The Influential Role of the Habitat on the Diversity Patterns of Free-Living Aquatic Nematode Assemblages in the Cuban Archipelago
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
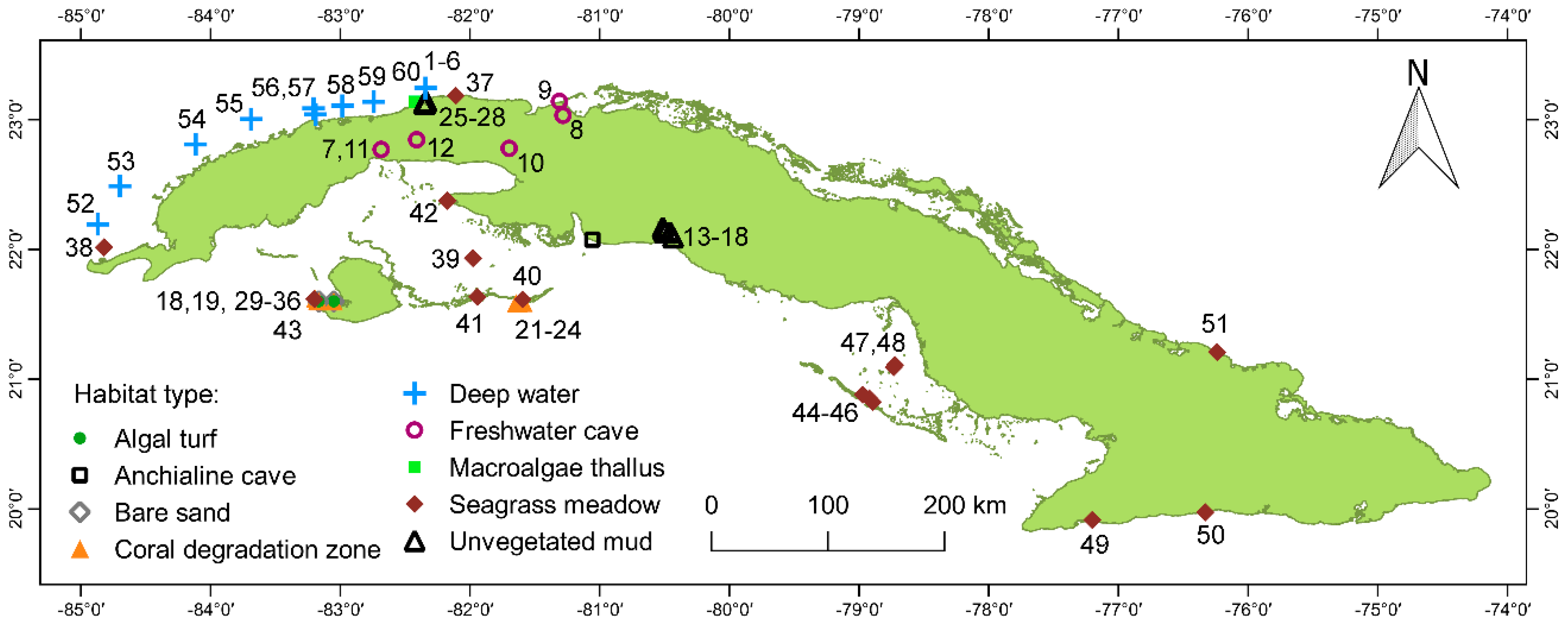
2.1. Study Sites and Habitats
2.2. Collection and Processing of Samples
2.3. Biological Traits
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
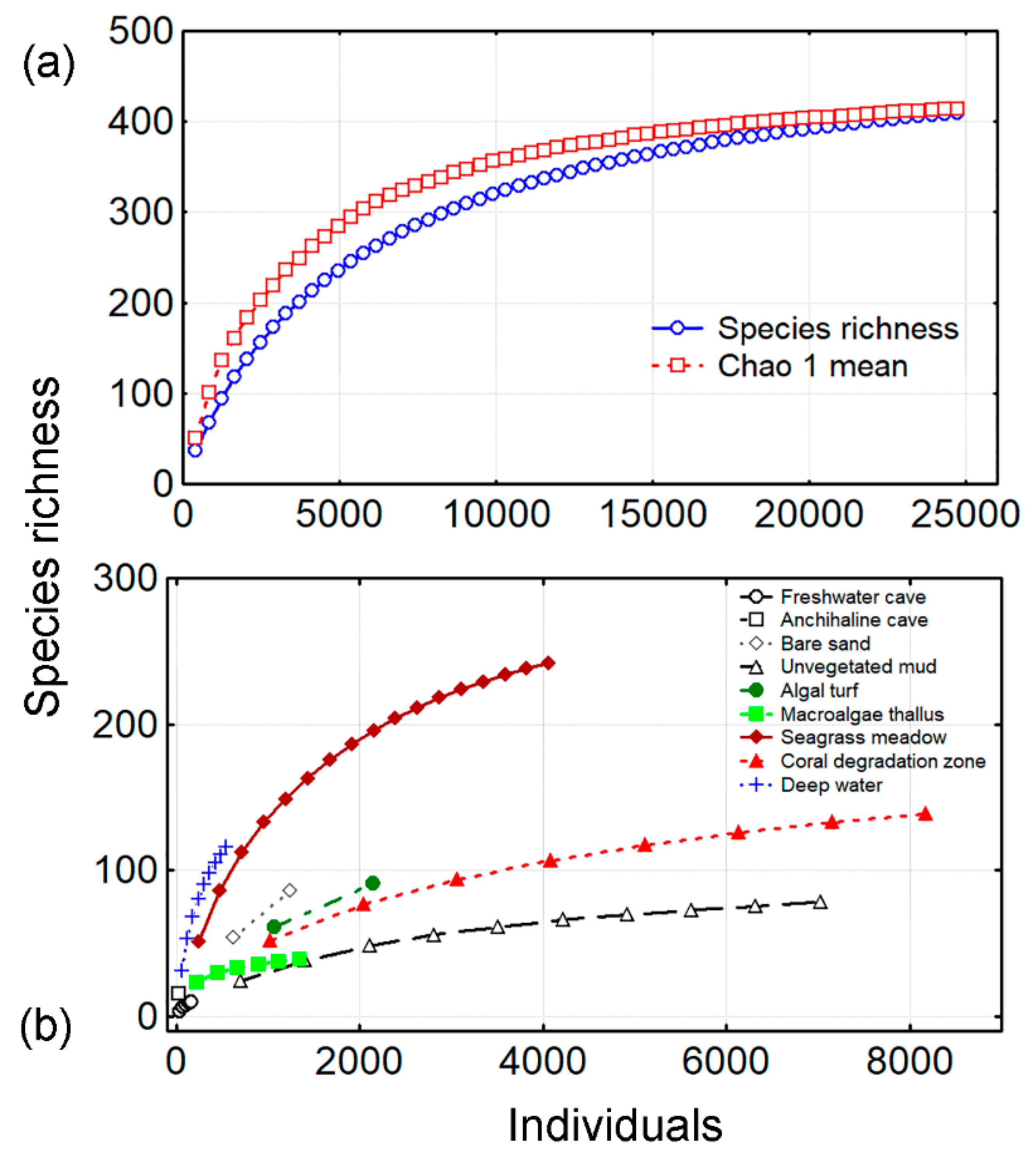
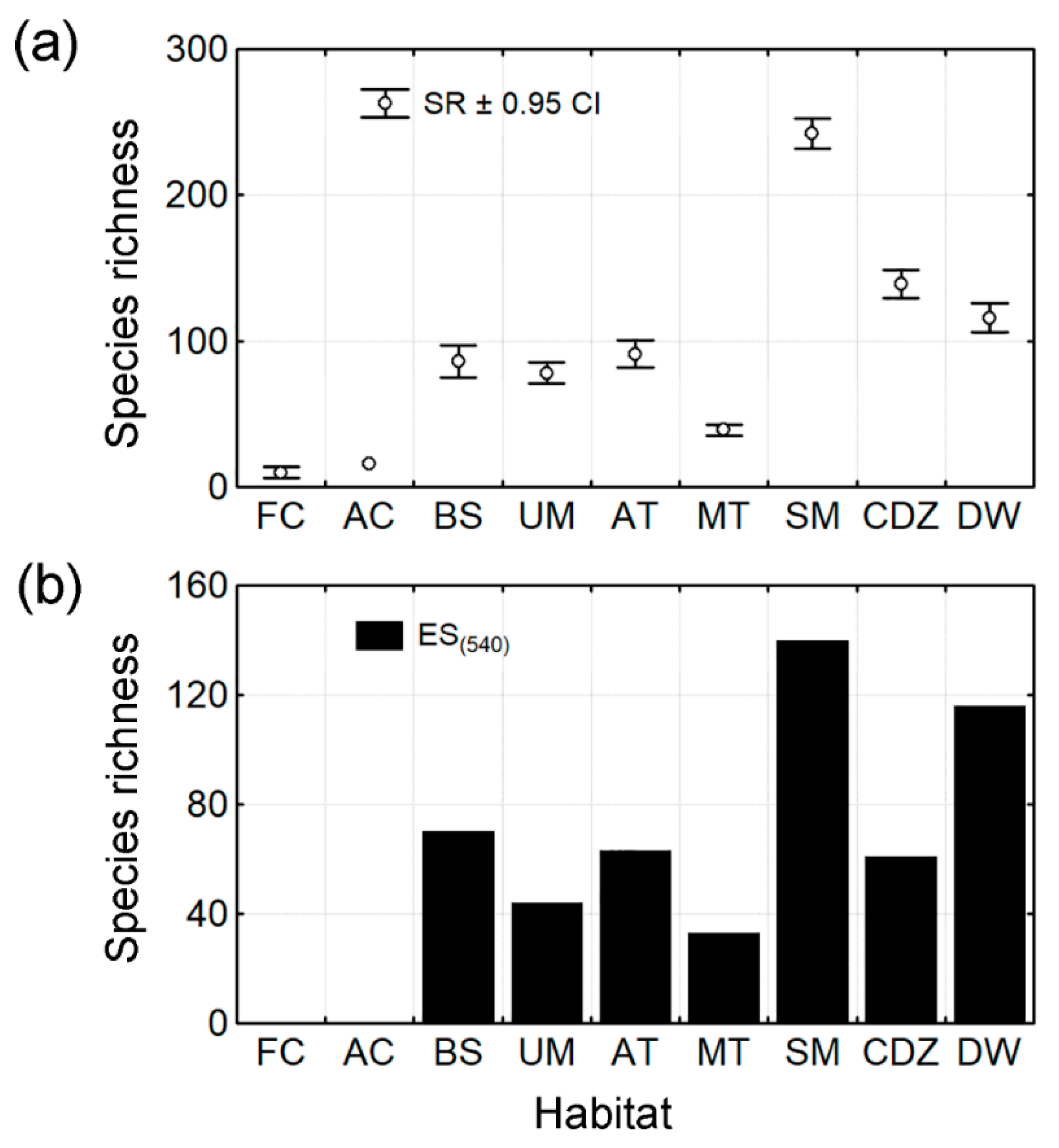
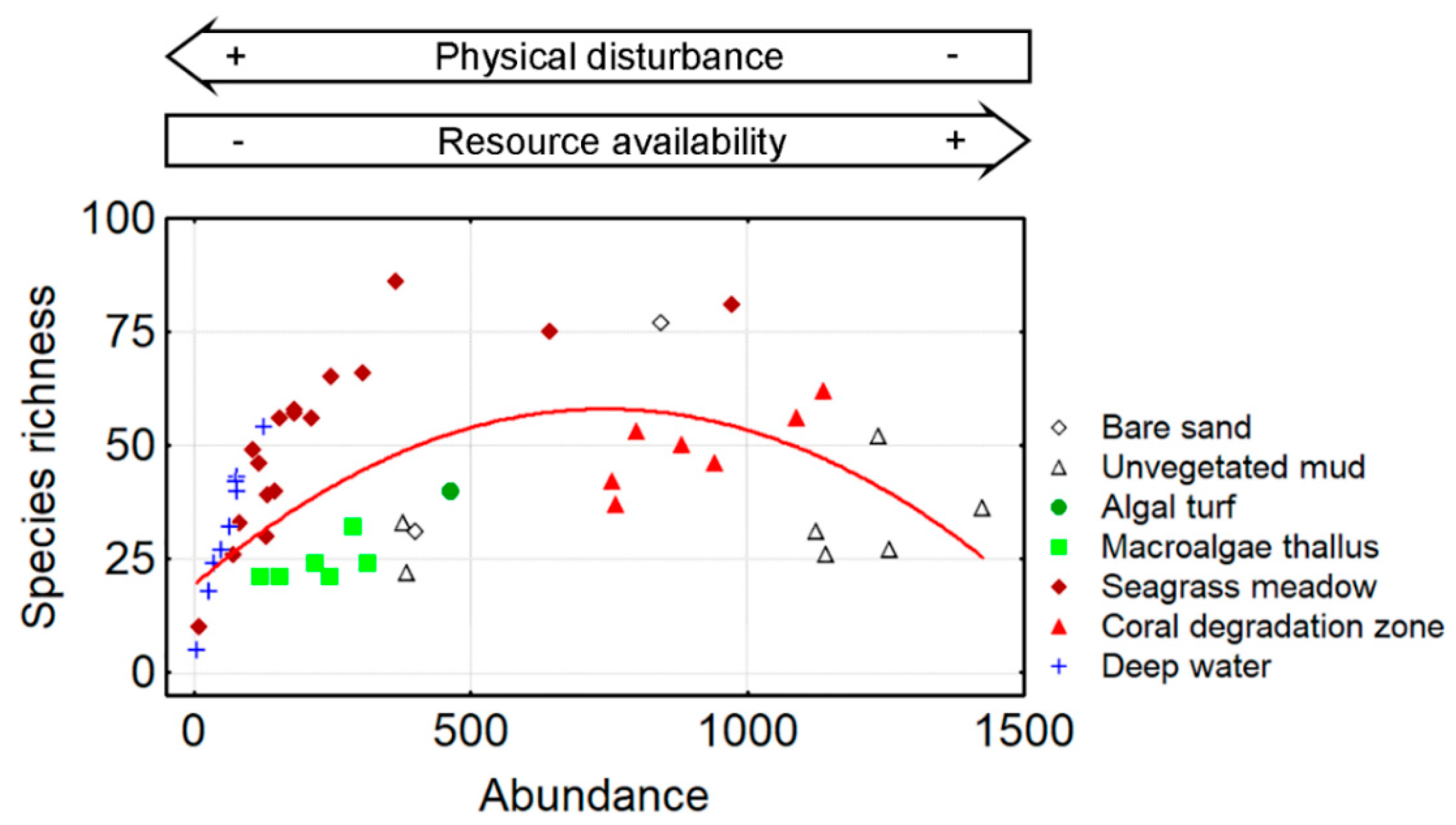
3.1. Species Richness
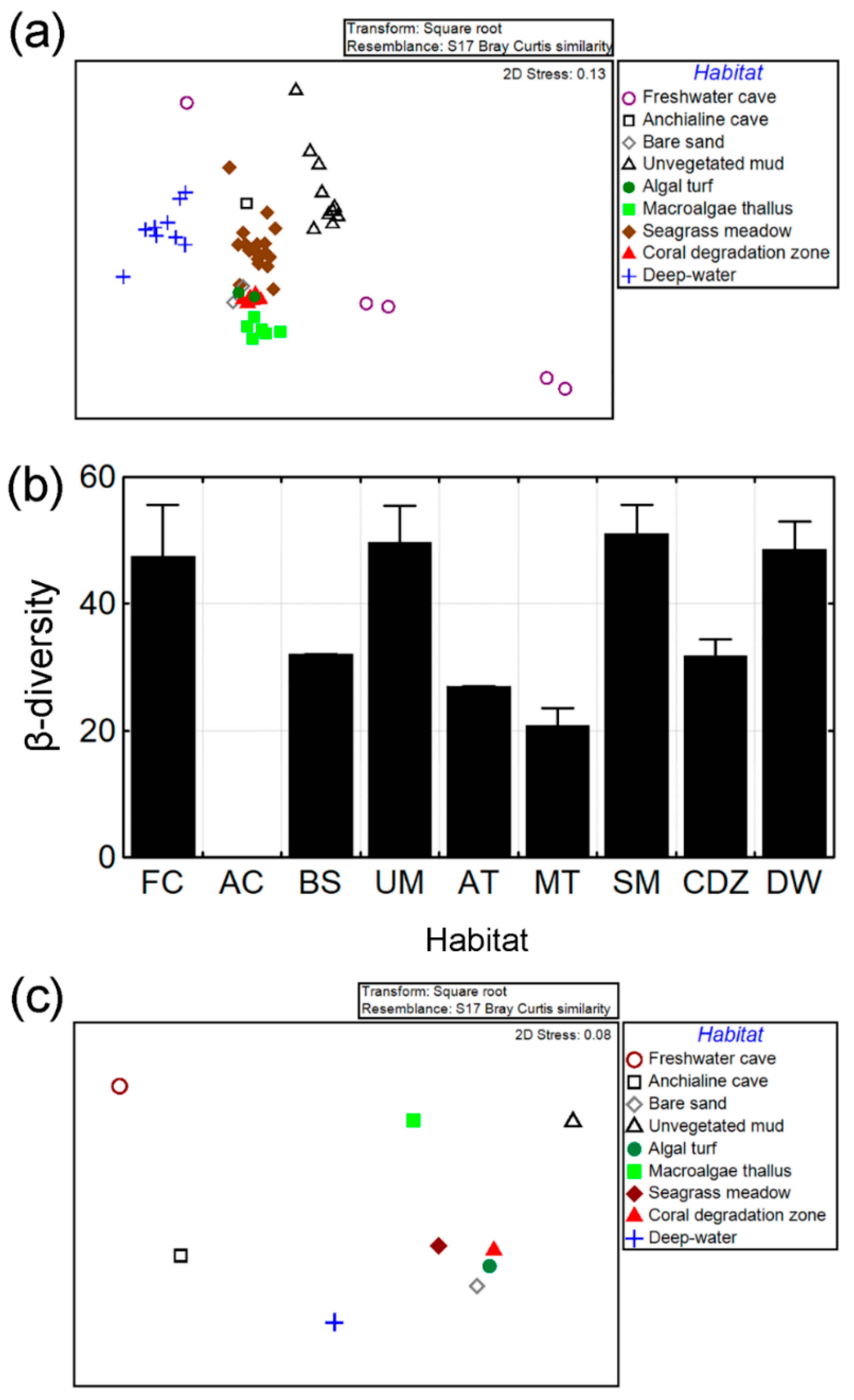
3.2. β-Diversity
3.3. Biological Traits
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Begon, M.; Townsend, C.R.; Harper, J.L. Ecology: From Individuals to Ecosystems; Blackwell Publishing: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Southwood, T.R.E. Habitat, the templet for ecological studies? J. Anim. Ecol. 1977, 46, 337–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Southwood, T.R.E. Tactics, strategies and templets. Oikos 1988, 52, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraro, S.P. Ecological periodic tables: In principle and practice. Oikos 2013, 122, 1541–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vellend, M. Conceptual synthesis in community ecology. Q. Rev. Biol. 2010, 85, 183–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraft, N.J.B.; Adler, P.B.; Godoy, O.; James, E.C.; Fuller, S.; Levine, J.M. Community assembly, coexistence and the environmental filtering metaphor. Funct. Ecol. 2015, 29, 592–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Townsend, C.R.; Hildrew, A.G. Species traits in relation to a habitat templet for river systems. Freshw. Biol. 1994, 31, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewitt, J.E.; Thrush, S.F.; Dayton, P.D. Habitat variation, species diversity and ecological functioning in a marine system. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2008, 366, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraro, S.P.; Cole, F.A. Ecological periodic tables for benthic macrofaunal usage of estuarine habitats in the US Pacific Northwest. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2011, 94, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraro, S.P.; Cole, F.A. Ecological periodic tables for benthic macrofaunal usage of estuarine habitats: Insights from a case study in Tillamook Bay, Oregon, USA. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2012, 102–103, 70–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.J.; Crist, T.O.; Chase, J.M.; Vellend, M.; Inouye, B.D.; Freestone, A.L.; Sanders, N.J.; Cornell, H.V.; Comita, L.S.; Davies, K.F.; et al. Navigating the multiple meanings of b diversity: A roadmap for the practicing ecologist. Ecol. Lett. 2011, 14, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heip, C.; Vincx, M.; Vranken, G. The ecology of marine nematodes. Oceanogr. Mar. Biol. Annu. Rev. 1985, 23, 399–489. [Google Scholar]
- Abebe, E.; Andrássy, I.; Traunspurger, W. Freshwater Nematodes: Ecology and Taxonomy; Abebe, E., Andrássy, I., Traunspurger, W., Eds.; CABI Publishing: Oxfordshire, UK, 2006; p. 253. [Google Scholar]
- Appeltans, W.; Ahyong, S.T.; Anderson, G.; Angel, M.V.; Artois, T.; Bailly, N.; Bamber, R.; Barber, A.; Bartsch, I.; Berta, A.; et al. The magnitude of global marine species diversity. Curr. Biol. 2012, 22, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moens, T.; Braeckman, U.; Derycke, S.; Fonseca, G.; Gallucci, F.; Gingold, R.; Guilini, K.; Ingels, J.; Leduc, D.; Vanaverbeke, J.; et al. Ecology of free-living marine nematodes. Hand. Zool. 2013, 2, 109–152. [Google Scholar]
- Danovaro, R.; Carugati, L.; Corinaldesi, C.; Gambi, C.; Guilini, K.; Pusceddu, A.; Vanreusel, A. Multiple spatial scale analyses provide new clues on patterns and drivers of deep-sea nematode diversity. Deep Sea Res. II 2013, 92, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosli, N.; Leduc, D.; Rowden, A.A.; Probert, P.K.; Clark, M.R. Regional and sediment depth differences in nematode community structure greater than between habitats on the New Zealand margin: Implications for vulnerability to anthropogenic disturbance. Prog. Oceanogr. 2018, 160, 26–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pusceddu, A.; Gambi, C.; Zeppilli, D.; Bianchelli, S.; Danovaro, R. Organic matter composition, metazoan meiofauna and nematode biodiversity in Mediterranean deep-sea sediments. Deep Sea Res. II 2009, 56, 755–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGill, B.J.; Enquist, B.J.; Weiher, E.; Westoby, M. Rebuilding community ecology from functional traits. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2006, 21, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huston, M. Biological Diversity: The Coexistence of Species on Changing Landscapes; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1994; p. 681. [Google Scholar]
- Connell, J.H. Diversity in tropical rain forests and coral reefs. Science 1978, 199, 1302–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, D.H. Species-energy theory: An extension of species-area theory. Oikos 1983, 41, 496–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raes, M.; De Troch, M.; Ndaro, S.G.M.; Muthumbi, A.; Guilini, K.; Vanreusel, A. The structuring role of microhabitat type in coral degradation zones: A case study with marine nematodes from Kenya and Zanzibar. Coral Reefs 2007, 26, 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raes, M.; Decraemer, W.; Vanreusel, A. Walking with worms: Coral-associated epifaunal nematodes. J. Biogeogr. 2008, 35, 2207–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semprucci, F.; Colantoni, P.; Sbrocca, C.; Baldelli, G.; Balsamo, M. Spatial patterns of distribution of meiofaunal and nematode assemblages in the Huvadhoo lagoon (Maldives, Indian Ocean). J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 2014, 94, 1377–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semprucci, F.; Cesaroni, L.; Guidi, L.; Balsamo, M. Do the morphological and functional traits of free-living marine nematodes mirror taxonomical diversity? Mar. Environ. Res. 2018, 135, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, T.M.T.; Venekey, V. Meiofauna and free-living nematodes in volcanic sands of a remote South Atlantic, oceanic island (Trindade, Brazil). J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasath, D.; Balasubramaniam, J.; Jayarat, K.A. Diversity and distribution of the free-living marine nematodes in the mangrove sediments of the Andaman Islands. Indian J. Geo Mar. Sci. 2018, 47, 2217–2224. [Google Scholar]
- Thai, T.T.; Lam, N.L.Q.; Yen, N.T.M.; Vanreusel, A.; Quang, N.X. Biodiversity and distribution patterns of free-living nematode communities in Ba Lai River, Ben Tree Province. Vietnam J. Sci. Technol. 2018, 56, 224–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Colwell, R.K.; Coddington, J.A. Estimating terrestrial biodiversity through extrapolation. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 1994, 345, 101–118. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gotelli, N.J.; Colwell, R.K. Estimating species richness. In Biological Diversity. Frontiers in Measurement and Assessment; Magurran, A.E., McGill, B.J., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2011; pp. 39–54. [Google Scholar]
- Violle, C.; Navas, M.L.; Vile, D.; Kazakou, E.; Fortunel, C.; Hummel, I.; Garnier, E. Let the concept of trait be functional! Oikos 2007, 116, 882–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiørboe, T.; Visser, A.; Andersen, K.H. A trait-based approach to ocean ecology. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2018, 75, 1849–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Plas, F. Biodiversity and ecosystem functioning in naturally assembled communities. Biol. Rev. 2019, 94, 1220–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bremner, J.; Rogers, S.I.; Frid, C.L.J. Assessing functional diversity in marine benthic ecosystems: A comparison of approaches. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2003, 254, 11–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bremner, J.; Rogers, S.I.; Frid, C.L.J. Methods for describing ecological functioning of marine benthic assemblages using biological traits analysis (BTA). Ecol. Ind. 2006, 6, 609–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schratzberger, M.; Warr, K.; Rogers, S.I. Functional diversity of nematode communities in the southwestern North Sea. Mar. Environ. Res. 2007, 63, 368–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves, A.S.; Veríssimo, H.; Costa, M.J.; Marques, J.C. Taxonomic resolution and Biological Traits Analysis (BTA) approaches in estuarine free-living nematodes. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2014, 138, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Liu, X.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Hua, E.; Zhang, Z. Effects of Yellow Sea Cold Water Mass on marine nematodes based on biological trait analysis. Mar. Environ. Res. 2018, 141, 167–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armenteros, M.; Ruiz-Abierno, A.; Fernández-Garcés, R.; Pérez-García, J.A.; Díaz-Asencio, L.; Vincx, M.; Decraemer, W. Biodiversity patterns of free-living marine nematodes in a tropical bay: Cienfuegos, Caribbean Sea. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2009, 85, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-García, J.A.; Marzo-Pérez, D.; Armenteros, M. Spatial scale influences diversity patterns of free-living nematode assemblages in coral degradation zones from the Caribbean Sea. Mar. Biodivers. 2019, 49, 1831–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrássy, I. Nematoden aus strand- und höhlenbiotopen von Kuba. Acta Zool. Acad. Sci. Hung. 1973, 19, 233–270. [Google Scholar]
- López-Cánovas, C.I.; Pastor De Ward, C. Lista de los nemátodos de la clase Adenophorea (Subclase Chromadoria y Enoplia) de los pastos marinos del archipiélago Sabana-Camagüey, Cuba. Poeyana 2006, 494, 38–42. [Google Scholar]
- Armenteros, M.; Pérez-García, J.A.; Pérez-Angulo, A.; Williams, J.P. Efficiency of extraction of meiofauna from sandy and muddy marine sediments. Rev. Investig. Marian. Univ. Habana 2008, 29, 113–118. [Google Scholar]
- De Grisse, A.T. Redescription ou modification de quelques techniques utilises dans l’ étude des nématodes phytoparasitaires. Meded. Rijksfac. Landbouwwet. Gent 1969, 34, 351–369. [Google Scholar]
- Platt, H.M.; Warwick, R.M. Free-Living Marine Nematodes. Part I. British Enoplids; The Linnean Society of London and The Estuarine and Brackish-Water Sciences Association: Cambridge, UK, 1983; Volume 28. [Google Scholar]
- Platt, H.M.; Warwick, R.M. Free-Living Marine Nematodes. Part II. British Chromadorids; The Linnean Society of London and The Estuarine and Brackish-water Sciences Association: Leiden, The Netherlands, 1988; Volume 38. [Google Scholar]
- Warwick, R.M.; Platt, H.M.; Somerfield, P.J. Free-Living Marine Nematodes. Part III. Monhysterids; The Linnean Society of London and The Estuarine and Coastal Sciences Association: Shrewsbury, UK, 1998; Volume 53. [Google Scholar]
- Bongers, T.; Alkemade, R.; Yeates, G.W. Interpretation of disturbance-induced maturity decrease in marine nematode assemblages by means of the Maturity Index. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1991, 76, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bongers, T.; Bongers, M. Functional diversity of nematodes. Appl. Soil Ecol. 1998, 10, 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bongers, T.; De Goede, R.G.M.; Korthals, G.W.; Yeates, G.W. Proposed changes of c–p classification for nematodes. Russ. J. Nematol. 1995, 3, 61–62. [Google Scholar]
- Wieser, W. Die Bezichung swischen Mundhöhlengestalt, Ernährungsweise und Vorkommen bei freilebenden marinen Nematoden. Ark. Zool. 1953, 4, 439–484. [Google Scholar]
- Thistle, D.; Lambshead, P.J.D.; Sherman, K.M. Nematode tail-shape groups respond to environmental differences in the deep sea. Vie Milieu 1995, 45, 107–115. [Google Scholar]
- Colwell, R.K. EstimateS: Statistical Estimation of Species Richness and Shared Species from Samples. Version 9. Available online: http://purl.oclc.org/estimates (accessed on 26 December 2018).
- Chao, A.; Chazdon, R.L.; Colwell, R.K.; Shen, T.J. Abundance-based similarity indices and their estimation when there are unseen species in samples. Biometrics 2006, 62, 361–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarke, K.R.; Gorley, R.N. Primer V6: User Manual/Tutorial; Primer-E, Ltd: Plymouth, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, M.J.; Gorley, R.N.; Clarke, K.R. PERMANOVA+ for PRIMER: Guide to Software and Statistical Methods; Primer-E, Ltd: Plymouth, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Armenteros, M.; Rojas-Corzo, A.; Ruiz-Abierno, A.; Derycke, S.; Backeljau, T.; Decraemer, W. Systematics and DNA barcoding of free-living marine nematodes with emphasis on tropical desmodorids using nuclear SSU rDNA and mitochondrial COI sequences. Nematology 2014, 16, 979–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macheriotou, L.; Guilini, K.; Bezerra, T.N.C.; Tytgat, B.; Nguyen, D.T.; Nguyen, T.X.P.; Noppe, F.; Armenteros, M.; Boufahja, F.; Rigaux, A.; et al. Metabarcoding free-living marine nematodes using curated 18S and CO1 reference sequence databases for species-level taxonomic assignments. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 9, 1211–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinmann, K.; Eggenberg, S.; Wohlgemuth, T.; Linder, H.P.; Zimmermann, N.E. Niches and noise—Disentangling habitat diversity and area effect on species diversity. Ecol. Complex. 2011, 8, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.X.; Yeh, H.M.; Mok, H.K. Meiofaunal communities in a tropical seagrass bed and adjacent unvegetated sediments with note on sufficient sample size for determining local diversity indices. Zool. Stud. 2015, 54, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udalov, A.A.; Azovsky, A.I.; Mokievsky, V.O. Depth-related pattern in nematode size: What does the depth itself really mean? Prog. Oceanogr. 2005, 67, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, J.; Baguley, J.; Montagna, P.A.; Rowe, G.T. Assessment of Longitudinal Gradients in Nematode Communities in the Deep Northern Gulf of Mexico and Concordance with Benthic Taxa. Int. J. Oceanogr. 2012, 2012, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Brooks, G.R.; Larson, R.A.; Schwing, P.T.; Diercks, A.R.; Armenteros, M.; Diaz-Asencio, M.; Martínez-Suárez, A.; Sanchez-Cabeza, J.A.; Ruiz-Fernandez, A.C.; Herguera, J.C.; et al. Gulf of Mexico (GoM) bottom sediments and depositional processes: A baseline for future oil spills. In Scenarios and Responses to Future Deep Oil Spills; Murawski, S.A., Ainsworth, C.H., Gilbert, S., Hollander, D.J., Paris, C.B., Schlüter, M., Wetzel, D.L., Eds.; Springer Nature: Basel, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 75–95. [Google Scholar]
- Vanreusel, A.; Fonseca, G.; Danovaro, R.; da Silva, M.C.; Esteves, A.M.; Ferrero, T.; Gad, G.; Galtsova, V.; Gambi, M.C.; Fonsêca-Genevois, V.G.; et al. The contribution of deep-sea macrohabitat heterogeneity to global nematode diversity. Mar. Ecol. 2010, 31, 6–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armenteros, M.; Ruiz-Abierno, A. Body size distribution of free-living marine nematodes from a Caribbean coral reef. Nematology 2015, 17, 1153–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemminga, M.A.; Duarte, C.M. Seagrass Ecology; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1999; p. 299. [Google Scholar]
- Danovaro, R.; Gambi, C. Biodiversity and trophic structure of nematode assemblages in seagrass systems: Evidence for a coupling with changes in food availability. Mar. Biol. 2002, 141, 667–677. [Google Scholar]
- Fisher, R. Spatial and temporal variations in nematode assemblages in tropical seagrass sediments. Hydrobiologia 2003, 493, 43–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, R.; Sheaves, M.J. Community structure and spatial variability of marine nematodes in tropical Australian pioneer seagrass meadows. Hydrobiologia 2003, 495, 143–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canion, C.R.; Heck, K.L., Jr. Effect of habitat complexity on predation success: Re-evaluating the current paradigm in seagrass beds. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2009, 393, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walters, K.; Bell, S.S. Diel patterns of active vertical migration in seagrass meiofauna. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1986, 34, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Quinto, A.; Falcón, L.I. Metagenome of Acropora palmata coral rubble: Potential metabolic pathways and diversity in the reef ecosystem. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0220117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armenteros, M.; Pérez-Angulo, A.; Regadera, R.; Beltrán, J.; Vincx, M.; Decraemer, W. Effects of heavy and chronic pollution on macro- and meiobenthos of Havana Bay, Cuba. Rev. Investig. Marina. Univ. Habana 2009, 30, 203–214. [Google Scholar]
- Díaz-Asencio, L.; Helguera, Y.; Fernández-Garcés, R.; Gómez-Batista, M.; Rosell, G.; Hernández, Y.; Pulido, A.; Armenteros, M. Two-year temporal response of benthic macrofauna and sediments to hypoxia in a tropical semi-enclosed bay (Cienfuegos, Cuba). Rev. Biol. Trop. 2016, 64, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Du Preez, G.; Majdi, N.; Swart, A.; Traunspurger, W.; Fourie, H. Nematodes in caves: A historical perspective on their occurrence, distribution and ecological relevance. Nematology 2017, 19, 627–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewitt, J.E.; Thrush, S.F.; Halliday, J.; Duffy, C. The importance of small-scale habitat structure for maintaining beta diversity. Ecology 2005, 86, 1619–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derycke, S.; Backeljau, T.; Moens, T. Dispersal and gene flow in free-living marine nematodes. Front. Zool. 2013, 10, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Culver, D.C.; Pipan, T.; Schneider, K. Vicariance, dispersal and scale in the aquatic subterranean fauna of karst regions. Freshw. Biol. 2009, 54, 918–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kritzer, J.P.; Delucia, M.B.; Greene, E.; Shumway, C.; Topolski, M.F.; Thomas-Blate, J.; Chiarella, L.A.; Davy, K.B.; Smith, K.P. The importance of benthic habitats for coastal fisheries. BioScience 2016, 66, 274–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tews, J.; Brose, U.; Grimm, V.; Tielbörger, K.; Wichmann, M.C.; Schwager, M.; Jeltsch, F. Animal species diversity driven by habitat heterogeneity/diversity: The importance of keystone structures. J. Biogeogr. 2004, 31, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-García, J.A.; Ruiz-Abierno, A.; Armenteros, M. Does morphology of host marine macroalgae drive the ecological structure of epiphytic meiofauna? J. Mar. Biol. Oceanogr. 2015, 4, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petchey, O.L.; Gaston, K.J. Functional diversity: Back to basics and looking forward. Ecol. Lett. 2006, 9, 741–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-García, J.A.; Díaz-Delgado, Y.; García-Machado, E.; Martínez-García, A.; Gonzalez, B.C.; Worsaae, K.; Armenteros, M. Nematode diversity of freshwater and anchialine caves of Western Cuba. Proc. Biol. Soc. Wash. 2018, 131, 144–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Zhang, Z.N. Nematode assemblages from submarine caves in Hong Kong. J. Nat. Hist. 2008, 42, 781–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ape, F.; Arigó, C.; Gristina, M.; Genovese, L.; Di Franco, A.; Di Lorenzo, M.; Baiata, P.; Aglieri, G.; Milisenda, G.; Mirto, S. Meiofaunal diversity and nematode assemblages in two submarine caves of a Mediterranean marine protected area. Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2016, 17, 202–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moens, T.; Vincx, M. Observations on the feeding ecology of estuarine nematodes. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 1997, 77, 211–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höckelmann, C.; Moens, T.; Jüttner, F. Odor compounds from cyanobacterial biofilms acting as attractants and repellents for free-living nematodes. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2004, 49, 1809–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traunspurger, W. Ecology of freshwater nematodes. Hand. Zool. 2013, 2, 153–169. [Google Scholar]

| Species | FC | AC | BS | UM | AT | MT | SM | CDZ | DW |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average within-habitat similarity | 25% | 36% | 26% | 46% | 68% | 25% | 53% | 27% | |
| Ironus ignavus | X | ||||||||
| Monhystrella sp. | X | ||||||||
| Aphanolaimus sp. | X | ||||||||
| Pomponema sp. | X | ||||||||
| Zalonema ditlevseni | X | X | X | ||||||
| Paradesmodora immersa | X | X | |||||||
| Desmodora pontica | X | X | X | X | |||||
| Tricoma sp. | X | X | X | ||||||
| Enoploides bisulcus | X | ||||||||
| Innocuonema asymmetricum | X | ||||||||
| Viscosia abyssorum | X | X | |||||||
| Sabatieria pulchra | X | ||||||||
| Terschellingia longicaudata | X | X | |||||||
| Terschellingia communis | X | ||||||||
| Euchromadora vulgaris | X | X | X | ||||||
| Epsilonema sp. | X | ||||||||
| Croconema cinctum | X | X | |||||||
| Euchromadora gaulica | X | X | |||||||
| Acanthopharynx denticulata | X | ||||||||
| Chromadora brevipapillata | X | ||||||||
| Paracanthonchus platypus | X | ||||||||
| Chromadorella paramucrodonta | X | ||||||||
| Chromadorella filiformis | X | X | |||||||
| Euchromadora atypica | X | ||||||||
| Marylynnia sp. | X | ||||||||
| Halichoanolaimus chordiurus | X | ||||||||
| Cheironchus vorax | X | ||||||||
| Mesacanthion sp. | X | ||||||||
| Desmoscolex sp. | X | ||||||||
| Halichoanolaimus sp. | X | ||||||||
| Dorylaimopsis punctata | X | ||||||||
| Setosabatieria hilarula | X | ||||||||
| Daptonema sp. | X | ||||||||
| Draconema sp. | X | ||||||||
| Endeolophos fossiferus | X | ||||||||
| Metadasynemella falciphalla | X | ||||||||
| Acantholaimus megamphis | X | ||||||||
| Cervonema macramphis | X | ||||||||
| Pselionema simile | X | ||||||||
| Bolbolaimus sp. | X | ||||||||
| Desmodorella tenuispiculum | X | ||||||||
| Acantholaimus maks | X | ||||||||
| Metadasynemella cassidiniensis | X |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Armenteros, M.; Pérez-García, J.A.; Marzo-Pérez, D.; Rodríguez-García, P. The Influential Role of the Habitat on the Diversity Patterns of Free-Living Aquatic Nematode Assemblages in the Cuban Archipelago. Diversity 2019, 11, 166. https://doi.org/10.3390/d11090166
Armenteros M, Pérez-García JA, Marzo-Pérez D, Rodríguez-García P. The Influential Role of the Habitat on the Diversity Patterns of Free-Living Aquatic Nematode Assemblages in the Cuban Archipelago. Diversity. 2019; 11(9):166. https://doi.org/10.3390/d11090166
Chicago/Turabian StyleArmenteros, Maickel, José Andrés Pérez-García, Diana Marzo-Pérez, and Patricia Rodríguez-García. 2019. "The Influential Role of the Habitat on the Diversity Patterns of Free-Living Aquatic Nematode Assemblages in the Cuban Archipelago" Diversity 11, no. 9: 166. https://doi.org/10.3390/d11090166
APA StyleArmenteros, M., Pérez-García, J. A., Marzo-Pérez, D., & Rodríguez-García, P. (2019). The Influential Role of the Habitat on the Diversity Patterns of Free-Living Aquatic Nematode Assemblages in the Cuban Archipelago. Diversity, 11(9), 166. https://doi.org/10.3390/d11090166






