Echinoids and Crinoids from Terra Nova Bay (Ross Sea) Based on a Reverse Taxonomy Approach
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling and DNA Extraction
2.2. Species Delimitation Methods
2.3. Morphological Identification
3. Results
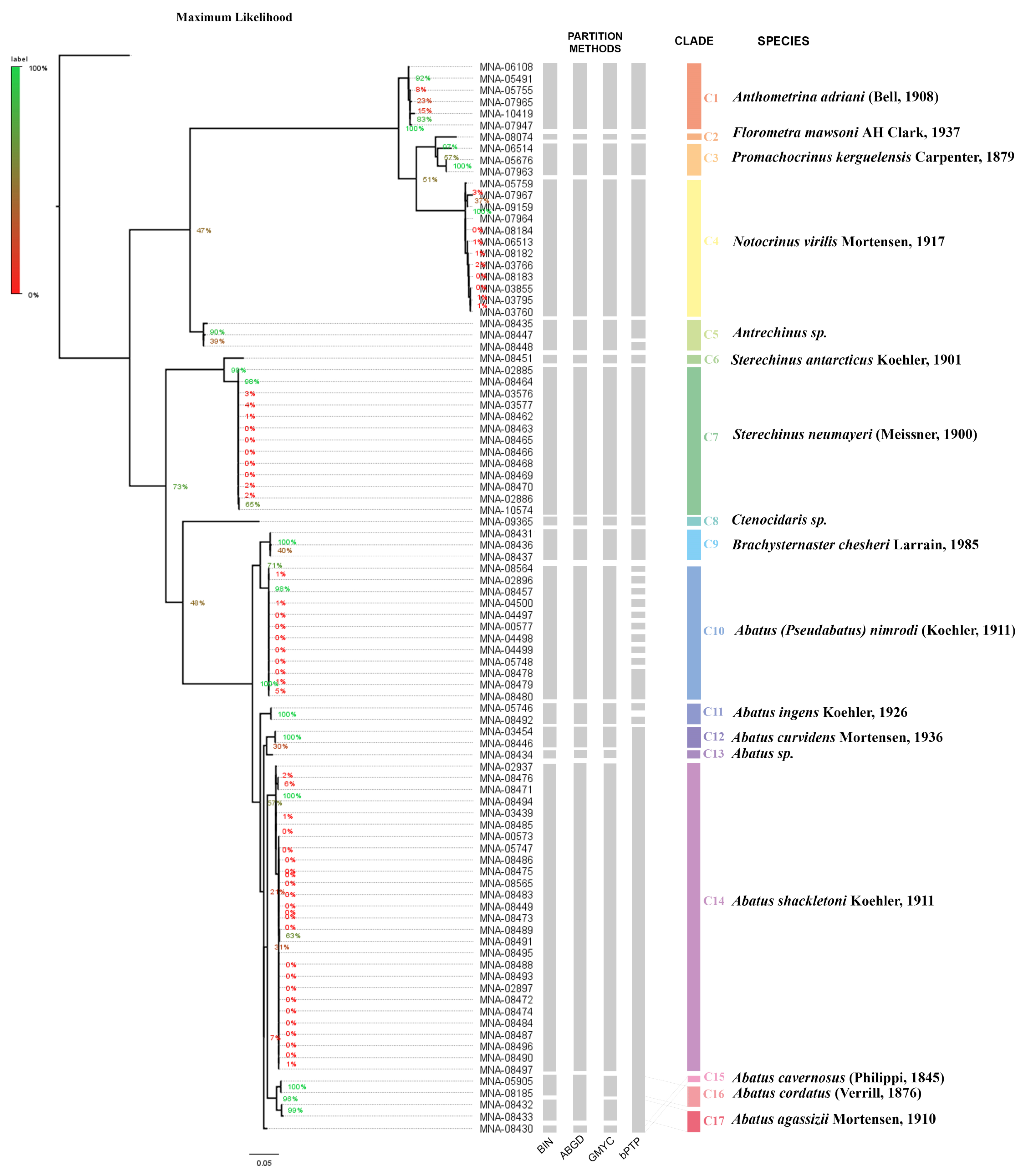
3.1. Molecular Results
3.1.1. Crinoidea
3.1.2. Echinoidea
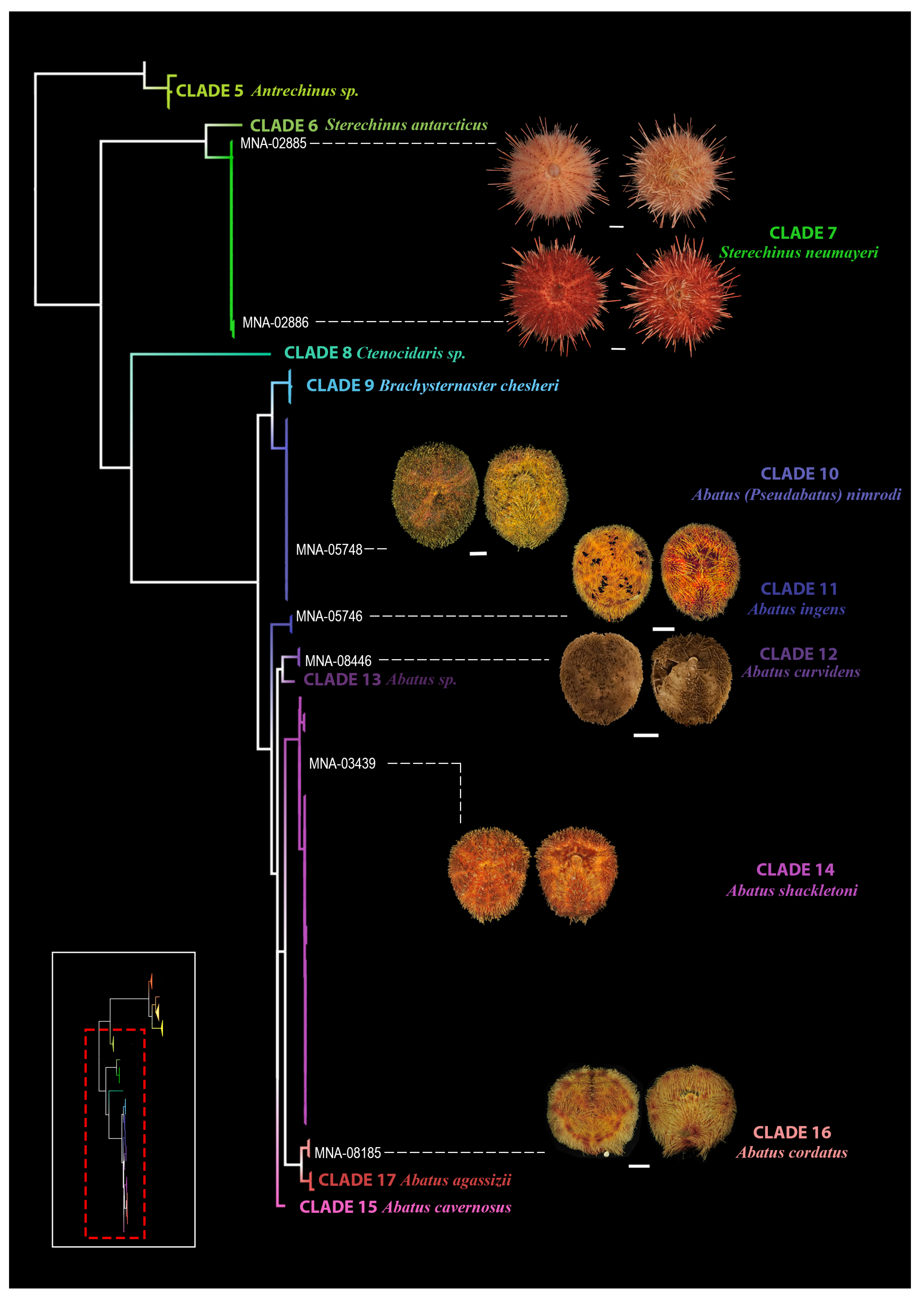
3.2. Morphological Analysis
3.3. Faunistic Inventory Revision
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wilkinson, M.D.; Dumontier, M.; Aalbersberg, I.J.; Appleton, G.; Axton, M.; Baak, A.; Blomberg, N.; Boiten, J.-W.; da Silva Santos, L.B.; Bourne, P.E. The FAIR Guiding Principles for Scientific Data Management and Stewardship. Sci. Data 2016, 3, 160018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenfeld, S.; Maturana, C.S.; Spencer, H.G.; Convey, P.; Saucède, T.; Brickle, P.; Bahamonde, F.; Jossart, Q.; Poulin, E.; Gonzalez-Wevar, C. Complete Distribution of the Genus Laevilitorina (Littorinimorpha: Littorinidae) in the Southern Hemisphere: Remarks and Natural History. ZooKeys 2022, 1127, 61–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebert, P.D.; Cywinska, A.; Ball, S.L.; DeWaard, J.R. Biological Identifications through DNA Barcodes. Proc. R. Soc. London. Ser. B Biol. Sci. 2003, 270, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carstens, B.C.; Pelletier, T.A.; Reid, N.M.; Satler, J.D. How to Fail at Species Delimitation. Mol. Ecol. 2013, 22, 4369–4383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Layton, K.K.; Corstorphine, E.A.; Hebert, P.D. Exploring Canadian Echinoderm Diversity through DNA Barcodes. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0166118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, A.G.; Pérez-Portela, R.; Griffiths, C.L. Determining the Correct Identity of South African Marthasterias (Echinodermata: Asteroidea). Afr. J. Mar. Sci. 2016, 38, 443–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knott, K.E.; Ringvold, H.; Blicher, M.E. Morphological and Molecular Analysis of Henricia Gray, 1840 (Asteroidea: Echinodermata) from the Northern Atlantic Ocean. Zool. J. Linn. Soc. 2018, 182, 791–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peck, L.S.; Clark, M.S.; Dunn, N.I. Morphological Variation in Taxonomic Characters of the Antarctic Starfish Odontaster Validus. Polar Biol. 2018, 41, 2159–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringvold, H.; Moum, T. On the Genus Crossaster (Echinodermata: Asteroidea) and Its Distribution. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0227223. [Google Scholar]
- Jossart, Q.; Kochzius, M.; Danis, B.; Saucède, T.; Moreau, C.V. Diversity of the Pterasteridae (Asteroidea) in the Southern Ocean: A Molecular and Morphological Approach. Zool. J. Linn. Soc. 2021, 192, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzzi, A.; Alvaro, M.C.; Danis, B.; Moreau, C.; Schiaparelli, S. Not All That Glitters Is Gold: Barcoding Effort Reveals Taxonomic Incongruences in Iconic Ross Sea Sea Stars. Diversity 2022, 14, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jossart, Q.; Sands, C.J.; Sewell, M.A. Dwarf Brooder versus Giant Broadcaster: Combining Genetic and Reproductive Data to Unravel Cryptic Diversity in an Antarctic Brittle Star. Heredity 2019, 123, 622–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uthicke, S.; Byrne, M.; Conand, C. Genetic Barcoding of Commercial Bêche-de-Mer Species (Echinodermata: Holothuroidea). Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2010, 10, 634–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christiansen, H.; Dettai, A.; Heindler, F.M.; Collins, M.A.; Duhamel, G.; Hautecoeur, M.; Steinke, D.; Volckaert, F.A.; Van de Putte, A.P. Diversity of Mesopelagic Fishes in the Southern Ocean-A Phylogeographic Perspective Using DNA Barcoding. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 6, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, G.W.; Freckleton, R.P. Declines in the Numbers of Amateur and Professional Taxonomists: Implications for Conservation. Anim. Conserv. Forum 2002, 5, 245–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puillandre, N.; Lambert, A.; Brouillet, S.; Achaz, G. ABGD, Automatic Barcode Gap Discovery for Primary Species Delimitation. Mol. Ecol. 2012, 21, 1864–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puillandre, N.; Modica, M.V.; Zhang, Y.; Sirovich, L.; Boisselier, M.-C.; Cruaud, C.; Holford, M.; Samadi, S. Large-Scale Species Delimitation Method for Hyperdiverse Groups. Mol. Ecol. 2012, 21, 2671–2691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meiklejohn, K.A.; Wallman, J.F.; Dowton, M. DNA Barcoding Identifies All Immature Life Stages of a Forensically Important Flesh Fly (Diptera: Sarcophagidae). J. Forensic Sci. 2013, 58, 184–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, R.D.; Holmes, B.H.; O’HARA, T.D. DNA Barcoding Discriminates Echinoderm Species. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2008, 8, 1202–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bribiesca-Contreras, G.; Solís-Marín, F.A.; Laguarda-Figueras, A.; Zaldívar-Riverón, A. Identification of Echinoderms (Echinodermata) from an Anchialine Cave in C Ozumel I Sland, M Exico, Using DNA Barcodes. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2013, 13, 1137–1145. [Google Scholar]
- Moreau, C.; Danis, B.; Jossart, Q.; Eléaume, M.; Sands, C.; Achaz, G.; Agüera, A.; Saucède, T. Is Reproductive Strategy a Key Factor in Understanding the Evolutionary History of Southern Ocean Asteroidea (Echinodermata)? Ecol. Evol. 2019, 9, 8465–8478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbizu, P.M.; Khodami, S.; Stöhr, S.; Laakmann, S. Molecular Species Delimitation of Icelandic Brittle Stars (Ophiuroidea). Pol. Polar Res. 2014, 35, 243–260. [Google Scholar]
- Boissin, E.; Hoareau, T.B.; Paulay, G.; Bruggemann, J.H. DNA Barcoding of Reef Brittle Stars (Ophiuroidea, Echinodermata) from the Southwestern Indian Ocean Evolutionary Hot Spot of Biodiversity. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 7, 11197–11203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christodoulou, M.; O’Hara, T.; Hugall, A.F.; Khodami, S.; Rodrigues, C.F.; Hilario, A.; Vink, A.; Martinez Arbizu, P. Unexpected High Abyssal Ophiuroid Diversity in Polymetallic Nodule Fields of the Northeast Pacific Ocean and Implications for Conservation. Biogeosciences 2020, 17, 1845–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janosik, A.M.; Mahon, A.R.; Halanych, K.M. Evolutionary History of Southern Ocean Odontaster Sea Star Species (Odontasteridae; Asteroidea). Polar Biol. 2011, 34, 575–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janosik, A.M.; Halanych, K.M. Unrecognized Antarctic Biodiversity: A Case Study of the Genus Odontaster (Odontasteridae; Asteroidea). Integr. Comp. Biol. 2010, 50, 981–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, D.L.; Macurda, D.B. Adaptive Radiation of the Comatulid Crinoids. Paleobiology 1977, 3, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.B.; Gale, A.S.; Monks, N.E. Sea-Level Change and Rock-Record Bias in the Cretaceous: A Problem for Extinction and Biodiversity Studies. Paleobiology 2001, 27, 241–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linse, K.; Walker, L.J.; Barnes, D.K. Biodiversity of Echinoids and Their Epibionts around the Scotia Arc, Antarctica. Antarct. Sci. 2008, 20, 227–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kier, P.M.; Grant, R.E. Echinoid Distribution and Habits, Key Largo Coral Reef Preserve, Florida. Smithson. Misc. Collect. 1965, 149, 1–68. [Google Scholar]
- Nebelsick, J.H. Biodiversity of Shallow-Water Red Sea Echinoids: Implications for the Fossil Record. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. United Kingd. 1996, 76, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, D.K.; Brockington, S. Zoobenthic Biodiversity, Biomass and Abundance at Adelaide Island, Antarctica. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2003, 249, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, B.; Choné, T.; Festeau, A.; Mooi, R.; De Ridder, C. Biodiversity of Antarctic Echinoids: A Comprehensive and Interactive Database. Sci. Mar. 2005, 69, 201–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, B.; Choné, T.; Mooi, R.; de Ridder, C. Antarctic Echinoidea. In Synopsis of the Antarctic Benthos, Volume 10. Theses Zoologicae; Wägele, J.W., Sieg, J., Eds.; Koeltz Scientific Books: Königstein, Germany, 2005; Volume 35, pp. 1–275. [Google Scholar]
- Cerrano, C.; Bavestrello, G.; Calcinai, B.; Cattaneo-Vietti, R.; Sarà, A. Asteroids Eating Sponges from Tethys Bay, East Antarctica. Antarct. Sci. 2000, 12, 425–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiantore, M.; Cattaneo-Vietti, R.; Elia, L.; Guidetti, M.; Antonini, M. Reproduction and Condition of the Scallop Adamussium Colbecki (Smith 1902), the Sea-Urchin Sterechinus Neumayeri (Meissner 1900) and the Sea-Star Odontaster Validus Koehler 1911 at Terra Nova Bay (Ross Sea): Different Strategies Related to Inter-Annual Variations in Food Availability. Polar Biol. 2002, 25, 251–255. [Google Scholar]
- C-CAMLR-XXXV, Report of the Thirty-Fifth Meeting of the Scientific Committee, Hobart, Australia, 17–21 October, Annex 6, 3.2, 3.7-3.9. 2016. CCAMLR CONSERVATION MEASURE 91-05 (2016) for the Ross Sea Region Marine Protected Area, Specifically, Addressing the Priorities of Annex 91-05/C. 2016. Available online: Https://Www.Ccamlr.Org/En/System/Files/e-Sc-Xxxv.Pdf (accessed on 30 May 2023).
- Chiantore, M.; Guidetti, M.; Cavallero, M.; De Domenico, F.; Albertelli, G.; Cattaneo-Vietti, R. Sea Urchins, Sea Stars and Brittle Stars from Terra Nova Bay (Ross Sea, Antarctica). Polar Biol. 2006, 29, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eléaume, M.; Hemery, L.G.; Améziane, N.; Roux, M. Southern Ocean Crinoids. In Biogeographic Atlas of the Southern Ocean; The Scientific Committee on Antarctic Research: Cambridge, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Ghiglione, C.; Alvaro, M.C.; Griffiths, H.J.; Linse, K.; Schiaparelli, S. Ross Sea Mollusca from the Latitudinal Gradient Program: R/V Italica 2004 Rauschert Dredge Samples. ZooKeys 2013, 37–48. [Google Scholar]
- Ghiglione, C.; Alvaro, M.C.; Cecchetto, M.; Canese, S.; Downey, R.; Guzzi, A.; Mazzoli, C.; Piazza, P.; Rapp, H.T.; Sarà, A. Porifera Collection of the Italian National Antarctic Museum (MNA), with an Updated Checklist from Terra Nova Bay (Ross Sea). ZooKeys 2018, 137–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piazza, P.; Blażewicz-Paszkowycz, M.; Ghiglione, C.; Alvaro, M.C.; Schnabel, K.; Schiaparelli, S. Distributional Records of Ross Sea (Antarctica) Tanaidacea from Museum Samples Stored in the Collections of the Italian National Antarctic Museum (MNA) and the New Zealand National Institute of Water and Atmospheric Research (NIWA). ZooKeys 2014, 49–60. [Google Scholar]
- Selbmann, L.; Onofri, S.; Zucconi, L.; Isola, D.; Rottigni, M.; Ghiglione, C.; Piazza, P.; Alvaro, M.C.; Schiaparelli, S. Distributional Records of Antarctic Fungi Based on Strains Preserved in the Culture Collection of Fungi from Extreme Environments (CCFEE) Mycological Section Associated with the Italian National Antarctic Museum (MNA). MycoKeys 2015, 10, 57. [Google Scholar]
- Cecchetto, M.; Alvaro, M.C.; Ghiglione, C.; Guzzi, A.; Mazzoli, C.; Piazza, P.; Schiaparelli, S. Distributional Records of Antarctic and Sub-Antarctic Ophiuroidea from Samples Curated at the Italian National Antarctic Museum (MNA): Check-List Update of the Group in the Terra Nova Bay Area (Ross Sea) and Launch of the MNA 3D Model ‘Virtual Gallery’. ZooKeys 2017, 61–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cecchetto, M.; Lombardi, C.; Canese, S.; Cocito, S.; Kuklinski, P.; Mazzoli, C.; Schiaparelli, S. The Bryozoa Collection of the Italian National Antarctic Museum, with an Updated Checklist from Terra Nova Bay, Ross Sea. ZooKeys 2019, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garlasché, G.; Karimullah, K.; Iakovenko, N.; Velasco-Castrillón, A.; Janko, K.; Guidetti, R.; Rebecchi, L.; Cecchetto, M.; Schiaparelli, S.; Jersabek, C.D. A Data Set on the Distribution of Rotifera in Antarctica. Biogeogr./Ital. Biogeogr. Soc. 2020, 35, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonello, G.; Grillo, M.; Cecchetto, M.; Giallain, M.; Granata, A.; Guglielmo, L.; Pane, L.; Schiaparelli, S. Distributional Records of Ross Sea (Antarctica) Planktic Copepoda from Bibliographic Data and Samples Curated at the Italian National Antarctic Museum (MNA): Checklist of Species Collected in the Ross Sea Sector from 1987 to 1995. ZooKeys 2020, 969, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grillo, M.; Huettmann, F.; Guglielmo, L.; Schiaparelli, S. Three-Dimensional Quantification of Copepods Predictive Distributions in the Ross Sea: First Data Based on a Machine Learning Model Approach and Open Access (FAIR) Data. Diversity 2022, 14, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koehler, R. Echinodemata Echinoidea Australasian Antarctic Expedition 1911–1914. Sci. Rep. Ser. C Zool. Bot. 1926, 3, 1–134. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, A.H. A Monograph of the Existing Crinoids; US Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, R.C. Treatise on Invertebrate Paleontology,(T) Echinodermata 2 (1-3),(T) Echinodermata; Paleontological Institute, University of Kansas: Lawrence, KS, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Speel, J.A.; Dearborn, J.H. Comatulid Crinoids from R/V Eltanin Cruises in the Southern Ocean. Biol. Antarct. Seas XIII 1983, 38, 1–60. [Google Scholar]
- Leray, M.; Knowlton, N. Censusing Marine Eukaryotic Diversity in the Twenty-First Century. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2016, 371, 20150331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronquist, F.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. MrBayes 3: Bayesian Phylogenetic Inference under Mixed Models. Bioinformatics 2003, 19, 1572–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huelsenbeck, J.P.; Ronquist, F. MRBAYES: Bayesian Inference of Phylogenetic Trees. Bioinformatics 2001, 17, 754–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, C.P.; Paulay, G. DNA Barcoding: Error Rates Based on Comprehensive Sampling. PLoS Biol. 2005, 3, e422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hebert, P.D.; Ratnasingham, S.; De Waard, J.R. Barcoding Animal Life: Cytochrome c Oxidase Subunit 1 Divergences among Closely Related Species. Proc. R. Soc. London. Ser. B Biol. Sci. 2003, 270, S96–S99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratnasingham, S.; Hebert, P.D. A DNA-Based Registry for All Animal Species: The Barcode Index Number (BIN) System. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e66213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujisawa, T.; Barraclough, T.G. Delimiting Species Using Single-Locus Data and the Generalized Mixed Yule Coalescent Approach: A Revised Method and Evaluation on Simulated Data Sets. Syst. Biol. 2013, 62, 707–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujita, M.K.; Leaché, A.D.; Burbrink, F.T.; McGuire, J.A.; Moritz, C. Coalescent-Based Species Delimitation in an Integrative Taxonomy. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2012, 27, 480–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leavitt, S.D.; Moreau, C.S.; Thorsten Lumbsch, H. The Dynamic Discipline of Species Delimitation: Progress toward Effectively Recognizing Species Boundaries in Natural Populations. In Recent Advances in Lichenology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 11–44. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Kapli, P.; Pavlidis, P.; Stamatakis, A. A General Species Delimitation Method with Applications to Phylogenetic Placements. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 2869–2876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markmann, M.; Tautz, D. Reverse Taxonomy: An Approach towards Determining the Diversity of Meiobenthic Organisms Based on Ribosomal RNA Signature Sequences. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2005, 360, 1917–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaloudi, E.; Papakostas, S.; Stamou, G.; Neděla, V.; Tihlaříková, E.; Zhang, W.; Declerck, S.A. Reverse Taxonomy Applied to the Brachionus Calyciflorus Cryptic Species Complex: Morphometric Analysis Confirms Species Delimitations Revealed by Molecular Phylogenetic Analysis and Allows the (Re) Description of Four Species. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0203168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appeltans, W.; Ahyong, S.T.; Anderson, G.; Angel, M.V.; Artois, T.; Bailly, N.; Bamber, R.; Barber, A.; Bartsch, I.; Berta, A. The Magnitude of Global Marine Species Diversity. Curr. Biol. 2012, 22, 2189–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheffers, B.R.; Joppa, L.N.; Pimm, S.L.; Laurance, W.F. What We Know and Don’t Know about Earth’s Missing Biodiversity. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2012, 27, 501–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekrem, T.; Willassen, E.; Stur, E. A Comprehensive DNA Sequence Library Is Essential for Identification with DNA Barcodes. Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 2007, 43, 530–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puillandre, N.; Strong, E.E.; Bouchet, P.; Boisselier, M.C.; Couloux, A.; Samadi, S. Identifying Gastropod Spawn from DNA Barcodes: Possible but Not yet Practicable. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2009, 9, 1311–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajibabaei, M.; deWaard, J.R.; Ivanova, N.V.; Ratnasingham, S.; Dooh, R.T.; Kirk, S.L.; Mackie, P.M.; Hebert, P.D. Critical Factors for Assembling a High Volume of DNA Barcodes. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2005, 360, 1959–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayton, P.K. Toward an Understanding of Community Resilience and the Potential Effects of Enrichments to the Benthos at McMurdo Sound, Antarctica. In Proceedings of the Colloquium on Conservation Problems in Antarctica, Blacksberg, VA, USA, 10–12 September 1971; pp. 81–96. [Google Scholar]
- Dayton, P.K. Observations of growth, dispersal and population dynamics of some sponges in mcmurds sound, antarctica. Colloq. Int. Du CNRS 1979, 291, 271–282. [Google Scholar]
- Dayton, P.K. Interdecadal Variation in an Antarctic Sponge and Its Predators from Oceanographic Climate Shifts. Science 1989, 245, 1484–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayton, P.K.; Robilliard, G.A.; Paine, R.T.; Dayton, L.B. Biological Accommodation in the Benthic Community at McMurdo Sound, Antarctica. Ecol. Monogr. 1974, 44, 105–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dearborn, J.H. Foods and Feeding Characteristics of Antarctic Asteroids and Ophiuroids. Adapt. Within Antarct. Ecosyst. 1977, 293–326. [Google Scholar]
- Dearborn, J.H.; Edwards, K.C. Analysis of Data on the Feeding Biology of Antarctic Sea Stars and Brittle Stars. Antarct. J. United States 1985, 19, 138–139. [Google Scholar]
- McClintock, J.B. Investigation of the Relationship between Invertebrate Predation and Biochemical Composition, Energy Content, Spicule Armament and Toxicity of Benthic Sponges at McMurdo Sound, Antarctica. Mar. Biol. 1987, 94, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
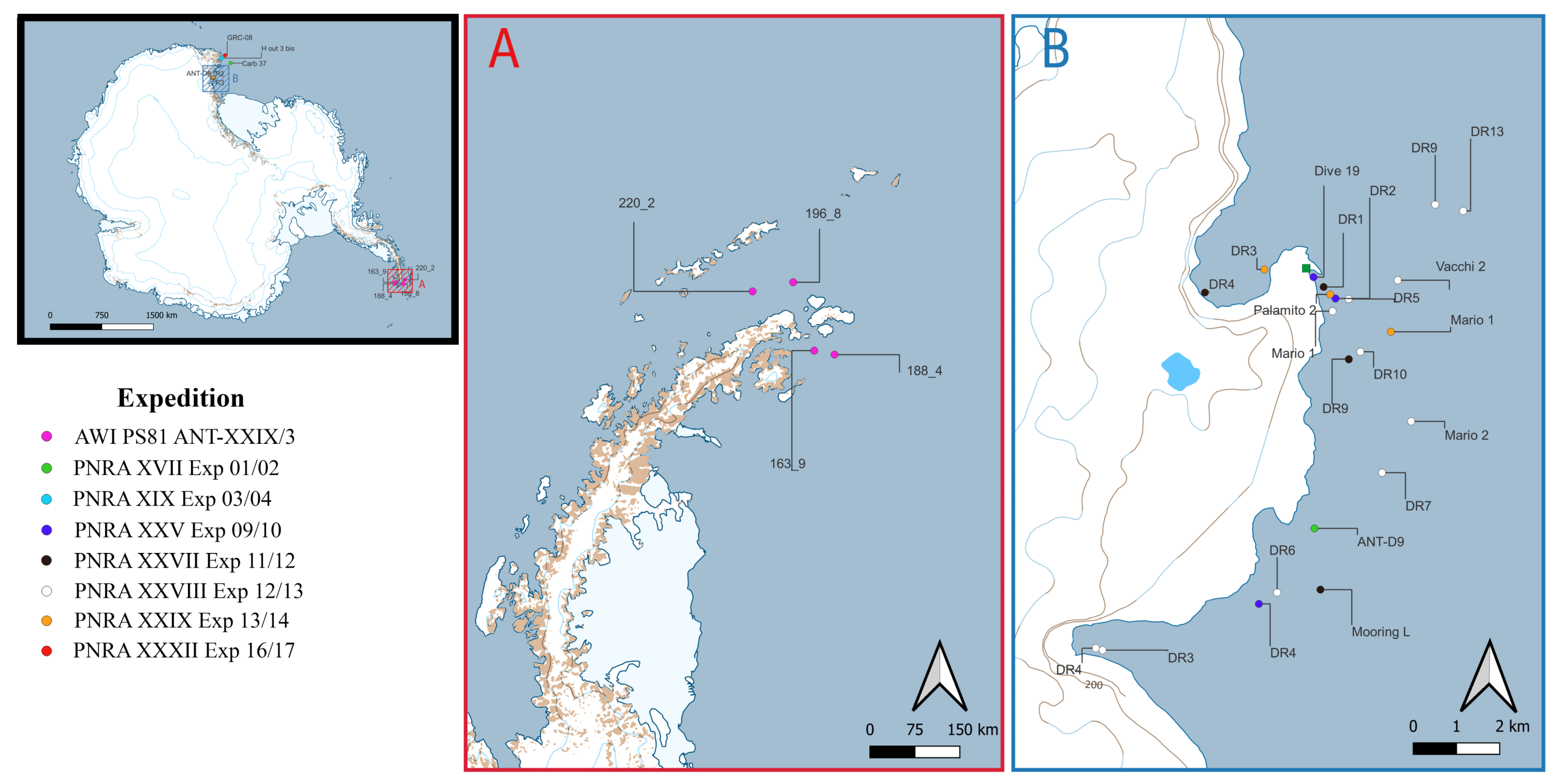

| Expedition | Station | Location | Year | Latitude | Longitude | Depth (m) | Sampling Methods | N |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AWI PS81 ANT-XXIX/3 | 163_9 | Weddell Sea | 2013 | −63.79600 | −56.31000 | 550.9 | AGT (Agassiz Trawl) | 3 |
| 188_4 | Weddell Sea | 2013 | −63.83933 | −55.62367 | 427 | AGT (Agassiz Trawl) | 1 | |
| 196_8 | Bransfield Strait | 2013 | −62.79667 | −57.08917 | 580 | AGT (Agassiz Trawl) | 3 | |
| 220_2 | Bransfield Strait | 2013 | −62.94533 | −58.39383 | 792 | AGT (Agassiz Trawl) | 1 | |
| PNRA XVII Exp 01/02 | ANT-D9 | Tethys Bay | 2002 | −74.74860 | 164.12467 | 113 | Dredge | 1 |
| Carb 37 | Mawson Bank | 2002 | −73.15133 | 174.29467 | 309 | Dredge | 1 | |
| PNRA XIX Exp 03/04 | H out 3 bis | Cape Hallett | 2004 | −72.29000 | 170.44000 | 258 | AGT (Agassiz Trawl) | 1 |
| R3 | Cape Russell | 2004 | −74.82167 | 164.19167 | 330 | AGT (Agassiz Trawl) | 1 | |
| R2 | Cape Russell | 2004 | −74.81667 | 164.30167 | 364 | AGT (Agassiz Trawl) | 1 | |
| PNRA XXV Exp 09/10 | Dive 19 | Road Bay | 2010 | −74.69647 | 164.12007 | 15 | Dive | 2 |
| DR2 | Road Bay | 2010 | −74.70082 | 164.13762 | 148 | Dredge | 11 | |
| DR4 | Adelie Cove | 2010 | −74.76450 | 164.08202 | 100 | Dredge | 8 | |
| PNRA XXVII Exp 11/12 | DR1 | Road Bay | 2012 | −74.69848 | 164.12812 | 100 | Dredge | 12 |
| DR4 | Tethys Bay | 2012 | −74.70010 | 164.03502 | 198 | Dredge | 10 | |
| DR9 | Faraglione | 2012 | −74.71337 | 164.14903 | 150 | Dredge | 4 | |
| Mooring L | Terra Nova Bay | 2012 | −74.76130 | 164.13032 | 149 | Mooring | 1 | |
| PNRA XXVIII Exp 12/13 | DR3 | Adelie Cove | 2013 | −74.77468 | 163.95948 | 77 | Dredge | 2 |
| DR4 | Adelie Cove | 2013 | −74.77430 | 163.95400 | 78 | Dredge | 1 | |
| DR5 | Road Bay | 2013 | −74.70087 | 164.14793 | 150 | Dredge | 3 | |
| DR6 | Caletta | 2013 | −74.76207 | 164.09623 | 146 | Dredge | 1 | |
| DR7 | Terra Nova Bay | 2013 | −74.73675 | 164.17702 | 240 | Dredge | 1 | |
| DR9 | MZS | 2013 | −74.68090 | 164.21433 | 522 | Dredge | 2 | |
| DR10 | Faraglione | 2013 | −74.71178 | 164.15802 | 250 | Dredge | 2 | |
| DR13 | MZS | 2013 | −74.68210 | 164.23640 | 525 | Dredge | 2 | |
| Mario 1 | Terra Nova Bay | 2013 | −74.70348 | 164.13550 | 137 | GN (Gill Net) | 3 | |
| Mario 2 | Terra Nova Bay | 2013 | −74.72597 | 164.19908 | 319 | LL (Long Line) | 1 | |
| Vacchi 2 | Tethys Bay | 2013 | −74.69677 | 164.18622 | 460 | GN (Gill Net) | 1 | |
| PNRA XXIX Exp 13/14 | DR3 | Tethys Bay | 2014 | −74.69508 | 164.08137 | 60 | Dredge | 3 |
| Mario 1 | Terra Nova Bay | 2014 | −74.70750 | 164.18167 | 242 | TN (Trammel Net) | 3 | |
| Palamito 2 | Terra Nova Bay | 2014 | −74.70000 | 164.13333 | 100 | LL (Long Line) | 3 | |
| PNRA XXXII Exp 16/17 | GRC-08 | Cape Hallett | 2017 | −71.98111 | 172.19383 | 750 | Dredge | 1 |
| Species | Arms | Cirri | Lateral Perisome |
|---|---|---|---|
| A. adriani | 10 with protuberance on the dorsal face of most of the arm joints | 50–60 | |
| F. mawsoni | 40–77 | ||
| P. kerguelensis | 20 each ray divided at primibrachial | ||
| N. virilis | up to 40 | pinnules contains large plates that are usually triangular in shape with rounded angles |
| Species | Globiferous Pedicellariae Shape | Diameter | Apical System Position | Labrum Size | Frontal Sinus | Apical System Plating |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S. antarcticus | valves with 1 to 3 lateral teeth | 20–50 mm | ||||
| S. neumayeri | valves with 1 to 3 lateral teeth | 10–20 mm | ||||
| A. (Pseuabatus) nimrodi | valves terminating in a series of small teeth | |||||
| A. agassizii | valves terminating in two long teeth | apical system subcentral | short, reaching no farther than the 1st adjacent ambulacral plates | |||
| A. cavernosus | valves terminating in 4 teeth | |||||
| A. cordatus | globiferous pedicellariae absent | |||||
| A. curvidens | valves terminating in two long teeth | apical system anterior | present | |||
| A. elongatus | valves terminating in two long teeth | apical system anterior | absent | |||
| A. ingens | valves terminating in two long teeth | apical system subcentral | long, extending between the 3rd and the 4th adjacent ambulacral plates | apical system not disjunct separate genitals 2 and 3 | ||
| A. shackletoni | valves terminating in two long teeth | apical system subcentral | long, extending between the 3rd and the 4th adjacent ambulacral plates |
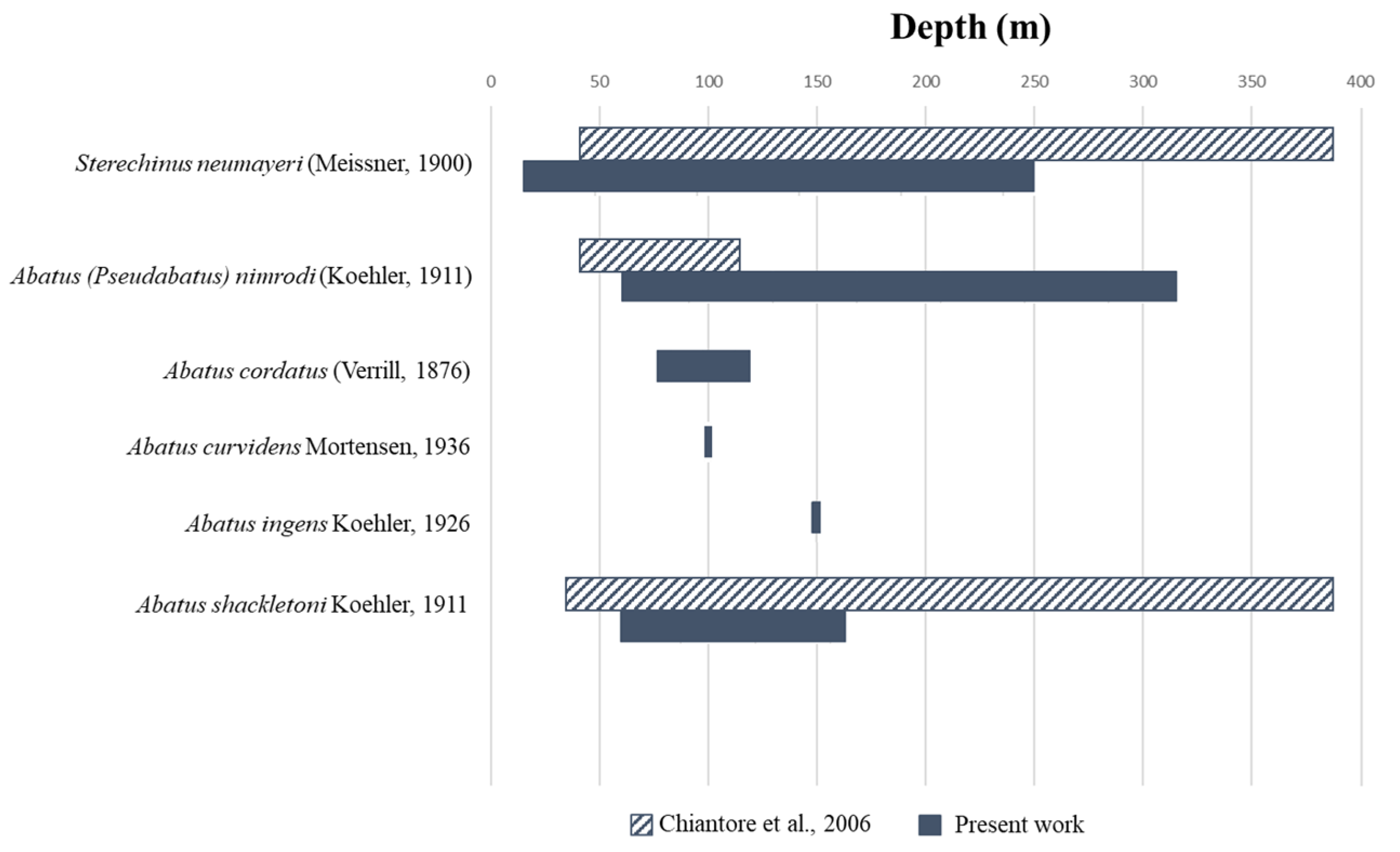
| Class | Family | Species | Depth Range (m) | Chaintore et al., 2006 | This Work |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Echinoidea | Echinidae | S. neumayeri | 15–380 | x | x |
| Schizasteridae | A. (Pseudabatus) nimrodi | 60–150 | x | x | |
| A. cordatus | 78–146 | x | |||
| A. curvidens | 100 | x | |||
| A. ingens | 148–150 | x | |||
| A. shackletoni | 36–380 | x | x | ||
| Crinoidea | Antedonidae | A. adriani | 250–522 | x | |
| F. mawsoni | 522 | x | |||
| P. kerguelensis | 137–525 | x | |||
| Notocrinidae | N. virilis | 137–525 | x |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guzzi, A.; Alvaro, M.C.; Cecchetto, M.; Schiaparelli, S. Echinoids and Crinoids from Terra Nova Bay (Ross Sea) Based on a Reverse Taxonomy Approach. Diversity 2023, 15, 875. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15070875
Guzzi A, Alvaro MC, Cecchetto M, Schiaparelli S. Echinoids and Crinoids from Terra Nova Bay (Ross Sea) Based on a Reverse Taxonomy Approach. Diversity. 2023; 15(7):875. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15070875
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuzzi, Alice, Maria Chiara Alvaro, Matteo Cecchetto, and Stefano Schiaparelli. 2023. "Echinoids and Crinoids from Terra Nova Bay (Ross Sea) Based on a Reverse Taxonomy Approach" Diversity 15, no. 7: 875. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15070875
APA StyleGuzzi, A., Alvaro, M. C., Cecchetto, M., & Schiaparelli, S. (2023). Echinoids and Crinoids from Terra Nova Bay (Ross Sea) Based on a Reverse Taxonomy Approach. Diversity, 15(7), 875. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15070875








