Smartphone-Based Microfluidic Colorimetric Sensor for Gaseous Formaldehyde Determination with High Sensitivity and Selectivity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. AHMT Method
2.2. Standard Gaseous Formaldehyde
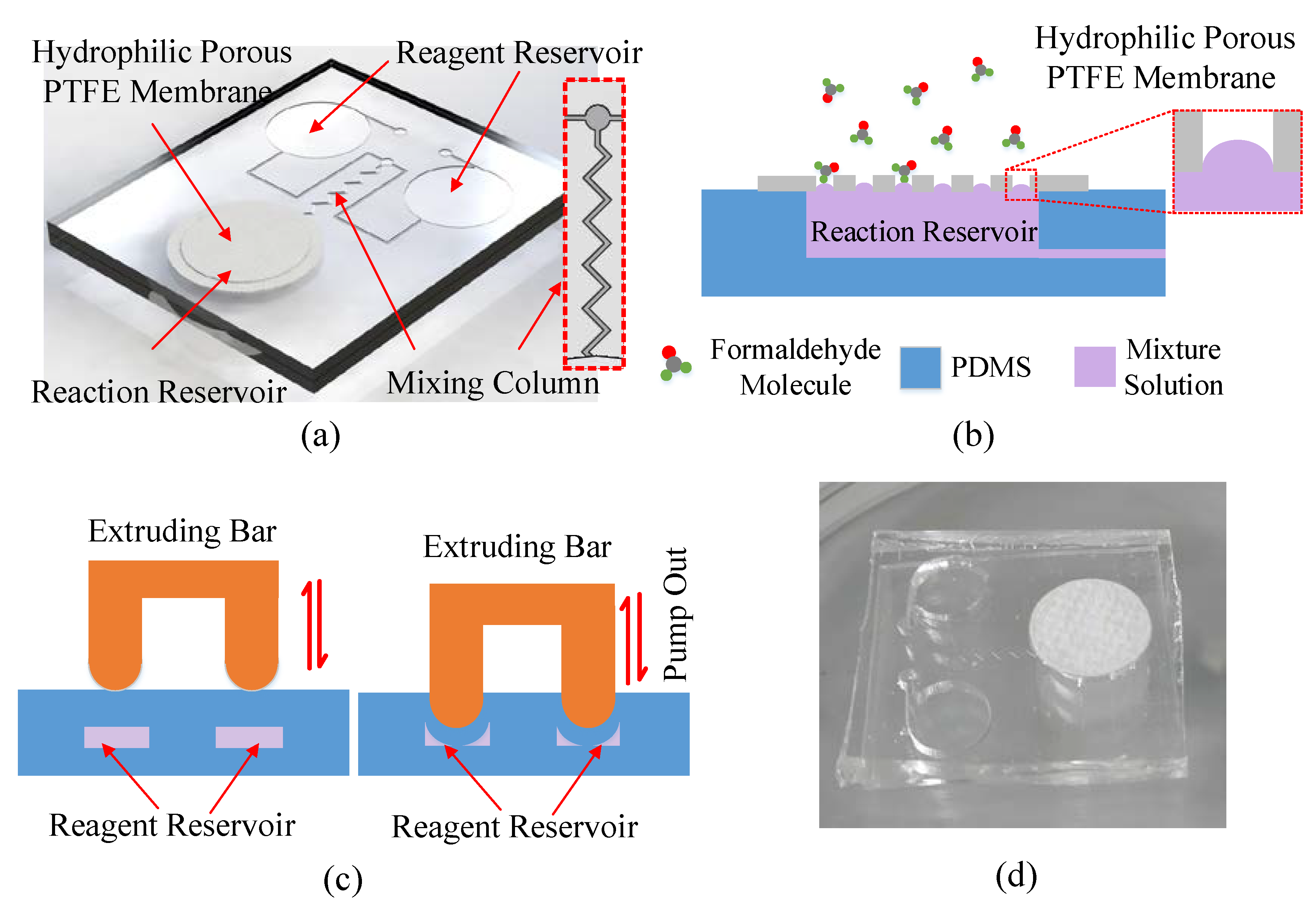
2.3. Microfluidic Chip Configuration
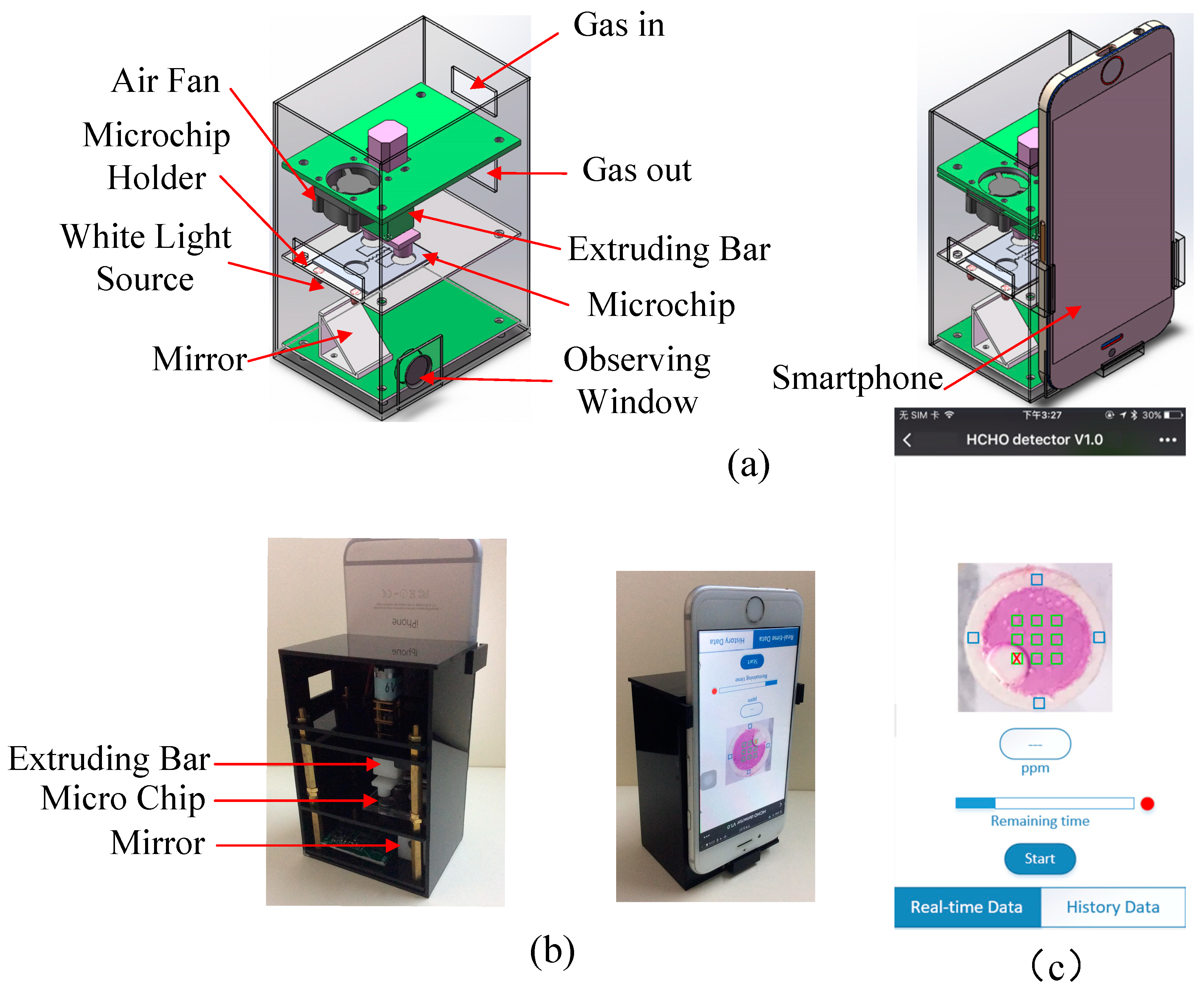
2.4. Smartphone-Based Formaldehyde Determination System
3. Results and Discussion
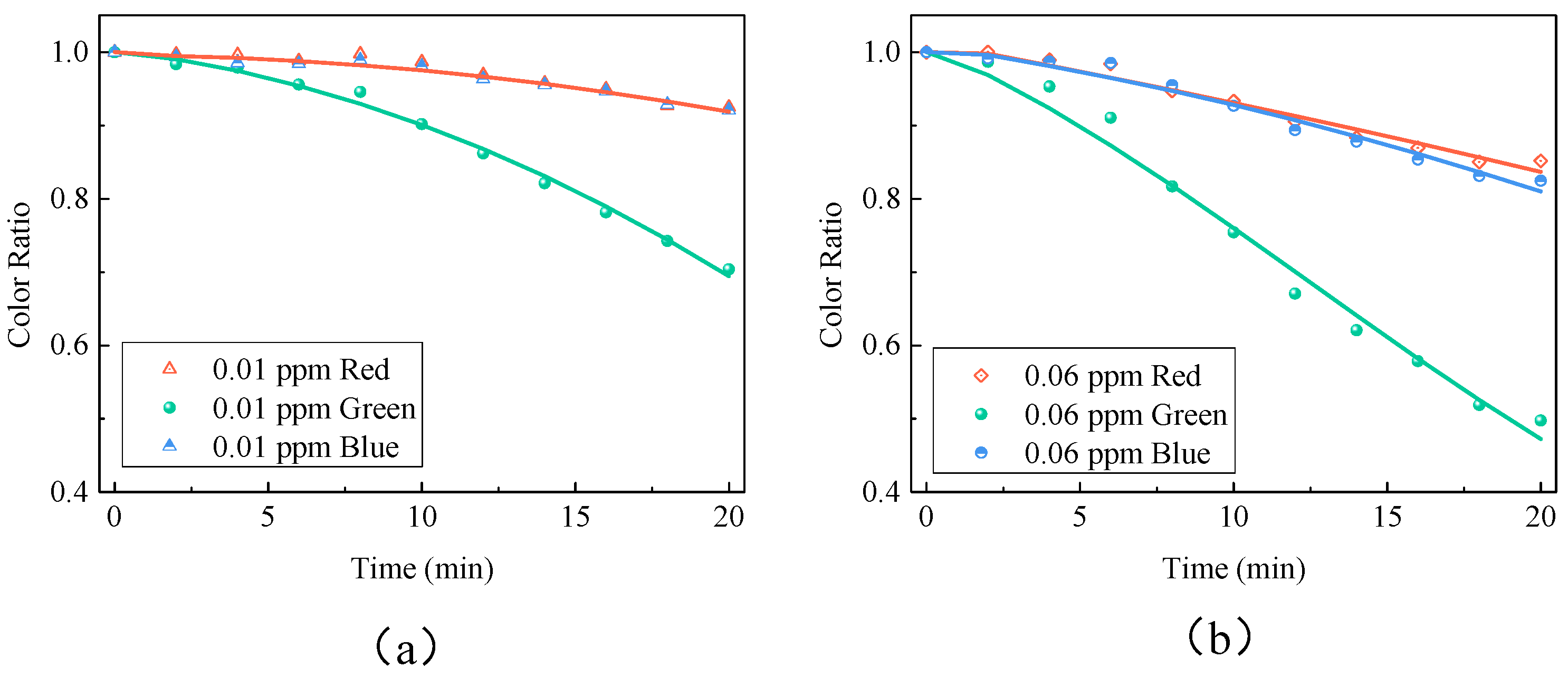
3.1. Relationship between Sampling Time and Color Ratios
3.2. Calibration of Smartphone-Based Microfluidic Colorimetric Sensor for Gaseous Formaldehyde Determination
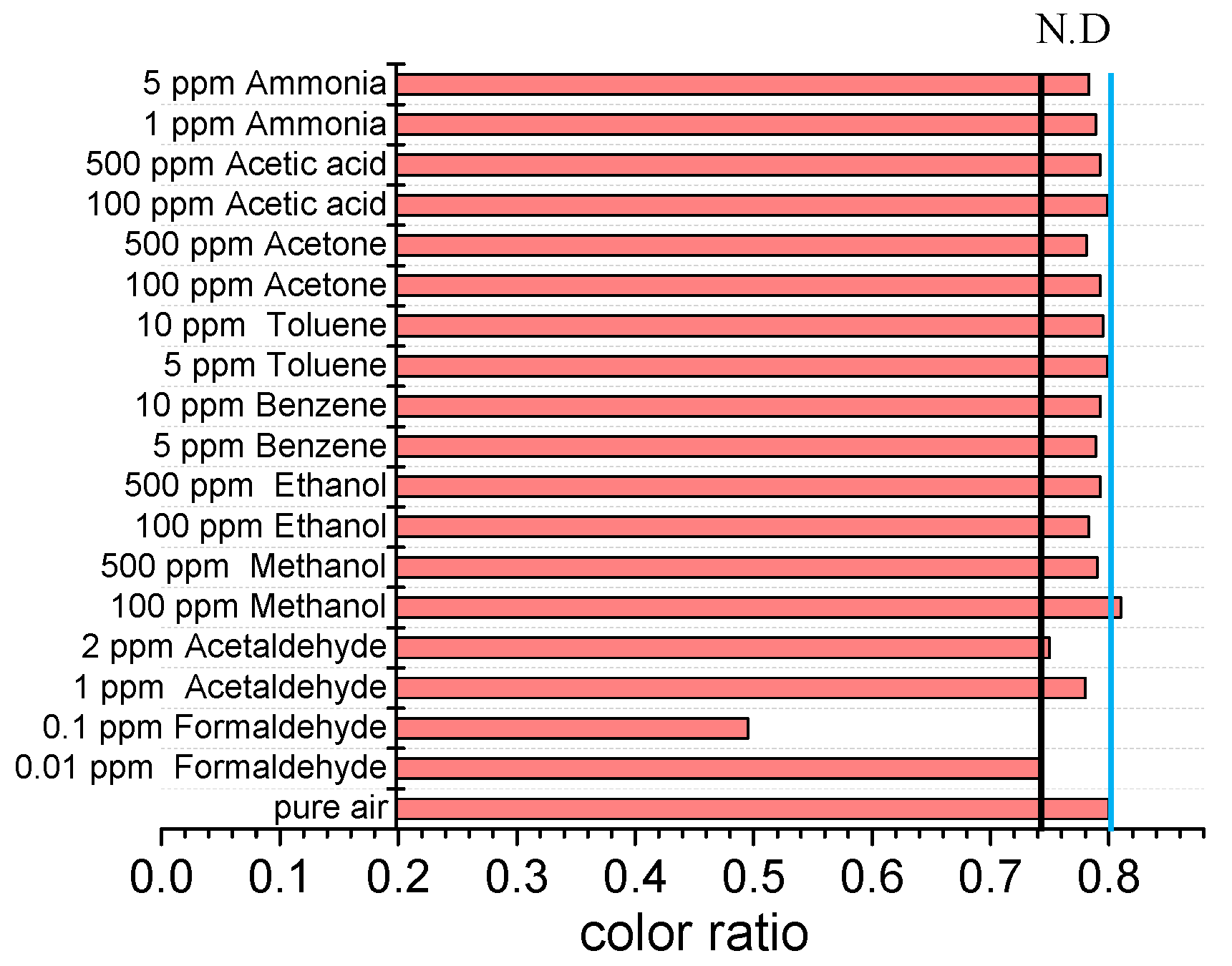
3.3. Selectivity of the Smartphone-Based Microfluidic Colorimetric Sensor
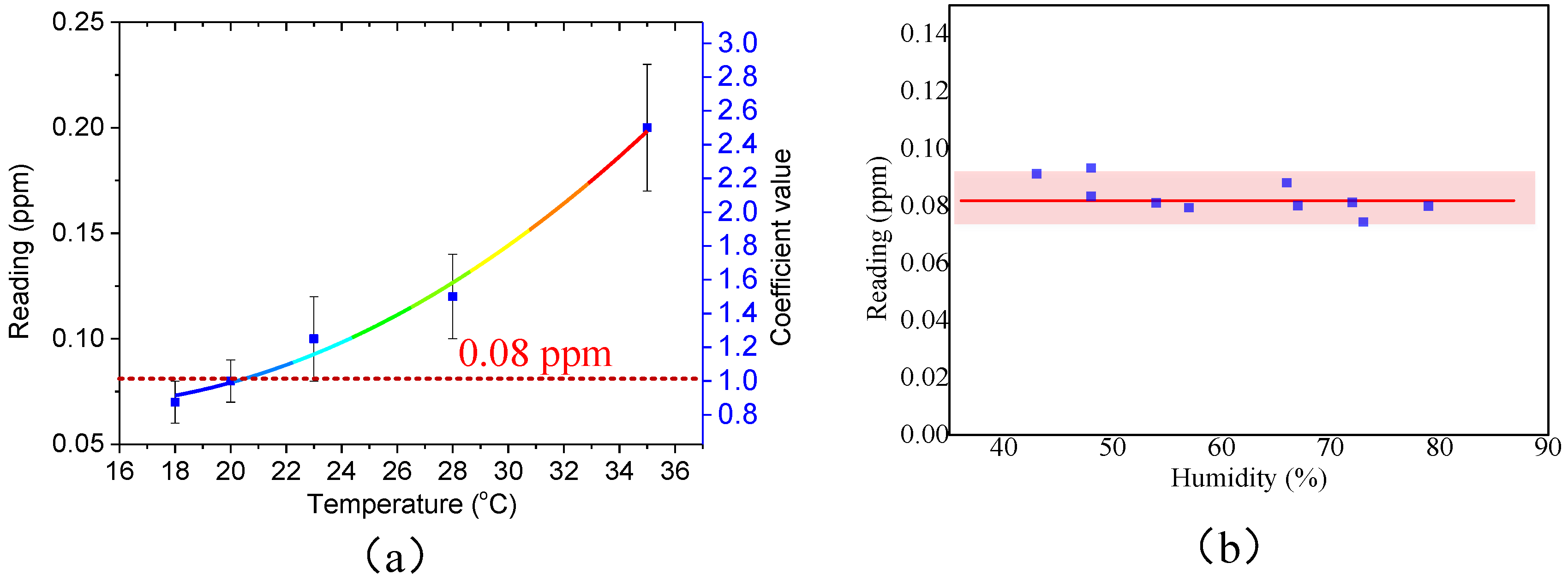
3.4. Effect of Temperature and Humidity
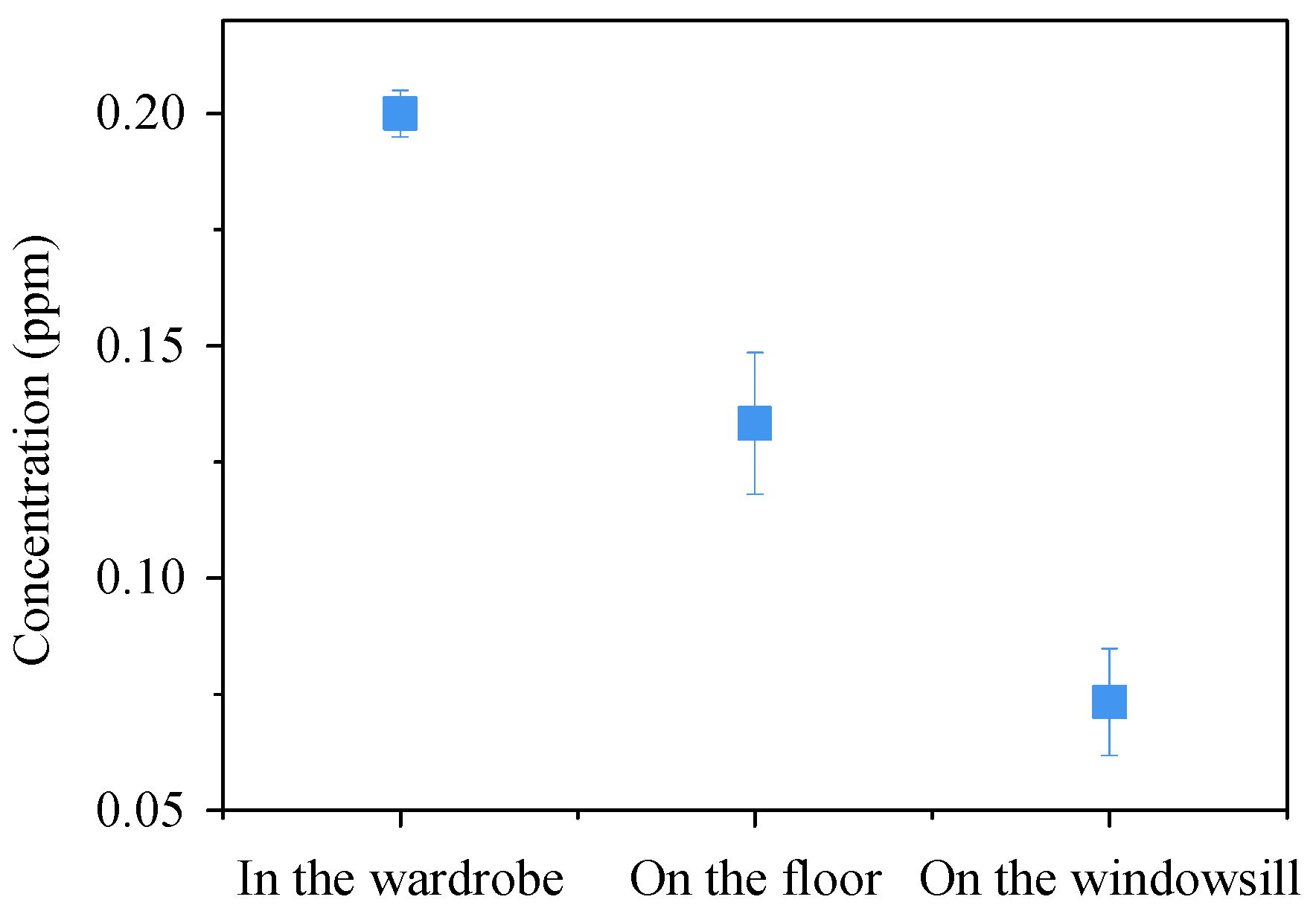
3.5. Determination of Formaldehyde in a Newly Decorated House
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tang, X.J.; Bai, Y.; Duong, A.; Smith, M.T.; Li, L.Y.; Zhang, L.P. Formaldehyde in China: Production, consumption, exposure levels, and health effects. Environ. Int. 2009, 35, 1210–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Material Safety Data Sheet Formaldehyde Solution, Reagnt, ACS MSDS. Available online: http://www.sciencelab.com/msds.php?msdsId=9924094 (accessed on 4 September 2018).
- Bunkoed, O.; Davis, F.; Kanatharana, P.; Thavarungkul, P.; Higson, S.P.J. Sol-gel based sensor for selective formaldehyde determination. Anal. Chim. Acta 2010, 659, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hopkins, J.R.; Still, T.; Al-Haider, S.; Fisher, I.R.; Lewis, A.C.; Seakins, P.W. A simplified apparatus for ambient formaldehyde detection via GC-pHID. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 2557–2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, F.R.; Coelho, L.H.G.; Lopes, M.L.A.; Carvalho, L.R.F.; da Silva, J.A.F.; do Lago, C.L.; Gutz, I.G.R. Environmental formaldehyde analysis by active diffusive sampling with a bundle of polypropylene porous capillaries followed by capillary zone electrophoretic separation and contactless conductivity detection. Talanta 2008, 76, 271–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dirksen, J.A.; Duval, K.; Ring, T.A. NiO thin-film formaldehyde gas sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2001, 80, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.Y.; Chiang, C.M.; Wang, Y.H.; Ma, R.H. A self-heating gas sensor with integrated NiO thin-film for formaldehyde detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2007, 122, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Xing, R.Q.; Song, J.; Xu, W.; Song, H.W. ZnO-SnO2 nanotubes surface engineered by Ag nanoparticles: Synthesis, characterization, and highly enhanced HCHO gas sensing properties. J. Mater. Chem. C 2013, 1, 2174–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, P.; Tang, Z.A.; Yu, J.; Zhang, F.T.; Wei, G.F.; Huang, Z.X.; Hu, Y. Study on a micro-gas sensor with SnO2-NiO sensitive film for indoor formaldehyde detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2008, 132, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.Q.; Ha, X.H.; Lou, X.D.; Xi, G.X.; Han, H.J.; Gao, Q.H. Selective detection of HCHO gas using mixed oxides of ZnO/ZnSnO3. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2007, 120, 694–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, P.; Qi, J.Q.; Yao, P.J. Silicon-based micro-gas sensors for detecting formaldehyde. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2009, 136, 399–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, C.P.; Cui, Y.W.; Wang, L.Y.; Sheng, E.H.; Shim, J.J.; Huang, J.R. Synthesis of the porous NiO/SnO2 microspheres and microcubes and their enhanced formaldehyde gas sensing performance. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 241, 298–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Liu, Y.J.; Zhou, X.D.; Hu, J.M. The fabrication and characterization of a formaldehyde odor sensor using molecularly imprinted polymers. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2005, 284, 378–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fatibello-Filho, O.; Suleiman, A.A.; Guilbault, G.G. Piezoelectric crystal sensor for the determination of formaldehyde in air. Talanta 1991, 38, 541–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunde, R.L.; Jarvi, E.J.; Rosentreter, J.J. A piezoelectric method for monitoring formaldehyde induced crosslink formation between poly-lysine and poly-deoxyguanosine. Talanta 2000, 51, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsubayashi, K.; Nishio, G.; Sawai, M.; Saito, T.; Kudo, H.; Saito, H.; Otsuka, K.; Noguer, T.; Marty, J.L. A bio-sniffer stick with FALDH (formaldehyde dehydrogenase) for convenient analysis of gaseous formaldehyde. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2008, 130, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demkiv, O.; Smutok, O.; Paryzhak, S.; Gayda, G.; Sultanov, Y.; Guschin, D.; Shkil, H.; Schuhmann, W.; Gonchar, M. Reagentless amperometric formaldehyde-selective biosensors based on the recombinant yeast formaldehyde dehydrogenase. Talanta 2008, 76, 837–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pretto, A.; Milani, M.R.; Cardoso, A.A. Colorimetric determination of formaldehyde in air using a hanging drop of chromotropic acid. J. Environ. Monit. 2000, 2, 566–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gigante, A.C.; Gotardo, M.A.; Tognolli, J.O.; Pezza, L.; Pezza, H.R. Spectrophotometric determination of formaldehyde with chromotropic acid in phosphoric acid medium assisted by microwave oven. Microchem. J. 2004, 77, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruo, Y.Y.; Nakamura, J.; Uchiyama, M.; Higuchi, M.; Izunli, K. Development of formaldehyde sensing element using porous glass impregnated with Schiff’s reagent. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2008, 129, 544–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toda, K.; Yoshioka, K.I.; Mori, K.; Hirata, S. Portable system for near-real time measurement of gaseous formaldehyde by means of parallel scrubber stopped-flow absorptiometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2005, 531, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Q.; Si, Y.; Mao, X.; Li, Y.; Yu, J.Y.; Wang, H.P.; Ding, B. Colorimetric sensor strips for formaldehyde assay utilizing fluoral-p decorated polyacrylonitrile nanofibrous membranes. Analyst 2013, 138, 5129–5136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guglielmino, M.; Bernhardt, P.; Trocquet, C.; Serra, C.A.; Le Calve, S. On-line gaseous formaldehyde detection by a microfluidic analytical method based on simultaneous uptake and derivatization in a temperature controlled annular flow. Talanta 2017, 172, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vignau-Laulhere, J.; Plaisance, H.; Mocho, P.; Raulin, K.; Bigay, Y.; Desauziers, V. Performance of the Radiello (R) diffusive sampler for formaldehyde measurement: The influence of exposure conditions and ozone interference. Anal. Methods 2015, 7, 5497–5503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruo, Y.Y.; Nakamura, J.; Uchiyama, M. Development of formaldehyde sensing element using porous glass impregnated with beta-diketone. Talanta 2008, 74, 1141–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzman, J.M.C.C.; Tayo, L.L.; Liu, C.C.; Wang, Y.N.; Fu, L.M. Rapid microfluidic paper-based platform for low concentration formaldehyde detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 255, 3623–3629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.C.; Wang, Y.N.; Fu, L.M.; Huang, Y.H. Microfluidic paper-based chip platform for formaldehyde concentration detection. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 332, 695–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamura, K.; Kerman, K.; Fujihara, M.; Nagatani, N.; Hashiba, T.; Tamiya, E. Development of a novel hand-held formaldehyde gas sensor for the rapid detection of sick building syndrome. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2005, 105, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanderwal, J.F.; Korf, C.; Kuypers, A.T.J.M.; Neele, J. Interference by Chemicals in the Determination of Formaldehyde. Environ. Int. 1989, 15, 517–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motyka, K.; Mikuska, P. Continuous fluorescence determination of formaldehyde in air. Anal. Chim. Acta 2004, 518, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruo, Y.Y.; Nakamura, J. Portable formaldehyde monitoring device using porous glass sensor and its applications in indoor air quality studies. Anal. Chim. Acta 2011, 702, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugita, T.; Ishiwata, H.; Yoshihira, K. Comparative Studies on the Determination of Formaldehyde by the Acetylacetone and 4-Amino-3-Hydrazino-5-Mercapto-1,2,4-Triazole Methods. J. Food Hyg. Soc. Jpn. 1988, 29, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Dasgupta, P.K. Solubility of Gaseous Formaldehyde in Liquid Water and Generation of Trace Standard Gaseous Formaldehyde. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1986, 20, 637–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekine, Y.; Katori, R.; Tsuda, Y.; Kitahara, T. Colorimetric monitoring of formaldehyde in indoor environment using built-in camera on mobile phone. Environ. Technol. 2016, 37, 1647–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, X.-L.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, H.-L.; Qiu, X.-B.; Yu, D.-L. Smartphone-Based Microfluidic Colorimetric Sensor for Gaseous Formaldehyde Determination with High Sensitivity and Selectivity. Sensors 2018, 18, 3141. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18093141
Guo X-L, Chen Y, Jiang H-L, Qiu X-B, Yu D-L. Smartphone-Based Microfluidic Colorimetric Sensor for Gaseous Formaldehyde Determination with High Sensitivity and Selectivity. Sensors. 2018; 18(9):3141. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18093141
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Xiao-Liang, Yan Chen, Hong-Lan Jiang, Xian-Bo Qiu, and Du-Li Yu. 2018. "Smartphone-Based Microfluidic Colorimetric Sensor for Gaseous Formaldehyde Determination with High Sensitivity and Selectivity" Sensors 18, no. 9: 3141. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18093141
APA StyleGuo, X.-L., Chen, Y., Jiang, H.-L., Qiu, X.-B., & Yu, D.-L. (2018). Smartphone-Based Microfluidic Colorimetric Sensor for Gaseous Formaldehyde Determination with High Sensitivity and Selectivity. Sensors, 18(9), 3141. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18093141




