Impact of Maternal Overweight and Obesity on Adipokines During Pregnancy and Lactation
Abstract
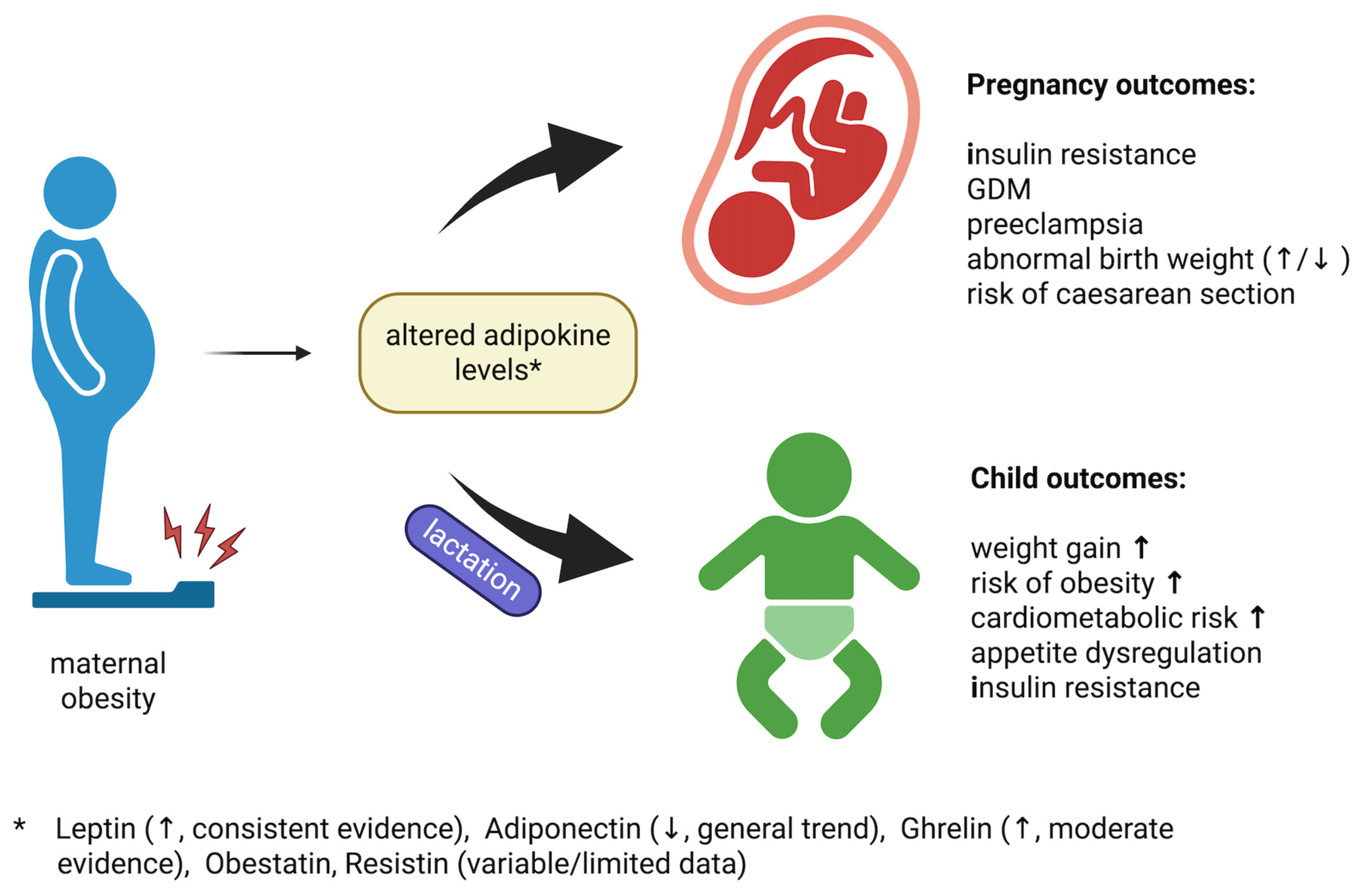
1. Introduction
2. Pregnancy and Lactation in Overweight and Obesity
3. Leptin
3.1. Pregnancy
3.2. Lactation
4. Adiponectin
4.1. Pregnancy
4.2. Lactation
5. Ghrelin
5.1. Pregnancy
5.2. Lactation
6. Obestatin
6.1. Pregnancy
6.2. Lactation
7. Resistin
7.1. Pregnancy
7.2. Lactation
8. Discussion
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Poston, L.; Caleyachetty, R.; Cnattingius, S.; Corvalán, C.; Uauy, R.; Herring, S.; Gillman, M.W. Preconceptional and Maternal Obesity: Epidemiology and Health Consequences. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2016, 4, 1025–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kent, L.; McGirr, M.; Eastwood, K.A. Global Trends in Prevalence of Maternal Overweight and Obesity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Routinely Collected Data Retrospective Cohorts. Int. J. Popul. Data Sci. 2024, 9, 2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves, F.C.R.; Moreira, A.; Moutinho, O. Maternal and Long-Term Offspring Outcomes of Obesity during Pregnancy. Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 2024, 309, 2315–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhtar, F. A Systematic Review of the Management of Maternal Obesity in Pregnancy: Antenatal Management, Outcomes, and Long-Term Implications on Maternal Health. Cureus 2025, 17, e87258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catalano, P.M.; Shankar, K. Obesity and Pregnancy: Mechanisms of Short Term and Long Term Adverse Consequences for Mother and Child. BMJ 2017, 356, j1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, E.B. The Complex Role of Adipokines in Obesity, Inflammation, and Autoimmunity. Clin. Sci. 2021, 135, 731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galic, S.; Oakhill, J.S.; Steinberg, G.R. Adipose Tissue as an Endocrine Organ. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2010, 316, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutaj, P.; Sibiak, R.; Jankowski, M.; Awdi, K.; Bryl, R.; Mozdziak, P.; Kempisty, B.; Wender-Ozegowska, E. The Role of the Adipokines in the Most Common Gestational Complications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinti, S.; Mitchell, G.; Barbatelli, G.; Murano, I.; Ceresi, E.; Faloia, E.; Wang, S.; Fortier, M.; Greenberg, A.S.; Obin, M.S. Adipocyte Death Defines Macrophage Localization and Function in Adipose Tissue of Obese Mice and Humans. J. Lipid Res. 2005, 46, 2347–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hildebrandt, X.; Ibrahim, M.; Peltzer, N. Cell Death and Inflammation during Obesity: “Know My Methods, WAT(Son)”. Cell Death Differ. 2022, 30, 279–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surmi, B.K.; Hasty, A.H. Macrophage Infiltration into Adipose Tissue: Initiation, Propagation and Remodeling. Future Lipidol. 2008, 3, 545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabbani, N.; Blüher, M.; Stepan, H.; Stumvoll, M.; Ebert, T.; Tönjes, A.; Schrey-Petersen, S. Adipokines in Pregnancy: A Systematic Review of Clinical Data. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jafari-Gharabaghlou, D.; Vaghari-Tabari, M.; Oghbaei, H.; Lotz, L.; Zarezadeh, R.; Rezaei, Y.R.; Ranjkesh, M.; Nouri, M.; Fattahi, A.; Nikanfar, S.; et al. Role of Adipokines in Embryo Implantation. Endocr. Connect. 2021, 10, R267–R278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downs, T.; da Silva Costa, F.; de Freitas Paganoti, C.; Holland, O.J.; Hryciw, D.H. Adiponectin and Leptin during Pregnancy: A Systematic Review of Their Association with Pregnancy Disorders, Fetal Growth and Placental Function. Endocrines 2024, 5, 382–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdeen, R.; Abdalla, H.; Parveen, N.; Iqbal, N.; Awadelkarim, A.; Mohamed, A.; Monowar, S.; Shahid, A.; Eldin, G.; Osman Elhussein, M.; et al. Adipokines in Preeclampsia: Disrupted Signaling Pathways and Novel Therapeutic Strategies. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2025, 30, 702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallardo, M.; Ferraro, S.; Daniele, A.; Nigro, E. GDM-Complicated Pregnancies: Focus on Adipokines. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2021, 48, 8171–8180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, E.; Duval, F.; Vialard, F.; Dieudonné, M.N. The Roles of Leptin and Adiponectin at the Fetal-Maternal Interface in Humans. Horm. Mol. Biol. Clin. Investig. 2015, 24, 47–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H. Adipocytokines in Obesity and Metabolic Disease. J. Endocrinol. 2014, 220, T47–T59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lager, S.; Powell, T.L. Regulation of Nutrient Transport across the Placenta. J. Pregnancy 2012, 2012, 179827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Çatlı, G.; Dündar, N.O.; Dündar, B.N. Adipokines in Breast Milk: An Update. J. Clin. Res. Pediatr. Endocrinol. 2014, 6, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voerman, E.; Santos, S.; Golab, B.P.; Amiano, P.; Ballester, F.; Barros, H.; Bergström, A.; Charles, M.A.; Chatzi, L.; Chevrier, C.; et al. Maternal Body Mass Index, Gestational Weight Gain, and the Risk of Overweight and Obesity across Childhood: An Individual Participant Data Meta-Analysis. PLoS Med. 2019, 16, e1002744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekaran, S.; Neal-Perry, G. Long-Term Consequences of Obesity on Female Fertility and the Health of the Offspring. Curr. Opin. Obstet. Gynecol. 2017, 29, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poston, L. Maternal Obesity, Gestational Weight Gain and Diet as Determinants of Offspring Long Term Health. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 26, 627–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godfrey, K.M.; Reynolds, R.M.; Prescott, S.L.; Nyirenda, M.; Jaddoe, V.W.V.; Eriksson, J.G.; Broekman, B.F.P. Influence of Maternal Obesity on the Long-Term Health of Offspring. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2017, 5, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azad, M.B.; Nickel, N.C.; Bode, L.; Brockway, M.; Brown, A.; Chambers, C.; Goldhammer, C.; Hinde, K.; McGuire, M.; Munblit, D.; et al. Breastfeeding and the Origins of Health: Interdisciplinary Perspectives and Priorities. Matern. Child Nutr. 2021, 17, e13109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenfeld, C.S. Homage to the “H” in Developmental Origins of Health and Disease. J. Dev. Orig. Health Dis. 2017, 8, 8–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lis-Kuberka, J.; Pupek, M.; Orczyk-Pawiłowicz, M. The Mother–Child Dyad Adipokine Pattern: A Review of Current Knowledge. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreas, N.J.; Kampmann, B.; Mehring Le-Doare, K. Human Breast Milk: A Review on Its Composition and Bioactivity. Early Hum. Dev. 2015, 91, 629–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misra, V.K.; Trudeau, S. The Influence of Overweight and Obesity on Longitudinal Trends in Maternal Serum Leptin Levels during Pregnancy. Obesity 2011, 19, 416–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zielinska-Pukos, M.A.; Kopiasz, Ł.; Hamulka, J. The Effect of Maternal Overweight/Obesity on Serum and Breastmilk Leptin, and Its Associations with Body Composition, Cardiometabolic Health Indices, and Maternal Diet: The BLOOM Study. Metabolites 2024, 14, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maple-Brown, L.; Ye, C.; Hanley, A.J.; Connelly, P.W.; Sermer, M.; Zinman, B.; Retnakaran, R. Maternal Pregravid Weight Is the Primary Determinant of Serum Leptin and Its Metabolic Associations in Pregnancy, Irrespective of Gestational Glucose Tolerance Status. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 97, 4148–4155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poniedziałek-Czajkowska, E.; Mierzyński, R.; Słodzińska, M.; Dłuski, D.; Leszczyńska-Gorzelak, B. Adipokines and C-Peptide in Overweight and Obese Pregnant Women. Ginekol. Pol. 2018, 89, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozias, M.K.; Li, S.; Hull, H.R.; Brooks, W.M.; Carlson, S.E. Relationship of Circulating Adipokines to Body Composition in Pregnant Women. Adipocyte 2015, 4, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karowicz-Bilińska, A.; Berner-Trąbska, M.; Kuś, E.; Brzozowska, M.; Kowalska-Koprek, U. The Assessment of Leptin Concentration and Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) in Relation to the Body Mass Index since 20th Week of Pregnancy. Ginekol. Pol. 2009, 80, 338–342. [Google Scholar]
- Malti, N.; Merzouk, H.; Bouhmama, L.; Saker, M.; Elhabiri, M.; Cherrak, S. Time Course of Changes in Leptin Levels and Their Relationships with Oxidant Status Biomarkers in Pregnant Women with Obesity. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2020, 14, CC01–CC05. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kugananthan, S.; Gridneva, Z.; Lai, C.T.; Hepworth, A.R.; Mark, P.J.; Kakulas, F.; Geddes, D.T. Associations between Maternal Body Composition and Appetite Hormones and Macronutrients in Human Milk. Nutrients 2017, 9, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadr Dadres, G.; Whitaker, K.M.; Haapala, J.L.; Foster, L.; Smith, K.D.; Teague, A.M.; Jacobs, D.R.; Kharbanda, E.O.; McGovern, P.M.; Schoenfuss, T.C.; et al. Relationship of Maternal Weight Status Before, During, and After Pregnancy with Breast Milk Hormone Concentrations. Obesity 2019, 27, 621–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamanillo, R.; Sánchez, J.; Serra, F.; Palou, A. Breast Milk Supply of MicroRNA Associated with Leptin and Adiponectin Is Affected by Maternal Overweight/Obesity and Influences Infancy BMI. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fields, D.A.; George, B.; Williams, M.; Whitaker, K.; Allison, D.B.; Teague, A.; Demerath, E.W. Associations between Human Breast Milk Hormones and Adipocytokines and Infant Growth and Body Composition in the First 6 Months of Life. Pediatr. Obes. 2017, 12 (Suppl. 1), 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernini, J.M.; Moreli, J.B.; Costa, R.A.A.; Negrato, C.A.; Rudge, M.V.C.; Calderon, I.M.P. Maternal Adipokines and Insulin as Biomarkers of Pregnancies Complicated by Overweight and Obesity. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2016, 8, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nien, J.K.; Mazaki-Tovi, S.; Romero, R.; Erez, O.; Kusanovic, J.P.; Gotsch, F.; Pineles, B.L.; Gomez, R.; Edwin, S.; Mazor, M.; et al. Plasma Adiponectin Concentrations in Non-Pregnant, Normal and Overweight Pregnant Women. J. Perinat. Med. 2007, 35, 522–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suto, M.; Maeda, K.; Sato, M.; Kaji, T.; Irahara, M. Plasma Adipokine Concentrations in Overweight/Obese Pregnant Women: A Longitudinal Study. Gynecol. Endocrinol. 2019, 35, 242–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tekin Guler, T.; Koc, N.; Kara Uzun, A.; Fisunoglu, M. The Association of Pre-Pregnancy BMI on Leptin, Ghrelin, Adiponectin and Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 in Breast Milk: A Case-Control Study. Br. J. Nutr. 2022, 127, 1675–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, W.A.; Kwon, M.R.; Cress, E.M.; Hamdy, R.C.; Cobarrubias, H. Maternal Body Mass Index and Presence of Appetite Regulating Hormones and Other Factors in Human Breast Milk. ETSU Fac. Work. 2017, 31 (Suppl. 1), 650.32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Rong, S.S.; Sun, X.; Ding, G.; Wan, W.; Zou, L.; Wu, S.; Li, M.; Wang, D. Associations of Breast Milk Adiponectin, Leptin, Insulin and Ghrelin with Maternal Characteristics and Early Infant Growth: A Longitudinal Study. Br. J. Nutr. 2018, 120, 1380–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, L.J.; Woo, J.G.; Geraghty, S.R.; Altaye, M.; Davidson, B.S.; Banach, W.; Dolan, L.M.; Ruiz-Palacios, G.M.; Morrow, A.L. Adiponectin Is Present in Human Milk and Is Associated with Maternal Factors. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 83, 1106–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, S.H.; Lewis, J.I.; Larnkjær, A.; Frøkiær, H.; Allen, L.H.; Mølgaard, C.; Michaelsen, K.F. Associations between Maternal Adiposity and Appetite-Regulating Hormones in Human Milk Are Mediated through Maternal Circulating Concentrations and Might Affect Infant Outcomes. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 1025439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, D.; Goruk, S.; Becker, A.B.; Subbarao, P.; Mandhane, P.J.; Turvey, S.E.; Lefebvre, D.; Sears, M.R.; Field, C.J.; Azad, M.B. Adiponectin, Leptin and Insulin in Breast Milk: Associations with Maternal Characteristics and Infant Body Composition in the First Year of Life. Int. J. Obes. 2018, 42, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tehranian, N.; Hosseini, M.; Ramezani-Tehrani, F.; Yousefi, S. Association of Serum Ghrelin with Weight Gain during Pregnancy in Overweight and Normal Women. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2019, 42, 809–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydin, S.; Aydin, S.; Ozkan, Y.; Kumru, S. Ghrelin Is Present in Human Colostrum, Transitional and Mature Milk. Peptides 2006, 27, 878–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreas, N.J.; Hyde, M.J.; Herbert, B.R.; Jeffries, S.; Santhakumaran, S.; Mandalia, S.; Holmes, E.; Modi, N. Impact of Maternal BMI and Sampling Strategy on the Concentration of Leptin, Insulin, Ghrelin and Resistin in Breast Milk across a Single Feed: A Longitudinal Cohort Study. BMJ Open 2016, 6, e010778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badillo-Suárez, P.A.; Rodríguez-Cruz, M.; Bernabe-García, M.; Villa-Morales, J.; Iglesias-Rodríguez, R.; Canizales-Quinteros, S.; Carmona-Sierra, F.V. Influence of Maternal Body Fat on Levels of Insulin, Insulin-Like Growth Factor-1, and Obestatin. J. Hum. Lact. 2022, 38, 619–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anggraini, S.; Yusrawati, Y.; Mayetti, M. Relationship Between Maternal and Fetal Resistin Levels in Obesity Nnd Normal to Anthropometry Newborn Babies. JoM 2018, 3, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santosa, I.; Shoji, H.; Awata, K.; Arai, Y.; Suganuma, H.; Shimizu, T. Resistin in Urine and Breast Milk: Relation to Type of Feeding and Anthropometry at 1-Month. Pediatr. Rep. 2022, 14, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.X.; Arany, Z. Maternal Cardiac Metabolism in Pregnancy. Cardiovasc. Res. 2014, 101, 545–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Meng, Y.; Shi, Y.; Fang, H.; Zhang, L. Maternal Hepatic Immunology during Pregnancy. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1220323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Li, Q.; Wang, H.; Ren, Y.; Zhang, L.; Yang, L. Maternal Nutrient Metabolism in the Liver during Pregnancy. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1295677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartlett, A.Q.; Vesco, K.K.; Purnell, J.Q.; Francisco, M.; Goddard, E.; Guan, X.; DeBarber, A.; Leo, M.C.; Baetscher, E.; Rooney, W.; et al. Pregnancy and Weaning Regulate Human Maternal Liver Size and Function. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2107269118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, M.E.; George, E.M.; Granger, J.P. The Heart During Pregnancy. Rev. Esp. Cardiol. 2011, 64, 1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibb, A.A.; Hill, B.G. Metabolic Coordination of Physiological and Pathological Cardiac Remodeling. Circ. Res. 2018, 123, 107–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pritschet, L.; Taylor, C.M.; Cossio, D.; Faskowitz, J.; Santander, T.; Handwerker, D.A.; Grotzinger, H.; Layher, E.; Chrastil, E.R.; Jacobs, E.G. Neuroanatomical Changes Observed over the Course of a Human Pregnancy. Nat. Neurosci. 2024, 27, 2253–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grattan, D.R.; Ladyman, S.R. Neurophysiological and Cognitive Changes in Pregnancy. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2020, 171, 25–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laway, B.A.; Mir, S.A. Pregnancy and Pituitary Disorders: Challenges in Diagnosis and Management. Indian J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 17, 996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, Y.W.; Onyekwelu, E.; Alam, U. Thyroid Disease in Pregnancy. Clin. Med. 2023, 23, 125–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zang, H.; Cong, X.; Shen, Q.; Chen, L.; Chen, X. Lipid Metabolism in Pregnancy Women with Hypothyroidism and Potential Influence on Pregnancy Outcome. J. Lipids 2024, 2024, 5589492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Assche, F.A.; Aerts, L.; Prins, F. De A Morphological Study of the Endocrine Pancreas in Human Pregnancy. Br. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 1978, 85, 818–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogensen, C.S.; Magkos, F.; Chabanova, E.; Mølgaard, C.; Geiker, N.R.W. Changes in Abdominal Adipose Tissues and Ectopic Fat Depots during Pregnancy Are Dissociated from Gestational Weight Gain. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2025, 33, 238–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Organ-Specific Alterations in Maternal Overweight|BioRender. Available online: https://app.biorender.com/citation/68d2f0f98c5f8d04aa2980c3 (accessed on 29 September 2025).
- Lubrano, C.; Locati, F.; Parisi, F.; Anelli, G.M.; Ossola, M.W.; Cetin, I. Gestational Weight Gain as a Modifiable Risk Factor in Women with Extreme Pregestational BMI. Nutrients 2025, 17, 736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habibi, N.; Mousa, A.; Tay, C.T.; Khomami, M.B.; Patten, R.K.; Andraweera, P.H.; Wassie, M.; Vandersluys, J.; Aflatounian, A.; Bianco-Miotto, T.; et al. Maternal Metabolic Factors and the Association with Gestational Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2022, 38, e3532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plows, J.F.; Stanley, J.L.; Baker, P.N.; Reynolds, C.M.; Vickers, M.H. The Pathophysiology of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartsch, E.; Medcalf, K.E.; Park, A.L.; Ray, J.G.; Al-Rubaie, Z.T.A.; Askie, L.M.; Berger, H.; Blake, J.; Graves, L.; Kingdom, J.C.; et al. Clinical Risk Factors for Pre-Eclampsia Determined in Early Pregnancy: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Large Cohort Studies. BMJ 2016, 353, i1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Jaramillo, P.; Barajas, J.; Rueda-Quijano, S.M.; Lopez-Lopez, C.; Felix, C. Obesity and Preeclampsia: Common Pathophysiological Mechanisms. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomimatsu, T.; Mimura, K.; Matsuzaki, S.; Endo, M.; Kumasawa, K.; Kimura, T. Preeclampsia: Maternal Systemic Vascular Disorder Caused by Generalized Endothelial Dysfunction Due to Placental Antiangiogenic Factors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korolova, D.; Suranyi, A.; Pavlenko, A.; Altorjay, A.T.; Zhuk, S.; Us, I.; Melnyk, Y.; Chernyshenko, V.; Vari, S.G. Obesity Is a Thrombotic Risk Factor in Pregnant Women. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 5310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, A.H. Venous Thromboembolism in Pregnancy. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2009, 29, 326–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luzardo-Ocampo, I.; Dena-Beltrán, J.L.; Ruiz-Herrera, X.; Ocampo-Ruiz, A.L.; Martínez de la Escalera, G.; Clapp, C.; Macotela, Y. Obesity-Derived Alterations in the Lactating Mammary Gland: Focus on Prolactin. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2023, 559, 111810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, C.J.; Adkins, L.M.; Tucker, A.; Brown, H.; Siegel, A.; Dotter-Katz, S. Impact of Excess Weight Gain on Risk of Postpartum Infection in Class III Obesity. AJP Rep. 2020, 10, e213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conner, S.N.; Verticchio, J.C.; Tuuli, M.G.; Odibo, A.O.; Macones, G.A.; Cahill, A.G. Maternal Obesity and Risk of Post-Cesarean Wound Complications. Am. J. Perinatol. 2013, 31, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hautakangas, T.; Uotila, J.; Kontiainen, J.; Huhtala, H.; Palomäki, O. Impact of Obesity on Uterine Contractile Activity during Labour: A Blinded Analysis of a Randomised Controlled Trial Cohort. BJOG 2022, 129, 1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uyl, N.; de Jonge, E.; Uyl-de Groot, C.; van der Marel, C.; Duvekot, J. Difficult Epidural Placement in Obese and Non-Obese Pregnant Women: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Obstet. Anesth. 2019, 40, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Wu, Y.; Li, S.; Zhang, D. Maternal Prepregnancy Obesity and the Risk of Shoulder Dystocia: A Meta-Analysis. BJOG 2018, 125, 407–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meenakshi; Reena, S.; Rai, S.N.; Kushwaha, K.P.; Vani, A. Obstetric Behavior and Pregnancy Outcome in Overweight and Obese Women: Maternal and Fetal Complications and Risks in Relation to Maternal Overweight and Obesity. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. India 2012, 62, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- SCHWARZ, E.B.; NOTHNAGLE, M. The Maternal Health Benefits of Breastfeeding. Am. Fam. Physician 2015, 91, 602–604. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Canul-Medina, G.; Fernandez-Mejia, C. Morphological, Hormonal, and Molecular Changes in Different Maternal Tissues during Lactation and Post-Lactation. J. Phys. Sci. 2019, 69, 825–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athonvarangkul, D.; Wysolmerski, J.J. Crosstalk within a Brain-Breast-Bone Axis Regulates Mineral and Skeletal Metabolism during Lactation. Front. Physiol. 2023, 14, 1121579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, A.W.; Bauman, D.E. Adaptations of Glucose Metabolism during Pregnancy and Lactation. J. Mammary Gland. Biol. Neoplasia 1997, 2, 265–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Roman, M.A.; Syed-Abdul, M.M.; Casey, B.M.; Alger, J.R.; Liu, Y.L.; Parks, E.J. Lactation Alters the Relationship between Liver Lipid Synthesis and Hepatic Fat Stores in the Postpartum Period. J. Lipid Res. 2022, 63, 100288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napso, T.; Yong, H.E.J.; Lopez-Tello, J.; Sferruzzi-Perri, A.N. The Role of Placental Hormones in Mediating Maternal Adaptations to Support Pregnancy and Lactation. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 387601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Röszer, T. Co-Evolution of Breast Milk Lipid Signaling and Thermogenic Adipose Tissue. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anhê, G.F.; Bordin, S. The Adaptation of Maternal Energy Metabolism to Lactation and Its Underlying Mechanisms. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2022, 553, 111697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Ramos-Roman, M.A.; Deng, Y. Metabolic Adaptation in Lactation: Insulin-Dependent and -Independent Glycemic Control. J. Transl. Int. Med. 2022, 10, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ladyman, S.R.; Brooks, V.L. Central Actions of Insulin during Pregnancy and Lactation. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2021, 33, e12946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stuebe, A.M.; Rich-Edwards, J.W. The Reset Hypothesis: Lactation and Maternal Metabolism. Am. J. Perinatol. 2009, 26, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, F.Q. Biology of Glucose Transport in the Mammary Gland. J. Mammary Gland. Biol. Neoplasia 2014, 19, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jevitt, C.; Hernandez, I.; Groër, M. Lactation Complicated by Overweight and Obesity: Supporting the Mother and Newborn. J. Midwifery Womens Health 2007, 52, 606–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Wang, X.; Zeng, J.; Zhang, G. Body Mass Index and Risk of Inflammatory Breast Disease: A Mendelian Randomization Study. Nutr. Hosp. 2024, 41, 96–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bever Babendure, J.; Reifsnider, E.; Mendias, E.; Moramarco, M.W.; Davila, Y.R. Reduced Breastfeeding Rates among Obese Mothers: A Review of Contributing Factors, Clinical Considerations and Future Directions. Int. Breastfeed. J. 2015, 10, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazur, D.; Satora, M.; Rekowska, A.K.; Kabała, Z.; Łomża, A.; Kimber-Trojnar, Ż.; Leszczyńska-Gorzelak, B. Influence of Breastfeeding on the State of Meta-Inflammation in Obesity—A Narrative Review. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2023, 45, 9003–9018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kac, G.; Benício, M.H.D.A.; Velásquez-Meléndez, G.; Valente, J.G.; Struchiner, C.J. Breastfeeding and Postpartum Weight Retention in a Cohort of Brazilian Women. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 79, 487–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Gao, H.; Vinyes-Pares, G.; Yu, K.; Ma, D.; Qin, X.; Wang, P. Association between Breastfeeding Duration and Postpartum Weight Retention of Lactating Mothers: A Meta-Analysis of Cohort Studies. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 37, 1224–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loy, S.L.; Chan, H.G.; Teo, J.X.; Chua, M.C.; Chay, O.M.; Ng, K.C. Breastfeeding Practices and Postpartum Weight Retention in an Asian Cohort. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perakakis, N.; Farr, O.M.; Mantzoros, C.S. Leptin in Leanness and Obesity: JACC State-of-the-Art Review. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2021, 77, 745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelesidis, T.; Kelesidis, I.; Chou, S.; Mantzoros, C.S. Narrative Review: The Role of Leptin in Human Physiology: Emerging Clinical Applications. Ann. Intern. Med. 2010, 152, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dornbush, S.; Aeddula, N.R. Physiology, Leptin. In StatPearls; StatPearls: Tampa, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Obradovic, M.; Sudar-Milovanovic, E.; Soskic, S.; Essack, M.; Arya, S.; Stewart, A.J.; Gojobori, T.; Isenovic, E.R. Leptin and Obesity: Role and Clinical Implication. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 585887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinkiewicz-Darol, E.; Martysiak-Żurowska, D.; Puta, M.; Adamczyk, I.; Barbarska, O.; Wesołowska, A.; Bernatowicz-ŁOjko, U. Nutrients and Bioactive Components of Human Milk After One Year of Lactation: Implication for Human Milk Banks. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2022, 74, 284–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moschos, S.; Chan, J.L.; Mantzoros, C.S. Leptin and Reproduction: A Review. Fertil. Steril. 2002, 77, 433–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolińska-Witort, E. The Involvement of Leptin in the Regulation of the Hypothalamus-Pituitary-Ovary Axis. Postępy Nauk. Med. 2007, 10, 420–424. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Chua, S. Leptin Function and Regulation. Compr. Physiol. 2018, 8, 351–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendler, I.; Blackwell, S.C.; Mehta, S.H.; Whitty, J.E.; Russell, E.; Sorokin, Y.; Cotton, D.B. The Levels of Leptin, Adiponectin, and Resistin in Normal Weight, Overweight, and Obese Pregnant Women with and without Preeclampsia. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2005, 193, 979–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, H.; Bhat, J.A.; Bhat, M.H.; Rashid, M.; Jan, R.; Afroze, D. Leptin in Obesity and Hypertension. Arter. Hypertens. 2022, 26, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dusserre, E.; Moulin, P.; Vidal, H. Differences in MRNA Expression of the Proteins Secreted by the Adipocytes in Human Subcutaneous and Visceral Adipose Tissues. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2000, 1500, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helland, I.B.; Reseland, J.E.; Saugstad, O.D.; Drevon, C.A. Smoking Related to Plasma Leptin Concentration in Pregnant Women and Their Newborn Infants. Acta Paediatr. 2001, 90, 282–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arroyo-Jousse, V.; Jaramillo, A.; Castaño-Moreno, E.; Lépez, M.; Carrasco-Negüe, K.; Casanello, P. Adipokines Underlie the Early Origins of Obesity and Associated Metabolic Comorbidities in the Offspring of Women with Pregestational Obesity. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2020, 1866, 165558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Knegt, V.E.; Hedley, P.L.; Kanters, J.K.; Thagaard, I.N.; Krebs, L.; Christiansen, M.; Lausten-Thomsen, U. The Role of Leptin in Fetal Growth during Pre-Eclampsia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, S.; Liu, Y.; Fan, P.; Yang, L.; Liu, X. Role of Leptin in the Pathophysiology of Preeclampsia. Placenta 2023, 142, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaiswar, S.P.; Priyadarshini, A.; Jaiswar, S.P.; Priyadarshini, A. Leptin and Female Reproductive Health. In Weight Management-Challenges and Opportunities; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tessier, D.R.; Ferraro, Z.M.; Gruslin, A. Role of Leptin in Pregnancy: Consequences of Maternal Obesity. Placenta 2013, 34, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palou, M.; Picó, C.; Palou, A. Leptin as a Breast Milk Component for the Prevention of Obesity. Nutr. Rev. 2018, 76, 875–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enstad, S.; Cheema, S.; Thomas, R.; Fichorova, R.N.; Martin, C.R.; O’Tierney-Ginn, P.; Wagner, C.L.; Sen, S. The Impact of Maternal Obesity and Breast Milk Inflammation on Developmental Programming of Infant Growth. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 75, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider-Worthington, C.R.; Bahorski, J.S.; Fields, D.A.; Gower, B.A.; Fernández, J.R.; Chandler-Laney, P.C. Associations Among Maternal Adiposity, Insulin and Adipokines in Circulation and Human Milk. J. Hum. Lact. 2020, 37, 714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilcol, Y.O.; Hizli, Z.B.; Ozkan, T. Leptin Concentration in Breast Milk and Its Relationship to Duration of Lactation and Hormonal Status. Int. Breastfeed. J. 2006, 1, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eilers, E.; Ziska, T.; Harder, T.; Plagemann, A.; Obladen, M.; Loui, A. Leptin Determination in Colostrum and Early Human Milk from Mothers of Preterm and Term Infants. Early Hum. Dev. 2011, 87, 415–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, B.D.; Ness, R.B.; Olsen, J.; Hougaard, D.M.; Skogstrand, K.; Roberts, J.M.; Haggerty, C.L. Serum Leptin Measured in Early Pregnancy Is Higher in Women with Preeclampsia Compared with Normotensive Pregnant Women. Hypertension 2015, 65, 594–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonseca, D.G.M.; Souza-Carmo, M.C.N.; Ruas, R.N.; Pereira, S.S.; Teixeira, L.G.; Alvarez-Leite, E.J.I. The Potential Role of Leptin in the Regulation of Maternal Weight during Pregnancy and Its Impact on Neonate Weight and Apgar. Obesities 2024, 4, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branham, K.K.R.; Sherman, E.; Golzy, M.; Drobnis, E.Z.; Schulz, L.C. Association of Serum Leptin at 24–28 Weeks Gestation with Initiation and Progression of Labor in Women. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 16016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krukowski, R.A.; Bursac, Z.; McGehee, M.A.; West, D. Exploring Potential Health Disparities in Excessive Gestational Weight Gain. J. Womens Health 2013, 22, 494–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Restall, A.; Taylor, R.S.; Thompson, J.M.D.; Flower, D.; Dekker, G.A.; Kenny, L.C.; Poston, L.; McCowan, L.M.E. Risk Factors for Excessive Gestational Weight Gain in a Healthy, Nulliparous Cohort. J. Obes. 2014, 2014, 148391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solis-Paredes, M.; Espinoy Sosa, S.; Estrada-Gutierrez, G.; Nava-Salazar, S.; Ortega-Castillo, V.; Rodriguez-Bosch, M.; Bravo-Flores, E.; Espejel-Nuñez, A.; Tolentino-Dolores, M.; Gaona-Estudillo, R.; et al. Maternal and Fetal Lipid and Adipokine Profiles and Their Association with Obesity. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2016, 2016, 7015626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logan, C.A.; Bornemann, R.; Koenig, W.; Reister, F.; Walter, V.; Fantuzzi, G.; Weyermann, M.; Brenner, H.; Genuneit, J.; Rothenbacher, D. Gestational Weight Gain and Fetal- Maternal Adiponectin, Leptin, and CRP: Results of Two Birth Cohorts Studies. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, srep41847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacroix, M.; Battista, M.C.; Doyon, M.; Moreau, J.; Patenaude, J.; Guillemette, L.; Ménard, J.; Ardilouze, J.L.; Perron, P.; Hivert, M.F. Higher Maternal Leptin Levels at Second Trimester Are Associated with Subsequent Greater Gestational Weight Gain in Late Pregnancy. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2016, 16, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schueler, J.; Alexander, B.; Hart, A.M.; Austin, K.; Enette Larson-Meyer, D. Presence and Dynamics of Leptin, GLP-1, and PYY in Human Breast Milk at Early Postpartum. Obesity 2013, 21, 1451–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson-Meyer, D.E.; Schueler, J.; Kyle, E.; Austin, K.J.; Hart, A.M.; Alexander, B.M. Appetite-Regulating Hormones in Human Milk: A Plausible Biological Factor for Obesity Risk Reduction? J. Hum. Lact. 2021, 37, 603–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunner, S.; Schmid, D.; Zang, K.; Much, D.; Knoeferl, B.; Kratzsch, J.; Amann-Gassner, U.; Bader, B.L.; Hauner, H. Breast Milk Leptin and Adiponectin in Relation to Infant Body Composition up to 2 Years. Pediatr. Obes. 2015, 10, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savino, F.; Sardo, A.; Rossi, L.; Benetti, S.; Savino, A.; Silvestro, L. Mother and Infant Body Mass Index, Breast Milk Leptin and Their Serum Leptin Values. Nutrients 2016, 8, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, B.E.; Patinkin, Z.; Palmer, C.; De La Houssaye, B.; Barbour, L.A.; Hernandez, T.; Friedman, J.E.; Krebs, N.F. Human Milk Insulin Is Related to Maternal Plasma Insulin and BMI: But Other Components of Human Milk Do Not Differ by BMI. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 71, 1094–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sims, C.R.; Lipsmeyer, M.E.; Turner, D.E.; Andres, A. Human Milk Composition Differs by Maternal BMI in the First 9 Months Postpartum. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 112, 548–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Logan, C.A.; Koenig, W.; Rothenbacher, D.; Genuneit, J. Determinants of Leptin in Human Breast Milk: Results of the Ulm SPATZ Health Study. Int. J. Obes. 2019, 43, 1174–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Judd, R.L. Adiponectin Regulation and Function. Compr. Physiol. 2018, 8, 1031–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achari, A.E.; Jain, S.K. Adiponectin, a Therapeutic Target for Obesity, Diabetes, and Endothelial Dysfunction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.M.; Doss, H.M.; Kim, K.S. Multifaceted Physiological Roles of Adiponectin in Inflammation and Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Fu, Z.; Liu, Z. Adiponectin and Insulin Cross Talk: The Microvascular Connection. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 2014, 24, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoramipour, K.; Chamari, K.; Hekmatikar, A.A.; Ziyaiyan, A.; Taherkhani, S.; Elguindy, N.M.; Bragazzi, N.L. Adiponectin: Structure, Physiological Functions, Role in Diseases, and Effects of Nutrition. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbe, A.; Bongrani, A.; Mellouk, N.; Estienne, A.; Kurowska, P.; Grandhaye, J.; Elfassy, Y.; Levy, R.; Rak, A.; Froment, P.; et al. Mechanisms of Adiponectin Action in Fertility: An Overview from Gametogenesis to Gestation in Humans and Animal Models in Normal and Pathological Conditions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalano, P.M.; Hoegh, M.; Minium, J.; Huston-Presley, L.; Bernard, S.; Kalhan, S.; Hauguel-De Mouzon, S. Adiponectin in Human Pregnancy: Implications for Regulation of Glucose and Lipid Metabolism. Diabetologia 2006, 49, 1677–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, L.K.; Ciaraldi, T.P.; Henry, R.R.; Wittgrove, A.C.; Phillips, S.A. Adipose Tissue Depot and Cell Size Dependency of Adiponectin Synthesis and Secretion in Human Obesity. Adipocyte 2013, 2, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaser, S.; Tatarczyk, T.; Stadlmayr, A.; Ciardi, C.; Ress, C.; Tschoner, A.; Sandhofer, A.; Paulweber, B.; Ebenbichler, C.F.; Patsch, J.R. Effect of Obesity and Insulin Sensitivity on Adiponectin Isoform Distribution. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2008, 38, 827–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Rosa, A.; Ludovica Monaco, M.; Capasso, M.; Forestieri, P.; Pilone, V.; Nardelli, C.; Buono, P.; Daniele, A. Adiponectin Oligomers as Potential Indicators of Adipose Tissue Improvement in Obese Subjects. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2013, 169, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva Rosa, S.C.; Liu, M.; Sweeney, G. Adiponectin Synthesis, Secretion and Extravasation from Circulation to Interstitial Space. Physiology 2021, 36, 134–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Sullivan, A.J.; Kriketos, A.D.; Martin, A.; Brown, M.A. Serum Adiponectin Levels in Normal and Hypertensive Pregnancy. Hypertens. Pregnancy 2006, 25, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pheiffer, C.; Dias, S.; Jack, B.; Malaza, N.; Adam, S. Adiponectin as a Potential Biomarker for Pregnancy Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savino, F.; Lupica, M.M.; Benetti, S.; Petrucci, E.; Liguori, S.A.; Cordero Di Montezemolo, L. Adiponectin in Breast Milk: Relation to Serum Adiponectin Concentration in Lactating Mothers and Their Infants. Acta Paediatr. 2012, 101, 1058–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fakhreldin, A.R. Maternal and Infantile Adiponectin as Marker for Anthropometric Parameters of Lactating Mothers and Their Breast-Fed Infants. Indian J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 22, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansson, N.; Nilsfelt, A.; Gellerstedt, M.; Wennergren, M.; Rossander-Hulthén, L.; Powell, T.L.; Jansson, T. Maternal Hormones Linking Maternal Body Mass Index and Dietary Intake to Birth Weight. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 87, 1743–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bawah, A.T.; Yeboah, F.A.; Nanga, S.; Alidu, H.; Ngala, R.A. Serum Adipocytokines and Adiposity as Predictive Indices of Preeclampsia. Clin. Hypertens. 2020, 26, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghiac, M.; Basu, S.; Presley, L.; Serre, D.; Catalano, P.M.; Hauguel-De Mouzon, S. Patterns of Adiponectin Expression in Term Pregnancy: Impact of Obesity. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 99, 3427–3434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jara, A.; Dreher, M.; Porter, K.; Christian, L.M. The Association of Maternal Obesity and Race with Serum Adipokines in Pregnancy and Postpartum: Implications for Gestational Weight Gain and Infant Birth Weight. Brain Behav. Immun. Health 2020, 3, 100053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangiao-Alvarellos, S.; Cordido, F. Effect of Ghrelin on Glucose-Insulin Homeostasis: Therapeutic Implications. Int. J. Pept. 2010, 2010, 234709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdalla, M.M.I. Ghrelin-Physiological Functions and Regulation. Eur. Endocrinol. 2015, 11, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delporte, C. Structure and Physiological Actions of Ghrelin. Scientifica (Cairo) 2013, 2013, 518909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khatib, M.N.; Gaidhane, S.; Gaidhane, A.M.; Simkhada, P.; Zahiruddin, Q.S. Ghrelin O Acyl Transferase (GOAT) as a Novel Metabolic Regulatory Enzyme. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2015, 9, LE01. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Z.T.; Luo, Q. Molecular Mechanisms and Health Benefits of Ghrelin: A Narrative Review. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, E.R.; Jialal, I. Biochemistry, Ghrelin. In StatPearls; StatPearls: Tampa, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Pradhan, G.; Samson, S.L.; Sun, Y. Ghrelin: Much More than a Hunger Hormone. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2013, 16, 619–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Loenen, M.R.; Geenen, B.; Arnoldussen, I.A.C.; Kiliaan, A.J. Ghrelin as a Prominent Endocrine Factor in Stress-Induced Obesity. Nutr. Neurosci. 2022, 25, 1413–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilcol, Y.O.; Hizli, B. Active and Total Ghrelin Concentrations Increase in Breast Milk during Lactation. Acta Paediatr. 2007, 96, 1632–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwakura, H.; Ensho, T.; Ueda, Y. Desacyl-Ghrelin, Not Just an Inactive Form of Ghrelin? A Review of Current Knowledge on the Biological Actions of Desacyl-Ghrelin. Peptides 2023, 167, 171050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, T.; Ida, T.; Shiimura, Y.; Matsui, K.; Oishi, K.; Kojima, M. Insights into the Regulation of Offspring Growth by Maternally Derived Ghrelin. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 852636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Yuan, C.; Li, Z.; Li, J.; Li, X.; Li, C.; Li, R.; Wang, S.R. Meta-Analysis of the Relationship between Obestatin and Ghrelin Levels and the Ghrelin/Obestatin Ratio with Respect to Obesity. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2011, 341, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuglsang, J. Ghrelin in Pregnancy and Lactation. Vitam. Horm. 2007, 77, 259–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuglsang, J.; Skjærbæk, C.; Espelund, U.; Frystyk, J.; Fisker, S.; Flyvbjerg, A.; Ovesen, P. Ghrelin and Its Relationship to Growth Hormones during Normal Pregnancy. Clin. Endocrinol. 2005, 62, 554–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dündar, N.O.; Dündar, B.; Cesur, G.; Yilmaz, N.; Sütu, R.; Özgüner, F. Ghrelin and Adiponectin Levels in Colostrum, Cord Blood and Maternal Serum. Pediatr. Int. 2010, 52, 622–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindsay, K.L.; Mashayekh, J.T.; Rodriguez, N.; Gyllenhammer, L.E. Relationship between Psychological Stress and Ghrelin Concentrations in Pregnant Women with Overweight or Obesity. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2022, 146, 105937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palik, E.; Baranyi, E.; Melczer, Z.; Audikovszky, M.; Szöcs, A.; Winkler, G.; Cseh, K. Elevated Serum Acylated (Biologically Active) Ghrelin and Resistin Levels Associate with Pregnancy-Induced Weight Gain and Insulin Resistance. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2007, 76, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydin, S.; Ozkan, Y.; Erman, F.; Gurates, B.; Kilic, N.; Colak, R.; Gundogan, T.; Catak, Z.; Bozkurt, M.; Akin, O.; et al. Presence of Obestatin in Breast Milk: Relationship among Obestatin, Ghrelin, and Leptin in Lactating Women. Nutrition 2008, 24, 689–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacquaniti, A.; Donato, V.; Chirico, V.; Buemi, A.; Buemi, M. Obestatin: An Interesting but Controversial Gut Hormone. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2011, 59, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.B.; Asakawa, A.; Cheng, K.C.; Li, Y.; Chaolu, H.; Tsai, M.; Inui, A. Biological Effects of Obestatin. Endocrine 2011, 39, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villarreal, D.; Pradhan, G.; Zhou, Y.; Xue, B.; Sun, Y. Diverse and Complementary Effects of Ghrelin and Obestatin. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontenot, E.; DeVente, J.E.; Seidel, E.R. Obestatin and Ghrelin in Obese and in Pregnant Women. Peptides 2007, 28, 1937–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lis-Kuberka, J.; Berghausen-Mazur, M.; Orczyk-Pawiłowicz, M. Evaluation of Selected Pro- and Anti-Inflammatory Adipokines in Colostrum from Mothers with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savino, F.; Benetti, S.; Lupica, M.M.; Petrucci, E.; Palumeri, E.; Di Montezemolo, L.C. Ghrelin and Obestatin in Infants, Lactating Mothers and Breast Milk. Horm. Res. Paediatr. 2012, 78, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Fan, X.; Yu, Y.; Wang, Y. Maternal Serum Ratio of Ghrelin to Obestatin Decreased in Preeclampsia. Pregnancy Hypertens. 2015, 5, 263–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pendeloski, K.P.T.; Ono, E.; Torloni, M.R.; Mattar, R.; Daher, S. Maternal Obesity and Inflammatory Mediators: A Controversial Association. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2017, 77, e12674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silha, J.V.; Krsek, M.; Skrha, J.V.; Sucharda, P.; Nyomba, B.L.G.; Murphy, L.J. Plasma Resistin, Adiponectin and Leptin Levels in Lean and Obese Subjects: Correlations with Insulin Resistence. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2003, 149, 331–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajala, M.W.; Obici, S.; Scherer, P.E.; Rossetti, L. Adipose-Derived Resistin and Gut-Derived Resistin-like Molecule–β Selectively Impair Insulin Action on Glucose Production. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 111, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvo, M.J.; Parra, H.; Santeliz, R.; Bautista, J.; Luzardo, E.; Villasmil, N.; Martínez, M.S.; Chacín, M.; Cano, C.; Checa-Ros, A.; et al. The Placental Role in Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: A Molecular Perspective. touchREVIEWS Endocrinol. 2024, 20, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sentinelli, F.; Romeo, S.; Arca, M.; Filippi, E.; Leonetti, F.; Banchieri, M.; Di Mario, U.; Baroni, M.G. Human Resistin Gene, Obesity, and Type 2 Diabetes: Mutation Analysis and Population Study. Diabetes 2002, 51, 860–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tripathi, D.; Kant, S.; Pandey, S.; Ehtesham, N.Z. Resistin in Metabolism, Inflammation, and Disease. FEBS J. 2020, 287, 3141–3149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokarewa, M.; Nagaev, I.; Dahlberg, L.; Smith, U.; Tarkowski, A. Resistin, an Adipokine with Potent Proinflammatory Properties. J. Immunol. 2005, 174, 5789–5795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, J.C.; Park, C.Y.; Lee, W.Y.; Lee, E.S.; Oh, S.W.; Park, S.W. Association of Plasma Levels of Resistin with Subcutaneous Fat Mass and Markers of Inflammation but Not with Metabolic Determinants or Insulin Resistance. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2009, 24, 695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Nien, J.K.; Gomez, R.; Espinoza, J.; Goncalves, L.; Hong, J.-S.; Edwin, S.; Hassan, S.; Mazor, M.; Romero, R. Resistin: A Hormone Which Induces Insulin Resistance Is Increased in Normal Pregnancy. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2004, 191, S52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Dong, M.; Fang, Q.; He, J.; Wang, Z.; Yang, X. Alterations of Serum Resistin in Normal Pregnancy and Pre-Eclampsia. Clin. Sci. 2005, 108, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, D.J.; Hill, T.G. Maternal Diet during Pregnancy and Adaptive Changes in the Maternal and Fetal Pancreas Have Implications for Future Metabolic Health. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1456629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floeck, A.; Ferrari, N.; Joisten, C.; Puth, M.T.; Strizek, B.; Dolscheid-Pommerich, R.; Gembruch, U.; Merz, W.M. Resistin in Pregnancy: Analysis of Determinants in Pairs of Umbilical Cord Blood and Maternal Serum. Cytokine X 2021, 3, 100052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Froń, A.; Orczyk-Pawiłowicz, M. Understanding the Immunological Quality of Breast Milk in Maternal Overweight and Obesity. Nutrients 2023, 15, 5016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Impact of Maternal Obesity–Related Adipokine Alter|BioRender. Available online: https://app.biorender.com/citation/68b453fce066110bf1676ffa (accessed on 23 September 2025).
- Golańska-Wróblewska, M.; Fryczak, J.; Siejka, A. Serum Levels of Sirtuins, Leptin and Adiponectin in Women with Pregnancy-Induced Hypertension. Cytokine 2024, 179, 156612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ormindean, C.M.; Ciortea, R.; Măluțan, A.M.; Bucuri, C.E.; Diculescu, D.M.; Iuhas, C.I.; Porumb, C.G.; Ormindean, V.; Roman, M.P.; Nati, I.D.; et al. Adipokines as Potential Biomarkers in Pregnancy: A Naturalistic Study of Adipokines in Pregnant Women and Newborns. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daskalakis, G.; Bellos, I.; Nikolakea, M.; Pergialiotis, V.; Papapanagiotou, A.; Loutradis, D. The Role of Serum Adipokine Levels in Preeclampsia: A Systematic Review. Metabolism 2020, 106, 154172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Gao, J.; Qu, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, X.; Liu, J. Serum Levels of Leptin, Adiponectin and Resistin in Relation to Clinical Characteristics in Normal Pregnancy and Preeclampsia. Clin. Chim. Acta 2016, 458, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoots, M.H.; Bourgonje, M.F.; Bourgonje, A.R.; Prins, J.R.; van Hoorn, E.G.M.; Abdulle, A.E.; Muller Kobold, A.C.; van der Heide, M.; Hillebrands, J.L.; van Goor, H.; et al. Oxidative Stress Biomarkers in Fetal Growth Restriction with and without Preeclampsia. Placenta 2021, 115, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, N.; Schmidt, N.; Schmidt, L.; Merz, W.M.; Brockmeier, K.; Dötsch, J.; Bae-Gartz, I.; Mahabir, E.; Joisten, C. Effect of Lifestyle Interventions during Pregnancy on Maternal Leptin, Resistin and Offspring Weight at Birth and One Year of Life. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahlavani, H.A.; Laher, I.; Weiss, K.; Knechtle, B.; Zouhal, H. Physical Exercise for a Healthy Pregnancy: The Role of Placentokines and Exerkines. J. Physiol. Sci. 2023, 73, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, E.C.; Li, M.; Hinkle, S.N.; Cao, Y.; Chen, J.; Wu, J.; Zhu, Y.; Cao, H.; Kemper, K.; Rennert, L.; et al. Adipokines in Early and Mid-Pregnancy and Subsequent Risk of Gestational Diabetes: A Longitudinal Study in a Multiracial Cohort. BMJ Open Diabetes Res. Care 2020, 8, 1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solis-Paredes, M.; Estrada-Gutierrez, G.; Perichart-Perera, O.; Montoya-Estrada, A.; Guzmán-Huerta, M.; Borboa-Olivares, H.; Bravo-Flores, E.; Cardona-Pérez, A.; Zaga-Clavellina, V.; Garcia-Latorre, E.; et al. Key Clinical Factors Predicting Adipokine and Oxidative Stress Marker Concentrations among Normal, Overweight and Obese Pregnant Women Using Artificial Neural Networks. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sargolzaei, J.; Chamani, E.; Kazemi, T.; Fallah, S.; Soori, H. The Role of Adiponectin and Adipolin as Anti-Inflammatory Adipokines in the Formation of Macrophage Foam Cells and Their Association with Cardiovascular Diseases. Clin. Biochem. 2018, 54, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihai, M.; Vladut, S.; Sonia-Teodora, L.; Laura Mihaela, S.; Victoria, N.; Irina Elena, M.; Claudiu, M. Correlation between Overweight, Obesity, Gestational Diabetes Mellitus, Adipokines (Adipolin and Adiponectin), and Adverse Pregnancy Outcomes: A Pilot Study. Medicina 2024, 60, 1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, B.E.; Levek, C.; Reynolds, R.M.; Rudolph, M.C.; MacLean, P.; Hernandez, T.L.; Friedman, J.E.; Krebs, N.F. Bioactive Components in Human Milk Are Differentially Associated with Rates of Lean and Fat Mass Deposition in Infants of Mothers with Normal vs. Elevated BMI. Pediatr. Obes. 2018, 13, 598–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badillo-Suárez, P.A.; Rodríguez-Cruz, M.; Nieves-Morales, X. Impact of Metabolic Hormones Secreted in Human Breast Milk on Nutritional Programming in Childhood Obesity. J. Mammary Gland. Biol. Neoplasia 2017, 22, 171–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lepe, M.; Bacardí Gascón, M.; Castañeda-González, L.M.; Pérez Morales, M.E.; Jiménez Cruz, A. Effect of Maternal Obesity on Lactation: Systematic Review. Nutr. Hosp. 2011, 26, 1266–1269. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Prior, E.; Santhakumaran, S.; Gale, C.; Philipps, L.H.; Modi, N.; Hyde, M.J. Breastfeeding after Cesarean Delivery: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of World Literature. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 95, 1113–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leghi, G.E.; Netting, M.J.; Lai, C.T.; Narayanan, A.; Dymock, M.; Rea, A.; Wlodek, M.E.; Geddes, D.T.; Muhlhausler, B.S. Reduction in Maternal Energy Intake during Lactation Decreased Maternal Body Weight and Concentrations of Leptin, Insulin and Adiponectin in Human Milk without Affecting Milk Production, Milk Macronutrient Composition or Infant Growth. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesur, G.; Ozguner, F.; Yilmaz, N.; Dundar, B. The Relationship between Ghrelin and Adiponectin Levels in Breast Milk and Infant Serum and Growth of Infants during Early Postnatal Life. J. Physiol. Sci. 2012, 62, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savino, F.; Fissore, M.F.; Liguori, S.A.; Oggero, R. Can Hormones Contained in Mothers’ Milk Account for the Beneficial Effect of Breast-Feeding on Obesity in Children? Clin. Endocrinol. 2009, 71, 757–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLacey, S.; Gurra, M.; Arzu, J.; Lowe, L.P.; Lowe, W.L.; Scholtens, D.M.; Josefson, J.L. Leptin and Adiposity Measures from Birth to Later Childhood: Findings from the HAPO Follow-Up Study. Pediatr. Obes. 2023, 19, e13087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, M.; Rifas-Shiman, S.L.; Belfort, M.B.; Taveras, E.M.; Oken, E.; Mantzoros, C.; Gillman, M.W. Gestational Glucose Tolerance and Cord Blood Leptin Levels Predict Slower Weight Gain in Early Infancy. J. Pediatr. 2011, 158, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chaoimh, C.; Murray, D.M.; Kenny, L.C.; Irvine, A.D.; O’Hourihane, J.B.; Kiely, M. Cord Blood Leptin and Gains in Body Weight and Fat Mass during Infancy. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2016, 175, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Simpson, J.; Smith, A.D.A.C.; Fraser, A.; Sattar, N.; Lindsay, R.S.; Ring, S.M.; Tilling, K.; Smith, G.D.; Lawlor, D.A.; Nelson, S.M. Programming of Adiposity in Childhood and Adolescence: Associations with Birth Weight and Cord Blood Adipokines. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 102, 499–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fields, D.A.; Schneider, C.R.; Pavela, G. A Narrative Review of the Associations between Six Bioactive Components in Breast Milk and Infant Adiposity. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2016, 24, 1213–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolaczynski, J.W.; Ohannesian, J.P.; Considine, R.V.; Marco, C.C.; Caro, J.F. Response of Leptin to Short-Term and Prolonged Overfeeding in Humans. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1996, 81, 4162–4165. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Lemas, D.J.; Young, B.E.; Ii, P.R.B.; Tomczik, A.C.; Soderborg, T.K.; Hernandez, T.L.; De La Houssaye, B.A.; Robertson, C.E.; Rudolph, M.C.; Ir, D.; et al. Alterations in Human Milk Leptin and Insulin Are Associated with Early Changes in the Infant Intestinal Microbiome. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 103, 1291–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heslehurst, N.; Vieira, R.; Akhter, Z.; Bailey, H.; Slack, E.; Ngongalah, L.; Pemu, A.; Rankin, J. The Association between Maternal Body Mass Index and Child Obesity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS Med. 2019, 16, e1002817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shipp, G.M.; Wosu, A.C.; Knapp, E.A.; Sauder, K.A.; Dabelea, D.; Perng, W.; Zhu, Y.; Ferrara, A.; Dunlop, A.L.; Deoni, S.; et al. Maternal Pre-Pregnancy BMI, Breastfeeding, and Child BMI. Pediatrics 2024, 153, 2023061466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hildebrand, J.S.; Ferguson, P.L.; Sciscione, A.C.; Grobman, W.A.; Newman, R.B.; Tita, A.T.; Wapner, R.J.; Nageotte, M.P.; Palomares, K.; Skupski, D.W.; et al. Breastfeeding Associations with Childhood Obesity and Body Composition: Findings from a Racially Diverse Maternal-Child Cohort. Child. Obes. 2022, 18, 178–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Kaur, H.; Choi, W.S.; Huang, T.T.K.; Lee, R.E.; Ahluwalia, J.S. Additive Interactions of Maternal Prepregnancy BMI and Breast-Feeding on Childhood Overweight. Obes. Res. 2005, 13, 362–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garner, C.D.; McKenzie, S.A.; Devine, C.M.; Thornburg, L.L.; Rasmussen, K.M. Obese Women Experience Multiple Challenges with Breastfeeding That Are Either Unique or Exacerbated by Their Obesity: Discoveries from a Longitudinal, Qualitative Study. Matern. Child Nutr. 2016, 13, e12344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lahav, Y.; Harison, E. Donate or Not to Donate-Willingness to Donate and Accept Donor Human Milk. Nutrients 2025, 17, 2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Adipokine | Biological Fluid | Alterations | References | Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| leptin | maternal serum | increased | Misra et al. [29] | 1.8× higher in OW/OB vs. NW (per kg body mass, early pregnancy) |
| Zielinska-Pukos et al. [30] | 1.4× higher in OW and 4.5× higher in OB vs. NW (during breast feeding) | |||
| Maple-Brown et al. [31] | Strong positive association with pre-pregnancy BMI (r = 0.54, p < 0.0001) in 2nd trimester | |||
| Poniedziałek-Czajkowska et al. [32] | Higher in OW/OB vs. NW at 24–34 weeks (43.44 ± 31.41 vs. 21.29 ± 12.67 ng/mL, p = 0.0001) | |||
| Ozias et al. [33] | OW/OB vs. NW: 66.3 ± 34.2 vs. 35.7 ± 19.3 ng/mL (p < 0.001); correlated with total fat mass (r = 0.782, p < 0.001) | |||
| maternal plasma | increased | Karowicz-Bilińska et al. [34] | Positive correlation with BMI in OB vs. NW women at 20–24 weeks (p = 0.008) | |
| Malti et al. [35] | ~40% higher in OB vs. NW across all trimesters | |||
| Kugananthan et al. [36] | Positively correlated with maternal fat mass percentage in both whole and skim milk (p = 0.008; p = 0.007) | |||
| breast milk | increased | Zielinska-Pukos et al. [30] | OB: up to 6.2× higher vs. NW | |
| Sadr Dadres et al. [37] | Positively associated with pre-pregnancy BMI (β = 0.525 crude; β = 0.494 adjusted; p < 0.001). Excessive gestational weight gain independently associated (adjusted β = 0.298; p = 0.009) | |||
| Zamanillo et al. [38] | 2.8-fold higher in OW/OB vs. NW at 1 month postpartum (p < 0.05); levels declined in NW but remained stable in OW/OB | |||
| Fields et al. [39] | OW mothers: +96.5%; OB mothers: +315.1% vs. NW | |||
| adiponectin | maternal serum | decreased | Vernini et al. [40] | Negatively correlated with gestational BMI (r = −0.29, p = 0.013) |
| maternal plasma | decreased | Nien et al. [41] | Median levels in OW vs. NW (7.40 [2.76–22.38] vs. 8.87 [2.77–25.03] mg/L; p < 0.05) (pregnant women) | |
| Suto et al. [42] | OW/OB vs. lean, 1st and 2nd trimester | |||
| no correlation | Ozias et al. [33] | No difference between NW and OW/OB in 3rd trimester | ||
| breast milk | decreased | Tekin Guler et al. [43] | Post-feed levels 12.84 ± 2.33 ng/mL (OB—pre-pregnancy BMI) vs. 13.95 ± 0.25 ng/mL (NW); p = 0.010 | |
| Clark et al. [44] | NW: 12.35 ng/mL vs. OB: 8.70 ng/mL; p = 0.052 | |||
| Yu et al. [45] | β = 0.06; 95% CI: 0.02 to 0.10; p = 0.001; samples collected on days 3, 42, and 90 postpartum | |||
| increased | Martin et al. [46] | β = 0.08 ± 0.02; p < 0.0001 (longitudinal data) | ||
| no correlation | Christensen et al. [47] | Samples collected at three postpartum visits (1–8.49 months) | ||
| Chan et al. [48] | Samples collected at 4 months postpartum. | |||
| Sadr Dadres et al. [37] | Samples collected at 1 and 3 months postpartum | |||
| ghrelin | maternal plasma | no correlation | Tehranian et al. [49] | No significant difference between OW and NW from 1st to 2nd trimester (p > 0.05) |
| increased | Aydin et al. [50] | Increase with postpartum weight loss, samples collected on days 1, 7, and 15 postpartum | ||
| breast milk | increased | Tekin Guler et al. [43] | Higher in OB (pre-pregnancy BMI, p = 0.025); levels decreased over lactation but remained consistently elevated in OB | |
| Aydin et al. [50] | r = 0.42, p = 0.19; samples collected on days 1, 7, and 15 postpartum | |||
| decreased | Yu et al. [45] | β = −0.08; 95% CI: −0.10 to −0.06; p < 0.001, samples collected on days 3, 42, and 90 postpartum | ||
| no correlation | Andreas et al. [51] | At 1 week and 3 months postpartum, with BMI at sampling | ||
| obestatin | breast milk | decreased | Badillo-Suárez et al. [52] | Lower concentrations at 3–7, 14–15, and 30 days postpartum (adjusted p < 0.001) of mothers with higher body fat percentage |
| resistin | maternal serum | Increased | Anggraini et al. [53] | Median levels: 1.41 (1.02–1.95) ng/mL in OB vs. 1.31 (0.74–1.52) ng/mL in NW (p< 0.05) |
| no correlation | Vernini et al. [40] | At 37–38 weeks of gestation, with gestational BMI assessed | ||
| maternal plasma | increase | Ozias et al. [33] | No difference between NW (7.6 ± 2.9 ng/mL) and OW/OB (7.6 ± 4.3 ng/mL); p = 0.001. Positively correlated with visceral/total fat ratio (p = 0.045) | |
| breast milk | no correlation | Andreas et al. [51] | At 1 week and 3 months postpartum, with BMI at sampling | |
| Santosa et al. [54] | At 1 month postpartum, with maternal BMI assessed pre-pregnancy, at delivery, and at 1 month postpartum |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Froń, A.; Tomecka, P.; Orczyk-Pawiłowicz, M. Impact of Maternal Overweight and Obesity on Adipokines During Pregnancy and Lactation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 9757. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199757
Froń A, Tomecka P, Orczyk-Pawiłowicz M. Impact of Maternal Overweight and Obesity on Adipokines During Pregnancy and Lactation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(19):9757. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199757
Chicago/Turabian StyleFroń, Anita, Paulina Tomecka, and Magdalena Orczyk-Pawiłowicz. 2025. "Impact of Maternal Overweight and Obesity on Adipokines During Pregnancy and Lactation" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 19: 9757. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199757
APA StyleFroń, A., Tomecka, P., & Orczyk-Pawiłowicz, M. (2025). Impact of Maternal Overweight and Obesity on Adipokines During Pregnancy and Lactation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(19), 9757. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199757






