Effect of Cocoa Supplementation on the Biochemical and Clinical Profile and the Somatosensory Processing of Diabetic Peripheral and Autonomic Neuropathy: A Randomized Clinical Trial
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
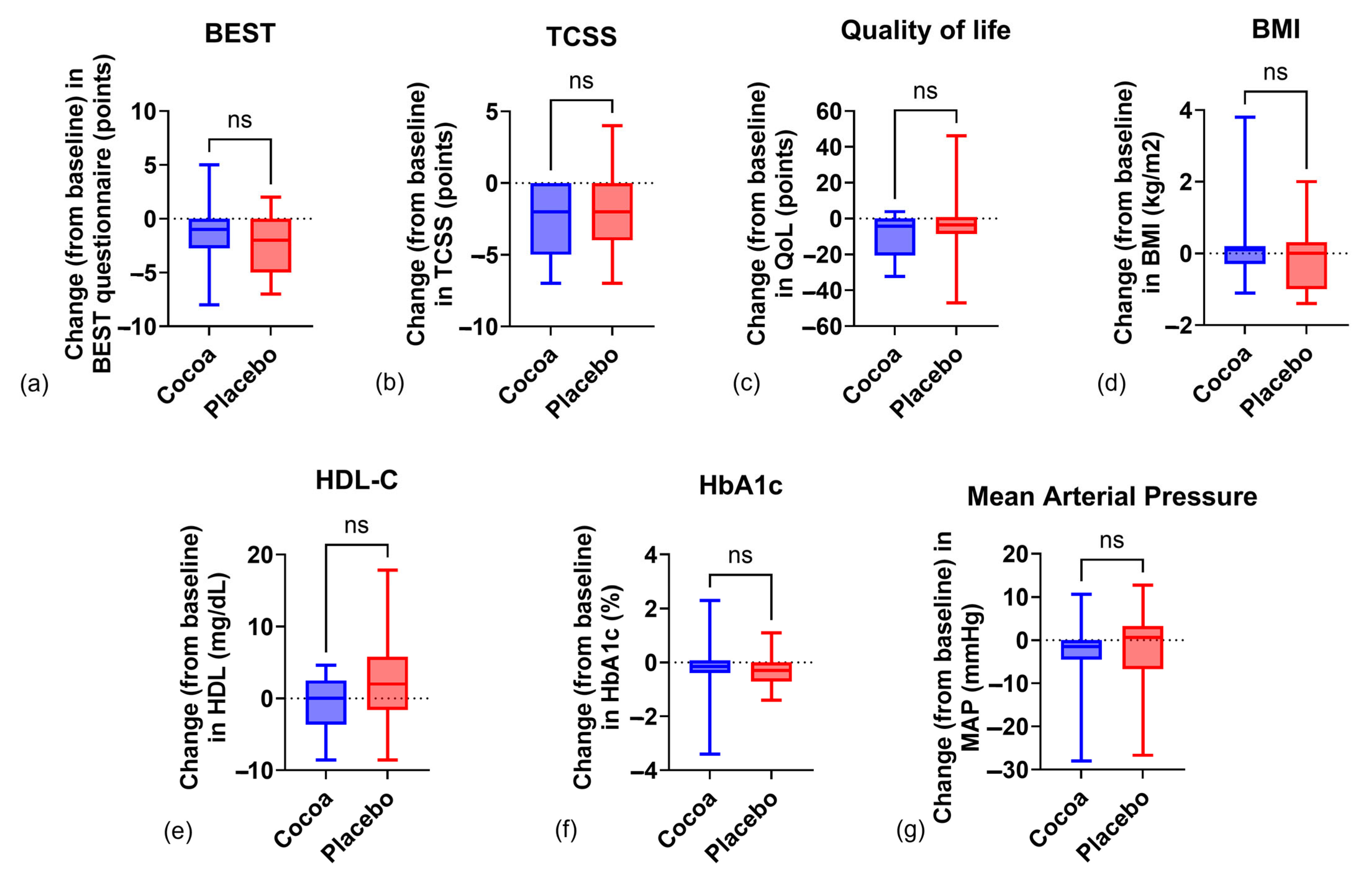
2.1. Anthropometric Indicators
2.2. Biochemical Indicators
2.3. Clinical Indicators
2.4. Sensorimotor Processing
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Sample Size
4.2. Dietary Intervention
4.3. Anthropometric Measurements
4.4. Clinical Parameters
4.5. Biochemical Parameters
4.6. Sensorimotor Processing: RDD of the H-Reflex
4.7. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AGEs | Advanced Glycation End Products |
| BMI | Body Mass Index |
| DAN | Diabetic Autonomic Neuropathy |
| DBP | Diastolic Blood Pressure |
| DN | Diabetic Neuropathy |
| DPN | Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy |
| DSP | Distal symmetric polyneuropathy |
| HbA1c | Glycated Hemoglobin |
| H-reflex | Hoffman Reflex |
| HDL-C | High-density lipoprotein cholesterol |
| IL | Interleukin |
| LDL-C | Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol |
| MAP | Mean Arterial Pressure |
| MCP-1 | Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 |
| NF-κB | Nuclear Factor-Kappa B |
| QoL | Quality of Life |
| RDD | Rate-Dependent Depression |
| ROS | Reactive Oxygen Species |
| SBP | Systolic Blood Pressure |
| SD | Standard Deviation |
| T2D | Type 2 Diabetes |
| TCSS | Toronto Clinical Scoring System |
| TGs | Triglycerides |
| TNFα | Tumoral Necrosis Factor Alpha |
| WtH ratio | Waist-to-Height Ratio |
References
- Blonde, L.; Umpierrez, G.E.; Reddy, S.S.; McGill, J.B.; Berga, S.L.; Bush, M.; Chandrasekaran, S.; Einhorn, D.; Galindo, R.J.; Gardner, T.W.; et al. American Association of Clinical Endocrinology Clinical Practice Guideline: Developing a Diabetes Mellitus Comprehensive Care Plan—2022 Update. Endocr. Pract. 2022, 28, 923–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galicia-Garcia, U.; Benito-Vicente, A.; Jebari, S.; Larrea-Sebal, A.; Siddiqi, H.; Uribe, K.B.; Ostolaza, H.; Martín, C. Pathophysiology of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar Rebolledo, F. Neuropatía Diabética. Aspectos Prácticos, Diagnósticos, Terapéuticos y Medidas Profilácticas, 3rd ed.; Aldrete Velasco, J., Ed.; Editorial Alfil: Ciudad de Mexico, Mexico, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. 12. Retinopathy, Neuropathy, and Foot Care: Standards of Care in Diabetes—2024. Diabetes Care 2024, 47 (Suppl. 1), S231–S243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibarra, R.C.T.; de Rocha, L.J.J.; Hernández, O.R.; Nieves, R.R.E.; Leyva, J.R. Prevalencia de neuropatía periférica en diabéticos tipo 2 en el primer nivel de atención. Rev. Med. Chile 2012, 140, 1126–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hicks, C.W.; Selvin, E. Epidemiology of Peripheral Neuropathy and Lower Extremity Disease in Diabetes. Curr. Diab Rep. 2019, 19, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldman, E.L.; Callaghan, B.C.; Pop-Busui, R.; Zochodne, D.W.; Wright, D.E.; Bennett, D.L.; Bril, V.; Russell, J.W.; Viswanathan, V. Diabetic Neuropathy. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2019, 5, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marathe, C.S.; Jones, K.L.; Wu, T.; Rayner, C.K.; Horowitz, M. Gastrointestinal Autonomic Neuropathy in Diabetes. Auton. Neurosci. 2020, 229, 102718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, L.; Lian, X.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Q.; Cai, Y.; Ma, H.; Yu, X. Understanding Diabetic Neuropathy: Focus on Oxidative Stress. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2020, 2020, 9524635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ristikj-Stomnaroska, D.; Risteska-Nejashmikj, V.; Papazova, M. Role of Inflammation in the Pathogenesis of Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy. Open Access Maced. J. Med. Sci. 2019, 7, 2267–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyenihi, A.B.; Ayeleso, A.O.; Mukwevho, E.; Masola, B. Antioxidant Strategies in the Management of Diabetic Neuropathy. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 515042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Secretaría de Salud. Diagnóstico y Tratamiento Médico Del Dolor Por Neuropatía Diabética En Adultos En El Primer Nivel de Atención; Secretaría de Salud: Ciudad de México, México, 2009.
- Palmieri, R.M.; Ingersoll, C.D.; Hoffman, M.A. The Hoffmann Reflflex: Methodologic Considerations and Applications for Use in Sports Medicine and Athletic Training Research. J. Athl. Train. 2004, 39, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Marshall, A.G.; Lee-Kubli, C.; Azmi, S.; Zhang, M.; Ferdousi, M.; Mixcoatl-Zecuatl, T.; Petropoulos, I.N.; Ponirakis, G.; Fineman, M.S.; Fadavi, H.; et al. Spinal Disinhibition in Experimental and Clinical Painful Diabetic Neuropathy. Diabetes 2017, 66, 1380–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salinas, L.F.; Trujillo-Condes, V.E.; Tecuatl, C.; Delgado-Lezama, R.; Cuellar, C.A. Impaired Rate-Dependent Depression of the H-Reflex in Type-2 Diabetes, Prediabetes, Overweight and Obesity: A Cross-Sectional Study. Medicine 2022, 101, e31046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worthington, A.; Kalteniece, A.; Ferdousi, M.; Donofrio, L.; Dhage, S.; Azmi, S.; Adamson, C.; Malik, R.A.; Calcutt, N.A.; Marshall, A.G. Optimal Utility of H-Reflex Rdd as a Biomarker of Spinal Disinhibition in Painful and Painless Diabetic Neuropathy. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pop-Busui, R.; Boulton, A.M.; Feldman, E.L.; Bril, V.; Freeman, R.; Malik, R.A.; Sosenko, J.M.; Ziegler, D. Diabetic Neuropathy: A Position Statement by the American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Care 2017, 40, 136–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pop-Busui, R.; Ang, L.; Boulton, A.J.; Feldman, E.L.; Marcus, R.L.; Mizokami-Stout, K.; Singleton, R.J.; Ziegler, D. Diagnosis and Treatment of Painful Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy; American Diabetes Association: Arlington, VA, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Uddin, M.S.; Al Mamun, A.; Rahman, M.A.; Kabir, M.T.; Alkahtani, S.; Alanazi, I.S.; Perveen, A.; Ashraf, G.M.; Bin-Jumah, M.N.; Abdel-Daim, M.M. Exploring the Promise of Flavonoids to Combat Neuropathic Pain: From Molecular Mechanisms to Therapeutic Implications. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caro-Ordieres, T.; Marín-Royo, G.; Opazo-Ríos, L.; Jiménez-Castilla, L.; Moreno, J.A.; Gómez-Guerrero, C.; Egido, J. The Coming Age of Flavonoids in the Treatment of Diabetic Complications. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaramillo Flores, M.E. Cocoa Flavanols: Natural Agents with Attenuating Effects on Metabolic Syndrome Risk Factors. Nutrients 2019, 11, 751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Araujo, Q.R.; Gattward, J.N.; Almoosawi, S.; Parada Costa Silva, M.D.G.C.; De Santana Dantas, P.A.; De Araujo Júnior, Q.R. Cacao and Human Health: From Head to Foot—A Review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2013, 56, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munguía, L.; Gutiérrez-Salmeán, G.; Hernández, M.; Ortiz, A.; Sánchez, M.E.; Nájera, N.; Meaney, E.; Rubio-Gayosso, I.; Ceballos, G. Beneficial Effects of a Flavanol-Enriched Cacao Beverage on Anthropometric and Cardiometabolic Profile in Overweight Subjects. Rev. Mex. Cardiol. 2015, 26, 78–86. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, L.; Li, X.; He, L.; Zheng, Y.; Lu, H.; Li, J.; Zhong, L.; Tong, R.; Jiang, Z.; Shi, J.; et al. Antidiabetic Potential of Flavonoids from Traditional Chinese Medicine: A Review. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2019, 47, 933–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Feo, M.; Paladini, A.; Ferri, C.; Carducci, A.; Del Pinto, R.; Varrassi, G.; Grassi, D. Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Nociceptive Effects of Cocoa: A Review on Future Perspectives in Treatment of Pain. Pain Ther. 2020, 9, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addepalli, V.; Suryavanshi, S.V. Catechin Attenuates Diabetic Autonomic Neuropathy in Streptozotocin Induced Diabetic Rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 108, 1517–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borghi, S.M.; Pinho-Ribeiro, F.A.; Fattori, V.; Bussmann, A.J.; Vignoli, J.A.; Camilios-Neto, D.; Casagrande, R.; Verri, W.A. Quercetin Inhibits Peripheral and Spinal Cord Nociceptive Mechanisms to Reduce Intense Acute Swimming-Induced Muscle Pain in Mice. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0162267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Sesso, H.D.; Kim, E.; Manson, J.E.; Friedenberg, G.; Clar, A.; Copeland, T.; Shadyab, A.H.; Wactawski-Wende, J.; Tinker, L.; et al. Cocoa Extract Supplementation and Risk of Type 2 Diabetes: The Cocoa Supplement and Multivitamin Outcomes Study (COSMOS) Randomized Clinical Trial. Diabetes Care 2023, 46, 2278–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, E.J.; Mendis, B.; Dunlop, M.; Schroeter, H.; Kwik-Uribe, C.; Macdonald, I.A. Cocoa Flavanol Supplementation and the Effect on Insulin Resistance in Females Who Are Overweight or Obese: A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2023, 15, 565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez Simón, M.I. El ABCD de La Evaluación Del Estado de Nutrición; Suverza Fernández, A., Haua Navarro, K., Eds.; McGraw-Hill: México City, México, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Instituto Mexicano del Seguro Social. Diagnóstico y Tratamiento Del Sobrepeso y Obesidad Exógena Guía De Evidencias y Recomendaciones: Guía de Práctica Clínica; Instituto Mexicano del Seguro Social: Ciudad de Mexico, Mexico, 2018.
- Kawai, T.; Autieri, M.V.; Scalia, R. Adipose Tissue Inflammation and Metabolic Dysfunction in Obesity. Am. J. Physiol. 2021, 320, C375–C391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dicks, L.; Kirch, N.; Gronwald, D.; Wernken, K.; Zimmermann, B.F.; Helfrich, H.-P.; Ellinger, S. Regular Intake of a Usual Serving Size of Flavanol-Rich Cocoa Powder Does Not Affect Cardiometabolic Parameters in Stably Treated Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Hypertension—A Double-Blinded, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- León-Flores, P.; Nájera, N.; Pérez, E.; Pardo, B.; Jimenez, F.; Diaz-Chiguer, D.; Villarreal, F.; Hidalgo, I.; Ceballos, G.; Meaney, E. Effects of Cacao By-Products and a Modest Weight Loss Intervention on the Concentration of Serum Triglycerides in Overweight Subjects: Proof of Concept. J. Med. Food 2020, 23, 745–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashwell, M.; Gunn, P.; Gibson, S. Waist-to-Height Ratio Is a Better Screening Tool than Waist Circumference and BMI for Adult Cardiometabolic Risk Factors: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Obes. Rev. 2012, 13, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostami, A.; Khalili, M.; Haghighat, N.; Eghtesadi, S.; Shidfar, F.; Heidari, I.; Ebrahimpour-Koujan, S.; Eghtesadi, M. High-Cocoa Polyphenol-Rich Chocolate Improves Blood Pressure in Patients with Diabetes and Hypertension. ARYA Atheroscler. 2015, 11, 21–29. [Google Scholar]
- American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. 6. Glycemic Goals and Hypoglycemia: Standards of Care in Diabetes—2025. Diabetes Care 2025, 48 (Suppl. 1), S128–S145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Diabetes Association. 10. Cardiovascular Disease and Risk Management: Standards of Care in Diabetes—2025. Diabetes Care 2025, 48 (Suppl. 1), S207–S238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordero, A.; Alegria-Ezquerra, E. TG/HDL Ratio as Surrogate Marker for Insulin Resistance. E-J. ESC Counc. Cardiol. Pract. 2009, 8, 16. [Google Scholar]
- Buonacera, A.; Stancanelli, B.; Colaci, M.; Malatino, L. Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratio: An Emerging Marker of the Relationships between the Immune System and Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atre, J.; Ganvir, S. Screening Instrument for Clinical Diagnosis of Peripheral Neuropathy in Diabetes-A Review. Indian J. Physiother. Occup. Ther. 2019, 13, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.Y.; Gong, Y.Y. Analysis of the Effect of Probucol-Mecobalamin Tablets Combination on Oxidative Stress in Patients with Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy. Neurosci. Lett. 2021, 741, 135484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Carmona, J.M.; Rodríguez-Moctezuma, R. Adaptación y Validación Del Instrumento de Calidad de Vida Diabetes 39 En Pacientes Mexicanos Con Diabetes Mellitus Tipo 2. Salud Publica Mex. 2006, 48, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tesfaye, S.; Chaturvedi, N.; Eaton, S.E.; Ward, J.D.; Manes, C.; Ionescu-Tirgoviste, C.; Witte, D.R.; Fuller, J.H. Vascular Risk Factors and Diabetic Neuropathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastroiacovo, D.; Kwik-Uribe, C.; Grassi, D.; Necozione, S.; Raffaele, A.; Pistacchio, L.; Righetti, R.; Bocale, R.; Lechiara, M.C.; Marini, C.; et al. Cocoa Flavanol Consumption Improves Cognitive Function, Blood Pressure Control, and Metabolic Profile in Elderly Subjects: The Cocoa, Cognition, and Aging (CoCoA) Study-A Randomized Controlled Trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 101, 538–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Worthington, A.; Kalteniece, A.; Ferdousi, M.; D′onofrio, L.; Dhage, S.; Azmi, S.; Adamson, C.; Hamdy, S.; Malik, R.A.; Calcutt, N.A.; et al. Spinal Inhibitory Dysfunction in Patients with Painful or Painless Diabetic Neuropathy. Diabetes Care 2021, 44, 1835–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Calcutt, N.A.; Zhou, X. Rate-Dependent Depression of the Hoffmann Reflex: Practical Applications in Painful Diabetic Neuropathy. Diabetes Metab. J. 2024, 48, 1029–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marshall, A.; Kalteniece, A.; Ferdousi, M.; Azmi, S.; Jude, E.B.; Adamson, C.; D’Onofrio, L.; Dhage, S.; Soran, H.; Campbell, J.; et al. Spinal Disinhibition: Evidence for a Hyperpathia Phenotype in Painful Diabetic Neuropathy. Brain Commun. 2023, 5, fcad051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mifflin, M.D.; St Jeor, S.T.; Hill, L.A.; Scott, B.J.; Daugherty, S.A.; Koh, Y.O. A New Predictive Equation for Resting Energy Expenditure in Healthy Individuals. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1990, 51, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamdy, O.; Ganda, O.P.; Maryniuk, M.; Gabbay, R.A. Clinical Nutrition Guideline for Overweight and Obese Adults with Type 2 Diabetes (T2D) or Prediabetes, or Those at High Risk for Developing T2D. 2018. Available online: https://joslin.org/-/media/files/joslin/joslin-clinical-nutrition-guideline-for-overweight-and-obese-adults.pdf (accessed on 27 August 2024).
- Favela, E.; Gutierrez, J.; Medina, M.; Rolón, M.; Sierra, C.; Viniegra, A. Diagnóstico y Tratamiento de La Hipertensión Arterial En El Primer Nivel de Atención; Instituto Mexicano del Seguro Social: Ciudad de Mexico, Mexico, 2014.
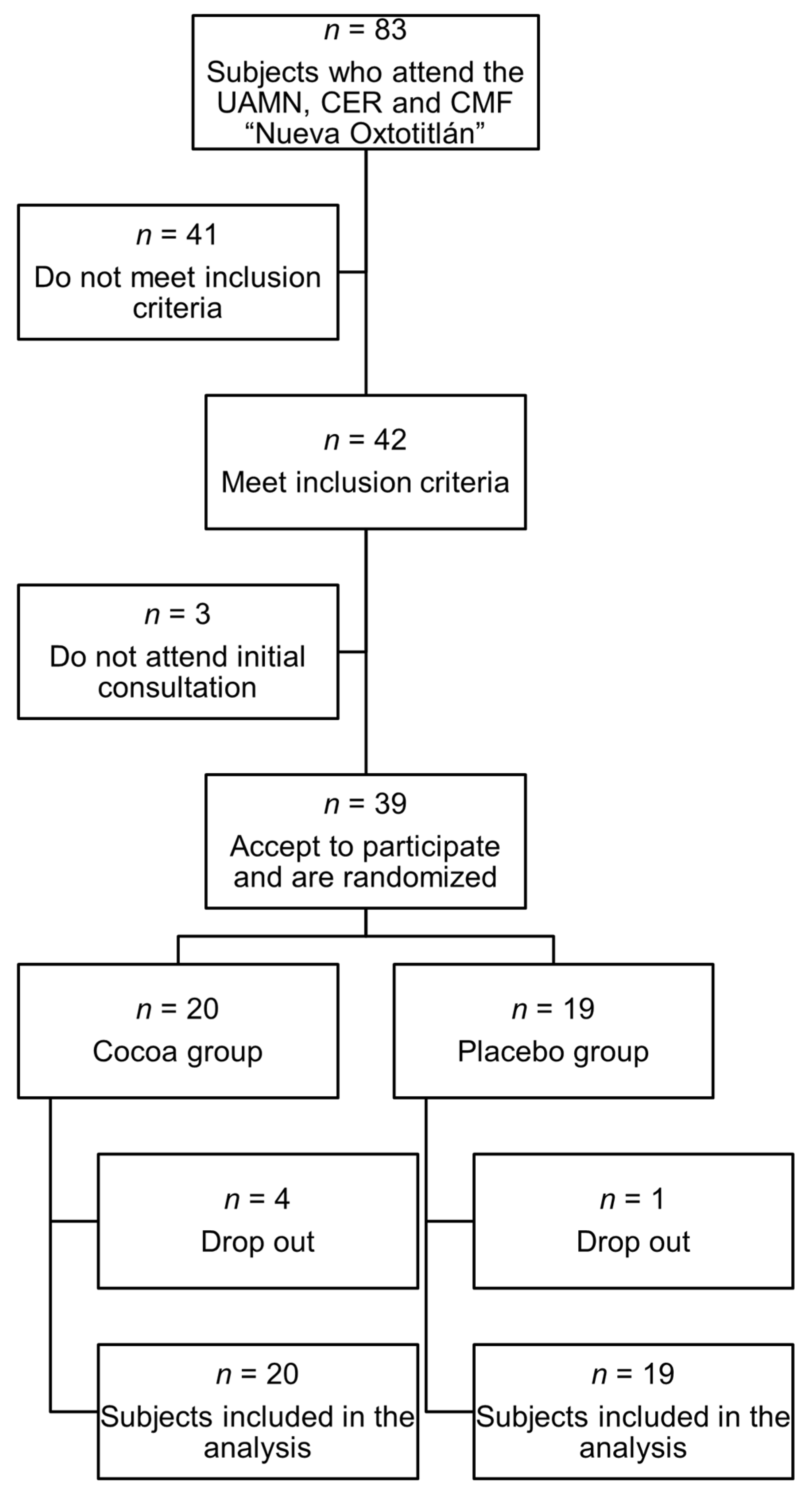
| Variable | Cocoa (Mean ± SD) | Placebo (Mean ± SD) | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total (n) | 20 | 19 | |
| Age | 53.6 ± 8.67 | 53.7 ± 6.34 | ns |
| Sex M/F | 10/10 | 7/12 | |
| Weight (kg) | 73.5 ± 14.1 | 82.8 ± 13.8 | 0.047 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 28.7 ± 4.35 | 32 ± 5.32 | 0.043 |
| Waist Circ (cm) | 96.7 ± 7.49 | 103.5 ± 13.1 | ns |
| Abd Circ (cm) | 100 ± 9.31 | 106 ± 11.4 | ns |
| SBP (mmHg) | 126 ± 14.6 | 127 ± 15.5 | ns |
| DBP (mmHg) | 79.9 ± 8.23 | 78.1 ± 7.98 | ns |
| BEST | 9.35 ± 2.75 | 9.05 ± 2.77 | ns |
| Bristol | 3.65 ± 1.3 | 3.84 ± 1.5 | ns |
| Altered Bristol (%) | 40 | 57 | ns |
| TCSS | 9.31 ± 3.98 | 6.89 ± 3.47 | 0.047 |
| QoL | 43.4 ± 26.8 | 35.6 ± 22.6 | ns |
| R2/R1 (n = 8) | 0.79 ± 0.45 | 0.77 ± 0.32 | ns |
| RDD 0.1 Hz | 1.09 ± 0.25 | 1.02 ± 0.12 | ns |
| RDD 1 Hz | 0.87 ± 0.35 | 0.88 ± 0.33 | ns |
| RDD 5 Hz | 0.91 ± 0.67 | 0.71 ± 0.38 | ns |
| RDD 10 Hz | 0.56 ± 0.47 | 0.71 ± 0.42 | ns |
| Glycemia (mg/dL) | 169 ± 62.6 | 195 ± 85.7 | ns |
| HbA1c (%) | 7.82 ± 1.9 | 8.28 ± 2.02 | ns |
| HbA1c (mmol/mol) | 62 ± 20.7 | 66.9 ± 22.1 | ns |
| TG (mg/dL) | 182 ± 81.4 | 179 ± 58.8 | ns |
| HDL (mg/dL) | 37.8 ± 9.52 | 38.2 ± 9.12 | ns |
| TG/HDL | 5.12 ± 2.84 | 4.99 ± 2.13 | ns |
| LDL (mg/dL) | 112 ± 31.8 | 108 ± 31.3 | ns |
| Neutrophil/lymphocyte | 1.96 ± 0.86 | 1.76 ± 0.55 | ns |
| Variable (Mean ± SD) | Cocoa | Placebo | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Week 0 | Week 4 | Week 8 | Week 12 | p | Week 0 | Week 4 | Week 8 | Week 12 | p | |
| Weight (kg) | 73.5 ± 14.1 | 74.4 ± 14.8 | 74.1 ± 14.7 | 73.8 ± 14.6 | ns | 82.8 ± 13.8 | 82.5 ± 13.9 | 83 ± 13.7 | 82.4 ± 13.9 | ns |
| Change from baseline | 0.38 ± 2.72 | −0.42 ± 2.18 ⇞ | ||||||||
| Waist Circ (cm) | 96.7 ± 7.49 | 96.5 ± 7.08 | 96 ± 7.33 | 95.9 ± 7.28 | ns | 103 ± 13.1 | 103 ± 11.7 | 103 ± 12.0 | 102 ± 12.0 | ns |
| Change from baseline | −0.80 ± 2.19 | −1.38 ± 4.11 ⇞ | ||||||||
| WtH ratio | 0.6 ± 0.04 | 0.6 ± 0.04 | 0.6 ± 0.04 | 0.6 ± 0.04 | ns | 0.64 ± 0.09 | 0.64 ± 0.08 | 0.64 ± 0.09 | 0.63 ± 0.09 | ns |
| Change from baseline | −0.00 ± 0.01 | −0.00 ± 0.02 ⇞ | ||||||||
| Glycemia (mg/dL) | 169 ± 62.6 | 152 ± 58.4 | ns | 195 ± 85.7 | 157 ± 63.6 | 0.002 ¥ | ||||
| Change from baseline | −17 ± 42.8 | −38.1 ± 55.9 ⇞ | ||||||||
| HbA1c (%) | 7.82 ± 1.9 | 7.72 ± 1.5 | ns | 8.28 ± 2.02 | 8 ± 2.04 | 0.04 ¥ | ||||
| Change from baseline | −0.17 ± 1.09 | −0.27 ± 0.60 ⇞ | ||||||||
| HbA1c (mmol/mol) | 62 ± 20.7 | 60.9 ± 16.4 | ns | 66.9 ± 22.1 | 64 ± 22.3 | ns | ||||
| Change from baseline | −1.04 ± 11.9 | −2.94 ± 6.58 ⇞ | ||||||||
| TG/HDL | 5.12 ± 2.84 | 5.1 ± 2.9 | ns | 4.99 ± 2.13 | 4.25 ± 1.31 | ns | ||||
| Change from baseline | −0.02 ± 1.98 | −0.74 ± 2.13 ⇞ | ||||||||
| HDL-C | 37.8 ± 9.52 | 36.9 ± 7.5 | ns | 38.2 ± 9.12 | 40.4 ± 6.26 | ns | ||||
| Change from baseline | −0.86 ± 3.71 | 2.18 ± 6.23 ⇞ | ||||||||
| Neutro/lymph | 1.96 ± 0.86 | 1.87 ± 1.07 | ns | 1.76 ± 0.55 | 1.92 ± 0.61 | ns | ||||
| Change from baseline | −0.09 ± 0.77 | 0.15 ± 0.45 ⇞ | ||||||||
| TCSS | 9.31 ± 3.98 | 6.68 ± 4.41 | 0.0001 ¥ | 6.89 ± 3.47 | 5.05 ± 2.91 | 0.012 ¥ | ||||
| Change from baseline | −2.63 ± 2.24 | −1.84 ± 2.77 ⇞ | ||||||||
| QoL | 43.4 ± 26.8 | 34.2 ± 25.8 | 0.0007 ¥ | 35.6 ± 22.6 | 30.4 ± 24.5 | ns | ||||
| Change from baseline | −9.19 ± 11.6 | −5.26 ± 19 ⇞ | ||||||||
| MBP (mmHg) | 95.1 ± 9.57 | 94 ± 9.36 | 93.8 ± 8.35 | 92.3 ± 10.3 | ns | 94.2 ± 8.86 | 96.1 ± 9.39 | 92.9 ± 7.06 | 91.9 ± 7.69 | ns |
| Change from baseline | −2.78 ± 8.02 | −2.84 ± 10.9 ⇞ | ||||||||
| BEST | 9.35 ± 2.75 | 9 ± 3.12 | 8.05 ± 2.64 | 7.9 ± 2.67 | 0.042 ¥ | 9.05 ± 2.77 | 7.94 ± 1.87 | 7.42 ± 2.52 | 6.84 ± 2.6 | 0.015 ¥ |
| Change from baseline | −1.45 ± 2.62 | −2.21 ± 2.59 ⇞ | ||||||||
| R2/R1 | 0.79 ± 0.45 (n = 8) | 0.87 ± 0.20 (n = 8) | ns | 0.77 ± 0.32 (n = 8) | 0.72 ± 0.22 (n = 10) | ns | ||||
| Change from baseline | 0.06 ± 0.32 | −0.02 ± 0.22 ⇞ | ||||||||
| Bristol (% of alteration) | 40 | 30 | ns | 57.8 | 52.6 | ns | ||||
| Change from baseline | −10 | −5.2 ⇞ | ||||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kababie-Ameo, R.; Gutiérrez-Salmeán, G.; Salinas-Hernández, L.F.; Trujillo-Condes, V.E.; Ramírez-Sánchez, I.; Cuellar, C.A. Effect of Cocoa Supplementation on the Biochemical and Clinical Profile and the Somatosensory Processing of Diabetic Peripheral and Autonomic Neuropathy: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8033. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26168033
Kababie-Ameo R, Gutiérrez-Salmeán G, Salinas-Hernández LF, Trujillo-Condes VE, Ramírez-Sánchez I, Cuellar CA. Effect of Cocoa Supplementation on the Biochemical and Clinical Profile and the Somatosensory Processing of Diabetic Peripheral and Autonomic Neuropathy: A Randomized Clinical Trial. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(16):8033. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26168033
Chicago/Turabian StyleKababie-Ameo, Rebeca, Gabriela Gutiérrez-Salmeán, Luisa Fernanda Salinas-Hernández, Virgilio Eduardo Trujillo-Condes, Israel Ramírez-Sánchez, and Carlos A. Cuellar. 2025. "Effect of Cocoa Supplementation on the Biochemical and Clinical Profile and the Somatosensory Processing of Diabetic Peripheral and Autonomic Neuropathy: A Randomized Clinical Trial" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 16: 8033. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26168033
APA StyleKababie-Ameo, R., Gutiérrez-Salmeán, G., Salinas-Hernández, L. F., Trujillo-Condes, V. E., Ramírez-Sánchez, I., & Cuellar, C. A. (2025). Effect of Cocoa Supplementation on the Biochemical and Clinical Profile and the Somatosensory Processing of Diabetic Peripheral and Autonomic Neuropathy: A Randomized Clinical Trial. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(16), 8033. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26168033






