Feeding and Reproductive Phenotypic Traits of the Sea Urchin Tripneustes gratilla in Seagrass Beds Impacted by Eutrophication
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
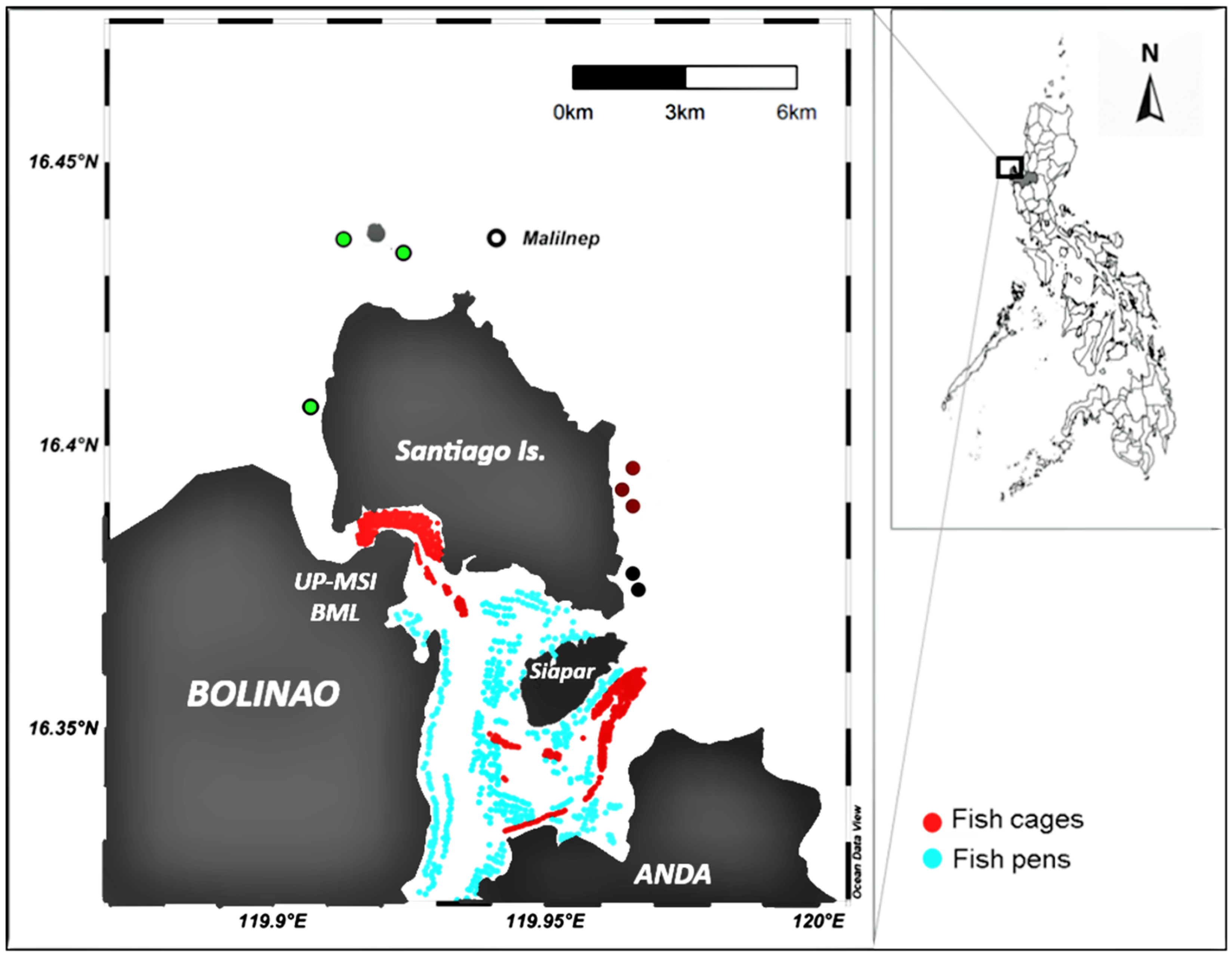
2.1. Study Stations and Sampling Design
2.2. Physical Water Parameters
2.3. Seagrass Parameters
2.4. Sea Urchin Parameters
2.4.1. Feeding and Somatic Traits
2.4.2. Reproductive Traits
2.5. Data Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Physical Water Parameters
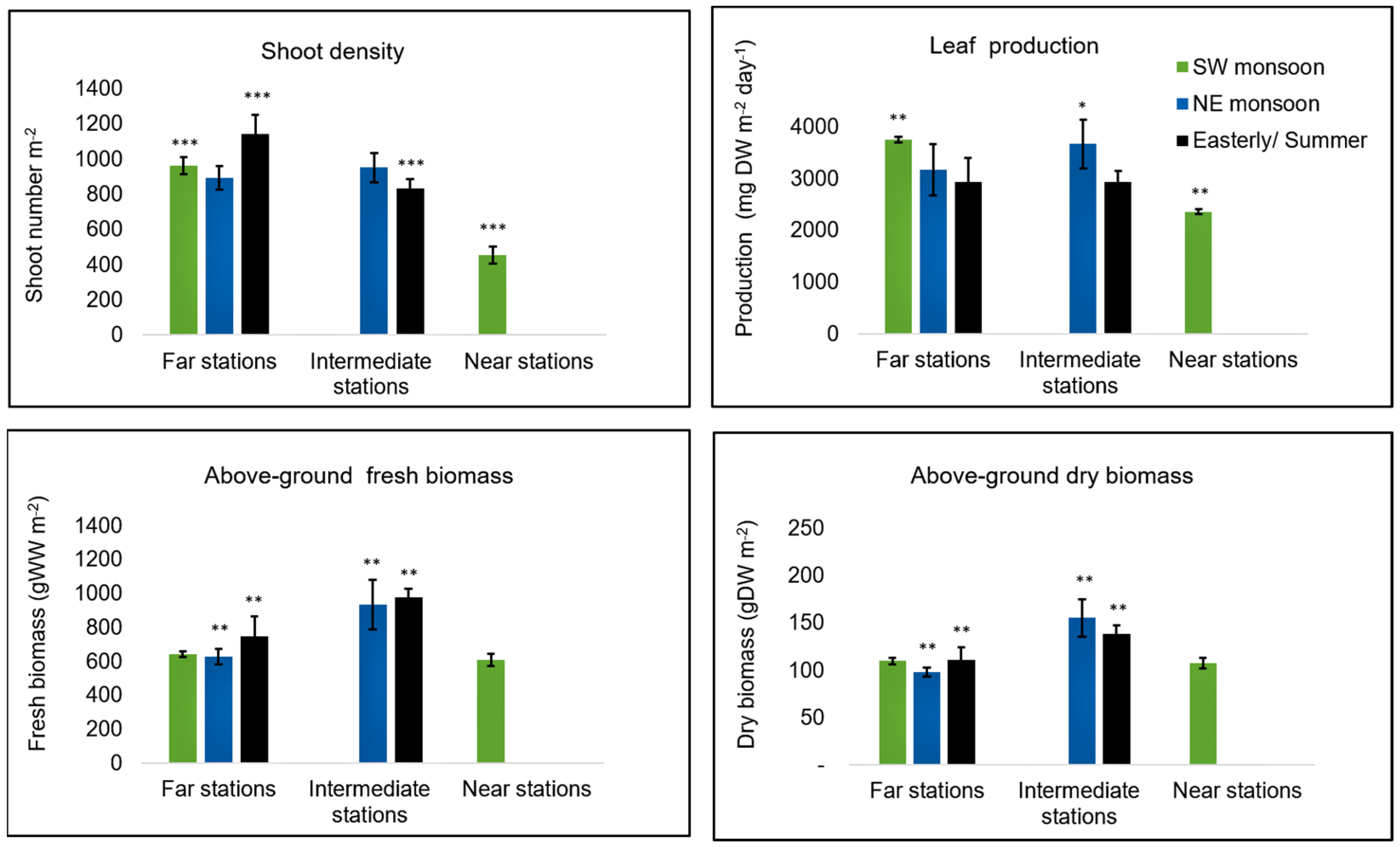
3.2. Seagrass Parameters
3.3. Sea Urchin Parameters
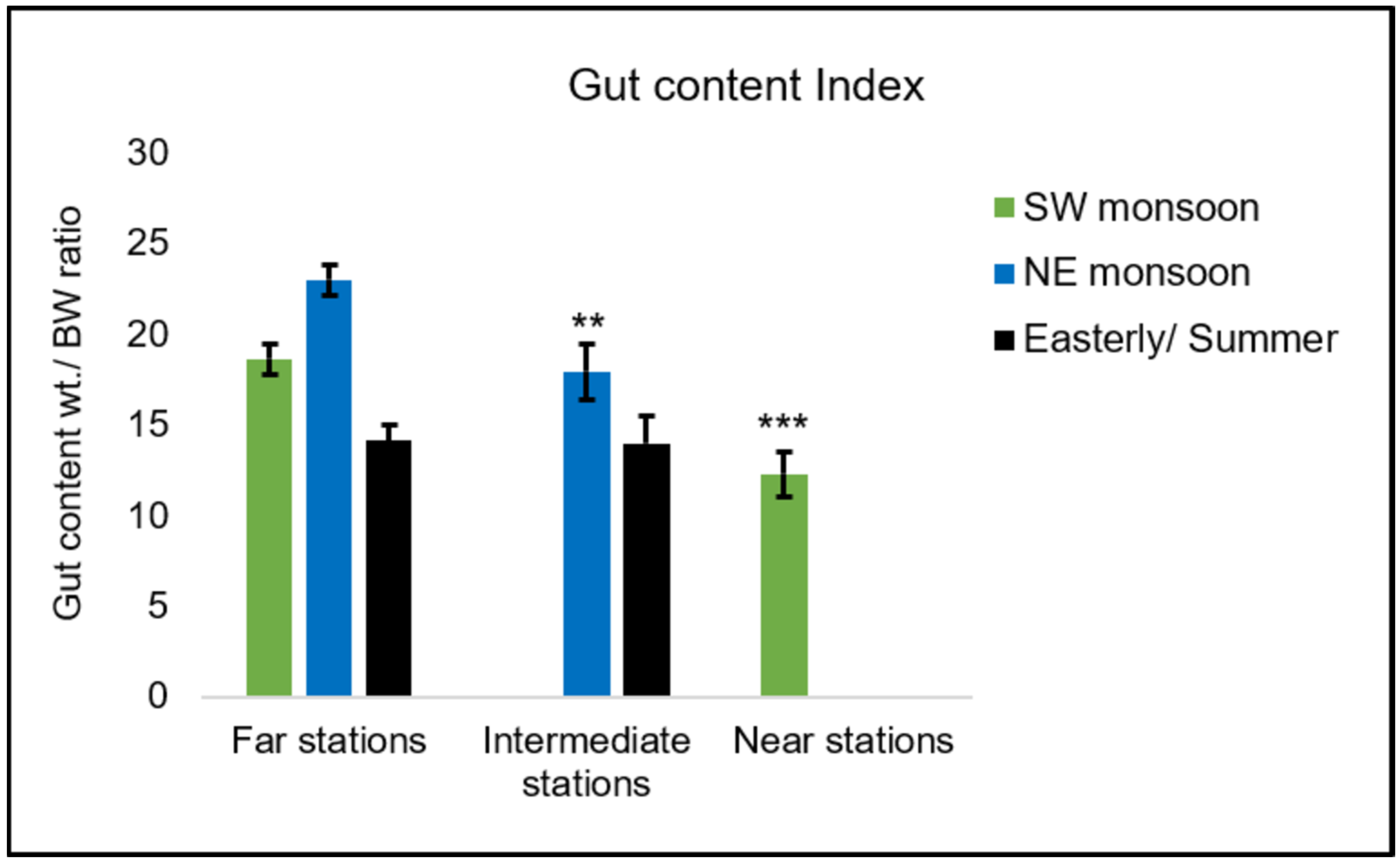
3.3.1. Gut Contents
3.3.2. Feeding Somatic Traits
3.3.3. Gonads
3.4. Relationship of Sea Urchin Phenotypic Traits, Seagrass and Water Parameters
4. Discussion
4.1. Seagrass Bed Condition
4.2. Condition of the Sea Urchin Populations
4.2.1. Diet
4.2.2. Feeding and Reproductive Phenotypic Traits
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Campbell, B.; Pauly, D. Mariculture: A global analysis of production trends since 1950. Mar. Policy 2013, 39, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tacon, A.G.J.; Forster, I.P. Aquafeeds and the environment: Policy implications. Aquaculture 2003, 226, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Primavera, J.H. Overcoming the impacts of aquaculture on the coastal zone. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2006, 49, 531–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tewfik, A.; Rasmussen, J.B.; McCann, K.S. Anthropogenic enrichment alters a marine benthic food web. Ecology 2005, 86, 2726–2736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anton, A.; Cebrian, J.; Heck, K.L.; Duarte, C.M.; Sheehan, K.L.; Miller, M.-E.C.; Foster, C.D. Decoupled effects (positive to negative) of nutrient enrichment on ecosystem services. Ecol. Appl. 2011, 1, 991–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, C.A.; Bannister, R.J.; Dworjanyn, S.A.; Husa, V.; Nichols, P.D.; Dempster, T. Aquaculture-derived trophic subsidy boosts populations of an ecosystem engineer. Aquacult. Environ. Interact. 2018, 10, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGlathery, K.J. Macroalgal blooms contribute to the decline of seagrass in nutrient-enriched coastal waters. J. Phycol. 2001, 37, 453–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkholder, J.M.; Tomasko, D.A.; Touchette, B.W. Seagrasses and eutrophication. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2007, 350, 46–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, S.L.; Heck, K.L., Jr. Seagrass Community Ecology. In Marine Community Ecology; Bertness, M.D., Gaines, S.D., Hay, M.E., Eds.; Sinauer Associates: Sundergland, MA, USA, 2001; pp. 317–337. [Google Scholar]
- Short, F.T.; Wyllie-Echeverria, S. Natural and human induced disturbance of seagrasses. Environ. Conserv. 1996, 23, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, C.M. The future of seagrass meadows. Environ. Conserv. 2002, 29, 192–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, D.I.; Kendrick, G.A.; McComb, A.J. Decline and Recovery of Seagrass Ecosystems-The Dynamics of Change. In Seagrasses: Biology, Ecology and Conservation; Larkum, A.W.D., Orth, E.J., Duarte, C.M., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 551–565. [Google Scholar]
- Coles, R.; Grech, A.; Rasheed, M.; McKenzie, L.; Unsworth, R.; Short, F. Seagrass Ecology and Threats in the Tropical Indo-Pacific Bioregion. In Seagrass: Ecology, Uses and Threats; Pirog, R.S., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Short, F.; Carruthers, T.; Dennison, W.; Waycott, M. Global seagrass distribution and diversity: A bioregional model. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2007, 350, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Short, F.T.; Polidoro, B.; Livingstone, S.R.; Carpenter, K.E.; Bandeira, S.; Bujang, J.S.; Calumpong, H.P.; Carruthers, T.J.; Coles, R.G.; Dennison, W.C.; et al. Extinction risk assessment of the world’s seagrass species. Biol. Conserv. 2011, 144, 1961–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Short, F.T.; Coles, R.; Fortes, M.D.; Victor, S.; Salik, M.; Isnain, I.; Andrew, J.; Seno, A. Monitoring in the Western Pacific region shows evidence of seagrass decline in line with global trends. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 83, 408–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortes, M.D.; Ooi, J.L.S.; Tan, Y.M.; Prathep, A.; Bujang, J.S.; Yaakub, M.S. Seagrass in Southeast Asia: A review of status and knowledge gaps, and a road map for conservation. Bot. Mar. 2018, 61, 269–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orth, R.J.; Carruthers, T.J.; Dennison, W.C.; Duarte, C.M.; Fourqurean, J.W.; Heck, K.L.; Hughes, A.R.; Kendrick, G.A.; Kenworthy, W.J.; Olyarnik, S.; et al. A global crisis for seagrass ecosystems. Bioscience 2006, 56, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ralph, P.J.; Tomasko, D.; Moore, K.; Seddon, S.; Macinnis, O.C.M. Human impacts on seagrasses: Eutrophication, sedimentation, and contamination. In Seagrasses: Biology, Ecology, and Conservation; Larkum, A.W.D., Orth, E.J., Duarte, C.M., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 567–593. [Google Scholar]
- Waycott, M.; Duarte, C.M.; Carruthers, T.J.B.; Orth, R.J.; Dennison, W.C.; Olyarnik, S.; Calladine, A.; Fourqurean, J.W.; Heck, K.L.; Hughes, A.R.; et al. Accelerating loss of seagrasses across the globe threatens coastal ecosystems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 12377–12381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Cui, L.; Liu, S.; Zhao, C.; Wu, Y.; Chen, Q.; Yu, S.; Li, J.; He, J.; Fang, Y.; et al. Historical changes in seagrass beds in a rapidly urbanizing area of Guangdong Province: Implications for conservation and management. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2020, 22, e01035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vizzini, S.; Mazzola, A. Stable isotope evidence for the environmental impact of a land-based fish farm in the western Mediterranean. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2004, 49, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vizzini, S.; Mazzola, A. The effects of anthropogenic organic matter inputs on stable carbon and nitrogen isotopes in organisms from different trophic levels in a southern Mediterranean coastal area. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 368, 723–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, J.M. Sea urchin life history strategies. In Sea Urchins: Biology and Ecology, 4th ed.; Lawrence, J.M., Ed.; Elsevier: London, UK, 2020; pp. 19–28. [Google Scholar]
- Talaue-McManus, L.T.; Kesner, K.P. Valuation of a Philippine municipal sea urchin fishery and implications of its collapse. In Philippine Coastal Resources under Stress; Juinio-Meñez, M.A.R., Newkirk, G.F., Eds.; Selected papers from the Fourth Annual Common Property Conference; University of the Philippines: Quezon City, Philippines, 1995; pp. 229–239. [Google Scholar]
- Juinio-Meñez, M.A.; Bangi, H.G.P.; Malay, M.C.D.; Pastor, D. Enhancing the recovery of depleted Tripneustes gratilla stocks through grow-out culture and restocking. Rev. Fish. Sci. 2008, 16, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrew, N.L.; Agatsuma, Y.; Ballesteros, E.; Bazhin, A.G.; Creaser, E.P.; Barnes, D.K.A.; Botsford, L.W.; Bradbury, A.; Campbell, A.; Dixon, J.D.; et al. Status and management of the world sea urchin fisheries. Oceanogr. Mar. Biol. Annu. Rev. 2002, 40, 343–425. [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence, J.M.; Agatsuma, Y. Tripneustes. In Sea Urchins: Biology and Ecology, 4th ed.; Lawrence, J.M., Ed.; Academic Press: London, UK; Elsevier: London, UK, 2020; pp. 681–703. [Google Scholar]
- Shimabukuro, S. Tripneustes gratilla (sea urchin). In Aquaculture in Tropical Areas; English ed.; Shokita, S., Kakazu, K., Tomori, A., Toma, T., Eds.; Prepared by M. Yamaguchi; Midoro Shobo: Tokyo, Japan, 1991; pp. 313–328. [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence, J.M.; Bazhin, A. Life-history strategies and the potential of sea urchins for aquaculture. J. Shellfish Res. 1998, 17, 1515–1522. [Google Scholar]
- Koike, I.; Mukai, H.; Nojima, S. The role of the sea urchin, Tripneustes gratilla (Linnaeus), in decomposition and nutrient cycling in a tropical seagrass bed. Ecol. Res. 1987, 2, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klumpp, D.W.; Salita-Espinosa, J.T.; Fortes, M.D. Feeding ecology and trophic role of sea urchins in a tropical seagrass community. Aquat. Bot. 1993, 45, 205–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentine, J.F.; Heck, K.L., Jr.; Busby, J.; Webb, D. Experimental evidence that herbivory can increase shoot density in a subtropical turtlegrass (Thalassia testudinum) meadow. Oecologia 1997, 112, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vonk, J.A.; Pijnappels, M.H.J.; Stapel, J. In situ quantification of Tripneustes gratilla grazing and its effects on three co-occurring tropical seagrass species. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2008, 360, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, S.-H.; Huang, Y.-H.; Lin, H.-J. Carbon budget of leaves of the tropical intertidal seagrass Thalassia hemprichii. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2013, 125, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conklin, E.J.; Smith, J.E. Abundance and spread of the invasive red algae, Kappaphycus spp. in Kane’ ohe Bay, Hawai’i and an experimental assessment of management options. Biol. Invasions 2005, 7, 1029–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stimson, J.; Cunha, T.; Philippoff, J. Food preferences and related behavior of the browsing sea urchin Tripneustes gratilla (Linnaeus) and its potential for use as a biological control agent. Mar. Biol. 2007, 151, 1761–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentine, J.P.; Edgar, G.J. Impacts of a population outbreak of the urchin Tripneustes gratilla amongst Lord Howe Island coral communities. Coral Reefs 2010, 29, 399–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westbrook, C.E.; Ringang, R.R.; Cantero, S.M.A.; HDAR, TNC Urchin Team; Toonen, R.J. Survivorship and feeding preferences among size classes of outplanted sea urchins, Tripneustes gratilla, and possible use as biocontrol for invasive alien algae. PeerJ 2015, 3, e1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cebrian, J.; Enriquez, S.; Fortes, M.; Agawin, N.; Vermaat, J.E.; Duarte, C.M. Epiphyte accrual on Posidonia oceanica. L Delile leaves: Implications for light absorption. Bot. Mar. 1999, 42, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furman, B.; Heck, K.I., Jr. Differential impacts of echinoid grazers on coral recruitment. Bull. Mar. Sci. 2009, 85, 121–132. [Google Scholar]
- Leopardas, V.; Honda, K.; Go, G.A.; Bolisay, K.; Pantallano, A.D.; Uy, W.; Fortes, M.D.; Nakaoka, M. Variation in macrofaunal communities of sea grass beds along a pollution gradient in Bolinao, northwestern Philippines. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 105, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McManus, J.W.; Nañola, C.L.; Reyes, R.B.; Kesner, K.N. Resource Ecology of the Bolinao Coral Reef System; ICLARM Studies Review, 22; International Center for Living Aquatic Resources Management: Manila, Philippines, 1992; p. 117. [Google Scholar]
- Holmer, M.; Marba, N.; Terrados, J.; Duarte, C.M.; Fortes, M.D. Impacts of milkfish (Chanos chanos) aquaculture on carbon and nutrient fluxes in the Bolinao area, Philippines. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2002, 44, 685–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmer, M.; Duarte, C.M.; Heilskov, A.; Olesen, B.; Terrados, J. Biogeochemical conditions in sediments enriched by organic matter from net-pen fish farms in the Bolinao area, Philippines. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2003, 46, 1470–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, C.P.; Sta. Maria, Y.Y.; Siringan, F.P.; Reotita, J.M.; Zamora, P.B.; Villanoy, C.L.; Sombrito, E.Z.; Azanza, R.V. Coastal pollution due to increasing nutrient flux in aquaculture sites. Environ. Geol. 2009, 58, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geček, S.; Legović, T. Towards carrying capacity assessment for aquaculture in the Bolinao Bay, Philippines: A numerical study of tidal circulation. Ecol. Modell. 2010, 221, 1394–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San Diego-McGlone, M.L.; Azanza, R.V.; Villanoy, C.L.; Jacinto, G.S. Eutrophic waters, algal bloom and fish kill in fish farming areas in Bolinao, Pangasinan, Philippines. Mar. Poll. Bull. 2008, 57, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortes, M.D.; Go, G.A.; Bolisay, K.; Nakaoka, M.; Uy, W.H.; Lopez, M.R.; Leopardas, V.; Leriorato, J.; Pantallano, A.; Paciencia, F.; et al. Seagrass response to mariculture-induced physico-chemical gradients in Bolinao, northwestern Philippines. In Proceedings of the 12th International Coral Reef Symposium, Cairns, Australia, 9–13 July 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka, T.; Go, G.A.; Watanabe, A.; Miyajima, T.; Nakaoka, M.; Uy, W.H.; Nadaoka, K.; Watanabe, S.; Fortes, M.D. 17-year change in species composition of mixed seagrass beds around Santiago Island, Bolinao, the northwestern Philippines. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 88, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrera, C.M.; Watanabe, A.; Miyajima, T.; San Diego-McGlone, M.L.; Morimoto, N.; Umezawa, Y.; Herrera, E.; Tsuchiya, T.; Yoshikai, M.; Nadaoka, K. Phosphorus as a driver of nitrogen limitation and sustained eutrophic conditions in Bolinao and Anda, Philippines, a mariculture-impacted tropical coastal area. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 105, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doty, S.M. Measurement of water movement in reference to benthic algal growth. Bot. Mar. 1971, 14, 32–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- English, S.; Wilkinson, C.; Baker, V. Seagrass Communities. Chapter 5. In Survey Manual for Tropical Marine Resources; ASEAN-Australia Marine Science Project; Australian Institute of Marine Science: Townsville, Australia, 1997; pp. 241–252. [Google Scholar]
- Burdick, D.M.; Kendrick, G.A. Standards for seagrass collection, identification, and sample design. In Global Seagrass Research Methods; Short, F.T., Coles, R.G., Eds.; Elsevier Science B.V.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2001; pp. 79–100. [Google Scholar]
- Duarte, C.M.; Kirkman, H. Methods for the measurement of seagrass abundance and depth distribution. In Global Seagrass Research Methods; Short, F.T., Coles, R.G., Eds.; Elsevier Science B.V.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2001; pp. 141–154. [Google Scholar]
- Vermaat, J.E.; Fortes, M.D.; Agawin, N.R.; Duarte, C.M.; Marbà, N.; Uri, J.S. Meadow maintenance, growth and productivity in a mixed Philippine seagrass bed. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1995, 124, 215–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Short, F.T.; Duarte, C.M. Methods for the measurement of seagrass growth and production. In Global Seagrass Research Methods; Short, F.T., Coles, R.G., Eds.; Elsevier Science B.V.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2001; pp. 155–182. [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence, J.M. The effect of stress and disturbance in Echinoderms. Zool. Sci. 1990, 7, 17–28. [Google Scholar]
- Tuason, A.Y.; Gomez, E.D. The reproductive biology of Tripneustes gratilla Linnaeus (Echinodermata: Echinoidea) with some notes on Diadema setosum Leske. Proc. Int. Symp. Mar. Biogeogr. Evol. South. Hemisph. 1979, 2, 707–716. [Google Scholar]
- Vaïtilingon, D.; Rasolofonirina, R.; Jangoux, M. Feeding preferences, seasonal gut repletion indices, and diel feeding patterns of the sea urchin Tripneustes gratilla (Echinodermata: Echinoidea) on a coastal habitat off Toliara (Madagascar). Mar. Biol. 2003, 143, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agatsuma, Y.; Sato, M.; Taniguchi, K. Factor causing brown-colored gonads of the sea urchin, Strongylocentrotus nudus, in northern Honshu, Japan. Aquaculture 2005, 249, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnette, T.; Zairin, M.; Mokoginta; Suprayudi, M.A.; Yulianda, F. Protein level and protein energy ratio that produce the best gonad quality of sea urchin Tripneustes gratilla. J. Biol. Life Sci. 2014, 5, 95–105. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, M.J. Permutation tests for univariate or multivariate analysis of variance and regression. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2001, 58, 626–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepard, R.N. The analysis of proximities: Multidimensional scaling with an unknown distance function. II. Psychometrika 1962, 27, 219–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruskal, J.B. Multidimensional Scaling by Optimizing Goodness of Fit to a Nonmetric Hypothesis. Psychometrika 1964, 29, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.J.; Willis, T.J. Canonical analysis of principal coordinates: A useful method of constrained ordination for ecology. Ecology 2003, 84, 511–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.J.; ter Braak, C.J.F. Permutation tests for multi-factorial analysis of variance. J. Stat. Comput. Simul. 2003, 73, 85–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McArdle, B.H.; Anderson, M.J. Fitting multivariate models to community data: A comment on distance-based redundancy analysis. Ecology 2001, 82, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, K.R.; Warwick, R.M. Change in Marine Communities: An Approach to Statistical Analysis and Interpretation, 2nd ed.; Primer-e Ltd., Plymouth Marine Laboratory: Plymouth, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Bach, S.S.; Borum, J.; Fortes, M.D.; Duarte, C.M. Species composition and plant performance of mixed seagrass beds along a siltation gradient at Cape Bolinao, the Philippines. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1998, 174, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watai, M.; Nakamura, Y.; Honda, K.; Bolisay, K.O.; Miyajima, T.; Nakaoka, M.; Fortes, M.D. Diet, growth, and abundance of two seagrass bed fishes along a pollution gradient caused by milkfish farming in Bolinao, northwestern Philippines. Fish Sci. 2015, 81, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eklöf, J.S.; de la Torre-Castro, M.; Gullström, M.; Uku, J.; Muthiga, N.; Lyimo, T.; Bandeira, S.O. Sea urchin overgrazing of seagrasses: A review of current knowledge on causes, consequences, and management. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2008, 79, 569–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, C.; Ferrat, L.; Pergent, G.; Pasqualini, V. Sea urchin–seagrasses interactions: Trophic links in a benthic ecosystem from a coastal lagoon. Hydrobiologia 2012, 699, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rollon, R.N.; Van Steveninck, E.D.D.R.; Van Vierssen, W.; Fortes, M.D. Contrasting recolonization strategies in multi-species seagrass meadows. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1998, 37, 450–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terrados, J.; Duarte, C.M.; Kamp-Nielsen, L.; Borum, J.; Agawin, N.S.R.; Fortes, M.D.; Gacia, E.; Lacap, D.; Lubanski, M.; Greve, T. Are seagrass growth and survival affected by reducing conditions in the sediment? Aquat. Bot. 1999, 65, 175–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uy, W.H.; Vermaat, J.E.; Hemminga, M.A. The Interactive Effect of Shading and Sediment Conditions on Growth and Photosynthesis of Two Seagrass Species, Thalassia hemprichii and Halodule uninervis. Functioning of Philippine Seagrass Species under Deteriorating Light Conditions. Ph.D. Dissertation, Wageningen University-International Institute for Infrastructural, Hydraulic and Environmental Engineering, Swets and Zeitlinger B.V., Lisse, The Netherlands, 2001; pp. 49–72. [Google Scholar]
- Mukai, H.; Nojima, S. A preliminary study on grazing and defecation rates of a seagrass grazer, Tripneustes gratilla (L.) (Echinidermata: Echinoidea), in Papua New Guinean seagrass beds. Spec. Publ. Makaishishima Mar. Biol. Stn. 1985, 84–191. [Google Scholar]
- Watts, S.A.; Lawrence, A.L.; Lawrence, J.M. Nutrition. In Sea Urchins: Biology and Ecology, 4th ed.; Lawrence, J.M., Ed.; Elsevier: London, UK, 2020; pp. 191–208. [Google Scholar]
- Ebert, T.A. Relative growth of sea urchin jaws: An example of plastic resource allocation. Bull. Mar. Sci. 1980, 30, 467–474. [Google Scholar]
- Black, R.; Codd, C.; Hebbert, D.; Vink, S.; Burt, J. The functional significance of the relative size of Aristotle’s lantern in the sea urchin Echinometra mathaei (de Blainville). J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1984, 77, 81–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levitan, D.R. Skeletal changes in the test and jaws of the sea urchin Diadema antillarum in response to food limitation. Mar. Biol. 1991, 111, 431–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, P.B.; Ebert, T.A. Plastic responses to limited food availability and spine damage in the sea urchin Strongylocentrotus purpuratus. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1991, 145, 205–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.G.; Garcia, S.C. Variation in purple sea urchin (Strongylocentrotus purpuratus) morphological traits in relation to resource availability. PeerJ 2021, 9, e11352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bangi, H.G.P. The Effect of Adult Nutrition on Somatic and Gonadal Growth, Egg Quality and Larval Development of the Sea Urchin Tripneustes gratilla Linnaeus 1758 (Echinodermata: Echinoidea). Master’s Thesis, Marine Science Institute, University of the Philippines Diliman, Quezon City, Philippines, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Böttger, S.A.; McClintock, J.B.; Klinger, T.S. Effects of organic and inorganic phosphates on feeding, absorption, nutrient allocation, growth, righting responses of the sea urchin Lytechinus variegatus. Mar. Biol. 2001, 138, 741–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böttger, S.A.; McClintock, J.B. The effects of organic and inorganic phosphates on fertilization and early development in the sea urchin Lytechinus variegatus (Echinodermata: Echinoidea). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C 2001, 129, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siikavuopio, S.I.; Dale, T.; Foss, A.; Mortensen, A. Effects of chronic ammonia exposure on gonad growth and survival in green sea urchin Strongylocentrotus droebachiensis. Aquaculture 2004, 242, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siikavuopio, S.I.; Dale, T.; Christiansen, J.S.; Nevermo, I. Effects of chronic nitrite exposure on gonad growth in green sea urchin Strongylocentrotus droebachiensis. Aquaculture 2004, 242, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, C.A.; Dworjanyn, S.A.; Nichols, P.D.; Mos, B.; Dempster, T. Future aquafeeds may compromise reproductive fitness in a marine invertebrate. Mar. Environ. Res. 2016, 122, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bangi, H.G.P.; Juinio-Meñez, M.A. Resource allocation trade-offs in the sea urchin Tripneustes gratilla under relative storminess and wave exposure. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2019, 608, 165–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Canonical Analysis of Principal Coordinates (CAP) Correlations | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eigenvalue | Correlation | Correlation sq. (δ2) | |||
| 1 | 0.9149 | 0.8371 | |||
| 2 | 0.7861 | 0.618 | |||
| m | % Var (1st PCO) | Total Allocation success (%) | 1st Correlation sq. (δ2) | p value | |
| 3 | 71.04 | 92.424 | 0.83709 | 0.001 | |
| Cross Validation (Leave-one-out allocation of observation to groups) | |||||
| Classified | Total | % correct | |||
| Original Groups | FAR stations | INTermediate stations | NEAR stations | ||
| FAR stations | 50 | 0 | 0 | 50 | 100 |
| INTermediate stations | 10 | 50 | 0 | 60 | 83.33 |
| NEAR stations | 0 | 0 | 22 | 22 | 100 |
| CAP Pearson correlatons (Response variables: T. gratilla and seagrass variables) | |||||||||
| GSI | ALI | GI | RI | GQlty | Shoot den | Leaf prod | FW biomass | DW biomass | |
| CAP1 | −0.663 | −0.599 | −0.621 | −0.504 | −0.503 | −0.849 | −0.565 | −0.132 | −0.0152 |
| CAP2 | −0.182 | −0.148 | −0.140 | −0.054 | −0.175 | 0.145 | 0.464 | 0.922 | 0.875 |
| CAP Pearson correlation (Environmental variables) | |||||||||
| SST | DF | Depth | |||||||
| CAP1 | 0.334 | −0.707 | −0.023 | ||||||
| CAP2 | 0.079 | −0.082 | 0.322 | ||||||
| PERMUTATION TEST Trace statistic = (tr(Q_m’HQ_m)) First squared canonical correlation = (delta_1^2) = δ12 Trace statistic: tr (Q_m’HQ_m): 1.45507 P: 0.0002 δ12: 0.83709 P: 0.0002 No. of permutations used: 4999 | |||||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bangi, H.G.P.; Juinio-Meñez, M.A. Feeding and Reproductive Phenotypic Traits of the Sea Urchin Tripneustes gratilla in Seagrass Beds Impacted by Eutrophication. Diversity 2023, 15, 843. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15070843
Bangi HGP, Juinio-Meñez MA. Feeding and Reproductive Phenotypic Traits of the Sea Urchin Tripneustes gratilla in Seagrass Beds Impacted by Eutrophication. Diversity. 2023; 15(7):843. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15070843
Chicago/Turabian StyleBangi, Helen Grace P., and Marie Antonette Juinio-Meñez. 2023. "Feeding and Reproductive Phenotypic Traits of the Sea Urchin Tripneustes gratilla in Seagrass Beds Impacted by Eutrophication" Diversity 15, no. 7: 843. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15070843
APA StyleBangi, H. G. P., & Juinio-Meñez, M. A. (2023). Feeding and Reproductive Phenotypic Traits of the Sea Urchin Tripneustes gratilla in Seagrass Beds Impacted by Eutrophication. Diversity, 15(7), 843. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15070843








