Influence of Changes in the Level of Volatile Compounds Emitted during Rapeseed Quality Degradation on the Reaction of MOS Type Sensor-Array
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Research Material
2.2. Ergosterol Analysis
2.3. SPME/GC-MS
2.4. Electronic Nose
2.5. Three-Parameter Method for Generation of Smellprints
2.6. Chemometrics
3. Results and Discussion
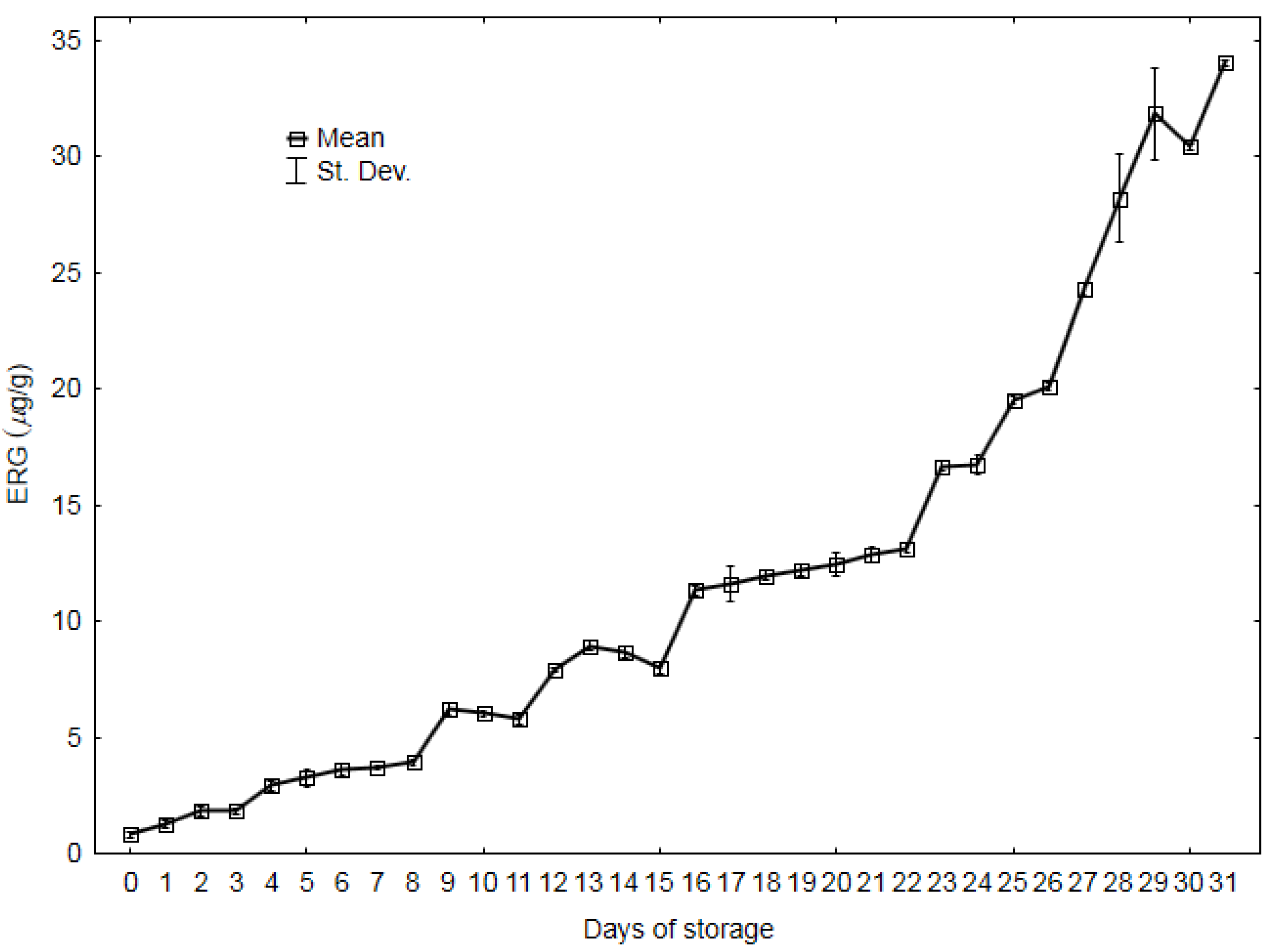
3.1. Ergosterol Content
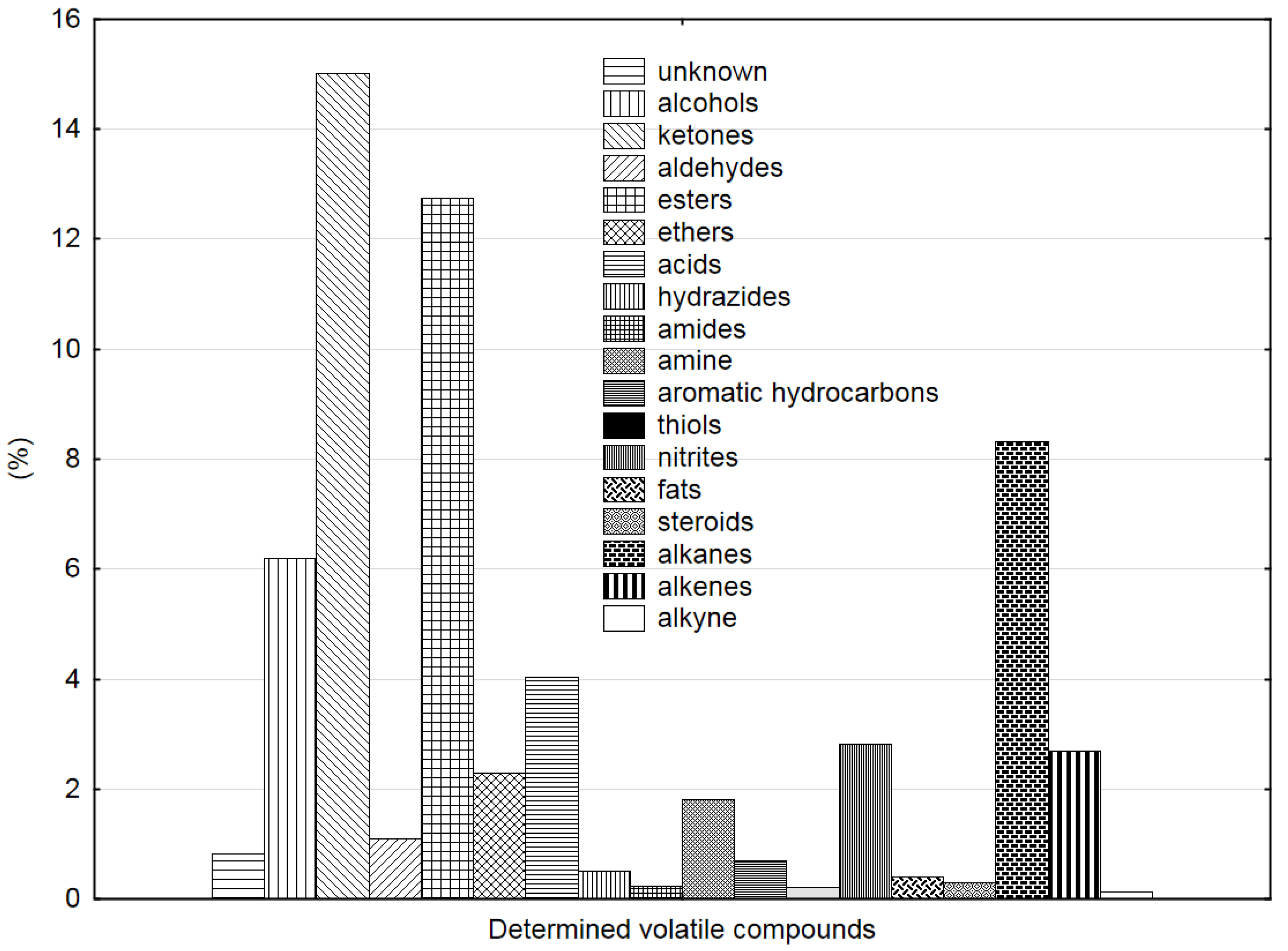
3.2. GC-MS Analysis
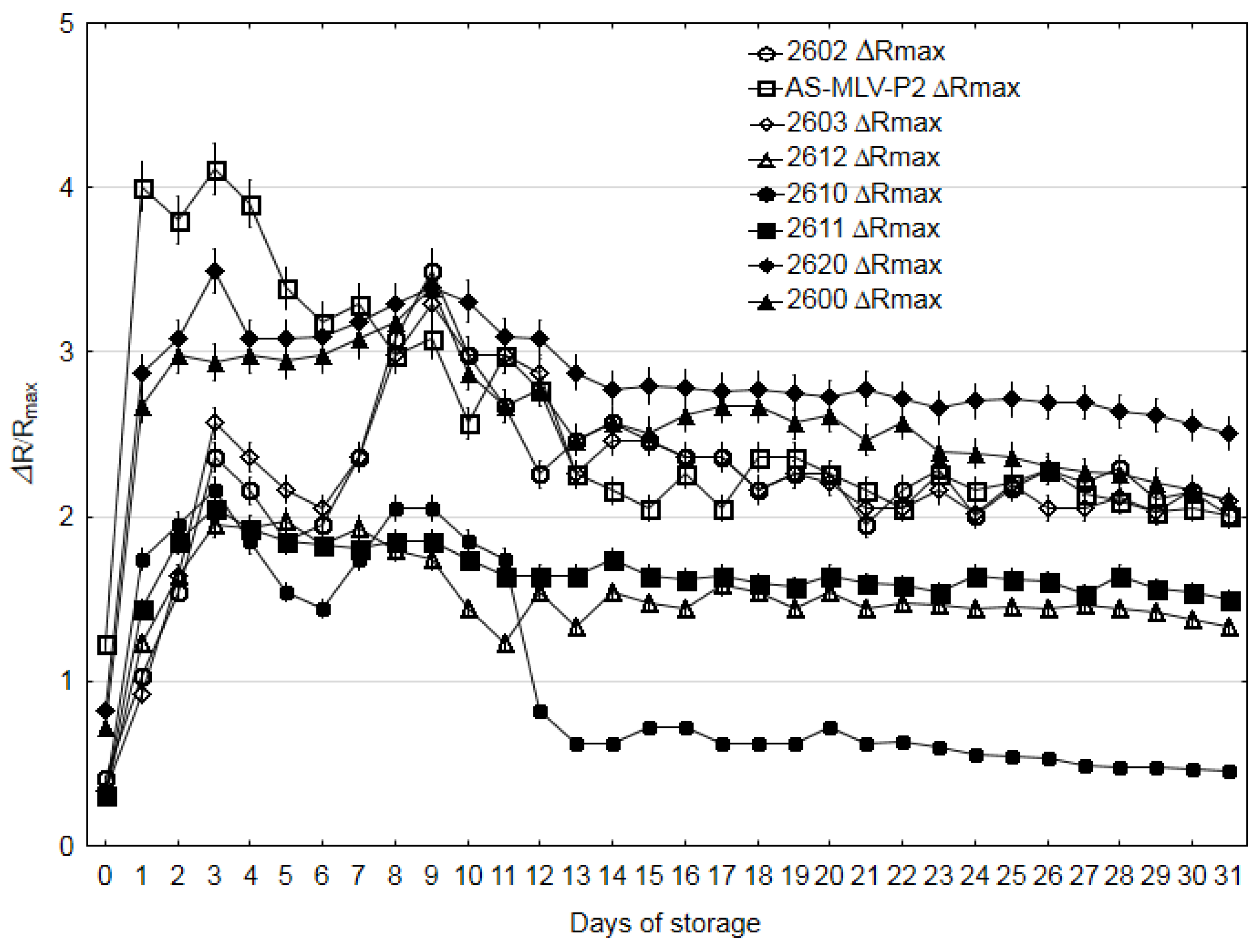
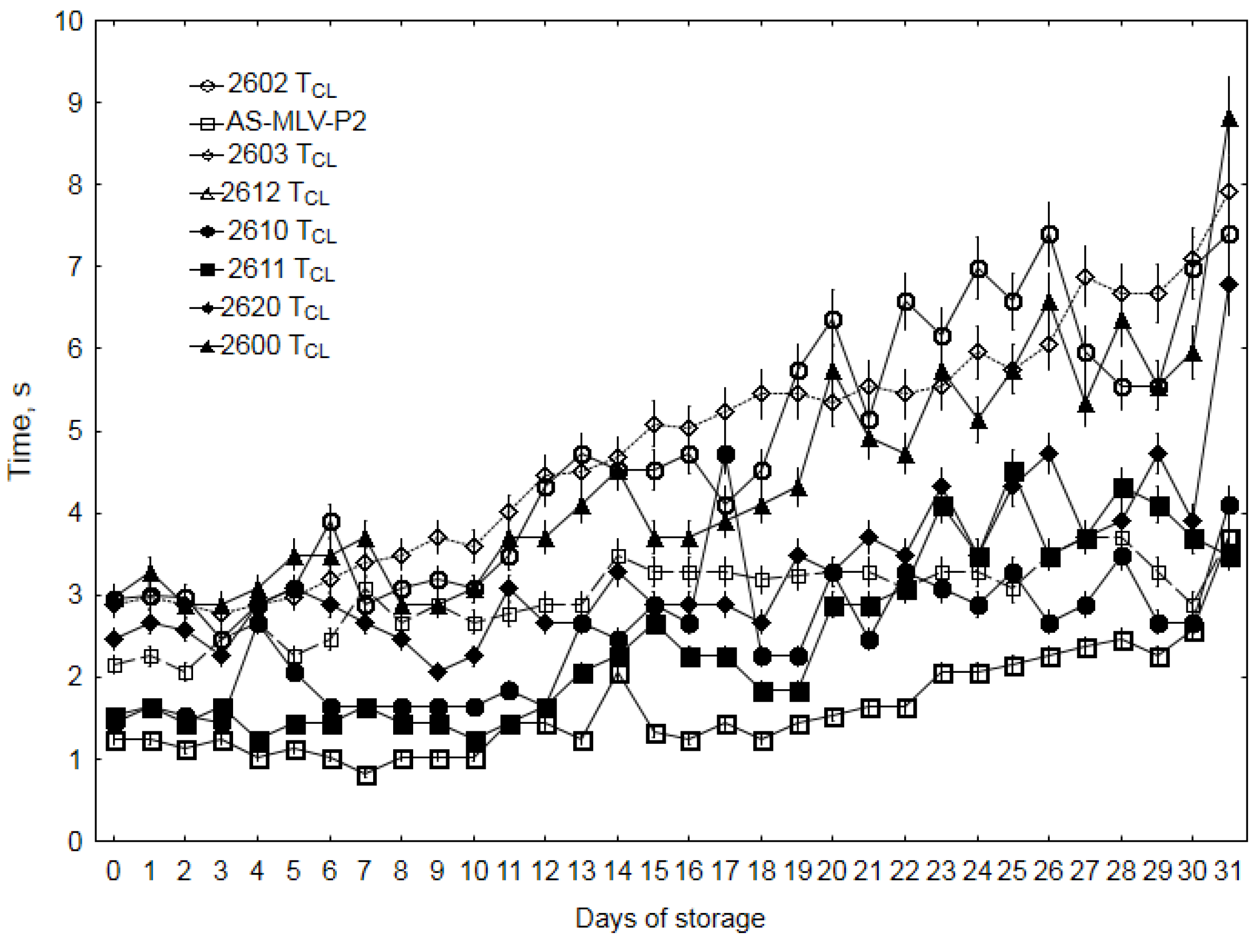
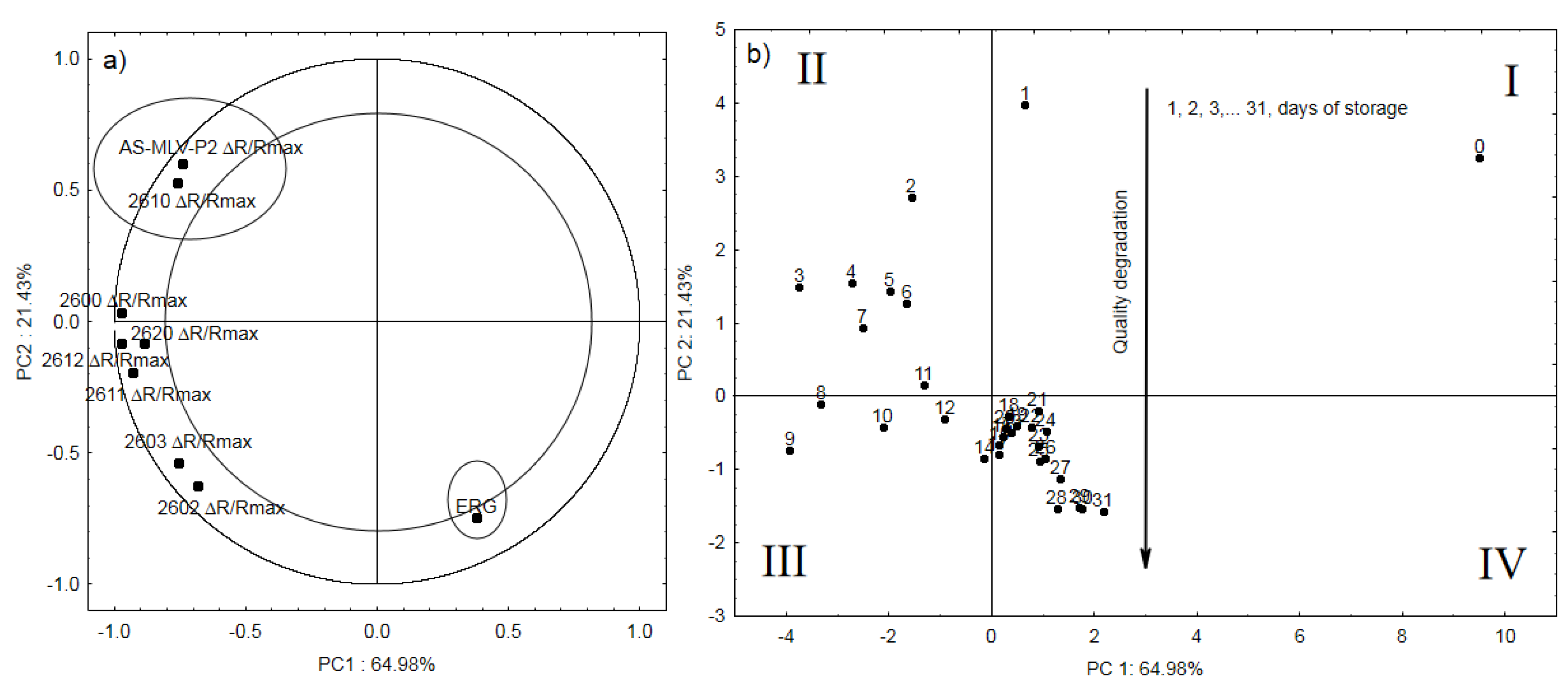
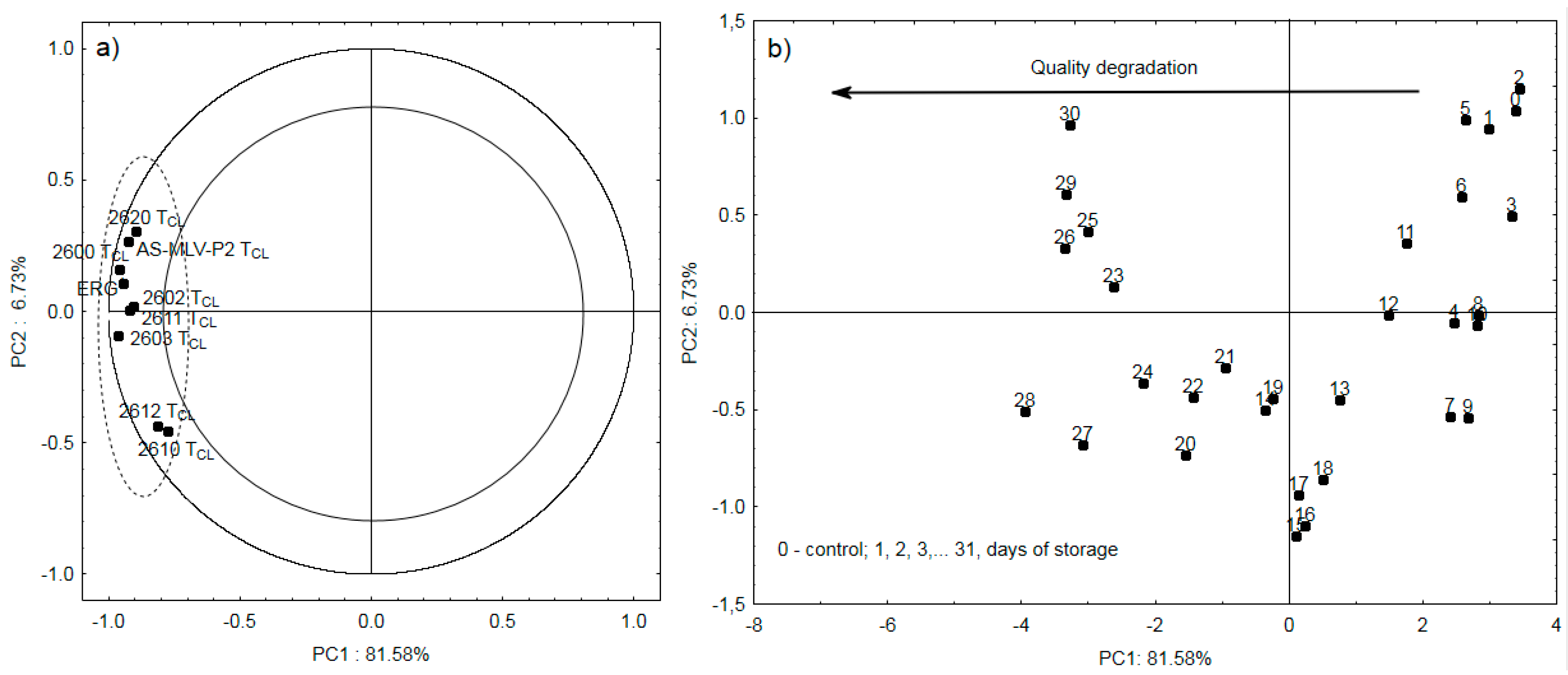
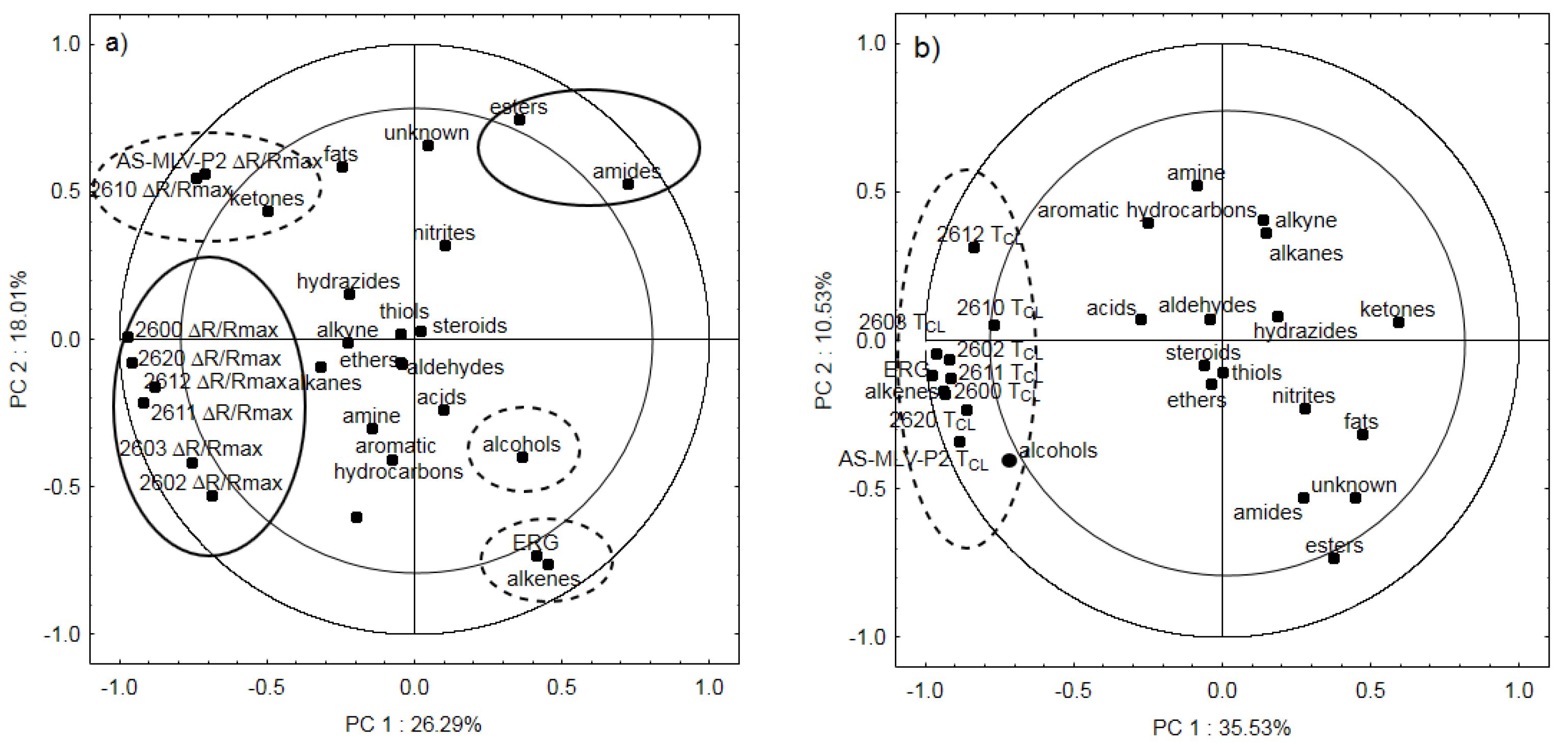
3.3. Electronic Nose Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Marek, G.; Dobrzański, B., Jr.; Oniszczuk, T.; Combrzyński, M.; Ćwikła, D.; Rusinek, R. Detection and Differentation of Volatile Compound Profiles in Roasted Coffee Arabica from Diffrent Countries Using an Electronic Nose and GC-MS. Sensors 2020, 20, 2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gębicki, J.; Szulczyński, B. Discrimination of selected fungi species based on their odour profile using prototypes of electronic nose instruments. Measurement 2018, 116, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczurek, A.; Maciejewska, M.; Bąk, B.; Wilde, J.; Siuda, M. Semiconductor gas sensor as a detector of Varroa destructor infestation of honey bee colonies—Statistical evaluation. Comput. Electron. Agr. 2019, 162, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbacz, M.; Malec, A.; Duda-Saternus, S.; Suchorab, Z.; Guz, Ł.; Łagód, G. Methods for Early Detection of Microbiological Infestation of Buildings Based on Gas Sensor Technologies. Chemosensors 2020, 8, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torri, L.; Piochi, M. Sensory methods and electronic nose as innovative tools for the evaluation of the aroma transfer propierties of food plastic bags. Food Res. Int. 2016, 85, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gancarz, M.; Wawrzyniak, J.; Gawrysiak-Witulska, M.; Wiącek, D.; Nawrocka, A.; Tadla, M.; Rusinek, R. Application of electronic nose with MOS sensors to prediction of rapeseed quality. Measurement 2017, 103, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonah, E.; Huang, X.Y.R.; Aheto, J.H.; Osae, R.; Golly, M. Electronic nose classification and differentiation of bacterial foodborne pathogens based on support vector machine optimized with particle swarm optimization algorithm. J. Food Process. Eng. 2019, 42, 13236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhu, W.; Han, Y.; Yang, Z.; Huang, Y. Single-Nanowire Fuse for Ionization Gas Detection. Sensors 2019, 19, 4358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.; Li, Z.; Xia, K.; Hao, D. Quantitative and Qualitative Analysis of Multicomponent Gas Using Sensor Array. Sensors 2019, 19, 3917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-H.; Mirzaei, A.; Kim, H.W.; Kim, H.J.; Quoc Vuong, P.; Kim, S.S. Novel X-Ray Radiation Sensor Based on Networked SnO2 Nanowires. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, S.; Lathrop, S.; Nabrzyski, J.; Ramakrishnan, L. Incorporating Scientific Workflows in Computing Research Processes. Comput. Sci. Eng. 2019, 21, 4–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabilla, S.I.; Sarno, R.; Triyana, K. Optimizing Threshold Using Pearson Correlation for Selecting Features of Electronic Nose Signals. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 2019, 12, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gancarz, M.; Nawrocka, A.; Rusinek, R. Identification of volatile organic compounds and their concentrations using a novel method analysis of MOS sensors signal. J. Food Sci. 2019, 84, 2077–2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rusinek, R.; Gancarz, M.; Krekora, M.; Nawrocka, A. A novel method for generation of a fingerprint using electronic nose on the example of rapeseed spoilage. J. Food Sci. 2019, 84, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rusinek, R.; Siger, A.; Gawrysiak-Witulska, M.; Rokosik, E.; Malaga-Toboła, U.; Gancarz, M. Application of an electronic nose for determination of pre-pressing treatment of rapeseed based on the analysis of volatile compounds contained in pressed oil. Int. J. Food Sci. Tech. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Xiuzhen, G.; Shukai, D.; Pengfei, J.; Lidan, W.; Chao, P.; Songlin, Z. Electronic nose feature extraction methods: A Review. Sensors 2015, 7804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusinek, R.; Kobyłka, R. Experimental study and discrete element method modeling of temperature distributions in rapeseed stored in model bin. J. Stored Prod. Res. 2014, 59, 254–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gawrysiak-Witulska, M.; Siger, A.; Rudzińska, M.; Stuper-Szablewska, K.; Rusinek, R. Effect of self-heating on the processing quality of rapeseed. Int. Agrophys. 2018, 32, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muniz-Wypych, A.S.; Costa, M.M.; Oliveria, A.R.S.; New, P.M.; Schober, S.; Mittelbach, M.; Ramos, L.P.; César-Oliveira, M.A.F. Phenolic compounds obtained from alkyl oleates as addi-tives to improve the oxidative stability of methyl rapeseed biodie-sel. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2017, 119, 1700179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gugala, M.; Sikorska, A.; Findura, F.; Kapela, K.; Malaga-Tobola, U.; Zarzecka, K.; Domanski, L. Effect of selected plant preparations containing biologically active compounds on winter rape (Brassica napus L.) yielding. Appl. Ecol. Env. Res. 2018, 17, 2779–2789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramson, A.; Smith, D.M. Determination of ergosterol in canola (Brassica napus L.) by liquid chromatograph. J. Stored Prod. Res. 2003, 39, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pronyk, C.; Abramson, D.; Muir, W.E.; White, N.D.G. Correlation of total ergosterol levels in stored canola with fungal deterioration. J. Stored Prod. Res. 2006, 42, 162–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippolis, V.; Pascale, M.; Cervellieri, S.; Damascelli, A.; Visconti, A. Screening of deoxynivalenol contamination in durum wheat by MOS-based electronic nose and identification of the relevant pattern of volatile compounds. Food Control 2014, 37, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeleń, H.H. Use of solid phase microextraction (SPME) for profiling fungal volatile metabolites. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2003, 36, 263–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gancarz, M.; Wawrzyniak, J.; Gawrysiak-Witulska, M.; Wiącek, D.; Nawrocka, A.; Rusinek, R. Electronic nose with polymer-composite sensors for monitoring fungal deterioration of stored rapeseed. Int Agrophys. 2017, 31, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, H.-E.; Raj, S.S.A.; Wong, S.H.; Tey, D.; Tan, H.-M. Estimation of fungal growth using the ergosterol assay: A rapid tool in assessing the microbiological status of grains and feeds. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2008, 46, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gawrysiak-Witulska, M.; Siger, A.; Rusinek, R. Degradation of tocopherols during rapeseed storage in simulated conditions of industrial silos. Int. Agrophys. 2016, 30, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-González, D.L.; Aparicio, R. Coupling MOS sensors and gas chromatography to interpret the sensor responsesto complex food aroma: Application to virgin olive oil. Food Chem. 2010, 120, 572–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusinek, R.; Gancarz, M.; Nawrocka, A. Application of an electronic nose with novel method for generation of smellprints for testing the suitability for consumption of wheat bread during 4-day storage. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 117, 108665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magan, N.; Evans, P. Volatiles as an indicator of fungal activity and differentiation between species, and the potential use of electronic nose technology for early detection of grain spoilage. J. Stored Prod. Res. 2000, 36, 319–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubiak, A.; Mikrut, Z. Rapeseed quality assessment using artificial nose and neural networks. Automation 2005, 9, 3. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Paolesse, R.; Alimelli, A.; Martinelli, E.; Di Natale, C.; Fanelli, C. Detection of fungal contamination of cereal grain samples by an electronic nose. Sensor Actuat B- Chem. 2006, 119, 425–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weikl, F.; Ghirardo, A.; Schnitzler, J.P.; Pritsch, P. Sesquiterpene emissions from Alternaria alternate and Fusarium oxysporum: Effects of age, nutrient availability, and co-cultivation. Sci. Rep. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubiak, A.; Wenzl, T.; Ulberth, F. Evaluation of the quality of postharvest rapeseed by means of an electronic nose. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2012, 92, 2200–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delgado-Rodriguez, M.; Ruiz-Montoya, M.; Giraldez, I.; Lopez, R.; Madejon, E.; Diaz, M.J. Use of electronic nose and GC-MS in detection and monitoring some VOC. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 51, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubiak, A. Rapeseed Analysis by an Electronic Nose. In Electronic Noses and Tongues in Food Science; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2016; pp. 93–101. [Google Scholar]
- Rusinek, R.; Rybczyński, R.; Gawrysiak-Witulska, M.; Nogala-Kałucka, M.; Siger, A.; Tys, J. The process parameters for non-typical seeds during simulated cold deep oil expression. Czech J. Food Sci. 2012, 30, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rusinek, R.; Jeleń, H.; Malaga-Toboła, U.; Molenda, M.; Gancarz, M. Influence of Changes in the Level of Volatile Compounds Emitted during Rapeseed Quality Degradation on the Reaction of MOS Type Sensor-Array. Sensors 2020, 20, 3135. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20113135
Rusinek R, Jeleń H, Malaga-Toboła U, Molenda M, Gancarz M. Influence of Changes in the Level of Volatile Compounds Emitted during Rapeseed Quality Degradation on the Reaction of MOS Type Sensor-Array. Sensors. 2020; 20(11):3135. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20113135
Chicago/Turabian StyleRusinek, Robert, Henryk Jeleń, Urszula Malaga-Toboła, Marek Molenda, and Marek Gancarz. 2020. "Influence of Changes in the Level of Volatile Compounds Emitted during Rapeseed Quality Degradation on the Reaction of MOS Type Sensor-Array" Sensors 20, no. 11: 3135. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20113135
APA StyleRusinek, R., Jeleń, H., Malaga-Toboła, U., Molenda, M., & Gancarz, M. (2020). Influence of Changes in the Level of Volatile Compounds Emitted during Rapeseed Quality Degradation on the Reaction of MOS Type Sensor-Array. Sensors, 20(11), 3135. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20113135







