Evaluation of Salmon, Tuna, and Beef Freshness Using a Portable Spectrometer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Instruments
2.2. Sample Preparation and Experiment Setup
2.3. Staphylococcus Aureus Culture
2.4. TBARS Assay
2.5. CNN-Based Machine Learning Algorithm
2.6. Sensitivity and Specificity
3. Results and Discussion
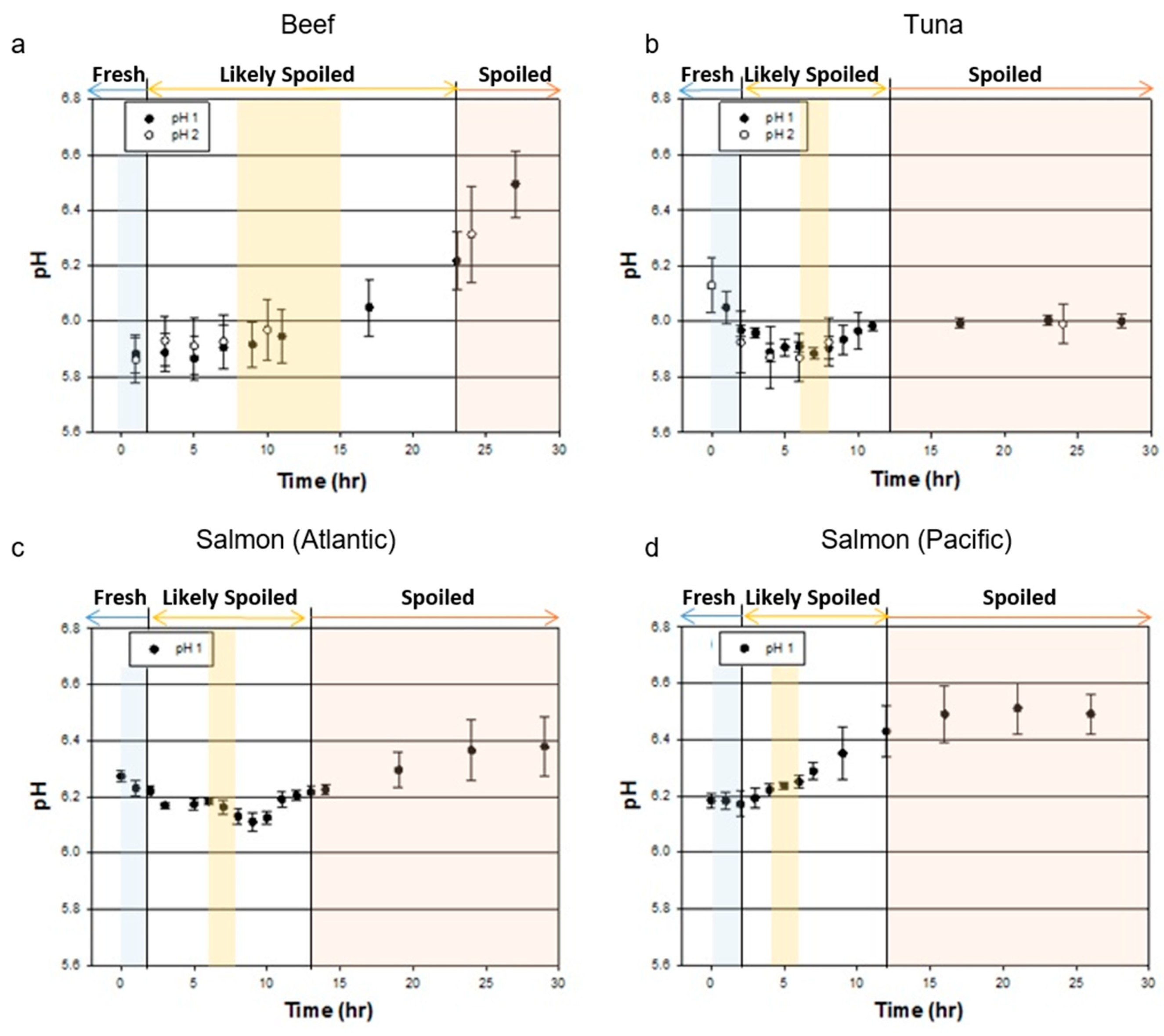
3.1. ph Values to Determine Food Freshness
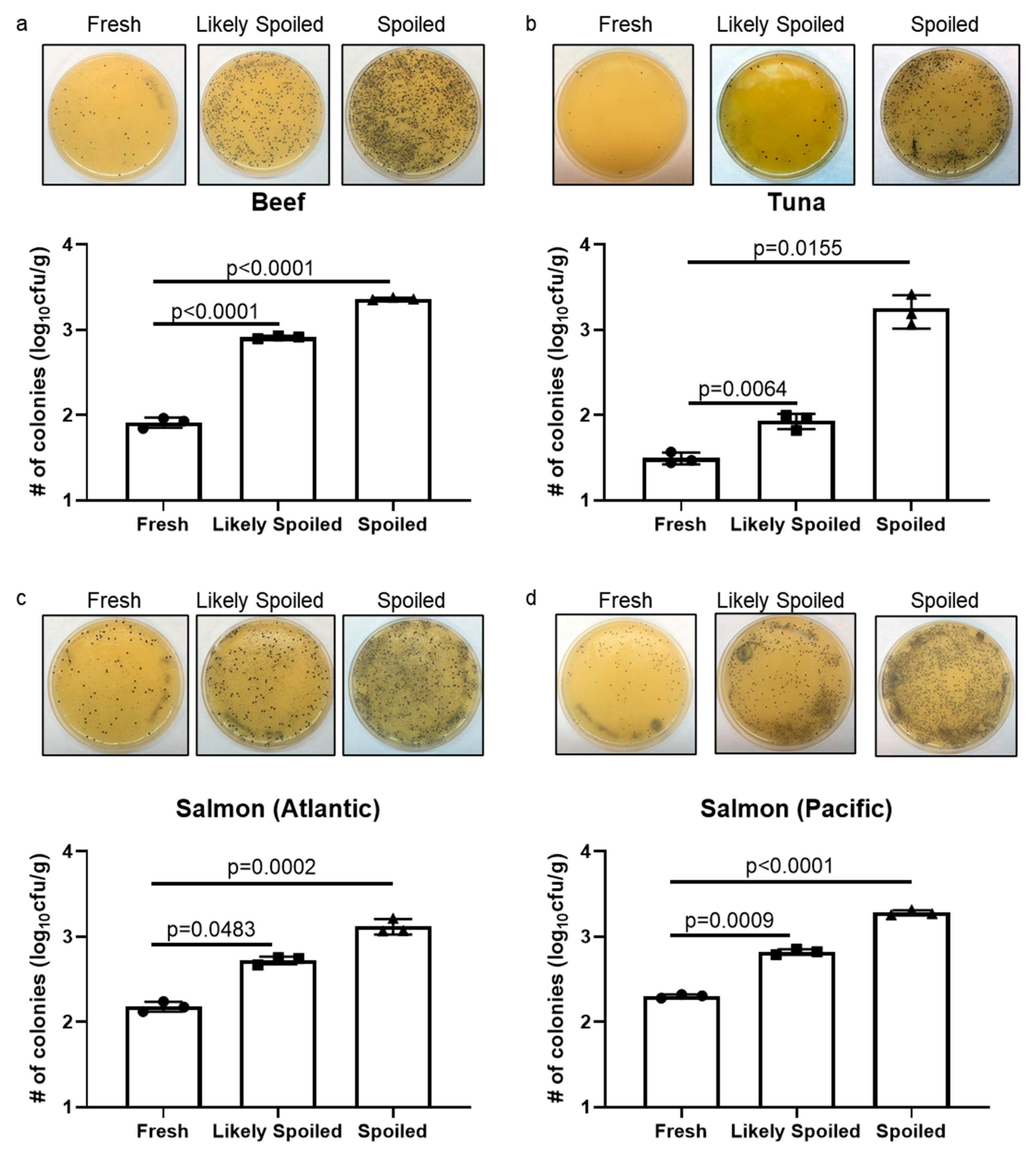
3.2. Staphylococcus Aureus and TBARS
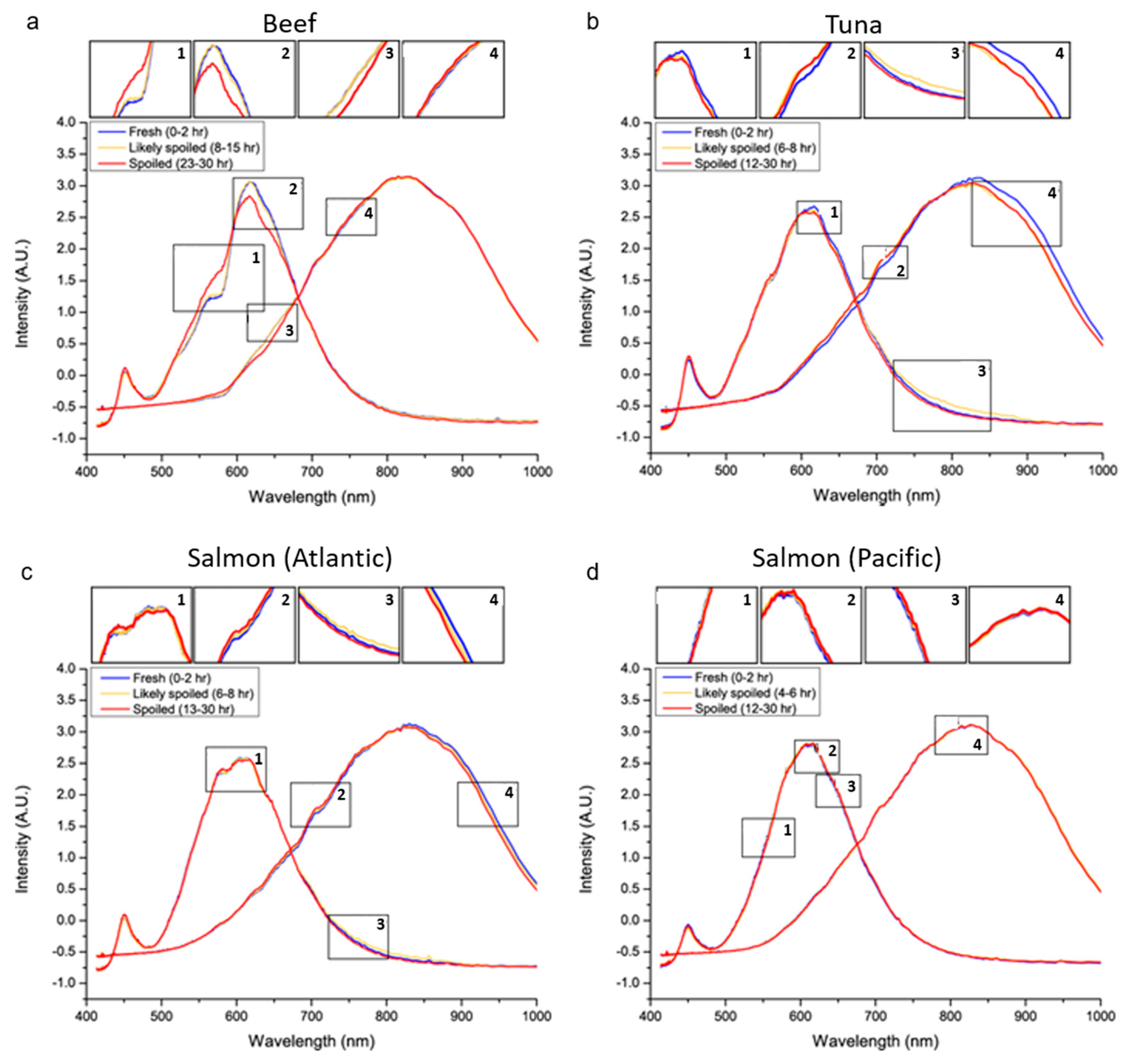
3.3. Data Classification
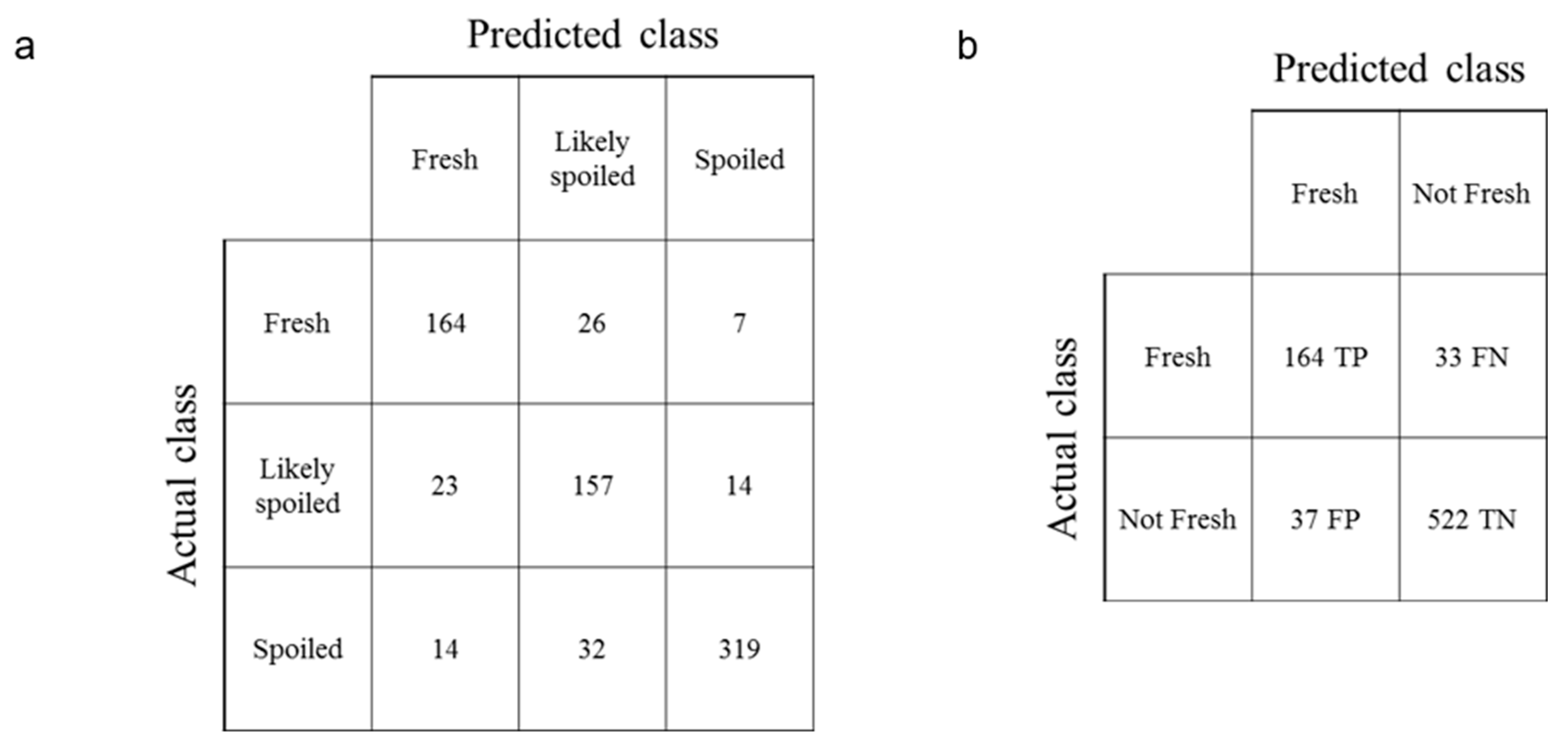
3.4. Validation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lambert, A.D.; Smith, J.P.; Dodds, K.L. Shelf-Life Extension and Microbiological Safety of Fresh Meat—A Review. Food Microbiol. 1991, 8, 267–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olafsdottir, G.; Martinsdottir, E.; Oehlenschlager, J.; Dalgaard, P.; Jensen, B.; Undeland, I.; Mackie, I.M.; Henehan, G.; Nielsen, J.; Nilsen, H. Methods to evaluate fish freshness in research and industry. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 1997, 8, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasanah, U.; Setyowati, M.; Efendi, R.; Muslem, M.; Md Sani, N.D.; Safitri, E.; Yook Heng, L.; Idroes, R. Preparation and Characterization of a Pectin Membrane-Based Optical pH Sensor for Fish Freshness Monitoring. Biosensors (Basel) 2019, 9, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, M.R.; Kube, P.D.; Taylor, R.S.; Elliott, N.G. Rapid compositional analysis of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) using visible-near infrared reflectance spectroscopy. Aquac. Res. 2014, 45, 798–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crichton, S.O.J.; Kirchner, S.M.; Porley, V.; Retz, S.; Von Gersdoiff, G.; Hensel, O.; Weygandt, M.; Sturm, B. Classification of organic beef freshness using VNIR hyperspectral imaging. Meat Sci. 2017, 129, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Qian, Z.; East, A.R. Does consumer-scale near-infrared (NIR) spectroscopy provide opportunities for kiwifruit quality measurement. In ISHS Acta Horticulturae 1218: IX International Symposium on Kiwifruit; International Society for Horticultural Science (ISHS): Leuven, Belgium, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.H.; Na, Y.; Kang, J. Spectrometers with Self- Compensation of Rotational Misalignment. U.S. Patent 10281327, 6 May 2019. [Google Scholar]
- LINKSQUARE. Available online: https://trademarks.justia.com/868/68/linksquare-86868200.html (accessed on 18 July 2020).
- Crocombe, R.A. Portable spectroscopy in 2019: Smaller, cheaper and in consumer products? In Proceedings of the SPIE 10983, Next-Generation Spectroscopic Technologies XII, Baltimore, MD, USA, 13 May 2019.
- You, H.; Kim, Y.; Lee, J.H.; Jang, B.J.; Choi, S. Food Powder Classification Using a Portable Visible-Near-Infrared Spectrometer. J. Electromagn. Eng. Sci. 2017, 17, 186–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food Manufacture. Available online: https://www.foodmanufacture.co.uk/Article/2018/10/02/Food-safety-culture-identified-in-latest-global-standards (accessed on 18 July 2020).
- Kanmani, R.; Sureshkumar, A.; Mugilan, A.; Praveena, V. Non-destructive Approach to Detect Pesticides in Fruits and Vegetables using IoT Technology. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Computer Communication and Informatics (ICCCI), Coimbatore, India, 22–24 January 2020. [Google Scholar]
- LeCun, Y.; Huang, F.J.; Bottou, L. Learning methods for generic object recognition with invariance to pose and lighting. In Proceedings of the 2004 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Washington, DC, USA, 27 June–2 July 2004; Volume 2, pp. 11–104. [Google Scholar]
- LeCun, Y.; Kavukcuoglu, K.; Farabet, C. Convolutional networks and applications in vision. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE international symposium on circuits and systems, Paris, France, 30 May–2 June 2010; pp. 253–256. [Google Scholar]
- Abdalrahman, L.S.; Wells, H.; Fakhr, M.K. Staphylococcus aureus is More Prevalent in Retail Beef Livers than in Pork and other Beef Cuts. Pathogens 2015, 4, 182–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 25 (NIPS 2012), Lake Tahoe, CA, USA, 3 December 2012; pp. 1097–1105. [Google Scholar]
- Gill, C.O. Meat Spoilage and Evaluation of the Potential Storage Life of Fresh Meat. J. Food Prot. 1983, 46, 444–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heising, J.K.; Bartels, P.V.; Van Boekel, M.A.J.S.; Dekker, M. Non-destructive sensing of the freshness of packed cod fish using conductivity and pH electrodes. J. Food Eng. 2014, 124, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huss, H.H. Quality and quality changes in fresh fish. In FAO Fisheries Technical Paper; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Via delle Terme di Caracalla: Rome, Italy, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Kuswandi, B.; Nurfawaidi, A. On-package dual sensors label based on pH indicators for real-time monitoring of beef freshness. Food Control 2017, 82, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miks-Krajnik, M.; Yoon, Y.J.; Ukuku, D.O.; Yuk, H.G. Volatile chemical spoilage indexes of raw Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) stored under aerobic condition in relation to microbiological and sensory shelf lives. Food Microbiol. 2016, 53, 182–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton, K.G.; Gill, C.O. The microbiology of DFD fresh meats: A review. Meat Sci. 1981, 5, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieslaw Przybylski, D.H. Meat Quality: Genetic and Environmental Factors; Taylor & Francis: Oxfordshire, UK, 2015; p. 488. [Google Scholar]
- Abbas, K.A.; Ebrahimian, M. A review on correlation between fish freshness and pH during cold storage. Am. J. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2008, 4, 416–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celia, C.G.; Silva, D.J.B.D.P.; Maria, L.N. Enes Dapkeviciu, Storage temperature effect on histamine formation in big eye tuna and skipjack. J. Food Sci. 1998, 63, 644–647. [Google Scholar]
- Eva Fathul Karamah, A.P.I. Nadifa Ismaningtyas, The applicaion of ozonated water to maintain the quality of tuna meat: The effect of contact time, contact temperature and ozone dosage. Iop Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 509, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Erikson, U.; Beyer, A.R.; Sigholt, T. Muscle high-energy phosphates and stress affect K-values during ice storage of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). J. Food Sci. 1997, 62, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schelin, J.; Wallin-Carlquist, N.; Cohn, M.T.; Lindqvist, R.; Barker, G.C.; Radstrom, P. The formation of Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxin in food environments and advances in risk assessment. Virulence 2011, 2, 580–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadariya, J.; Smith, T.C.; Thapaliya, D. Staphylococcus aureus and staphylococcal food-borne disease: An ongoing challenge in public health. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 827965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominguez, R.; Pateiro, M.; Gagaoua, M.; Barba, F.J.; Zhang, W.; Lorenzo, J.M. A Comprehensive Review on Lipid Oxidation in Meat and Meat Products. Antioxidants (Basel) 2019, 8, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancini, R.A.; Hunt, M.C. Current research in meat color. Meat Sci. 2005, 71, 100–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nilsen, H.; Esaiassen, M.; Heia, K.; Sigernes, F. Visible/near-infrared spectroscopy: A new tool for the evaluation of fish freshness? J. Food Sci. 2002, 67, 1821–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimiya, T.; Sivertsen, A.H.; Heia, K. VIS/NIR spectroscopy for non-destructive freshness assessment of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) fillets. J. Food Eng. 2013, 116, 758–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Sample | Salmon (Atlantic) | Salmon (Pacific) | Tuna | Beef | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Device | |||||||||
| Training | Verify | Training | Verify | Training | Verify | Training | Verify | ||
| D1 | SA1 | SA4 | SP1 | SP4 | T1 | B1 | |||
| D2 | SA2 | SA5 | SP2 | SP5 | T2, T3 | B2, B3 | |||
| D3 | SA3 | SP3 | T4 | B4 | B9 | ||||
| D4 | SA6, SA7 | SP6, SP7 | T5 | T9 | B5 | B10 | |||
| D5 | SA8, SA9 | SP8, SP9 | T6 | T10, T11 | B6 | ||||
| D6 | SA10, SA11 | SP10, SP11 | T7 | B7 | |||||
| D7 | SA12 | SP12 | T8 | B8 | B11 | ||||
| D8 | SA13 | SP13 | T12 | B12, B13 | |||||
| D9 | SA14 | SP14 | T13, T14 | B14 | |||||
| D10 | SA15 | SP15 | T15 | B15 | |||||
| D11 | T16 | B16 | |||||||
| D12 | T17 | ||||||||
| Total # | 3 | 12 | 3 | 12 | 8 | 9 | 8 | 8 | |
| Salmon (Atlantic) | Salmon (Pacific) | Tuna | Beef | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fresh | 1031 | 1055 | 840 | 1545 |
| Likely spoiled | 1042 | 1095 | 978 | 1803 |
| Spoiled | 1129 | 1457 | 1045 | 1694 |
| (a) Salmon (Atlantic) | ||||
| Fresh | Likely Spoiled | Spoiled | Accuracy | |
| Fresh | 164 | 26 | 7 | 83% |
| Likely spoiled | 23 | 157 | 14 | 81% |
| Spoiled | 14 | 32 | 319 | 87% |
| (b) Salmon (Pacific) | ||||
| Fresh | Likely Spoiled | Spoiled | Accuracy | |
| Fresh | 73 | 9 | 4 | 85% |
| Likely spoiled | 10 | 68 | 12 | 76% |
| Spoiled | 3 | 7 | 136 | 93% |
| (c) Tuna | ||||
| Fresh | Likely Spoiled | Spoiled | Accuracy | |
| Fresh | 153 | 4 | 9 | 92% |
| Likely spoiled | 23 | 168 | 12 | 83% |
| Spoiled | 8 | 29 | 293 | 89% |
| (d) Beef | ||||
| Fresh | Likely Spoiled | Spoiled | Accuracy | |
| Fresh | 134 | 18 | 3 | 86% |
| Likely spoiled | 20 | 259 | 2 | 92% |
| Spoiled | 3 | 9 | 258 | 96% |
| (a) Sensitivity | ||||
| Salmon (Atlantic) | Salmon (Pacific) | Tuna | Beef | |
| Fresh | 0.83 | 0.85 | 0.92 | 0.86 |
| Likely spoiled | 0.81 | 0.76 | 0.83 | 0.92 |
| Spoiled | 0.87 | 0.93 | 0.89 | 0.96 |
| (b) Specificity | ||||
| Salmon (Atlantic) | Salmon (Pacific) | Tuna | Beef | |
| Fresh | 0.93 | 0.94 | 0.94 | 0.96 |
| Likely spoiled | 0.90 | 0.93 | 0.93 | 0.94 |
| Spoiled | 0.95 | 0.91 | 0.94 | 0.99 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moon, E.J.; Kim, Y.; Xu, Y.; Na, Y.; Giaccia, A.J.; Lee, J.H. Evaluation of Salmon, Tuna, and Beef Freshness Using a Portable Spectrometer. Sensors 2020, 20, 4299. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20154299
Moon EJ, Kim Y, Xu Y, Na Y, Giaccia AJ, Lee JH. Evaluation of Salmon, Tuna, and Beef Freshness Using a Portable Spectrometer. Sensors. 2020; 20(15):4299. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20154299
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoon, Eui Jung, Youngsik Kim, Yu Xu, Yeul Na, Amato J. Giaccia, and Jae Hyung Lee. 2020. "Evaluation of Salmon, Tuna, and Beef Freshness Using a Portable Spectrometer" Sensors 20, no. 15: 4299. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20154299
APA StyleMoon, E. J., Kim, Y., Xu, Y., Na, Y., Giaccia, A. J., & Lee, J. H. (2020). Evaluation of Salmon, Tuna, and Beef Freshness Using a Portable Spectrometer. Sensors, 20(15), 4299. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20154299





