Co-Supplementation of Policosanol and Banaba Leaf Extract Exhibited a Cooperative Effect Against Hyperglycemia and Dyslipidemia in Zebrafish: Highlighting Vital Organ Protection Against High-Cholesterol and High-Galactose Diet
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
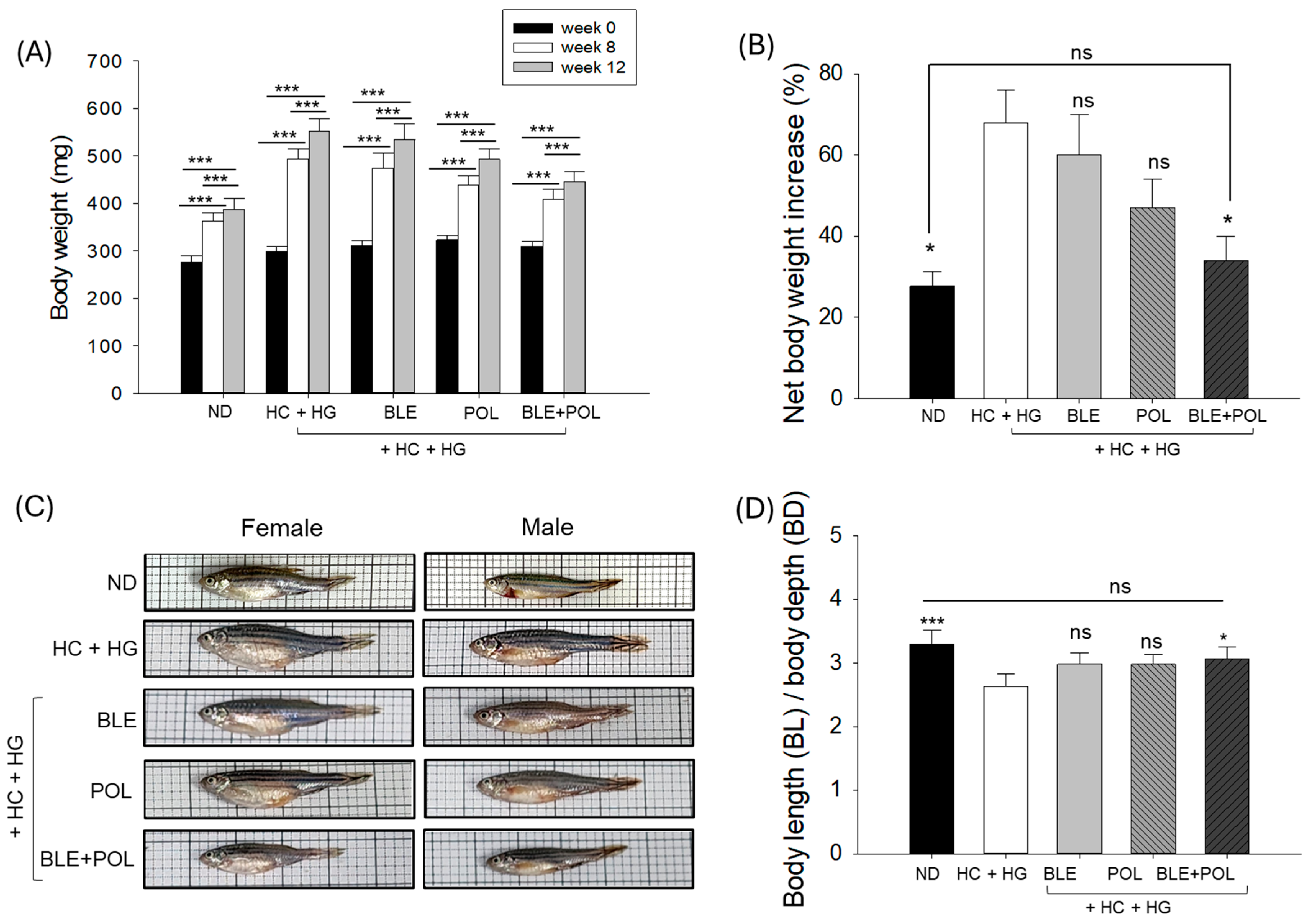
2.1. Survivability and Changes in Body Weight
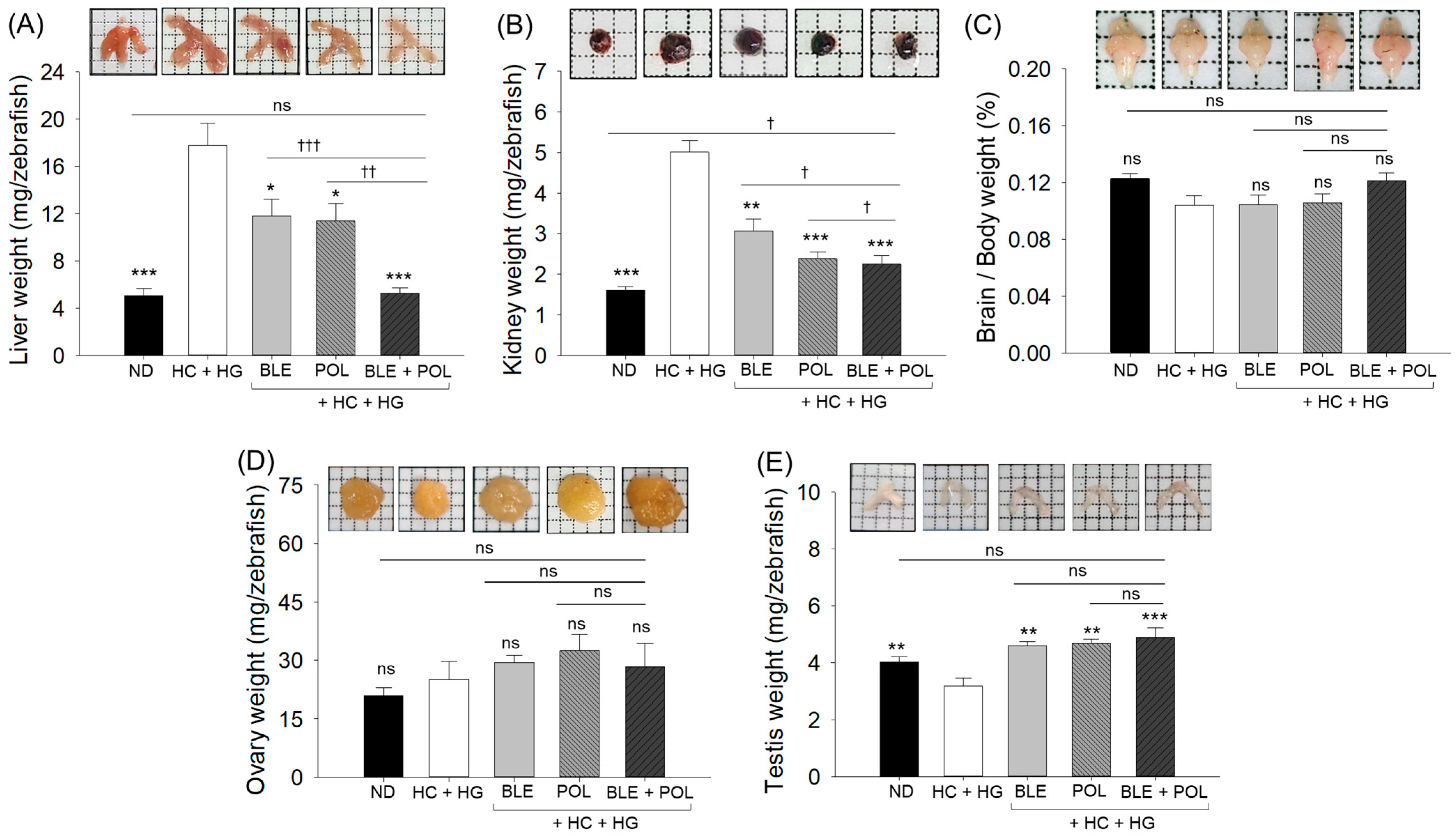
2.2. Changes in Morphology and Organ Weights
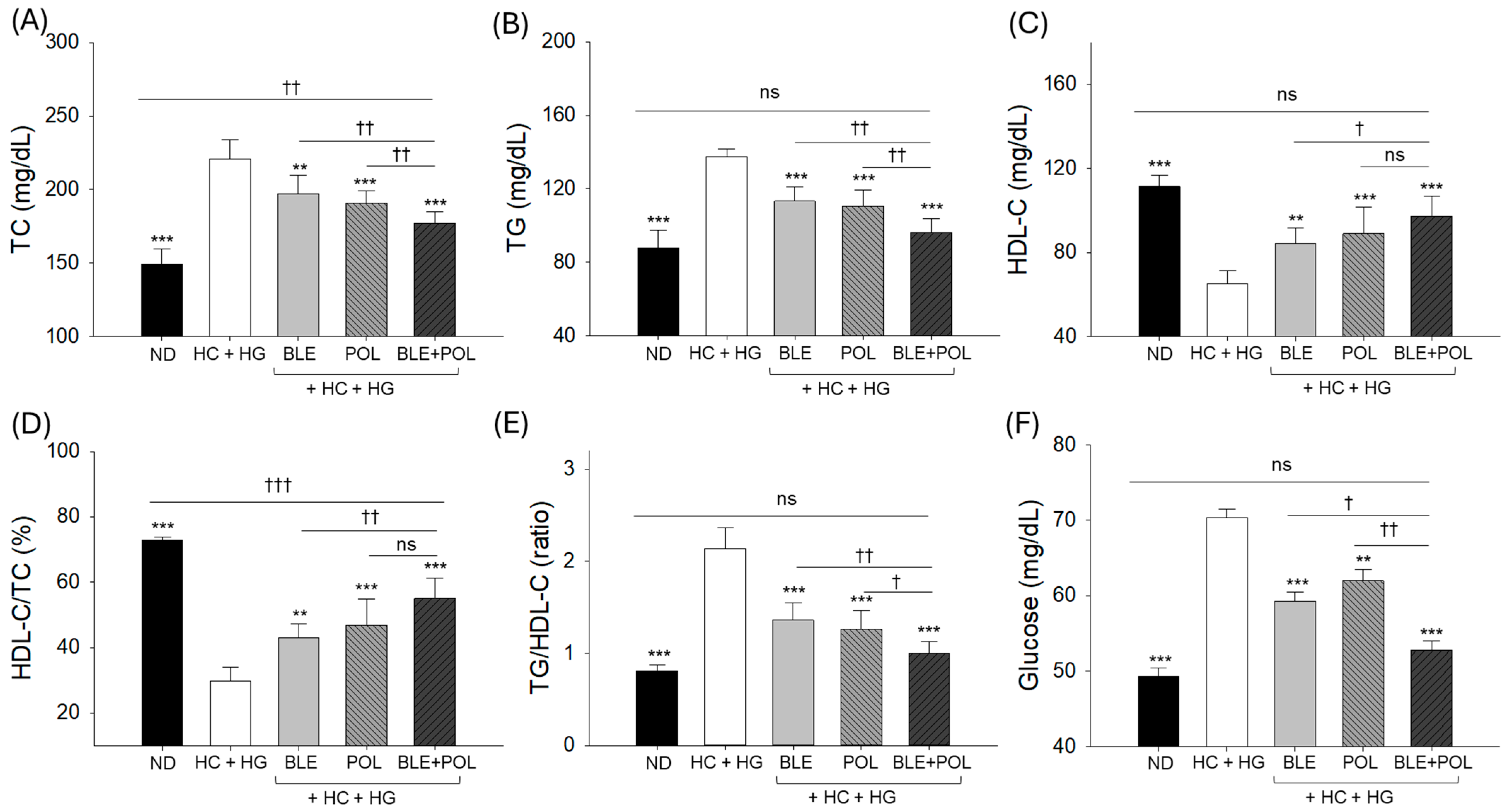
2.3. Blood Lipoprotein Profile and Glucose Levels
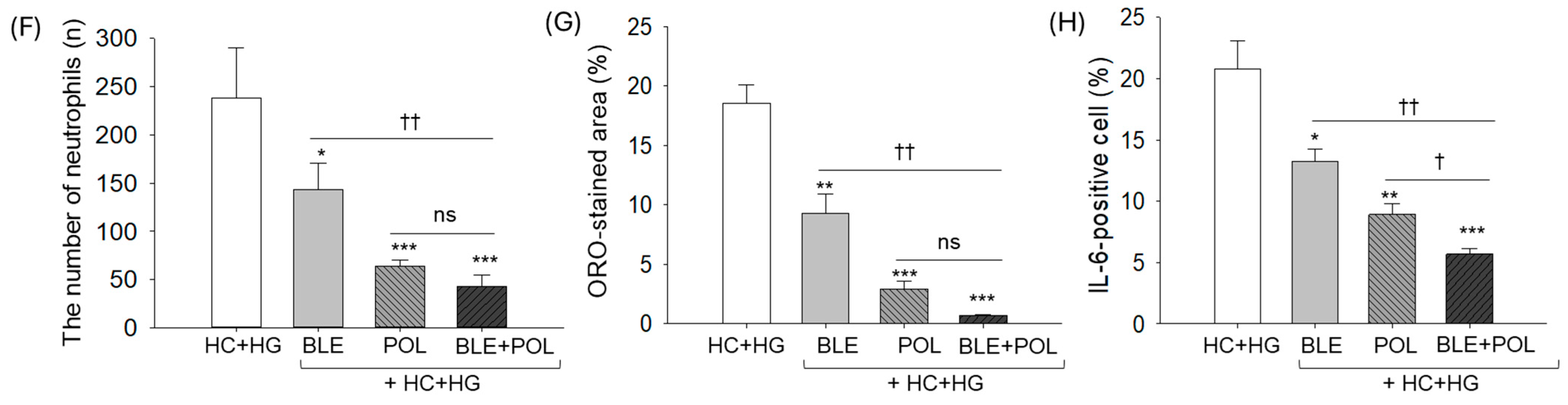
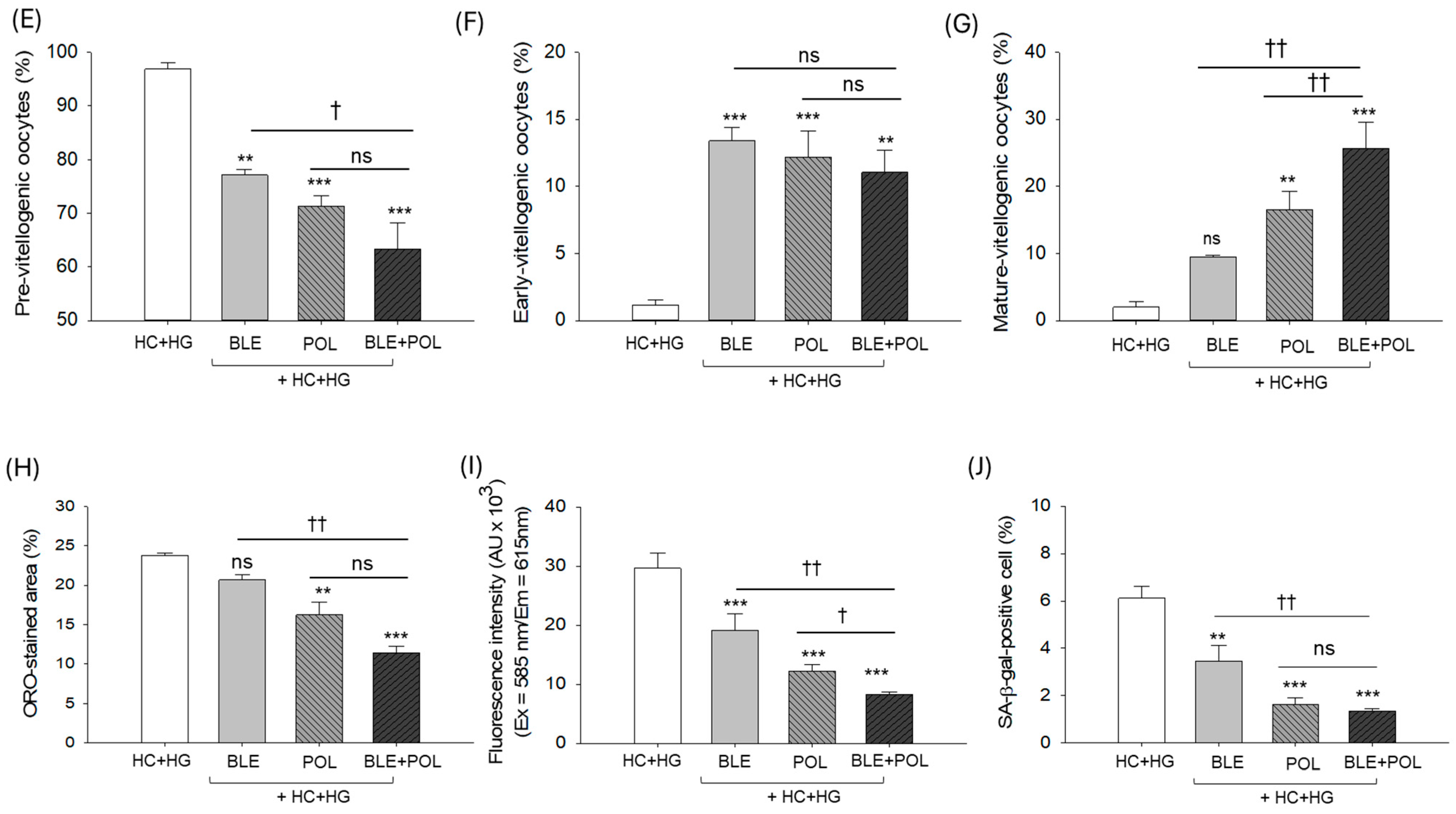
2.4. Oxidative Stress, Antioxidant, and Hepatic Function Variables in Blood
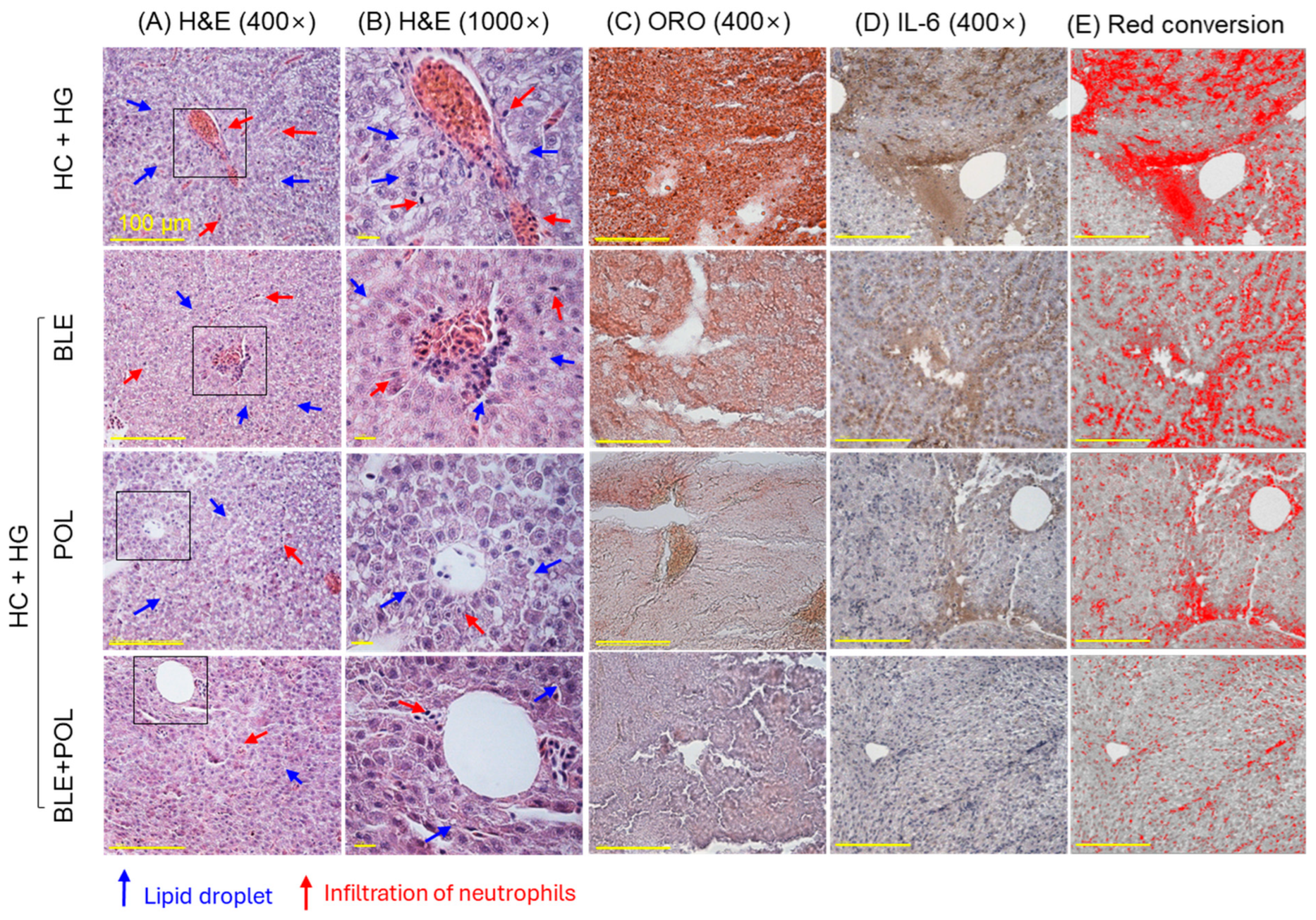
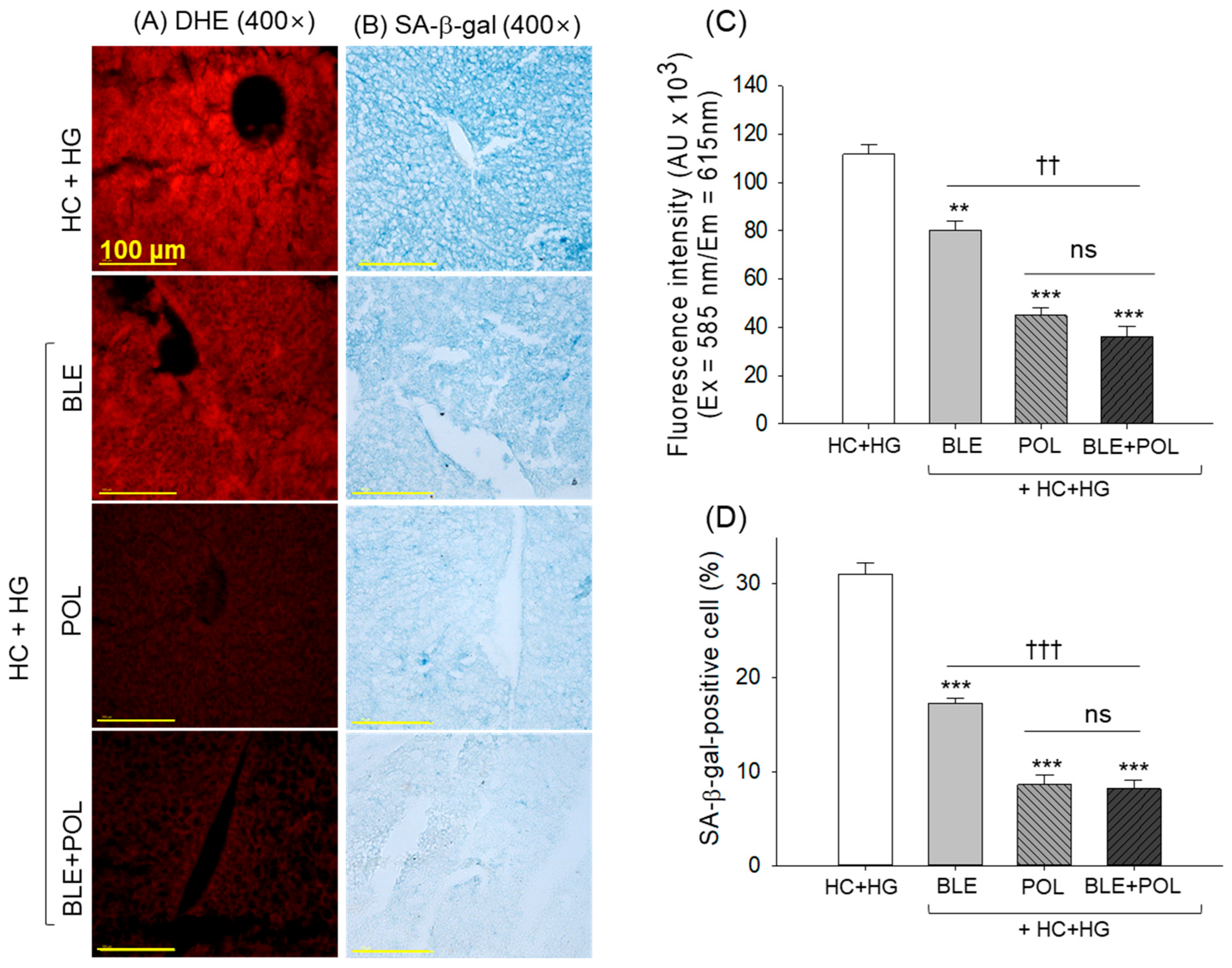
2.5. Liver Histology
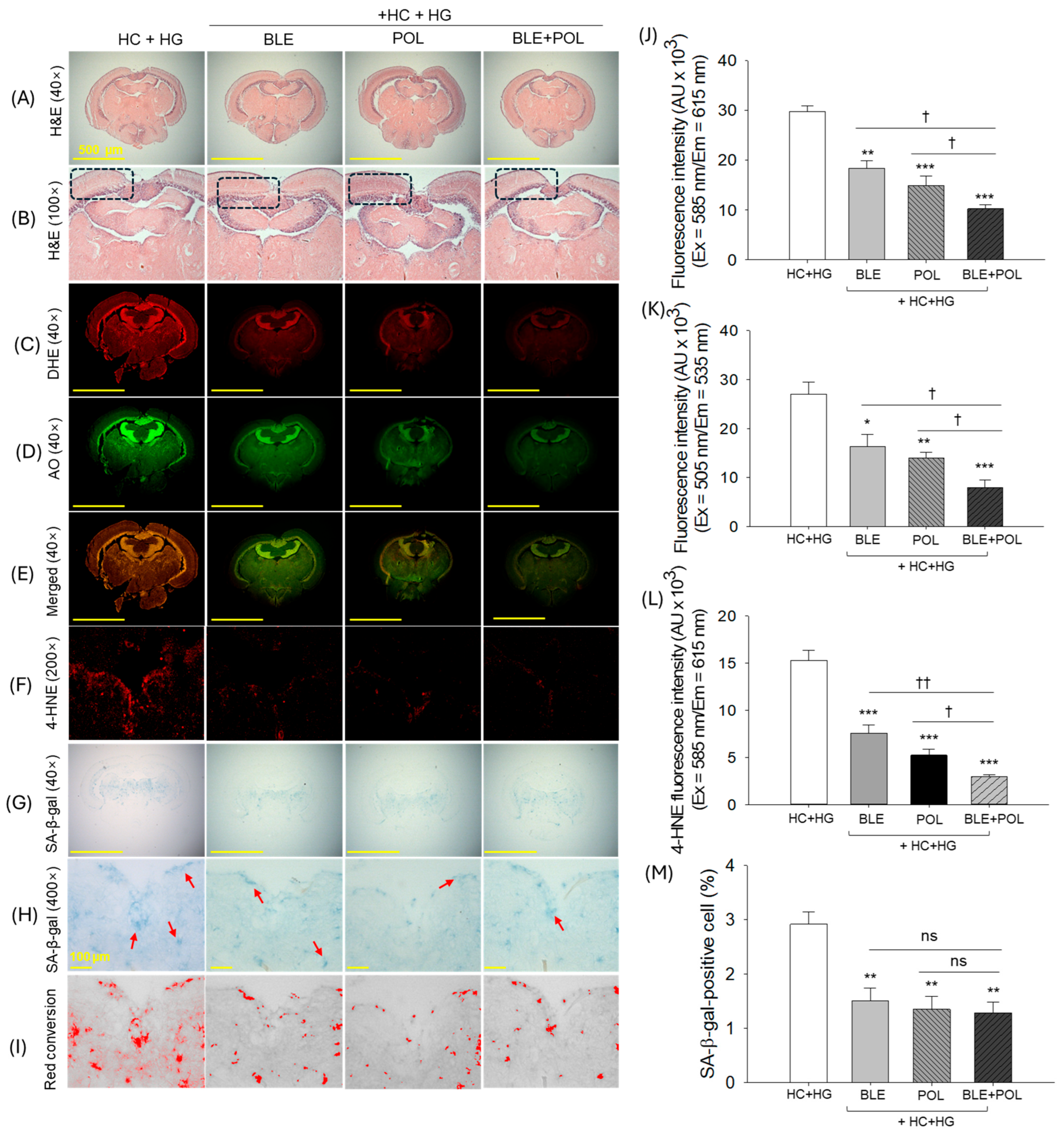
2.6. Dihydroethidium (DHE) Fluorescence Staining and Senescent-Associated β-Galactosidase Staining
2.7. Kidney Histology
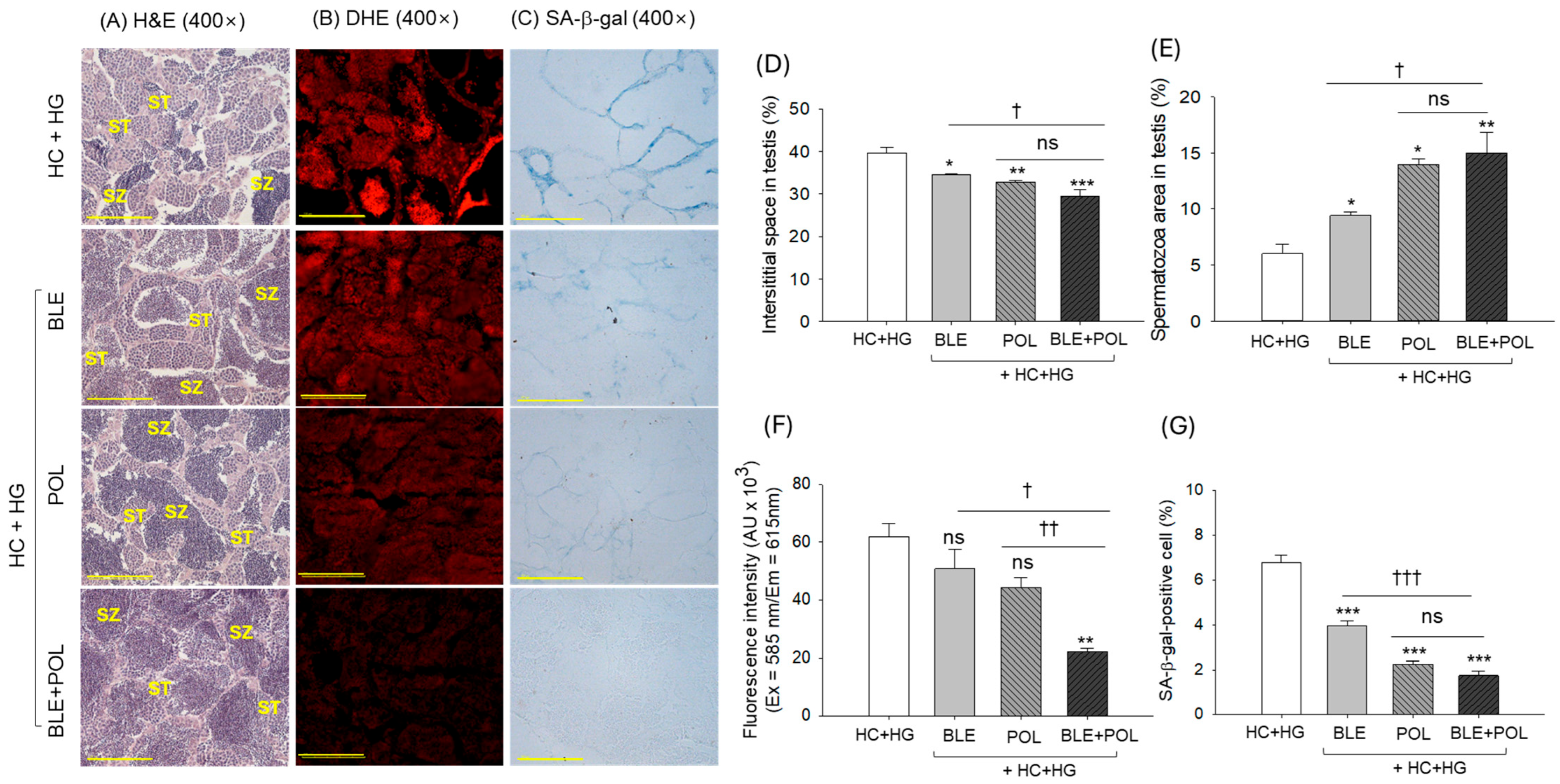
2.8. Histology of Testicular Tissue
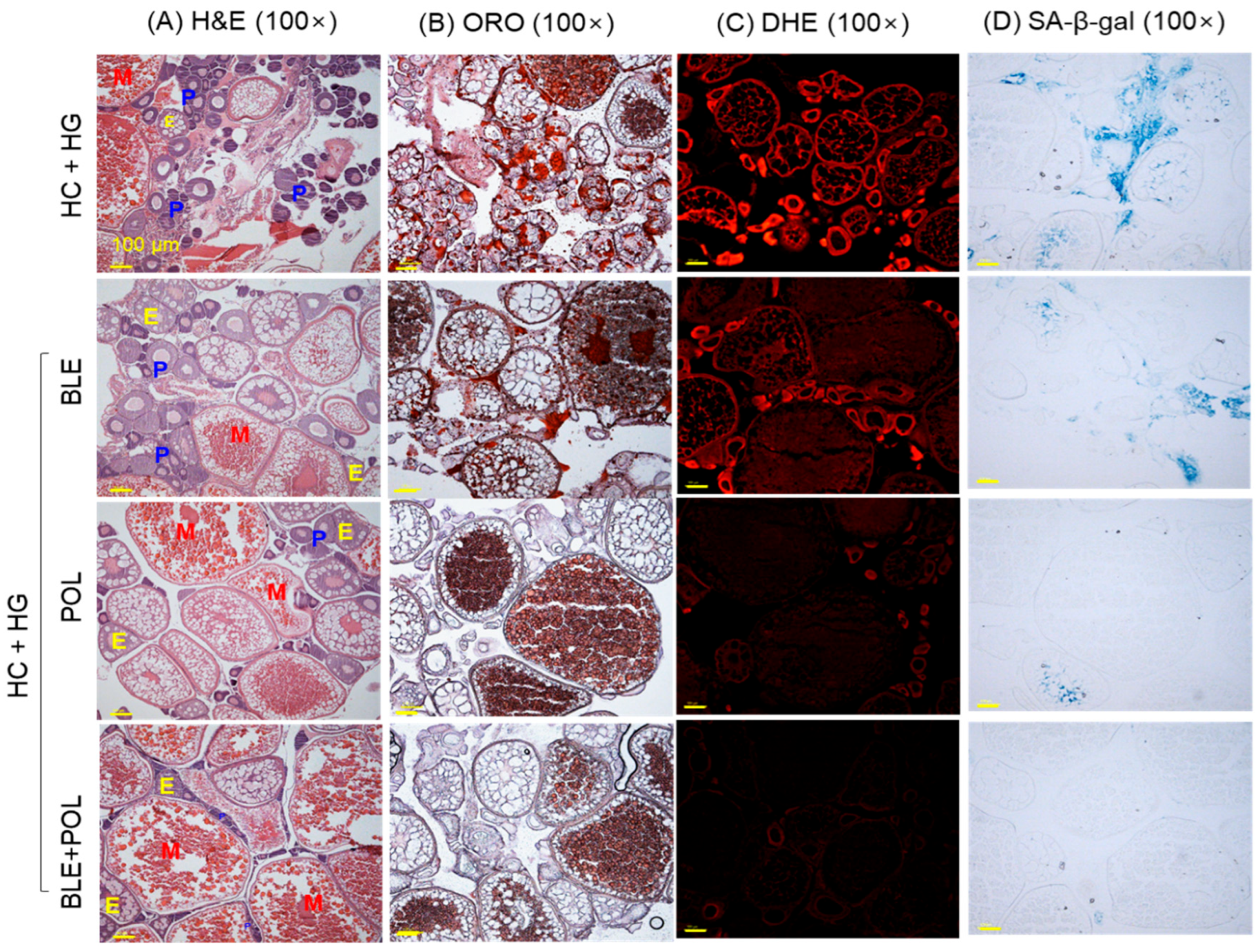
2.9. Histology of Ovarian Tissue
2.10. Histological Analysis of the Brain
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Zebrafish Culturing
4.3. Formulation of the Specialized Diet and Zebrafish Feeding
4.4. Zebrafish Euthanasia and Collection of Blood and Organs
4.5. Quantification of Blood Lipoprotein, Hepatic Function Enzymes, and Glucose Levels
4.6. Blood Oxidative Variables, Ferric Ion Reduction (FRA), and Paraoxonase (PON) Activity
4.7. Historical Analysis and Immunohistochemistry (IHC)
4.8. Dihydroethidium (DHE), Acridine Orange (AO), and Senescent Staining
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- de Oliveira, L.L.H.; de Assis, A.C.R.; Giraldez, V.Z.R.; Scudeler, T.L.; Soares, P.R. Dyslipidemia: A narrative review on pharmacotherapy. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crichton, G.E.; Alkerwi, A. Physical activity, sedentary behavior time and lipid levels in the observation of cardiovascular risk factors in Luxembourg study. Lipids Health Dis. 2015, 14, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speliotes, E.K.; Balakrishnan, M.; Friedman, L.S.; Corey, K.E. Treatment of dyslipidemia in common liver diseases. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 16, 1189–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suh, S.H.; Kim, S.W. Dyslipidemia in patients with chronic kidney disease: An updated overview. Diabetes Metab. J. 2023, 47, 612–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Xie, Y.; Qu, L.; Zhang, M.; Mo, Z. Dyslipidemia involvement in the development of polycystic ovary syndrome. Taiwan J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2019, 58, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitfield, M.; Guiton, R.; Rispal, J.; Acar, N.; Kocer, A.; Drevet, J.R.; Saez, F. Dyslipidemia alters sperm maturation and ca-pacitation in LXR-null mice. Reproduction 2017, 154, 827–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahalle, N.; Garg, M.; Naik, S.S.; Kulkarni, M.V. Study of pattern of dyslipidemia and its correlation with cardiovascular risk factors in patients with proven coronary artery disease. Indian J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 18, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azman, K.F.; Safdar, A.; Zakaria, R. D-galactose-induced liver aging model: Its underlying mechanisms and potential therapeutic interventions. Exp. Gerontol. 2021, 150, 111372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo-Htay, C.; Palee, S.; Apaijai, N.; Chattipakorn, S.C.; Chattipakorn, N. Effects of d-galactose-induced ageing on the heart and its potential interventions. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2018, 22, 1392–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadigh-Eteghad, S.; Majdi, A.; McCann, S.K.; Mahmoudi, J.; Vafaee, M.S.; Macleod, M.R. D-galactose-induced brain ageing model: A systematic review and meta-analysis on cognitive outcomes and oxidative stress indices. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0184122. [Google Scholar]
- Umbayev, B.; Askarova, S.; Almabayeva, A.; Saliev, T.; Masoud, A.R.; Bulanin, D. Galactose-induced skin aging: The role of oxidative stress. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2020, 7145656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haider, S.; Liaquat, L.; Shahzad, S.; Sadir, S.; Madiha, S.; Batool, Z.; Tabassum, S.; Saleem, S.; Naqvi, F.; Perveen, T. A high dose of short-term exogenous D-galactose administration in young male rats produces symptoms simulating the natural aging process. Life Sci. 2015, 124, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bala, S.; Ganz, M.; Babuta, M.; Zhuang, Y.; Csak, T.; Calenda, C.D.; Szabo, G. Steatosis, inflammasome upregulation, and fibrosis are attenuated in miR-155 deficient mice in a high fat-cholesterol-sugar diet-induced model of NASH. Lab. Investig. 2021, 101, 1540–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paraskevas, K.I.; Gloviczki, P.; Antignani, P.L.; Comerota, A.J.; Dardik, A.; Davies, A.H.; Eckstein, H.-H.; Faggioli, G.; Fernandes, J.F.; Fraedrich, G. Benefits and drawbacks of statins and non-statin lipid lowering agents in carotid artery disease. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2022, 73, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, N.C.; Watts, G.F.; Eckel, R.H. Statin toxicity. Circ. Res. 2019, 124, 328–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.-Y.; Jiao, R.; Ma, K.Y. Cholesterol-lowering nutraceuticals and functional foods. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 8761–8773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Peng, J.; Zhang, K.; Wang, L.; Feng, T.; Nhamdriel, T.; Fan, G. Phytochemicals for the treatment of metabolic diseases: Evidence from clinical studies. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 165, 115274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askarpour, M.; Ghaedi, E.; Roshanravan, N.; Hadi, A.; Mohammadi, H.; Symonds, M.E.; Miraghajani, M. Policosanol supplementation significantly improves blood pressure among adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Complement. Ther. Med. 2019, 45, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olatunji, L.K.; Jimoh, A.O.; Tukur, U.M.; Imam, M.U. A review of the effects of policosanol on metabolic syndrome. Clin. Complement. Med. Pharmacol. 2022, 2, 100058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.L.; Xu, R.X.; Zhu, C.G.; Wu, N.Q.; Cui, Z.P.; Li, J.J. Policosanol attenuates statin-induced increases in serum proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 when combined with atorvastatin. Evid. Based Compl. Alt. 2014, 2014, 926087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.-Y.; Jiao, Q.-P.; Chen, S.-Y.; Sheng, J.; Jiang, H.; Lu, J.; Zheng, S.-B.; Fang, N.-Y. Efficacy and safety of policosanol plus fenofibrate combination therapy in elderly patients with mixed dyslipidemia: A randomized, controlled clinical study. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2018, 356, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanai, H.; Katsuyama, H.; Hamasaki, H.; Abe, S.; Tada, N.; Sako, A. Effects of dietary fat intake on HDL metabolism. J. Clin. Med. Res. 2015, 7, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, K.-H.; Kim, S.-J.; Yadav, D.; Kim, J.-Y.; Kim, J.-R. Consumption of Cuban policosanol improves blood pressure and lipid profile via enhancement of HDL functionality in healthy women subjects: Randomized, double-blinded, and placebo-controlled study. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 2018, 4809525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini, M.R.; Kazeminejad, S.; Jalalzadeh, M.; Majd, S.S.; Kavyani, Z.; Askari, G.; Hekmatdoost, A. The effects of policosanol supplementation on blood glucose: A systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2024, 212, 111709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stohs, S.J.; Miller, H.; Kaats, G.R. A review of the efficacy and safety of banaba (Lagerstroemia speciosa L.) and corosolic acid. Phytother. Res. 2012, 26, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousa, A.M.; El-Sammad, N.M.; Abdel-Halim, A.H.; Anwar, N.; Khalil, W.K.B.; Nawwar, M.; Hashim, A.N.; Elsayed, E.A.; Hassan, S.K. Lagerstroemia speciosa (L.) pers leaf extract attenuates lung tumorigenesis via alleviating oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, H.; Yuan, B.; Gothai, S.; Arulselvan, P.; Song, X.; Chen, L. Dietary triterpenes in the treatment of type 2 diabetes: To date. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 72, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, L.S.; Singh, W.S. Multifaceted therapeutic potential of corosolic acid: A novel bioactive compound. Obes. Med. 2024, 49, 100548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, K.-H.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, Y.; Bahuguna, A.; Kim, J.-E. Synergistic efficacy of policosanol (Raydel®) and banaba leaf extract to treat hyperglycemia and dyslipidemia in streptozotocin-induced diabetic and hyperlipidemic zebrafish (Danio rerio): Protection of liver and kidney with enhanced tissue regeneration. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patton, E.E.; Zon, L.I.; Langenau, D.M. Zebrafish disease models in drug discovery: From preclinical modelling to clinical trials. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2021, 20, 611–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, L.; Liu, C.; Miller, Y.I. Zebrafish models of dyslipidemia: Relevance to atherosclerosis and angiogenesis. Transl. Res. 2014, 163, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, S.; Zhang, W.; Jiang, L.; Wang, G.; Jeon, Y.; Ding, Y.; Li, Y. Protective effects of the secondary metabolites from Quercus salicina Blume against gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity in zebrafish (Danio rerio) model. Comp. Biochen. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2024, 283, 109952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brinza, I.; Boiangiu, R.S.; Honceriu, I.; Abd-Alkhalek, A.M.; Osman, S.M.; Eldahshan, O.A.; Todirascu-Ciornea, E.; Dumitru, G.; Hritcu, L. Neuroprotective potential of Origanum majorana L. Essential oil against Scopolamine-Induced memory deficits and oxidative stress in a zebrafish model. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhao, K.; Gao, L.; Zhao, J. Cholesterol-induced toxicity: An integrated view of the role of cholesterol in multiple diseases. Cell Metab. 2021, 33, 1911–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, P.; Lozano, P.; Ros, G.; Solano, F. Hyperglycemia and oxidative Stress: An integral, updated and critical overview of their metabolic interconnections. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Nan, F.; Liang, H.; Shu, P.; Fan, X.; Song, X.; Hou, Y.; Zhang, D. Excessive intake of sugar: An accomplice of inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 988481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azman, K.F.; Zakaria, R. D-Galactose-induced accelerated aging model: An overview. Biogerontology 2019, 20, 763–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, K.-H.; Nam, H.-S.; Kim, N.-Y.; Lee, M.-S.; Kang, D.-J. Combination therapy of Cuban policosanol (Raydel®, 20 mg) and intensive exercise for 12 Weeks resulted in improvements in obesity, Hypertension, and dyslipidemia without a decrease in serum coenzyme Q10: Enhancement of lipoproteins quality and antioxidant functionality in obese participants. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannarella, R.; Garofalo, V.; Calogero, A.E. Anti-dyslipidemic and anti-diabetic properties of corosolic acid: A narrative review. Endocrines 2023, 4, 616–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Jia, Y.; Thach, T.T.; Han, Y.; Kim, B.; Wu, C.; Kim, Y.; Seo, W.D.; Lee, S.J. Hexacosanol reduces plasma and hepatic cholesterol by activating AMP-activated protein kinase and suppression of sterol regulatory element-binding protein-2 in HepG2 and C57BL/6J mice. Nutr. Res. 2017, 43, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.-Y.; Kim, S.-M.; Kim, S.-J.; Lee, E.-Y.; Kim, J.-R.; Cho, K.-H. Consumption of policosanol enhances HDL functionality via CETP inhibition and reduces blood pressure and visceral fat in young and middle-aged subjects. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2017, 39, 889–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imerb, N.; Thonusin, C.; Pratchayasakul, W.; Arunsak, B.; Nawara, W.; Ongnok, B.; Aeimlapa, R.; Charoenphandhu, N.; Chattipakorn, N.; Chattipakorn, S.C. D-galactose-induced aging aggravates obesity-induced bone dyshomeostasis. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 8580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajaj, S.; Khan, A. Antioxidants and diabetes. Indian J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 16, S267–S271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Leng, J.; Li, J.J.; Tang, J.F.; Li, Y.; Liu, B.L.; Wen, X.D. Corosolic acid inhibits adipose tissue inflammation and ameliorates insulin resistance via AMPK activation in high-fat fed mice. Phytomedicine 2016, 23, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ottum, M.S.; Mistry, A.M. Advanced glycation end products: Modifiable environmental factors profoundly mediate insulin resistance. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2015, 57, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pareek, A.; Suthar, M.; Rathore, G.S.; Bansal, V.; Kumawat, T. In vitro antioxidant studies of Lagerstroemia speciosa leaves. Pharmacogn. J. 2010, 2, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tidke, P.S.; Patil, C.R. Nrf2 activator corosolic acid meliorates alloxan induced diabetic nephropathy in mice. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2017, 7, 797–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, X.; Xiong, X.; Zhu, H.; Chen, R.; Zhang, S.; Chen, G.; Jian, Z. Nrf2 regulates oxidative stress and Its role in cerebral ischemic stroke. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, K.-H.; Kim, J.-E.; Nam, H.-S.; Kang, D.-J.; Baek, S.-H. Comparison of policosanols via incorporation into reconstituted high-density lipoproteins: Cuban policosanol (Raydel®) exerts the highest antioxidant, anti-glycation, and anti-inflammatory activity. Molecules 2023, 28, 6715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Cui, R.; Zhao, J.; Mo, R.; Peng, L.; Yan, M. Corosolic acid protects hepatocytes against ethanol-induced damage by modulating mitogen-activated protein kinases and activating autophagy. Eur. J. Pharm. 2016, 791, 578–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nousis, L.; Kanavaros, P.; Barbouti, A. Oxidative stress-induced cellular senescence: Is labile iron the connecting link? Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahadevan, M.; Kasiske, B.L. Hyperlipidemia in kidney disease causes and consequences. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2002, 11, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çiftci, G.; Tuna, E. Effects of cholesterol and Lactobacillus acidophilus on testicular function. Clin. Exp. Reprod. Med. 2021, 48, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.-Y.; Chang, T.-C.; Lin, S.-H.; Wu, S.-T.; Cha, T.-L.; Tsao, C.-W. Metformin ameliorates testicular function and spermatogenesis in male mice with high-fat and high-cholesterol diet-induced obesity. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, L.; Lin, L.; Xiao, W.; Li, Y. L-theanine protects rat kidney from D-galactose-induced injury via inhibition of the AGEs/RAGE signaling pathway. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2022, 927, 175072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Yang, C.Y.; Zhang, M.; Lu, X.M.; Cao, W.S.; Xie, C.F.; Li, X.T.; Wu, J.S.; Zhong, C.Y.; Geng, S.S. Protective effects of ginseng stem-leaf saponins on D-galactose-induced reproductive injury in male mice. Aging 2021, 13, 8916–8928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salman, T.M.; Olayaki, L.A.; Alagbonsi, I.A.; Oyewopo, A.O. Spermatotoxic effects of galactose and possible mechanisms of action. Middle East Fertil. Soc. J. 2016, 21, 2–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamagishi, S.; Matsui, T. Advanced glycation end products, oxidative stress and diabetic nephropathy. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2010, 3, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Yu, Y.H.; Wang, S.T.; Ren, J.; Camer, D.; Hua, Y.Z.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, J.; Xue, D.L.; Zhang, X.F.; et al. Chlorogenic acid protects D-galactose-induced liver and kidney injury via antioxidation and anti-inflammation effects in mice. Pharm. Biol. 2016, 54, 1027–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoshdel, F.; Golmohammadi, M.G.; Dost, M.J.; Najafzade, N.; Salimnejad, R. Impact of caffeic acid on the testicular damages in D-galactose-induced aging model in mice. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2022, 25, 1190–1195. [Google Scholar]
- Pandey, A.K.; Gupta, A.; Tiwari, M.; Prasad, S.; Pandey, A.N.; Yadav, P.K.; Sharma, A.; Sahu, K.; Asrafuzzaman, S.; Vengayil, D.T.; et al. Impact of stress on female reproductive health disorders: Possible beneficial effects of shatavari (Asparagus racemosus). Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 103, 46–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, K.-H.; Nam, H.-S.; Baek, S.-H.; Kang, D.-J.; Na, H.; Komatsu, T.; Uehara, Y. Beneficial effect of Cuban policosanol on blood pressure and serum lipoproteins accompanied with lowered glycated hemoglobin and enhanced high-density lipoprotein functionalities in a randomized, placebo-controlled, and double-blinded trial with healthy Japanese. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5185. [Google Scholar]
- Yaffe, K.; Lindquist, K.; Schwartz, A.V.; Vitartas, C.; Vittinghoff, E.; Satterfield, S.; Simonsick, E.M.; Launer, L.; Rosano, C.; Cauley, J.A.; et al. Advanced glycation end product level, diabetes, and accelerated cognitive aging. Neurology 2011, 77, 1351–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Cunha, N.M.; Sergi, D.; Lane, M.M.; Naumovski, N.; Gamage, E.; Rajendran, A.; Kouvari, M.; Gauci, S.; Dissanayka, T.; Marx, W.; et al. The effects of dietary advanced glycation end-products on neurocognitive and mental disorders. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Budni, J.; Pacheco, R.; da Silva, S.; Garcez, M.L.; Mina, F.; Bellettini-Santos, T.; de Medeiros, J.; Voss, B.C.; Steckert, A.V.; Valvassori, S.d.S.; et al. Oral administration of D-galactose induces cognitive impairments and oxidative damage in rats. Behav. Brain Res. 2016, 302, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Yang, H.; Huo, L.; Gao, J.; Chen, H.; Gao, W. Protective effect of tetrahydropalmatine against d-galactose induced memory impairment in rat. Physiol. Behav. 2016, 154, 114–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.-X.; Li, H.-Y.; Li, Y.-Q.; Kong, L.-D. Can medicinal plants and bioactive compounds combat lipid peroxidation product 4-HNE-induced deleterious effects? Biomolecules 2020, 10, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, M.; Man, S.; Sun, B.; Ma, L.; Guo, L.; Huang, L.; Gao, W. Gut liver brain axis in diseases: The implications for therapeutic interventions. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, A.S.; Cordeiro, T.M.; Dos Santos Lacerda Soares, T.M.; Ferreira, R.N.; Simões e Silva, A.C. Kidney-brain axis inflammatory crosstalk: From bench to bedside. Clin. Sci. 2017, 131, 1093–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, K.-H.; Kim, J.-E.; Bahuguna, A.; Kang, D.-J. Long-term supplementation of ozonated sunflower oil improves dyslipidemia and hepatic inflammation in hyperlipidemic zebrafish: Suppression of oxidative stress and inflammation against carboxymethyllysine toxicity. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, K.-H.; Kim, J.-E.; Lee, M.-S.; Bahuguna, A. Oral supplementation of ozonated sunflower oil augments plasma antioxidant and anti-Inflammatory abilities with enhancement of high-density lipoproteins functionality in rats. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, A.H.; Jacobson, K.A.; Rose, J.; Zeller, R. Hematoxylin and eosin staining of tissue and cell sections. Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2008, 2008, pdb-prot4986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shull, L.C.; Sen, R.; Menzel, J.; Goyama, S.; Kurokawa, M.; Artinger, K.B. The conserved and divergent roles of Prdm3 and Prdm16 in zebrafish and mouse craniofacial development. Dev. Biol. 2020, 461, 132–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, K.-H.; Bahuguna, A.; Kang, D.-J.; Kim, J.-E. Prolonged supplementation of ozonated sunflower oil bestows an antiaging effect, improves blood lipid profile and spinal deformities, and protects vital organs of zebrafish (Danio rerio) against age-related degeneration: Two-years consumption study. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cho, K.-H.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, Y.; Bahuguna, A.; Kim, J.-E.; Jeon, C. Co-Supplementation of Policosanol and Banaba Leaf Extract Exhibited a Cooperative Effect Against Hyperglycemia and Dyslipidemia in Zebrafish: Highlighting Vital Organ Protection Against High-Cholesterol and High-Galactose Diet. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 7669. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167669
Cho K-H, Lee SH, Lee Y, Bahuguna A, Kim J-E, Jeon C. Co-Supplementation of Policosanol and Banaba Leaf Extract Exhibited a Cooperative Effect Against Hyperglycemia and Dyslipidemia in Zebrafish: Highlighting Vital Organ Protection Against High-Cholesterol and High-Galactose Diet. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(16):7669. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167669
Chicago/Turabian StyleCho, Kyung-Hyun, Sang Hyuk Lee, Yunki Lee, Ashutosh Bahuguna, Ji-Eun Kim, and Cheolmin Jeon. 2025. "Co-Supplementation of Policosanol and Banaba Leaf Extract Exhibited a Cooperative Effect Against Hyperglycemia and Dyslipidemia in Zebrafish: Highlighting Vital Organ Protection Against High-Cholesterol and High-Galactose Diet" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 16: 7669. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167669
APA StyleCho, K.-H., Lee, S. H., Lee, Y., Bahuguna, A., Kim, J.-E., & Jeon, C. (2025). Co-Supplementation of Policosanol and Banaba Leaf Extract Exhibited a Cooperative Effect Against Hyperglycemia and Dyslipidemia in Zebrafish: Highlighting Vital Organ Protection Against High-Cholesterol and High-Galactose Diet. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(16), 7669. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167669






