Argulus from the Pascagoula River, MS, USA, with an Emphasis on Those of the Threatened Gulf Sturgeon, Acipenser oxyrinchus desotoi
Abstract
1. Introduction
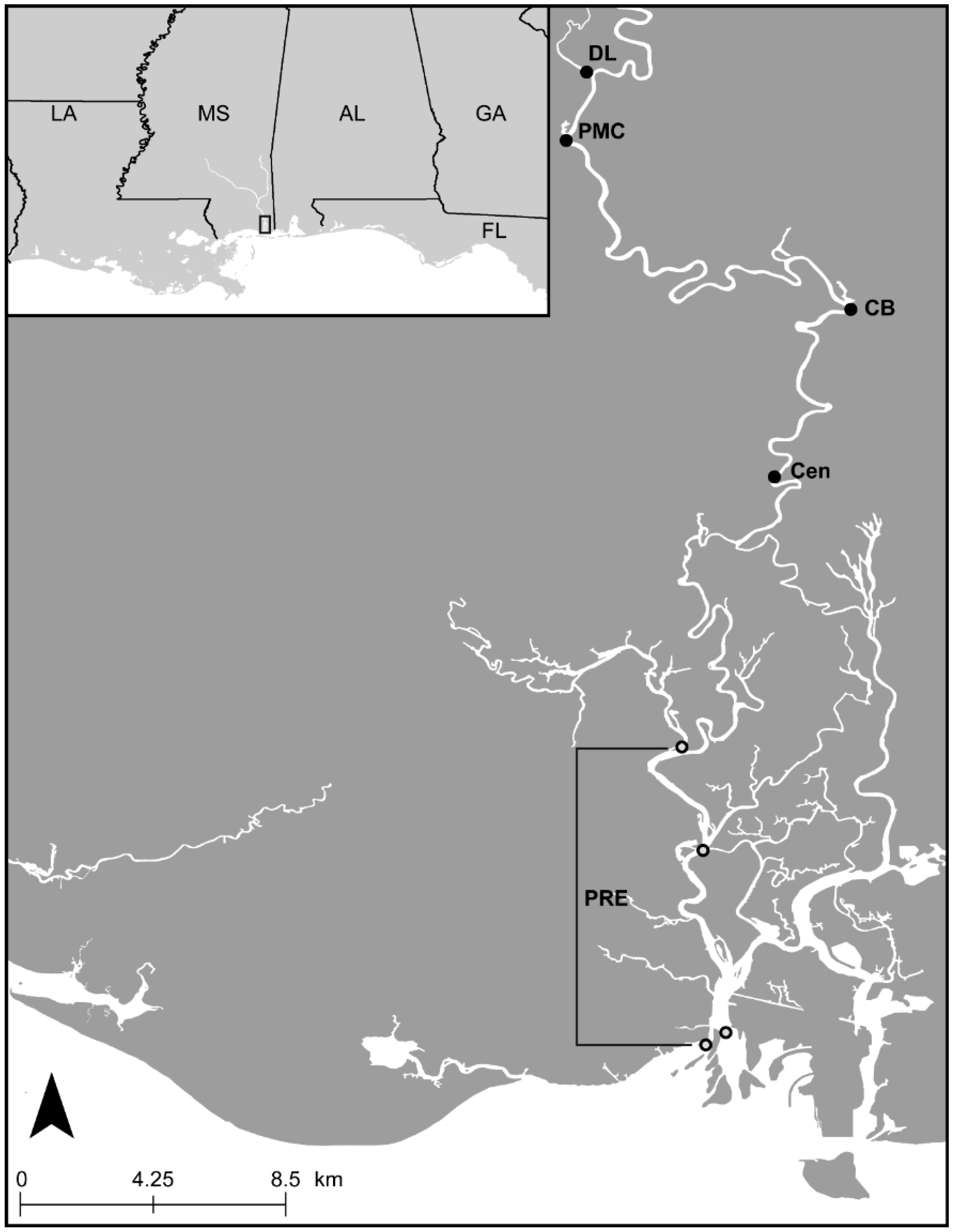
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Collection and Specimen Preparation
2.2. Genetic Techniques and Comparison
2.3. Ecological Data and Analyses
3. Results
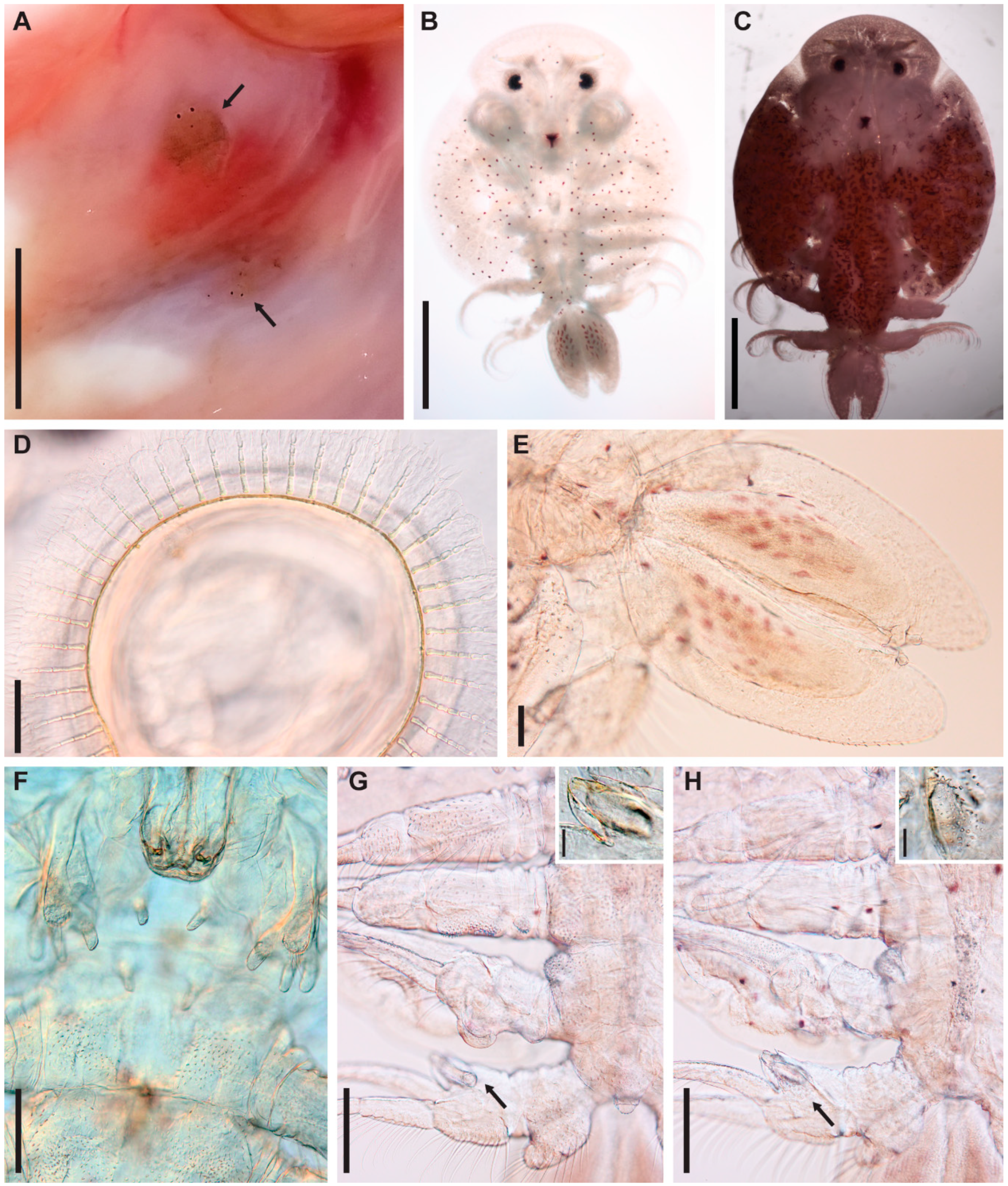
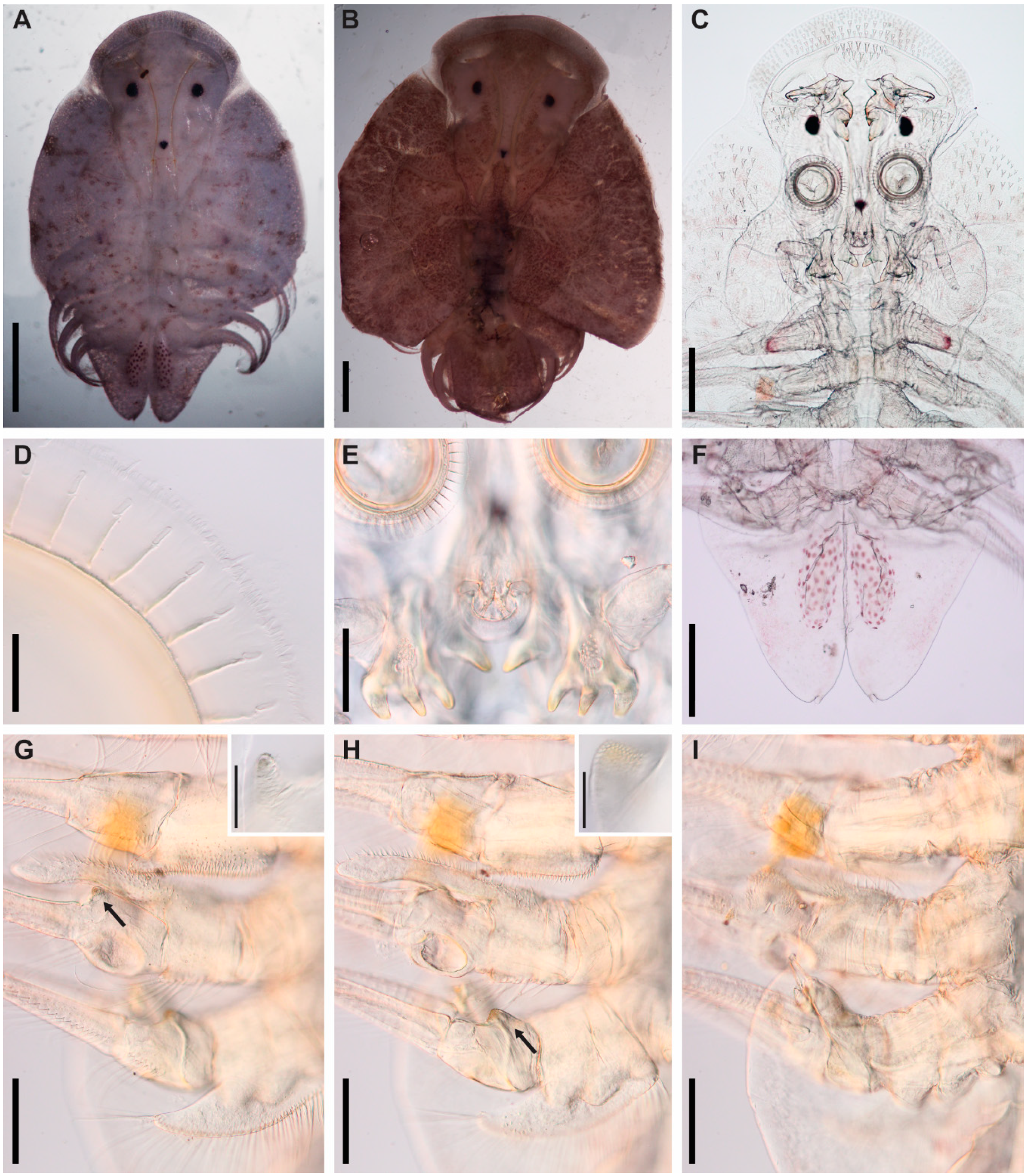
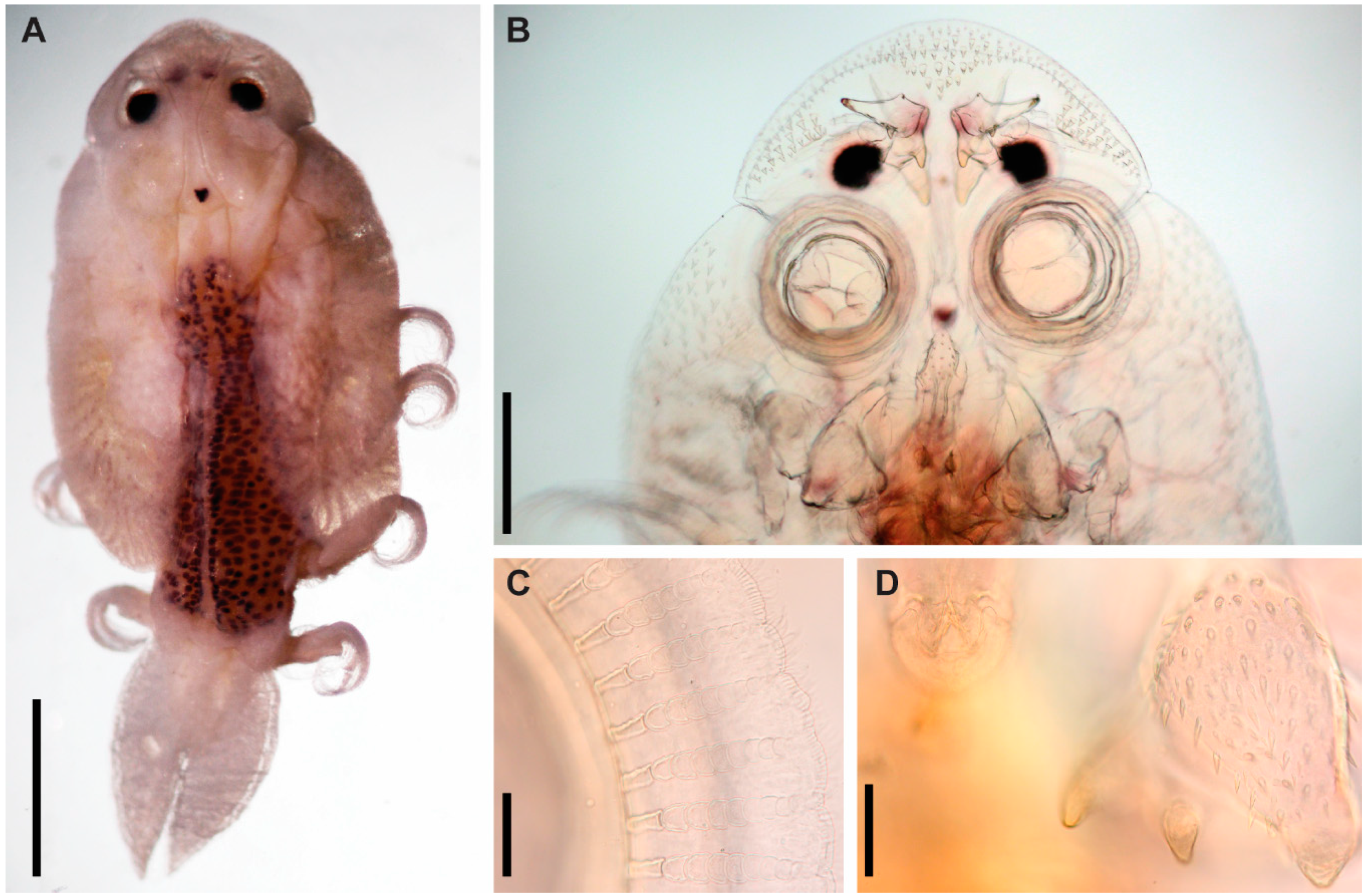
3.1. Argulus flavescens Wilson, 1916
3.2. Argulus americanus Wilson, 1902
3.3. Argulus bicolor Bere, 1936
3.4. Molecular Results
3.5. Ecology of Argulus flavescens
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Estuary | Census Site | Cumbest Bluff | Paper Mill Camp | Dead Lake | |
| 2016 | |||||
| June | - | - | 1 | - | - |
| July | - | - | - | - | - |
| August | - | - | - | - | - |
| September | - | - | 15 | 1 | 8 |
| October | - | 16 | 20 | - | - |
| November | - | - | - | - | - |
| 2017 | |||||
| June | - | - | - | - | - |
| July | - | - | - | - | - |
| August | - | - | - | - | - |
| September | - | - | 1 | 7 | 13 |
| October | - | 0 | 4 | 0 | - |
| November | 2 | - | - | - | - |
| 2018 | |||||
| June | - | - | 4 | - | - |
| July | - | - | - | - | 5 |
| August | - | - | 10 | - | 3 |
| September | - | - | - | - | - |
| October | - | 0 | 33 | 6 | 0 |
| November | 1 | 1 | - | - | - |
| 2019 | |||||
| April | 1 | - | - | - | - |
| May | 5 | - | - | - | - |
| June | 4 | - | 5 | - | - |
| July | - | - | - | - | 6 |
| August | - | - | 14 | - | - |
| September | - | - | 16 | 7 | - |
References
- Poly, W.J. Global diversity of fishlice (Crustacea: Branchiura: Argulidae) in freshwater. Hydrobiologia 2008, 595, 209–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Møller, O.S. Branchiura (Crustacea)—Survey of historical literature and taxonomy. Arthropod Syst. Phylogeny 2009, 67, 41–55. [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguti, S. Parasitic Copepoda and Branchiura of Fishes; Interscience: New York, NY, USA, 1963. [Google Scholar]
- Neethling, L.A.M.; Avenant-Oldewage, A. Branchiura—A compendium of the geographical distribution and a summary of their biology. Crustaceana 2016, 89, 1243–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overstreet, R.M.; Dyková, I.; Hawkins, W.E. Branchiura. In Microscopic Anatomy of Invertebrates Volume 9: Crustacea; Harrison, F.W., Humes, A.G., Eds.; Wiley-Liss, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1991; pp. 385–413. [Google Scholar]
- Lester, R.J.G.; Hayward, C.J. Phylum Arthropoda. In Fish Diseases and Disorders. Volume 1: Protozoan and Metazoan Infections; Woo, P.T.K., Ed.; CABI: Wallingford, UK, 2006; pp. 466–565. [Google Scholar]
- Meehean, O.L. A review of the parasitic Crustacea of the genus Argulus in the collections of the United States National Museum. Proc. U. S. Natl. Museum 1940, 88, 459–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trujillo-González, A.; Becker, J.A.; Hutson, K.S. Parasite Dispersal from the Ornamental Goldfish Trade. In Advances in Parasitology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; Volume 100, pp. 239–281. ISBN 9780128151693. [Google Scholar]
- Poly, W.J. Branchiura (Crustacea) of the Gulf of Mexico. In Gulf of Mexico-Origins, Waters, and Biota. Biodiversity; Felder, D.L., Camp, D.K., Eds.; Texas A&M University Press: College Station, TX, USA, 2009; pp. 837–840. [Google Scholar]
- Sulak, K.J.; Parauka, F.; Slack, W.T.; Ruth, R.T.; Randall, M.T.; Luke, K.; Mettee, M.F.; Price, M.E. Status of scientific knowledge, recovery progress, and future research directions for the Gulf sturgeon, Acipenser oxyrinchus desotoi Vladykov, 1955. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2016, 32, 87–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heise, R.J.; Slack, W.T.; Ross, S.T.; Dugo, M.A. Gulf sturgeon summer habitat use and fall migration in the Pascagoula River, Mississippi, USA. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2005, 21, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulak, K.J.; Berg, J.J.; Randall, M. Feeding habitats of the Gulf sturgeon, Acipenser oxyrinchus desotoi, in the Suwannee and Yellow rivers, Florida, as identified by multiple stable isotope analyses. Environ. Biol. Fishes 2012, 95, 237–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritts, A.K.; Fritts, M.W.; Peterson, D.L.; Fox, D.A.; Bringolf, R.B. Critical linkage of imperiled species: Gulf Sturgeon as host for Purple Bankclimber mussels. Freshw. Sci. 2012, 31, 1223–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heard, R.W.; Mclelland, J.A.; Foster, J.M. Direct and Indirect Observations on the Diet, Seasonal Occurrence, and Distribution of the Gulf sturgeon, Acipenser oxyrinchus Desotoi Vladykov, 1955 from the Choctawhatchee Bay System, Florida, in Relation to Macroinvertebrate Assemblages and Para.; Report to U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service: Panama City, FL, USA, 1998; pp. 1–33. [Google Scholar]
- Paperna, I. Diseases caused by parasites in the aquaculture of warm water fish. Annu. Rev. Fish Dis. 1991, 1, 155–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overstreet, R.M.; Hawkins, W.E. Diseases and mortalities of fishes and other animals in the Gulf of Mexico. In Habitats and Biota of the Gulf of Mexico: Before the Deepwater Horizon Oil Spill; Springer New York: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 1589–1738. [Google Scholar]
- Ross, S.T. Inland fishes of Mississippi; University Press of Mississippi: Jackson, MS, USA, 2001; ISBN 1578062462. [Google Scholar]
- Markmann, M.; Tautz, D. Reverse taxonomy: An approach towards determining the diversity of meiobenthic organisms based on ribosomal RNA signature sequences. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2005, 360, 1917–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Møller, O.S.; Olesen, J.; Avenant-Oldewage, A.; Thomsen, P.F.; Glenner, H. First maxillae suction discs in Branchiura (Crustacea): Development and evolution in light of the first molecular phylogeny of Branchiura, Pentastomida, and other “Maxillopoda”. Arthropod Struct. Dev. 2008, 37, 333–346. [Google Scholar]
- von Reumont, B.M.; Meusemann, K.; Szucsich, N.U.; Dell’Ampio, E.; Gowri-Shankar, V.; Bartel, D.; Simon, S.; Letsch, H.O.; Stocsits, R.R.; Luan, Y.; et al. Can comprehensive background knowledge be incorporated into substitution models to improve phylogenetic analyses? A case study on major arthropod relationships. BMC Evol. Biol. 2009, 9, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mallatt, J.M.; Garey, J.R.; Shultz, J.W. Ecdysozoan phylogeny and Bayesian inference: First use of nearly complete 28S and 18S rRNA gene sequences to classify the arthropods and their kin. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oakley, T.H.; Cunningham, C.W. Molecular phylogenetic evidence for the independent evolutionary origin of an arthropod compound eye. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 1426–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, K.; Kuma, K.; Toh, H.; Miyata, T. MAFFT version 5: Improvement in accuracy of multiple sequence alignment. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bush, A.O.; Lafferty, K.D.; Lotz, J.M.; Shostak, A.W. Parasitology meets ecology on its own terms: Margolis et al. revisited. J. Parasitol. 1997, 83, 575–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parauka, F.M.; Duncan, M.S.; Lang, P.A. Winter coastal movement of Gulf of Mexico sturgeon throughout northwest Florida and southeast Alabama. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2011, 27, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nash, R.D.M.; Valencia, A.H.; Geffen, A.J.; Meek, A. The origin of Fulton’s condition factor—Setting the record straightitle. Fisheries 2006, 31, 236–238. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, C.B. Copepod parasites of freshwater fishes and their economic relations to mussel glochidia. Bull. Bur. Fish. 1916, 34, 1–76. [Google Scholar]
- Mueller, J.F. Notes on some parasitic copepods and a mite, chiefly from Florida fresh water fishes. Am. Midl. Nat. 1936, 17, 807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bangham, R.V. Parasites of freshwater fish of southern Florida. Proc. Florida Acad. Sci. 1940, 5, 289–307. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, L.S. Parasites of the carp, Cyprinus carpio L. in Lake Texoma, Oklahoma. J. Parasitol. 1957, 43, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cressey, R.F. The genus Argulus (Crustacea: Branchiura) of the United States. EPA Biota Freshw. Ecosyst. Identif. Man. 1972, 2, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Poly, W.J. Host and locality records of the fish ectoparasite, Argulus (Branchiura), from Ohio (U.S.A.). Crustaceana 1997, 70, 867–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poly, W.J. New state, host, and distribution records of the fish ectoparasite, Argulus (Branchiura), from Illinois (U.S.A.). Crustaceana 1998, 71, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, C.B. Argulidae from the Shubenacadie River, Nova Scotiatle. Can. Field-Naturalist 1920, 34, 149–151. [Google Scholar]
- Suárez-Morales, E.; Kim, I.-H.; Castellanos, I. A new geographic and host record for Argulus flavescens Wilson, 1916 (Crustacea, Arguloida), from southeastern Mexico. Bull. Mar. Sci. 1998, 62, 293–296. [Google Scholar]
- Bangham, R.V.; Venard, C.E. Studies on parasites of Reelfoot Lake fish. IV. Distribution studies and checklist of parasites. J. Tennessee Acad. Sci. 1942, 17, 22–38. [Google Scholar]
- Goin, C.J.; Ogren, L.H. Parasitic copepods (Argulidae) on amphibians. J. Parasitol. 1956, 42, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeatman, H.C. Redescription of the freshwater branchiuran crustacean, Argulus diversus Wilson, with a comparison of related species. J. Parasitol. 1965, 51, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimura, S.; Asai, M. Argulus americanus (Crustacea: Branchiura) parasitic on the bowfin, Amia calva, imported from North America. Fish Pathol. 1984, 18, 199–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAllister, C.T.; Poly, W.J.; Box, P.O.; Robison, H.W.; Drive, W.M.; Hill, M.K. Argulus spp. (Crustacea: Branchiura) on fishes from Arkansas and Oklahoma: New geographic distribution records. Proc. Oklahoma Acad. Sci. 2017, 96, 94–96. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, C.B. North American parasitic copepods of the family Argulidae, with a bibliography of the group and a systematic review of all known species. Proc. United States Natl. Museum 1902, 25, 635–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bere, R. Parasitic copepods from Gulf of Mexico fish. Am. Midl. Nat. 1936, 17, 577–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paperna, I.; Zwerner, D.E. Parasites and diseases of striped bass, Morone saxatilis (Walbaum), from the lower Chesapeake Bay. J. Fish Biol. 1976, 9, 267–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cressey, R.F. Marine Flora and Fauna of the Northeastern United States Crustacea: Branchiura; NOAA Technical Report NMFS CIRC; 413; National Marine Fisheries Service: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 1978.
- Dynesius, M.; Nilsson, C. Fragmentation and flow regulation of river systems in the northern third of the world. Science 1994, 266, 753–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadeh, H.; Alsarakibi, M.; Li, G. Analysis of genetic variability within Argulus japonicus from representatives of Africa, Middle East, and Asia revealed by sequences of three mitochondrial DNA genes. Parasitol. Res. 2010, 107, 547–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulin, R.; George-Nascimento, M. The scaling of total parasite biomass with host body mass. Int. J. Parasitol. 2007, 37, 359–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulin, R. Evolutionary Ecology of Parasites; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2007; ISBN 9780691120850. [Google Scholar]
- Esser, H.J.; Foley, J.E.; Bongers, F.; Herre, E.A.; Miller, M.J.; Prins, H.H.T.; Jansen, P.A. Host body size and the diversity of tick assemblages on Neotropical vertebrates. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2016, 5, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuris, A.M.; Blaustein, A.R.; Alio, J.J. Hosts as islands. Am. Nat. 1980, 116, 570–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Videler, J.J.; Stamhuis, E.J.; Müller, U.K.; van Duren, L.A. The scaling and structure of aquatic animal wakes. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2002, 42, 988–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikheev, V.N.; Pasternak, A.F.; Valtonen, E.T. Behavioural adaptations of argulid parasites (Crustacea: Branchiura) to major challenges in their life cycle. Parasites Vectors 2015, 8, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikheev, V.N.; Mikheev, A.V.; Pasternak, A.F.; Valtonen, E.T. Light-mediated host searching strategies in a fish ectoparasite, Argulus foliaceus L. (Crustacea: Branchiura). Parasitology 2000, 120, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterson, M.S.; Havrylkoff, J.M.; Grammer, P.O.; Mickle, P.F.; Slack, W.T. Consistent spatiotemporal estuarine habitat use during emigration or immigration of a western population of Gulf sturgeon. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 2016, 145, 27–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arendt, K.E.; Jónasdóttir, S.H.; Hansen, P.J.; Gärtner, S. Effects of dietary fatty acids on the reproductive success of the calanoid copepod Temora longicornis. Mar. Biol. 2005, 146, 513–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Travnichek, V.H. Movement of flathead catfish in the Missouri River: Examining opportunities for managing river segments for different fishery goals. Fish. Manag. Ecol. 2004, 11, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vokoun, J.C.; Rabeni, C.F. Variation in an annual movement cycle of flathead catfish within and between two Missouri watersheds. North Am. J. Fish. Manag. 2005, 25, 563–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, M.L.; Burr, B.M.; Walsh, S.J.; Bart, H.L.; Cashner, R.C.; Etnier, D.A.; Freeman, B.J.; Kuhajda, B.R.; Mayden, R.L.; Robison, H.W.; et al. Diversity, Distribution, and Conservation Status of the Native Freshwater Fishes of the Southern United States. Fisheries 2000, 25, 7–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, M.R.; DeVries, D.R.; Wright, R.A.; Ludsin, S.A.; Fryer, B.J. Otolith microchemistry reveals substantial use of freshwater by southern flounder in the northern Gulf of Mexico. Estuaries Coasts 2011, 34, 630–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appy, R.G.; Dadswell, M.J. Parasites of Acipenser brevirostrum LeSueur and Acipenser oxyrhynchus Mitchill (Osteichchthes: Acipenseridae) in the Saint John River Estuary, N.B., with a description of Caballeronema pseudoargumentosus sp.n. (Nematoda: Spirurida). Can. J. Zool. 1978, 56, 1382–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fast, M.D.; Sokolowski, M.S.; Dunton, K.J.; Bowser, P.R. Dichelesthium oblongum (Copepoda: Dichelesthiidae) infestation in wild-caught Atlantic sturgeon, Acipenser oxyrinchus oxyrinchus. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2009, 66, 2141–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popielarczyk, R.; Kolman, R. Preliminary analysis of ectoparasites of the sturgeon Acipenser oxyrinchus oxyrinchus (Mitchill, 1815) originating from different water habitats. Ann. Parasitol. 2013, 59, 139–141. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hilton, E.J.; Kynard, B.; Balazik, M.T.; Horodysky, A.Z.; Dillman, C.B. Review of the biology, fisheries, and conservation status of the Atlantic sturgeon, (Acipenser oxyrinchus oxyrinchus Mitchill, 1815). J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2016, 32, 30–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulak, K.J.; Edwards, R.E.; Hill, G.W.; Randall, M.T. Why do sturgeons jump? Insights from acoustic investigations of the Gulf sturgeon in the Suwannee River, Florida, USA. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2002, 18, 617–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
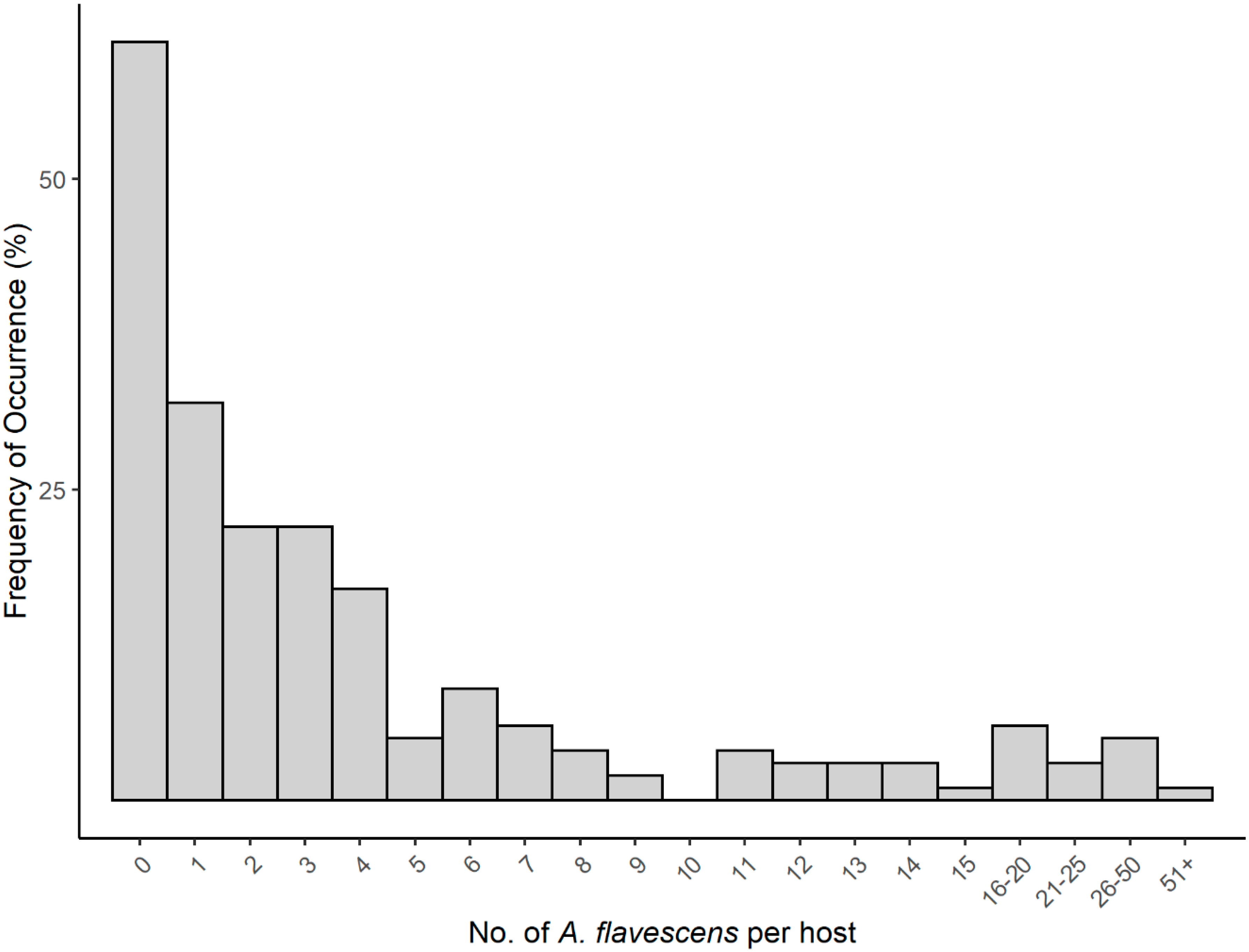
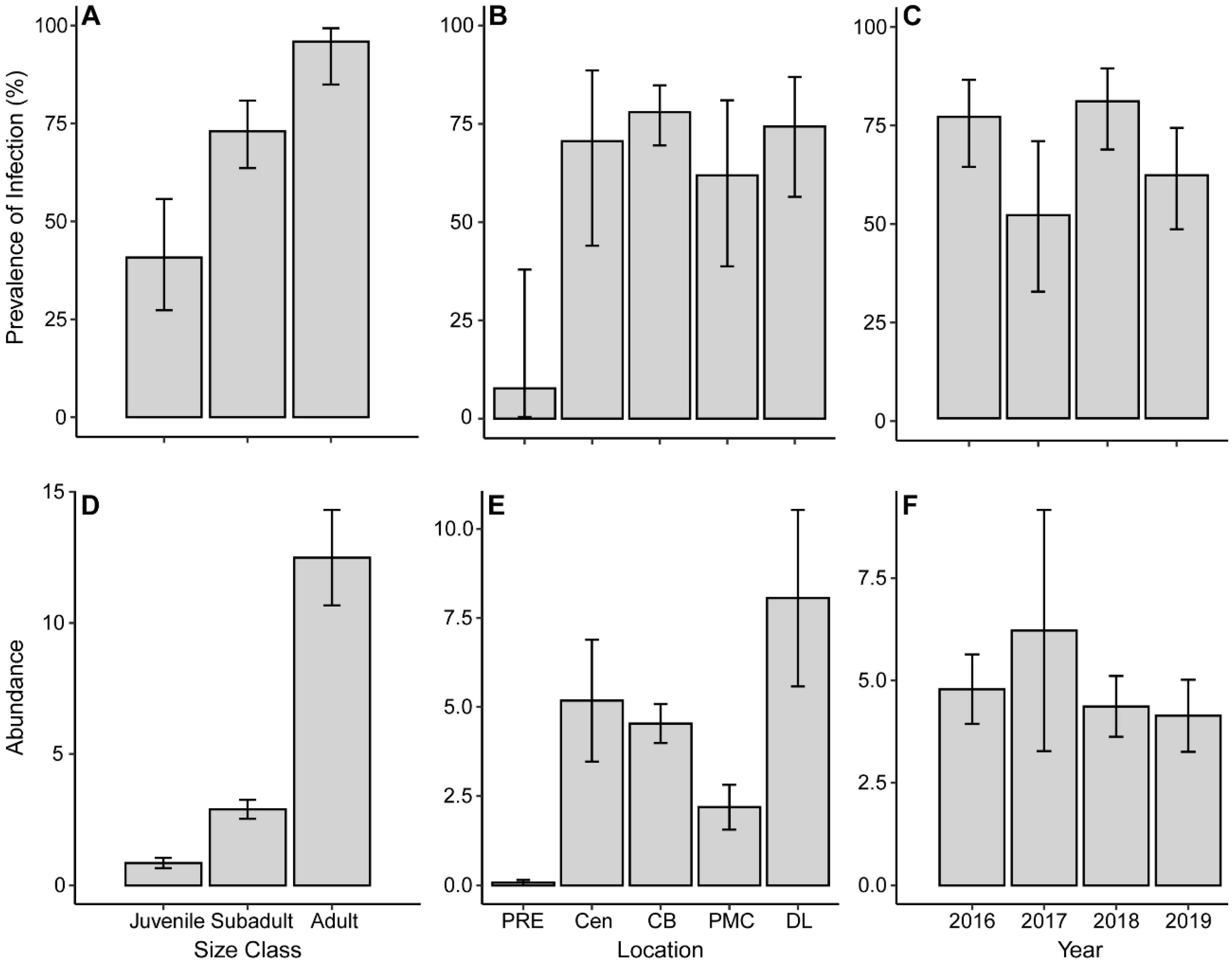
| Size Class | Estuary | Census Site | Cumbest Bluff | Paper Mill Camp | Dead Lake |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2016 | |||||
| Juvenile | 0 | 5 | 2 | 0 | 6 |
| Subadult | 0 | 7 | 22 | 1 | 2 |
| Adult | 0 | 4 | 12 | 0 | 0 |
| 2017 | |||||
| Juvenile | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 7 |
| Subadult | 2 | 0 | 4 | 5 | 3 |
| Adult | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 3 |
| 2018 | |||||
| Juvenile | 0 | 1 | 10 | 1 | 2 |
| Subadult | 1 | 0 | 28 | 4 | 5 |
| Adult | 0 | 0 | 9 | 1 | 1 |
| 2019 | |||||
| Juvenile | 8 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 1 |
| Subadult | 2 | 0 | 18 | 5 | 2 |
| Adult | 0 | 0 | 12 | 2 | 3 |
| Species | n | Argulus sp. AY210804 | Argulus sp. AF363322 | A. americanus | A. bicolor | A. foliaceus EU370442 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A. flavescens | 13 | 0.0–0.3 (0–2) | 0.0–0.4 (0–3) | 4.4 (26–28) | 7.4–7.6 (43–48) | 5.2–5.6 (45–38) |
| A. americanus | 1 | 4.3 (28) | 4.5 (29) | – | 7.8 (50) | 3.4 (22) |
| A. bicolor | 1 | 7.4 (47) | 7.6 (48) | – | – | 7.1 (45) |
| A. foliaceus EU370442 | – | 5.0 (36) | 5.2 (39) | – | – | – |
| Variable | Estimate | SE | Z | Pr (>|Z|) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | 276.524 | 143.135 | 1.932 | 0.053 |
| FL (cm) | 0.027 | 0.004 | 6.702 | <0.001 |
| rkm | 0.020 | 0.007 | 2.875 | 0.004 |
| Condition | 1.755 | 1.103 | 1.591 | 0.112 |
| Year | −0.139 | 0.071 | −1.956 | 0.051 |
| Common Name | Scientific Name | Size Range | PRE | Cen | CB | PMC | DL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2018 | |||||||
| Atlantic stingray | Hypanus sabinus | 25.0–37.8 † | 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| bowfin | Amia calva | 86.5 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| spotted gar | Lepisosteus oculatus | 70.0–136.0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 8 | 0 |
| longnose gar | Lepisosteus osseus | 84.2–143.8 | 17 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 1 |
| Gulf menhaden | Brevoortia patronus | 19.0–21.0 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| gizzard shad | Dorosoma cepedianum | 35.6–42.0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7 | 0 |
| striped anchovy | Anchoa hepsetus | 11.4 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| quillback | Carpiodes cyprinus | 37.2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| small mouth buffalo | Ictiobus bubalus | 31.0–72.4 | 0 | 0 | 14 | 8 | 6 |
| hardhead catfish | Ariopsis felis | 39.5–41.1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| gafftopsail catfish | Bagre marinus | 52.1–60.6 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| blue catfish | Ictalurus furcatus | 57.2–100.0 | 0 | 0 | 7 | 0 | 0 |
| channel catfish | Ictalurus punctatus | 49.5 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| flathead catfish | Pylodictis olivaris | 52.6–78.6 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 1 | 0 |
| southern flounder | Paralichthys lethostigma | 37 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| freshwater drum | Aplodinotus grunniens | 57.2–68.8 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 3 | 0 |
| sand seatrout | Cynoscion arenarius | 20.4–30.2 | 19 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| black drum | Pogonias cromis | 37.8–90.8 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| sheepshead | Archosargus probatocephalus | 52.4–55.6 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 2019 | |||||||
| longnose gar | Lepisosteus osseus | 101.2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| gizzard shad | Dorosoma cepedianum | 31.4–44.0 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 7 | 0 |
| quillback | Carpiodes cyprinus | 29.8 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| small mouth buffalo | Ictiobus bubalus | 61.4–70.2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 0 |
| grass carp | Ctenopharyngodon idella | 110.5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| channel catfish | Ictalurus punctatus | 39.4–59.2 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 |
| flathead catfish | Pylodictis olivaris | 59.0–79.2 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| freshwater drum | Aplodinotus grunniens | 67.2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Andres, M.J.; Higgs, J.M.; Grammer, P.O.; Peterson, M.S. Argulus from the Pascagoula River, MS, USA, with an Emphasis on Those of the Threatened Gulf Sturgeon, Acipenser oxyrinchus desotoi. Diversity 2019, 11, 232. https://doi.org/10.3390/d11120232
Andres MJ, Higgs JM, Grammer PO, Peterson MS. Argulus from the Pascagoula River, MS, USA, with an Emphasis on Those of the Threatened Gulf Sturgeon, Acipenser oxyrinchus desotoi. Diversity. 2019; 11(12):232. https://doi.org/10.3390/d11120232
Chicago/Turabian StyleAndres, Michael J., Jeremy M. Higgs, Paul O. Grammer, and Mark S. Peterson. 2019. "Argulus from the Pascagoula River, MS, USA, with an Emphasis on Those of the Threatened Gulf Sturgeon, Acipenser oxyrinchus desotoi" Diversity 11, no. 12: 232. https://doi.org/10.3390/d11120232
APA StyleAndres, M. J., Higgs, J. M., Grammer, P. O., & Peterson, M. S. (2019). Argulus from the Pascagoula River, MS, USA, with an Emphasis on Those of the Threatened Gulf Sturgeon, Acipenser oxyrinchus desotoi. Diversity, 11(12), 232. https://doi.org/10.3390/d11120232






