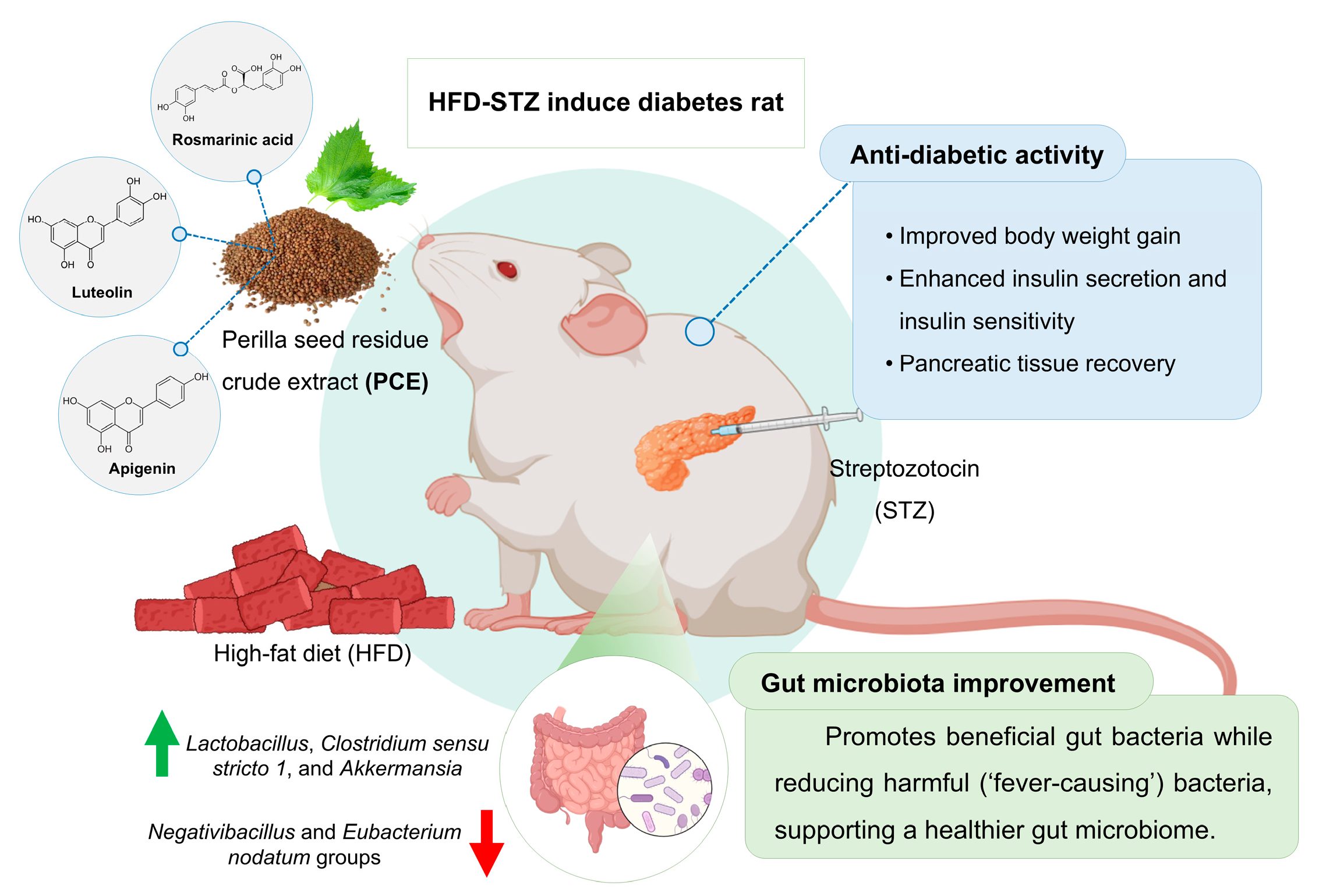
Perilla frutescens Seed Residue Extract Restores Gut Microbial Balance and Enhances Insulin Function in High-Fat Diet and Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Perilla Seed Residue Crude Extract (PCE) Characteristics
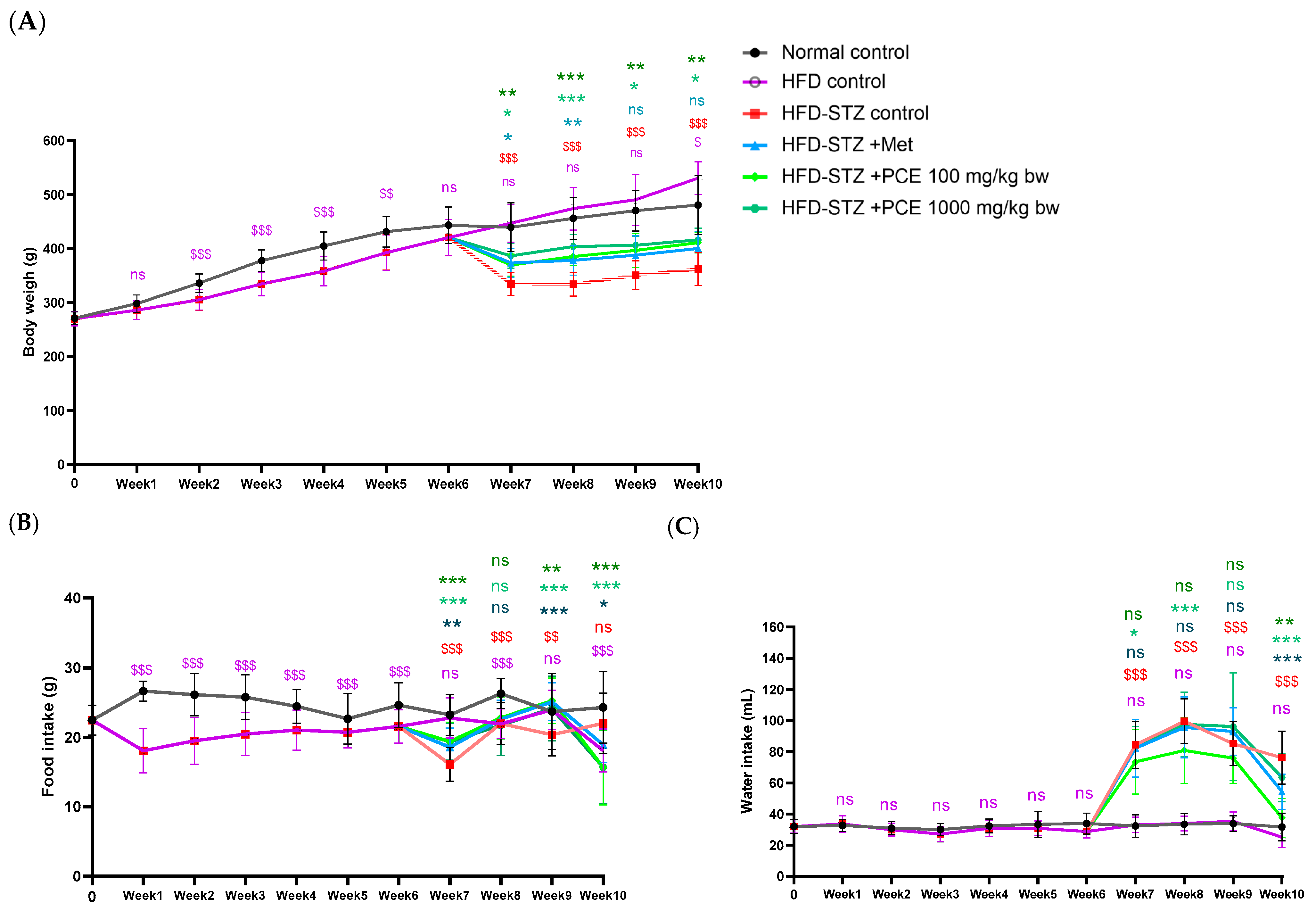
2.2. Effects of PCE on Growth Parameters in Diabetic Rats
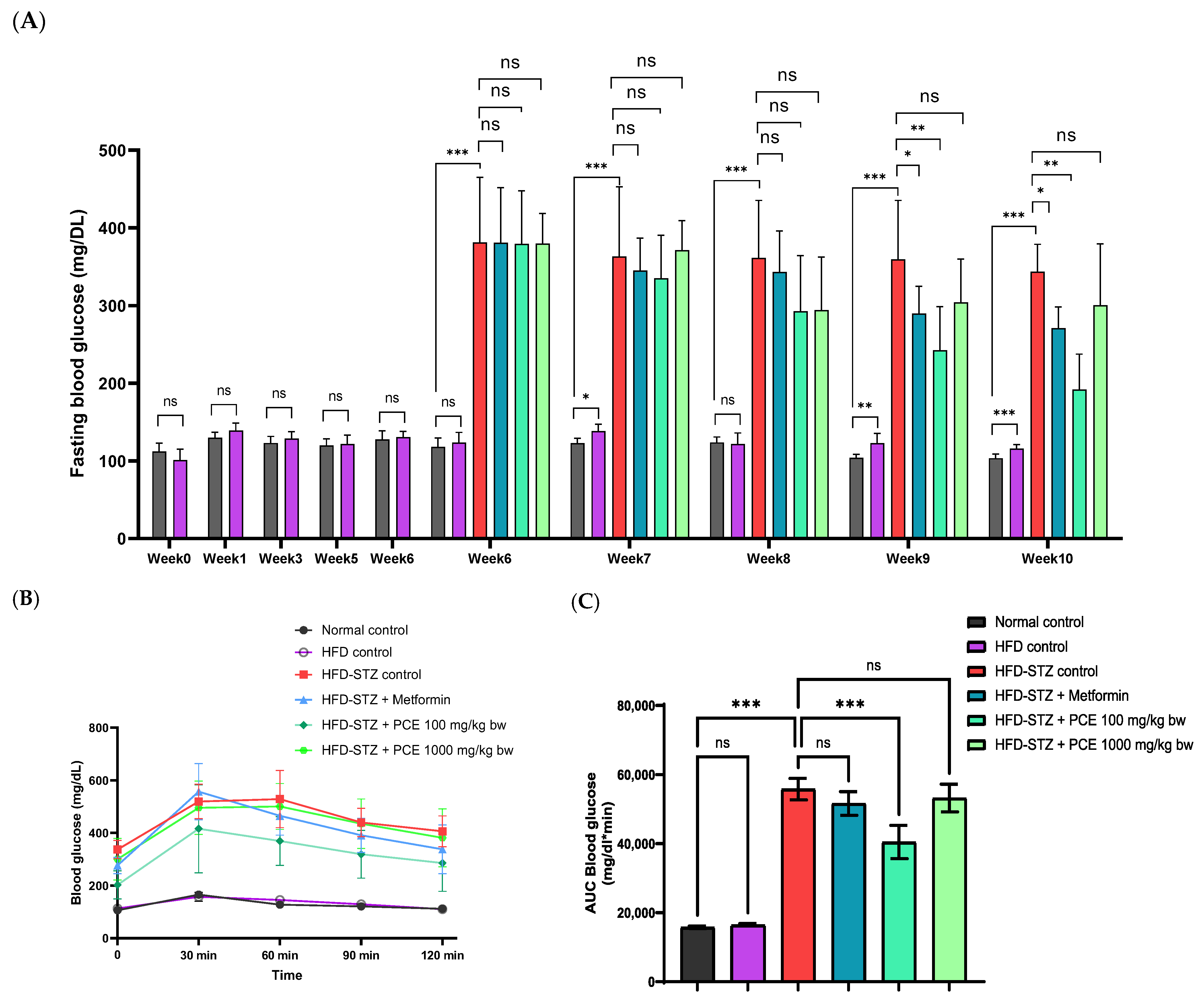
2.3. Effects of PCE on Glucose Utilization (FBG Level and OGTT)
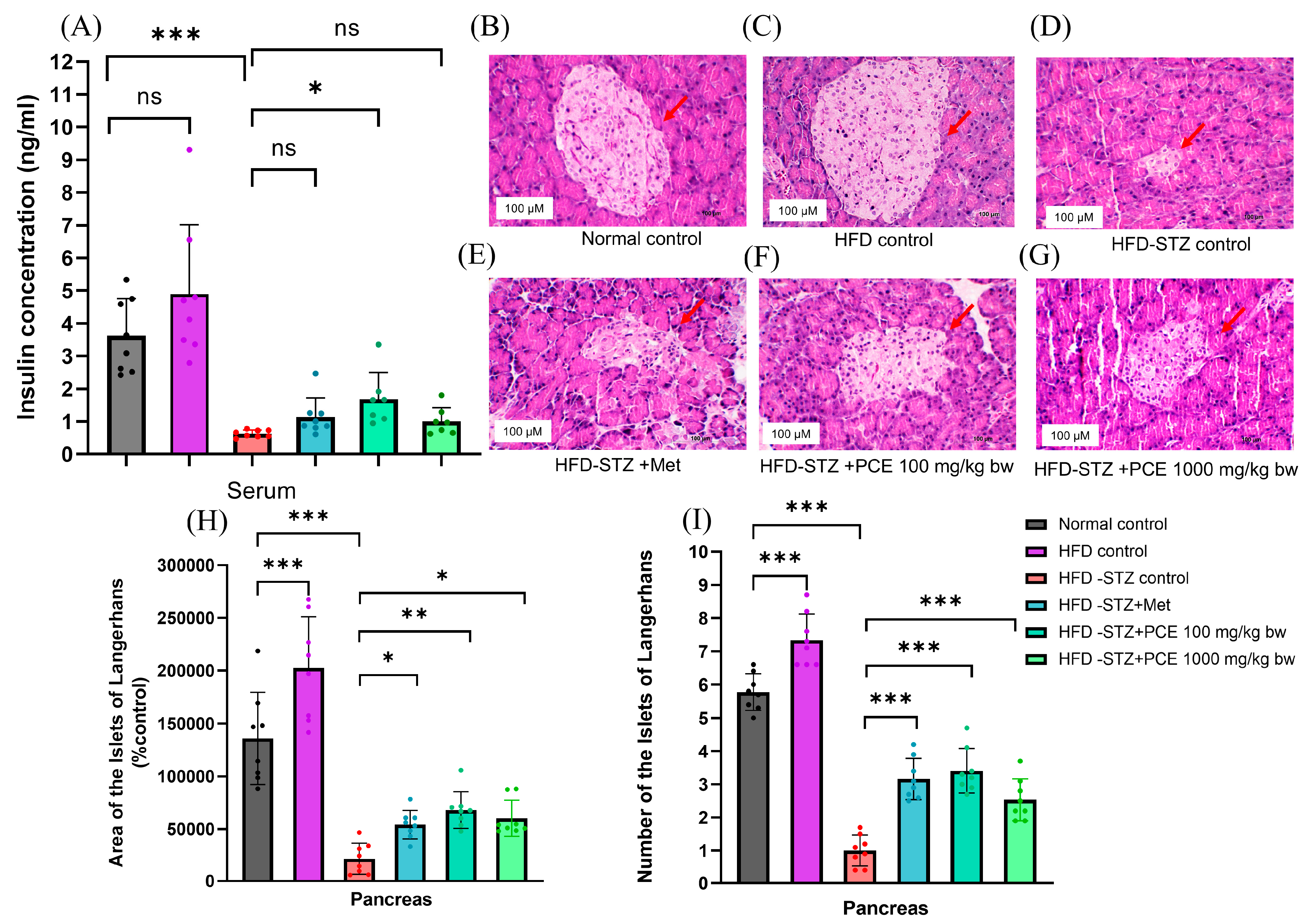
2.4. Effects of PCE on Insulin Secretion and Pathological Appearance of the Pancreas
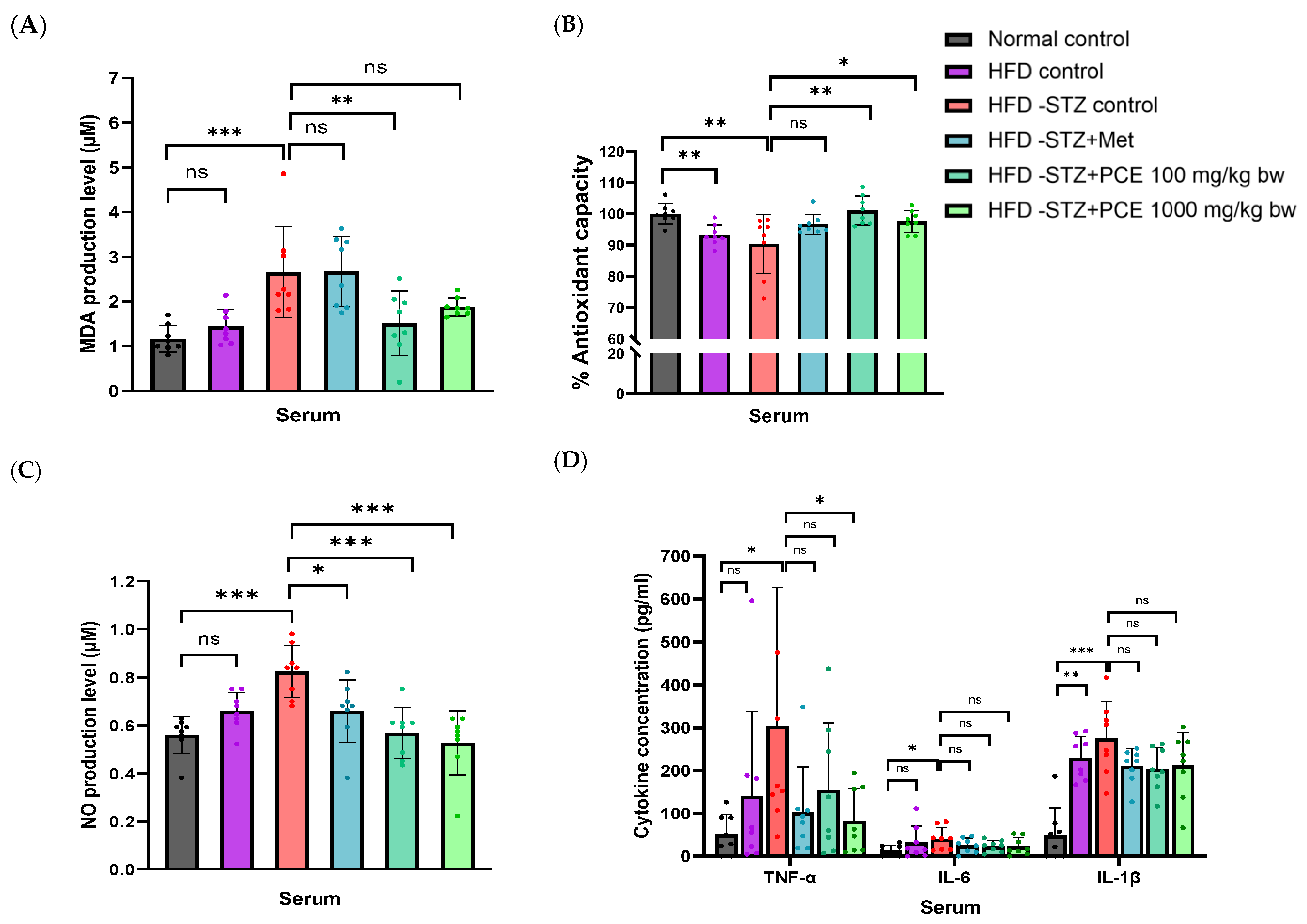
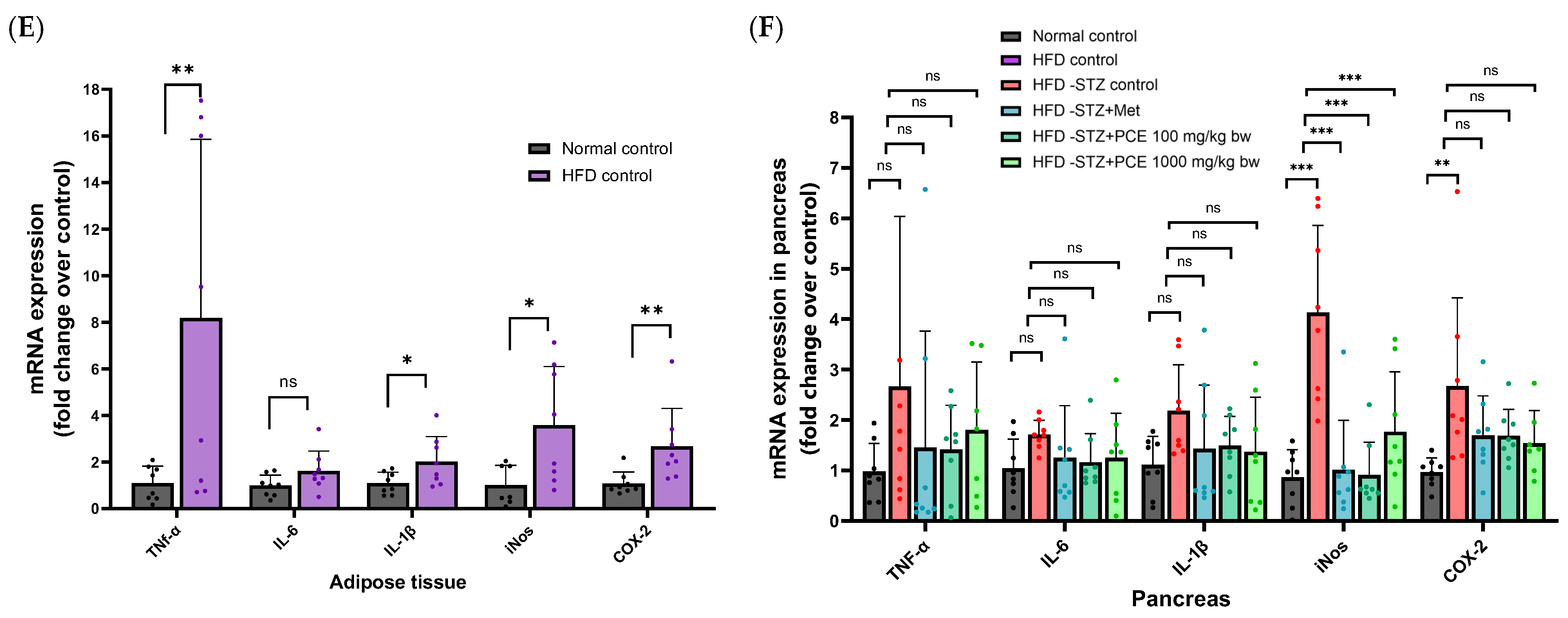
2.5. Effects of Perilla Seed Residue on Oxidative Stress and Inflammation
2.6. Effects of PCE on Serum Lipid in HFD-STZ-Induced Diabetic Rats
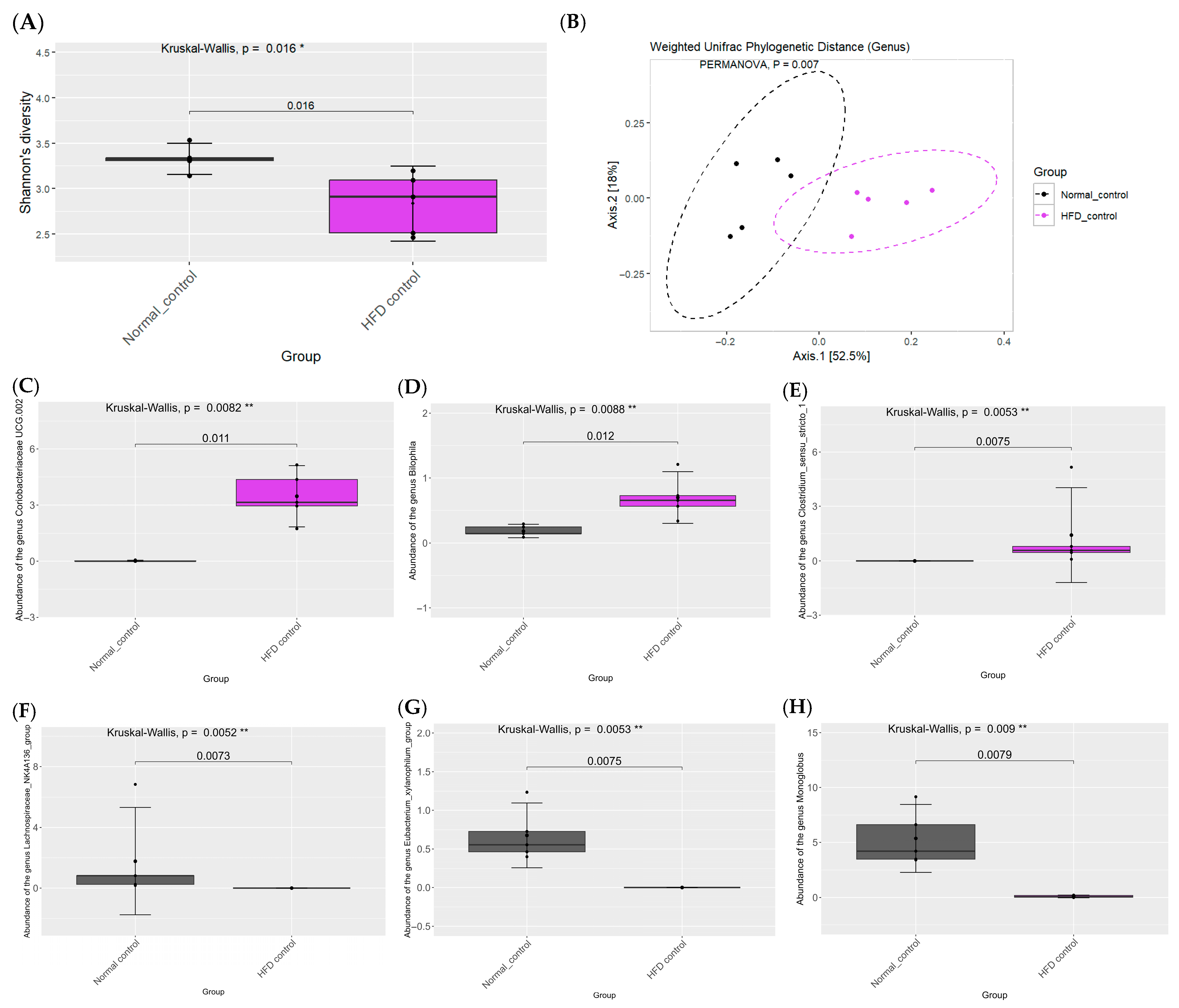
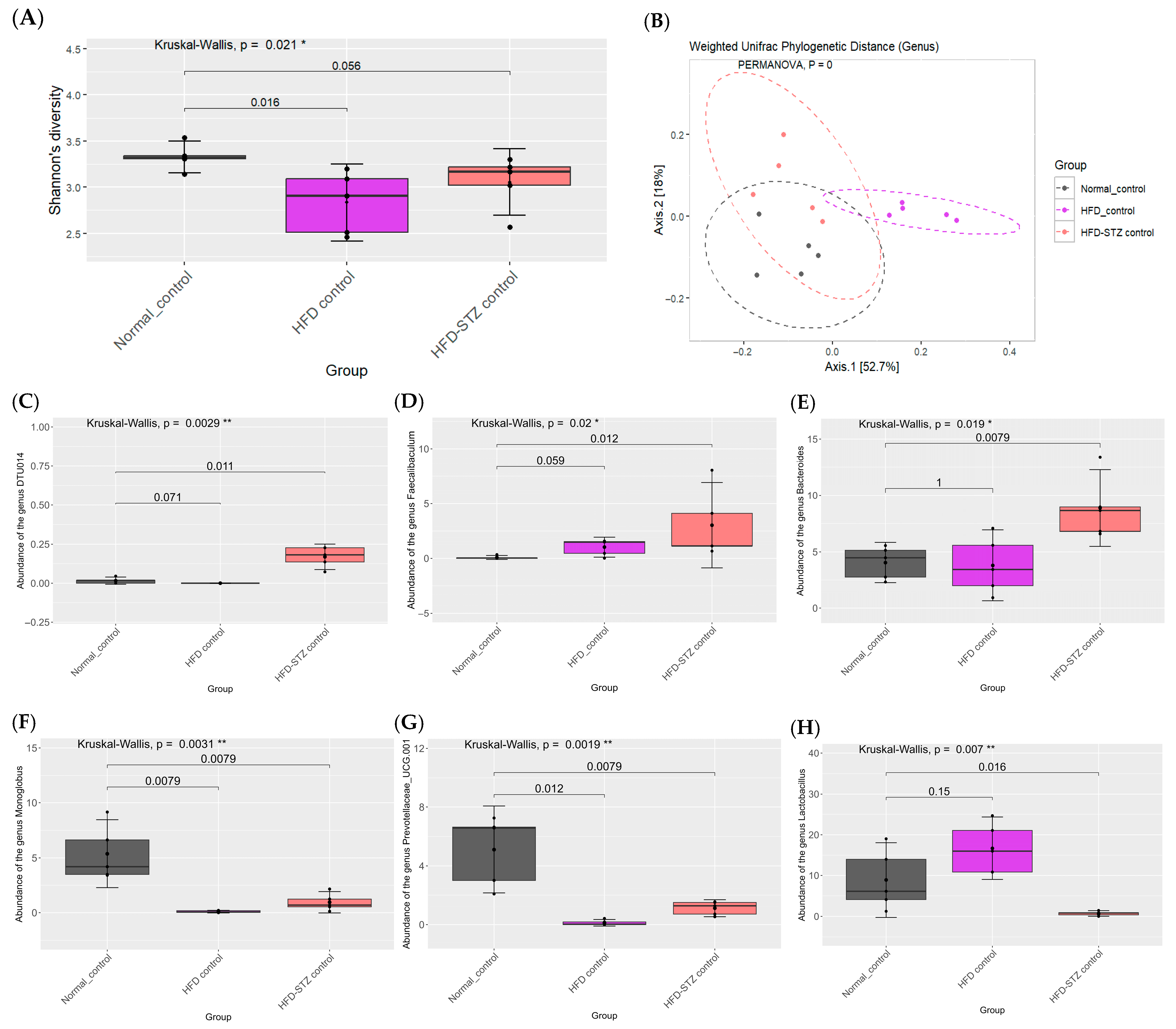
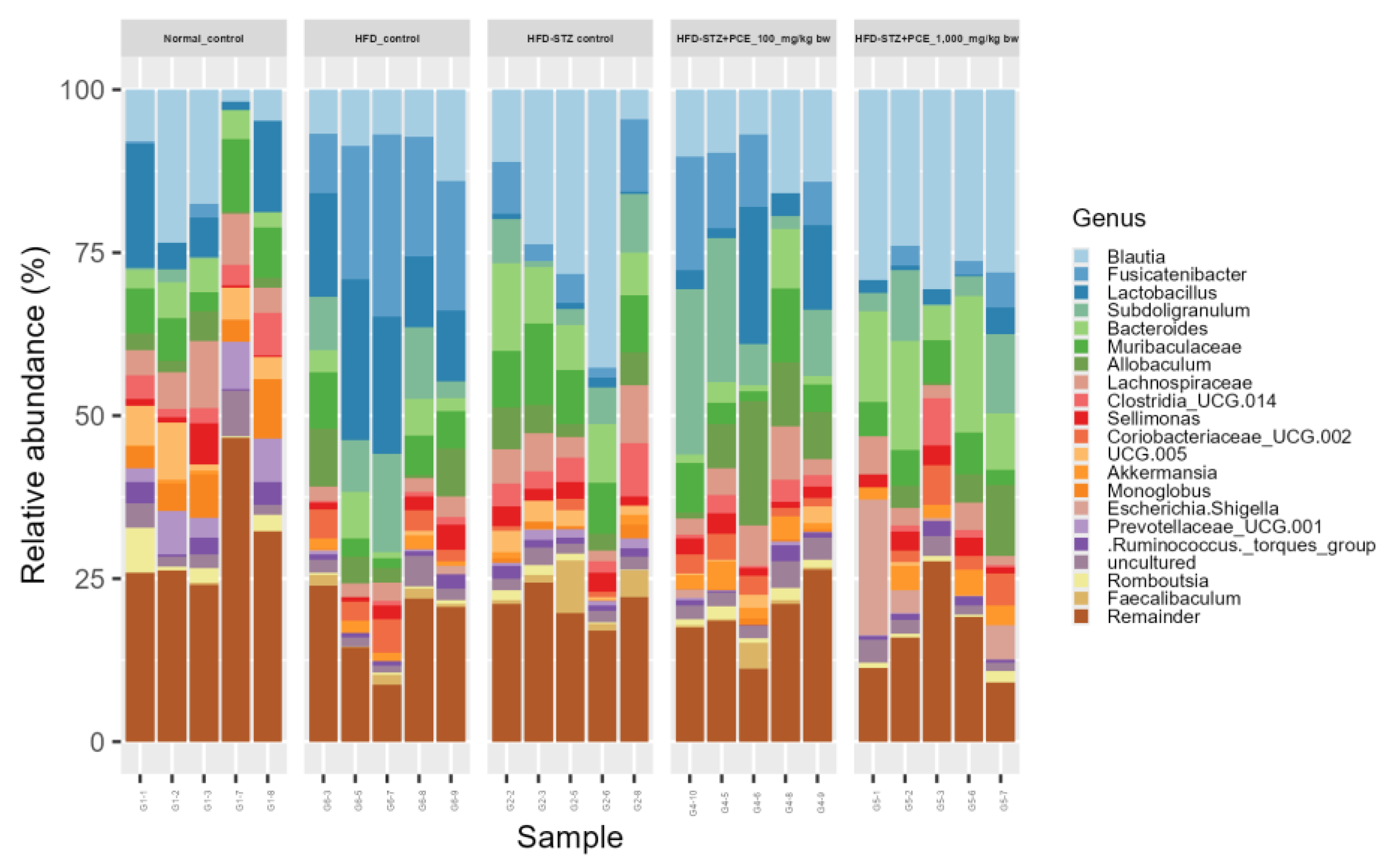
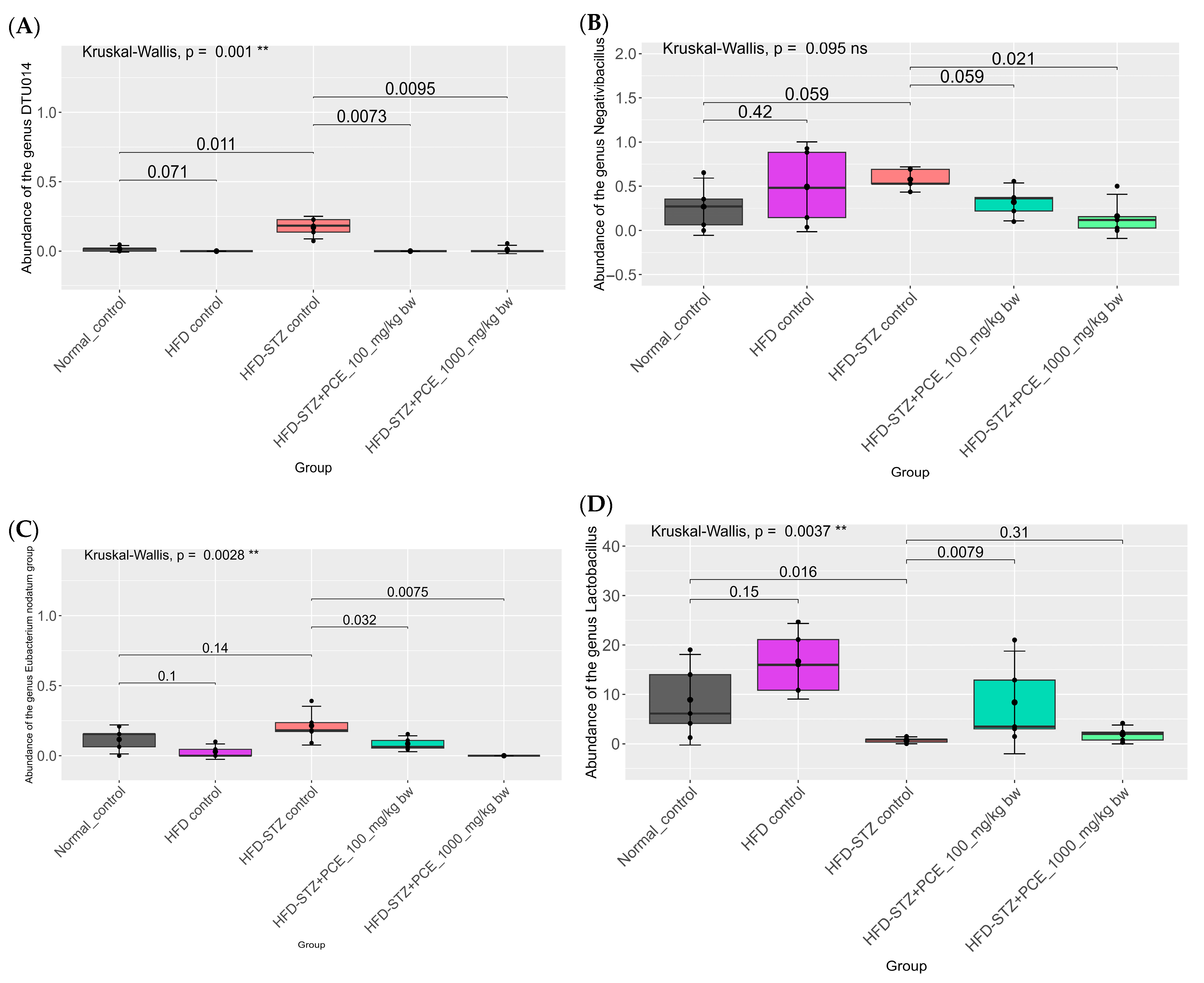
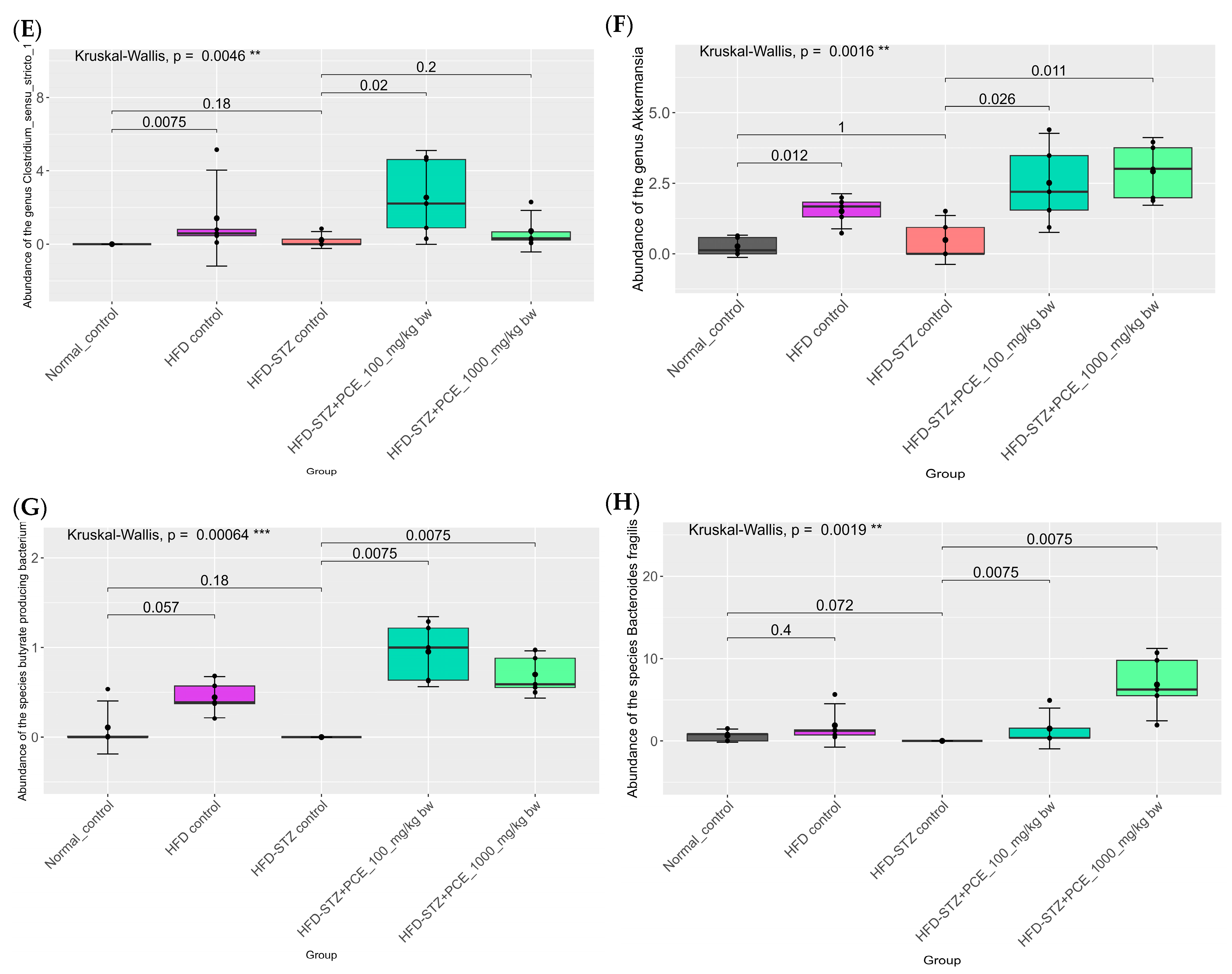
2.7. Effects of PCE on Diversity of Gut Microbiome
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Material and Extraction
4.2. Measurement of Total Phenolic Content
4.3. Measurement of Total Flavonoid Content
4.4. Determination of ABTS and DPPH by Free Radical Scavenging Assay
4.5. Ferric Reducing Antioxidant Power (FRAP) Assay
4.6. Oxygen Radical Absorbance Capacity (ORAC) Assay
4.7. Measurement of Known Active Compounds in PCE by HPLC
4.8. High-Fat Diet Production and Characterization
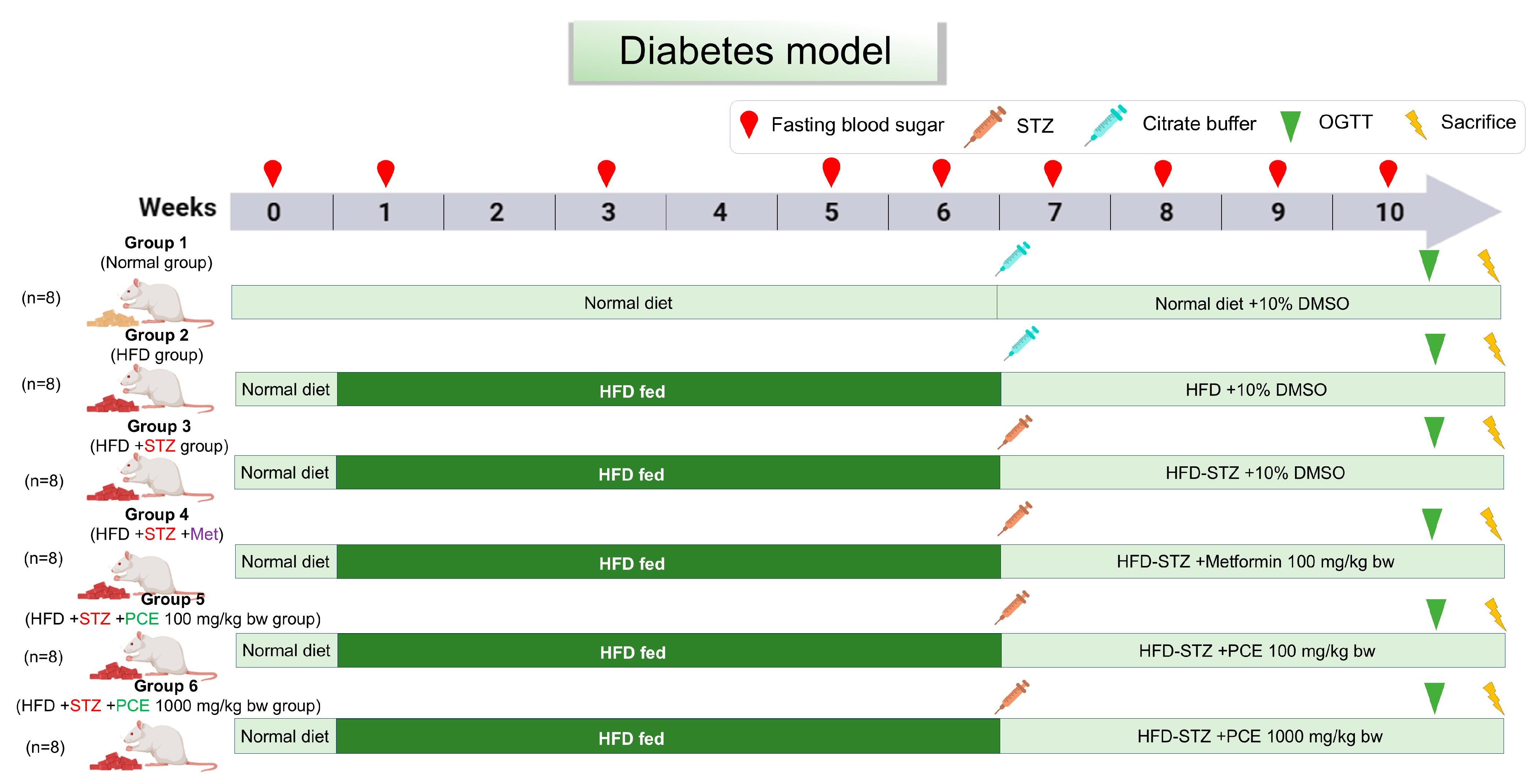
4.9. Animal and Experimental Protocol
4.10. Euthanasia and Tissue Collection
4.11. Glucose Tolerance Measurement
4.12. Fasting Serum Insulin Level
4.13. Examination of Pancreatic Beta Cell Pathology
4.14. Biochemical Analysis (Lipid Profile, MDA, Nitric Oxide)
4.15. Measurement of Inflammatory Cytokines in Serum
4.16. Determination of Level of Expression of Inflammatory Cytokines
4.17. Gut Microbiome Analysis
4.18. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| cDNA | complementary DNA |
| DNA | Deoxyribonucleic acid |
| mL | Milliliter |
| nm | Nanometer |
| PCE | Perilla seed residue crude extract |
| RNA | Ribonucleic acid |
| mg/kg bw | Milligram/kilogram of bodyweight |
| Met | Metformin |
| mg/dL | Milligrams per deciliter |
| HFD-STZ | High-fat diet induces diabetes with streptozotocin |
| STZ | Streptozotocin |
References
- Committee ADAPP. 2. Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes: Standards of Care in Diabetes—2024. Diabetes Care 2023, 47 (Suppl. 1), S20–S42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zhou, L.; Yin, W.; Hu, C.; Zuo, X. Trends of the burden of type 2 diabetes mellitus attributable to high body mass index from 1990 to 2019 in China. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1193884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Xu, Y.; Pan, X.; Xu, J.; Ding, Y.; Sun, X.; Song, X.; Ren, Y.; Shan, P. Global, regional, and national burden and trend of diabetes in 195 countries and territories: An analysis from 1990 to 2025. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 14790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Committee ADAPP. 11. Chronic kidney disease and risk management: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes—2022. Diabetes Care 2022, 45 (Suppl. 1), S175–S184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donner, D. Therapeutic Effects of Selective Androgen Receptor Modulation in the Treatment of Cardiac, Metabolic and Bone Pathologies Associated with Androgen Decline and Obesity. Ph.D. Thesis, Griffith University, Nathan, Australia, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Vilas-Boas, E.A.; Almeida, D.C.; Roma, L.P.; Ortis, F.; Carpinelli, A.R. Lipotoxicity and β-Cell Failure in Type 2 Diabetes: Oxidative Stress Linked to NADPH Oxidase and ER Stress. Cells 2021, 10, 3328. [Google Scholar]
- Eizirik, D.C.L.; Cardozo, A.K.; Cnop, M. The Role for Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Diabetes Mellitus. Endocr. Rev. 2008, 29, 42–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foretz, M.; Guigas, B.; Viollet, B. Metformin: Update on mechanisms of action and repurposing potential. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2023, 19, 460–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rena, G.; Hardie, D.G.; Pearson, E.R. The mechanisms of action of metformin. Diabetologia 2017, 60, 1577–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pernicova, I.; Korbonits, M. Metformin—Mode of action and clinical implications for diabetes and cancer. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2014, 10, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semwal, D.K.; Kumar, A.; Aswal, S.; Chauhan, A.; Semwal, R.B. Protective and therapeutic effects of natural products against diabetes mellitus via regenerating pancreatic β-cells and restoring their dysfunction. Phytother. Res. 2021, 35, 1218–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, Y.S. Plant-derived compounds targeting pancreatic beta cells for the treatment of diabetes. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 2015, 629863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickramasinghe, A.S.D.; Kalansuriya, P.; Attanayake, A.P. Herbal Medicines Targeting the Improved β-Cell Functions and β-Cell Regeneration for the Management of Diabetes Mellitus. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2021, 2021, 2920530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donath, M.Y.; Shoelson, S.E. Type 2 diabetes as an inflammatory disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 11, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregor, M.F.; Hotamisligil, G.S. Inflammatory mechanisms in obesity. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 29, 415–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Li, Y.; Cai, Z.; Li, S.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, F.; Liang, S.; Zhang, W.; Guan, Y.; Shen, D.; et al. A metagenome-wide association study of gut microbiota in type 2 diabetes. Nature 2012, 490, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurung, M.; Li, Z.; You, H.; Rodrigues, R.; Jump, D.B.; Morgun, A.; Shulzhenko, N. Role of gut microbiota in type 2 diabetes pathophysiology. EBioMedicine 2020, 51, 102590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cani, P.D.; Van Hul, M. Gut microbiota in overweight and obesity: Crosstalk with adipose tissue. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024, 21, 164–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karlsson, F.H.; Tremaroli, V.; Nookaew, I.; Bergström, G.; Behre, C.J.; Fagerberg, B.; Nielsen, J.; Bäckhed, F. Gut metagenome in European women with normal, impaired and diabetic glucose control. Nature 2013, 498, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Chatelier, E.; Nielsen, T.; Qin, J.; Prifti, E.; Hildebrand, F.; Falony, G.; Arumugam, M.; Batto, J.-M.; Kennedy, S.; Leonard, P.; et al. Richness of human gut microbiome correlates with metabolic markers. Nature 2013, 500, 541–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilg, H.; Moschen, A.R. Microbiota and diabetes: An evolving relationship. Gut 2014, 63, 1513–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, H.; Lee, J.-H.; Lloyd, J.; Walter, P.; Rane, S.G. Beneficial metabolic effects of a probiotic via butyrate-induced GLP-1 hormone secretion. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 25088–25097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canfora, E.E.; Meex, R.C.; Venema, K.; Blaak, E.E. Gut microbial metabolites in obesity, NAFLD and T2DM. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2019, 15, 261–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Zhang, F.; Ding, X.; Wu, G.; Lam, Y.Y.; Wang, X.; Fu, H.; Xue, X.; Lu, C.; Ma, J.; et al. Gut bacteria selectively promoted by dietary fibers alleviate type 2 diabetes. Science 2018, 359, 1151–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, A.; De Vadder, F.; Kovatcheva-Datchary, P.; Bäckhed, F. From dietary fiber to host physiology: Short-chain fatty acids as key bacterial metabolites. Cell 2016, 165, 1332–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pannalue JCaA. Ngamon, the Amazing Omega from the Top of the Mountain: Highland Research and Development Institute. (Public Organization; 2559). Available online: https://www.hrdi.or.th/Articles/Detail/9 (accessed on 3 July 2019).
- Hou, T.; Netala, V.R.; Zhang, H.; Xing, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, Z. Perilla frutescens: A Rich Source of Pharmacological Active Compounds. Molecules 2022, 27, 3578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, G.; Robu, S.; Flutur, M.-M.; Cioanca, O.; Vasilache, I.-A.; Adam, A.-M.; Mircea, C.; Nechita, A.; Harabor, V.; Harabor, A.; et al. Applications of Perilla frutescens Extracts in Clinical Practice. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chantana, W.; Hu, R.; Buddhasiri, S.; Thiennimitr, P.; Tantipaiboonwong, P.; Chewonarin, T. The Extract of Perilla frutescens Seed Residue Attenuated the Progression of Aberrant Crypt Foci in Rat Colon by Reducing Inflammatory Processes and Altered Gut Microbiota. Foods 2023, 12, 988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasileva, L.V.; Savova, M.S.; Tews, D.; Wabitsch, M.; Georgiev, M.I. Rosmarinic acid attenuates obesity and obesity-related inflammation in human adipocytes. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2021, 149, 112002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charalabopoulos, A.; Davakis, S.; Lambropoulou, M.; Papalois, A.; Simopoulos, C.; Tsaroucha, A. Apigenin Exerts Anti-inflammatory Effects in an Experimental Model of Acute Pancreatitis by Down-regulating TNF-α. In Vivo 2019, 33, 1133–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ju, W.; Wang, X.; Shi, H.; Chen, W.; Belinsky, S.A.; Lin, Y. A critical role of luteolin-induced reactive oxygen species in blockage of tumor necrosis factor-activated nuclear factor-κB pathway and sensitization of apoptosis in lung cancer cells. Mol. Pharmacol. 2007, 71, 1381–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Z.; Li, S.; Lin, Z.; Yang, R.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, J.; Yang, S.; Chen, A. Identification and quantitation of phenolic compounds from the seed and pomace of perilla frutescens using HPLC/PDA and HPLC-ESI/QTOF/MS/MS. Phytochem. Anal. 2014, 25, 508–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, G.Y.; Han, Y.S.; Sim, K.H.; Kim, M.H. Phenolic compounds, antioxidant capacity, and α-amylase and α-glucosidase inhibitory activity of ethanol extracts of perilla seed meal. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 11, 4596–4606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Den Hartogh, D.J.; Vlavcheski, F.; Tsiani, E. Muscle Cell Insulin Resistance Is Attenuated by Rosmarinic Acid: Elucidating the Mechanisms Involved. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, A.K.; Dutta, P.P.; Yakin, J.; Borah, J.C.; Talukdar, N.C. A Review on the Mode of Action of the Gluconeogeic Enzyme, Phosphoenolpyruvate Carboxykinase (PEPCK) and Its Regulation of Diabetes Induced Hyperglycaemia with Special Emphasis on Plant Derived PEPCK Modulators. Ann. Multidiscip. Res. Innov. Technol. 2022, 1, 23–34. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.-H.; Hong, Y.; Zhang, T.-Y.; Chen, Y.-X.; Wei, Z.-J.; Gao, C.-Y. Rosmarinic acid exerts anti-inflammatory effect and relieves oxidative stress via Nrf2 activation in carbon tetrachloride-induced liver damage. Food Nutr. Res. 2022, 66, 10-29219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Wu, J.; Xu, S.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, X.-J. Rosmarinic acid alleviates intestinal inflammatory damage and inhibits endoplasmic reticulum stress and smooth muscle contraction abnormalities in intestinal tissues by regulating gut microbiota. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e01914-23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Song, W.; Li, D.; Jin, X. Apigenin in the regulation of cholesterol metabolism and protection of blood vessels. Exp. Ther. Med. 2017, 13, 1719–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Firrman, J.; Zhang, L.; Arango-Argoty, G.; Tomasula, P.; Liu, L.; Xiao, W.; Yam, K. Apigenin impacts the growth of the gut microbiota and alters the gene expression of Enterococcus. Molecules 2017, 22, 1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dissook, S.; Umsumarng, S.; Mapoung, S.; Semmarath, W.; Arjsri, P.; Srisawad, K.; Dejkriengkraikul, P. Luteolin-rich fraction from Perilla frutescens seed meal inhibits spike glycoprotein S1 of SARS-CoV-2-induced NLRP3 inflammasome lung cell inflammation via regulation of JAK1/STAT3 pathway: A potential anti-inflammatory compound against inflammation-induced long-COVID. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 1072056. [Google Scholar]
- Ntalouka, F.; Tsirivakou, A. Luteolin: A promising natural agent in management of pain in chronic conditions. Front. Pain. Res. 2023, 4, 1114428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, E.-Y.; Jung, U.J.; Park, T.; Yun, J.W.; Choi, M.-S. Luteolin Attenuates Hepatic Steatosis and Insulin Resistance Through the Interplay Between the Liver and Adipose Tissue in Mice with Diet-Induced Obesity. Diabetes 2014, 64, 1658–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshmukh, H.; Mendóza, R.; Santos, J.M.; Sivaprakasam, S.; Elmassry, M.M.; Miranda, J.M.; Phamet, P.Q.; Driver, Z.; Bender, M.; Dufour, J.M.; et al. Effect of Peanut Shell Extract and Luteolin on Gut Microbiota and High-Fat Diet-Induced Sequelae of the Inflammatory Continuum in a Metabolic Syndrome-like Murine Model. Nutrients 2025, 17, 2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, V.A. Defining and Characterizing the Progression of Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2009, 32 (Suppl. 2), S151–S156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Li, J.; Haller, M.J.; Schatz, D.A.; Rong, L. Modeling the progression of Type 2 diabetes with underlying obesity. PLOS Comput. Biol. 2023, 19, e1010914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.; Gholipourmalekabadi, M.; Shafikhani, S.H. Animal models for type 1 and type 2 diabetes: Advantages and limitations. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1359685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skovsø, S. Modeling type 2 diabetes in rats using high fat diet and streptozotocin. J. Diabetes Investig. 2014, 5, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakuludomkan, W.; Yeewa, R.; Subhawa, S.; Khanaree, C.; Bonness, A.I.; Chewonarin, T. Effects of Fermented Houttuynia cordata Thunb. on Diabetic Rats Induced by a High-Fat Diet with Streptozotocin and on Insulin Resistance in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes. J. Nutr. Metab. 2021, 2021, 6936025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, I.J. Diabetic dyslipidemia: Causes and consequences. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 86, 965–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haran, J.P.; McCormick, B.A. Aging, frailty, and the microbiome—How dysbiosis influences human aging and disease. Gastroenterology 2021, 160, 507–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Sun, B.; Yu, D.; Zhu, C. Gut microbiota: An important player in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 834485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iatcu, O.C.; Hamamah, S.; Covasa, M. Harnessing Prebiotics to Improve Type 2 Diabetes Outcomes. Nutrients 2024, 16, 3447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, E.A.; Velazquez, K.T.; Herbert, K.M. Influence of high-fat diet on gut microbiota: A driving force for chronic disease risk. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care. 2015, 18, 515–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Chen, Q.; Wu, H.; Liu, H.; Jing, C.; Gong, A.; Zhang, Y. Exploring a novel therapeutic strategy: The interplay between gut microbiota and high-fat diet in the pathogenesis of metabolic disorders. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1291853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, K.S.; Bourwis, N.; Dolan, S.; Lang, S.; Spencer, J.; Craft, J.A. Characterisation of gut microbiota of obesity and type 2 diabetes in a rodent model. Biosci. Microbiota Food Health 2021, 40, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.; Xu, L.; Nie, Y.; Liu, L.; Liu, Z.; Yang, Y. Murine gut microbial interactions exert antihyperglycemic effects. ISME J. 2025, 19, wraf028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Muthurayar, T.; Karthika, S.; Gayathri, S.; Varalakshmi, P.; Ashokkumar, B. Anti-Diabetic Potentials of Lactobacillus Strains by Modulating Gut Microbiota Structure and β-Cells Regeneration in the Pancreatic Islets of Alloxan-Induced Diabetic Rats. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins 2025, 17, 1096–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sáez-Lara, M.J.; Robles-Sanchez, C.; Ruiz-Ojeda, F.J.; Plaza-Diaz, J.; Gil, A. Effects of probiotics and synbiotics on obesity, insulin resistance syndrome, type 2 diabetes and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A review of human clinical trials. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagannathan, R.; Neves, J.S.; Dorcely, B.; Chung, S.T.; Tamura, K.; Rhee, M.; Bergman, M. The Oral Glucose Tolerance Test: 100 Years Later. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2020, 13, 3787–3805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Cui, J.; Li, S.; Huang, B. Causal Relationships Between Gut Microbiota, Metabolites, and Diabetic Nephropathy: Insights from a Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Analysis. Int. J. Nephrol. Renov. Dis. 2024, 17, 319–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Que, Y.; Cao, M.; He, J.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, Q.; Yan, C.; Lin, A.; Lin, Y.; Wu, Z.; Zhu, D.; et al. Gut bacterial characteristics of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and the application potential. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 722206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Jia, X.; Cong, B. Advances in the mechanism of metformin with wide-ranging effects on regulation of the intestinal microbiota. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1396031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perman, E.; Schnürer, A.; Björn, A.; Moestedt, J. Serial anaerobic digestion improves protein degradation and biogas production from mixed food waste. Biomass Bioenergy 2022, 161, 106478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.-Q.; Ye, S.-N.; Huang, Y.-H.; Ou, Y.-W.; Chen, K.-Y.; Chen, J.-S.; Tang, S.B. Gut microbiota induced abnormal amino acids and their correlation with diabetic retinopathy. Int. J. Ophthalmol. 2024, 17, 883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Zhang, Y. Mechanism and application of Lactobacillus in type 2 diabetes-associated periodontitis. Front. Public Health 2023, 11, 1248518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, R.; Chen, R. Exploring the causal connection: Insights into diabetic nephropathy and gut microbiota from whole-genome sequencing databases. Ren. Fail. 2024, 46, 2385065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayman, E.I.; Schwartz, B.A.; Polmann, M.; Gumabong, A.C.; Nieuwdorp, M.; Cickovski, T.; Mathee, K. Differences in gut microbiota between Dutch and South-Asian Surinamese: Potential implications for type 2 diabetes mellitus. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 4585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yang, G.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, Z.; Jiang, X.; Xin, Y. Function of Akkermansia muciniphila in type 2 diabetes and related diseases. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1172400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darra, A.; Singh, V.; Jena, A.; Popli, P.; Nada, R.; Gupta, P.; Bhadada, S.K.; Singh, A.K.; Sharma, V.; Bhattacharya, A.; et al. Hyperglycemia is associated with duodenal dysbiosis and altered duodenal microenvironment. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 11038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, T.; Tremaroli, V. Therapeutic potential of butyrate for treatment of type 2 diabetes. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 761834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.; Li, D.; Feng, N.; Shamoon, M.; Sun, Z.; Ding, L.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W.; Sun, J.; Chen, Y.Q. Anti-diabetic effects of Clostridium butyricum CGMCC0313. 1 through promoting the growth of gut butyrate-producing bacteria in type 2 diabetic mice. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 7046. [Google Scholar]
- Tantipaiboonwong, P.; Pintha, K.; Chaiwangyen, W.; Chewonarin, T.; Pangjit, K.; Chumphukam, O.; Kangwan, N.; Suttajit, M. Anti-hyperglycaemic and anti-hyperlipidaemic effects of black and red rice in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. ScienceAsia 2017, 43, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand-Williams, W.; Cuvelier, M.-E.; Berset, C. Use of a free radical method to evaluate antioxidant activity. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 1995, 28, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benzie, I.F.; Strain, J.J. The ferric reducing ability of plasma (FRAP) as a measure of “antioxidant power”: The FRAP assay. Anal. Biochem. 1996, 239, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dávalos, A.; Gómez-Cordovés, C.; Bartolomé, B. Extending applicability of the oxygen radical absorbance capacity (ORAC−fluorescein) assay. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pintha, K.; Yodkeeree, S.; Pitchakarn, P.; Limtrakul, P. Anti-invasive activity against cancer cells of phytochemicals in red jasmine rice (Oryza sativa L.). Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2014, 15, 4601–4607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaiyasut, C.; Kusirisin, W.; Lailerd, N.; Lerttrakarnnon, P.; Suttajit, M.; Srichairatanakool, S. Effects of phenolic compounds of fermented Thai indigenous plants on oxidative stress in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2011, 2011, 749307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abd El-Shakour, A.; El-Ebiarie, A.S.; Ibrahim, Y.H.; Abdel Moneim, A.; El-Mekawy, A.M. Effect of benzene on oxidative stress and the functions of liver and kidney in rats. J. Environ. Occup. Health 2015, 4, 34–39. [Google Scholar]

| Compound | Total Amounts |
|---|---|
| Rosmarinic acid (mg/g extract) | 25.97 ± 0.24 |
| Luteolin (mg/g extract) | 9.01 ± 1.19 |
| Apigenin (mg/g extract) | 3.25 ± 0.78 |
| Assay Methods (Unit of Antioxidant Equivalent) | Antioxidant Capacity |
|---|---|
| DPPH (mg ascorbic acid equivalent/g of PCE) | 94.61 ± 2.87 |
| ABTS (mg Trolox equivalent/g of PCE) | 94.91 ± 5.09 |
| FRAP (mg Trolox equivalent/g of PCE) | 107.99 ± 9.40 |
| ORAC (mg Trolox equivalent/g of PCE) | 668.51 ± 9.85 |
| Metabolic Parameter | Total Triglycerides (mg/dL) | Total Cholesterol (mg/dL) | LDL-C (mg/dL) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Normal control | 80.25 ± 25.65 | 66.38 ± 13.16 | 7.23 ± 1.94 |
| HFD control | 66.38 ± 22.67 | 70.50 ± 8.85 | 11.57 ± 2.90 |
| HFD-STZ control | 193.13 ± 66.21 ** | 99.63 ± 16.14 *** | 14.00 ± 4.47 ** |
| HFD-STZ + Metformin (100 mg/kg bw) | 202.88 ± 84.86 | 99.00 ± 19.13 | 13.96 ± 2.94 |
| HFD-STZ + PCE 100 mg/kg bw | 76.62 ± 27.47 aa | 82.12 ± 14.92 | 14.97 ± 5.22 |
| HFD-STZ + PCE 1000 mg/kg bw | 137.88 ± 66.75 | 99.38 ± 15.52 | 14.33 ± 2.22 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Deethai, P.; Siriwathanakul, C.; Pitchakarn, P.; Imsumran, A.; Wongnoppavich, A.; Dissook, S.; Chewonarin, T. Perilla frutescens Seed Residue Extract Restores Gut Microbial Balance and Enhances Insulin Function in High-Fat Diet and Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8176. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178176
Deethai P, Siriwathanakul C, Pitchakarn P, Imsumran A, Wongnoppavich A, Dissook S, Chewonarin T. Perilla frutescens Seed Residue Extract Restores Gut Microbial Balance and Enhances Insulin Function in High-Fat Diet and Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(17):8176. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178176
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeethai, Pattharaphong, Chatsiri Siriwathanakul, Pornsiri Pitchakarn, Arisa Imsumran, Ariyaphong Wongnoppavich, Sivamoke Dissook, and Teera Chewonarin. 2025. "Perilla frutescens Seed Residue Extract Restores Gut Microbial Balance and Enhances Insulin Function in High-Fat Diet and Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 17: 8176. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178176
APA StyleDeethai, P., Siriwathanakul, C., Pitchakarn, P., Imsumran, A., Wongnoppavich, A., Dissook, S., & Chewonarin, T. (2025). Perilla frutescens Seed Residue Extract Restores Gut Microbial Balance and Enhances Insulin Function in High-Fat Diet and Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(17), 8176. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178176







_Bonness.jpeg)


