Highly Sensitive FPW-Based Microsystem for Rapid Detection of Tetrahydrocannabinol in Human Urine
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Fabrication of FPW-Based THC Biosensor and Design of Readout System Circuit
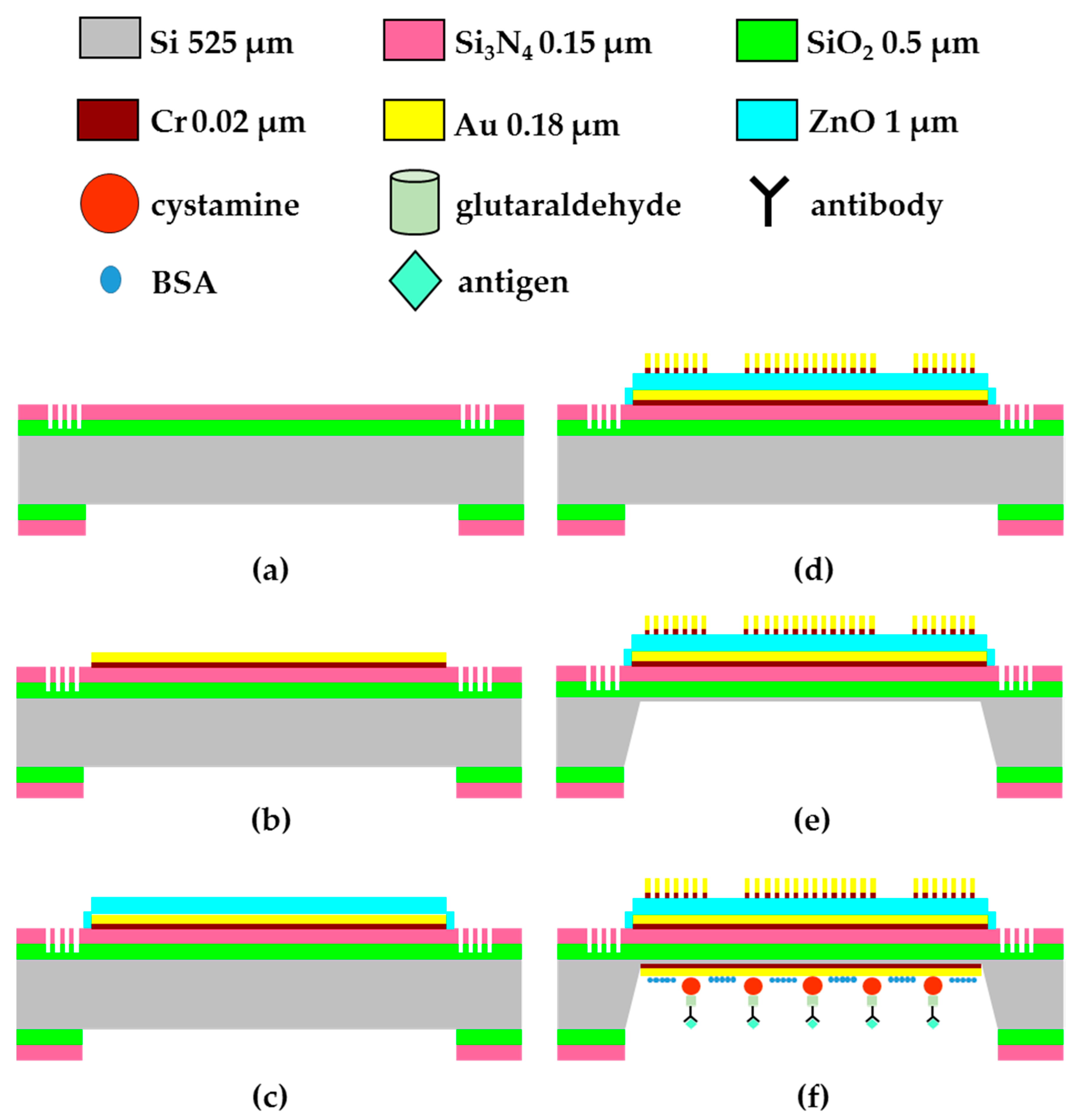
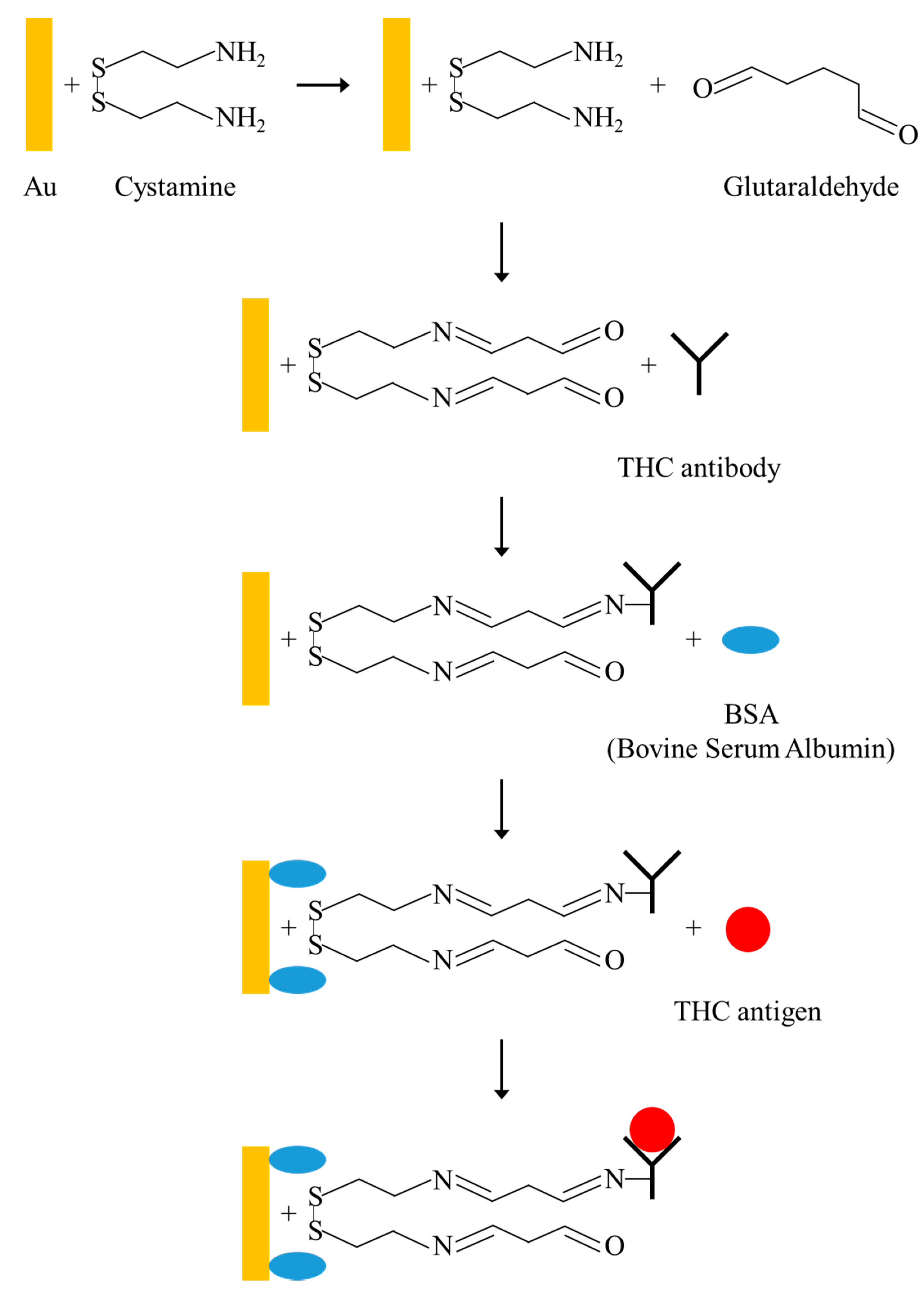
2.1. Fabrication of FPW-Based THC Biosensor
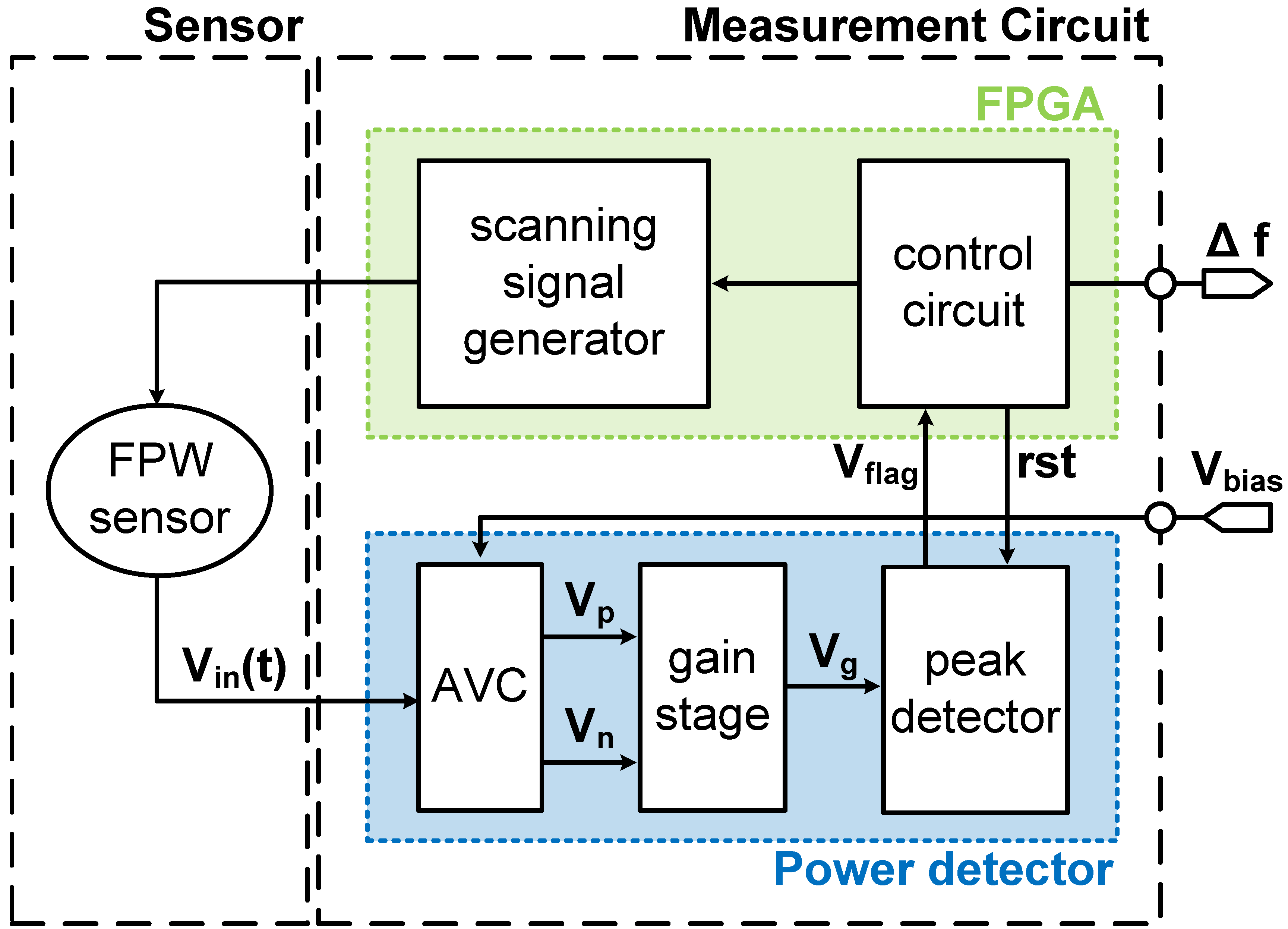
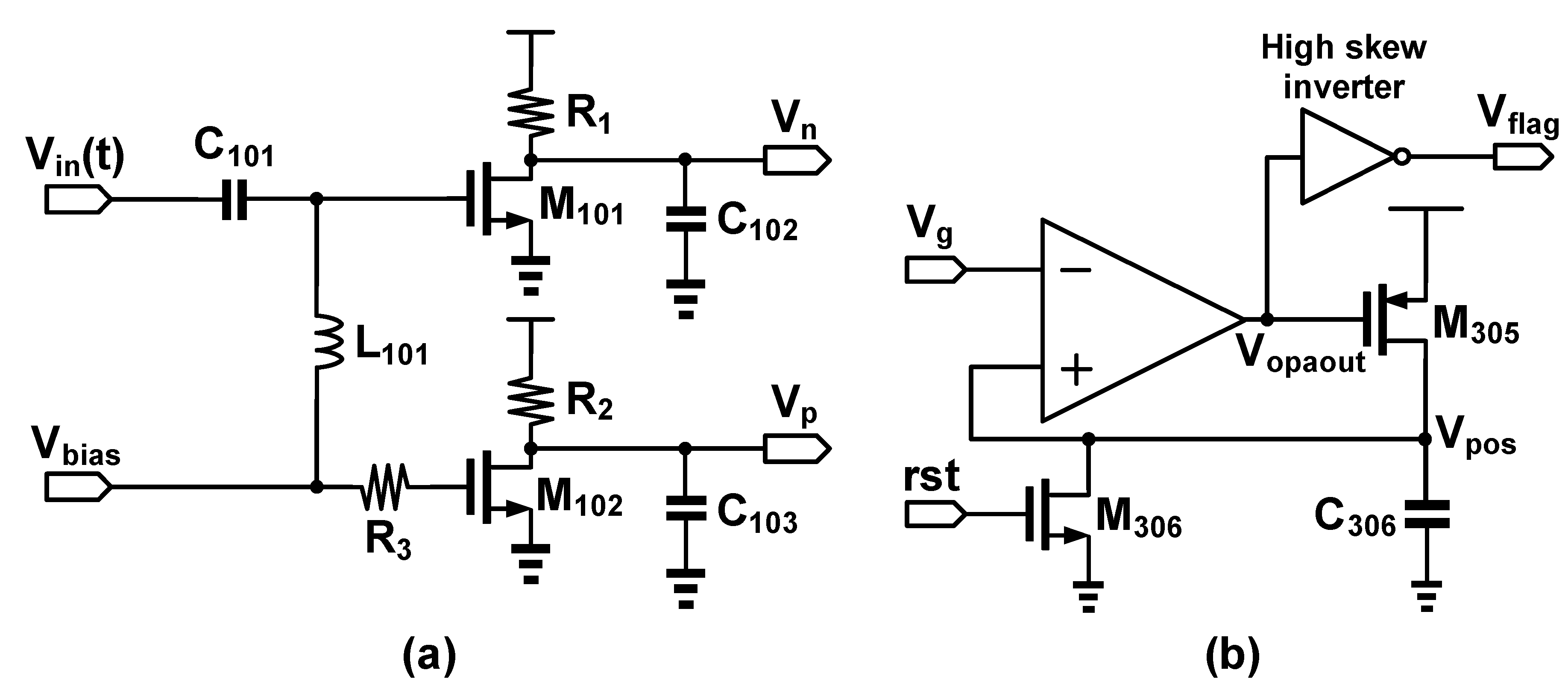
2.2. FPW Readout System Circuit Design
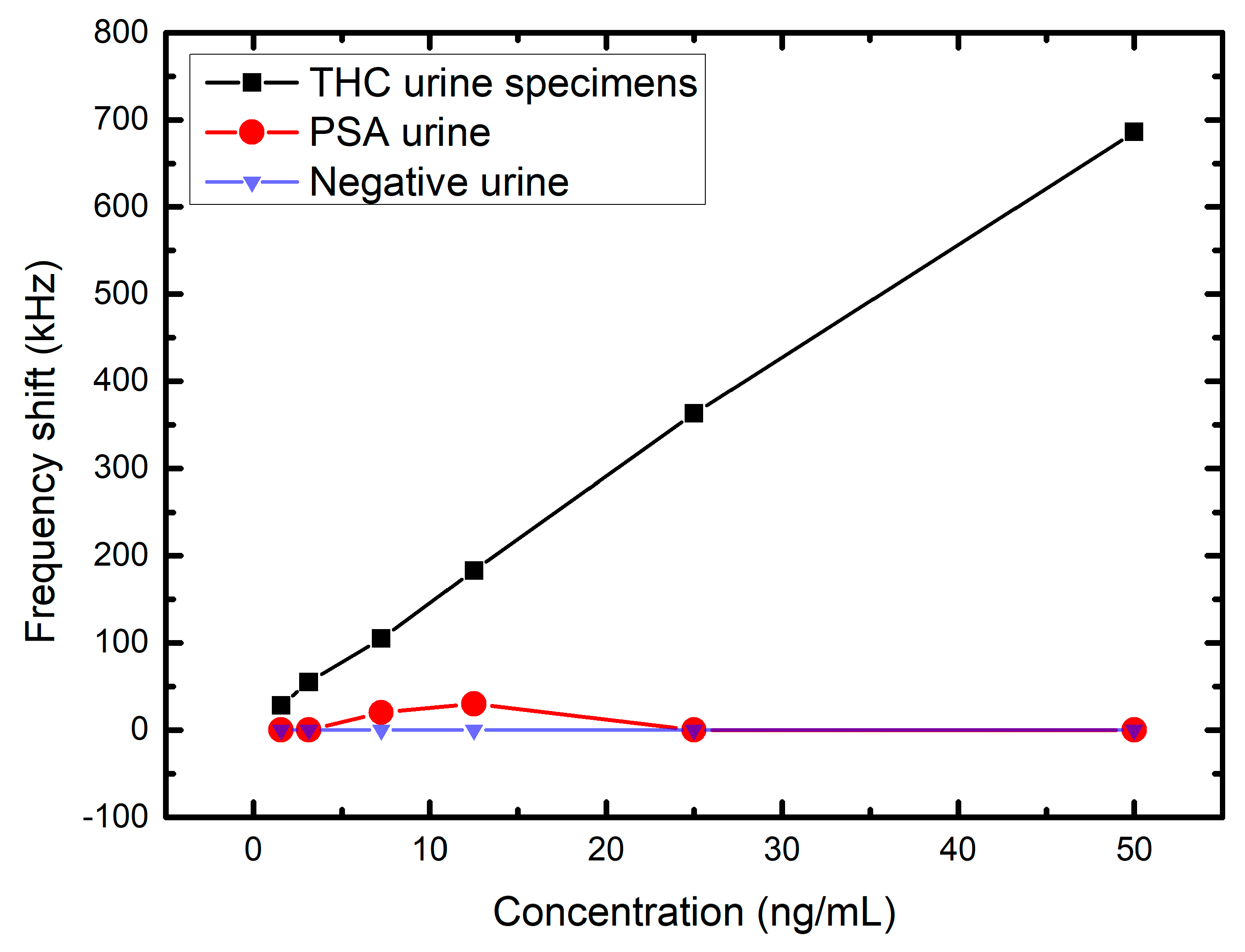
2.3. Preparation of the THC Urine Specimens
3. Experimental Results and Analysis
3.1. Characterization of the Proposed FPW-Based THC Biosensor
3.2. Measurement of FPW Readout System Prototype
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, S.F.; Hsu, J.; Tsay, W.I. The trend of drug abuse in Taiwan during the years 1999 to 2011. J. Food Drug Anal. 2013, 4, 390–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.Y.; Yu, W.J.; Chang, W.T.; Han, E.; Chung, H.; Li, J.H. Comparison of illegal drug use pattern in Taiwan and Korea from 2006 to 2014. Subst. Abuse Treat. Prev. Policy 2016, 11, 624–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wohlfarth, A.; Weinmann, W. Bioanalysis of new designer drugs. Bioanalysis 2010, 2, 965–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agius, R.; Nadulski, T.; Moore, M. Validation of LUCIO®-Direct-ELISA kits for the detection of drugs of abuse in urine: Application to the new German driving licenses re-granting guidelines. Forensic Sci. Int. 2012, 215, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.S. Optical biosensors for label-free detection of biomolecular interactions. Instrum. Sci. Technol. 2014, 42, 109–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backer, B.D.; Debrus, B.; Lebrun, P.; Theunis, L.; Dubois, N.; Decock, L.; Verstraete, A.; Hubert, P.; Charlier, C. Innovative development and validation of an HPLC/DAD method for the qualitative and quantitative determination of major cannabinoids in cannabis plant material. J. Chromatogr. B 2009, 877, 4115–4124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zgair, A.; Wong, J.C.M.; Sabri, A.; Fischer, P.M.; Barrett, D.A.; Constantinescu, C.S.; Gershkovich, P. Development of a simple and sensitive HPLC–UV method for the simultaneous determination of cannabidiol and ∆9-tetrahydrocannabinol in rat plasma. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2015, 114, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caplan, Y.H. Abbott phencyclidine and barbiturates abused drug assays: Valuation and comparison ofADx FPIA, TDx FPIA, EMIT, and GC/MS methods. J. Forensic Sci. 1989, 34, 289–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.Y.; Kim, J.Y.; Kwon, W.; In, M.K.; Kim, Y.E.; Paeng, K.-J. Method development for simultaneous determination of amphetamine type stimulants and cannabinoids in urine using GC-MS. Microchem. J. 2013, 110, 326–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geiser, L.; Cherkaoui, S.; Veuthey, J.L. Simultaneous analysis of some amphetamine derivatives in urine by nonaqueous capillary capillary electrophoresis coupled to electrospary ionization mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2000, 895, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, I.Y.; Lee, M.C. Development of a FPW allergy biosensor for human IgE detection by MEMS and cystamine-based SAM technologies. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2008, 132, 340–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamurthy, S.; Atashbar, M.Z.; Bazuin, B.J. Burst transceiver unit for wireless passive SAW sensing system. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2009, 58, 3476–3753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballantine, D.S., Jr.; White, R.M.; Martin, S.J.; Ricco, A.J.; Frye, G.C.; Zellars, E.T.; Wohltjen, H. Acoustic Wave Sensors: Theory, Design, and Physicochemical Application; Academic Press: Salt Lake, UT, USA, 1996; pp. 36–134. [Google Scholar]
- Grate, J.W.; Stephen, J.M.; Richard, M.W. Acoustic wave microsensors. Anal. Chem. 1993, 65, 940A–948A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, V.; Lucklum, R. Overview of Acoustic-Wave Microsensors: In Piezoelectric Transducers and Applications, 2nd ed.; Arnau, A., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.C.; Sung, T.C.; Liao, C.H.; Chang, C.M.; Lan, J.W.; Huang, I.Y. A CEA concentration measurement system using FPW biosensors and frequency-shift readout IC. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Electronics, Circuits and Systems (ICECS), Busan, Korea, 17–19 November 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Lan, J.W.; Huang, I.Y.; Lin, Y.C.; Lin, C.Y.; Chen, J.L.; Hsieh, C.H. Development of an FPW Biosensor with Low Insertion Loss and High Fabrication Yield for Detection of Carcinoembryonic Antigen. Sensors 2016, 16, 1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schreiber, F. Structure and growth of self-assembling monolayers. Prog. Surf. Sci. 2000, 65, 151–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, J.C.; Estroff, L.A.; Kriebel, J.K.; Nuzzo, R.G.; Whitesides, G.M. Self-assembled monolayers of thiolates on metals as a form of nanotechnology. Chem. Rev. 2005, 105, 1103–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vericat, C.; Vela, M.E.; Corthey, G.; Pensa, E.; Cortes, E.; Fonticelli, M.H.; Ibanez, F.; Benitez, G.E.; Carro, P.; Salvarezza, R.C. Self-assembled monolayers of thiolateson metals: A review article on sulfur-metal chemistry and surface structures. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 27730–27754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.H.; Lin, Y.R.; Tsai, Y.D.; Chen, Y.C.; Wang, C.C. A frequency-shift readout system for FPW allergy biosensor. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on IC Design Technology (ICICDT), Kaohsiung, Taiwan, 2–4 May 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.C.; Hsu, C.H.; Tsai, Y.D.; Chen, Y.C.; Lee, M.C.; Huang, I.Y. A fast FPW-based protein concentration measurement system. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), Seoul, Korea, 20–23 May 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, T.J.; Hsiao, W.C.; Wang, C.C. 20 MHz accurate peak detector for FPW allergy biosensor with digital calibration. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Integrated Circuits (ISIC), Singapore, 12–14 December 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.C.; Wang, D.S.; Chen, S.Y.; Chang, C.M. A wide range and high conversion gain power detector for frequency shift sensing applications. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Midwest Symposium on Circuits and Systems (MWSCAS), Fort Collins, CO, USA, 2–5 August 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.H.; Wang, C.C. Feed-forward output swing prediction AGC with parallel-detect singular-store peak detector. Microelectron. J. 2012, 43, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Product Information of MaxSignal® THC ELISA Test Kit. Available online: http://www.biooscientific.com/Forensic-Drug-Detection/MaxSignal-THC-ELISA-Test-Kit (accessed on 11 April 2016).
- Khajuria, H.; Nayak, B.P. Detection of ∆9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) in hair using GC-MS. Egypt. J. Forensic Sci. 2014, 4, 17–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.C.; Liao, C.H.; Chang, C.M.; Lan, J.W.; Huang, I.Y. A fast CEA analyzer prototype for point of care testing. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Electron Devices and Solid-State Circuits (EDSSC), Chengdu, China, 18–20 June 2014. [Google Scholar]

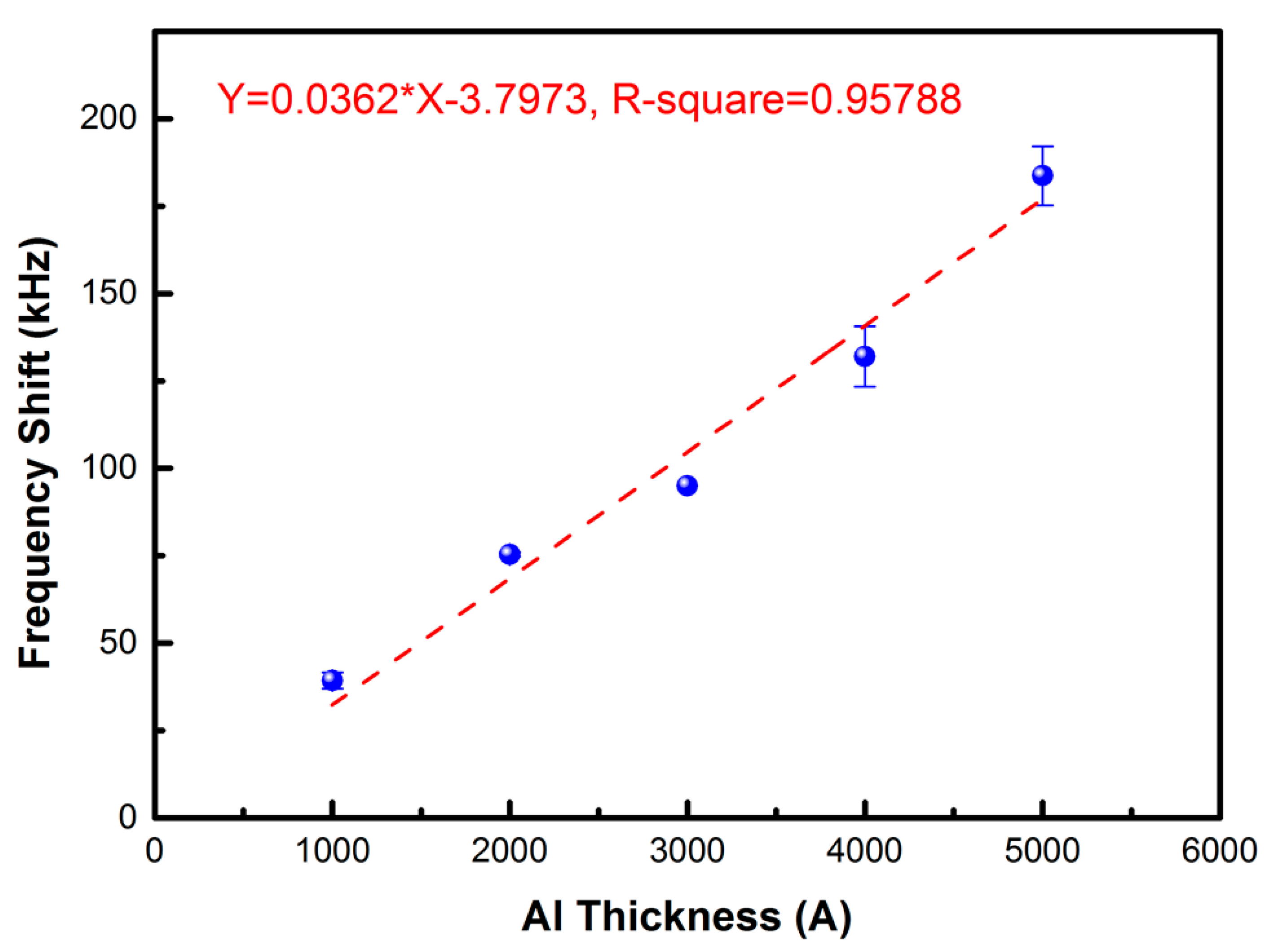
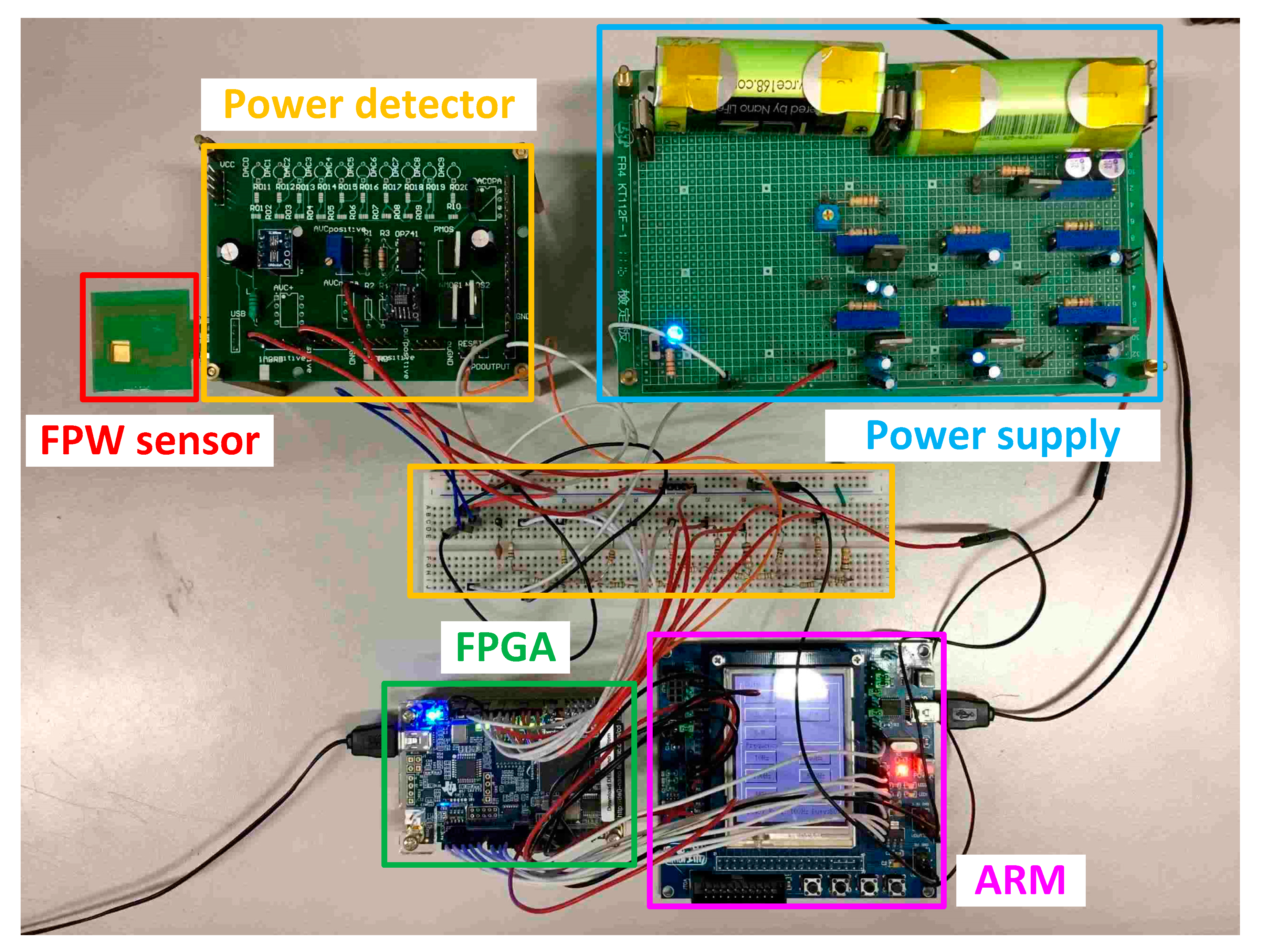
| Device | Mass Sensitivity (cm2/g) | Motion at Surface | Wave Velocity (Relative to Liquid) | Operating Frequency (MHz) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TSM | 1–10 | Transverse | Fast | 1–10 |
| SAW | 100–200 | Transverse and normal | Fast | 30–300 |
| APM | 20–40 | Transverse | Fast | 25–200 |
| FPW | 100–1000 | Transverse and normal | Slow | 2–20 |
| References | This Work | [26] | [7] | [27] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Technology | FPW | ELISA | HPLC | GC/MS |
| Year | 2017 | 2017 | 2015 | 2014 |
| Detection time | <10 min | <2 h | >20 min | >1 h |
| Limit of detection | 1.5625 ng/mL | 0.1 ng/mL | 10 ng/mL | 0.1 ng/mg |
| Linear range | 1.5625–50 ng/mL | 0.05–100 ng/mL | 10–104 ng/mL | 0.16–2.3 ng/mg |
| Testing equipment size | Portable | Non-portable | Massive equipment | Massive equipment |
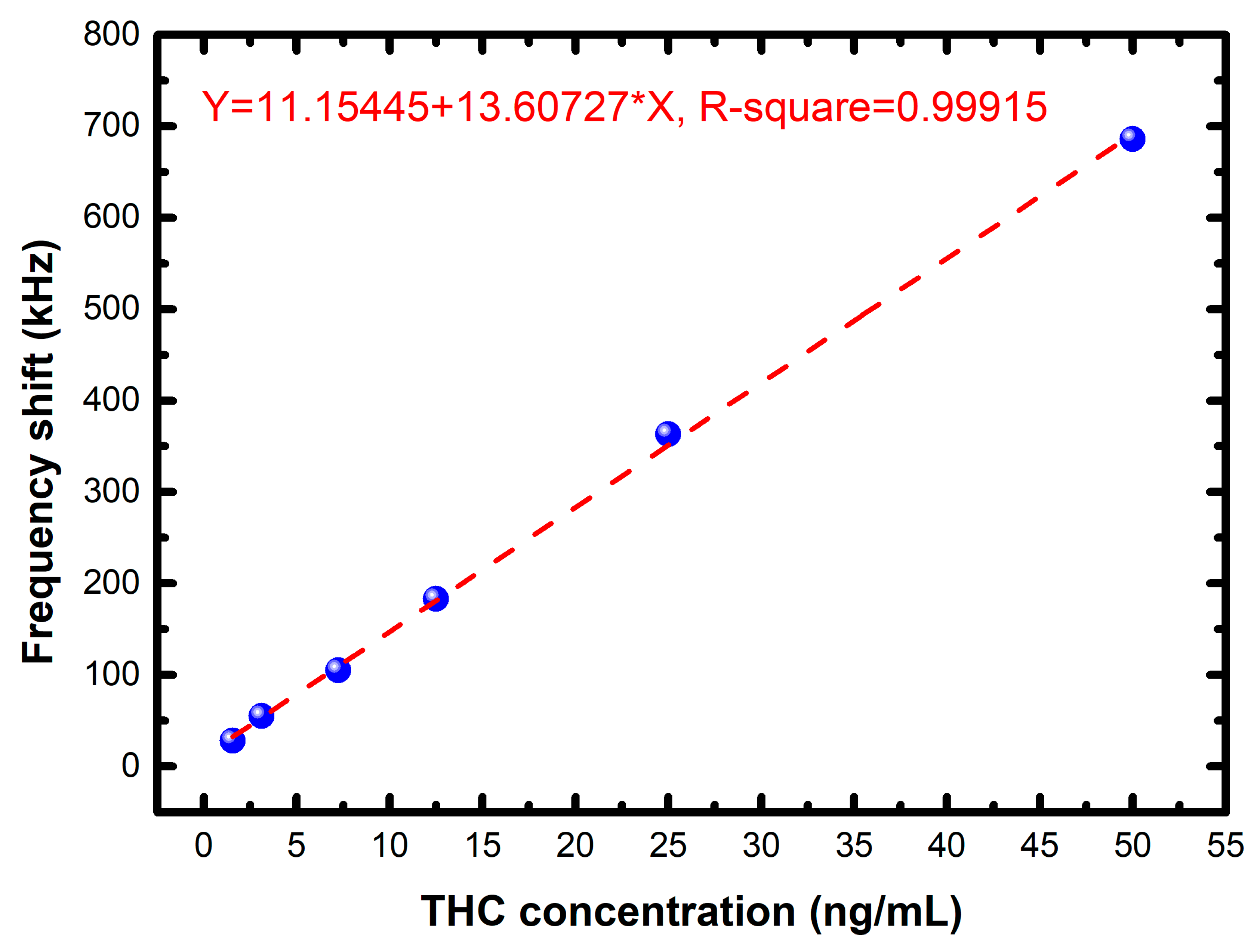
| THC Concentration (ng/mL) | Frequency Shift (kHz) |
|---|---|
| 1.5625 | 28 |
| 3.125 | 55 |
| 7.25 | 105 |
| 12.5 | 183 |
| 25 | 363 |
| 50 | 686 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lan, J.-W.; Hsieh, C.-H.; Huang, I.-Y.; Lin, Y.-C.; Tsai, T.-Y.; Wang, C.-C. Highly Sensitive FPW-Based Microsystem for Rapid Detection of Tetrahydrocannabinol in Human Urine. Sensors 2017, 17, 2760. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17122760
Lan J-W, Hsieh C-H, Huang I-Y, Lin Y-C, Tsai T-Y, Wang C-C. Highly Sensitive FPW-Based Microsystem for Rapid Detection of Tetrahydrocannabinol in Human Urine. Sensors. 2017; 17(12):2760. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17122760
Chicago/Turabian StyleLan, Je-Wei, Chia-Hsu Hsieh, I-Yu Huang, Yu-Cheng Lin, Tsung-Yi Tsai, and Chua-Chin Wang. 2017. "Highly Sensitive FPW-Based Microsystem for Rapid Detection of Tetrahydrocannabinol in Human Urine" Sensors 17, no. 12: 2760. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17122760
APA StyleLan, J.-W., Hsieh, C.-H., Huang, I.-Y., Lin, Y.-C., Tsai, T.-Y., & Wang, C.-C. (2017). Highly Sensitive FPW-Based Microsystem for Rapid Detection of Tetrahydrocannabinol in Human Urine. Sensors, 17(12), 2760. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17122760






