Aquaporin-4 in Stroke and Brain Edema—Friend or Foe?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. AQP4 in Healthy Brain Water Homeostasis
3. Biphasic Roles of AQP4 in Cytotoxic vs. Vasogenic Edema
4. Evidence from Animal Models of Stroke and Edema
5. Molecular Regulation of AQP4: Post-Transcriptional and Signaling Pathway Control
6. Therapeutic Targeting of AQP4: Opportunities and Hurdles
7. Therapeutic Challenges and Opportunities Targeting AQP4
8. Future Directions
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO EMRO|Stroke, Cerebrovascular Accident|Health Topics. Available online: http://www.emro.who.int/health-topics/stroke-cerebrovascular-accident/index.html (accessed on 25 May 2025).
- Cheng, Y.; Lin, Y.; Shi, H.; Cheng, M.; Zhang, B.; Liu, X.; Shi, C.; Wang, Y.; Xia, C.; Xie, W. Projections of the Stroke Burden at the Global, Regional, and National Levels up to 2050 Based on the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2024, 13, e036142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Y.; Zhou, C.; Piao, Z.; Yuan, H.; Jiang, H.; Wei, H.; Zhou, Y.; Nan, G.; Ji, X. Cerebral Edema after Ischemic Stroke: Pathophysiology and Underlying Mechanisms. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 988283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeHoff, G.; Lau, W. Medical Management of Cerebral Edema in Large Hemispheric Infarcts. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 857640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadopoulos, M.C.; Verkman, A.S. Aquaporin-4 and Brain Edema. Pediatr. Nephrol. Berl. Ger. 2007, 22, 778–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadopoulos, M.C.; Manley, G.T.; Krishna, S.; Verkman, A.S. Aquaporin-4 Facilitates Reabsorption of Excess Fluid in Vasogenic Brain Edema. FASEB J. 2004, 18, 1291–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manley, G.T.; Fujimura, M.; Ma, T.; Noshita, N.; Filiz, F.; Bollen, A.W.; Chan, P.; Verkman, A.S. Aquaporin-4 Deletion in Mice Reduces Brain Edema after Acute Water Intoxication and Ischemic Stroke. Nat. Med. 2000, 6, 159–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagelhus, E.A.; Ottersen, O.P. Physiological Roles of Aquaporin-4 in Brain. Physiol. Rev. 2013, 93, 1543–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amiry-Moghaddam, M.; Ottersen, O.P. The Molecular Basis of Water Transport in the Brain. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2003, 4, 991–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, A.; Moritz, T.J.; Ratelade, J.; Verkman, A.S. Super-Resolution Imaging of Aquaporin-4 Orthogonal Arrays of Particles in Cell Membranes. J. Cell Sci. 2012, 125, 4405–4412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iliff, J.J.; Wang, M.; Liao, Y.; Plogg, B.A.; Peng, W.; Gundersen, G.A.; Benveniste, H.; Vates, G.E.; Deane, R.; Goldman, S.A.; et al. A Paravascular Pathway Facilitates CSF Flow Through the Brain Parenchyma and the Clearance of Interstitial Solutes, Including Amyloid β. Sci. Transl. Med. 2012, 4, ra111–ra147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mestre, H.; Mori, Y.; Nedergaard, M. The Brain’s Glymphatic System: Current Controversies. Trends Neurosci. 2020, 43, 458–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasmussen, M.K.; Mestre, H.; Nedergaard, M. The Glymphatic Pathway in Neurological Disorders. Lancet Neurol. 2018, 17, 1016–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, B.; Zador, Z.; Verkman, A.S. Glial Cell Aquaporin-4 Overexpression in Transgenic Mice Accelerates Cytotoxic Brain Swelling. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 15280–15286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, X.-N.; Xie, L.-L.; Liang, R.; Sun, X.-L.; Fan, Y.; Hu, G. AQP4 Knockout Aggravates Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury in Mice. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2012, 18, 388–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bloch, O.; Papadopoulos, M.C.; Manley, G.T.; Verkman, A.S. Aquaporin-4 Gene Deletion in Mice Increases Focal Edema Associated with Staphylococcal Brain Abscess. J. Neurochem. 2005, 95, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, M.d.C.; Hirt, L.; Bogousslavsky, J.; Regli, L.; Badaut, J. Time Course of Aquaporin Expression after Transient Focal Cerebral Ischemia in Mice. J. Neurosci. Res. 2006, 83, 1231–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filippidis, A.S.; Carozza, R.B.; Rekate, H.L. Aquaporins in Brain Edema and Neuropathological Conditions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 18, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.; Lin, L.; Yin, L.; Hao, X.; Tian, J.; Zhang, X.; Ren, Y.; Li, C.; Yang, Y. Acutely Inhibiting AQP4 With TGN-020 Improves Functional Outcome by Attenuating Edema and Peri-Infarct Astrogliosis After Cerebral Ischemia. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 870029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, A.-H.; Tai, S.-H.; Huang, S.-Y.; Chang, L.-D.; Chen, L.-Y.; Chen, Y.-N.; Hsu, H.-H.; Lee, E.-J. Melatonin Improves Vasogenic Edema via Inhibition to Water Channel Aquaporin-4 (AQP4) and Metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) Following Permanent Focal Cerebral Ischemia. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Igarashi, H.; Huber, V.J.; Tsujita, M.; Nakada, T. Pretreatment with a Novel Aquaporin 4 Inhibitor, TGN-020, Significantly Reduces Ischemic Cerebral Edema. Neurol. Sci. 2011, 32, 113–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bojarskaite, L.; Nafari, S.; Ravnanger, A.K.; Frey, M.M.; Skauli, N.; Åbjørsbråten, K.S.; Roth, L.C.; Amiry-Moghaddam, M.; Nagelhus, E.A.; Ottersen, O.P.; et al. Role of Aquaporin-4 Polarization in Extracellular Solute Clearance. Fluids Barriers CNS 2024, 21, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haj-Yasein, N.N.; Vindedal, G.F.; Eilert-Olsen, M.; Gundersen, G.A.; Skare, Ø.; Laake, P.; Klungland, A.; Thorén, A.E.; Burkhardt, J.M.; Ottersen, O.P.; et al. Glial-Conditional Deletion of Aquaporin-4 (Aqp4) Reduces Blood-Brain Water Uptake and Confers Barrier Function on Perivascular Astrocyte Endfeet. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 17815–17820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnan, K.; Campos, P.B.; Nguyen, T.N.; Tan, C.W.; Chan, S.L.; Appleton, J.P.; Law, Z.; Hollingworth, M.; Kirkman, M.A.; England, T.J.; et al. Cerebral Edema in Intracerebral Hemorrhage: Pathogenesis, Natural History, and Potential Treatments from Translation to Clinical Trials. Front. Stroke 2023, 2, 1256664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, H.; Tang, Y.; Dong, Q. Protection of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor to Brain Edema Following Intracerebral Hemorrhage and Its Involved Mechanisms: Effect of Aquaporin-4. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e66051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, H.; Ding, H.; Tang, Y.; Dong, Q. Erythropoietin Protects against Hemorrhagic Blood–Brain Barrier Disruption through the Effects of Aquaporin-4. Lab. Investig. 2014, 94, 1042–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, E.; Sun, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, A.; Yan, J. Aquaporin4 Knockout Aggravates Early Brain Injury Following Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Through Impairment of the Glymphatic System in Rat Brain. In Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: Neurological Care and Protection; Martin, R.D., Boling, W., Chen, G., Zhang, J.H., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 59–64. ISBN 978-3-030-04615-6. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, E.; Peng, X.; Ma, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, L.; Yan, J. The Involvement of Aquaporin-4 in the Interstitial Fluid Drainage Impairment Following Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2021, 12, 611494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, A.; Li, J.; Xiong, R.; Xia, Y.; Jiang, X.; Cao, F.; Lu, H.; Xu, J.; Shan, F. Inhibition of HIF-1α-AQP4 Axis Ameliorates Brain Edema and Neurological Functional Deficits in a Rat Controlled Cortical Injury (CCI) Model. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 2701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitchen, P.; Salman, M.M.; Halsey, A.M.; Clarke-Bland, C.; MacDonald, J.A.; Ishida, H.; Vogel, H.J.; Almutiri, S.; Logan, A.; Kreida, S.; et al. Targeting Aquaporin-4 Subcellular Localization to Treat Central Nervous System Edema. Cell 2020, 181, 784–799.e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Lei, L.; Zhou, H.; Lu, X.; Cai, F.; Li, T. Roles of Micro Ribonucleic Acids in Astrocytes After Cerebral Stroke. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 890762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nesverova, V.; Törnroth-Horsefield, S. Phosphorylation-Dependent Regulation of Mammalian Aquaporins. Cells 2019, 8, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Z.; Sun, Y.; Wang, B.; Sun, Q.; Yang, G.; Bian, L. Involvement of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Pathways in Ferrous Iron-Induced Aquaporin-4 Expression in Cultured Astrocytes. Neurotoxicology 2019, 73, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markou, A.; Unger, L.; Abir-Awan, M.; Saadallah, A.; Halsey, A.; Balklava, Z.; Conner, M.; Törnroth-Horsefield, S.; Greenhill, S.D.; Conner, A.; et al. Molecular Mechanisms Governing Aquaporin Relocalisation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Biomembr. 2022, 1864, 183853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitchen, P.; Day, R.E.; Taylor, L.H.J.; Salman, M.M.; Bill, R.M.; Conner, M.T.; Conner, A.C. Identification and Molecular Mechanisms of the Rapid Tonicity-Induced Relocalization of the Aquaporin 4 Channel. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 16873–16881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Sun, S.Q.; Lu, W.T.; Xu, J.; Gan, S.W.; Chen, Z.; Qiu, G.P.; Huang, S.Q.; Zhuo, F.; Liu, Q.; et al. The Internalization and Lysosomal Degradation of Brain AQP4 after Ischemic Injury. Brain Res. 2013, 1539, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okuno, K.; Taya, K.; Marmarou, C.R.; Ozisik, P.; Fazzina, G.; Kleindienst, A.; Gulsen, S.; Marmarou, A. The Modulation of Aquaporin-4 by Using PKC-Activator (Phorbol Myristate Acetate) and V1a Receptor Antagonist (SR49059) Following Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion/Reperfusion in the Rat. Acta Neurochir. Suppl. 2008, 102, 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buck, T.M.; Eledge, J.; Skach, W.R. Evidence for Stabilization of Aquaporin-2 Folding Mutants by N-Linked Glycosylation in Endoplasmic Reticulum. Am. J. Physiol.-Cell Physiol. 2004, 287, C1292–C1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salman, M.M.; Kitchen, P.; Halsey, A.; Wang, M.X.; Törnroth-Horsefield, S.; Conner, A.C.; Badaut, J.; Iliff, J.J.; Bill, R.M. Emerging Roles for Dynamic Aquaporin-4 Subcellular Relocalization in CNS Water Homeostasis. Brain 2022, 145, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Cao, C.; Liu, J.; Liu, Y.; Lu, J.; Yu, H.; Li, X.; Wu, J.; Yu, Z.; Li, H.; et al. Dystrophin 71 Deficiency Causes Impaired Aquaporin-4 Polarization Contributing to Glymphatic Dysfunction and Brain Edema in Cerebral Ischemia. Neurobiol. Dis. 2024, 199, 106586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishida, H.; Vogel, H.J.; Conner, A.C.; Kitchen, P.; Bill, R.M.; MacDonald, J.A. Simultaneous Binding of the N- and C-Terminal Cytoplasmic Domains of Aquaporin 4 to Calmodulin. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Biomembr. 2022, 1864, 183837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoki, K.; Uchihara, T.; Tsuchiya, K.; Nakamura, A.; Ikeda, K.; Wakayama, Y. Enhanced Expression of Aquaporin 4 in Human Brain with Infarction. Acta Neuropathol. 2003, 106, 121–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stokum, J.A.; Mehta, R.I.; Ivanova, S.; Yu, E.; Gerzanich, V.; Simard, J.M. Heterogeneity of Aquaporin-4 Localization and Expression after Focal Cerebral Ischemia Underlies Differences in White versus Grey Matter Swelling. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2015, 3, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Shao, L.; Ma, L. Cerebral Edema Formation After Stroke: Emphasis on Blood–Brain Barrier and the Lymphatic Drainage System of the Brain. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 716825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleffner, I.; Bungeroth, M.; Schiffbauer, H.; Schäbitz, W.-R.; Ringelstein, E.B.; Kuhlenbäumer, G. The Role of Aquaporin-4 Polymorphisms in the Development of Brain Edema After Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion. Stroke 2008, 39, 1333–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dardiotis, E.; Paterakis, K.; Tsivgoulis, G.; Tsintou, M.; Hadjigeorgiou, G.F.; Dardioti, M.; Grigoriadis, S.; Simeonidou, C.; Komnos, A.; Kapsalaki, E.; et al. AQP4 Tag Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms in Patients with Traumatic Brain Injury. J. Neurotrauma 2014, 31, 1920–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czyżewski, W.; Litak, J.; Sobstyl, J.; Mandat, T.; Torres, K.; Staśkiewicz, G. Aquaporins: Gatekeepers of Fluid Dynamics in Traumatic Brain Injury. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 6553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramiro, L.; Simats, A.; Penalba, A.; Garcia-Tornel, A.; Rovira, A.; Mancha, F.; Bustamante, A.; Montaner, J. Circulating Aquaporin-4 as A Biomarker of Early Neurological Improvement in Stroke Patients: A Pilot Study. Neurosci. Lett. 2020, 714, 134580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandra, A.; Farrell, C.; Wilson, H.; Dervenoulas, G.; De Natale, E.R.; Politis, M. Aquaporin-4 Polymorphisms Predict Amyloid Burden and Clinical Outcome in the Alzheimer’s Disease Spectrum. Neurobiol. Aging 2021, 97, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez de San José, N.; Halbgebauer, S.; Steinacker, P.; Anderl-Straub, S.; Abu-Rumeileh, S.; Barba, L.; Oeckl, P.; Bellomo, G.; Gaetani, L.; Toja, A.; et al. Aquaporin-4 as a Cerebrospinal Fluid Biomarker of Alzheimer’s Disease. Transl. Neurodegener. 2024, 13, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucchinetti, C.F.; Mandler, R.N.; McGavern, D.; Bruck, W.; Gleich, G.; Ransohoff, R.M.; Trebst, C.; Weinshenker, B.; Wingerchuk, D.; Parisi, J.E.; et al. A Role for Humoral Mechanisms in the Pathogenesis of Devic’s Neuromyelitis Optica. Brain J. Neurol. 2002, 125, 1450–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadopoulos, M.C.; Verkman, A.S. Aquaporin 4 and Neuromyelitis Optica. Lancet Neurol. 2012, 11, 535–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tradtrantip, L.; Zhang, H.; Saadoun, S.; Phuan, P.-W.; Lam, C.; Papadopoulos, M.C.; Bennett, J.L.; Verkman, A.S. Anti-Aquaporin-4 Monoclonal Antibody Blocker Therapy for Neuromyelitis Optica. Ann. Neurol. 2012, 71, 314–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pittock, S.J.; Berthele, A.; Fujihara, K.; Kim, H.J.; Levy, M.; Palace, J.; Nakashima, I.; Terzi, M.; Totolyan, N.; Viswanathan, S.; et al. Eculizumab in Aquaporin-4–Positive Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorder. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 614–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, G.; Yang, G.-Y. Aquaporin-4: A Potential Therapeutic Target for Cerebral Edema. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verkman, A.S.; Smith, A.J.; Phuan, P.-W.; Tradtrantip, L.; Anderson, M.O. The Aquaporin-4 Water Channel as a Potential Drug Target in Neurological Disorders. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2017, 21, 1161–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abir-Awan, M.; Kitchen, P.; Salman, M.M.; Conner, M.T.; Conner, A.C.; Bill, R.M. Inhibitors of Mammalian Aquaporin Water Channels. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanimura, Y.; Hiroaki, Y.; Fujiyoshi, Y. Acetazolamide Reversibly Inhibits Water Conduction by Aquaporin-4. J. Struct. Biol. 2009, 166, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Migliati, E.; Meurice, N.; DuBois, P.; Fang, J.S.; Somasekharan, S.; Beckett, E.; Flynn, G.; Yool, A.J. Inhibition of Aquaporin-1 and Aquaporin-4 Water Permeability by a Derivative of the Loop Diuretic Bumetanide Acting at an Internal Pore-Occluding Binding Site. Mol. Pharmacol. 2009, 76, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, K.-X.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Hou, L.-W.; Fan, D.-X.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, X.-L.; Jia, T.-M.; Lou, J.-Y. Effects of Dexamethasone on Aquaporin-4 Expression in Brain Tissue of Rat with Bacterial Meningitis. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 3090–3096. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nicchia, G.P.; Frigeri, A.; Liuzzi, G.M.; Svelto, M. Inhibition of Aquaporin-4 Expression in Astrocytes by RNAi Determines Alteration in Cell Morphology, Growth, and Water Transport and Induces Changes in Ischemia-Related Genes. FASEB J. Off. Publ. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol. 2003, 17, 1508–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Liang, C.; Peng, S.; Bao, S.; Xue, F.; Lian, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, G. Aquaporin-4 Activation Facilitates Glymphatic System Function and Hematoma Clearance Post-Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Glia 2025, 73, 368–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, R.; Cheng, J.; Yu, J.; Li, S.; Ma, H.; Zhao, Y. Trifluoperazine Reduces Apoptosis and Inflammatory Responses in Traumatic Brain Injury by Preventing the Accumulation of Aquaporin4 on the Surface of Brain Cells. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2023, 20, 797–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, M.E.; Mueller, H.A.; Froehner, S.C. In Vivo Requirement of the α-Syntrophin PDZ Domain for the Sarcolemmal Localization of nNOS and Aquaporin-4. J. Cell Biol. 2001, 155, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozlu, S.; Caban, S.; Yerlikaya, F.; Fernandez-Megia, E.; Novoa-Carballal, R.; Riguera, R.; Yemisci, M.; Gursoy-Ozdemir, Y.; Dalkara, T.; Couvreur, P.; et al. An Aquaporin 4 Antisense Oligonucleotide Loaded, Brain Targeted Nanoparticulate System Design. Pharm. 2014, 69, 340–345. [Google Scholar]
- Hablitz, L.M.; Plá, V.; Giannetto, M.; Vinitsky, H.S.; Stæger, F.F.; Metcalfe, T.; Nguyen, R.; Benrais, A.; Nedergaard, M. Circadian Control of Brain Glymphatic and Lymphatic Fluid Flow. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hablitz, L.M.; Vinitsky, H.S.; Sun, Q.; Stæger, F.F.; Sigurdsson, B.; Mortensen, K.N.; Lilius, T.O.; Nedergaard, M. Increased Glymphatic Influx Is Correlated with High EEG Delta Power and Low Heart Rate in Mice under Anesthesia. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaav5447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Yoo, R.-E.; Choi, S.H. Glymphatic Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Part I—Methodologies for Evaluation of the Glymphatic System. Investig. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2023, 27, 196–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohene, Y.; Harrison, I.F.; Nahavandi, P.; Ismail, O.; Bird, E.V.; Ottersen, O.P.; Nagelhus, E.A.; Thomas, D.L.; Lythgoe, M.F.; Wells, J.A. Non-Invasive MRI of Brain Clearance Pathways Using Multiple Echo Time Arterial Spin Labelling: An Aquaporin-4 Study. Neuroimage 2019, 188, 515–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alghanimy, A.; Martin, C.; Gallagher, L.; Holmes, W.M. The Effect of a Novel AQP4 Facilitator, TGN-073, on Glymphatic Transport Captured by Diffusion MRI and DCE-MRI. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0282955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braun, M.; Sevao, M.; Keil, S.A.; Gino, E.; Wang, M.X.; Lee, J.; Haveliwala, M.A.; Klein, E.; Agarwal, S.; Pedersen, T.; et al. Macroscopic Changes in Aquaporin-4 Underlie Blast Traumatic Brain Injury-Related Impairment in Glymphatic Function. Brain 2024, 147, 2214–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Huang, C.; Guo, Q.; Chu, H. Aquaporin-4 and Cognitive Disorders. Aging Dis. 2022, 13, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eidsvaag, V.A.; Enger, R.; Hansson, H.; Eide, P.K.; Nagelhus, E.A. Human and Mouse Cortical Astrocytes Differ in Aquaporin-4 Polarization toward Microvessels. Glia 2017, 65, 964–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

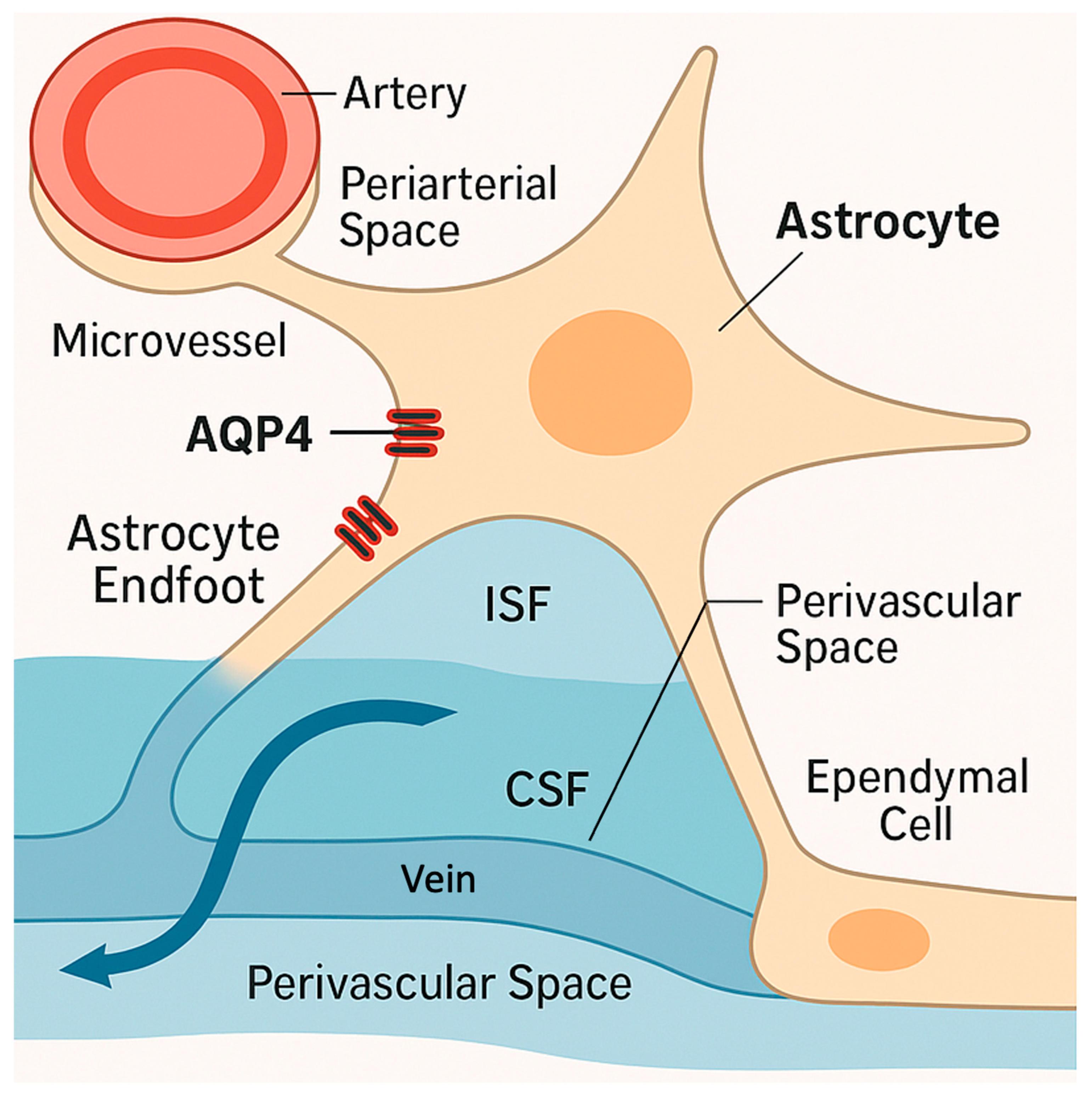
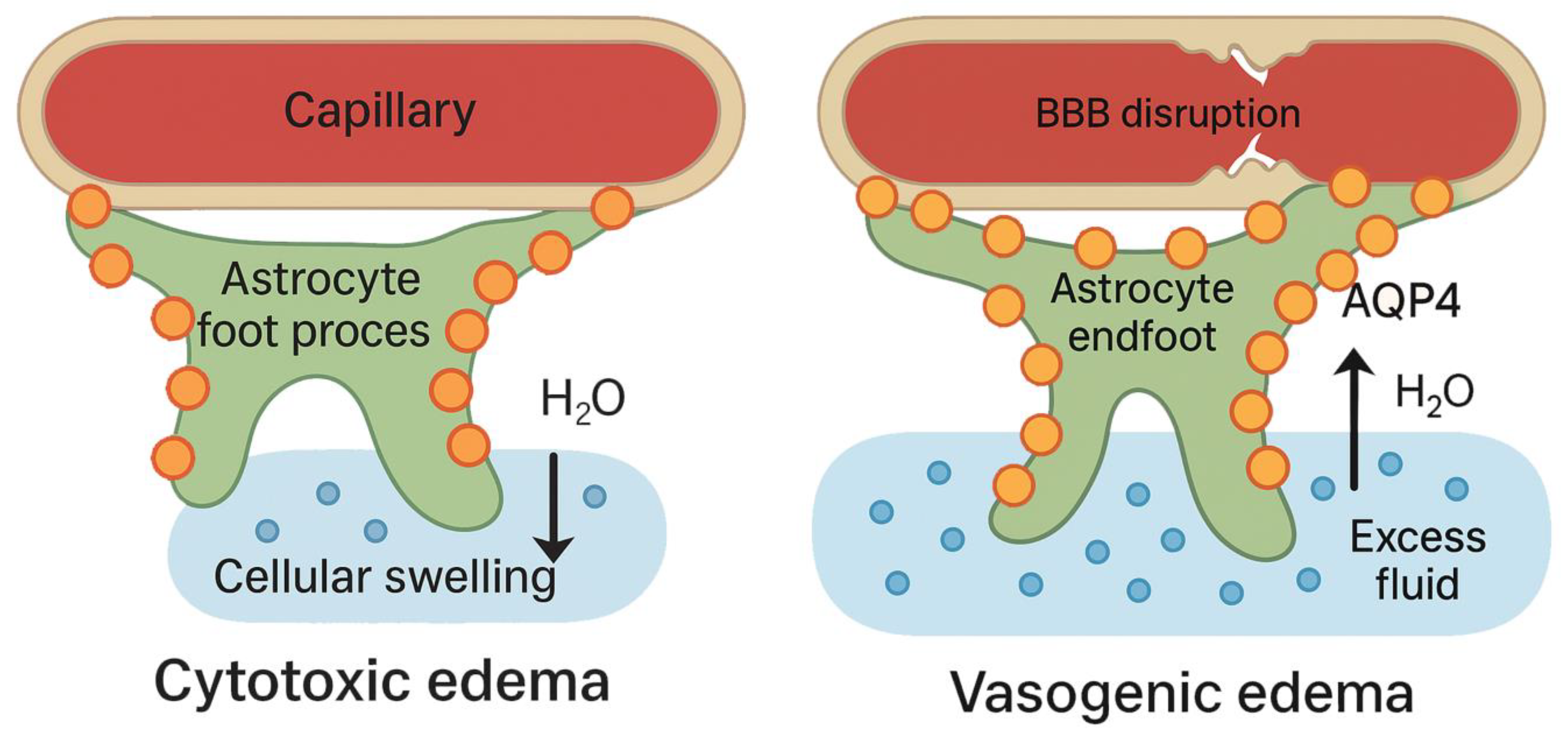
| Context | Type of Edema | Effect of AQP4 Deletion | Interpretation | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acute Ischemic Stroke (MCAO, water intoxication) | Cytotoxic | ↓ Edema, ↓ infarct volume, ↓ intracranial pressure (ICP); improved outcomes | AQP4 facilitates rapid water influx in astrocytes, exacerbating cytotoxic swelling | [7,14,15] |
| Cortical Freeze Injury | Vasogenic | ↑ Edema, ↑ ICP; worsened outcomes | AQP4 necessary for extracellular fluid clearance; absence impairs reabsorption | [5,6,16] |
| Intracerebral Hemorrhage | Vasogenic | ↑ Edema volume, ↑ neuronal death, ↑ BBB disruption | AQP4 supports removal of blood-derived fluid; deletion worsens injury | [25,26] |
| Subarachnoid Hemorrhage | Vasogenic | ↓ Glymphatic flow, ↑ early brain injury, ↑ edema | AQP4 essential for CSF-ISF exchange; its loss impairs glymphatic function | [27,28] |
| Brain Abscess | Vasogenic | ↑ ICP, ↑ water content, impaired edema resolution | AQP4 enables fluid clearance in infection-related vasogenic edema | [16] |
| Spinal Cord Injury | Mixed (early cytotoxic + late vasogenic) | ↑ Edema, impaired recovery; trafficking blockade beneficial | Phase-specific role; targeting localization rather than full deletion is advantageous | [30] |
| Therapeutic Strategy | Mechanism of Action | Experimental Evidence | Stroke Phase | Proposed Clinical Use | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TGN-020 | Selective AQP4 inhibitor; blocks water permeability | Reduces cytotoxic edema and improves neurological outcome in MCAO rodent models | Hyperacute (≤6 h) | Inhibition during early cytotoxic edema to limit astrocytic swelling | [19,21,62] |
| Trifluoperazine (TFP) | Calmodulin inhibitor; prevents AQP4 translocation to astrocyte membrane | Reduces surface AQP4 localization, astrocytic swelling, and improves outcome in spinal cord injury and TBI models | Hyperacute (≤6 h) | Prevents AQP4 redistribution to astrocytic endfeet during early ischemia | [51,53] |
| siRNA/antisense oligonucleotides | Gene silencing of AQP4 mRNA | Decreases AQP4 expression, alters ischemia-related gene response (GLUT1, HK), reduces edema in rodent models | Hyperacute | Potential early inhibition of AQP4 expression (limited by delivery timing) | [50,55] |
| Acetazolamide/Bumetanide | Reported indirect AQP4 modulation; primarily diuretics | Weak or non-specific inhibition; off-target effects; limited efficacy in direct AQP4 blockade | Unclear; preclinical only | Not recommended as specific AQP4 inhibitors | [47,48] |
| Dexamethasone | Downregulates AQP4 expression via glucocorticoid receptor signalling | Shown to reduce AQP4 in vasogenic edema contexts (e.g., tumors, meningitis) | Subacute (24–72 h) | May support edema resolution, but unproven in stroke | [49] |
| Eculizumab/Aquaporumab | Monoclonal antibodies targeting AQP4 autoimmunity | Not applicable to stroke directly; supports concept that AQP4 loss is deleterious | Chronic (for autoimmune CNS edema) | Demonstrates harm of AQP4 dysfunction; indirect relevance to vasogenic edema | [42,43] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
García Ríos, C.A.; Leon-Rojas, J.E. Aquaporin-4 in Stroke and Brain Edema—Friend or Foe? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8178. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178178
García Ríos CA, Leon-Rojas JE. Aquaporin-4 in Stroke and Brain Edema—Friend or Foe? International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(17):8178. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178178
Chicago/Turabian StyleGarcía Ríos, Cecilia Alejandra, and Jose E. Leon-Rojas. 2025. "Aquaporin-4 in Stroke and Brain Edema—Friend or Foe?" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 17: 8178. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178178
APA StyleGarcía Ríos, C. A., & Leon-Rojas, J. E. (2025). Aquaporin-4 in Stroke and Brain Edema—Friend or Foe? International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(17), 8178. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178178








