Cardiolipin-Based Lipopolyplex Platform for the Delivery of Diverse Nucleic Acids into Gram-Negative Bacteria
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
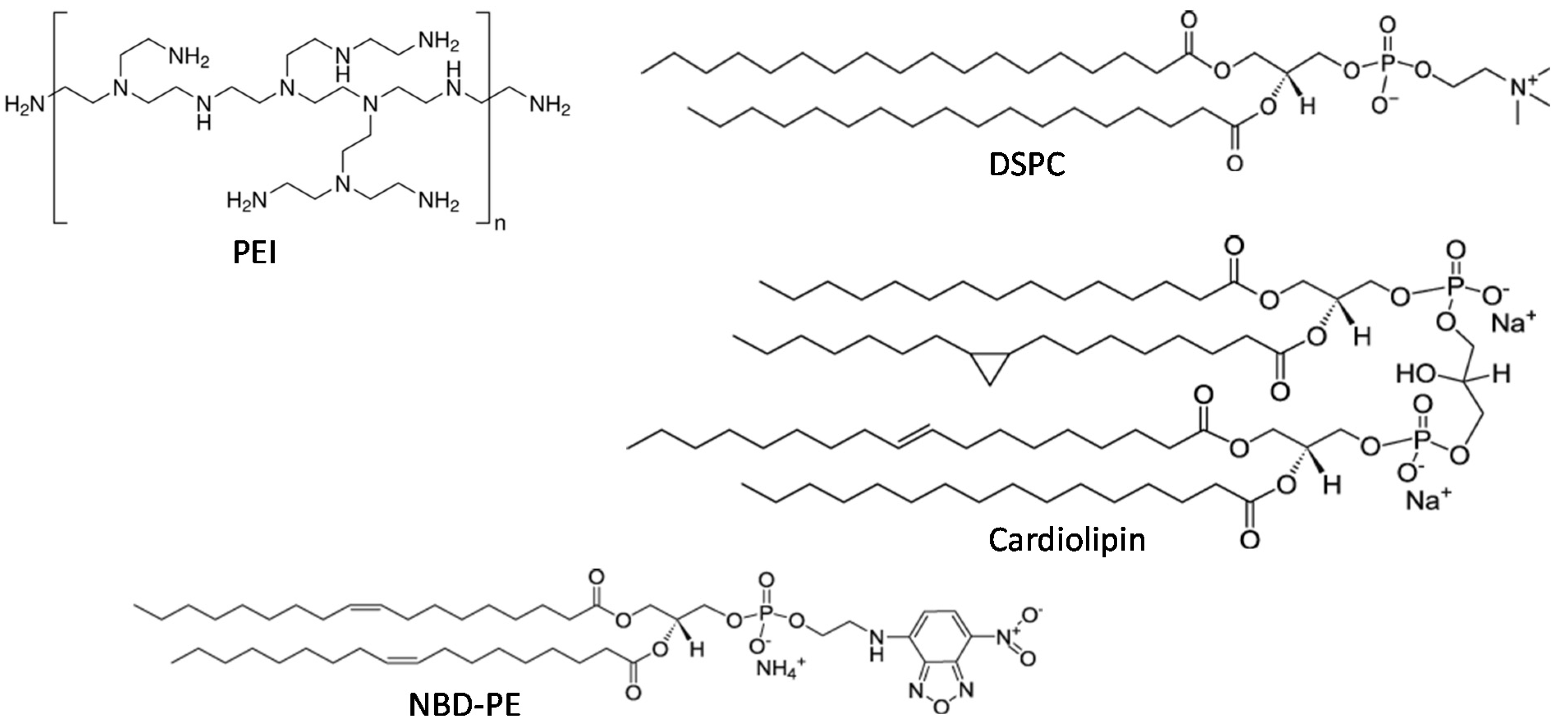
2.1. Preparation and Characterization of LPN
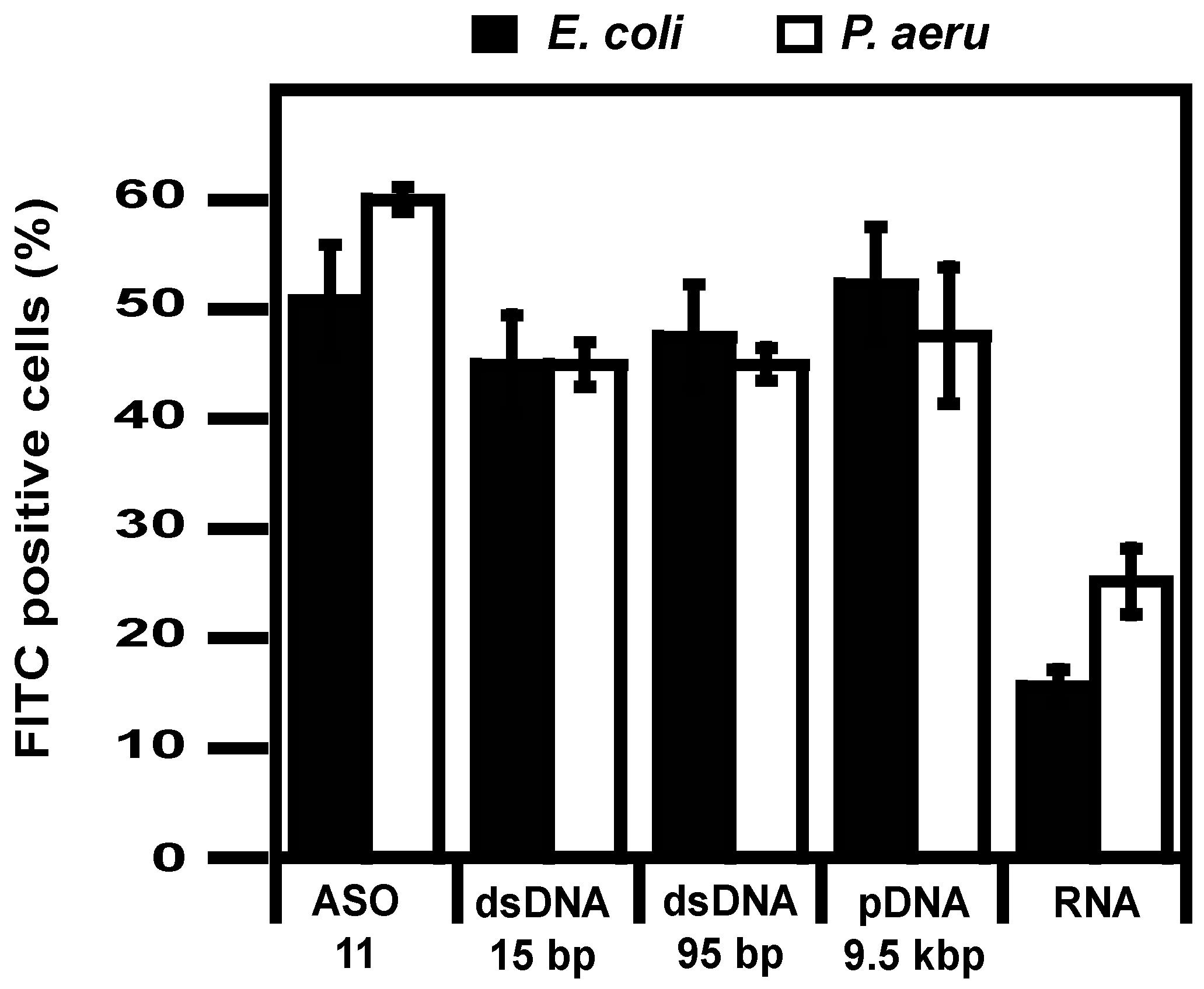
2.2. Delivery
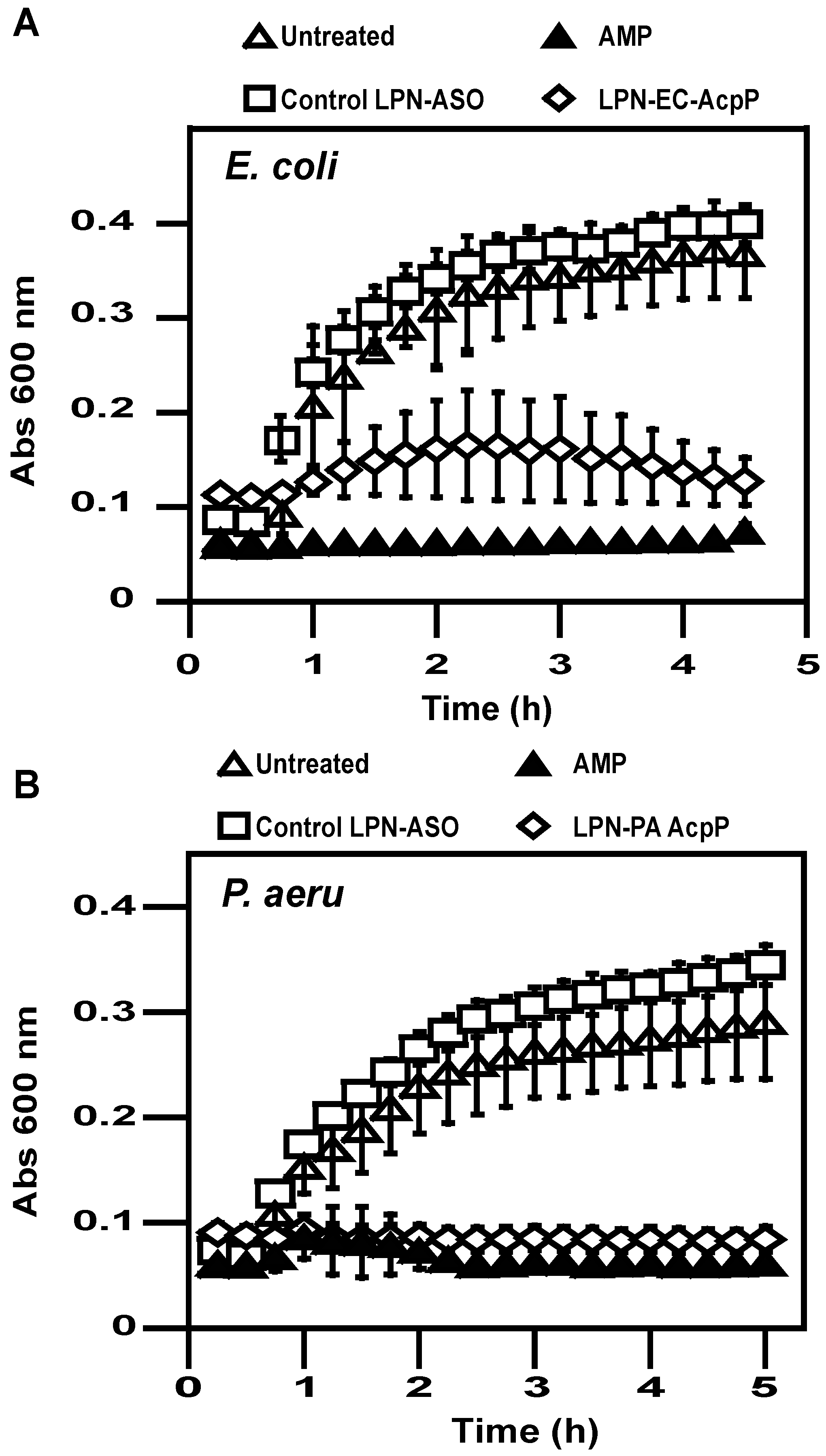
2.3. Antibacterial Activity
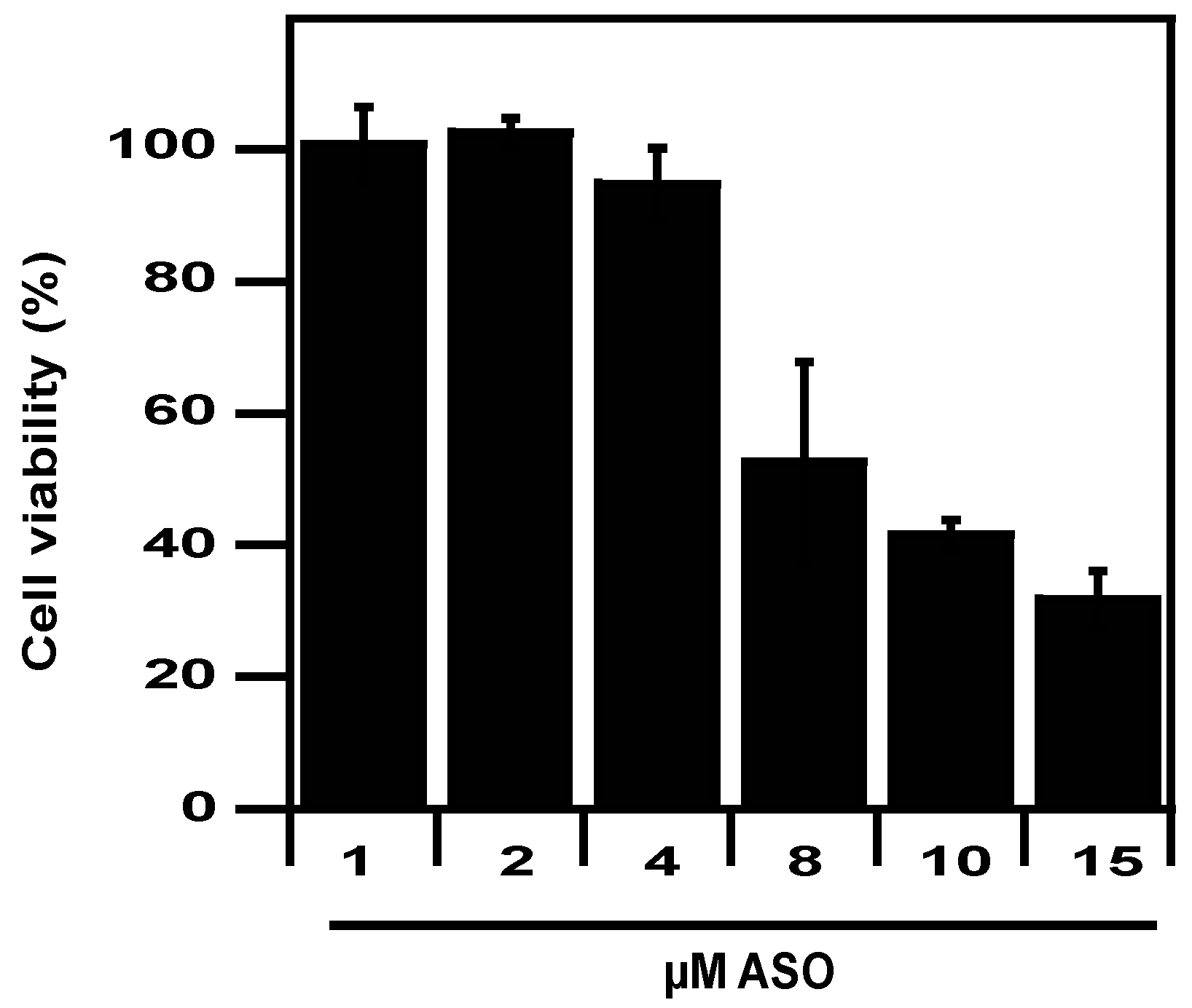
2.4. Eukaryotic Safety
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents
4.2. Bacteria
4.3. Nucleic Acids
4.4. Liposome Preparation
4.5. Preparation of Lipopolyplexes
4.6. LPN Characterizations
4.7. Flow Cytometry
4.8. Bacterial Growth Assay
4.9. Cytotoxicity Towards Eukaryotic Cells
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Coates, A.R.; Halls, G.; Hu, Y. Novel classes of antibiotics or more of the same? Br. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 163, 184–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nambiar, S.; Laessig, K.; Toerner, J.; Farley, J.; Cox, E. Antibacterial drug development: Challenges, recent developments, and future considerations. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 96, 147–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Organization, W.H. Antimicrobial Resistance: Global Report on Surveillance; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, X.-Y.; Mao, X.-G.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Z.; Hu, Y.; Hou, Z.; Li, M.-K.; Meng, J.-R.; Luo, X.-X. Advances in the delivery of antisense oligonucleotides for combating bacterial infectious diseases. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2018, 14, 745–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McArthur, M.; Bibb, M.J. Manipulating and understanding antibiotic production in Streptomyces coelicolor A3 (2) with decoy oligonucleotides. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 1020–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bikard, D.; Barrangou, R. Using CRISPR-Cas systems as antimicrobials. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2017, 37, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, K.L.; Sooter, L.J. Single-stranded DNA aptamers against pathogens and toxins: Identification and biosensing applications. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davydova, A.; Vorobjeva, M.; Pyshnyi, D.; Altman, S.; Vlassov, V.; Venyaminova, A. Aptamers against pathogenic microorganisms. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 42, 847–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, C.O.K.; Huang, C.; Pan, Q.; Lee, J.; Hao, Q.; Chan, T.-F.; Lo, N.W.S.; Ang, I.L.; Koon, A.; Ip, M. A Small RNA Transforms the Multidrug Resistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to Drug Susceptibility. Mol. Ther.-Nucleic Acids 2019, 16, 218–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, H.; Ho, J.; Liu, X.; Zhang, L.; Wong, S.H.; Chan, M.T.; Wu, W.K. Potential and use of bacterial small RNAs to combat drug resistance: A systematic review. Infect. Drug Res. 2017, 10, 521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakashima, N.; Tamura, T. Gene silencing in Escherichia coli using antisense RNA s expressed from doxycycline-inducible vectors. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2013, 56, 436–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, R.S.; Figueiredo, C.; Azevedo, N.F.; Braeckmans, K.; De Smedt, S.C. Nanomaterials and molecular transporters to overcome the bacterial envelope barrier: Towards advanced delivery of antibiotics. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2018, 136, 28–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abushahba, M.F.; Mohammad, H.; Thangamani, S.; Hussein, A.A.; Seleem, M.N. Impact of different cell penetrating peptides on the efficacy of antisense therapeutics for targeting intracellular pathogens. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 20832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, S.M.; Sturge, C.R.; Marshall-Batty, K.R.; Felder-Scott, C.F.; Jain, R.; Geller, B.L.; Greenberg, D.E. Antisense Inhibitors Retain Activity in Pulmonary Models of Burkholderia Infection. ACS infect. Dis. 2018, 4, 806–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puckett, S.E.; Reese, K.A.; Mitev, G.M.; Mullen, V.; Johnson, R.C.; Pomraning, K.R.; Mellbye, B.L.; Tilley, L.D.; Iversen, P.L.; Freitag, M. Bacterial resistance to antisense peptide phosphorodiamidate morpholino oligomers. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 6147–6153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fillion, P.; Desjardins, A.; Sayasith, K.; Lagacé, J. Encapsulation of DNA in negatively charged liposomes and inhibition of bacterial gene expression with fluid liposome-encapsulated antisense oligonucleotides. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Biomembr. 2001, 1515, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Paredes, A.; Sitia, L.; Ruyra, A.; Morris, C.J.; Wheeler, G.N.; McArthur, M.; Gasco, P. Solid lipid nanoparticles for the delivery of anti-microbial oligonucleotides. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2019, 134, 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, J.; Bai, H.; Jia, M.; Ma, X.; Hou, Z.; Xue, X.; Zhou, Y.; Luo, X. Restoration of antibiotic susceptibility in fluoroquinolone-resistant Escherichia coli by targeting acrB with antisense phosphorothioate oligonucleotide encapsulated in novel anion liposome. J. Antibiot. 2012, 65, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, J.; He, G.; Wang, H.; Jia, M.; Ma, X.; Da, F.; Wang, N.; Hou, Z.; Xue, X.; Li, M. Reversion of antibiotic resistance by inhibiting mecA in clinical methicillin-resistant Staphylococci by antisense phosphorothioate oligonucleotide. J. Antibiot. 2015, 68, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; Wang, H.; Hou, Z.; Chen, T.; Fu, J.; Ma, X.; He, G.; Xue, X.; Jia, M.; Luo, X. Novel anion liposome-encapsulated antisense oligonucleotide restores susceptibility of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and rescues mice from lethal sepsis by targeting mecA. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2009, 53, 2871–2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Meng, J.; Jia, M.; Ma, X.; He, G.; Yu, J.; Wang, R.; Bai, H.; Hou, Z.; Luo, X. oprM as a new target for reversion of multidrug resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa by antisense phosphorothioate oligodeoxynucleotides. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2010, 60, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Midoux, P.; Pichon, C. Lipid-based mRNA vaccine delivery systems. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2015, 14, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perche, F.; Benvegnu, T.; Berchel, M.; Lebegue, L.; Pichon, C.; Jaffrès, P.-A.; Midoux, P. Enhancement of dendritic cells transfection in vivo and of vaccination against B16F10 melanoma with mannosylated histidylated lipopolyplexes loaded with tumor antigen messenger RNA. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2011, 7, 445–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Moignic, A.; Malard, V.; Benvegnu, T.; Lemiègre, L.; Berchel, M.; Jaffrès, P.-A.; Baillou, C.; Delost, M.; Macedo, R.; Rochefort, J.; et al. Preclinical evaluation of mRNA trimannosylated lipopolyplexes as therapeutic cancer vaccines targeting dendritic cells. J. Control. Release 2018, 278, 110–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Jeught, K.; De Koker, S.; Bialkowski, L.; Heirman, C.; Tjok Joe, P.; Perche, F.; Maenhout, S.; Bevers, S.; Broos, K.; Deswarte, K.; et al. Dendritic Cell Targeting mRNA Lipopolyplexes Combine Strong Antitumor T-Cell Immunity with Improved Inflammatory Safety. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 9815–9829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perche, F.; Lambert, O.; Berchel, M.; Jaffrès, P.-A.; Pichon, C.; Midoux, P. Gene transfer by histidylated lipopolyplexes: A dehydration method allowing preservation of their physicochemical parameters and transfection efficiency. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 423, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonçalves, C.; Berchel, M.; Gosselin, M.-P.; Malard, V.; Cheradame, H.; Jaffres, P.-A.; Guégan, P.; Pichon, C.; Midoux, P. Lipopolyplexes comprising imidazole/imidazolium lipophosphoramidate, histidinylated polyethyleneimine and siRNA as efficient formulation for siRNA transfection. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 460, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godbey, W.; Wu, K.K.; Mikos, A.G. Poly (ethylenimine) and its role in gene delivery. J. Control. Release 1999, 60, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranneh, A.H.; Takemoto, H.; Sakuma, S.; Awaad, A.; Nomoto, T.; Mochida, Y.; Matsui, M.; Tomoda, K.; Naito, M.; Nishiyama, N. An Ethylenediamine-based Switch to Render the Polyzwitterion Cationic at Tumorous pH for Effective Tumor Accumulation of Coated Nanomaterials. Angew. Chem. 2018, 130, 5151–5155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Simpson, J.D.; Fuchs, A.V.; Rolfe, B.E.; Thurecht, K.J. Effects of surface charge of hyperbranched polymers on cytotoxicity, dynamic cellular uptake and localization, hemotoxicity, and pharmacokinetics in mice. Mol. Pharm. 2017, 14, 4485–4497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, H.; Leong, W.; Leong, K.W.; Chen, C.; Zhao, Y. Walking the line: The fate of nanomaterials at biological barriers. Biomaterials 2018, 174, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chonn, A.; Cullis, P.; Devine, D. The role of surface charge in the activation of the classical and alternative pathways of complement by liposomes. J. Immunol. 1991, 146, 4234–4241. [Google Scholar]
- Fasugba, O.; Gardner, A.; Mitchell, B.G.; Mnatzaganian, G. Ciprofloxacin resistance in community-and hospital-acquired Escherichia coli urinary tract infections: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. BMC Infect. Dis. 2015, 15, 545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zervos, M.J.; Hershberger, E.; Nicolau, D.P.; Ritchie, D.J.; Blackner, L.K.; Coyle, E.A.; Donnelly, A.J.; Eckel, S.F.; Eng, R.H.; Hiltz, A. Relationship between fluoroquinolone use and changes in susceptibility to fluoroquinolones of selected pathogens in 10 United States teaching hospitals, 1991–2000. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2003, 37, 1643–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atkin, S.D.; Abid, S.; Foster, M.; Bose, M.; Keller, A.; Hollaway, R.; Sader, H.S.; Greenberg, D.E.; Finklea, J.D.; Castanheira, M. Multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa from sputum of patients with cystic fibrosis demonstrates a high rate of susceptibility to ceftazidime–avibactam. Infect. Drug Resist. 2018, 11, 1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centres for Disease Control and Prevention. Antibiotic Resistance Threats in the United States, 2013; Centres for Disease Control and Prevention, US Department of Health and Human Services: Antlanta, GA, USA, 2013.
- Paradies, G.; Paradies, V.; De Benedictis, V.; Ruggiero, F.M.; Petrosillo, G. Functional role of cardiolipin in mitochondrial bioenergetics. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Bioenerget. 2014, 1837, 408–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sosunov, V.; Mischenko, V.; Eruslanov, B.; Svetoch, E.; Shakina, Y.; Stern, N.; Majorov, K.; Sorokoumova, G.; Selishcheva, A.; Apt, A. Antimycobacterial activity of bacteriocins and their complexes with liposomes. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2007, 59, 919–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.-Y.; Weibel, D.B. Organization and function of anionic phospholipids in bacteria. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 4255–4267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lungwitz, U.; Breunig, M.; Blunk, T.; Göpferich, A. Polyethylenimine-based non-viral gene delivery systems. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2005, 60, 247–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinnapireddy, S.R.; Duse, L.; Strehlow, B.; Schäfer, J.; Bakowsky, U. Composite liposome-PEI/nucleic acid lipopolyplexes for safe and efficient gene delivery and gene knockdown. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2017, 158, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.-L.; Feng, C.-L.; Zheng, W.-S.; Huang, S.; Zhang, W.-X.; Wu, H.-N.; Zhan, Y.; Han, Y.-X.; Wu, S.; Jiang, J.-D. Tumor-selective lipopolyplex encapsulated small active RNA hampers colorectal cancer growth in vitro and in orthotopic murine. Biomaterials 2017, 141, 13–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Persano, S.; Guevara, M.L.; Li, Z.; Mai, J.; Ferrari, M.; Pompa, P.P.; Shen, H. Lipopolyplex potentiates anti-tumor immunity of mRNA-based vaccination. Biomaterials 2017, 125, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benincasa, M.; Barrière, Q.; Runti, G.; Pierre, O.; Bourge, M.; Scocchi, M.; Mergaert, P. Single cell flow cytometry assay for peptide uptake by bacteria. Bio-Protocol 2016, 6, e2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuutila, J.; Lilius, E.M. Flow cytometric quantitative determination of ingestion by phagocytes needs the distinguishing of overlapping populations of binding and ingesting cells. Cytom. Part A 2005, 65, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilley, L.D.; Hine, O.S.; Kellogg, J.A.; Hassinger, J.N.; Weller, D.D.; Iversen, P.L.; Geller, B.L. Gene-specific effects of antisense phosphorodiamidate morpholino oligomer-peptide conjugates on Escherichia coli and Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium in pure culture and in tissue culture. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2006, 50, 2789–2796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geller, B.L.; Deere, J.; Tilley, L.; Iversen, P.L. Antisense phosphorodiamidate morpholino oligomer inhibits viability of Escherichia coli in pure culture and in mouse peritonitis. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2005, 55, 983–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.-C.; Wu, Y.-Q.; Cao, D.; Zhang, W.-B.; Wang, H.-H. Only acyl carrier protein 1 (AcpP1) functions in Pseudomonas aeruginosa fatty acid synthesis. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikravesh, A.; Dryselius, R.; Faridani, O.R.; Goh, S.; Sadeghizadeh, M.; Behmanesh, M.; Ganyu, A.; Klok, E.J.; Zain, R.; Good, L. Antisense PNA accumulates in Escherichia coli and mediates a long post-antibiotic effect. Mol. Ther. 2007, 15, 1537–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sousa, S.A.; Ramos, C.G.; Almeida, F.; Meirinhos-Soares, L.; Wopperer, J.; Schwager, S.; Eberl, L.; Leitao, J.H. Burkholderia cenocepacia J2315 acyl carrier protein: A potential target for antimicrobials’ development? Microb. Pathog. 2008, 45, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McArthur, M. Transcription Factor Decoys for the Treatment and Prevention of Infections Caused by Bacteria Including Clostridium Difficile. U.S. Patent App. 13/802,103, 18 September 2014. [Google Scholar]
- McArthur, M. Transcription Factor Decoys. European Patent EP2552455B1, 28 December 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Renner, L.D.; Weibel, D.B. Cardiolipin microdomains localize to negatively curved regions of Escherichia coli membranes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 6264–6269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegarty, J.P.; Krzeminski, J.; Sharma, A.K.; Guzman-Villanueva, D.; Weissig, V.; Stewart Sr, D.B. Bolaamphiphile-based nanocomplex delivery of phosphorothioate gapmer antisense oligonucleotides as a treatment for Clostridium difficile. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 11, 3607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marín-Menéndez, A.; Montis, C.; Díaz-Calvo, T.; Carta, D.; Hatzixanthis, K.; Morris, C.J.; McArthur, M.; Berti, D. Antimicrobial nanoplexes meet model bacterial membranes: The key role of cardiolipin. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 41242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Traglia, G.M.; Sala, C.D.; Fuxman Bass, J.I.; Soler-Bistué, A.J.; Zorreguieta, A.; Ramírez, M.S.; Tolmasky, M.E. Internalization of locked nucleic acids/DNA hybrid oligomers into Escherichia coli. BioRes. Open Access 2012, 1, 260–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setyawati, M.I.; Kutty, R.V.; Tay, C.Y.; Yuan, X.; Xie, J.; Leong, D.T. Novel theranostic DNA nanoscaffolds for the simultaneous detection and killing of Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 21822–21831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thibault, T.; Degrouard, J.; Baril, P.; Pichon, C.; Midoux, P.; Malinge, J.-M. Production of DNA minicircles less than 250 base pairs through a novel concentrated DNA circularization assay enabling minicircle design with NF-κB inhibition activity. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 45, e26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosal, A.; Nielsen, P.E. Potent antibacterial antisense peptide–peptide nucleic acid conjugates against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Nucleic Acid Ther. 2012, 22, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apte, A.; Koren, E.; Koshkaryev, A.; Torchilin, V.P. Doxorubicin in TAT peptide-modified multifunctional immunoliposomes demonstrates increased activity against both drug-sensitive and drug-resistant ovarian cancer models. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2014, 15, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tros de Ilarduya, C.; García, L.; Düzgünes, N. Liposomes and lipopolymeric carriers for gene delivery. J. Microencapsul. 2010, 27, 602–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Reznikoff, G.; Dranoff, G.; Rock, K.L. Cloned dendritic cells can present exogenous antigens on both MHC class I and class II molecules. J. Immunol. 1997, 158, 2723–2730. [Google Scholar]


| Nucleic Acid | Size (nm) | Zeta Potential (mV) |
|---|---|---|
| 11 nt ssASO | 100 ± 4 | 8 ± 1.5 |
| 15 bp dsDNA | 120 ± 8 | 10 ± 3 |
| 95 bp dsDNA | 100 ± 7 | 6.2 ± 1.7 |
| 9 kbp pDNA | 214 ± 18 | 9 ± 4 |
| 1000 nt RNA | 166 ± 10 | 13 ± 2 |
| Nucleic Acid | Size (nm) | PDI | Zeta Potential (mV) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 11 nt ssASO | 140 ± 8 | 0.20 ± 0.02 | 6.1 ± 4.7 |
| 15 bp dsDNA | 150 ± 12 | 0.26 ± 0.04 | 5 ± 3 |
| 95 bp dsDNA | 157 ± 9 | 0.24 ± 0.04 | 9.7 ± 4.7 |
| 9 kbp pDNA | 174 ± 10 | 0.40 ± 0.08 | 0.5 ± 0.4 |
| 1000 nt RNA | 156 ± 15 | 0.27 ± 0.03 | 7.4 ± 3.7 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Perche, F.; Le Gall, T.; Montier, T.; Pichon, C.; Malinge, J.-M. Cardiolipin-Based Lipopolyplex Platform for the Delivery of Diverse Nucleic Acids into Gram-Negative Bacteria. Pharmaceuticals 2019, 12, 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph12020081
Perche F, Le Gall T, Montier T, Pichon C, Malinge J-M. Cardiolipin-Based Lipopolyplex Platform for the Delivery of Diverse Nucleic Acids into Gram-Negative Bacteria. Pharmaceuticals. 2019; 12(2):81. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph12020081
Chicago/Turabian StylePerche, Federico, Tony Le Gall, Tristan Montier, Chantal Pichon, and Jean-Marc Malinge. 2019. "Cardiolipin-Based Lipopolyplex Platform for the Delivery of Diverse Nucleic Acids into Gram-Negative Bacteria" Pharmaceuticals 12, no. 2: 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph12020081
APA StylePerche, F., Le Gall, T., Montier, T., Pichon, C., & Malinge, J.-M. (2019). Cardiolipin-Based Lipopolyplex Platform for the Delivery of Diverse Nucleic Acids into Gram-Negative Bacteria. Pharmaceuticals, 12(2), 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph12020081







