Evaluating the Dose-Dependent Effects of Human Umbilical Cord-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells in a Preclinical Model of Interstitial Lung Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
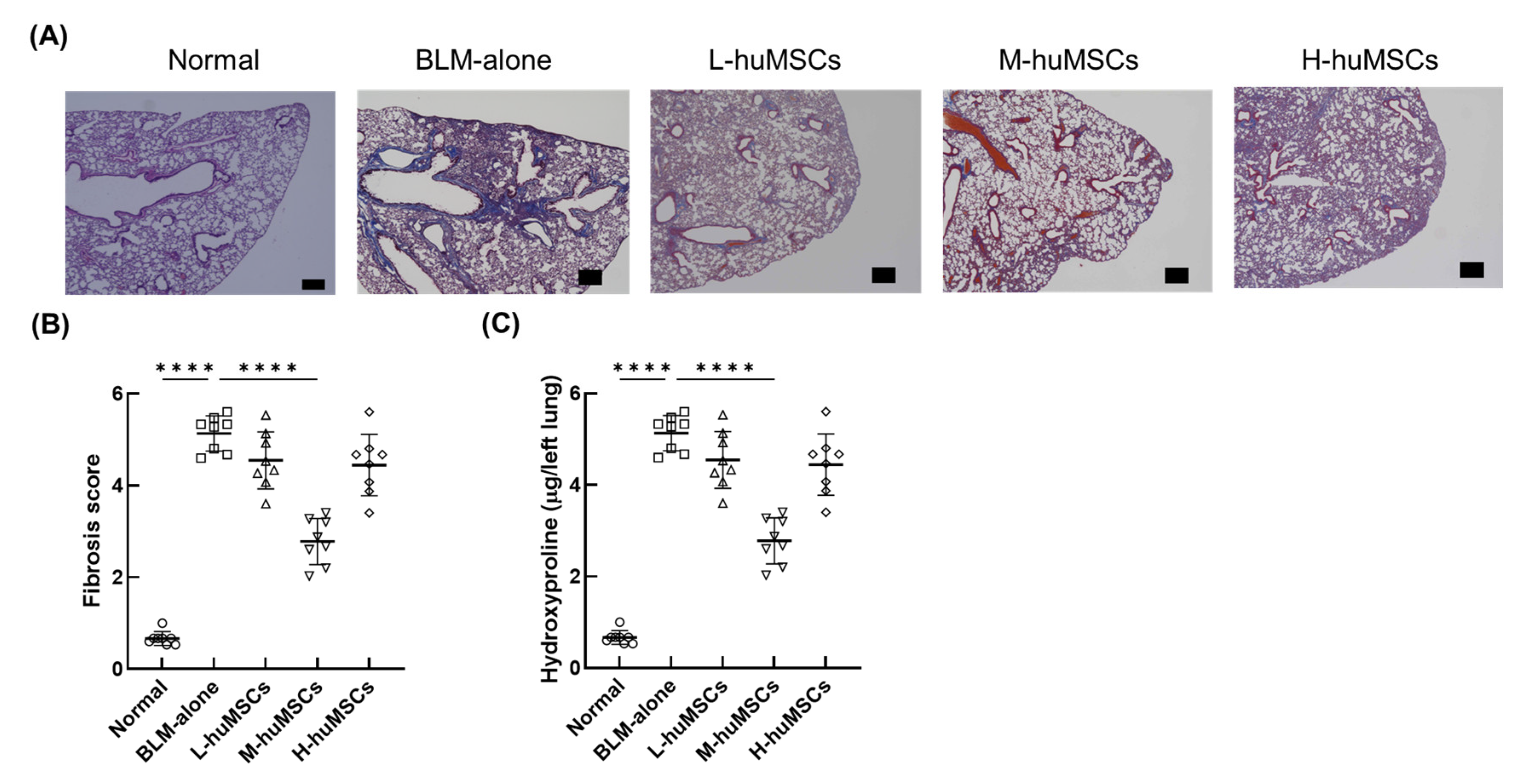
2.1. Therapeutic Effects of Human uMSCs on Pulmonary Fibrosis in ILD
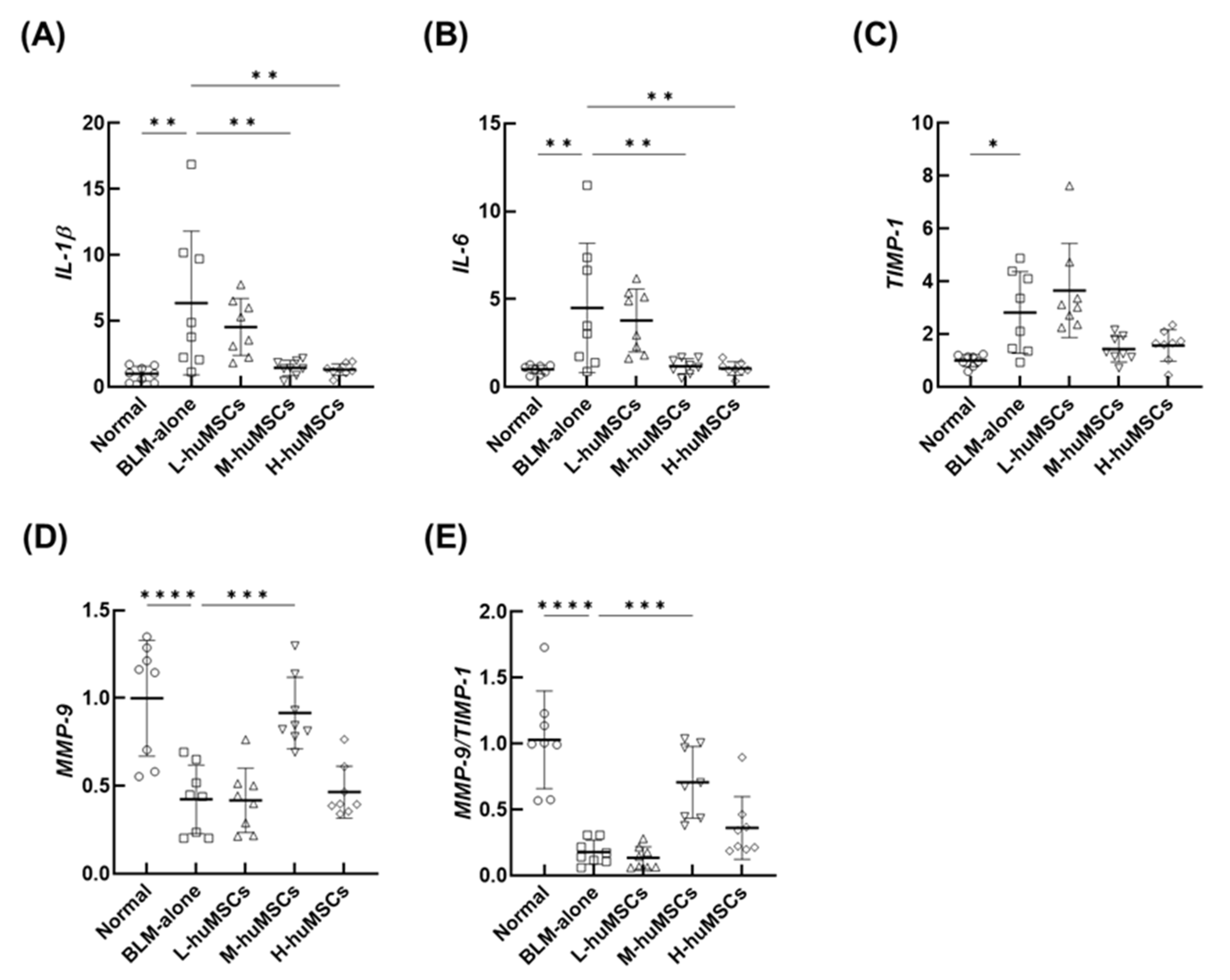
2.2. The huMSCs Regulated the Genes Associated with the Anti-Inflammatory and Antifibrotic Effects in ILD
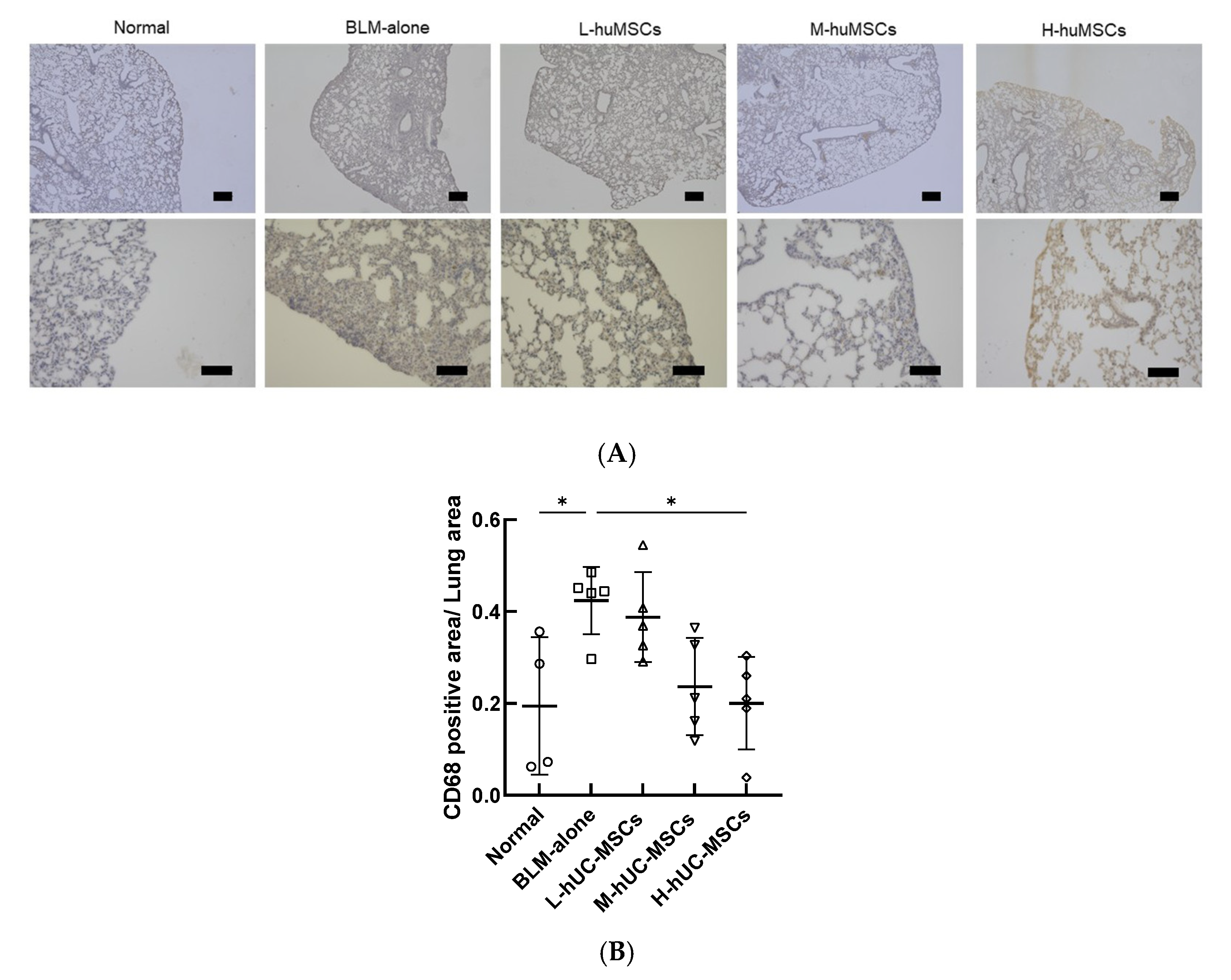
2.3. Immunohistochemical Analysis of CD68-Positive Macrophages
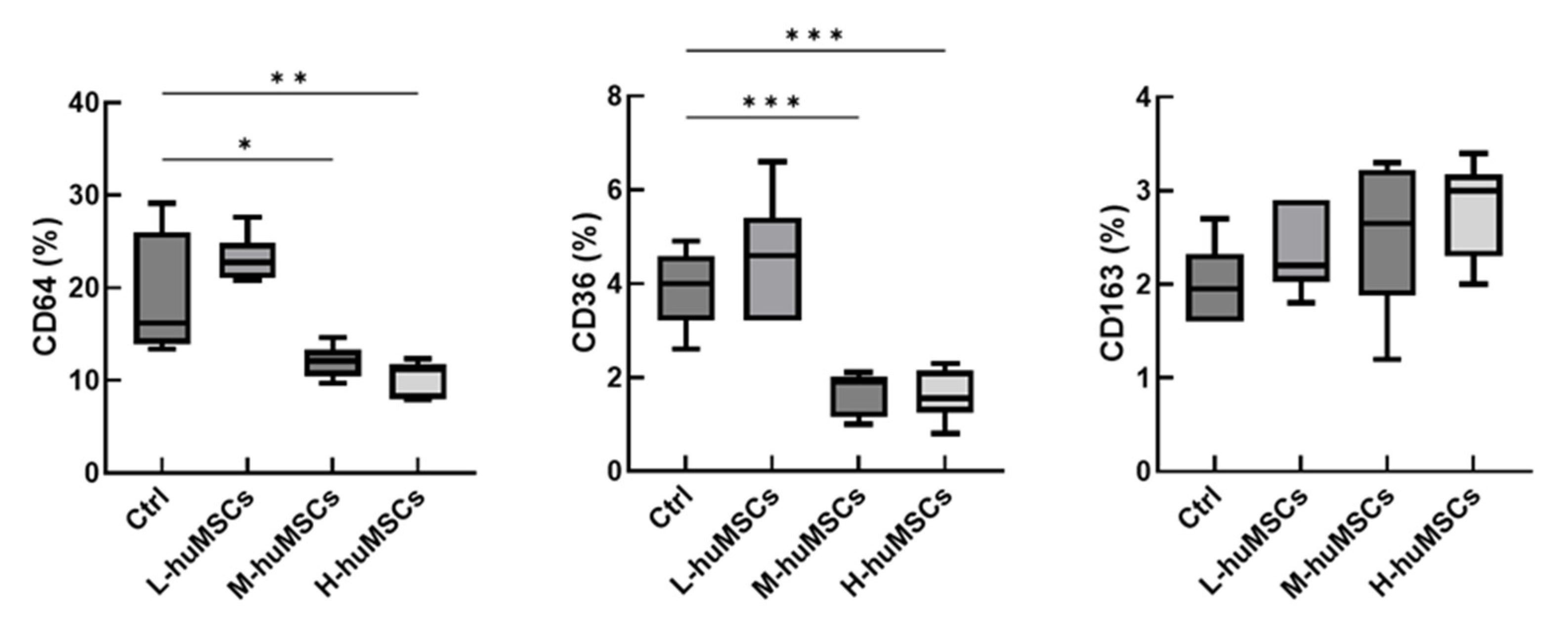
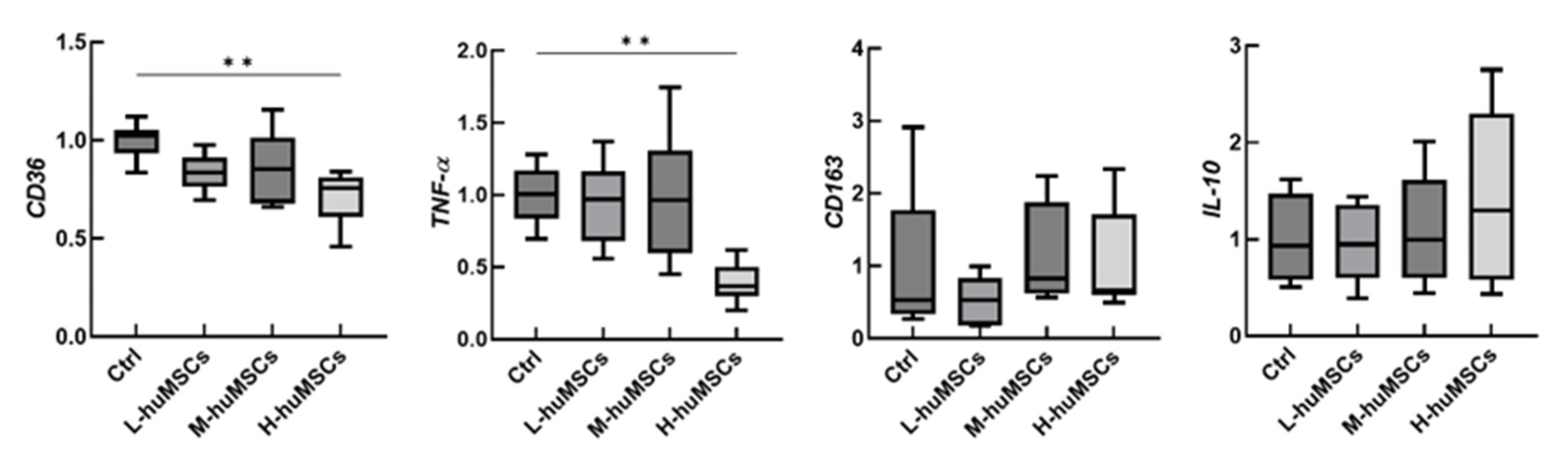
2.4. The huMSCs Suppressed the Polarization of Mouse Macrophages Toward M1 Dominance In Vitro
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Ethics
4.2. Materials
4.3. huMSCs
4.4. Animal Models and Surgical Procedure
4.5. Preparation of Mouse Macrophages and Co-Culture with huMSCs
4.6. Flow Cytometry
4.7. In Vitro qRT-PCR of Macrophages
4.8. Histology and Fibrosis Assessment
4.9. Hydroxyproline Assay
4.10. In Vivo Lung qRT-PCR
4.11. Immunohistochemical Staining
4.12. Immunohistochemical Analysis of CD68-Positive Macrophages
4.13. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| bFGF | Basic fibroblast growth factor |
| BLM | Bleomycin |
| CTD | Connective tissue disease |
| FBS | Fetal bovine serum |
| huMSC | Human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cell |
| ILD | Interstitial lung disease |
| IMDM | Iscove’s Modified Dulbecco’s Medium |
| P/S | Penicillin/streptomycin |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered saline |
| uMSC | Umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cell |
References
- Fischer, A.; du Bois, R. Interstitial lung disease in connective tissue disorders. Lancet 2012, 380, 689–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeganathan, N.; Sathananthan, M. Connective tissue disease-related interstitial lung disease: Prevalence, patterns, predictors, prognosis, and treatment. Lung 2020, 198, 735–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vacchi, C.; Sebastiani, M.; Cassone, G.; Cerri, S.; Della Casa, G.; Salvarani, C.; Manfredi, A. Therapeutic options for the treatment of interstitial lung disease related to connective tissue diseases: A narrative review. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tashkin, D.P.; Elashoff, R.; Clements, P.J.; Goldin, J.; Roth, M.D.; Furst, D.E.; Arriola, E.; Silver, R.; Strange, C.; Bolster, M.; et al. Cyclophosphamide versus placebo in scleroderma lung disease. N. E. J. Med. 2006, 354, 2655–2666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Wu, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhao, C.; Li, T.; Li, T.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, H.; Mao, B.; Liu, W. Efficacy and safety of antifibrotic agents in the treatment of CTD-ILD and RA-ILD: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Respir. Med. 2023, 216, 107329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, M.B.; Moncivais, K.; Caplan, A.I. Mesenchymal stem cells: Environmentally responsive therapeutics for regenerative medicine. Exp. Mol. Med. 2013, 45, e54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, L.; Liu, N.; Bao, C.L.; Yang, D.Z.; Ma, G.X.; Yi, W.H.; Xiao, G.Z.; Cao, H.L. Mesenchymal stem cells in fibrotic diseases—The two sides of the same coin. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2023, 44, 268–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maumus, M.; Jorgensen, C.; Noel, D. Mesenchymal stem cells in regenerative medicine applied to rheumatic diseases: Role of secretome and exosomes. Biochimie 2013, 95, 2229–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Nicola, M.; Carlo-Stella, C.; Magni, M.; Milanesi, M.; Longoni, P.D.; Matteucci, P.; Grisanti, S.; Gianni, A.M. Human bone marrow stromal cells suppress T-lymphocyte proliferation induced by cellular or nonspecific mitogenic stimuli. Blood 2002, 99, 3838–3843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nauta, A.J.; Fibbe, W.E. Immunomodulatory properties of mesenchymal stromal cells. Blood 2007, 110, 3499–3506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, S.; Kotani, T.; Saito, T.; Suzuka, T.; Mori, T.; Takeuchi, T. Low-molecular-weight heparin enhanced therapeutic effects of human adipose-derived stem cell administration in a mouse model of lupus nephritis. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 792739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, T.; Kotani, T.; Suzuka, T.; Matsuda, S.; Takeuchi, T.; Sato, T. Adipose-derived stem/stromal cells with heparin-enhanced anti-inflammatory and antifibrotic effects mitigate induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2022, 629, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuka, T.; Kotani, T.; Saito, T.; Matsuda, S.; Sato, T.; Takeuchi, T. Therapeutic effects of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem/stromal cells with enhanced migration ability and hepatocyte growth factor secretion by low-molecular-weight heparin treatment in bleomycin-induced mouse models of systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2022, 24, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagamura-Inoue, T.; He, H. Umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells: Their advantages and potential clinical utility. World J. Stem Cells 2014, 6, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McElreavey, K.D.; Irvine, A.I.; Ennis, K.T.; McLean, W.H. Isolation, culture and characterisation of fibroblast-like cells derived from the Wharton’s jelly portion of human umbilical cord. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 1991, 19, 29S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, K.; Zheng, K.; Li, D.; Lu, H.; Wang, S.; Sun, X. Impact of adipose tissue or umbilical cord derived mesenchymal stem cells on the immunogenicity of human cord blood derived endothelial progenitor cells. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0178624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, K.E.; Weiss, M.L.; Mitchell, B.M.; Martin, P.; Davis, D.; Morales, L.; Helwig, B.; Beerenstrauch, M.; Abou-Easa, K.; Hildreth, T.; et al. Matrix cells from Wharton’s jelly form neurons and glia. Stem Cells 2003, 21, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, J.; Zhang, H.; Hua, B.; Wang, H.; Lu, L.; Shi, S.; Hou, Y.; Zeng, X.; Gilkeson, G.S.; Sun, L. Allogenic mesenchymal stem cells transplantation in refractory systemic lupus erythematosus: A pilot clinical study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2010, 69, 1423–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.W.; Hung, S.P.; Wu, H.H.; Wu, W.M.; Yang, A.H.; Tsai, H.L.; Yang, L.Y.; Lee, O.K. Therapeutic effects of umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in experimental lupus nephritis. Cell Transplant. 2011, 20, 245–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tipnis, S.; Viswanathan, C.; Majumdar, A.S. Immunosuppressive properties of human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells: Role of B7-H1 and IDO. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2010, 88, 795–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, F.; Gao, F.; Li, Q.; Liu, Z. Therapeutic effect of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells modified by angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 gene on bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis injury. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 11, 2387–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, M.; Rezaee, M.A.; Mohammadi, M.; Rezaie, M.J.; Jalili, A.; Rahmani, M.R. Attenuating effect of long-term culture of umbilical cord vein mesenchymal stromal cells on pulmonary fibrosis in C57BL/6 mice. Iran. J. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2017, 16, 501–510. [Google Scholar]
- Moroncini, G.; Paolini, C.; Orlando, F.; Capelli, C.; Grieco, A.; Tonnini, C.; Agarbati, S.; Mondini, E.; Saccomanno, S.; Goteri, G.; et al. Mesenchymal stromal cells from human umbilical cord prevent the development of lung fibrosis in immunocompetent mice. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0196048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orlando, F.; Paolini, C.; Agarbati, S.; Tonnini, C.; Grieco, A.; Capelli, C.; Introna, M.; Provinciali, M.; Gabrielli, A.; Moroncini, G. Induction of mouse lung injury by endotracheal injection of bleomycin. J. Vis. Exp. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, K.A.; Wang, S.Y.; Yeh, C.C.; Fu, T.W.; Fu, Y.Y.; Ko, T.L.; Chiu, M.M.; Chen, T.H.; Tsai, P.J.; Fu, Y.S. Reversal of bleomycin-induced rat pulmonary fibrosis by a xenograft of human umbilical mesenchymal stem cells from Wharton’s jelly. Theranostics 2019, 9, 6646–6664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, K.A.; Yeh, C.C.; Kuo, F.H.; Lin, W.R.; Hsu, C.W.; Chen, T.H.; Fu, Y.S. Comparison of reversal of rat pulmonary fibrosis of nintedanib, pirfenidone, and human umbilical mesenchymal stem cells from Wharton’s jelly. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2020, 11, 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Gou, H.; Zhou, O.; Qiu, H.; Liu, H.; Fu, Z.; Chen, L. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells combined with pirfenidone upregulates the expression of RGS2 in the pulmonary fibrosis in mice. Respir. Res. 2022, 23, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, G.; Jiang, H.; Li, M.; Zhu, Z.; Ren, F.; Wang, Y.; Yan, M.; et al. Umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells preferentially modulate macrophages to alleviate pulmonary fibrosis. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2024, 15, 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, X.; Liao, R.; Li, X.; Zhang, C.; Huo, S.; Qin, L.; Xiong, Y.; He, T.; Xiao, G.; Zhang, T. Mesenchymal stem cells in treating human diseases: Molecular mechanisms and clinical studies. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2025, 10, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.W.; Myeong, S.H.; Lee, N.H.; Kim, H.; Son, H.J.; Chang, J.W.; Lee, N.K.; Na, D.L. Immunosuppressant drugs mitigate immune responses generated by human mesenchymal stem cells transplanted into the mouse parenchyma. Cell Transplant. 2021, 30, 9636897211019025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norte-Munoz, M.; Gallego-Ortega, A.; Lucas-Ruiz, F.; Gonzalez-Riquelme, M.J.; Changa-Espinoza, Y.I.; Galindo-Romero, C.; Ponsaerts, P.; Vidal-Sanz, M.; Garcia-Bernal, D.; Agudo-Barriuso, M. Immune recognition of syngeneic, allogeneic and xenogeneic stromal cell transplants in healthy retinas. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2022, 13, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.W.; Lee, N.K.; Yang, J.H.; Son, H.J.; Bang, S.I.; Chang, J.W.; Na, D.L. A comparison of immune responses exerted following syngeneic, allogeneic, and xenogeneic transplantation of mesenchymal stem cells into the mouse brain. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diehl, R.; Ferrara, F.; Muller, C.; Dreyer, A.Y.; McLeod, D.D.; Fricke, S.; Boltze, J. Immunosuppression for in vivo research: State-of-the-art protocols and experimental approaches. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2017, 14, 146–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, J.H., Jr.; Lazo, J.S. High dose continuous infusion of bleomycin in mice: A new model for drug-induced pulmonary fibrosis. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1987, 243, 1185–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hubner, R.H.; Gitter, W.; El Mokhtari, N.E.; Mathiak, M.; Both, M.; Bolte, H.; Freitag-Wolf, S.; Bewig, B. Standardized quantification of pulmonary fibrosis in histological samples. Biotechniques 2008, 44, 507–511, 514–517 . [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koike, A.; Arai, S.; Yamada, S.; Nagae, A.; Saita, N.; Itoh, H.; Uemoto, S.; Totani, M.; Ikemoto, M. Dynamic mobility of immunological cells expressing S100A8 and S100A9 in vivo: A variety of functional roles of the two proteins as regulators in acute inflammatory reaction. Inflammation 2012, 35, 409–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Author, Year [References] | Animal | Cell Source and Treatment | BLM Dose | Number of Injected Cells (×106) | Transplant Time After Modeling (Route) | Outcome Time | Major Treatment Effects |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min, 2015 [21] | C57BL/6 mice | huMSCs | 40 mg/kg | ND | 0 d (IV) | 7, 14, 28 d | ↓ Lung collagen, ↓ IL-1β, ↓ IL-6, ↑ MMP-9 |
| Moradi, 2017 [22] | 6–8 w C57BL/6 mice | huMSCs | 2 mg/kg | 0.5 | 15 min (IT) | 21 d | ↓ Lung collagen, ↓ Ashcroft score, NS in weight, ↓ IL-1, ↓ IL-6 |
| Moroncini, 2018 [23] | 12–16 w C57BL/6 mice | huMSCs | 1.5 mg/kg | 0.25 | 24 h and 7 d (IV) | 8, 14, 21 d | ↓ Ashcroft score, ↓ IL-1β, ↓ IL-6, ↓ TIMP-1 |
| Orlando, 2019 [24] | 12–16 w C57BL/6 mice | huMSCs | 1.5 mg/kg | 0.25 | 24 h and 7 d (IV) | 8, 14, 21 d | ↓ Lung collagen, ↓ Soluble collagen, ↑ Weight |
| Chu, 2019 [25] | SD rats | huMSCs | 8 mg/kg | 5, 25 | 21 d (IT) | 49 d | ↓ Lung collagen, ↑ IL-6, ↑ MMP-9 |
| Chu, 2020 [26] | 8 w SD rats | huMSCs | 5 mg/rat | 25 | 21 d (IT) | 49 d | ↓ Lung collagen, ↑ Weight, ↓ IL-1, ↓ IL-6, ↑ MMP-9, NS in αSMA |
| Xian, 2022 [27] | 7-w C57BL/6 male mice | huMSCs and pirfenidone (30 mg/kg) | 3 mg/kg | 0.5 | 7 d (IV) | 21 d | ↓ Lung collagen, ↓ Ashcroft score, ↑ Survival,↓ Fibrosis markers (Col1a1, Col1a2, α-SMA), ↑ RGS2 expression |
| Meng, 2024 [28] | 6–8 w C57BL/6 mice | huMSCs | 2 mg/kg | 1 | 3, 9, 15 d (IV) | 21, 29 d | ↓ Lung collagen, ↓ Ashcroft score, ↑ Lung function, ↓ Inflammatory cytokines, ↓ M1 macrophages, ↑ M2 macrophages |
| Current Study | 13-w C57BL/6 mice | huMSCs | 3 mg/mouse | 0.001 (L), 0.01 (M), 0.1 (H) | 7 d (IV) | 28 d | ↓ Lung collagen, ↓ Ashcroft score,↓ IL-1β, ↓ IL-6, ↓ TIMP-1, ↑ MMP-9, ↓ M1 macrophage polarization |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kotani, T.; Saito, T.; Masutani, R.; Uemura, S.; Matsuda, S.; Suzuka, T.; Ikemoto, M.; Takeuchi, T. Evaluating the Dose-Dependent Effects of Human Umbilical Cord-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells in a Preclinical Model of Interstitial Lung Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 10016. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262010016
Kotani T, Saito T, Masutani R, Uemura S, Matsuda S, Suzuka T, Ikemoto M, Takeuchi T. Evaluating the Dose-Dependent Effects of Human Umbilical Cord-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells in a Preclinical Model of Interstitial Lung Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(20):10016. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262010016
Chicago/Turabian StyleKotani, Takuya, Takashi Saito, Ryota Masutani, Satsuki Uemura, Shogo Matsuda, Takayasu Suzuka, Masaki Ikemoto, and Tohru Takeuchi. 2025. "Evaluating the Dose-Dependent Effects of Human Umbilical Cord-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells in a Preclinical Model of Interstitial Lung Disease" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 20: 10016. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262010016
APA StyleKotani, T., Saito, T., Masutani, R., Uemura, S., Matsuda, S., Suzuka, T., Ikemoto, M., & Takeuchi, T. (2025). Evaluating the Dose-Dependent Effects of Human Umbilical Cord-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells in a Preclinical Model of Interstitial Lung Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(20), 10016. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262010016






