The Coordinated Interplay Between MMP13 and Pro-Migratory MMPs in Collective Cell Migration of Zebrafish Keratocytes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
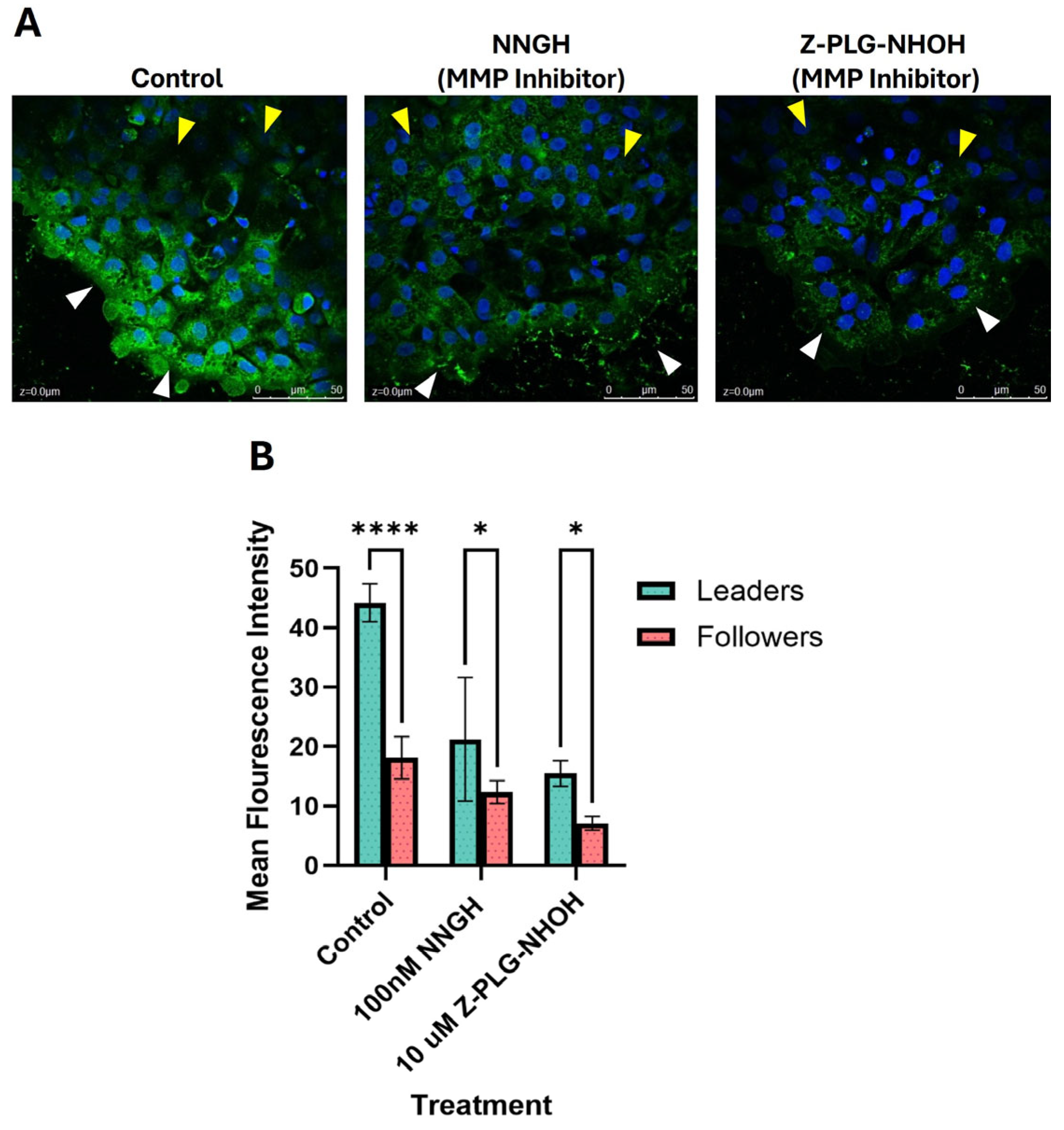
2.1. Localization of MMP Activity in the Cell Sheet
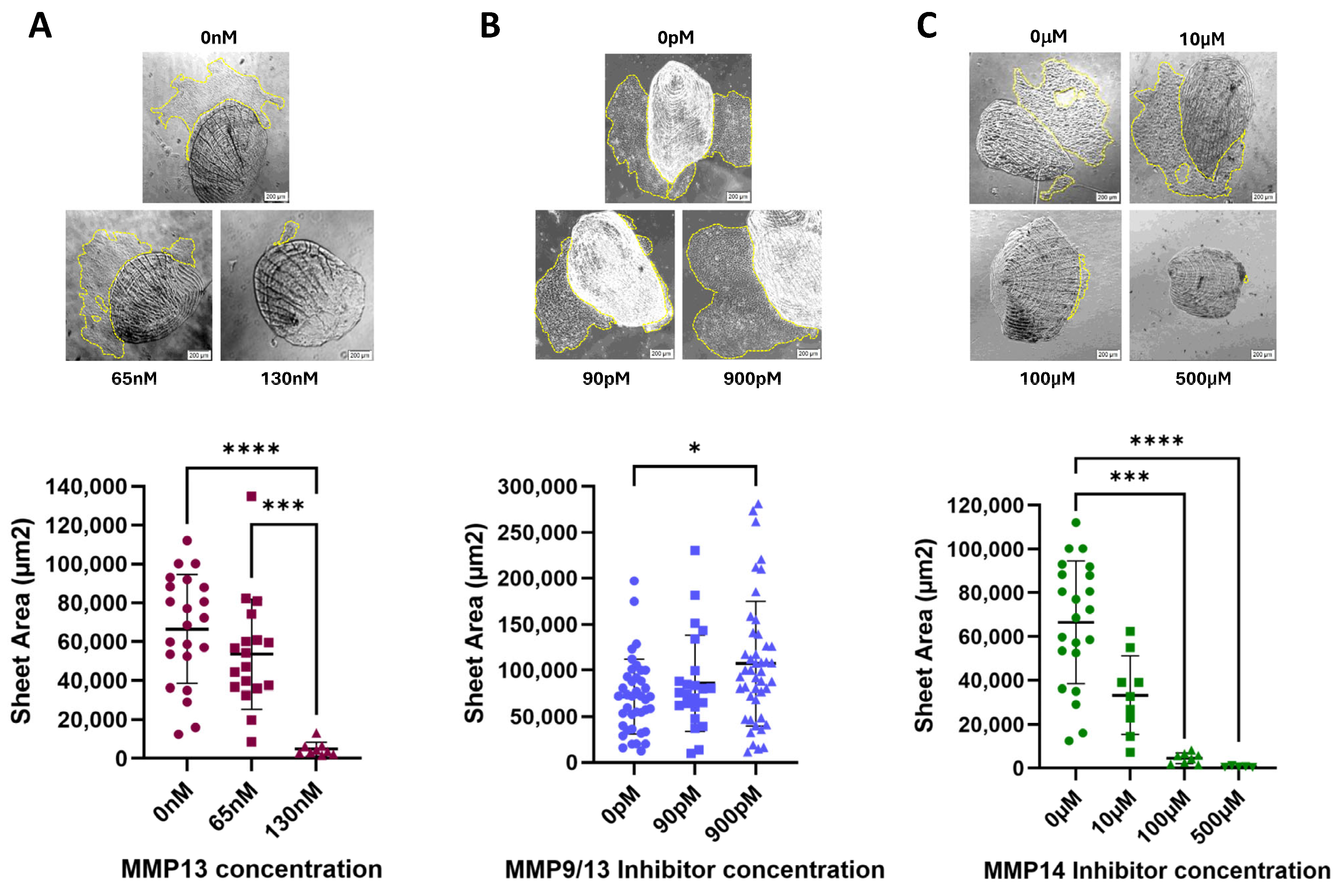
2.2. Effect of MMP13 and MMP14 on Collective Cell Migration
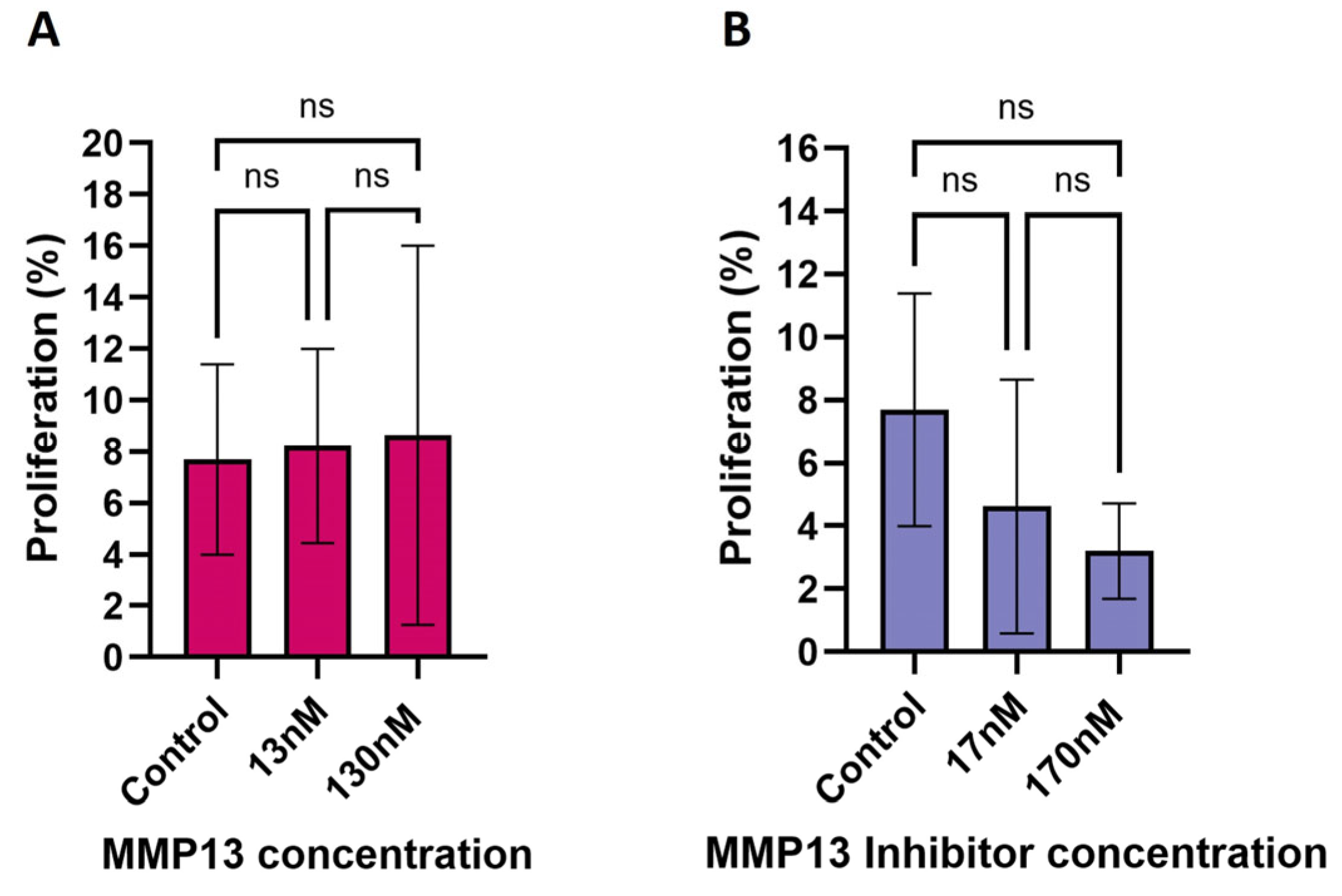
2.3. Effect of MMP13 and MMP14 on Cell Proliferation
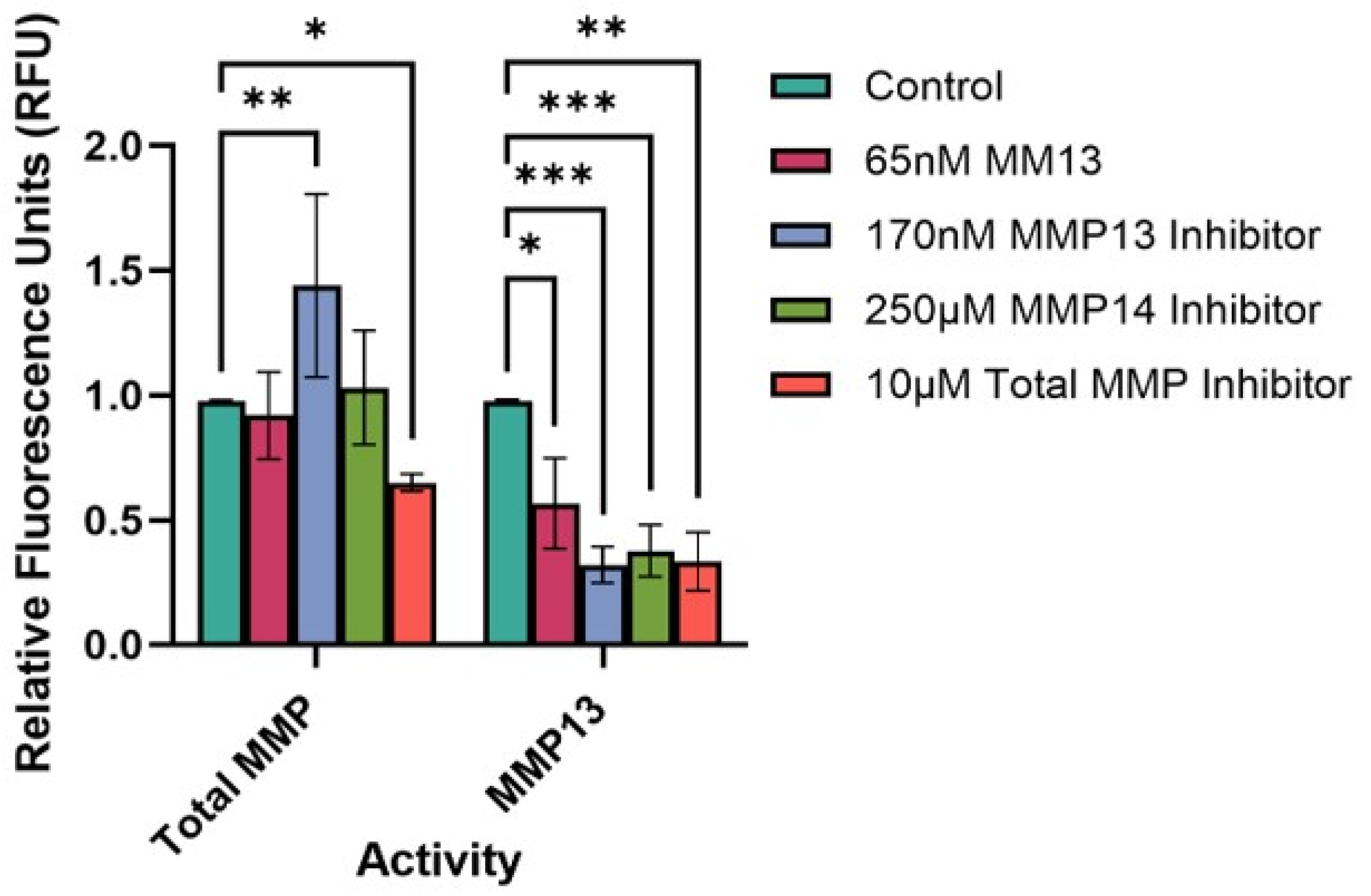
2.4. FRET Assay of MMP Activity in Culture Supernatants
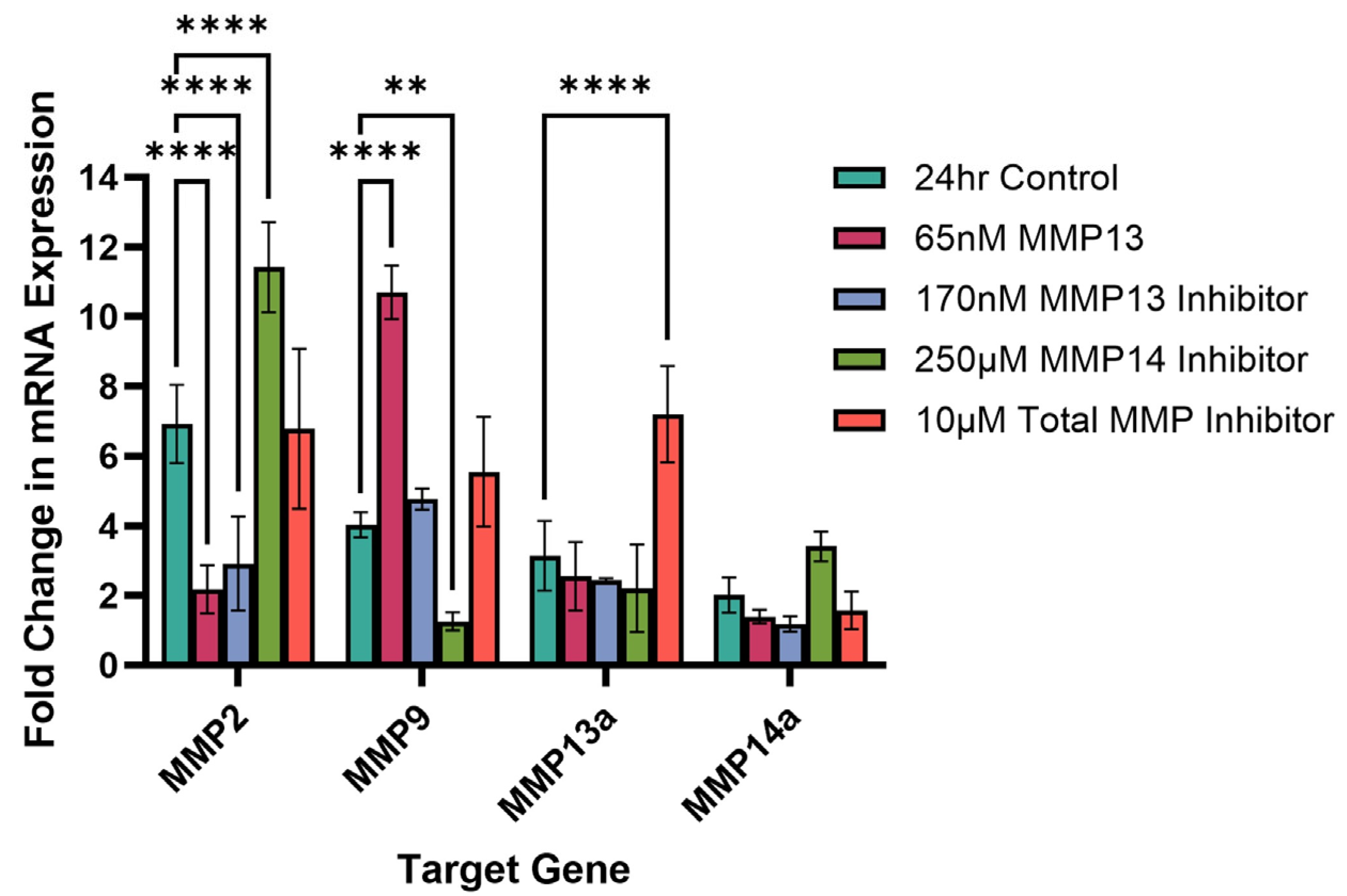
2.5. Effect of Recombinant MMP13 and MMP Inhibitors on MMP mRNA Expression
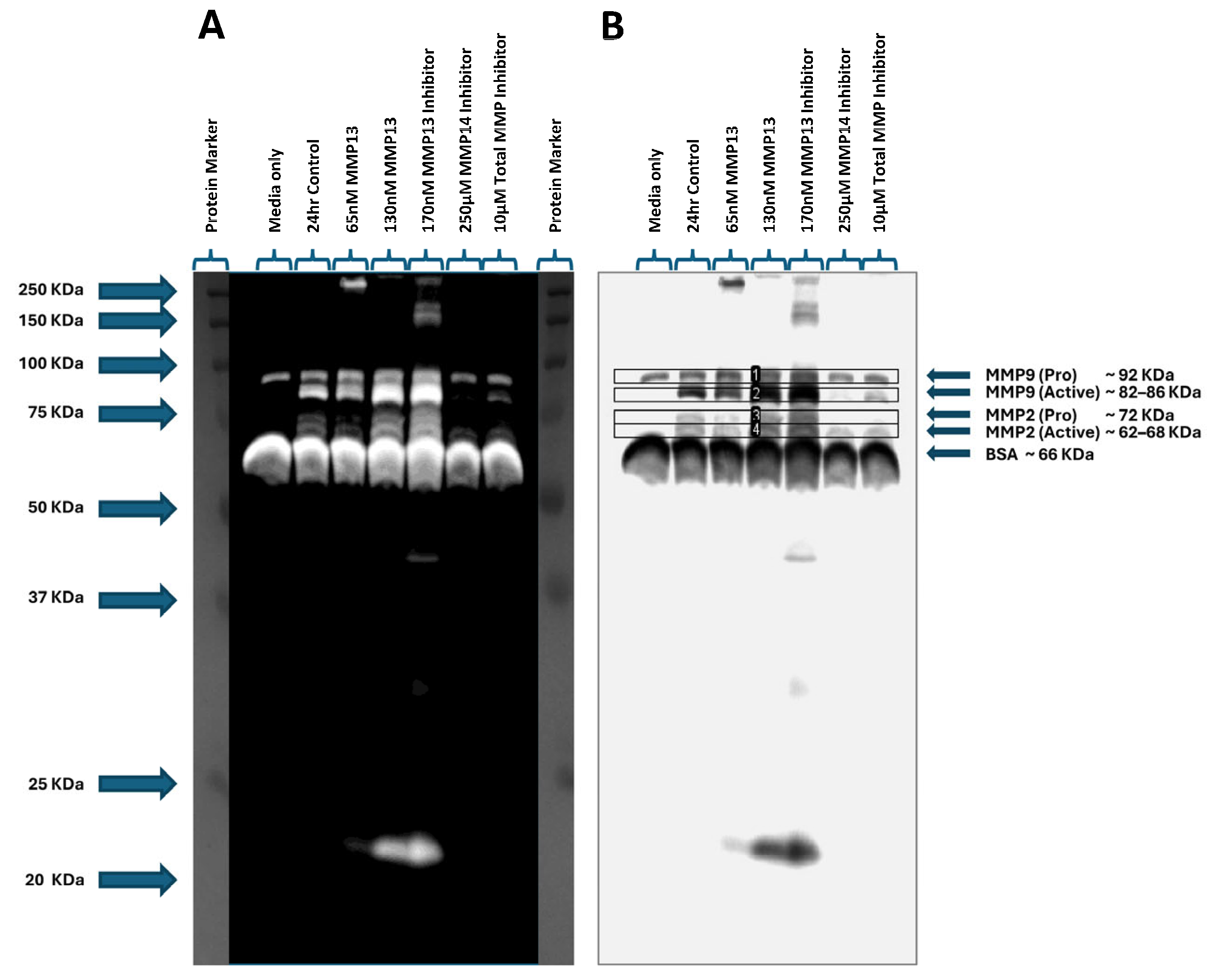
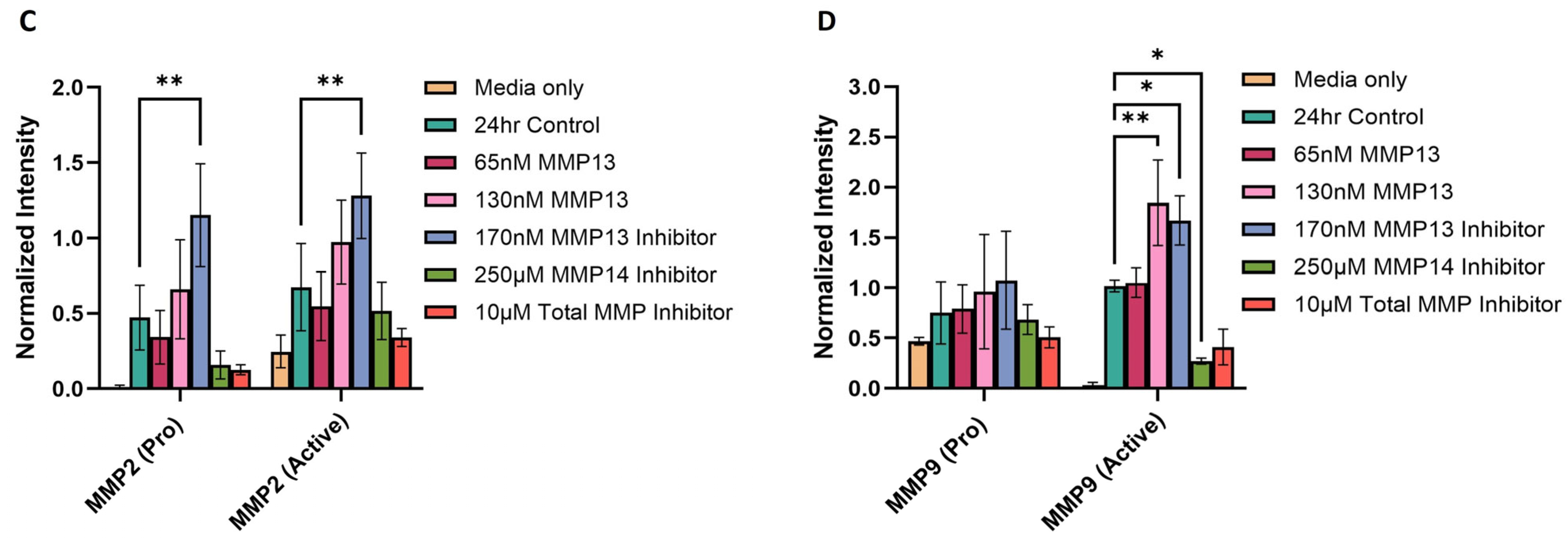
2.6. MMP Gelatinase Activity
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Keratocyte Explant Cultures
4.2. DQ Gel Assay
4.3. Cell Sheet Migration Assays
- Recombinant MMP13: 65 nM and 130 nM
- MMP13-specific inhibitor (WAY170523): 1 µM, 10 µM, and 100 µM
- MMP9/13-specific inhibitor I: 90 pM and 900 pM
- MMP14-specific inhibitor (NSC405020): 10 µM, 100 µM, and 500 µM
4.4. Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer (FRET) MMP Assays
4.5. EdU Proliferation Assay
4.6. RNA Isolation, mRNA Amplification and cDNA Synthesis
4.7. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qPCR)
4.8. Gelatin Zymography
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Inaki, M.; Vishnu, S.; Cliffe, A.; Rorth, P. Effective guidance of collective migration based on differences in cell states. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 2027–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rorth, P. Fellow travellers: Emergent properties of collective cell migration. EMBO Rep. 2012, 13, 984–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raftopoulou, M.; Hall, A. Cell migration: Rho GTPases lead the way. Dev. Biol. 2004, 265, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahar-Shany, K.; Ravid, A.; Koren, R. Upregulation of MMP-9 production by TNFalpha in keratinocytes and its attenuation by vitamin D. J. Cell Physiol. 2010, 222, 729–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, T.M.; Sumner, A.J.; Reyes, J.F.; Pascual, A.S.; Uppalapati, C.K.; Cooper, K.E.; Leyva, K.J.; Hull, E.E. Matrix metalloproteinases and collective cell migration in 24 h primary zebrafish explant cultures: MMP13 plays an inhibitory role and MMP14 may respond to stretch during reepithelialisation. Cell Biol. Int. Rep. 2013, 20, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Ishihara, A.; Oxford, G.; Johnson, B.; Jacobson, K. Regulation of cell movement is mediated by stretch-activated calcium channels. Nature 1999, 400, 382–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aihara, E.; Hentz, C.L.; Korman, A.M.; Perry, N.P.J.; Prasad, V.; Shull, G.E.; Montrose, M.H. In Vivo Epithelial Wound Repair Requires Mobilization of Endogenous Intracellular and Extracellular Calcium. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 33585–33597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, D.C.; Sanders, L.C.; Bokoch, G.M.; Gill, G.N. Activation of LIM-kinase by Pak1 couples Rac/Cdc42 GTPase signalling to actin cytoskeletal dynamics. Nat. Cell Biol. 1999, 1, 253–259. [Google Scholar]
- Singer, C.F.; Marbaix, E.; Lemoine, P.; Courtoy, P.J.; Eeckhout, Y. Local cytokines induce differential expression of matrix metalloproteinases but not their tissue inhibitors in human endometrial fibroblasts. Eur. J. Biochem. 1999, 259, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broughton, G., 2nd; Janis, J.E.; Attinger, C.E. The basic science of wound healing. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2006, 117 (Suppl. S7), 12s–34s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, M.; Jackson, C.J. Autocrine Actions of Matrix Metalloproteinase (MMP)-2 Counter the Effects of MMP-9 to Promote Survival and Prevent Terminal Differentiation of Cultured Human Keratinocytes. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2008, 128, 2676–2685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeisberg, M.; Neilson, E.G. Biomarkers for epithelial-mesenchymal transitions. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 1429–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; DiPietro, L.A. Factors Affecting Wound Healing. J. Dent. Res. 2010, 89, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, B.; Pascual, A.; de Beus, A.; Cooper, K.; Hull, E. TGFb (transforming growth factor b) and keratocyte motility in 24-hour zebrafish explant cultures. Cell Biol. Int. 2011, 35, 1131–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamouille, S.; Xu, J.; Derynck, R. Molecular mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 15, 178–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapanan, J.L.; Cooper, K.E.; Leyva, K.J.; Hull, E.E. During collective migration, leader keratocytes generate tension in sheet and may become follower or individually migrating cells. Exp. Cell Res. 2014, 326, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yook, J.I.; Li, X.Y.; Ota, I.; Hu, C.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, N.H.; Cha, S.Y.; Ryu, J.K.; Choi, Y.J.; Kim, J.; et al. A Wnt-Axin2-GSK3beta cascade regulates Snail1 activity in breast cancer cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 2006, 8, 1398–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldron, A.L.; Schroder, P.A.; Bourgon, K.L.; Bolduc, J.K.; Miller, J.L.; Pellegrini, A.D.; Dubois, A.L.; Blaszkiewicz, M.; Townsend, K.L.; Rieger, S. Oxidative stress-dependent MMP-13 activity underlies glucose neurotoxicity. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2018, 32, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Webb, S.E.; Lau, T.C.K.; Cheng, S.H. Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) mediate leukocyte recruitment during the inflammatory phase of zebrafish heart regeneration. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 7199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sternlicht, M.D.; Werb, Z. How matrix metalloproteinases regulate cell behavior. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2001, 17, 463–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Mandal, M.; Chakraborti, T.; Mandal, A.; Chakraborti, S. Structure and evolutionary aspects of matrix metalloproteinases: A brief overview. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2003, 253, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, D.E.; Alonso, D.F.; Yoshiji, H.; Thorgeirsson, U.P. Tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases: Structure, regulation and biological functions. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 1997, 74, 111–122. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Bai, S.; Zhang, X.; Nagase, H.; Sarras, M.P., Jr. The expression of novel membrane-type matrix metalloproteinase isoforms is required for normal development of zebrafish embryos. Matrix Biol. J. Int. Soc. Matrix Biol. 2003, 22, 279–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, S.; Thummel, R.; Godwin, A.R.; Nagase, H.; Itoh, Y.; Li, L.; Evans, R.; McDermott, J.; Seiki, M.; Sarras, M.P., Jr. Matrix metalloproteinase expression and function during fin regeneration in zebrafish: Analysis of MT1-MMP, MMP2 and TIMP2. Matrix Biol. J. Int. Soc. Matrix Biol. 2005, 24, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Parks, W.C. Role of matrix metalloproteinases in epithelial migration. J. Cell. Biochem. 2009, 108, 1233–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmisano, R.; Itoh, Y. Analysis of MMP-dependent cell migration and invasion. Methods Mol. Biol. 2010, 622, 379–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, G.; Nagase, H. Localizing matrix metalloproteinase activities in the pericellular environment. FEBS J. 2011, 278, 2–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hire, J.M.; Evanson, J.L.; Johnson, P.C.; Zumbrun, S.D.; Guyton, M.K.; McPherson, J.C., 3rd; Bojescul, J.A. Variance of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase (TIMP) concentrations in activated, concentrated platelets from healthy male donors. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2014, 9, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howes, J.M.; Bihan, D.; Slatter, D.A.; Hamaia, S.W.; Packman, L.C.; Knauper, V.; Visse, R.; Farndale, R.W. The recognition of collagen and triple-helical toolkit peptides by MMP-13: Sequence specificity for binding and cleavage. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 24091–24101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löffek, S.; Schilling, O.; Franzke, C.W. Series “matrix metalloproteinases in lung health and disease”: Biological role of matrix metalloproteinases: A critical balance. Eur. Respir. J. 2011, 38, 191–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeBert, D.C.; Squirrell, J.M.; Rindy, J.; Broadbridge, E.; Lui, Y.; Zakrzewska, A.; Eliceiri, K.W.; Meijer, A.H.; Huttenlocher, A. Matrix metalloproteinase 9 modulates collagen matrices and wound repair. Development 2015, 142, 2136–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyatt, R.A.; Crawford, B.D. Post-translational activation of Mmp2 correlates with patterns of active collagen degradation during the development of the zebrafish tail. Dev. Biol. 2021, 477, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborti, S.; Mandal, M.; Das, S.; Mandal, A.; Chakraborti, T. Regulation of matrix metalloproteinases: An overview. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2003, 253, 269–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillegass, J.M.; Villano, C.M.; Cooper, K.R.; White, L.A. Matrix Metalloproteinase-13 Is Required for Zebra fish (Danio rerio) Development and Is a Target for Glucocorticoids. Toxicol. Sci. 2007, 100, 168–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page-McCaw, A.; Ewald, A.J.; Werb, Z. Matrix metalloproteinases and the regulation of tissue remodelling. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007, 8, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagase, H.; Fields, G.B. Human matrix metalloproteinase specificity studies using collagen sequence-based synthetic peptides. Biopolymers 1996, 40, 399–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillegass, J.M.; Villano, C.M.; Cooper, K.R.; White, L.A. Glucocorticoids alter craniofacial development and increase expression and activity of matrix metalloproteinases in developing zebrafish (Danio rerio). Toxicol. Sci. 2008, 102, 413–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pendás, A.M.; Knäuper, V.; Puente, X.S.; Llano, E.; Mattei, M.G.; Apte, S.; Murphy, G.; López-Otín, C. Identification and characterization of a novel human matrix metalloproteinase with unique structural characteristics, chromosomal location, and tissue distribution. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 4281–4286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoh, Y. MT1-MMP: A key regulator of cell migration in tissue. IUBMB Life 2006, 58, 589–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klee, E.W. The zebrafish secretome. Zebrafish 2008, 5, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, T.M.; Pascual, A.S.; Uppalapati, C.K.; Cooper, K.E.; Leyva, K.J.; Hull, E.E. Zebrafish keratocyte explant cultures as a wound healing model system: Differential gene expression & morphological changes support epithelial–mesenchymal transition. Exp. Cell Res. 2013, 319, 1815–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyatt, R.A.; Keow, J.Y.; Harris, N.D.; Haché, C.A.; Li, D.H.; Crawford, B.D. The zebrafish embryo: A powerful model system for investigating matrix remodeling. Zebrafish 2009, 6, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Pritchard, D.M.; Yu, L.G. Regulation and Function of Matrix Metalloproteinase-13 in Cancer Progression and Metastasis. Cancers 2022, 14, 3263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieschke, G.J.; Currie, P.D. Animal models of human disease: Zebrafish swim into view. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2007, 8, 353–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strähle, U.; Scholz, S.; Geisler, R.; Greiner, P.; Hollert, H.; Rastegar, S.; Schumacher, A.; Selderslaghs, I.; Weiss, C.; Witters, H.; et al. Zebrafish embryos as an alternative to animal experiments--a commentary on the definition of the onset of protected life stages in animal welfare regulations. Reprod. Toxicol. 2012, 33, 128–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, P.; Feng, Y. Inflammation: Wound healing in zebrafish. Nature 2009, 459, 921–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seomun, Y.; Kim, J.T.; Joo, C.K. MMP-14 mediated MMP-9 expression is involved in TGF-beta1-induced keratinocyte migration. J. Cell Biochem. 2008, 104, 934–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winter, S.; Kohl, A.; Huppertz, A.; Herold-Mende, C.; Wiest, T.; Komposch, G.; Tomakidi, P. Expression of mRNAs encoding for growth factors, ECM molecules, and MMP13 in mono-cultures and co-cultures of human periodontal ligament fibroblasts and alveolar bone cells. Cell Tissue Res. 2005, 319, 467–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Celardo, I.; Antonov, A.; Amelio, I.; Annicchiarico-Petruzzelli, M.; Melino, G. p63 transcriptionally regulates the expression of matrix metallopeptidase 13. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 1279–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Quillard, T.; Tesmenitsky, Y.; Croce, K.; Travers, R.; Shvartz, E.; Koskinas, K.C.; Sukhova, G.K.; Aikawa, E.; Aikawa, M.; Libby, P. Selective inhibition of matrix metalloproteinase-13 increases collagen content of established mouse atherosclerosis. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2011, 31, 2464–2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juncker-Jensen, A.; Lund, L.R. Phenotypic overlap between MMP-13 and the plasminogen activation system during wound healing in mice. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e16954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurens, N.; Koolwijk, P.; de Maat, M.P. Fibrin structure and wound healing. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2006, 4, 932–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osenkowski, P.; Toth, M.; Fridman, R. Processing, shedding, and endocytosis of membrane type 1-matrix metalloproteinase (MT1-MMP). J. Cell. Physiol. 2004, 200, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meierjohann, S.; Hufnagel, A.; Wende, E.; Kleinschmidt, M.A.; Wolf, K.; Friedl, P.; Gaubatz, S.; Schartl, M. MMP13 mediates cell cycle progression in melanocytes and melanoma cells: In vitro studies of migration and proliferation. Mol. Cancer 2010, 9, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, S.E.; Parks, W.C. Metalloproteinases and their inhibitors: Regulators of wound healing. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2008, 40, 1334–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, B.R.; Szelenyi, E.R.; Warren, G.L.; Urso, M.L. Alterations in mRNA and protein levels of metalloproteinases-2, -9, and -14 and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-2 responses to traumatic skeletal muscle injury. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2009, 297, C1501–C1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hattori, N.; Mochizuki, S.; Kishi, K.; Nakajima, T.; Takaishi, H.; D’Armiento, J.; Okada, Y. MMP-13 Plays a Role in Keratinocyte Migration, Angiogenesis, and Contraction in Mouse Skin Wound Healing. Am. J. Pathol. 2009, 175, 533–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leeman, M.F.; Curran, S.; Murray, G.I. The structure, regulation, and function of human matrix metalloproteinase-13. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2002, 37, 149–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leeman, M.F.; McKay, J.A.; Murray, G.I. Matrix metalloproteinase 13 activity is associated with poor prognosis in colorectal cancer. J. Clin. Pathol. 2002, 55, 758–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, H.; Leong, D.; Smith, L.R.; Barton, E.R. Matrix metalloproteinase 13 is a new contributor to skeletal muscle regeneration and critical for myoblast migration. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2013, 305, C529–C538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoari, A. Potential of MMP-2 and MMP-9 Gelatinase Blockade as a Therapeutic Strategy in Fibrosarcoma Treatment: A Decadal Review. Targets 2024, 2, 104–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frankowski, H.; Gu, Y.H.; Heo, J.H.; Milner, R.; Del Zoppo, G.J. Use of gel zymography to examine matrix metalloproteinase (gelatinase) expression in brain tissue or in primary glial cultures. Methods Mol. Biol. 2012, 814, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Gene | Primer Sequence |
| MMP2 | F: GAG CTC TCA TGG CTC CTA TCT A R: TGG CTT GTC TGT TGG TTC TC |
| MMP9 | F: TTT GCC CTG ATC GTG GAT AC R: GGG AAA CCC TCC ACG TAT TT |
| MMP13a | F: CTG GCC TGA GAT TCC AGA TAA C R: CAT AGA GAG CCC AAA CCT TCT C |
| MMP14a | F: GAC AAA GAA GTG AGA CCA GAG G R: TTT CTG CAT GGC CGA GAT AG |
| β-actin | F: GCA AAG GGA GGT AGT TGT CTA A R: GAG GAG GGC AAA GTG GTA AA |
| Elongation Factor 1α (EF1α) | F: ATG CCC TTG ATG CCA TTC T R: CCC ACA GGT ACA GTT CCA ATA C |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Uppalapati, C.K.; Jeffery, M.A.; Pascual, A.S.; Hull, E.E.; Leyva, K.J. The Coordinated Interplay Between MMP13 and Pro-Migratory MMPs in Collective Cell Migration of Zebrafish Keratocytes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 11192. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262211192
Uppalapati CK, Jeffery MA, Pascual AS, Hull EE, Leyva KJ. The Coordinated Interplay Between MMP13 and Pro-Migratory MMPs in Collective Cell Migration of Zebrafish Keratocytes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(22):11192. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262211192
Chicago/Turabian StyleUppalapati, Chandana K., Marquise A. Jeffery, Agnes S. Pascual, Elizabeth E. Hull, and Kathryn J. Leyva. 2025. "The Coordinated Interplay Between MMP13 and Pro-Migratory MMPs in Collective Cell Migration of Zebrafish Keratocytes" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 22: 11192. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262211192
APA StyleUppalapati, C. K., Jeffery, M. A., Pascual, A. S., Hull, E. E., & Leyva, K. J. (2025). The Coordinated Interplay Between MMP13 and Pro-Migratory MMPs in Collective Cell Migration of Zebrafish Keratocytes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(22), 11192. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262211192






