General
Reagents were purchased from Merck, Sigma-Aldrich and Acros organics with commercial, analytic or HPLC grade.
Solvents were evaporated from solutions in a rotary evaporator Heidolph Laborota 4010 equipped with a ROTAVAP valve control.
4.2. Syntheses
Ethyl 2-((4-chlorobenzoyl)thio)acetate (I), Ethyl 2-((3-nitrobenzoyl)thio)acetate (II) and Ethyl 2-((4-nitrobenzoyl)thio)acetate (III) (Figure 1) were prepared with Ethyl 2-mercaptoacetate (1 mmol) dissolved in pyridine and the corresponding substituted-benzoyl chloride (1 mmol) was added to this dissolution. (4-chlorobenzoyl chloride, 3-nitrobenzoyl chloride and of 4-nitrobenzoyl chloride for I, II and III respectively). The reaction mixture was stirred for 1 h at room temperature. The reaction mixture was treated with 1 M hydrochloric acid (5 mL) and methylene chloride (5 mL) and washed thoroughly with distilled water. The organic layer was dried over sodium sulfate anhydride, the solvent was removed in a rotatory evaporator and the residue was recrystallized from methanol and dried under vacuum.
4.3. Spectroscopical Characterization
Melting points (m.p.) were recorded in an Electrothermal 9100 apparatus. Infrared spectra in KBr pellets were measured between 4000 and 400 cm−1 (4 cm−1 resolution) with and FT-IR spectrometer Thermo-Nicolet IR200. The mass spectra were measured with a CG-MS Shimadzu QP-2010 spectrometer with a HP-5 column. NMR spectra were measured at 298 K on a Bruker DPX 200 spectrometer. The compounds were dissolved in CDCl3. Chemical shifts, δ, are given in ppm relative to TMS (δ = 0 ppm) and are referenced by using the residual undeuterated solvent signal. Coupling constants, J, are reported in Hz, multiplicities being marked as: singlet (s), doublet (d), triplet (t), double triplet (dt) of multiplet (m).
4.4. Toxins Isolation
The PLA2 from C. d. cumanensis was obtained from a pool venom of four specimens maintained in captivity at the serpentarium of the University of Antioquia (Medellín, Colombia).
The enzyme was purified through reverse-phase HPLC on C-18 column eluted at 1.0 mL/min with a gradient from 0% to 100% of acetonitrile in 0.1% trifluoroacetic acid (v/v). The absorbance in the effluent solution was recorded at wavelength of 280 nm [26].
Baxt-I was isolated from a venom pool collected from adult specimens of B. atrox from Meta, southeastern Colombia, via ion-exchange chromatography (CM-Sephadex C25) following the protocol described by Patiño et al. (2010) [27]. For both proteins, the purity was judged by RP-HPLC and SDS-PAGE.
4.5. Inhibition of PLA2 Activity Using 4-nitro-3-octanoyloxybenzoic acid (4N3OBA) as Monodispersed Substrate
The measurements of enzymatic activity using the monodispersed substrate 4N3OBA were performed according to the method described by Holzer and Mackessy (1996), and adapted for a 96-well ELISA plate. The standard assay contained 200 μL of buffer (10 mM Tris–HCl, 10 mM CaCl2, 100 mM NaCl, pH 8.0), 20 μL of 10 mM of substrate (4NO3BA), 20 μL of sample (20 μg PLA2 or 20 μg PLA2 + several concentrations of compounds) and 20 μL of water. The negative control was only buffer. The inhibitory effect of the studied thioesters on PLA2 activity was determined through co-incubation of the enzyme with each concentration of the compound for 30 min at 37 °C. After the incubation period, the sample was added to the assay and the reaction was monitored at 425 nm for 40 min (at 10 min intervals) at 37 °C. The quantity of chromophore released (4-nitro-3-hydroxy benzoic acid) was proportional to the enzymatic activity, and the IC50 value was determined from a logistic-dose response curve.
4.6. Inhibition of Proteolytic Activity
The inhibition of proteolytic activity was measured using the EnzCheck® Gelatinase/Collagenase assay kit (Molecular Probes Inc., Eugene, Oregon, USA) following the protocol described by Preciado et al. (2017) with modification [28]. Briefly, aliquots of 80 μL of each triterpenic acid in concentrations from 15 to 500 μM, or buffer (0.05 M Tris-HCl, 0.15 M NaCl, 5 mM CaCl2, 0.2 mM sodium azide) as positive control, were added to each well of a 96-well plate. Then, 20 μL of DQ-gelatin followed by 100 μL of active Batx-I (1 μg/μL) were added, and the fluorescence intensity was measured by a Synergy HT Multi-Mode Microplate Reader (BioTek Instruments, Inc.; Winooski, USA) for excitation at 485 nm and emission detection at 515 nm at each minute for 60 min. Each reaction was performed in triplicate.
4.7. Computational Studies
Compounds (I–III) were built using Gauss View 5 [29]. The geometric parameters for the more stable conformers were calculated at the B3LYP/6-31++G (d,p) level of approximation using GAUSSIAN 09 [30]. Molecular docking was carried out on a personal computer using Autodock Vina [31]. The structure of the PLA2 (PDB code 2QOG) from Crotalus durissus terrificus that showed 57% of homology with the PLA2 from C. d. cumanensis [24] was used in this study.
Protein structure was prepared using the Protein Preparation module implemented in the Maestro program and uploaded without water molecules. Hydrogen atoms were automatically added to the protein according to the chemical nature of each amino acid, on the basis of the ionized form expected in physiological condition. This module also controls the atomic charges assignment. The 3D structure of the protein was relaxed through constrained local minimization, using the OPLS force fields in order to remove possible structural mismatches due to the automatic procedure employed to add the hydrogen atoms. When necessary, bonds, bond orders, hybridizations and hydrogen atoms were added, charges were assigned (a formal charge of +2 for Ca ion) and flexible torsions of ligands were detected.
To perform molecular docking experiments of compounds I–III with PLA2, the α-carbon of His48 was used as the center of the grid (X = 44.981, Y = 27.889 and Z = 46.392), whose size was 24 Å3. Exhaustiveness = 20. Finally, the ligand poses with best affinity were chosen, and a visual inspection of the interactions at the active site was performed and recorded using the open functionalities of Discovery Studio Visualizer and UCSF Chimera (www.cgl.ucsf.edu/chimera/). Physicochemical properties with importance in oral bioavailability for compounds I–III were calculated using Molinspiration [32].
4.8. Statistical Analysis
In order to determine significant differences between the concentrations of the compounds I–III used in the inhibition of the enzymes metalloproteinase and PLA2, two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s test was applied. In all cases, a difference with a p < 0.05 was considered significant.
5. Conclusions
Thioesters derived from 2-sulfenyl ethylacetate inhibited, in a specific way, PLA2 activity in micromolar concentrations. Although, we found that compounds II and III could inhibit the activity of Batx, IC50 values were around 10 times higher than those found for PLA2. It is suggested that inhibition of PLA2 activity is due to blockade of the active site and the interaction with amino acids involved in catalysis and binding substrate. Our results also suggest that compound III may be subject to further studies to develop inhibitors of snake venom PLA2.
Supplementary Materials
NMR, IR and MS spectra of synthesized compounds are available as supplementary material, https://www.mdpi.com/1424-8247/12/2/80/s1.
Author Contributions
Synthesis, purification, spectroscopical characterization, quantum chemical calculations I.C.H.C.; toxins isolation, biological activity studies, molecular docking J.A.P. and L.M.P. Formal analysis, writing, review and editing, I.C.H.C.; J.A.P. and L.M.P.
Funding
This research was funded by Comité para el Desarrollo de la Investigación, Universidad de Antioquia (UdeA), (CODI-CIQF-217).
Acknowledgments
This project was developed with the permission to access to genetic resources and their derived products from Ministerio de Ambiente y Desarrollo Sostenible No. 152 of 2017, resolution 2405, Colombia.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Chippaux, J. Snakebite envenomation turns again into a neglected tropical disease! J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 23, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Available online: http://www.webcitation.org/78DbPvhth (accessed on 8 May 2019).
- Instituto Nacional de Salud. Available online: http://www.webcitation.org/78DfIpikC (accessed on 8 May 2019).
- Cilibrasi, C.; Riva, G.; Romano, G.; Cadamuro, M.; Bazzoni, R.; Butta, V.; Paoletta, L.; Dalpra, L.; Strazzabosco, M.; Lavitrano, M.; et al. Resveratrol impairs glioma stem cells proliferation and motility by modulating the wnt signaling pathway. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0169854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutiérrez, J.M.; Rucavado, A. Snake venom metalloproteinases: Their role in the pathogenesis of local tissue damage. Biochimie 2000, 82, 841–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Six, D.A.; Dennis, E.A. The expanding superfamily of phospholipase A2 enzymes: Classification and characterization. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2000, 1488, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kini, R.M. Excitement ahead: Structure, function and mechanism of snake venom phospholipase A2 enzymes. Toxicon 2003, 42, 827–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Squaiella-Baptistão, C.C.; Sant’Anna, O.A.; Marcelino, J.R.; Tambourgi, D.V. The history of antivenoms development: Beyond Calmette and Vital Brazil. Toxicon 2018, 150, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, J.M.; Rucavado, A.; Escalante, T.; Herrera, C.; Fernández, J.; Lomonte, B.; Fox, J.W. Unresolved issues in the understanding of the pathogenesis of local tissue damage induced by snake venoms. Toxicon 2018, 148, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lättig, J.; Böhl, M.; Fischer, P.; Tischer, S.; Tietböhl, C.; Menschikowski, M.; Gutzeit, H.O.; Metz, P.; Pisabarro, M.T. Mechanism of inhibition of human secretory phospholipase A2 by flavonoids: Rationale for lead design. J. Comput.-Aided Mol. Des. 2007, 21, 473–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henao Castañeda, I.C.; Pereañez, J.A.; Jios, J.L. Substituted thiobenzoic acid S-benzyl esters as potential inhibitors of a snake venom phospholipase A2: Synthesis, spectroscopic and computational studies. J. Mol. Struct. 2012, 1028, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, A.K.; Doley, R.; Saikia, D. Isolation of a snake venom phospholipase A2 (PLA2) inhibitor (AIPLAI) from leaves of Azadirachta indica (Neem): Mechanism of PLA2 inhibition by AIPLAI in vitro condition. Toxicon 2008, 51, 1548–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereañez, J.A.; Núñez, V.; Patiño, A.C. Inhibitory effects of bile acids on enzymatic and pharmacological activities of a snake venom phospholipase A2 from group IIA. Protein J. 2011, 30, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Betancur, I.; Pereañez, J.A.; Patiño, A.C.; Benjumea, D. Inhibitory effect of pinostrobin from Renealmia alpinia, on the enzymatic and biological activities of a PLA2. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 89, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereañez, J.A.; Patiño, A.C.; Núñez, V.; Osorio, E. The biflavonoid morelloflavone inhibits the enzymatic and biological activities of a snake venom phospholipase A2. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 2014, 220, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henao Castañeda, I.C.; Della Védova, C.O.; Piro, O.E.; Metzler-Nolte, N.; Jios, J.L. Synthesis of two new thioesters bearing ferrocene: Vibrational characterization and ab initio calculations. X-ray crystal structure of S-(2-methoxyphenyl)ferrocenecarbothioate. Polyhedron 2010, 29, 827–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castañeda, I.C.H.; Jios, J.L.; Piro, O.E.; Tobón, G.E.; Della Védova, C.O. Conformational and vibrational analysis of S-(2-methoxyphenyl)-4-substituted-benzenecarbothioates, using X-ray, infrared and Raman spectroscopy and theoretical calculations. J. Mol. Struct. 2007, 842, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warrell, D.A. Clinical Toxicology of Snakebite in Asia. In Handbook of Clinical Toxicology of Animal Venoms and Poisons; CRC Press: New York, NY, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Escalante, T.; Rucavado, A.; Fox, J.W.; María, J.; Picado, I.C.; De Microbiología, F.; Rica, U.D.C.; Rica, C. Key events in microvascular damage induced by snake venom. J. Proteom. 2011, 74, 1781–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angulo, Y.; Lomonte, B.; Rica, U.D.C.; Jose, S.; Rica, C.; De Medicina, E.; Rica, U.D.C.; Jose, S.; Rica, C. Toxicon Biochemistry and toxicology of toxins purified from the venom of the snake Bothrops asper. Toxicon 2009, 54, 949–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rrez, Â.; Leo, G.; Rojas, G.; Lomonte, B.; Rucavado, A.; Chaves, F.; Rojas, G.; Lomonte, B.; Rucavado, A. nNeutralization of local tissue damage induced by Bothrops asper (terciopelo) snake venom. Toxicon 1998, 36, 1529–1538. [Google Scholar]
- Berg, O.G.; Gelb, M.H. Interfacial Enzymology: The Secreted Phospholipase A2-Paradigm. Chem. Rev. 2001, 101, 2613–2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emmanuel, A.; Okafor, I.; Fortunatus, E.C.; Colin, L.; Jonathan, I.F.; Andrew, N.C.; Ferdinand, C.C. The Role of Calcium on the Active Site of Snake Venom Phospholipase A2: Molecular Dynamics Simulations. Comput. Biol. Bioinform. 2016, 4, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvador, G.; dos Santos, J.; Lomonte, B.; Fontes, M.R.M. Biochimie: Crystal structure of a phospholipase A2 from Bothrops asper venom: Insights into a new putative “myotoxic cluster”. Biochimie 2017, 133, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, F.F.; Borges, R.J.; Dreyer, T.R.; Salvador, G.H.M.; Cavalcante, W.L.G.; Pai, M.D.; Gallacci, M.; Fontes, M.R.M. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj: Structural basis of phospholipase A2-like myotoxin inhibition by chicoric acid, a novel potent inhibitor of ophidian toxins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2018, 1862, 2728–2737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nu, V.; Marangoni, S.; Ponce-soto, L.A. Biochemical and biological characterization of a PLA 2 from crotoxin complex of Crotalus durissus cumanensis. Toxicon 2009, 53, 534–542. [Google Scholar]
- Patiño, A.C.; Pereañez, J.A.; Núñez, V.; Benjumea, D.M.; Fernandez, M.; Rucavado, A.; Sanz, L.; Calvete, J.J. Isolation and biological characterization of Batx-I, a weak hemorrhagic and fi brinogenolytic PI metalloproteinase from Colombian Bothrops atrox venom. Toxicon 2010, 56, 936–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preciado, L.M.; Rey-Suárez, P.; Henao, I.C.; Pereañez, J.A. Betulinic, oleanolic and ursolic acids inhibit the enzymatic and biological effects induced by a P-I snake venom metalloproteinase. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 2018, 279, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dennington, R.; Keith, T.; Millam, J. Gauss View, Version 5; Semichem Inc.: Shawnee Mission, KS, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R. Gaussian 09, Revision, B.01; Gaussian, Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Trott, O.; Olson, A.J. Software News and Update AutoDock Vina: Improving the Speed and Accuracy of Docking with a New Scoring Function, Efficient Optimization, and Multithreading. J. Comput. Chem. 2009, 31, 455–461. [Google Scholar]
- Molinspiration. Available online: https://www.molinspiration.com/cgi-bin/properties (accessed on 21 November 2018).
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).