A Scalable Sub-Picosecond TDC Based on Analog Sampling of Dual-Phase Signals from a Free-Running Oscillator
Abstract
1. Introduction
State-of-the-Art TDCs
- latency, which corresponds to the time between the end of the measured time interval and the availability of the measurement result; architectures with zero latency are usually referred to as flash TDCs;
- dead time, which refers to the period during which a measurement channel is unavailable after the end of the measured time interval;
- maximum count rate, which is limited by the dead time and defines the highest sustainable event rate for the system;
- resolution, defined as the minimum resolvable time interval;
- single-shot precision, or simply precision, which refers to the agreement between repeated measurements, often described as the root mean square (RMS) deviation;
- full-scale range, corresponding to the maximum time interval that the TDC can measure;
- average power consumption required per channel.
2. Materials and Methods
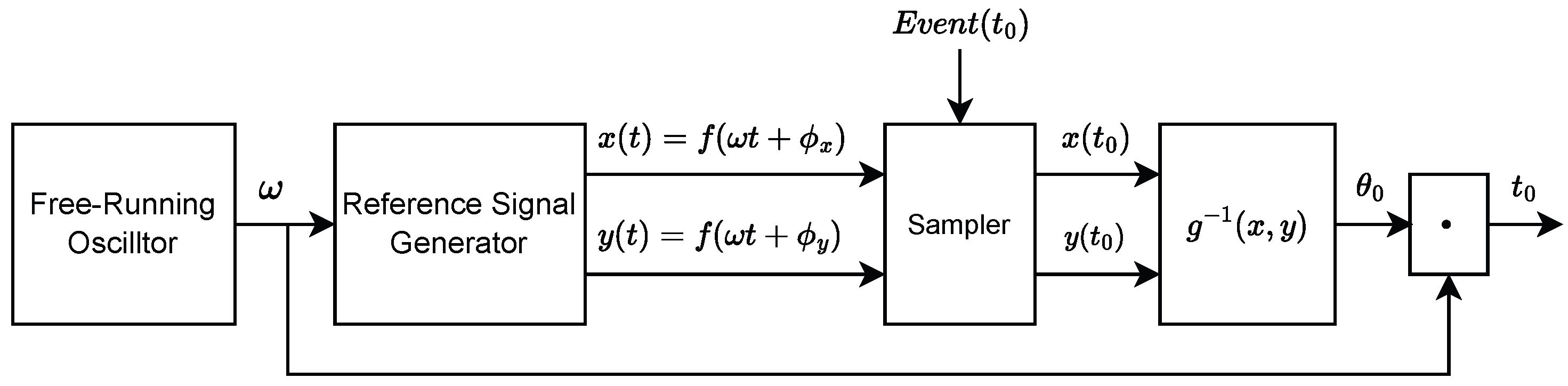
2.1. The Proposed TDC Architecture
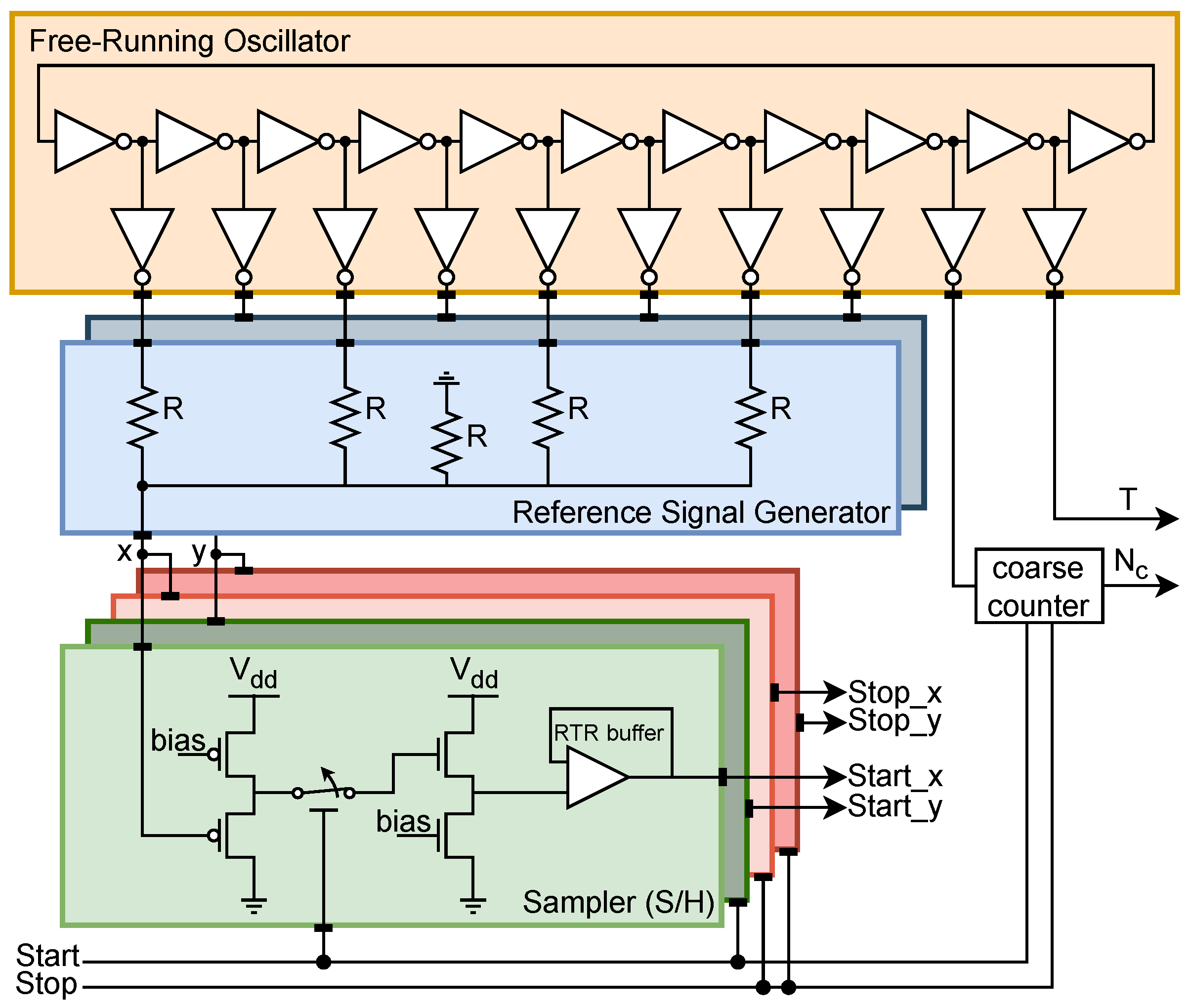
2.2. The Demonstrator ASIC
2.3. Single-Shot Precision Analysis
2.3.1. Uncertainty on the Fine Measurement
2.3.2. Uncertainty on the Coarse Measurement
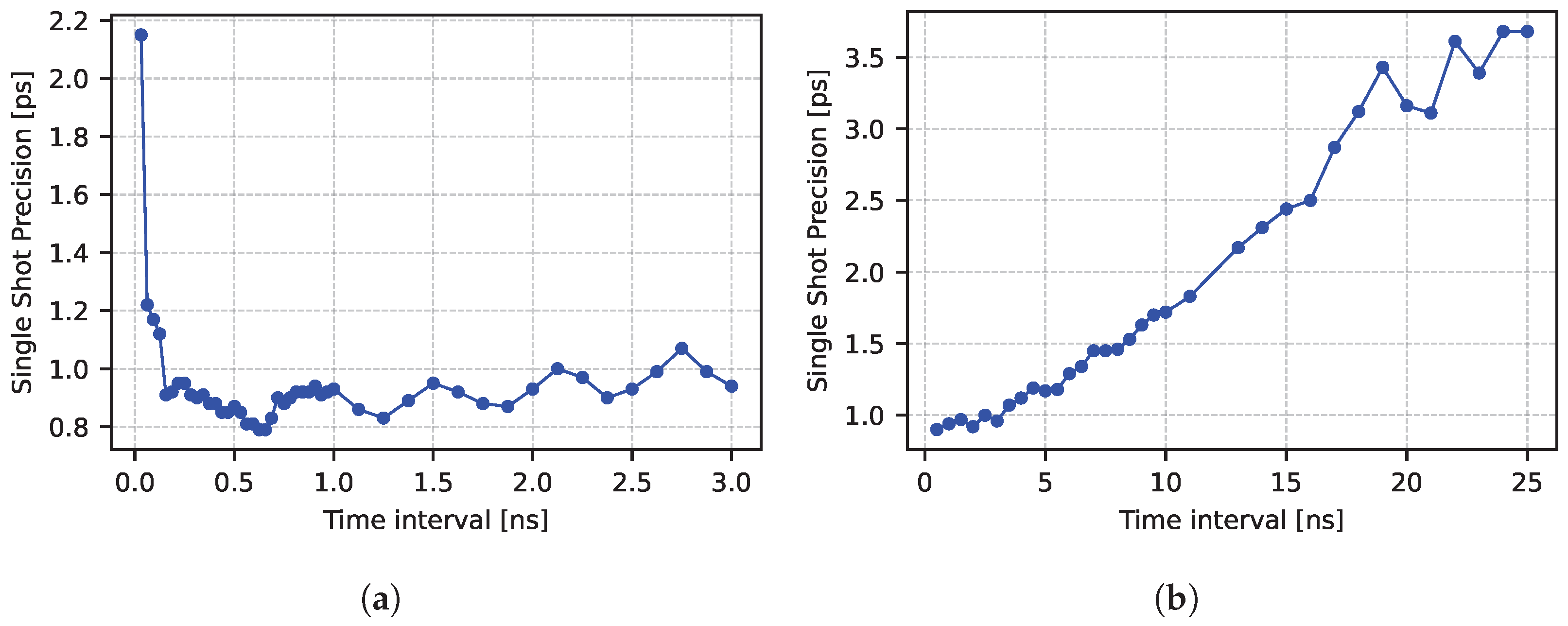
2.3.3. Precision for Short and Long Ranges
2.4. Measurement Setup
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. System Calibration
3.2. Single-Shot Precision
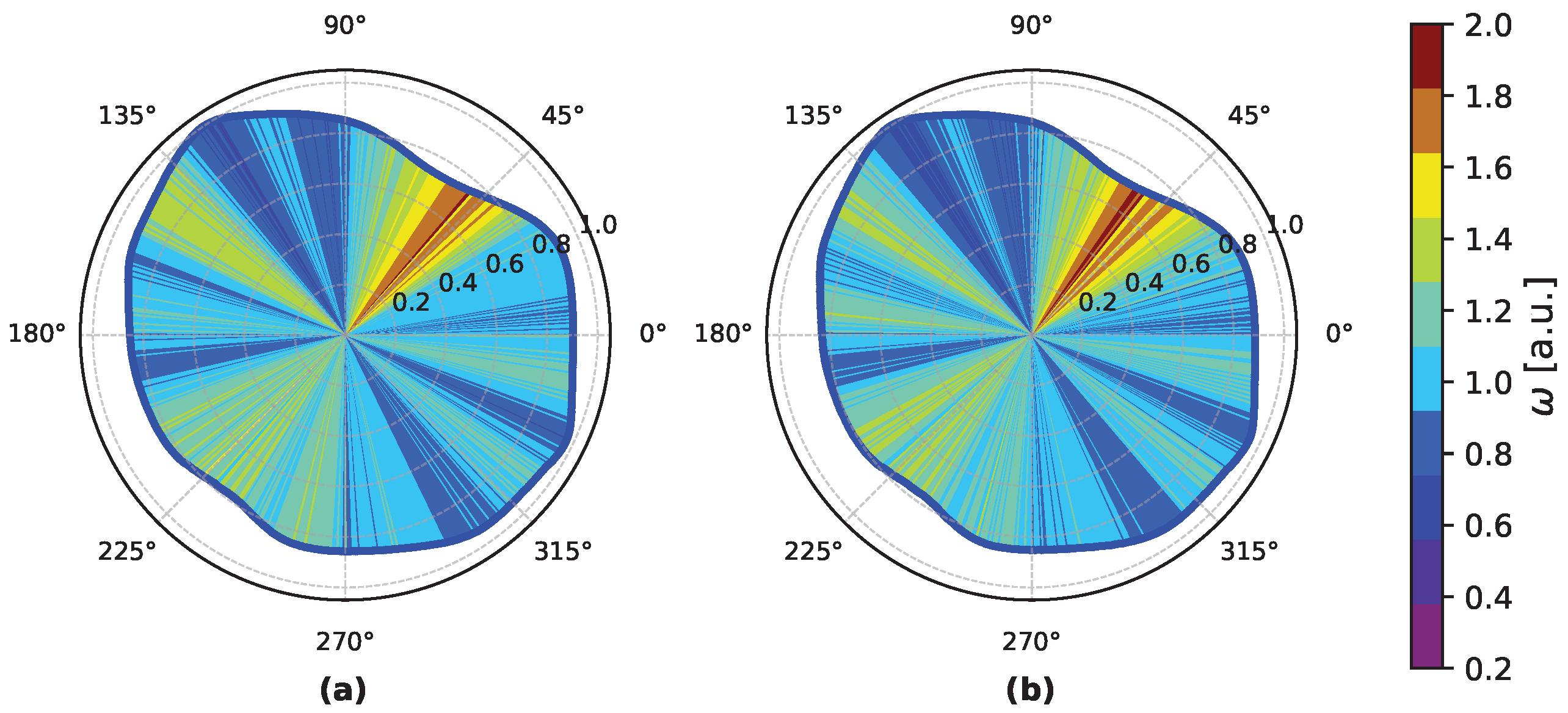
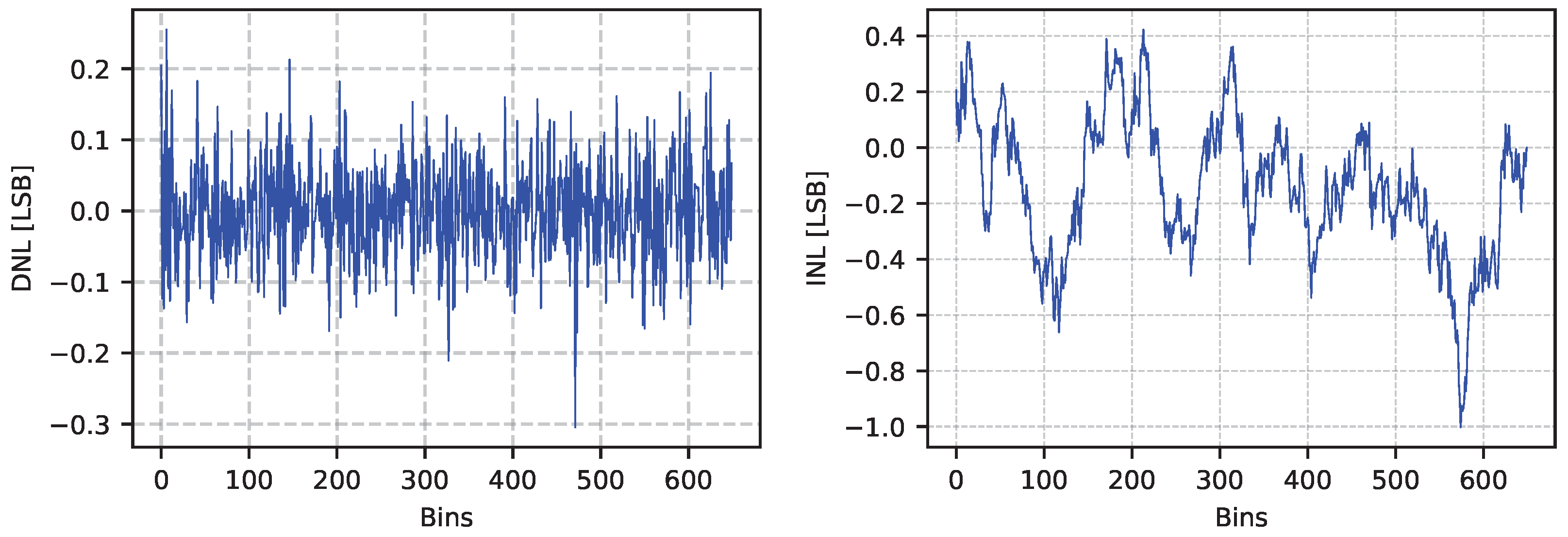
3.3. Linearity
3.4. Temperature Stability
3.5. Count Rate and ADC Resolution
4. Conclusions
5. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
References
- Scott, R.; Jiang, W.; Deen, M.J. CMOS Time-to-Digital Converters for Biomedical Imaging Applications. IEEE Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2023, 16, 627–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapp, J.; Ma, Y.; Dawson, R.M.A.; Goyal, V.K. High-Flux Single-Photon Lidar. Optica 2021, 8, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korzh, B.; Zhao, Q.Y.; Allmaras, J.P.; Frasca, S.; Autry, T.M.; Bersin, E.A.; Beyer, A.D.; Briggs, R.M.; Bumble, B.; Colangelo, M.; et al. Demonstration of Sub-3 Ps Temporal Resolution with a Superconducting Nanowire Single-Photon Detector. Nat. Photonics 2020, 14, 250–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talala, T.; Kaikkonen, V.A.; Keränen, P.; Nikkinen, J.; Härkönen, A.; Savitski, V.G.; Reilly, S.; Dziechciarczyk, Ł.; Kemp, A.J.; Guina, M.; et al. Time-Resolved Raman Spectrometer With High Fluorescence Rejection Based on a CMOS SPAD Line Sensor and a 573-Nm Pulsed Laser. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70, 6004110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinelli, F.; Valerio, P.; Cardarelli, R.; Charbon, E.; Iacobucci, G.; Nessi, M.; Paolozzi, L. A Massively Scalable Time-to-Digital Converter with a PLL-free Calibration System in a Commercial 130 Nm Process. J. Instrum. 2021, 16, P11023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, H.; Yu, X.; Zhang, J.; Cao, G. A Review of Advancements and Trends in Time-to-Digital Converters Based on FPGA. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2024, 73, 2004525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Lee, S.; Miyahara, M.; Matsuzawa, A. Sub-Picosecond Resolution and High-Precision TDC for ADPLLs Using Charge Pump and SAR-ADC. Ieice Trans. Fundam. Electron. Commun. Comput. Sci. 2015, E98.A, 476–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Dai, F.F.; Wang, H. A Reconfigurable Vernier Time-to-Digital Converter with 2-D Spiral Comparator Array and Second-Order Δ Sigma Linearization. IEEE J. Solid State Circuits 2018, 53, 738–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acconcia, G.; Malanga, F.; Farina, S.; Ghioni, M.; Rech, I. A 1.9 ps-rms Precision Time-to-Amplitude Converter with 782 fs LSB and 0.79%-rms DNL. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2023, 72, 2003711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, K.; Kumar Kaushik, B.; Singh, R. Analysis of Propagation Delay Deviation under Process Induced Threshold Voltage Variation. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2011, 17, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daigneault, M.A.; David, J.P. A Novel 10 Ps Resolution TDC Architecture Implemented in a 130 nm Process FPGA. In Proceedings of the 8th IEEE International NEWCAS Conference, Online, 20–23 June 2010; pp. 281–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altruda, S.; Christiansen, J.; Horstmann, M.; Perktold, L.; Porret, D.; Prinzie, J. PicoTDC: A Flexible 64 Channel TDC with Picosecond Resolution. J. Instrum. 2023, 18, P07012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhou, D. An 8.5-Ps Two-Stage Vernier Delay-Line Loop Shrinking Time-to-Digital Converter in 130-Nm Flash FPGA. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2018, 67, 406–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paolozzi, L.; Valerio, P.; Iacobucci, G.; Cardarelli, R. Device and Method for Measuring the Relative Time of Arrival of Signals. EP EP3591477B1, 9 January 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Hajimiri, A.; Limotyrakis, S.; Lee, T. Jitter and Phase Noise in Ring Oscillators. IEEE J. Solid State Circuits 1999, 34, 790–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keysight. M8195A 65 GSa/s Arbitrary Waveform Generator. Available online: https://www.keysight.com/us/en/product/M8195A/65-gsa-s-arbitrary-waveform-generator.html (accessed on 30 July 2025).
- STM32F303RE—Mainstream Mixed Signals MCUs Arm Cortex-M4 Core with DSP and FPU, 512 Kbytes of Flash Memory, 72 MHz CPU, MPU, CCM, 12-Bit ADC 5 MSPS, PGA, Comparators—STMicroelectronics. Available online: https://www.st.com/en/microcontrollers-microprocessors/stm32f303re.html (accessed on 30 July 2025).
- Nguyen, V.N.; Pham, X.T.; Lee, J.W. An 8.5 Ps Resolution, Cyclic Vernier TDC Using a Stage-Gated Ring Oscillator and DWA-Based Dynamic Element Matching in 28 Nm CMOS. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2022, 71, 2002012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Deen, M.J.; Peng, H. A Low-Power Gateable Vernier Ring Oscillator Time-to-Digital Converter for Biomedical Imaging Applications. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 2016, 10, 445–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








| This Work | [9] | [7] | [18] | [8] | [19] | [12] | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Application | TCSPC/HEP | TCSPC | PLL | Imaging | DPLL | Medical Imaging | HEP | |||
| Architecture | TAC + counter | TAC | TAC + ADC | DEM Vernier a | 2-D spiral Vernier | TDC VGRO b | DLL | |||
| Process [nm] | 130 CMOS | 350 BiCMOS | 65 CMOS | 28 CMOS | 45 CMOS | 130 CMOS | 65 CMOS | |||
| Range [ns] | 3 | 25 | 12.5 | 100 | ±0.41 | 17.4 | ±0.32 | 9 | 204,000 | |
| Resolution [ps] | 0.95 | 0.782 | 6.1 | 0.8 | 8.5 | 1.25 | 7.3 | 3 | 12 | |
| Bits | 23 3 | 26 c | 14 | 10 | 11 | 8 | 7 | 26 | ||
| Precision min [ps-rms] | 0.79 | 1.9 | - | 1.1 | 7.5 | 0.35 | 8.4 | 1.35 | 3.65 | |
| DNL max [LSB] | 0.56 | 0.018 | - | 1 | 0.23 | 0.25 | 3.2 | - | ||
| DNL RMS [LSB] | 0.07 | - | 0.13 | 0.08 | - | - | 0.8 | 0.82 | ||
| INL max [LSB] | 1.43 | 0.025 | - | 3.1 | 2.3 | 0.34 | 3.5 | 0.44 | ||
| INL RMS [LSB] | 0.25 | - | - | - | - | 1.2 | 0.14 | |||
| Count Rate [Mcps] | 22 | 12.3 | 50 | 15 | 80 | 2.4 | - | |||
| Power per channel [mW] | 4.1 d | 70 | 2.9 | 0.2 | 0.69 | 1.2 | 20 | 13 | ||
| Area [] | 0.0014 e | 0.2 f | 0.02 | 0.006 g | 0.04 h | 0.03 | 1.14 i | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cardella, R.; Iodice, L.; Paolozzi, L.; Kugathasan, T.; Picardi, A.; Fenoglio, C.A.; Valerio, P.; Martinelli, F.; Cardarelli, R.; Iacobucci, G. A Scalable Sub-Picosecond TDC Based on Analog Sampling of Dual-Phase Signals from a Free-Running Oscillator. Sensors 2025, 25, 5577. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25175577
Cardella R, Iodice L, Paolozzi L, Kugathasan T, Picardi A, Fenoglio CA, Valerio P, Martinelli F, Cardarelli R, Iacobucci G. A Scalable Sub-Picosecond TDC Based on Analog Sampling of Dual-Phase Signals from a Free-Running Oscillator. Sensors. 2025; 25(17):5577. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25175577
Chicago/Turabian StyleCardella, Roberto, Luca Iodice, Lorenzo Paolozzi, Thanushan Kugathasan, Antonio Picardi, Carlo Alberto Fenoglio, Pierpaolo Valerio, Fulvio Martinelli, Roberto Cardarelli, and Giuseppe Iacobucci. 2025. "A Scalable Sub-Picosecond TDC Based on Analog Sampling of Dual-Phase Signals from a Free-Running Oscillator" Sensors 25, no. 17: 5577. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25175577
APA StyleCardella, R., Iodice, L., Paolozzi, L., Kugathasan, T., Picardi, A., Fenoglio, C. A., Valerio, P., Martinelli, F., Cardarelli, R., & Iacobucci, G. (2025). A Scalable Sub-Picosecond TDC Based on Analog Sampling of Dual-Phase Signals from a Free-Running Oscillator. Sensors, 25(17), 5577. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25175577











