Hydrogel Microdomain Encapsulation of Stable Functionalized Silver Nanoparticles for SERS pH and Urea Sensing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Silver Nanoparticle Synthesis
2.3. AgNP Monolayer Modification
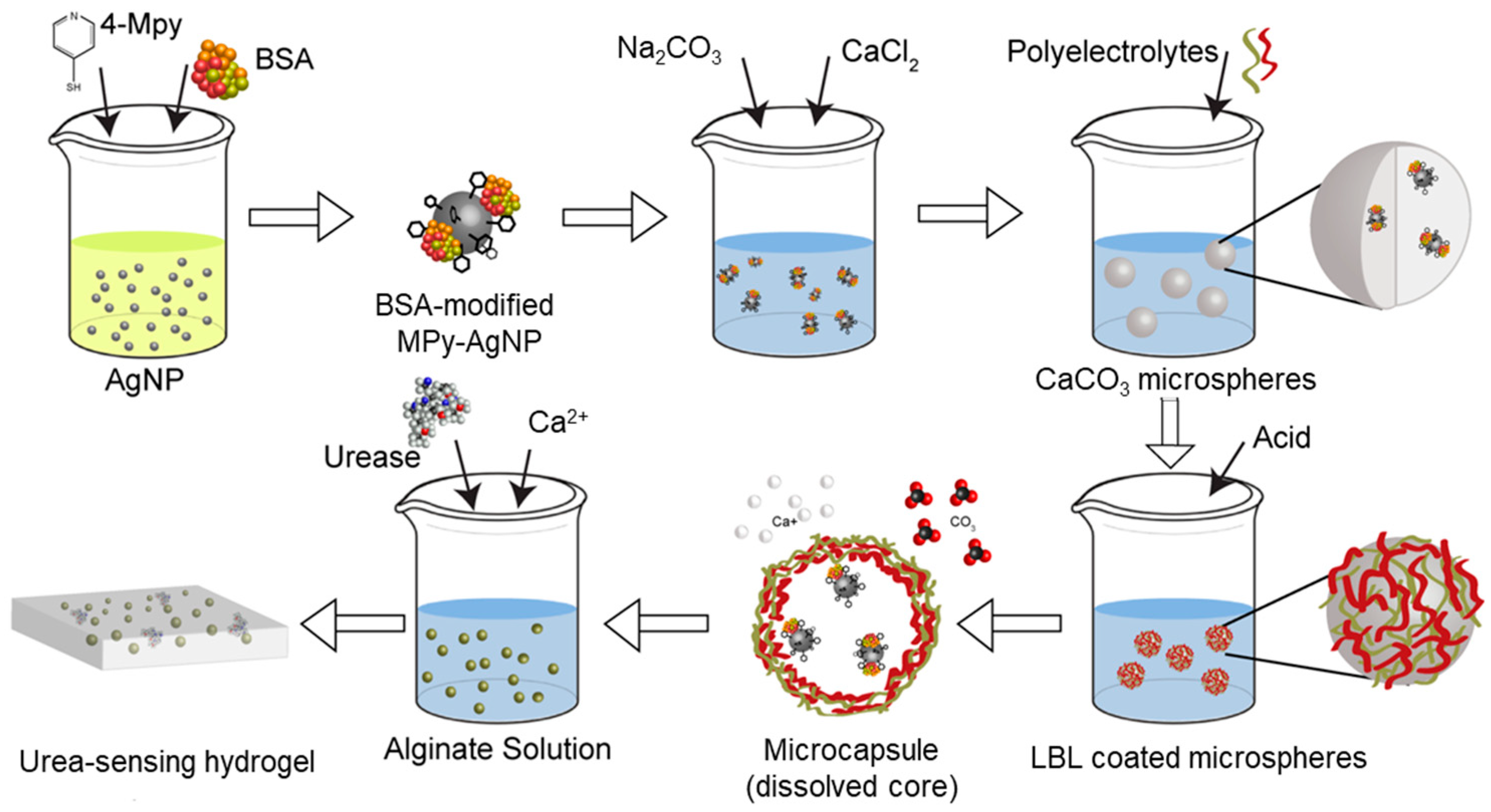
2.4. Encapsulation of BSA-Modified MPy-AgNPs in Microcapsules
2.5. Fabrication of pH Sensing Hydrogel
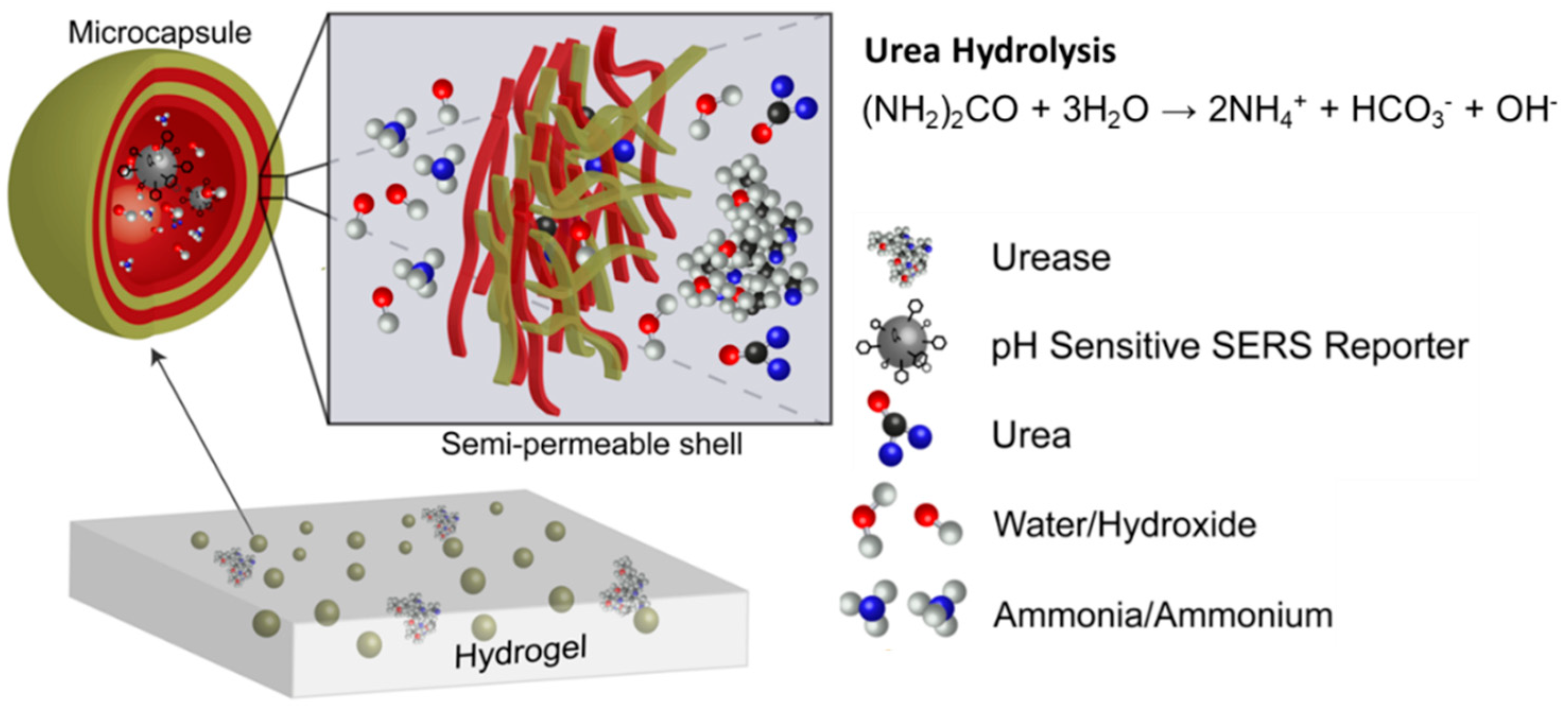
2.6. Fabrication of Urea Sensing Hydrogel
2.7. UV-vis Measurements
2.8. SERS
3. Results and Discussion
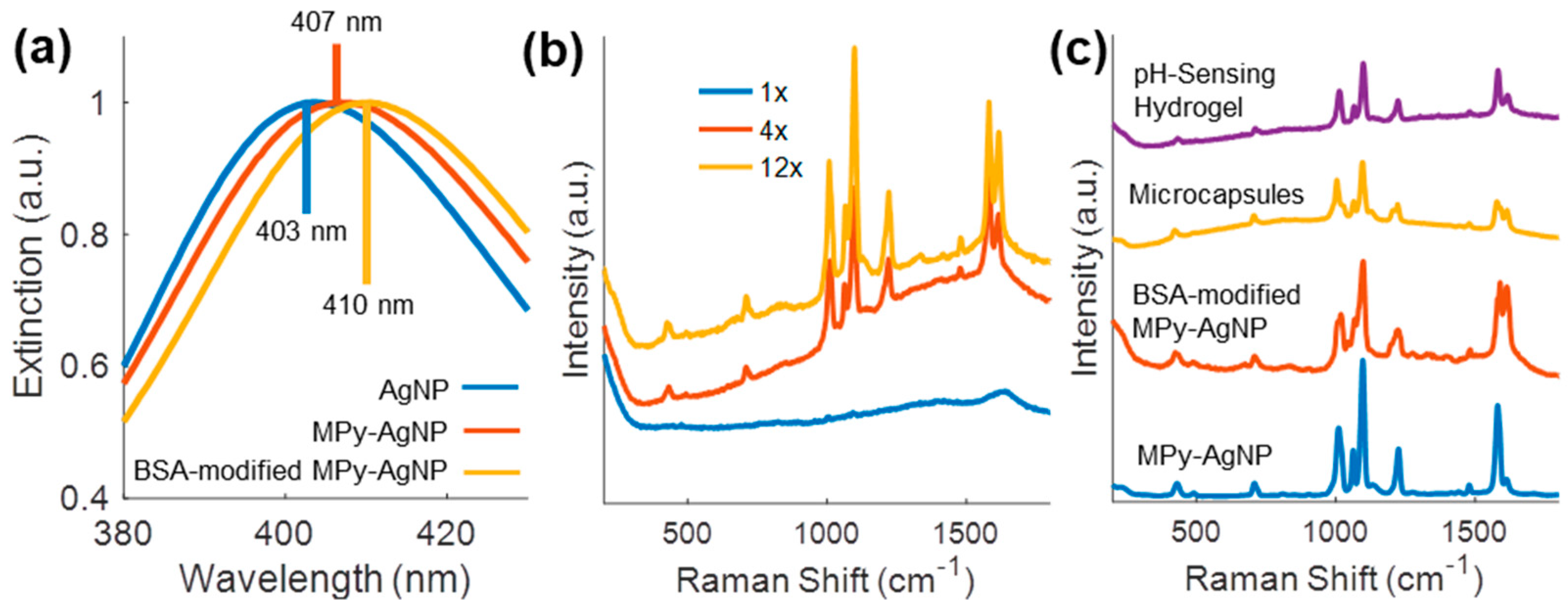
3.1. Sensor Synthesis
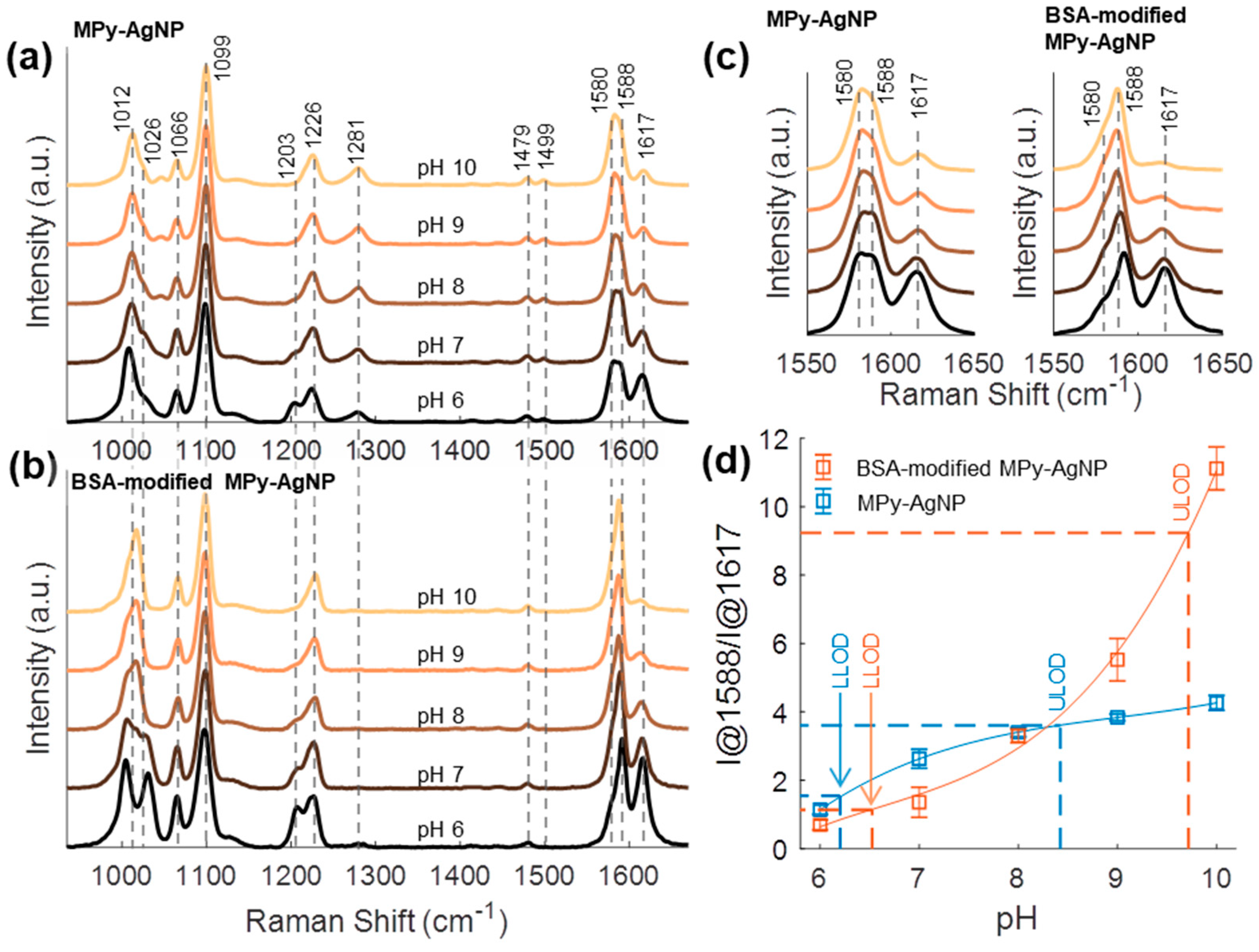
3.2. BSA Corona Improves MPy-AgNP pH Response
3.3. BSA-Modified MPy-AgNP Sensitivity Loss Due to Ca2+ Ions
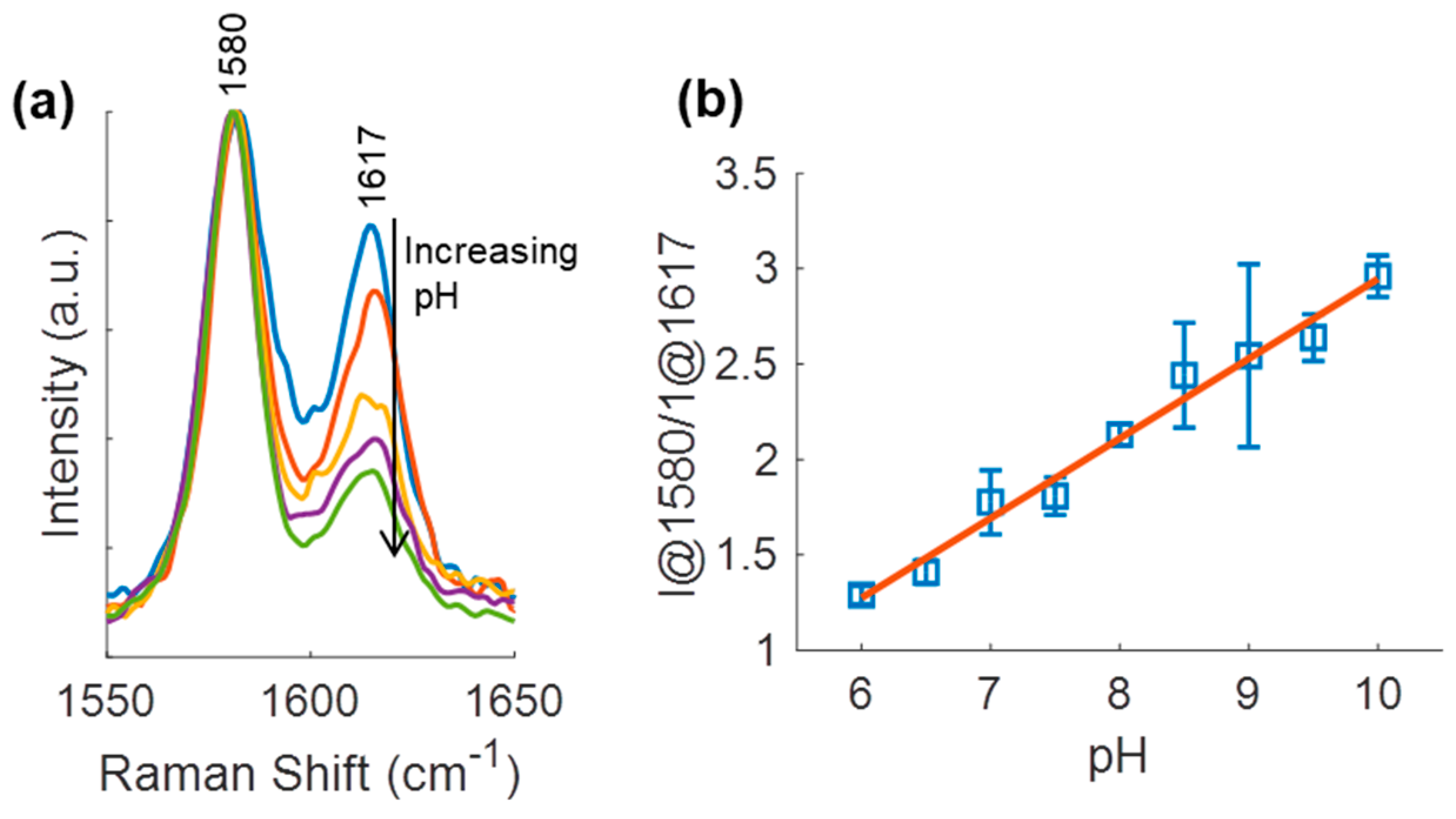
3.4. pH Sensing Hydrogel pH Response
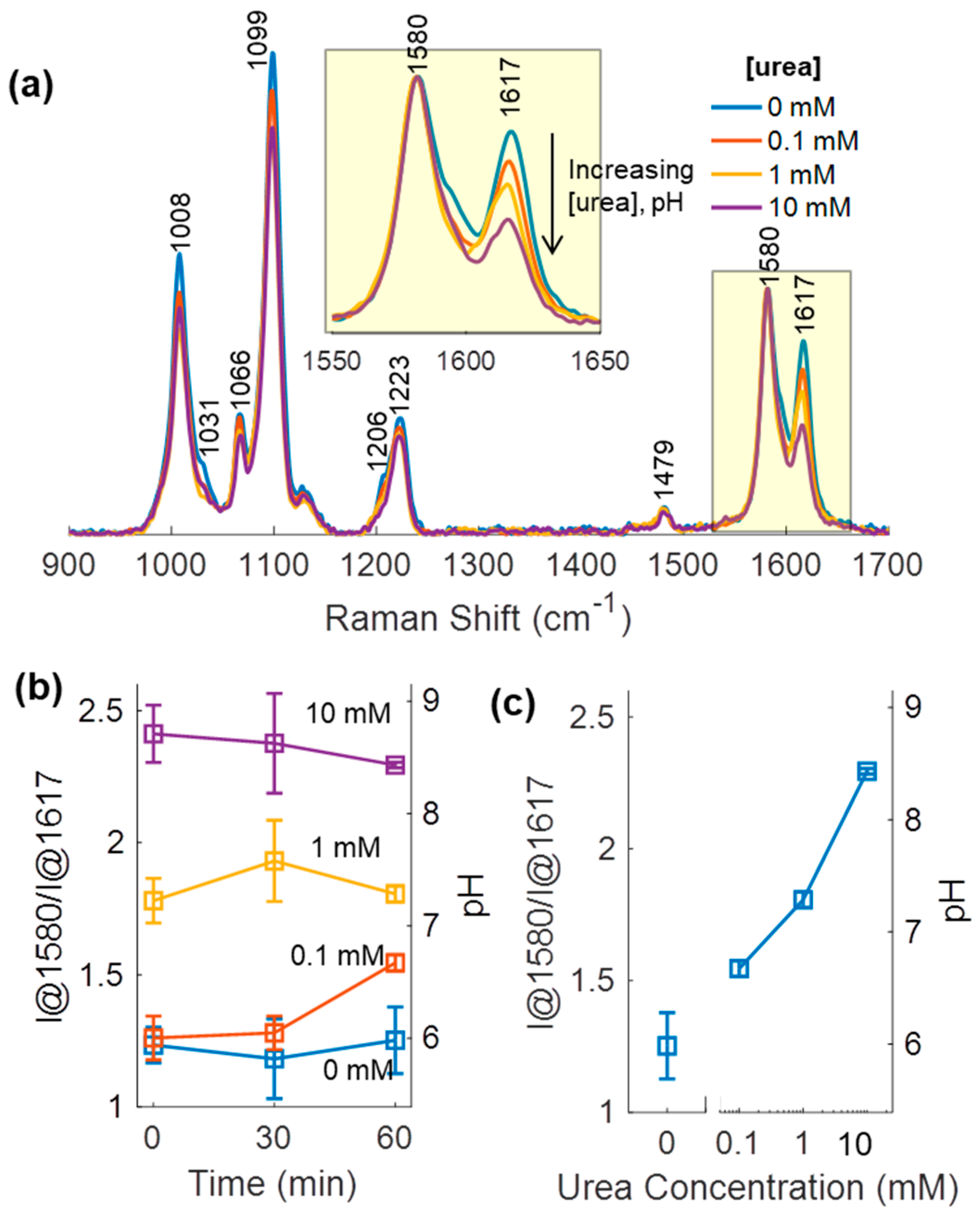
3.5. Urea Sensing Hydrogel Urea Response
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gray, M.; Meehan, J.; Ward, C.; Langdon, S.P.; Kunkler, I.H.; Murray, A.; Argyle, D. Implantable biosensors and their contribution to the future of precision medicine. Vet. J. 2018, 239, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cappon, G.; Acciaroli, G.; Vettoretti, M.; Facchinetti, A.; Sparacino, G. Wearable continuous glucose monitoring sensors: A revolution in diabetes treatment. Electronics 2017, 6, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajami, S.; Teimouri, F. Features and application of wearable biosensors in medical care. J. Res. Med. Sci. 2015, 20, 1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumari, P.; Mathew, L.; Syal, P. Increasing trend of wearables and multimodal interface for human activity monitoring: A review. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 90, 298–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnard, K.D.; Kropff, J.; Choudhary, P.; Neupane, S.; Bain, S.C.; Kapitza, C.; Forst, T.; Link, M.; Mdingi, C.; DeVries, J.H. Acceptability of implantable continuous glucose monitoring sensor. J. Diabet. Sci. Technol. 2018, 12, 634–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eversense Continuous Glucose Montioring System—P160048. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices/recently-approved-devices/eversense-continuous-glucose-montioring-system-p160048 (accessed on 19 May 2019).
- Kim, J.; Jeerapan, I.; Sempionatto, J.R.; Barfidokht, A.; Mishra, R.K.; Campbell, A.S.; Hubble, L.J.; Wang, J. Wearable bioelectronics: Enzyme-based body-worn electronic devices. Acc. Chem. Res. 2018, 51, 2820–2828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazakova, L.I.; Shabarchina, L.I.; Sukhorukov, G.B. Co-encapsulation of enzyme and sensitive dye as a tool for fabrication of microcapsule based sensor for urea measuring. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 11110–11117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rong, G.; Corrie, S.R.; Clark, H.A. In vivo biosensing: Progress and perspectives. ACS Sens. 2017, 2, 327–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.Q.; Srivastava, R.; McShane, M.J. Encapsulation of glucose oxidase and an oxygen-quenched fluorophore in polyelectrolyte-coated calcium alginate microspheres as optical glucose sensor systems. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2005, 21, 212–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, S.R.; McShane, M.J. Fluorescence glucose monitoring based on transduction of enzymatically-driven pH changes within microcapsules. Sens. Lett. 2006, 4, 433–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreft, O.; Javier, A.M.; Sukhorukov, G.B.; Parak, W.J. Polymer microcapsules as mobile local pH-sensors. J. Mater. Chem. 2007, 17, 4471–4476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaraja, A.T.; Sooresh, A.; Meissner, K.E.; McShane, M.J. Processing and characterization of stable, pH-sensitive layer-by-layer modified colloidal quantum dots. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 6194–6202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Y.-H.; Nagaraja, A.; Biswas, A.; Marks, H.; Coté, G.L.; McShane, M.J. SERS-based hydrogel sensors for pH and enzymatic substrates. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE SENSORS, Busan, Korea, 1–4 November 2015; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- You, Y.; Nagaraja, A.; Biswas, A.; Hwang, J.; Cote, G.; McShane, M. SERS-active smart hydrogels with modular microdomains: From pH to glucose sensing. IEEE Sens. J. 2016, 17, 941–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osaka, T.; Komaba, S.; Amano, A.; Fujino, Y.; Mori, H. Electrochemical molecular sieving of the polyion complex film for designing highly sensitive biosensor for creatinine. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2000, 65, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, P.C.; Singh, G. Tetraphenylborate doped polyaniline based novel pH sensor and solid-state urea biosensor. Talanta 2001, 55, 773–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, H.-C.; Doong, R.-A. Simultaneous determination of pH, urea, acetylcholine and heavy metals using array-based enzymatic optical biosensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2005, 20, 1796–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thurston, R.V. Aqueous Ammonia Equilibrium: Tabulation of Percent Un-Ionized Ammonia; Environmental Research Laboratory, Office of Research and Development: Duluth, MN, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Jdanova, A.; Poyard, S.; Soldatkin, A.; Jaffrezic-Renault, N.; Martelet, C. Conductometric urea sensor. Use of additional membranes for the improvement of its analytical characteristics. Anal. Chim. Acta 1996, 321, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senillou, A.; Jaffrezic-Renault, N.; Martelet, C.; Cosnier, S. A miniaturized urea sensor based on the integration of both ammonium based urea enzyme field effect transistor and a reference field effect transistor in a single chip. Talanta 1999, 50, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Premanode, B.; Toumazou, C. A novel, low power biosensor for real time monitoring of creatinine and urea in peritoneal dialysis. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2007, 120, 732–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sant, W.; Temple-Boyer, P.; Chanié, E.; Launay, J.; Martinez, A. On-line monitoring of urea using enzymatic field effect transistors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2011, 160, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kaushik, A.; Solanki, P.R.; Ansari, A.A.; Sumana, G.; Ahmad, S.; Malhotra, B.D. Iron oxide-chitosan nanobiocomposite for urea sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2009, 138, 572–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solanki, P.R.; Kaushik, A.; Ansari, A.A.; Sumana, G.; Malhotra, B. Zinc oxide-chitosan nanobiocomposite for urea sensor. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 93, 163903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, R.K.; Srivastava, S.; Narayanan, T.N.; Mahlotra, B.D.; Vajtai, R.; Ajayan, P.M.; Srivastava, A. Functionalized multilayered graphene platform for urea sensor. ACS Nano 2011, 6, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olesberg, J.T.; Arnold, M.A.; Flanigan, M.J. Online measurement of urea concentration in spent dialysate during hemodialysis. Clin. Chem. 2004, 50, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thavarungkul, P.; Håkanson, H.; Holst, O.; Mattiasson, B. Continuous monitoring of urea in blood during dialysis. Biosens. Bioelectron. 1991, 6, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamponi, S.; Cicero, B.L.; Mascini, M.; Della Ciana, L.; Sacco, S. Urea solid-state biosensor suitable for continuous dialysis control. Talanta 1996, 43, 1373–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuart, D.A.; Yuen, J.M.; Shah, N.; Lyandres, O.; Yonzon, C.R.; Glucksberg, M.R.; Walsh, J.T.; Van Duyne, R.P. In vivo glucose measurement by surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 7211–7215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Y.; Schechinger, M.; Locke, A.; Coté, G.; McShane, M. Nanoengineered capsules for selective SERS analysis of biological samples. In Proceedings of the Optical Diagnostics and Sensing XVIII: Toward Point-of-Care Diagnostics, San Francisco, CA, USA, 20 February 2018; p. 1050103. [Google Scholar]
- Zavaleta, C.L.; Smith, B.R.; Walton, I.; Doering, W.; Davis, G.; Shojaei, B.; Natan, M.J.; Gambhir, S.S. Multiplexed imaging of surface enhanced Raman scattering nanotags in living mice using noninvasive Raman spectroscopy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 13511–13516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinman, S.L.; Frontiera, R.R.; Henry, A.-I.; Dieringer, J.A.; Van Duyne, R.P. Creating, characterizing, and controlling chemistry with SERS hot spots. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 21–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.; Yang, J.-K.; Noh, M.S.; Jo, A.; Jeong, S.; Lee, M.; Lee, S.; Chang, H.; Lee, H.; Jeon, S.-J. One-step synthesis of silver nanoshells with bumps for highly sensitive near-IR SERS nanoprobes. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 4415–4421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.; Jeong, S.; Park, Y.; Yim, J.; Jun, B.H.; Kyeong, S.; Yang, J.K.; Kim, G.; Hong, S.; Lee, L.P. Near-Infrared SERS Nanoprobes with plasmonic Au/Ag hollow-shell assemblies for in vivo multiplex detection. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2013, 23, 3719–3727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, X.; Peng, X.-H.; Ansari, D.O.; Yin-Goen, Q.; Chen, G.Z.; Shin, D.M.; Yang, L.; Young, A.N.; Wang, M.D.; Nie, S. In vivo tumor targeting and spectroscopic detection with surface-enhanced Raman nanoparticle tags. Nat. Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weissleder, R. A Clearer Vision for In Vivo Imaging; Nature Publishing Group: London, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, X.-S.; Hu, P.; Cui, Y.; Zong, C.; Feng, J.-M.; Wang, X.; Ren, B. BSA-coated nanoparticles for improved SERS-based intracellular pH sensing. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 12250–12257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, J.Y.; Lu, F.; Stern, D.A.; Hubbard, A.T. Surface chemistry of mercaptopyridines at Ag(111) electrodes studied by EELS, LEED, Auger spectroscopy and electrochemistry. J. Electroanal. Chem. Interfacial Electrochem. 1990, 292, 245–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldwin, J.; Schühler, N.; Butler, I.S.; Andrews, M.P. Integrated optics evanescent wave surface enhanced Raman scattering (IO-EWSERS) of mercaptopyridines on a planar optical chemical bench: Binding of hydrogen and copper ion. Langmuir 1996, 12, 6389–6398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.S.; Kim, K.; Kim, M.S. Raman spectroscopic investigation of the adsorption of 4-mercaptopyridine on a silver-sol surface. J. Mol. Struct. 1997, 407, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.-Z.; Xia, N.; Liu, Z.-F. SERS titration of 4-mercaptopyridine self-assembled monolayers at aqueous buffer/gold interfaces. Anal. Chem. 1999, 71, 1354–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, L.-J.; Noda, H.; Hara, Y.; Osawa, M. Effect of solution pH on the structure of a 4-mercaptopyridine monolayer self-assembled on Au(111). J. Electroanal. Chem. 2000, 489, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Zhao, B.; Xu, W.; Li, B.; Fan, Y. Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy study on the structure changes of 4-mercaptopyridine adsorbed on silver substrates and silver colloids. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2002, 58, 2827–2834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.-S.; Hu, P.; Zhong, J.-H.; Zong, C.; Wang, X.; Liu, B.-J.; Ren, B. Laser power dependent surface-enhanced raman spectroscopic study of 4-mercaptopyridine on uniform gold nanoparticle-assembled substrates. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 3750–3757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, B.L.; Carron, K.T. Dynamic raman scattering studies of coated gold nanoparticles: 4-mercaptopyridine, 4-mercaptophenol, and benzenethiol. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 20905–20913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Y.; Biswas, A.; Nagaraja, A.T.; Hwang, J.; Cote, G.L.; McShane, M.J. Multidomain-based responsive materials with dual mode optical readouts. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 14286–14295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, A.; Nagaraja, A.T.; McShane, M.J. Fabrication of nanocapsule carriers from multilayer-coated vaterite calcium carbonate nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 21193–21201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukhorukov, G.B.; Brumen, M.; Donath, E.; Möhwald, H. Hollow polyelectrolyte shells: Exclusion of polymers and donnan equilibrium. J. Phys. Chem. B 1999, 103, 6434–6440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, A.; Nagaraja, A.T.; You, Y.-H.; Roberts, J.R.; McShane, M.J. Cross-linked nanofilms for tunable permeability control in a composite microdomain system. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 71781–71790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, J.R.; Ritter, D.W.; McShane, M.J. A design full of holes: Functional nanofilm-coated microdomains in alginate hydrogels. J. Mater. Chem. B 2013, 1, 3195–3201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Cao, Z.; Bai, T.; Carr, L.; Ella-Menye, J.-R.; Irvin, C.; Ratner, B.D.; Jiang, S. Zwitterionic hydrogels implanted in mice resist the foreign-body reaction. Nat. Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ananth, A.N.; Daniel, S.K.; Sironmani, T.A.; Umapathi, S. PVA and BSA stabilized silver nanoparticles based surface–enhanced plasmon resonance probes for protein detection. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2011, 85, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, T.A.; Kipke, D.R.; Brandon, T. Calcium alginate gel: A biocompatible and mechanically stable polymer for endovascular embolization. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2001, 54, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauck, T.S.; Ghazani, A.A.; Chan, W.C. Assessing the effect of surface chemistry on gold nanorod uptake, toxicity, and gene expression in mammalian cells. Small 2008, 4, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayavarapu, R.G.; Petersen, W.; Hartsuiker, L.; Chin, P.; Janssen, H.; Van Leeuwen, F.W.; Otto, C.; Manohar, S.; Van Leeuwen, T.G. In vitro toxicity studies of polymer-coated gold nanorods. Nanotechnology 2010, 21, 145101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, C.A.; Connor, R.E.; Heller, A. Biocompatible, glucose-permeable hydrogel for in situ coating of implantable biosensors. Biomaterials 1997, 18, 1665–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leopold, N.; Lendl, B. A new method for fast preparation of highly surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) active silver colloids at room temperature by reduction of silver nitrate with hydroxylamine hydrochloride. J. Phys. Chem. B 2003, 107, 5723–5727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paramelle, D.; Sadovoy, A.; Gorelik, S.; Free, P.; Hobley, J.; Fernig, D.G. A rapid method to estimate the concentration of citrate capped silver nanoparticles from UV-visible light spectra. Analyst 2014, 139, 4855–4861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wattanavichean, N.; Casey, E.; Nichols, R.J.; Arnolds, H. Discrimination between hydrogen bonding and protonation in the spectra of a surface-enhanced Raman sensor. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2018, 20, 866–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, S.; Fujiwara, K.; Watarai, H. Surface-enhanced Raman scattering from oleate-stabilized silver colloids at a liquid/liquid interface. Anal. Sci. 2004, 20, 1347–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.C.; Lee, S.M.; Park, T.S.; Lee, B.S. Preparation of colloidal silver nanoparticles by chemical reduction method. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2009, 26, 153–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ershov, B.; Henglein, A. Optical spectrum and some chemical properties of colloidal thallium in aqueous solution. J. Phys. Chem. 1993, 97, 3434–3436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanh, N.T.K.; Rosenzweig, Z. Development of an aggregation-based immunoassay for anti-protein A using gold nanoparticles. Anal. Chem. 2002, 74, 1624–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saroff, H.; Lewis, M. The binding of calcium ions to serum albumin. J. Phys. Chem. 1963, 67, 1211–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Lenhart, J.J.; Walker, H.W. Dissolution-accompanied aggregation kinetics of silver nanoparticles. Langmuir 2010, 26, 16690–16698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettit, N.; Smith, A.; Freedman, R.; Burns, R.G. Soil urease: Activity, stability and kinetic properties. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1976, 8, 479–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Quinn, A.; You, Y.-H.; McShane, M.J. Hydrogel Microdomain Encapsulation of Stable Functionalized Silver Nanoparticles for SERS pH and Urea Sensing. Sensors 2019, 19, 3521. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19163521
Quinn A, You Y-H, McShane MJ. Hydrogel Microdomain Encapsulation of Stable Functionalized Silver Nanoparticles for SERS pH and Urea Sensing. Sensors. 2019; 19(16):3521. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19163521
Chicago/Turabian StyleQuinn, Alexander, Yil-Hwan You, and Michael J. McShane. 2019. "Hydrogel Microdomain Encapsulation of Stable Functionalized Silver Nanoparticles for SERS pH and Urea Sensing" Sensors 19, no. 16: 3521. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19163521
APA StyleQuinn, A., You, Y.-H., & McShane, M. J. (2019). Hydrogel Microdomain Encapsulation of Stable Functionalized Silver Nanoparticles for SERS pH and Urea Sensing. Sensors, 19(16), 3521. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19163521




