A Cost-Effective Reference-Less Semiconductor Ion Sensor with Anodic Aluminum Oxide Film
Highlights
- Developed a low-cost reference-less ion sensor using AAO films.
- Achieved 57.8 mV/pH sensitivity and demonstrated non-destructive monitoring for milk freshness.
- Enables miniaturized, cost-effective ion sensors.
- Promises portable, disposable platforms for food safety and diagnostics.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
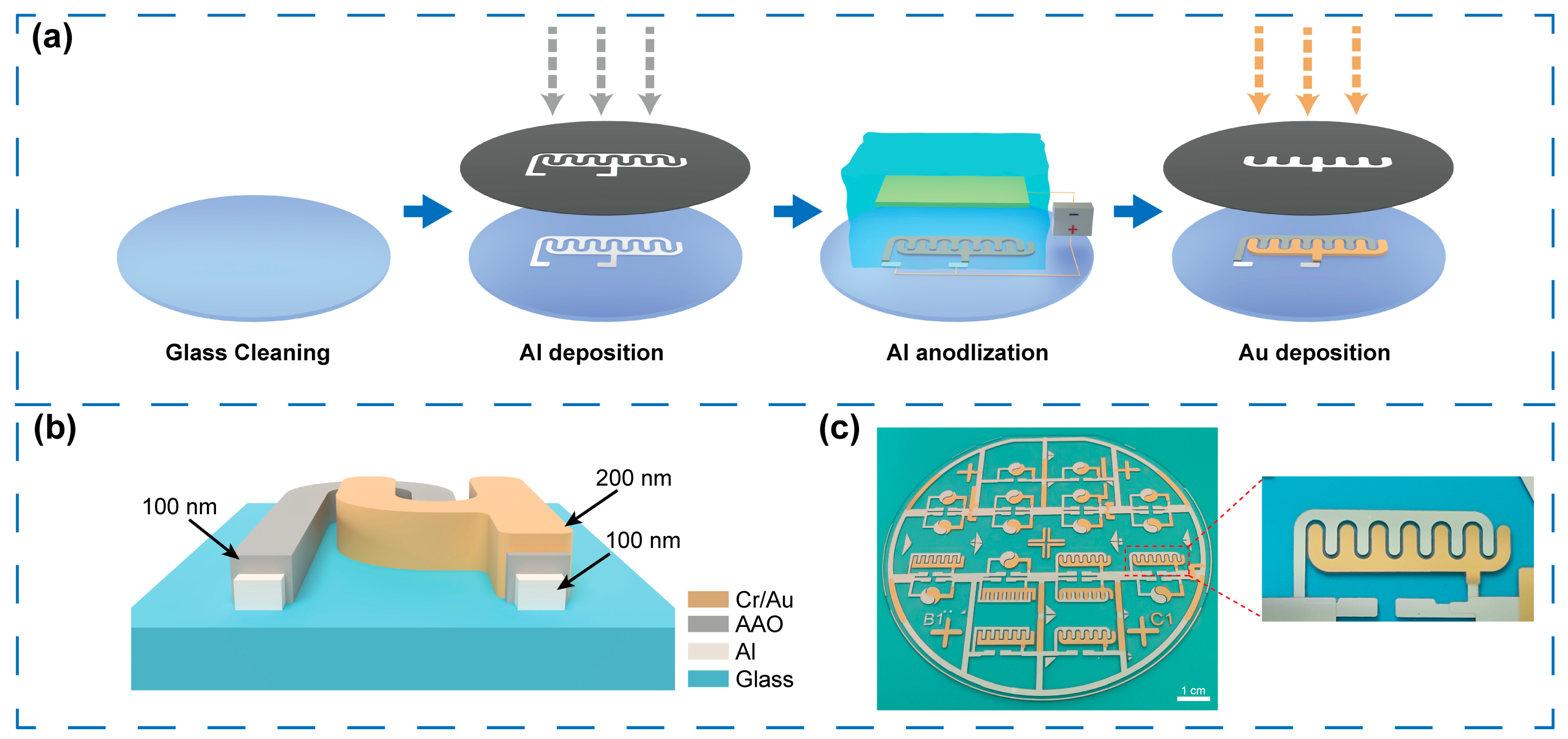
2.1. Sensor Structure and Materials
2.2. Working Principle of RELESIS
2.3. Fabrication Process
2.4. Electrical Measurement
3. Results and Discussion
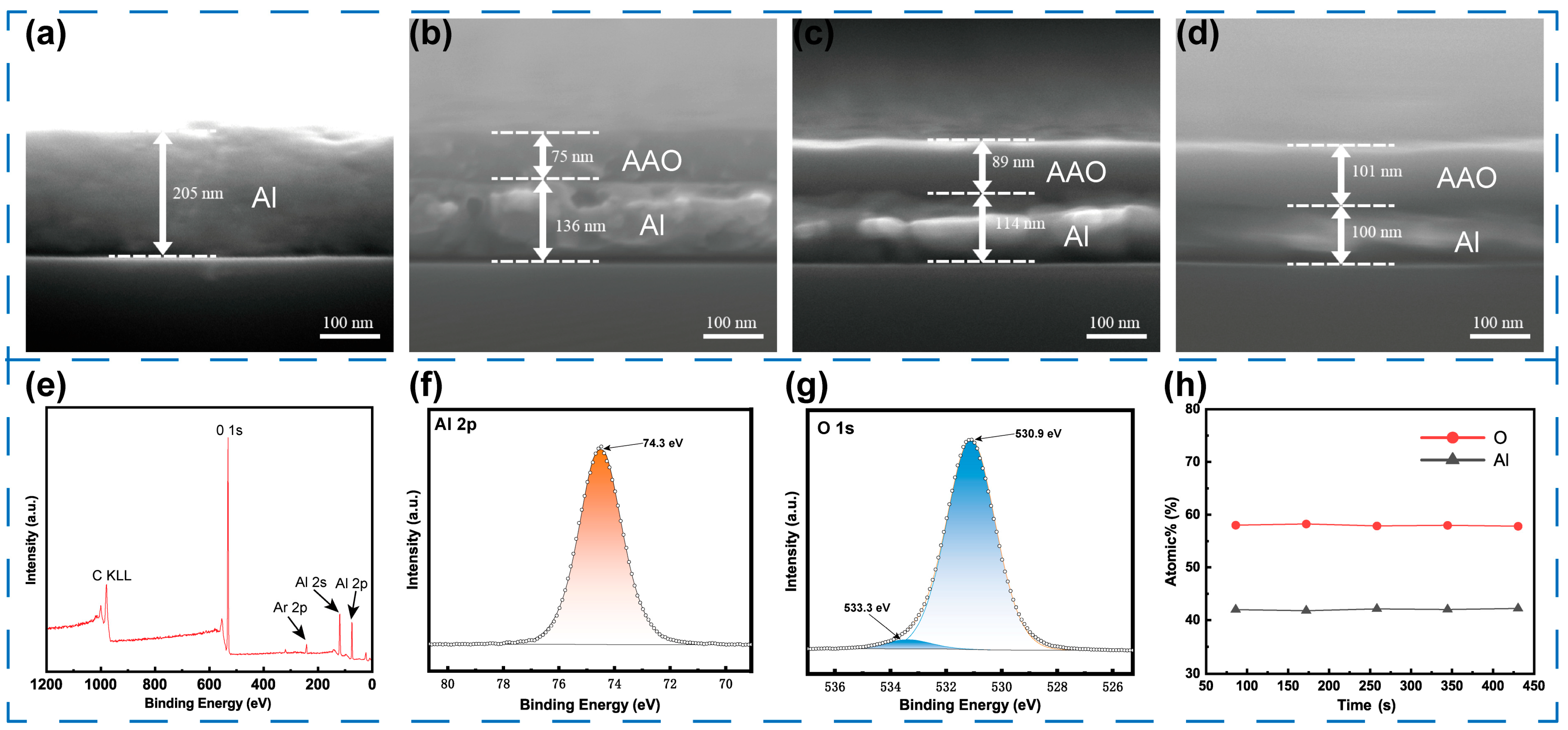
3.1. Morphologies of AAO Film
3.2. Thickness of AAO Film
3.3. Characterizations of AAO Film
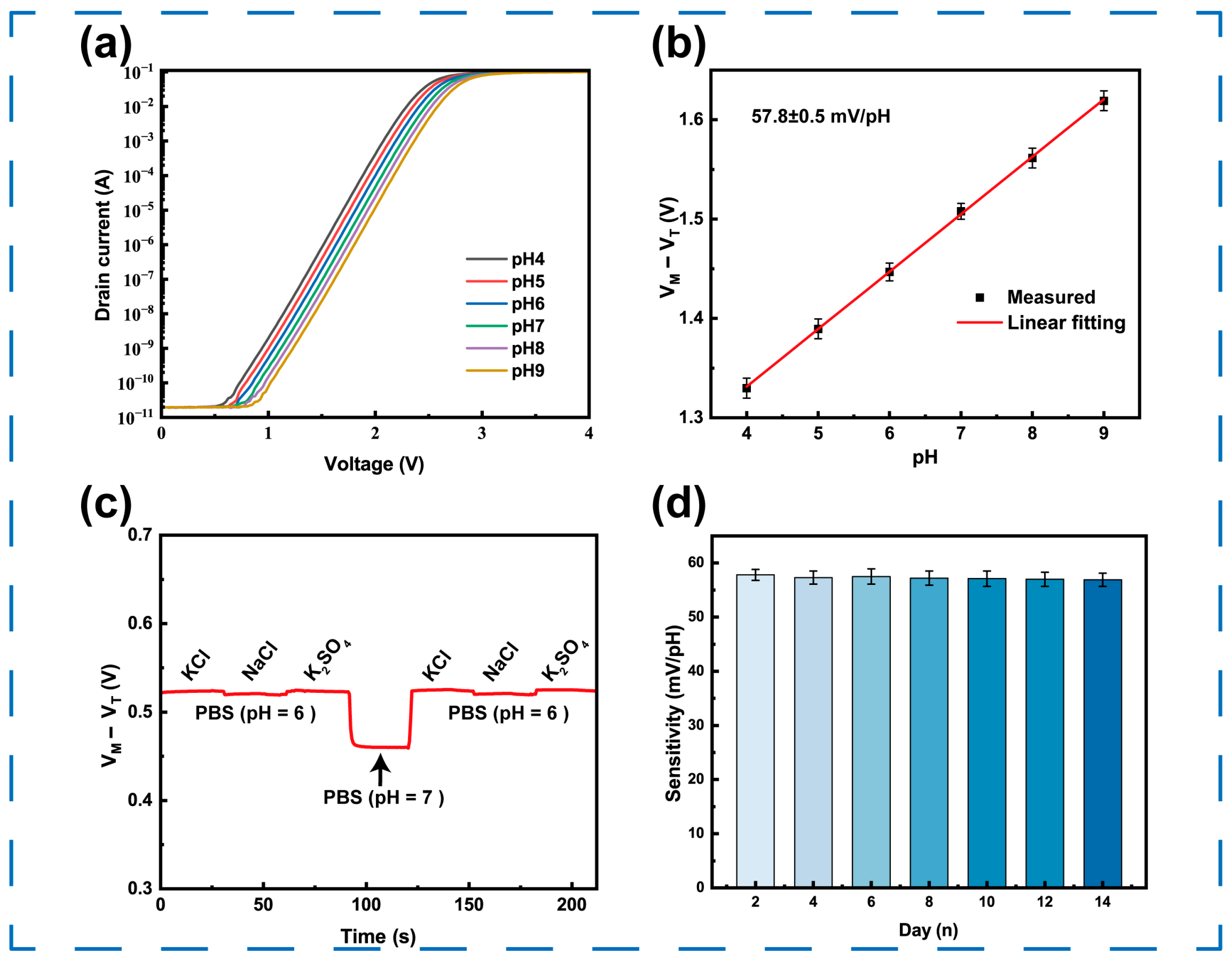
3.4. pH Response
3.5. Selectivity and Stability
3.6. Comparative Evaluation
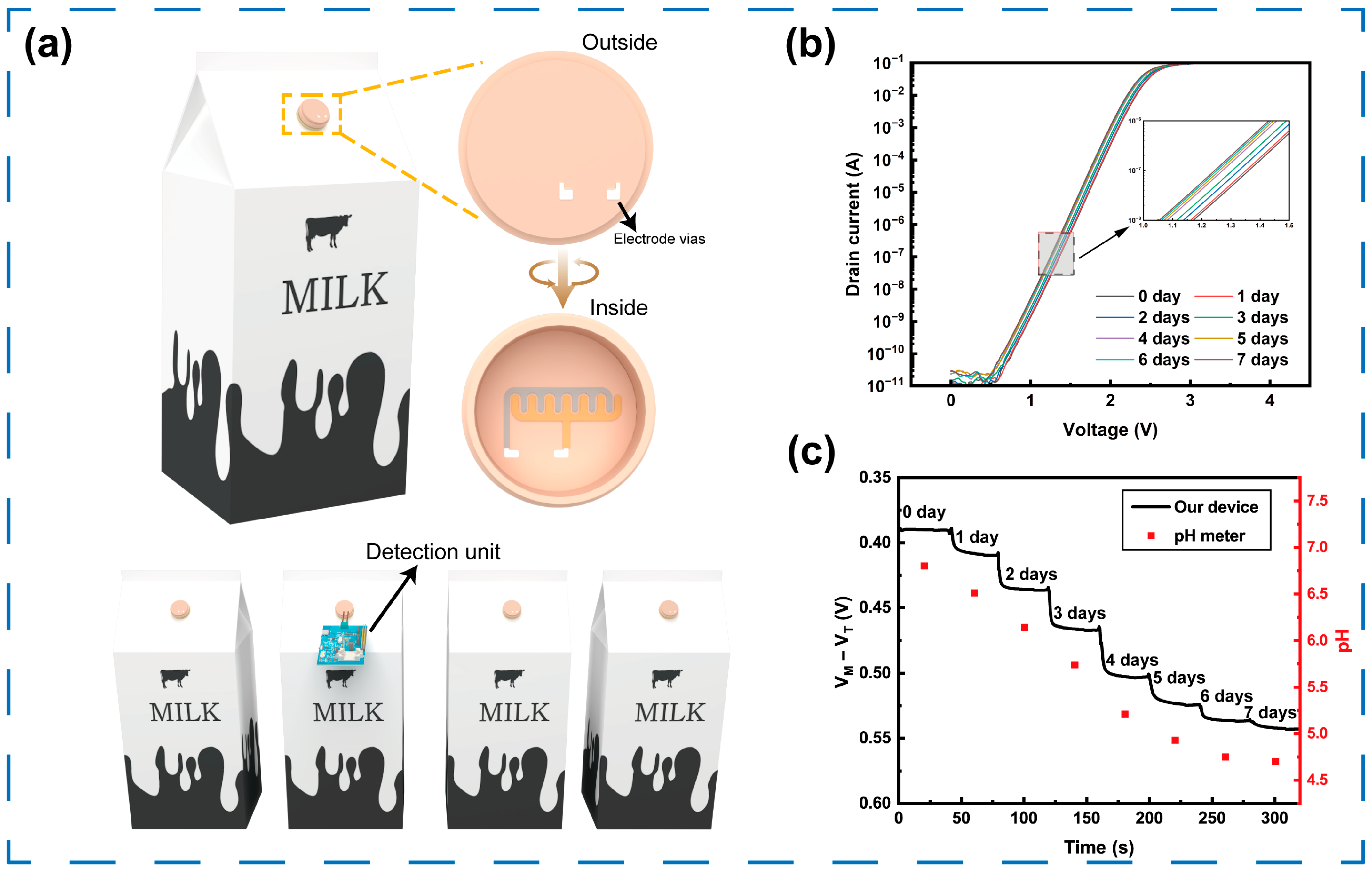
3.7. Demonstration
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kassal, P.; Steinberg, M.D.; Steinberg, I.M. Wireless chemical sensors and biosensors: A review. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 266, 228–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.; Mukherjee, A.; Bytesnikova, Z.; Ashrafi, A.M.; Richtera, L.; Adam, V. 2D graphene-based advanced nanoarchitectonics for electrochemical biosensors: Applications in cancer biomarker detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2024, 250, 116050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergveld, P. Development of an ion-sensitive solid-state device for neurophysiological measurements. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1970, 17, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, S.L.; Sun, P.; Xiao, G.; Tang, Q.; Sun, X.Y.; Zhao, H.Y.; Zhao, S.; Lu, H.B.; Yue, Z. ISFET-based sensors for (bio)chemical applications: A review. Electrochem. Sci. Adv. 2023, 3, 2100207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergveld, P. Thirty years of ISFETOLOGY–What happened in the past 30 years and what may happen in the next 30 years. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2003, 88, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, C.; Zheng, Q.Y.; Hu, W.-C.; Xia, X.-H. Emerging advances in biosensor technologies for quorum sensing signal molecules. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2025, 417, 33–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gest, A.M.M.; Sahan, A.Z.; Zhong, Y.; Lin, W.; Mehta, S.; Zhang, J. Molecular spies in action: Genetically encoded fluorescent biosensors light up cellular signals. Chem. Rev. 2024, 124, 12573–12660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.; Hu, J.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, L.M.; Bai, W.Y.; Wang, L.; Li, J.L.; Yan, L.; Zhang, Z.F.; Bai, H.; et al. ISFET biosensor with loop-mediated isothermal amplification for electronic rapid detection of mycoplasma pneumoniae. Sensors 2025, 25, 1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.U.; Cho, W.J. Smart pH sensing: A self-sensitivity programmable platform with multi-functional charge-trap-flash ISFET technology. Sensors 2024, 24, 1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.H.; Iyama, Y.; Kawaguchi, S.; Takarada, T.; Sato, H.; Nomoto, R.; Tadenuma, K.; Falina, S.; Syamsul, M.; Shintani, Y.; et al. Ion-sensitive stainless steel vessel for all-solid-state pH sensing system incorporating pH-insensitive diamond solution gate field-effect transistors. IEEE Sens. J. 2023, 23, 9110–9119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bataka, E.P.; Maletsika, P.; Nakas, C.T. Formal assessment of agreement and similarity between an open-source and a reference industrial device with an application to a low-cost pH logger. Sensors 2024, 24, 490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shylendra, S.P.; Wajrak, M.; Alameh, K.; Kang, J.J. Nafion modified titanium nitride pH sensor for future biomedical applications. Sensors 2023, 23, 699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janata, J. Thirty years of CHEMFETs–A personal view. Electroanalysis 2004, 16, 1831–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.H.; Liu, S.B.; Chang, S.P. Performance improvement of a ZnGa2O4 extended-gate field-effect transistor pH sensor. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 15304–15310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grudtsov, V.P.; Eganova, E.M.; Gubanova, O.V.; Goryachev, A.V.; Puchnin, K.V.; Ryazantsev, D.V.; Kuznetsov, A.E.; Komarova, N.V. On the atomic layer deposition of tantalum oxide for field effect sensors. Semiconductors 2024, 58, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arya, S.K.; Wong, C.C.; Jeon, Y.J.; Barisal, T.; Park, M.K. Advances in complementary-metal-oxide-semiconductor-based integrated biosensor arrays. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 5116–5158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okazaki, S.; Yoshida, K.; Kodera, N.; Ujiie, S.; Nishimatsu, Y.; Tanaka, Y.; Gomei, T.; Yamada, M.; Sakuraba, S.; Masuko, T. Potentiometric free chlorine detection without using conventional reference electrodes. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2021, 168, 117516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marecek, V. A polarizable reference electrode. Electrochem. Commun. 2022, 141, 107354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartoszewicz, B.; Lewenstam, A.; Migdalski, J. Solid-contact electrode with composite PVC-based 3D-printed membrane. Optimization of fabrication and performance. Sensors 2021, 21, 4909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tintelott, M.; Kremers, T.; Ingebrandt, S.; Pachauri, V.; Vu, X.T. Realization of a PEDOT:PSS/graphene oxide on-chip pseudo-reference electrode for integrated ISFETs. Sensors 2022, 22, 2999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovira, M.; Lafaye, C.; Demuru, S.; Kunnel, B.P.; Aymerich, J.; Cuenca, J.; Serra-Graells, F.; Margarit-Taulé, J.M.; Haque, R.; Saubade, M.; et al. Assessing the performance of a robust multiparametric wearable patch integrating silicon-based sensors for real-time continuous monitoring of sweat biomarkers. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2024, 262, 116560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gubanova, O.; Poletaev, A.; Komarova, N.; Grudtsov, V.; Ryazantsev, D.; Shustinskiy, M.; Shibalov, M.; Kuznetsov, A. A novel extended gate ISFET design for biosensing application compatible with standard CMOS. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2024, 177, 108387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, R.X.; Zhang, J.K.; Yang, H.; Sun, C.L.; Xu, M.; Zhang, S.L.; Wu, D.P. Modelling and characterization of novel reference-less semiconductor ion sensor for pH sensing. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 281, 60–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, S.W.; Yang, H.; Wu, D.P. Carbon ion implantation-modified hafnium oxide to construct a RELESIS for pH sensing. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2024, 45, 2522–2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, R.; Zhang, J.; Sun, C.; Xu, M.; Zhang, S.-L.; Wu, D. A reference-less semiconductor ion sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 254, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasilyev, V.Y. Review: Atomic layer deposition of silicon dioxide thin films. ECS J. Solid State Sci. Technol. 2021, 10, 053004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.W.; Khor, O.K.; Liao, M.W.; Chung, C.K. Sensitivity evolution and enhancement mechanism of porous anodic aluminum oxide humidity sensor using magnetic field. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 199, 384–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.S.; Park, S.; Zhang, J.W.; Wilson, J.; Li, Y.P.; Xin, Q.; Majewski, L.; Song, A.M. One-volt IGZO thin-flm transistors with ultra-thin, solution-processed AlxOy gate dielectric. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2018, 39, 375–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergveld, P.; Vanhal, R.E.G.; Eijkel, J.C.T. The remarkable similarity between the acid-base properties of ISFETs and proteins and the consequences for the design of ISFET biosensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 1995, 10, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fung, C.D.; Cheung, P.W.; Ko, W.H. A generalized theory of an electrolyte-insulator-semiconductor field-effect transistor. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 1986, 33, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yates, D.E.; Levine, S.; Healy, T.W. Site-binding model of electrical double-layer at oxide-water interface. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. I 1974, 70, 1807–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku, C.A.; Yu, C.Y.; Hung, C.W.; Chung, C.K. Advances in the fabrication of nanoporous anodic aluminum oxide and its applications to sensors: A review. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 2853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sagar, S.; Mohammadian, N.; Park, S.; Majewski, L.A.; Das, B.C. Ultra-thin anodized aluminium dielectric films: The effect of citric acid concentration and low-voltage electronic applications. Nanotechnology 2020, 31, 255705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Xu, D.W.; Liu, Q.Q.; Wang, Q.; Yu, H.W.; Zhu, X.F.; Song, Y. Bipolar electrochemical anodization route for the fabrication of porous anodic alumina with nanopore gradients. Langmuir 2021, 37, 4340–4346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloprogge, J.T.; Duong, L.V.; Wood, B.J.; Frost, R.L. XPS study of the major minerals in bauxite: Gibbsite, bayerite and (pseudo-)boehmite. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 296, 572–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.P.; Hwu, J.G. Using anodization to oxidize ultrathin aluminum film for high-k gate dielectric application. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2003, 150, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, H.J.; Cho, W.J. Fabrication of high performance ion-sensitive field-effect transistors using an engineered sensing membrane for bio-sensor application. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2012, 51, 02BL05. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.L.; Yang, P.Y.; Hsieh, T.Y.; Hwang, C.C.; Juang, M.H. pH-sensing characteristics of hydrothermal Al-doped ZnO nanostructures. J. Nanomater. 2013, 2013, 152079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.J.H.; Chen, C.Y. Ion-sensitive field-effect transistors with periodic-groove channels fabricated using nanoimprint lithography. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2013, 34, 541–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.N.; Chen, H.J.H.; Hsieh, K.C. Study on sensing properties of ion-sensitive field-effect-transistors fabricated with stack sensing membranes. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2016, 37, 1642–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabah, F.A.; Ahmed, N.M.; Hassan, Z.; Almessiere, M.A. Influences of substrate type on the pH sensitivity of CuS thin films EGFET prepared by spray pyrolysis deposition. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2017, 63, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.N.; Chen, H.J.H.; Huang, Y.C.; Hsieh, K.C. Electrolyte-insulator-semiconductor pH sensors with arrayed patterns manufactured by nano imprint technology. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2018, 165, 767–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.W.; Pan, T.M. Sensing performance of stable TiN extended-gate field-effect transistor pH sensors in a wide short annealing temperature range. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2020, 41, 489–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, S.W.; Yang, H.; Zhang, Y.F.; Su, X.; Wu, D.P. Effect of microwave annealing on the sensing characteristics of HfO2 thin film for high sensitive pH-EGFET sensor. Micromachines 2023, 14, 1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laenge, K. Bulk and surface acoustic wave biosensors for milk analysis. Biosensors 2022, 12, 602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosikowski, F.V. Induced and natural inhibitory behavior of milk and significance to antibiotic disc assay testing. J. Dairy Sci. 1963, 46, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Sensing Material | Fabrication Method | pH Range | Sensitivity (mV/pH) | Hysteresis (mV) | Cost | Reference Electrode | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al2O3 | ALD | 3–11 | 54.7 | 1.85 | High | Ag/AgCl | [37] |
| AZO | RF Sputtering | 1–3 | 57.9 | - | High | Ag/AgCl | [38] |
| Si3N4 | LPCVD | 4–10 | 58.7 | 16 | High | Ag/AgCl | [39] |
| APTES/SiO2 | Thermal oxidation | 4–10 | 50.9 | 4 | Low | Ag/AgCl | [40] |
| CuS | Solution process | 4–10 | 23.3 | 0.48 | Low | Ag/AgCl | [41] |
| SiO2 | LPCVD | 4–10 | 54.8 | 9 | High | Ag/AgCl | [42] |
| TiN | DC sputtering | 2–12 | 58 | 2 | High | Ag/AgCl | [43] |
| HfO2 | ALD | 5–9 | 59.6 | 44.2 | High | Ag/AgCl | [44] |
| ZnGa2O4 | RF Sputtering | 2–12 | 23.14 | - | High | Ag/AgCl | [14] |
| Ta2O5 | ALD | 2–10 | 56 | 5 | High | Ag/AgCl | [15] |
| Al2O3 | Anodizing | 4–9 | 57.8 | 7 | Low | Reference-less | This work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhong, Y.; Sun, P.; Hou, Z.; Yu, M.; Wu, D. A Cost-Effective Reference-Less Semiconductor Ion Sensor with Anodic Aluminum Oxide Film. Sensors 2025, 25, 6690. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25216690
Zhong Y, Sun P, Hou Z, Yu M, Wu D. A Cost-Effective Reference-Less Semiconductor Ion Sensor with Anodic Aluminum Oxide Film. Sensors. 2025; 25(21):6690. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25216690
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhong, Yiming, Peng Sun, Zhidong Hou, Mingyang Yu, and Dongping Wu. 2025. "A Cost-Effective Reference-Less Semiconductor Ion Sensor with Anodic Aluminum Oxide Film" Sensors 25, no. 21: 6690. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25216690
APA StyleZhong, Y., Sun, P., Hou, Z., Yu, M., & Wu, D. (2025). A Cost-Effective Reference-Less Semiconductor Ion Sensor with Anodic Aluminum Oxide Film. Sensors, 25(21), 6690. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25216690







