Sensor Fusion for Power Line Sensitive Monitoring and Load State Estimation
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Fault Detection
1.2. Contribution
- The original principle of a specifically adapted EKF as observer that estimates the fault condition of the power line of electrical health device management (fluctuation of the mains voltage of the power line in Europe is in the tolerance of at a mains frequency of ; see DIN IEC 60038 [28].
- The original principle of another EKF for a state estimation of the secondary galvanic decoupled side of a two-winding transformer and the electrical load resistance .
2. Problem Formulation
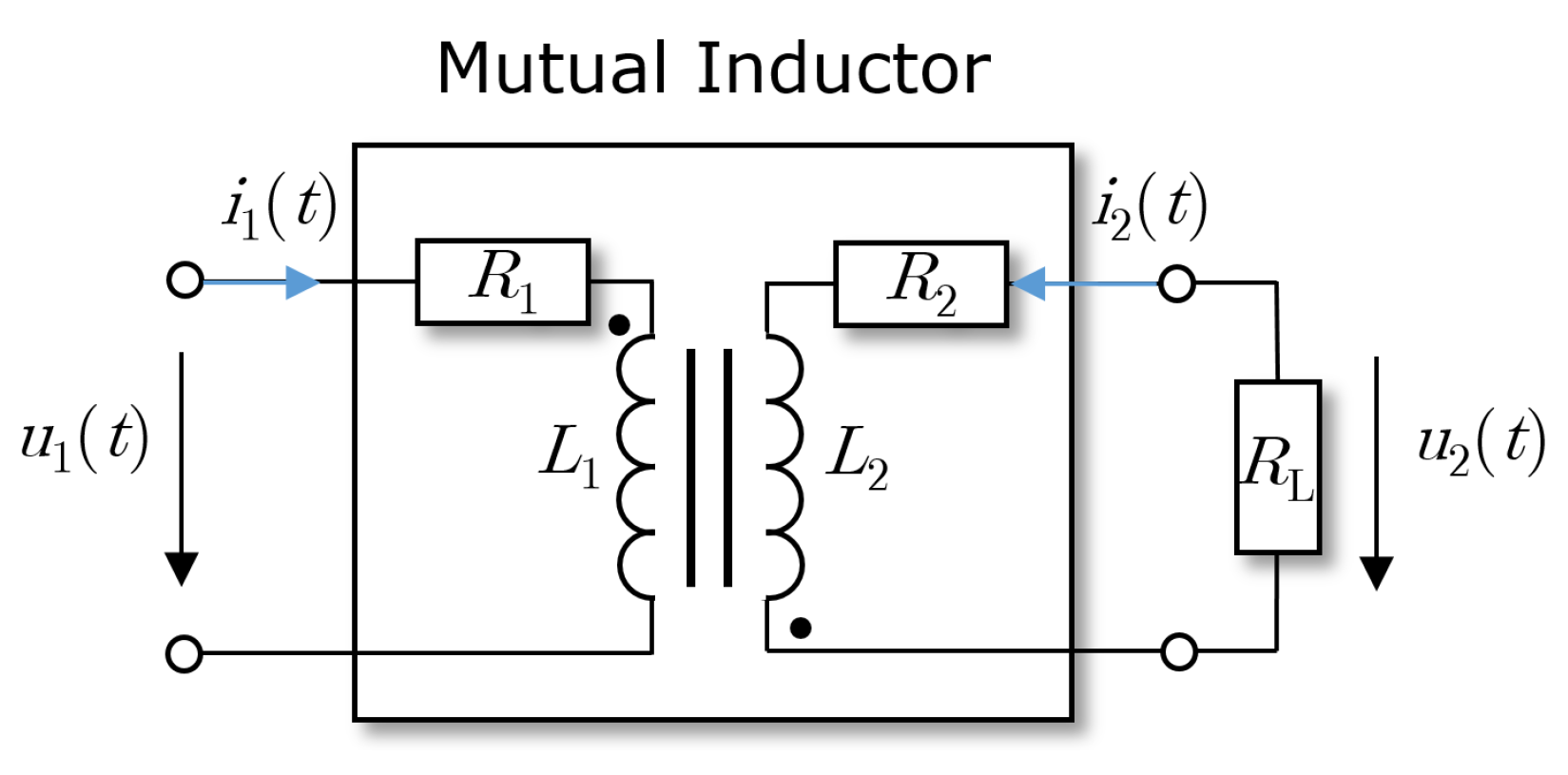
2.1. Mutual Inductor and Transformer
2.2. Transformer System
3. EKF Methods
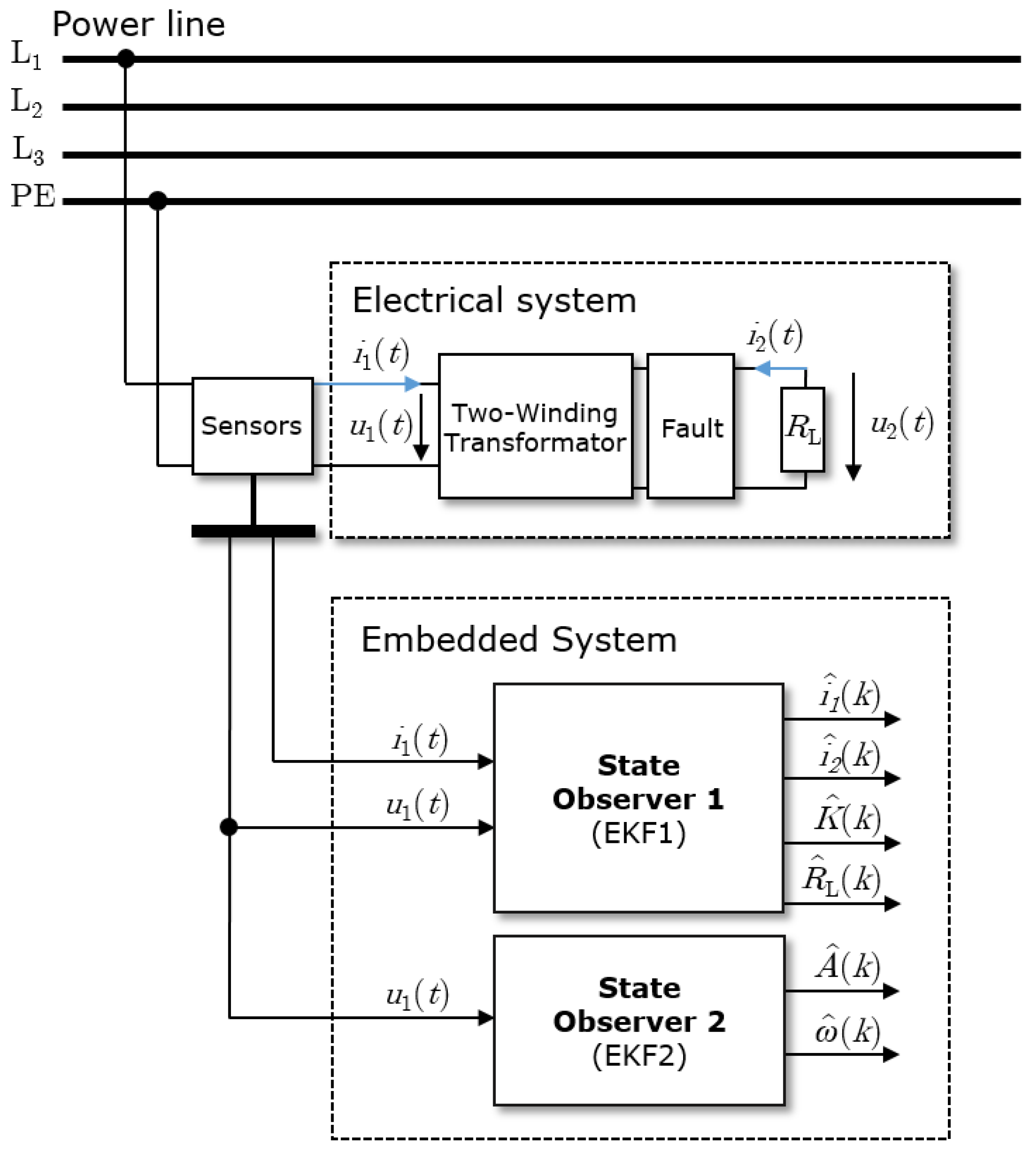
3.1. State Observer for the Mutual Inductance and Load–EKF1
3.2. State Observer for the Power Line Condition– EKF2
3.3. Observability Analysis
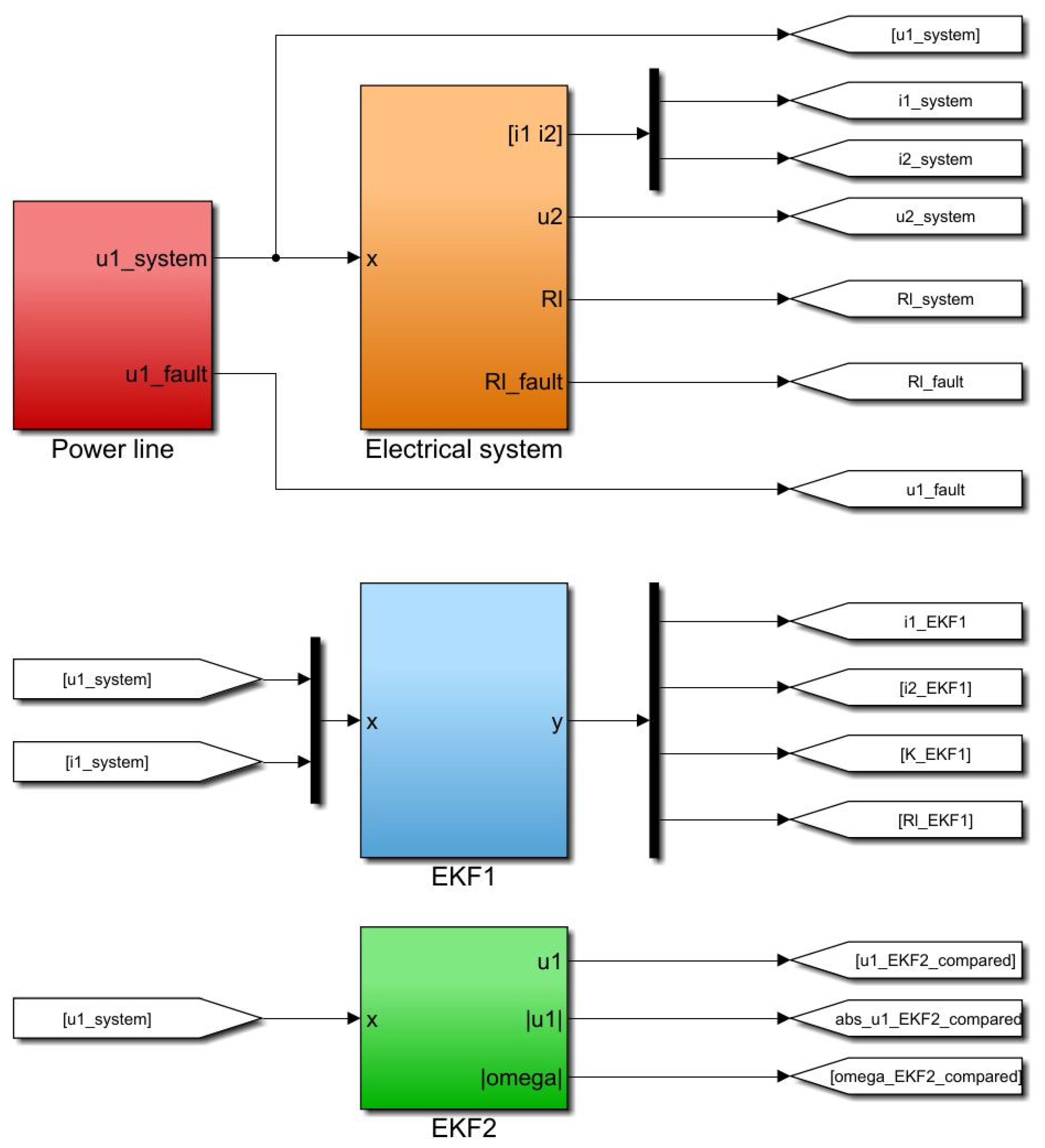
4. Experiment Setup
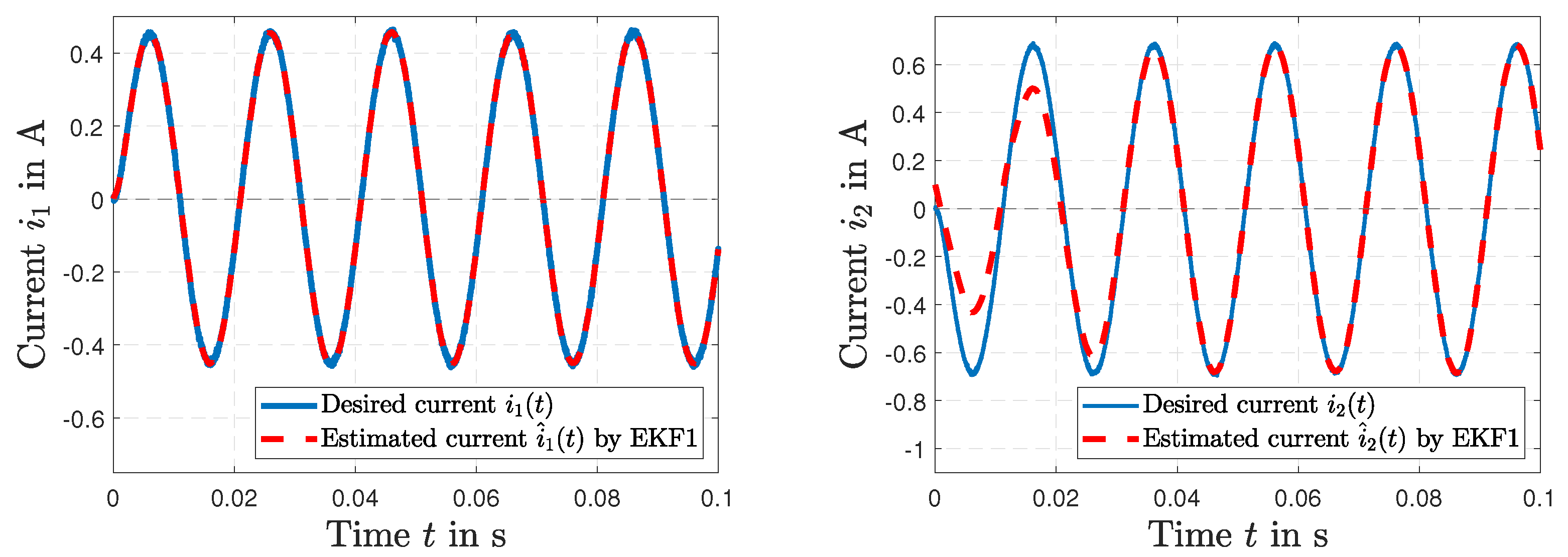
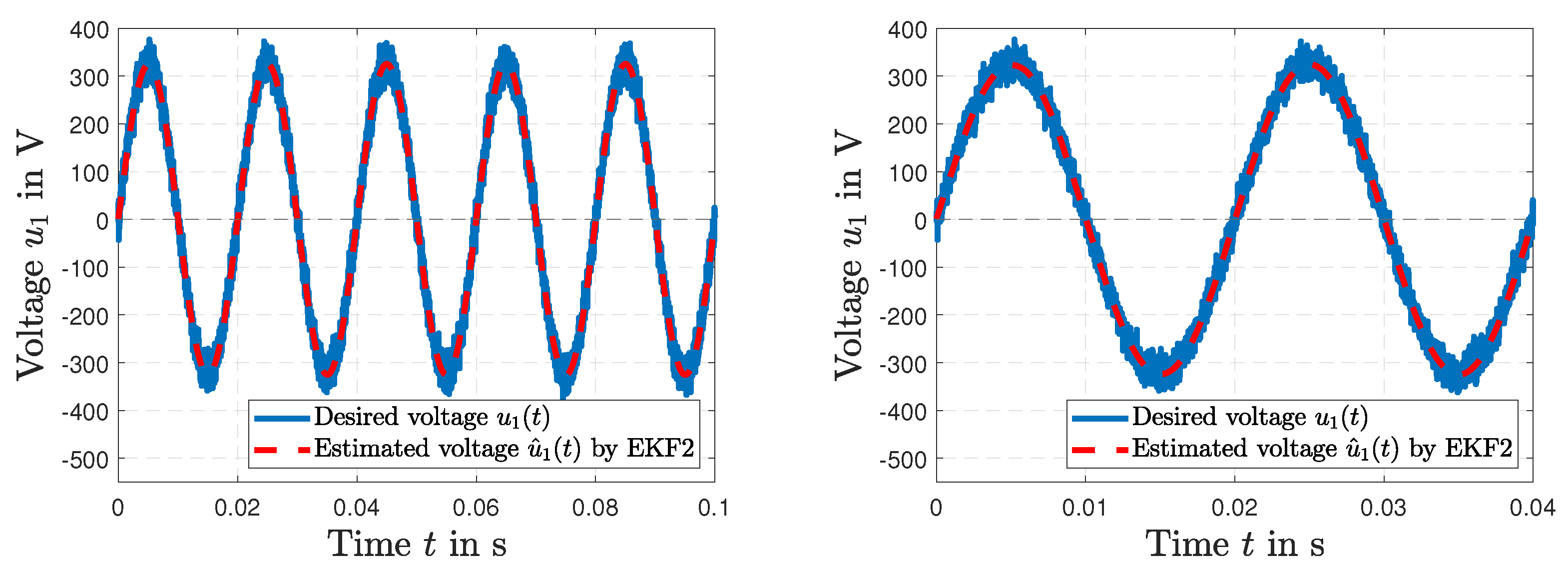
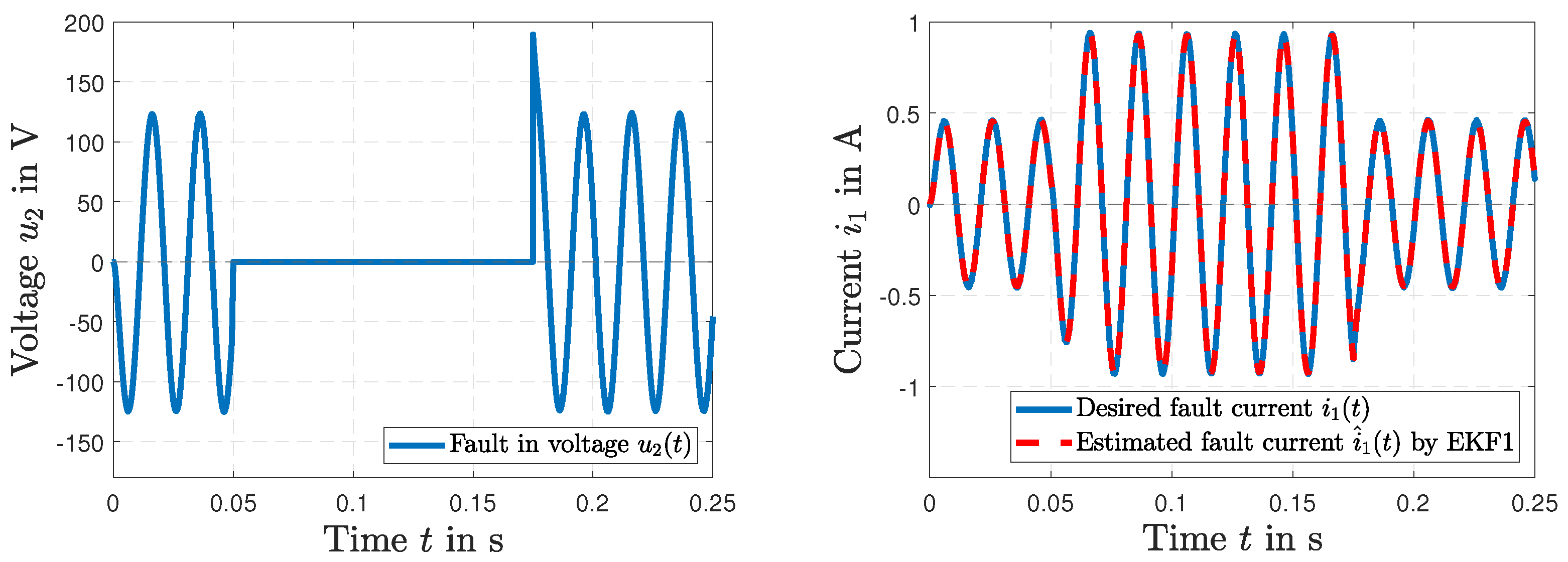
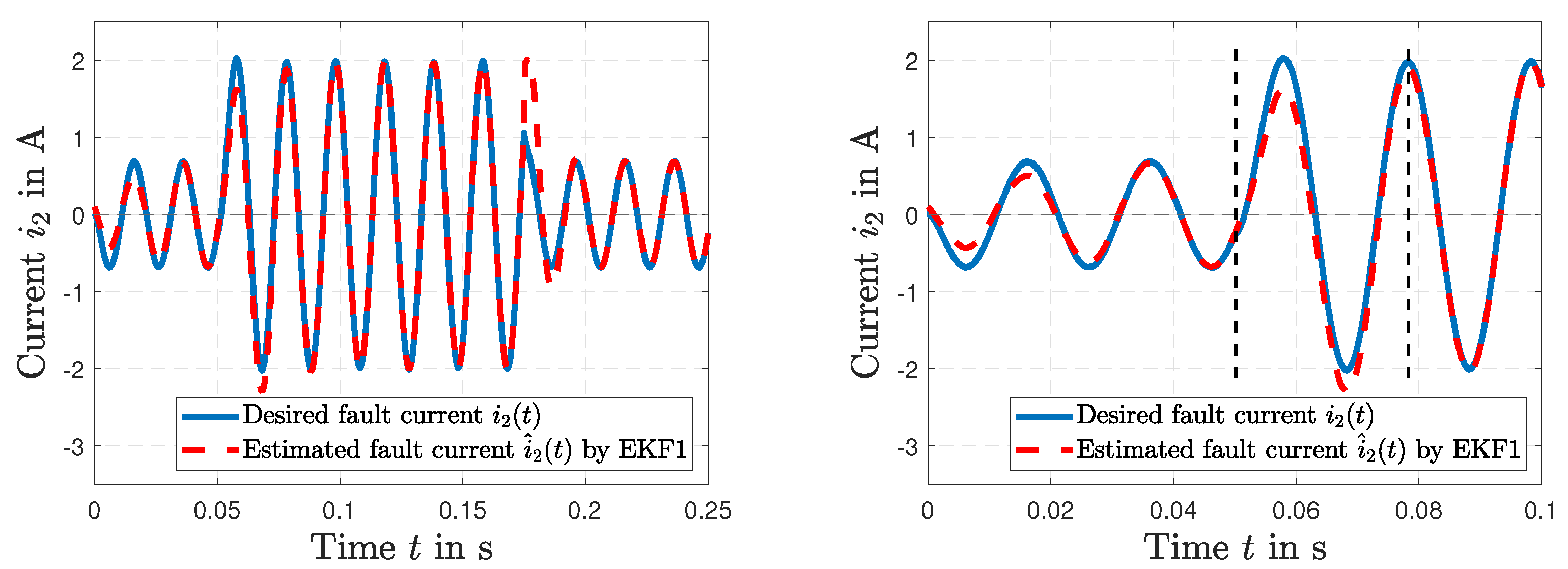
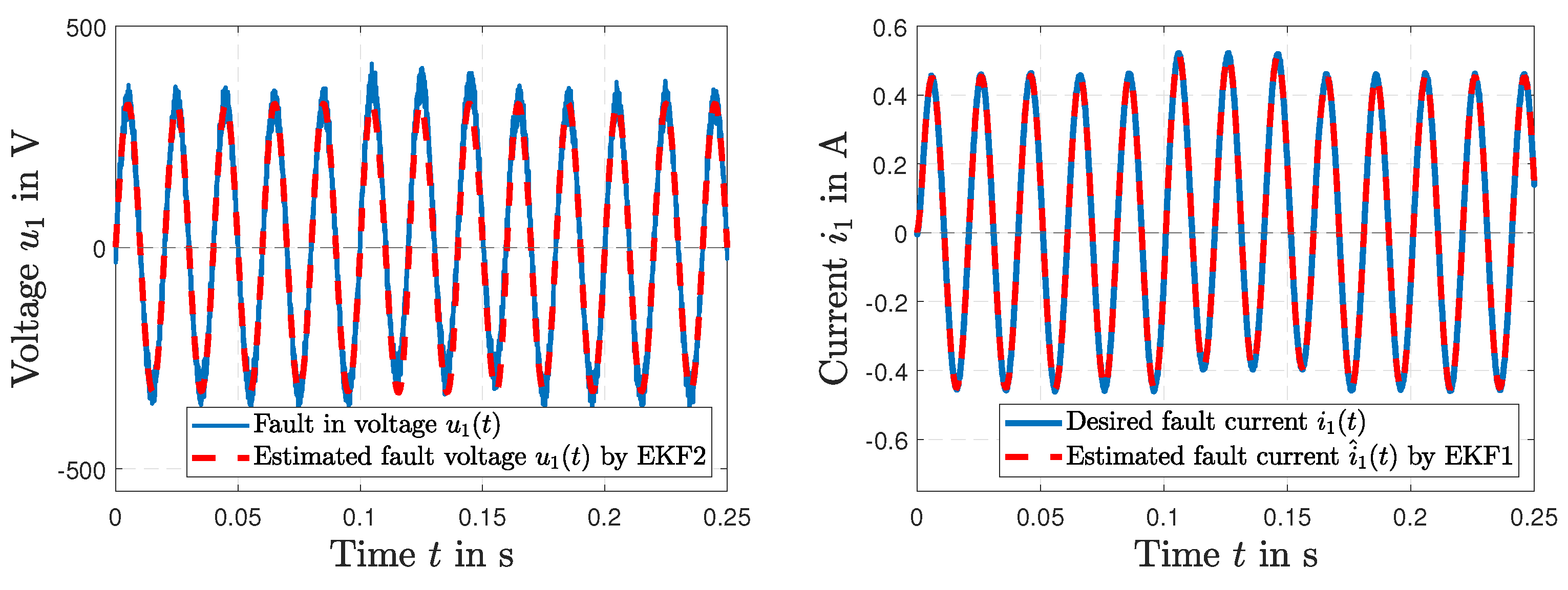
5. Results and Discussion
6. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations and Nomenclature
| The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript: | |
| ARX | Autoregressive model with exogenous input |
| DC | Direct current |
| DIN | Designation of standards; German Institute for Standardization |
| EKF | Extended Kalman filter |
| FDD | Fault detection and diagnosis |
| IEC | Designation of standards; International Electrotechnical Commission |
| ISO | Designation of standards; International Organization for Standardization |
| KF | Kalman filter |
| PMSG | Permanent magnet synchronous generator |
| UKF | Unscented Kalman filter |
| The following nomenclature is used in this manuscript: | |
| A | Amplitude |
| Matrix of the system dynamics | |
| State-input feedback matrix | |
| Nonlinear state function | |
| , | Electrical voltages across the primary and secondary winding, respectively |
| , | Electrical currents of the primary and secondary winding, respectively |
| , , M | Primary, secondary, and mutual inductances of transformer, respectively |
| Lie derivatives | |
| White noise variable | |
| Pre-compensation matrix | |
| Scalar output measurement function | |
| Output Jacobian measurement matrix, respectively | |
| J | Assessment criteria |
| Jacobian matrix | |
| K | Inductive coupling coefficient |
| Kalman gain | |
| Nonlinear observability matrix | |
| Natural numbers | |
| Number of possible determinants | |
| Numbers of columns and rows of observability matrix, respectively | |
| Posterior and a priori estimation error covariance matrix | |
| Covariance matrices of process noise, respectively | |
| Variance matrices of soft sensors | |
| Primary and secondary winding and electrical load resistances, respectively | |
| Continuous time, start time, and stop time, respectively | |
| Sampling period | |
| System state | |
| A posteriori estimation of system state | |
| A priori estimation of system state | |
| Angular frequency | |
| Angular phase | |
| Primary stray flux and core flux of transformer, respectively | |
| Phase noises | |
Appendix A
| Listing A1. Observability test for EKF1. |
 |
| Listing A2. Observability test for EKF2. |
 |
References
- Schimmack, M.; Mercorelli, P. An Adaptive Derivative Estimator for Fault-Detection Using a Dynamic System with a Suboptimal Parameter. Algorithms 2019, 12, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercorelli, P. A Fault Detection and Data Reconciliation Algorithm in Technical Processes with the Help of Haar Wavelets Packets. Algorithms 2017, 10, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Peng, B.; Xie, P.; Cheng, C. A Novel Data-Driven Fault Detection Method Based on Stable Kernel Representation for Dynamic Systems. Sensors 2023, 23, 5891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IEC 61508; Functional Safety of Electrical/Electronic/Programmable Electronic Safety-related Systems. International Electrical Commission: London, UK, 2010; ISBN 978-2-88910-524-3.
- ISO 26262; Road vehicles – Functional Safety Standard. International Organization for Standardization: London, UK, 2018.
- Peniak, P.; Rástočný, K.; Kanáliková, A.; Bubeníková, E. Simulation of Virtual Redundant Sensor Models for Safety-Related Applications. Sensors 2022, 22, 778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, S.; Oberrath, J.; Mercorelli, P. A Sensor Fault Detection Scheme as a Functional Safety Feature for DC-DC Converters. Sensors 2021, 21, 6516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalman, R.E. A New Approach to Linear Filtering and Prediction Problems. J. Basic Eng. 1960, 82, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, B.; Moore, J. Optimal Filtering; Prentice-Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Welch, G.; Bishop, G. An Introduction to the Kalman Filter; University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill: Chapel Hill, NC, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Terzic, B.; Jadric, M. Design and Implementation of the Extended Kalman Filter for the Speed and Rotor Position Estimation of Brushless DC Motor. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2001, 48, 1065–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Foo, G.; Vilathgamuwa, M.; Tsengt, K.; Bhangu, B.; Gajanayake, C. Sensor Fault Detection, Isolation and System Reconfiguration Based on Extended Kalman Filter for Induction Motor Drives. Iet Electr. Power Appl. 2013, 7, 607–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, T.; Simon, D.L. Application of a Bank of Kalman Filters for Aircraft Engine Fault Diagnostics. In Proceedings of the ASME Turbo Expo 2003, Atlanta, GA, USA, 16–19 June 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, H.; Iwami, T.; Yuzawa, H.; Suzuki, M. Typical Faults of Air Conditioning Systems and Fault Detection by ARX Model and Extended Kalman Filter Technical Report; American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers Inc.: Atlanta, GA, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Gunda, S.K.; Dhanikonda, S. Discrimination of Transformer Inrush Currents and Internal Fault Currents Using Extended Kalman Filter Algorithm (EKF). Energies 2021, 14, 6020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Sayed, W.; Abd El Geliel, M.; Lotfy, A. Fault Diagnosis of PMSG Stator Inter-Turn Fault Using Extended Kalman Filter and Unscented Kalman Filter. Energies 2020, 13, 2972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, X.; Ma, X.; Chen, Z.; Xue, M.; Zhang, P. High-Order Compensation Topology Integration for High-Tolerant Wireless Power Transfer. Energies 2023, 16, 638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankowska, K.; Dybkowski, M. A Current Sensor Fault Tolerant Control Strategy for PMSM Drive Systems Based on Cri Markers. Energies 2021, 14, 3443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Mrabet, Z.; Sugunaraj, N.; Ranganathan, P.; Abhyankar, S. Random Forest Regressor-Based Approach for Detecting Fault Location and Duration in Power Systems. Sensors 2022, 22, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazemi, Z.; Naseri, F.; Yazdi, M.; Farjah, E. An EKF-SVM machine Learning-based Approach for Fault Detection and Classification in Three-phase Power Transformers. IET Sci. Meas. Technol. 2021, 15, 130–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, A.R. Fault Detection and Diagnosis in Power Transformers: A Comprehensive Review and Classification of Publications and Methods. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2022, 209, 107990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abid, A.; Khan, M.T.; Iqbal, J. A Review on Fault Detection and Diagnosis Techniques: Basics and Beyond. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2021, 54, 3639–3664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Huang, C.; He, J. Fault Detection, Classification and Location for Transmission Lines and Distribution Systems: A Review on the Methods. High Volt. 2016, 1, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiviyanathan, V.A.; Ker, P.J.; Leong, Y.S.; Abdullah, F.; Ismail, A.; Jamaludin, M.Z. Power Transformer Insulation System: A Review on the Reactions, Fault Detection, Challenges and Future Prospects. Alexandria Engin. J. 2022, 61, 7697–7713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griepentrog, G. Method and Configuration for Identifying Short Circuits in Low-Voltage Networks. U.S. Patent No 6,313,639, 6 November 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Janabi, S.; Rawat, S.; Patel, A.; Al-Shourbaji, I. Design and Evaluation of a Hybrid System for Detection and Prediction of Faults in Electrical Transformers. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2015, 67, 324–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Guo, P. Diagnosis of Interturn Faults of Voltage Transformer Using Excitation Current and Phase Difference. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2022, 134, 105979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DIN IEC 60038; IEC standard voltages. International Electrotechnical Commission: London, UK, 2003.
- Trung, N.K.; Diep, N.T. Coupling coefficient observer based on Kalman filter for dynamic wireless charging systems. Int. J. Power Electron. Drive Syst. (IJPEDS) 2023, 14, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schimmack, M.; Haus, B.; Mercorelli, P. An EKF as an Observer in a Control Structure for Health Monitoring of a Metal–Polymer Hybrid Soft Actuator. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatronics 2018, 23, 1477–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schimmack, M.; Pöschke, F.; Mercorelli, P. Comparison of EKF and TSO for Health Monitoring of a Textile-Based Heater Structure and its Control. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatronics 2021, 27, 2634–2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermann, R.; Krener, A. Nonlinear Controllability and Observability. IEEE Trans. Automat. Control 1977, 22, 728–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isisdori, A. Nonlinear Control Systems, 3rd ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1995; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]




| (t), : | 1.01 | |||||||||
| (t), : | 5.62 | |||||||||
| (t), : | ||||||||||
| (t), : | 8.96 | 1.56 | 2.53 | 3.37 | 5.79 | 3.50× 10 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schimmack, M.; Belda, K.; Mercorelli, P. Sensor Fusion for Power Line Sensitive Monitoring and Load State Estimation. Sensors 2023, 23, 7173. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23167173
Schimmack M, Belda K, Mercorelli P. Sensor Fusion for Power Line Sensitive Monitoring and Load State Estimation. Sensors. 2023; 23(16):7173. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23167173
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchimmack, Manuel, Květoslav Belda, and Paolo Mercorelli. 2023. "Sensor Fusion for Power Line Sensitive Monitoring and Load State Estimation" Sensors 23, no. 16: 7173. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23167173
APA StyleSchimmack, M., Belda, K., & Mercorelli, P. (2023). Sensor Fusion for Power Line Sensitive Monitoring and Load State Estimation. Sensors, 23(16), 7173. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23167173






