Sensor-Based Evaluation of Purslane-Enriched Biscuits Using Multivariate Feature Selection and Spectral Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sensor-Based Framework
2.2. Collection and Analysis of Data for Optimizing the Technical Procedure
2.3. Purslane Supplements
2.4. Biscuit Receipt and Technological Parameters
2.5. Analytical Methods
2.5.1. Determination of Physicochemical Characteristics
2.5.2. Determination of Thermal Losses
2.5.3. Determination of Elemental Composition
2.5.4. Determination of Spread Factor
2.5.5. Sensory Evaluation of Biscuits
2.5.6. Obtaining Color Digital Images
2.5.7. Calculation of Color Difference
2.5.8. Calculation of Color Indices
2.5.9. Obtaining Spectral Characteristics and Calculation of Spectral Indices
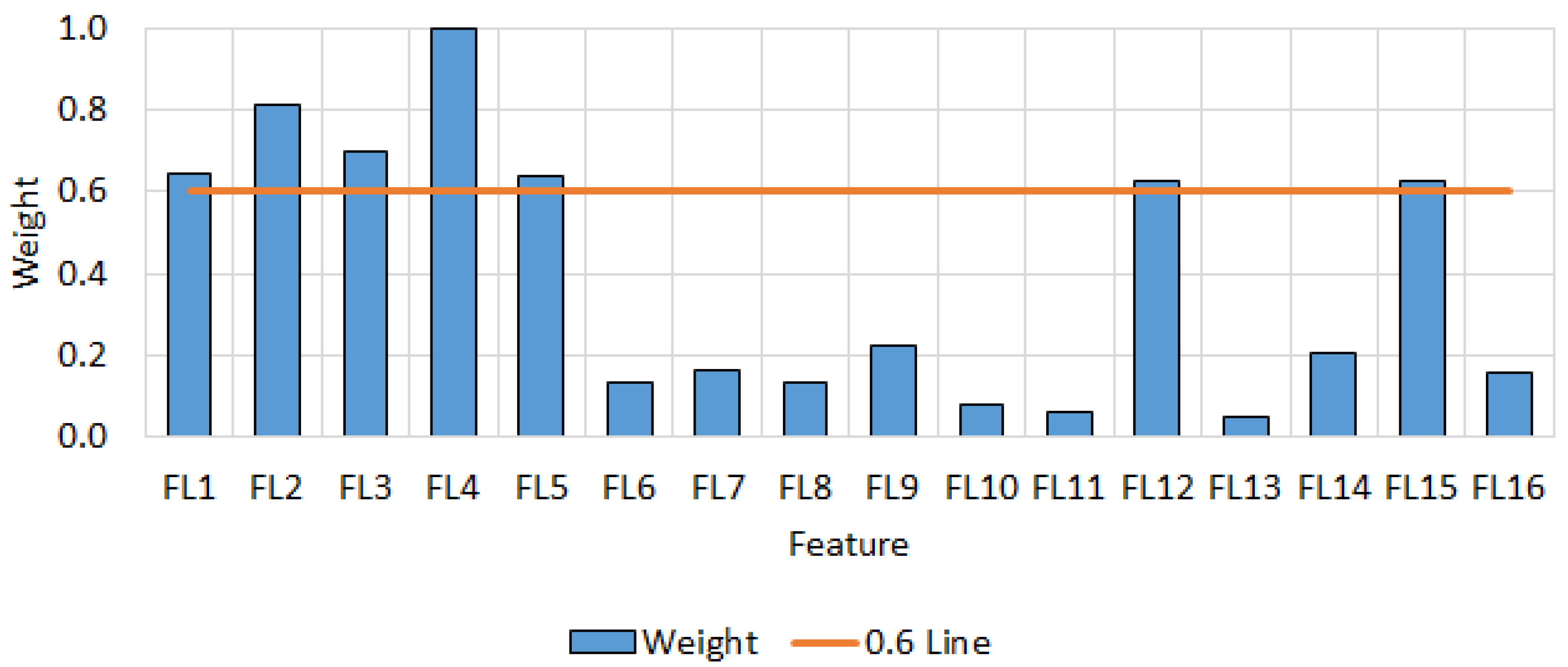
2.5.10. Feature Vectors and Selection of Informative Features
2.5.11. Data Reduction Method
2.5.12. Regression Model and a Linear Programming Algorithm
2.6. Statistical Analysis
2.7. Literature Data
3. Results
3.1. Preparation and Analysis of Real Biscuits
3.1.1. Analysis of the Raw Material
3.1.2. Flour Analysis
3.1.3. Dough Analysis
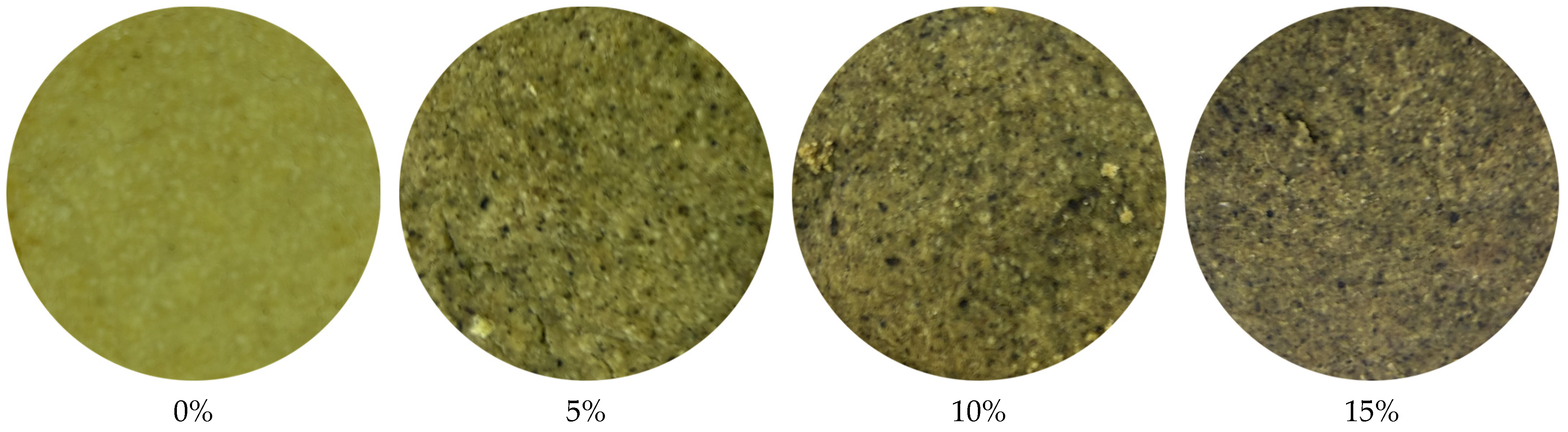
3.1.4. Biscuit Analysis
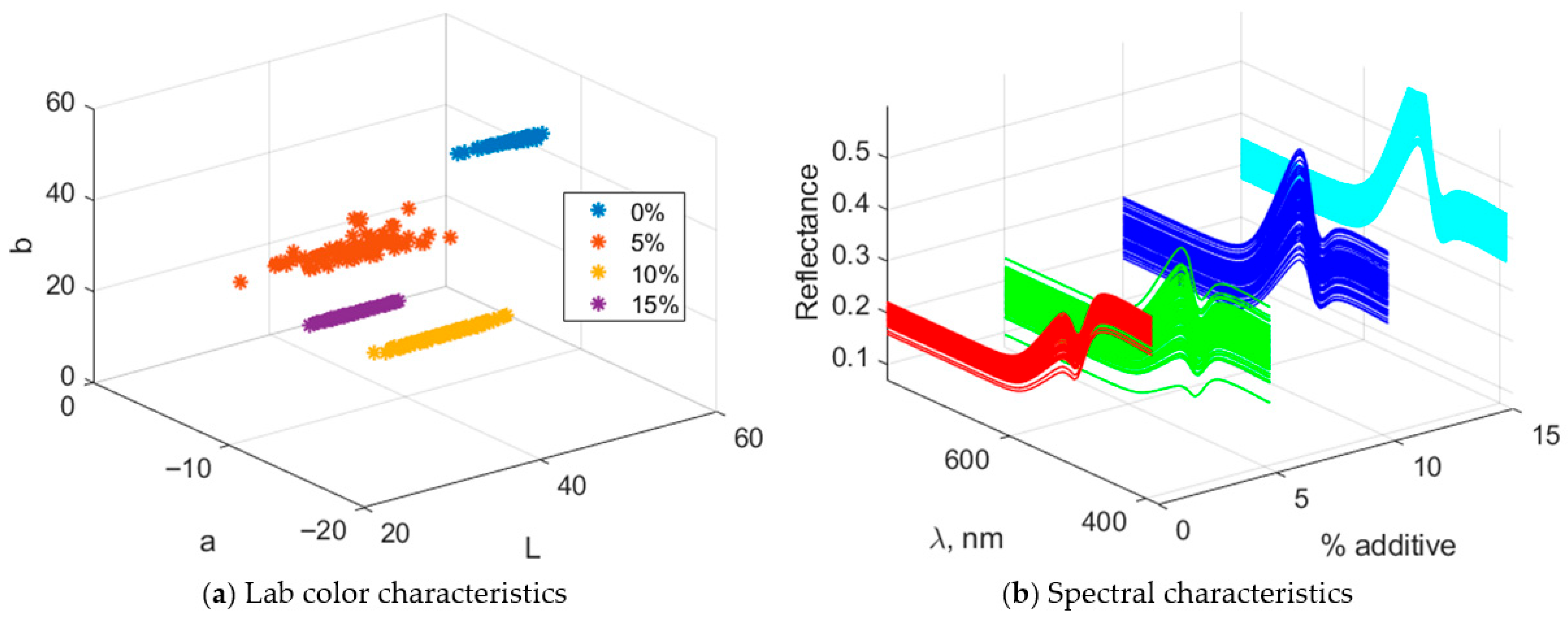
3.2. Statistical Analysis and Determination of the Optimal Additive Amount
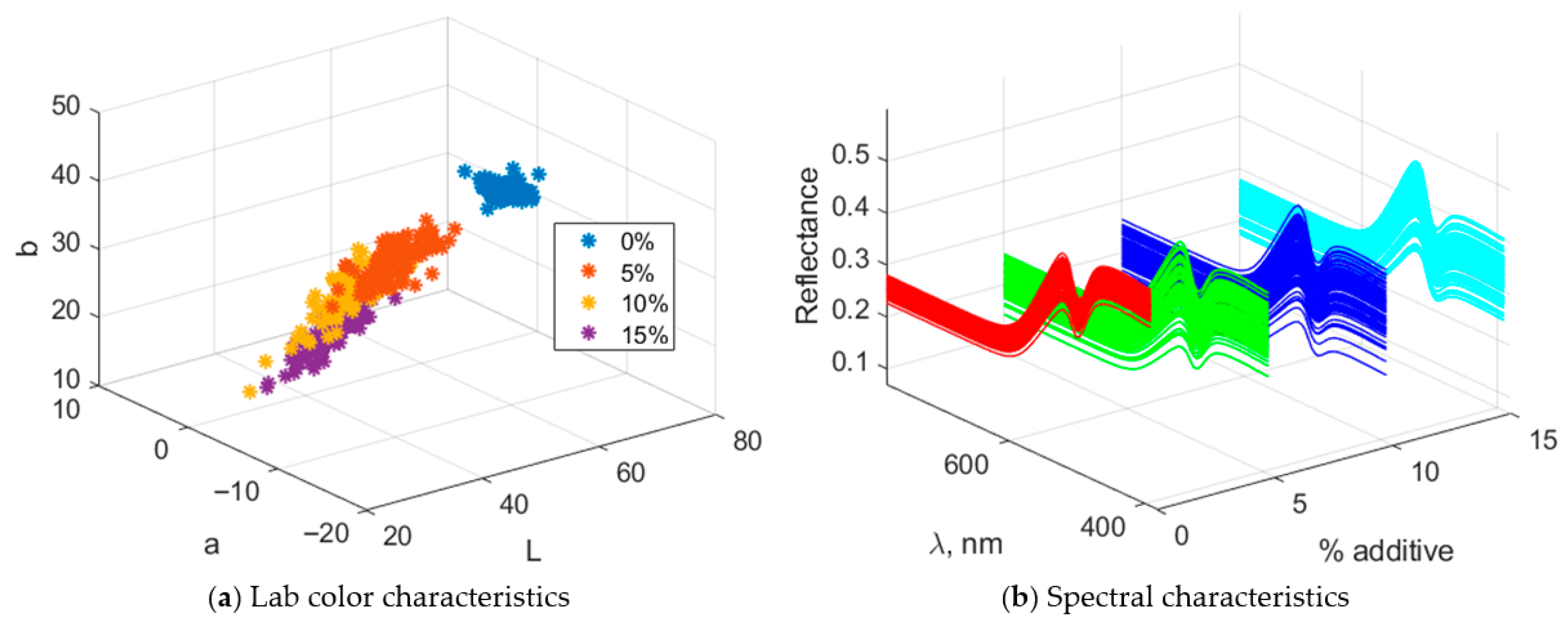
3.3. Research and Selection of the Optimal Purslane Supplement Amount by Literature Data
3.4. A Comparative Analysis Between Data from Experimental (Real) Biscuits and Literature Data
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PCA | Principal Component Analysis |
| AACC | American Association of Cereal Chemists |
| ANOVA | Analysis of variance |
| CIE | International Commission on Illumination |
| DoE | Design of Experiment |
| EC | Electrical conductivity |
| ENSs | Extractive nitrogen substances |
| ISO | International Standard Organization |
| LMS | Long, medium, short—color model |
| LSD | Least Significant Difference |
| ORP | Oxidation-reduction potential |
| PCR | Principal Component Regression |
| pH | Active acidity |
| PR | People Republic |
| RReliefF | Relief Feature Selection for Regression |
| RGB | Red, green, blue—color model |
| R&D | Research and Development |
| SE | Standard error |
| SF | Spread factor |
| TDSs | Total dissolved solids |
| TLs | Thermal losses |
Appendix A
| Compound | Content |
|---|---|
| Crude protein, % (DM) | 20.11 |
| Crude fat, % (DM) | 4.25 |
| Crude fiber, % (DM) | 9.73 |
| K, mg·100 g−1 (DM) | 2925 |
| Mg, mg·100 g−1 (DM) | 1256 |
| Ca, mg·100 g−1 (DM) | 982 |
| Na, mg·100 g−1 (DM) | 152 |
| P, mg·100 g−1 (DM) | 62.25 |
| Fe, mg 100 g−1 (DM) | 53.73 |
| Zn, mg·100 g−1 (DM) | 5.68 |
| Vitamin C, mg·100 g−1 (FW) | 14.52 |
| Total Titratable Organic Acids, % (FW) | 0.21 |
| Stage | Time | Temperature | Designation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | - | 20–22 °C | Preliminary preparation of ingredients |
| 2 | - | 20–22 °C | Measuring of ingredients |
| 3 | 5–10 min | 18–20 °C | Preparation of a crumbly butter base for shaping the biscuits (dough) |
| 4 | 30–40 min | 3–4 °C | Chilling |
| 5 | - | 18–20 °C | Rolling out |
| 6 | - | 18–20 °C | Shaping |
| 7 | - | 18–20 °C | Arranging on baking trays |
| 8 | 10–12 min | 200 °C | Baking |
| 9 | 1 h | 20–22 °C | Cooling |
| 10 | - | 20–22 °C | Packaging |
| 11 | - | 20–22 °C | Storage |


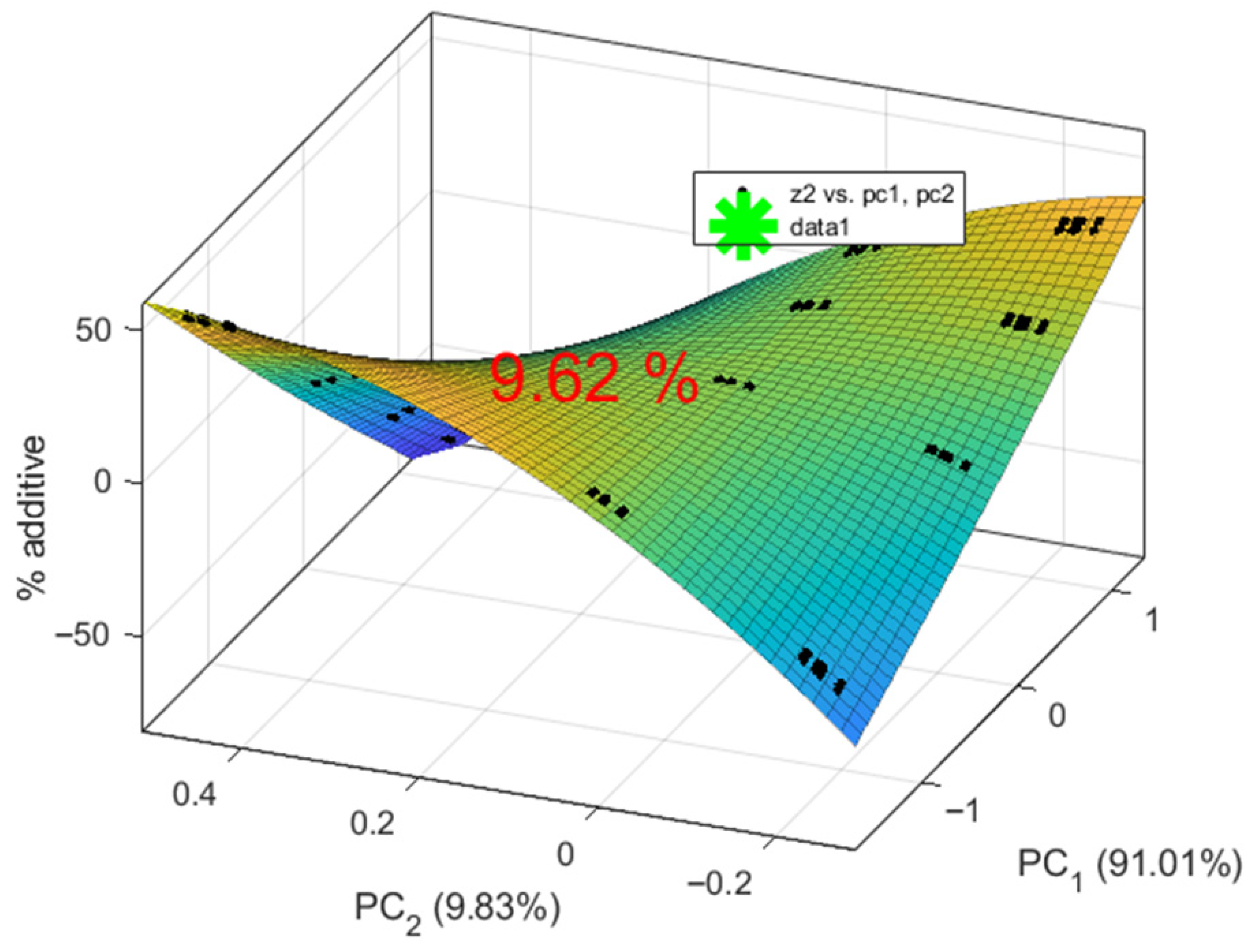
| Principal Component | PC1 | PC2 | PC3 | PC4 | PC5 | PC6 | PC7 | PC8 | PC9 | PC10 | PC11 | PC12 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Feature | |||||||||||||
| F2 | −0.15 | 0.40 | 0.35 | −0.16 | −0.04 | 0.64 | 0.15 | 0.17 | 0.19 | 0.34 | 0.16 | −0.16 | |
| F3 | −0.14 | 0.40 | 0.37 | −0.11 | −0.07 | −0.13 | −0.21 | −0.10 | 0.28 | −0.37 | −0.30 | 0.54 | |
| F6 | −0.14 | 0.39 | 0.41 | −0.07 | 0.15 | −0.52 | 0.04 | −0.07 | −0.45 | 0.04 | 0.15 | −0.37 | |
| F7 | 0.17 | 0.38 | −0.35 | −0.12 | −0.46 | −0.22 | 0.04 | 0.50 | 0.07 | 0.04 | −0.35 | −0.22 | |
| F8 | 0.17 | 0.39 | −0.39 | −0.09 | −0.04 | −0.14 | −0.34 | −0.34 | 0.19 | 0.29 | 0.51 | 0.16 | |
| F9 | 0.17 | 0.40 | −0.39 | −0.10 | 0.48 | 0.28 | 0.32 | −0.16 | −0.28 | −0.32 | −0.17 | 0.05 | |
| F10 | 0.32 | 0.11 | 0.16 | 0.42 | −0.47 | 0.01 | 0.50 | −0.11 | −0.18 | −0.11 | 0.27 | 0.27 | |
| F11 | 0.32 | 0.11 | 0.14 | 0.43 | −0.01 | 0.09 | −0.21 | −0.45 | 0.24 | 0.02 | −0.38 | −0.47 | |
| F12 | 0.33 | 0.11 | 0.12 | 0.46 | 0.42 | 0.00 | −0.30 | 0.57 | −0.05 | 0.08 | 0.10 | 0.19 | |
| F13 | 0.42 | −0.10 | 0.16 | −0.37 | −0.23 | 0.26 | −0.41 | 0.06 | −0.25 | −0.47 | 0.23 | −0.18 | |
| F14 | 0.42 | −0.11 | 0.18 | −0.33 | 0.01 | −0.01 | 0.00 | −0.14 | −0.31 | 0.56 | −0.38 | 0.31 | |
| F15 | 0.43 | −0.11 | 0.18 | −0.31 | 0.27 | −0.28 | 0.40 | 0.08 | 0.56 | −0.09 | 0.16 | −0.12 | |
Appendix B
| FL | FL1 | FL2 | FL3 | FL4 | FL5 | FL6 | FL7 | FL8 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| %A | |||||||||
| 0 | 4.44 ± 0.25 | 4.5 ± 0.12 | 4.33 ± 0.3 | 4.39 ± 0.15 | 4.44 ± 0.12 | 4.56 ± 0.18 | 4.56 ± 0.29 | 10.1 ± 0.03 | |
| 2 | 4.17 ± 0.27 | 4.33 ± 0.03 | 4.22 ± 0.14 | 4.44 ± 0.25 | 4.17 ± 0.03 | 4.28 ± 0.18 | 4.28 ± 0.12 | 16.68 ± 1.15 | |
| 3 | 4.83 ± 0.16 | 4.38 ± 0.11 | 4.78 ± 0.33 | 4.5 ± 0.27 | 4.83 ± 0.24 | 4.56 ± 0.22 | 4.94 ± 0.3 | 33.36 ± 1.15 | |
| 4 | 4.33 ± 0.26 | 4.44 ± 0.06 | 4.39 ± 0.23 | 4.64 ± 0.27 | 4.33 ± 0.1 | 4.44 ± 0.24 | 4.88 ± 0.03 | 50.05 ± 1.68 | |
| 5 | 4.83 ± 0.29 | 4.3 ± 0.21 | 4.8 ± 0.1 | 4.79 ± 0.19 | 4.89 ± 0.34 | 4.73 ± 0.2 | 4.81 ± 0.31 | 66.73 ± 4.64 | |
| 6 | 4.11 ± 0.01 | 4.17 ± 0.12 | 4.17 ± 0.14 | 4.71 ± 0.01 | 4.11 ± 0.15 | 4.22 ± 0.04 | 4.78 ± 0.14 | 83.41 ± 2.53 | |
| 8 | 3.61 ± 0.18 | 3.67 ± 0.16 | 3.72 ± 0.17 | 4.64 ± 0.05 | 3.67 ± 0.03 | 3.78 ± 0.08 | 4.75 ± 0.21 | 83.41 ± 4.82 | |
| 9 | 4.72 ± 0.15 | 3.78 ± 0 | 4.72 ± 0.2 | 4.56 ± 0.01 | 4.72 ± 0.08 | 4.61 ± 0.02 | 4.72 ± 0.03 | 83.41 ± 3.01 | |
| 10 | 3.89 ± 0.24 | 3.89 ± 0.25 | 4.44 ± 0.22 | 4.44 ± 0.17 | 5 ± 0.34 | 4.61 ± 0.03 | 3.33 ± 0.1 | 83.41 ± 1.25 | |
| 15 | 4.28 ± 0.06 | 3.85 ± 0.07 | 3.78 ± 0.12 | 3.8 ± 0.2 | 4.09 ± 0.24 | 4.61 ± 0.24 | 3.91 ± 0.07 | 83.41 ± 2.33 | |
| 20 | 3.33 ± 0.06 | 3.33 ± 0.18 | 3.33 ± 0.02 | 3.33 ± 0.05 | 4.44 ± 0.14 | 4.61 ± 0.22 | 3.89 ± 0.08 | 83.41 ± 3.66 | |
| 30 | 2.22 ± 0.02 | 2.78 ± 0.02 | 2.78 ± 0.03 | 2.22 ± 008 | 2.78 ± 0.09 | 4.61 ± 0.05 | 5 ± 0.23 | 83.41 ± 5.66 | |
| FL | FL9 | FL10 | FL11 | FL12 | FL13 | FL14 | FL15 | FL16 | |
| %A | |||||||||
| 0 | 1.8 ± 0.02 | 66.68 ± 3.94 | 2.02 ± 0.07 | 21.4 ± 0.83 | 4.74 ± 0.04 | 3.35 ± 0.04 | 6.77 ± 0.38 | 34.98 ± 2.03 | |
| 2 | 1.39 ± 0.07 | 65.28 ± 0.61 | 2.48 ± 0.07 | 20.82 ± 0.63 | 4.16 ± 0.05 | 3.99 ± 0.21 | 8.39 ± 0.15 | 34.98 ± 0.12 | |
| 3 | 0.97 ± 0.02 | 63.87 ± 2.68 | 2.93 ± 0.2 | 20.25 ± 0.46 | 3.59 ± 0.21 | 4.63 ± 0.31 | 10 ± 0.07 | 69.96 ± 2.05 | |
| 4 | 0.93 ± 0.05 | 65.39 ± 0.52 | 1.79 ± 0.07 | 15.81 ± 0.64 | 3.01 ± 0.04 | 4.98 ± 0.34 | 11.62 ± 0.16 | 104.93 ± 5.86 | |
| 5 | 0.88 ± 0.05 | 66.92 ± 0.97 | 0.65 ± 0 | 11.37 ± 0.54 | 2.44 ± 0.04 | 5.33 ± 0.01 | 13.23 ± 0.34 | 139.91 ± 1.01 | |
| 6 | 2.89 ± 0.15 | 65.23 ± 3.63 | 2.29 ± 0.04 | 21.53 ± 0.1 | 1.86 ± 0.11 | 3.34 ± 0.13 | 14.85 ± 0.31 | 174.89 ± 4.01 | |
| 8 | 1.59 ± 0.06 | 61.69 ± 1.72 | 3.78 ± 0.02 | 21.65 ± 1.1 | 7.32 ± 0.38 | 4.26 ± 0.1 | 7.75 ± 0.24 | 174.89 ± 668 | |
| 9 | 1.45 ± 0 | 58.14 ± 2.74 | 5.27 ± 0.29 | 21.77 ± 1.44 | 5.9 ± 0.01 | 5.18 ± 0.17 | 9.75 ± 0.08 | 174.89 ± 7.91 | |
| 10 | 1.3 ± 0.04 | 60.15 ± 0.78 | 3.8 ± 0.17 | 18.98 ± 0.55 | 4.47 ± 0.29 | 5.04 ± 0.32 | 11.76 ± 0.05 | 174.89 ± 8.75 | |
| 15 | 1.16 ± 0.07 | 62.17 ± 1.18 | 2.34 ± 0.04 | 16.19 ± 1.07 | 3.05 ± 0.06 | 4.91 ± 0.16 | 13.77 ± 0.49 | 174.89 ± 9.4 | |
| 20 | 1.01 ± 0.07 | 64.18 ± 2.23 | 0.87 ± 0.06 | 13.4 ± 0.74 | 1.63 ± 0.01 | 4.77 ± 0.11 | 15.77 ± 0.33 | 174.89 ± 8.1 | |
| 30 | 1.01 ± 0.03 | 64.18 ± 2.75 | 0.87 ± 0.06 | 13.4 ± 0.84 | 1.63 ± 0.1 | 4.77 ± 0.17 | 15.77 ± 0.49 | 174.89 ± 0.15 | |
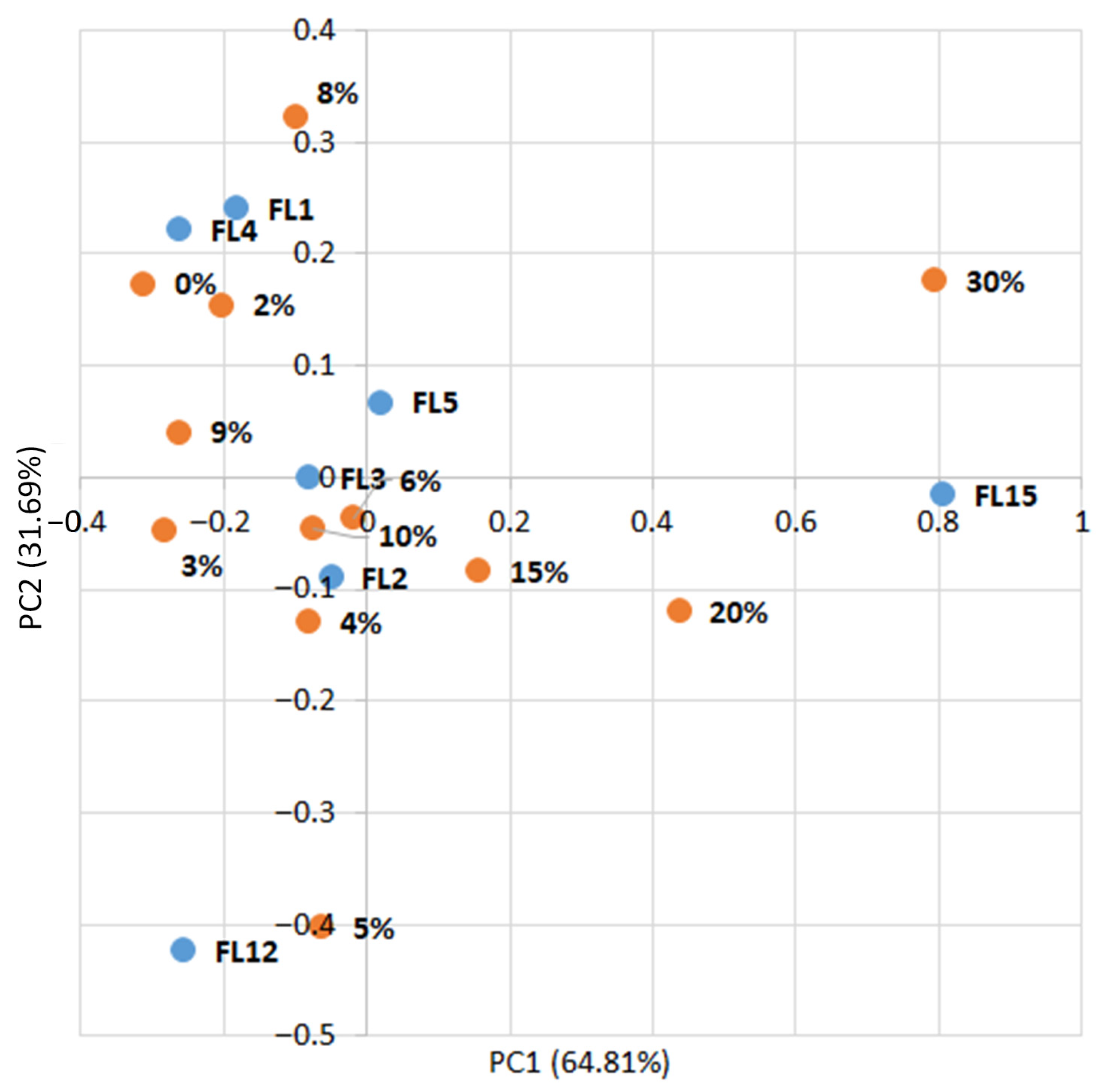
| Principal Component | PC1 | PC2 | PC3 | PC4 | PC5 | PC6 | PC7 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Feature | ||||||||
| FL1 | −0.41 | −0.35 | −0.01 | 0.01 | −0.55 | −0.47 | −0.43 | |
| FL2 | −0.30 | −0.17 | −0.08 | −0.46 | −0.35 | 0.73 | 0.08 | |
| FL3 | −0.35 | −0.28 | 0.02 | 0.15 | −0.04 | −0.22 | 0.85 | |
| FL4 | −0.44 | −0.17 | 0.19 | −0.48 | 0.68 | −0.15 | −0.16 | |
| FL5 | −0.26 | −0.37 | 0.04 | 0.71 | 0.27 | 0.41 | −0.23 | |
| FL12 | −0.36 | 0.57 | 0.70 | 0.15 | −0.17 | 0.07 | 0.00 | |
| FL15 | 0.48 | −0.53 | 0.68 | −0.12 | −0.09 | 0.03 | 0.03 | |
References
- Auerman, L.Y. Tekhnologiya Khlebopekarnogo Proizvodstva; Professiya: St. Petersburg, Russia, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Kurbanov, N.G. Izuchenie Kolichestvennogo Sostava Pischevykh Volokon v Khlebobulochnykh Izdeliyakh s Dobavkami Portulaka. Azerb. Technol. Univ. Vestnik 2011, 19–20, 71–79. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, A.; Sreedha, S.; Kashyap, A.K.; Singh, P.; Ramchiary, N. A Review on Bioactive Phytochemicals and Pharmacological Importance of Purslane (Portulaca oleracea L.). Heliyon 2021, 8, e08669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syed, S.; Fatima, N.; Kabeer, G. Portulaca oleracea L.: A Mini Review on Phytochemistry and Pharmacology. Int. J. Biol. Biotechnol. 2016, 13, 637–641. [Google Scholar]
- Gurbanov, N.; Yusifova, M.; Tagiyev, M.; Nasrullayeva, G.; Kazimova, İ. Determining the qualitative parameters of powder from the stalks of garden purslane (Portulaca oleracea L.) and its application in the production of functional bakery products. East.-Eur. J. Enterp. Technol. 2023, 1, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, K.M.; Mokhtar, S.M. Effect of Drying Methods on the Antioxidant Capacity, Color and Phytochemicals of Portulaca oleracea L. Leaves. J. Nutr. Food Sci. 2014, 4, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abeer, G.A.; Eman, S. Nutritional Quality of Purslane and Its Crackers. Middle East J. Appl. Sci. 2014, 4, 448–454. [Google Scholar]
- Hanan, A.A.; Sobhy, M.A.; Kawkab, A.A.; Zeinab, A.R.; Wedad, A.H. Chemical and Remedial Effects of Portulaca oleracea Plant. Life Sci. J. 2014, 11, 31–42. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, V.; Chugh, V.; Dwivedi, S.V.; Sharma, K.D. Food and Nutraceutical Value of Purslane (Portulaca oleracea L.). Pharma Innov. J. 2020, 9, 419–424. [Google Scholar]
- Petropoulos, S.A.; Karkanis, A.; Fernandes, Â.; Barros, L.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R. Chemical Composition and Yield of Six Genotypes of Common Purslane (Portulaca oleracea L.): An Alternative Source of Omega-3 Fatty Acids. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2015, 70, 420–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.K.; Juraimi, A.S.; Hossain, M.S.; Nahar, M.A.U.; Ali, M.E.; Rahman, M.M. Purslane Weed: A Prospective Plant Source of Nutrition. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 951019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farag, M.A.; Zeinab, T.A.S. Metabolomics-Driven Analysis of Portulaca Leaf Taxa. Phytochemistry 2019, 161, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Poyatos, M.D.P.; Llorent-Martínez, E.J.; Ruiz-Medina, A. Phytochemical Composition and Antioxidant Activity of Portulaca oleracea: Influence of Steaming. Foods 2021, 10, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karomatov, I.D.; Abdukhalilova, M.K. New Life in Herb Medicine Purslane. Biol. Integr. Med. 2017, 6, 211–222. [Google Scholar]
- Kurbanov, N.G.; Tagiev, M.M. Portulak—Syr’e Pischevoy Promyshlennosti. Pishch. Prom. 1992, 12, 21. [Google Scholar]
- Kurbanov, N.G.; Tagiev, M.M.; Bayramova, K.I.; Bakhtiyarova, S.G. Vodopoglotitelnaya Sposobnost’ i Tekhnologicheskie Svoystva Sushenogo Portulaka. In Proceedings of the Conference “Aktual’nye Problemy Pishchevoy Promyshlennosti”, Gyandzha, Azerbaijan, 10 April 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Kurbanov, N.G. Belkovaya Pasta iz Ogorodnogo Portulaka—Perspektivnaya Pischevaya Dobavka. In Proceedings of the International Conference “Functional Food Products”, Krasnodar, Russia, 4–7 June 2001; pp. 128–129. [Google Scholar]
- Kurbanov, N.G. Izuchenie Vliyanie Poroshka Portulaka na Protsessy Strukturoobrazovaniya v Teste iz Pshenichnoy Muki. Gyandzha Sci. Cent. 2008, 34, 102–109. [Google Scholar]
- Rayan, A.M.; Swailam, H.M.; Hamed, Y.S. Composition, Structure, and Techno-Functional Characteristics of the Flour, Protein Concentrate, and Protein Isolate from Purslane (Portulaca oleracea L.) Seeds. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2022, 77, 543–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramanian, M.; Sree Varagi, S.; Sathies Kumar, T.; Sowmiya, K.; Prashithaa, N. IoT-Enhanced Quality Bread Assurance System (IQBAS). In Proceedings of the 2023 Intelligent Computing and Control for Engineering and Business Systems (ICCEBS), Chennai, India, 14–15 December 2023; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bax, C.; di Diodoro, B.; Ticozzi, A.; Dellarosa, N.; Corazza, F.; Langfelder, G.; Capelli, L. Smart Odour Sensing for Automated Monitoring of Bread Products. Proceedings 2024, 97, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kılcı, O.; Koklu, M. Automated Classification of Biscuit Quality Using YOLOv8 Models in Food Industry. Food Anal. Methods 2025, 18, 815–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, M.; Rudy, M.; Duma-Kocan, P.; Stanisławczyk, R. Electronic Sensing Technologies in Food Quality Assessment: A Comprehensive Literature Review. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zherkova, Z.; Grozeva, N.; Todorova, M.; Tzanova, M. Nutritional Value and Chemical Composition of Common Purslane (Portulaca oleracea L.) from Different Regions in Bulgaria. Ecol. Balk. 2024, 16, 176. [Google Scholar]
- Peksel, A.; Arisan-Atac, I.; Yanardag, R. Antioxidant Activities of Aqueous Extracts of Purslane (Portulaca oleracea subsp. Sativa L.). Ital. J. Food Sci. 2006, 18, 295–308. [Google Scholar]
- Naeem, M.Y.; Jabran, K.; Özden, M.; Bakhsh, A. Assessment of morphological and biochemical characteristics of common purslane (Portulaca oleracea L.) accessions. Pak. J. Agric. Sci. 2022, 59, 1017–1028. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, G.; El Gazzar, M.; Hashem, M.; Galal, W. Evaluation of some bakery products enriched with purslane. Food Technol. Res. J. 2023, 2, 98–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waleed, Z.B.; Salwa, G.A.; Czakó, M. Optimization of purslane plant using cooking and pickling processes for reducing oxalate content. J. Adv. Agric. 2018, 8, 1384–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Method 02-52.01; Hydrogen-Ion Activity (pH)-Electrometric Method. AACC International: St. Paul, MN, USA, 1999.
- Method 44-15.02; Moisture—Air-Oven Methods. AACC International: St. Paul, MN, USA, 1999.
- BDS EN ISO 5983-1:2006; Animal Feeding Stuffs—Determination of Nitrogen Content and Calculation of Crude Protein—Part 1: Kjeldahl Method. Bulgarian Institute for Standardization: Sofia, Bulgaria, 2006.
- BDS ISO 6492:2007; Animal Feeding Stuffs—Determination of Fat Content. Bulgarian Institute for Standardization: Sofia, Bulgaria, 2007.
- BDS ISO 6496:2000; Animal Feeding Stuffs—Determination of Moisture and Other Volatile Matter. Bulgarian Institute for Standardization: Sofia, Bulgaria, 2000.
- BDS ISO 5984:2022; Animal Feeding Stuffs—Determination of Crude Ash Content. Bulgarian Institute for Standardization: Sofia, Bulgaria, 2022.
- BDS EN ISO 13299:2016; Sensory Analysis—Methodology—General Guidance. Bulgarian Institute for Standardization: Sofia, Bulgaria, 2016.
- BNS 441:1987; Bulgarian National Standard—Biscuits. General Requirements. Bulgarian Institute for Standardization: Sofia, Bulgaria, 1987.
- Vilaseca, M.; Pujol, J.; Arjona, M.; Martínez-Verdú, F.M. Color visualization system for near-infrared multispectral images. In Proceedings of the Conference on Colour in Graphics, Imaging, and Vision, Aachen, Germany, 5–8 April 2004; Society of Imaging Science and Technology: Springfield, VA, USA; Volume 2, pp. 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, A.; Wang, G.; Rush, S.A.; Martin, J.A.; Belant, J.L.; Butler, A.B.; Godwin, D. Machine learning of large-scale spatial distributions of wild turkeys with high-dimensional environmental data. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 9, 5938–5949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mladenov, M. Model-based approach for assessment of freshness and safety of meat and dairy products using a simple method for hyperspectral analysis. J. Food Nutr. Res. 2020, 59, 108–119. [Google Scholar]
- Robnik-Šikonja, M.; Kononenko, I. Theoretical and Empirical Analysis of ReliefF and RReliefF. Mach. Learn. 2003, 53, 23–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgieva, T.; Mihaylova, A.; Daskalov, P. Research of the possibilities for determination of some basic soil properties using image processing. In Proceedings of the 2020 7th International Conference on Energy Efficiency and Agricultural Engineering (EE&AE), Ruse, Bulgaria, 12–14 November 2020; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klunklin, W.; Savage, G. Biscuits: Substitution of Wheat Flour with Purple Rice Flour. Adv. Food Sci. Eng. 2018, 2, 81–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastud, S.K.; Mote, G.V.; Sahoo, A.K. Development of Value-Added Products Using Purslane (Portulaca oleracea). J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. 2018, 7, 1761–1766. [Google Scholar]
- Salehi, M.; Ghorbani, M.; Sadeghi Mahoonk, A.; Khomeiri, M. Physicochemical, Antioxidant and Sensory Properties of Yogurt Fortified with Common Purslane (Portulaca oleracea) Extract. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2021, 15, 4288–4296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salihu, S.; Gashi, N.; Hasani, E. Effect of Plant Extracts Addition on the Physico-Chemical and Sensory Properties of Biscuits. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 9674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goubgou, M.; Songré-Ouattara, L.T.; Bationo, F.; Lingani-Sawadogo, H.; Traoré, Y.; Savadogo, A. Biscuits: A systematic review and meta-analysis of improving the nutritional quality and health benefits. Food Prod. Process. Nutr. 2021, 3, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Framework Stage | Sensor | Measurement (The Data) | Purpose in Study |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Sensor Data Acquisition | |||
| 1.1. Spectral Sensor | VIS Spectrophotometer, Video Sensor | Spectral Signatures (Reflectance data across a specified wavelength range, e.g., 390–730 nm) | Rapid, non-destructive measurement of biscuit composition. |
| 1.2. Basic Chemical Sensors | pH Meter with electrode probe | pH Value | Objective measurement of biscuit acidity, which affects shelf-life, texture, and flavor. |
| Electrical Conductivity (EC) Meter with probe | Electrical Conductivity µS/cm | Measures ionic content; can correlate with overall structural changes. | |
| 2. Data Processing and Modeling | |||
| 2.1. Preprocessing | Data Processing Software (Matlab, MS Excel) | Noise Reduction (Smoothing, baseline correction, scatter correction) | Removes physical artifacts from raw spectral data to enhance chemical information. |
| 2.2. Multivariate Analysis (The Framework’s Core) | Machine Learning/Chemometric Algorithms (PCA) | Feature Selection and Model Creation (PCA loadings) | Identifies the most relevant spectral and chemical features that correlate with a target property. |
| 3. Evaluation and Interpretation | |||
| 3.1. Results Visualization | Statistical Figures | Score Plots, Loading Plots, Regression curves | Visually demonstrates sample grouping, spectral regions, and the predictive accuracy of the final model. |
| 3.2. Final Interpretation | Scientific Reasoning | Performance Metrics: R2, SE, p-value, F-criteria | Validates the effectiveness of the sensor-based approach and discusses its potential for future application. |
| % Additive | 0 | 5 | 10 | 15 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Raw Material | |||||
| Wheat flour, g | 100 | 95 | 90 | 85 | |
| Purslane flour, g | 0 | 5 | 10 | 15 | |
| Cow butter, g | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | |
| Salt, g | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| Egg yolk, g | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | |
| P | № | C | P | № | C | P | № | C | P | № | C | P | № | C | P | № | C |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | F1 | pH | D | F10 | C2 | B | F19 | EC | B | F28 | dE | B | F37 | S | B | F46 | P |
| F | F2 | TDS | D | F11 | C3 | B | F20 | ORP | B | F29 | D | B | F38 | Ch | B | F47 | Zn |
| F | F3 | EC | D | F12 | C4 | B | F21 | C1 | B | F30 | H | B | F39 | OA | B | F48 | M |
| F | F4 | ORP | D | F13 | S1 | B | F22 | C2 | B | F31 | SF | B | F40 | Ca | B | F49 | DM |
| D | F5 | pH | D | F14 | S2 | B | F23 | C3 | B | F32 | TL | B | F41 | Cu | B | F50 | CP |
| D | F6 | TDS | D | F15 | S3 | B | F24 | C4 | B | F33 | GA | B | F42 | Fe | B | F51 | CF |
| D | F7 | EC | D | F16 | dE | B | F25 | S1 | B | F34 | C | B | F43 | K | B | F52 | CFB |
| D | F8 | ORP | B | F17 | pH | B | F26 | S2 | B | F35 | A | B | F44 | Mg | B | F53 | CA |
| D | F9 | C1 | B | F18 | TDS | B | F27 | S3 | B | F36 | T | B | F45 | Mn | B | F54 | NNE |
| Feature | Meaning | Feature | Meaning |
|---|---|---|---|
| FL1 | Appearance | FL9 | Ash, % |
| FL2 | Chewing Resistance | FL10 | Carbohydrate, % |
| FL3 | Color | FL11 | Crude Fiber, % |
| FL4 | Odor | FL12 | Fat, % |
| FL5 | Overall Acceptability | FL13 | Hardness, kg |
| FL6 | Taste | FL14 | Moisture, % |
| FL7 | Texture | FL15 | Protein, % |
| FL8 | Antioxidant Activity, %RSA | FL16 | Total Phenolic Compound, mgGAE/100 g |
| Characteristic | Mean ± SD |
|---|---|
| Ph | 5.56 ± 0.08 |
| TDS, ppm | 2651.5 ± 43.5 |
| EC, µS/cm | 5354.5 ± 93.5 |
| ORP, Mv | 146.5 ± 12.5 |
| % Additive | 0 | 5 | 10 | 15 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Characteristic | |||||
| pH | 7.45 ± 0.02 | 7.52 ± 0.02 | 7.37 ± 0.03 | 7.35 ± 0.04 | |
| TDS, ppm | 602 ± 10 | 1245.5 ± 42.5 | 1605.5 ± 391.5 | 1901 ± 687 | |
| EC, µS/cm | 1205 ± 21 | 2506 ± 77 | 3223 ± 794 | 3802.5 ± 1373.5 | |
| ORP, mV | 47 ± 11 | 40.5 ± 9.5 | 46.5 ± 4.5 | 46.5 ± 3.5 | |
| % Additive | 0 | 5 | 10 | 15 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Characteristic | |||||
| pH | 6.74 ± 0.04 | 7.355 ± 0.07 | 7.34 ± 0 | 7.43 ± 0.04 | |
| TDS, ppm | 1877 ± 40 | 2058.5 ± 153.5 | 2264 ± 359 | 2752.5 ± 129.5 | |
| EC, µS/cm | 3762.5 ± 56.5 | 4132.5 ± 321.5 | 4528.5 ± 717.5 | 5519 ± 273 | |
| ORP, mV | 31 ± 2 | 29.5 ± 3.5 | 27.5 ± 1.5 | 21.5 ± 0.5 | |
| % Additive | 0 | 5 | 10 | 15 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Color Index | |||||
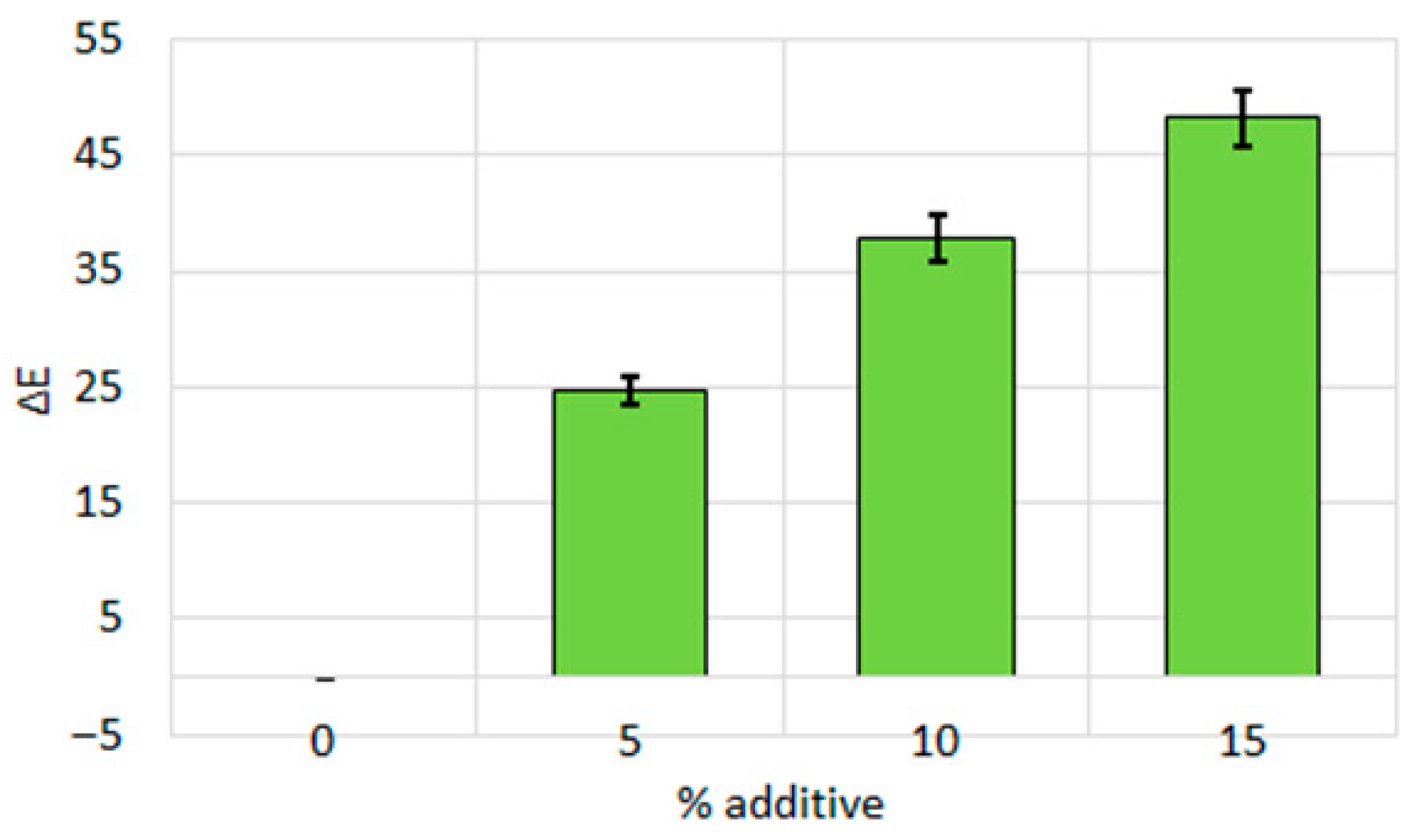
| C1 | 110.73 ± 0.49 | 86.43 ± 0.43 | 69.17 ± 0.4 | 70.21 ± 0.25 | |
| C2 | 144.07 ± 0.79 | 117.5 ± 2.02 | 78.1 ± 0.84 | 57.7 ± 0.52 | |
| C3 | 88.73 ± 0.96 | 84.17 ± 1.6 | 59.25 ± 0.83 | 53.98 ± 0.51 | |
| C4 | 137.4 ± 1.93 | 145.99 ± 2.54 | 115.98 ± 1.65 | 106.49 ± 1.02 | |
| % Additive | 0 | 5 | 10 | 15 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spectral Index | |||||
| S1 | 0.66 ± 0.02 | 0.62 ± 0.01 | 0.57 ± 0.02 | 0.58 ± 0.02 | |
| S2 | 0.51 ± 0.03 | 0.55 ± 0.03 | 0.92 ± 0.02 | 1.16 ± 0.01 | |
| S3 | 0.21 ± 0.01 | 0.23 ± 0.02 | 0.27 ± 0.01 | 0.27 ± 0.02 | |
| % Additive | 0 | 5 | 10 | 15 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Element | |||||
| Ca, mg/kg | 950.53 ± 4.62 | 1001.48 ± 1.8 | 1272.53 ± 2.45 | 1523.51 ± 2.53 | |
| Cu, mg/kg | 2.8 ± 0.21 | 4.01 ± 0.2 | 4.8 ± 0.23 | 5.91 ± 0.19 | |
| Fe, mg/kg | 40.81 ± 0.37 | 65.22 ± 0.3 | 61.57 ± 0.26 | 70.13 ± 0.24 | |
| K, mg/kg | 1434.85 ± 4.23 | 3372.94 ± 2.94 | 4687.33 ± 6.66 | 5187.78 ± 7.63 | |
| Mg, mg/kg | 287.97 ± 5.34 | 557.93 ± 2.08 | 685.08 ± 3.03 | 764.46 ± 1.41 | |
| Mn, mg/kg | 4.86 ± 0.19 | 6.75 ± 0.26 | 7.65 ± 0.26 | 8.73 ± 0.26 | |
| P, % | 0.15 ± 0.01 | 0.15 ± 0.01 | 0.17 ± 0.01 | 0.17 ± 0.01 | |
| Zn, mg/kg | 9.42 ± 0.21 | 10.56 ± 0.2 | 11.7 ± 0.21 | 12.22 ± 0.2 | |
| % Additive | 0 | 5 | 10 | 15 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Characteristic, % | |||||
| Moisture | 3.91 ± 003 | 3.47 ± 0.05 | 3.56 ± 0.06 | 3.29 ± 0.02 | |
| Dry matter | 96.09 ± 0.2 | 96.53 ± 0.2 | 96.44 ± 0.3 | 96.71 ± 0.2 | |
| Crude proteins | 10.23 ± 0.07 | 10.36 ± 0.08 | 10.72 ± 0.1 | 10.51 ± 0.17 | |
| Crude fats | 30.93 ± 0.42 | 31.65 ± 0.42 | 32.44 ± 0.42 | 31.47 ± 0.42 | |
| Crude fibers | 19.79 ± 0.45 | 19.15 ± 0.49 | 22.67 ± 0.46 | 23.77 ± 0.51 | |
| Crude ash | 1.33 ± 0.03 | 2.27 ± 0.04 | 2.95 ± 0.03 | 3.85 ± 0.04 | |
| Nitrogen-free extractives | 33.81 ± 0.4 | 33.1 ± 0.2 | 27.66 ± 0.3 | 27.11 ± 0.4 | |
| % Additive | 0 | 5 | 10 | 15 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Characteristic | |||||
| pH | 7.18 ± 0.06 | 7.29 ± 0.06 | 7.28 ± 0.08 | 7.37 ± 0.02 | |
| TDS, ppm | 1904 ± 30 | 2089.5 ± 215.5 | 2285.5 ± 411.5 | 2429.5 ± 555.5 | |
| EC, µS/cm | 3801 ± 53 | 4174.5 ± 426.5 | 4611.5 ± 863.5 | 4816.5 ± 1068.5 | |
| ORP, mV | 70.5 ± 16.5 | 51.5 ± 2.5 | 56.5 ± 1.5 | 33.5 ± 0.5 | |
| % Additive | 0 | 5 | 10 | 15 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Characteristic | |||||
| D, mm | 46.99 ± 14.87 | 48.25 ± 15.27 | 47.47 ± 15.02 | 47.67 ± 15.08 | |
| h, mm | 7.62 ± 2.43 | 7.13 ± 2.31 | 6.76 ± 2.2 | 6.45 ± 2.05 | |
| SF | 6.18 ± 0.29 | 6.8 ± 0.53 | 7.06 ± 0.54 | 7.4 ± 0.27 | |
| TL, % | 20 ± 0.2 | 21 ± 0.21 | 22 ± 0.23 | 22 ± 0.22 | |
| % Additive | 0 | 5 | 10 | 15 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Characteristic | |||||
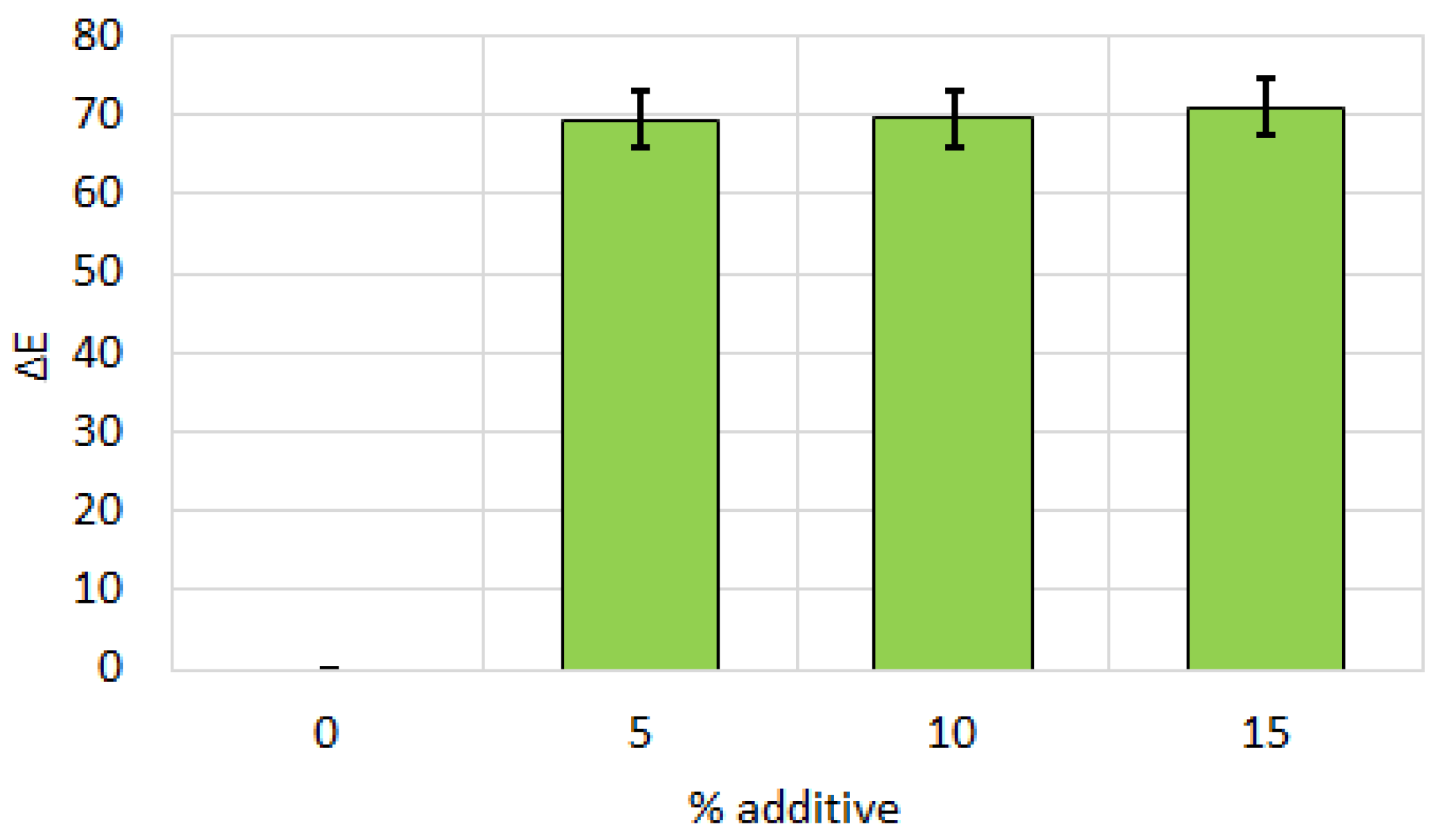
| General appearance | 5 ± 0 | 4.5 ± 0.58 | 3.5 ± 1 | 3.75 ± 0.5 | |
| Consistency | 5 ± 0 | 4.5 ± 0.58 | 3.5 ± 1 | 3.5 ± 0.58 | |
| Aroma | 5 ± 0 | 4.75 ± 0.5 | 3.75 ± 1.26 | 3.75 ± 0.5 | |
| Taste | 5 ± 0 | 4.25 ± 0.5 | 3.75 ± 1.5 | 3.25 ± 0.5 | |
| Smell | 5 ± 0 | 4.5 ± 0.58 | 4 ± 1.41 | 4 ± 0 | |
| Chewiness | 4.75 ± 0.5 | 4.25 ± 0.5 | 3.75 ± 1.26 | 3.75 ± 0.96 | |
| Overall evaluation | 4.96 ± 0.08 | 4.46 ± 0.54 | 3.71 ± 1.24 | 3.67 ± 0.51 | |
| % Additive | 0 | 5 | 10 | 15 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Color Index | |||||
| C1 | 104.97 ± 0.09 | 93.25 ± 0.43 | 88.95 ± 1.65 | 83.72 ± 0.91 | |
| C2 | 124.53 ± 0.23 | 118.89 ± 1.3 | 111.81 ± 0.31 | 98.58 ± 0.54 | |
| C3 | 75.04 ± 0.27 | 81.41 ± 0.8 | 81.45 ± 0.5 | 76.9 ± 0.77 | |
| C4 | 118.43 ± 0.39 | 136.85 ± 1.59 | 139.79 ± 1.93 | 135.69 ± 1.88 | |
| % Additive | 0 | 5 | 10 | 15 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spectral Index | |||||
| S1 | 0.62 ± 0.01 | 0.62 ± 0.01 | 0.62 ± 0.01 | 0.61 ± 0.01 | |
| S2 | 0.8 ± 0.01 | 0.64 ± 0.02 | 0.66 ± 0.02 | 0.75 ± 0.02 | |
| S3 | 0.24 ± 0.01 | 0.23 ± 0.01 | 0.24 ± 0.01 | 0.24 ± 0.01 | |
| Feature (Experimental) | Meaning | PC1 | PC2 | Feature (Literature) | Meaning | PC1 | PC2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F33 | General appearance | −0.53 | 0.2 | FL1 | Appearance | −0.41 | −0.35 |
| F38 | Chewiness | −0.57 | 0.02 | FL2 | Chewing resistance | −0.3 | −0.17 |
| F34 | Aroma | −0.58 | 0.23 | FL4 | Odor | −0.44 | −0.17 |
| F35 | Taste | −0.55 | 0.16 | FL6 | Taste | −0.36 | 0.57 |
| F36 | Smell | −0.51 | 0.29 | FL4 | Odor | −0.44 | −0.17 |
| F39 | Overall acceptance | −0.57 | 0.14 | FL5 | Overall acceptability | −0.26 | −0.37 |
| F46 | Protein | −0.31 | −0.39 | FL15 | Protein | 0.48 | −0.53 |
| F48 | Moisture | — | — | FL14 | Moisture | −0.36 | 0.57 |
| F51 | Crude fiber | −0.18 | −0.36 | FL11 | Crude fiber | −0.35 | −0.27 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baycheva, S.; Zlatev, Z.; Grozeva, N.; Kolev, T.; Tzanova, M.; Zherkova, Z. Sensor-Based Evaluation of Purslane-Enriched Biscuits Using Multivariate Feature Selection and Spectral Analysis. Sensors 2025, 25, 7548. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25247548
Baycheva S, Zlatev Z, Grozeva N, Kolev T, Tzanova M, Zherkova Z. Sensor-Based Evaluation of Purslane-Enriched Biscuits Using Multivariate Feature Selection and Spectral Analysis. Sensors. 2025; 25(24):7548. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25247548
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaycheva, Stanka, Zlatin Zlatev, Neli Grozeva, Toncho Kolev, Milena Tzanova, and Zornitsa Zherkova. 2025. "Sensor-Based Evaluation of Purslane-Enriched Biscuits Using Multivariate Feature Selection and Spectral Analysis" Sensors 25, no. 24: 7548. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25247548
APA StyleBaycheva, S., Zlatev, Z., Grozeva, N., Kolev, T., Tzanova, M., & Zherkova, Z. (2025). Sensor-Based Evaluation of Purslane-Enriched Biscuits Using Multivariate Feature Selection and Spectral Analysis. Sensors, 25(24), 7548. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25247548









