Strengthening the Role of PSMC5 as a Potential Gene Associated with Neurodevelopmental Disorders
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
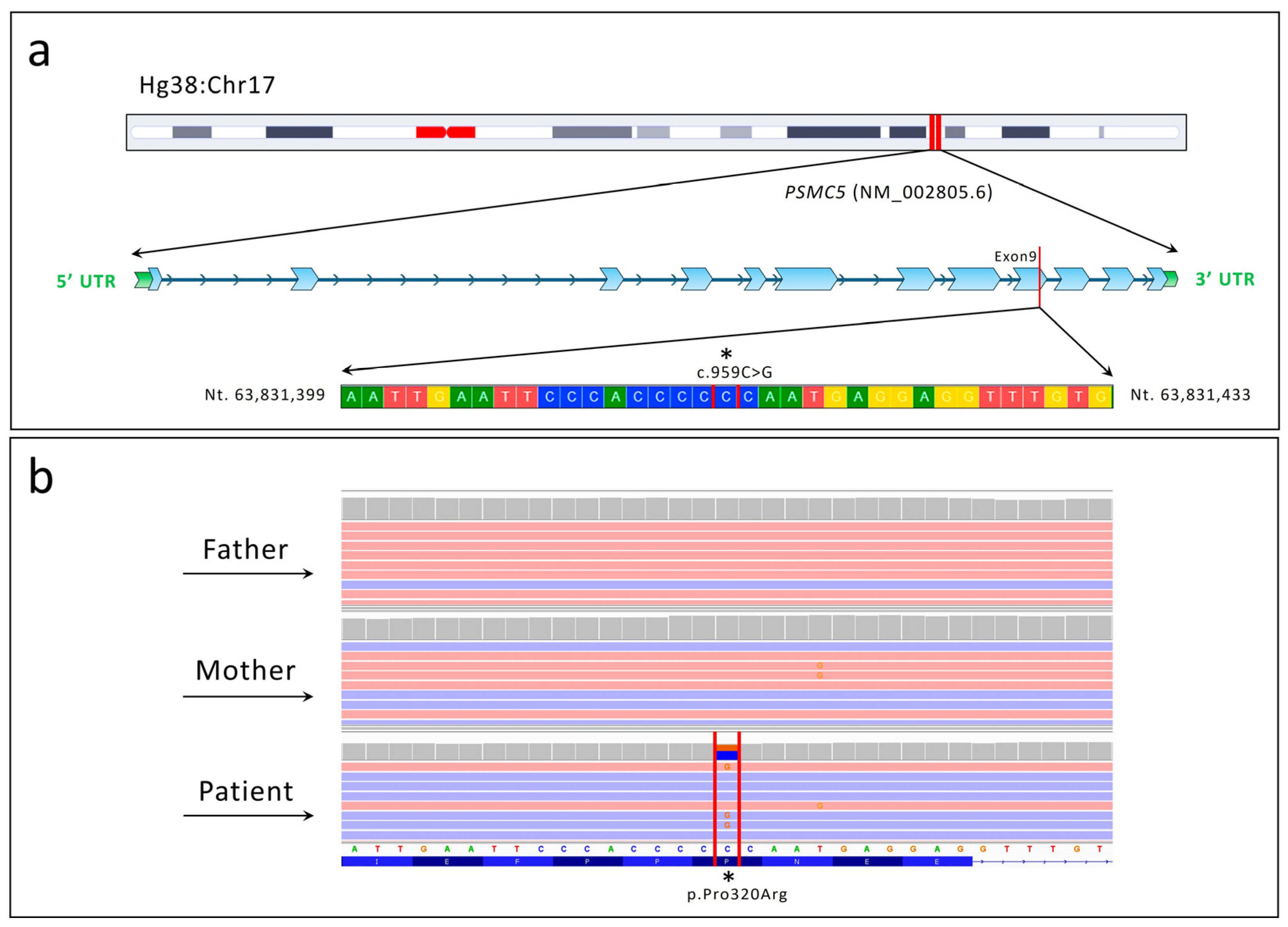
2.1. Clinical Report
2.2. Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS)
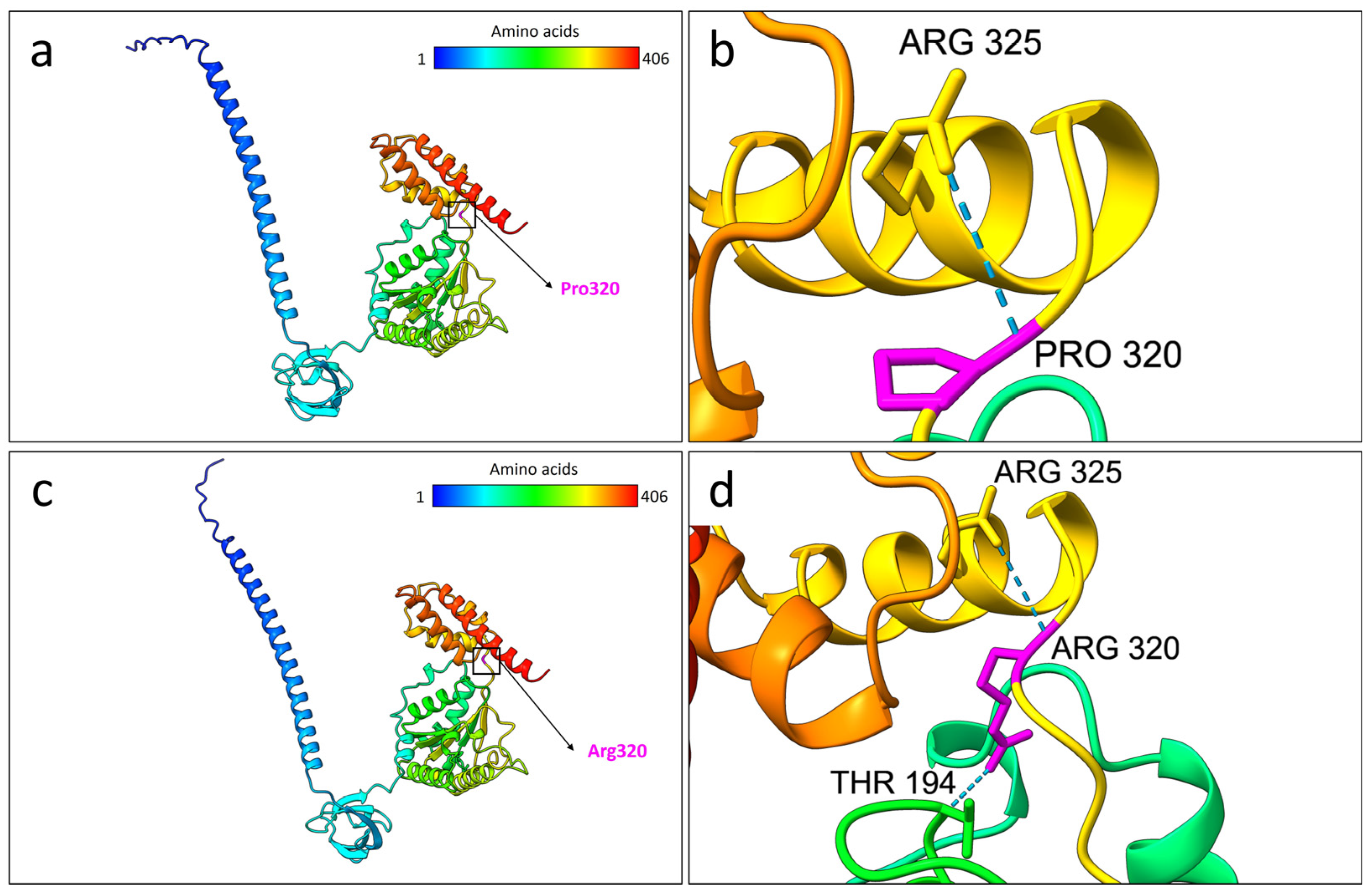
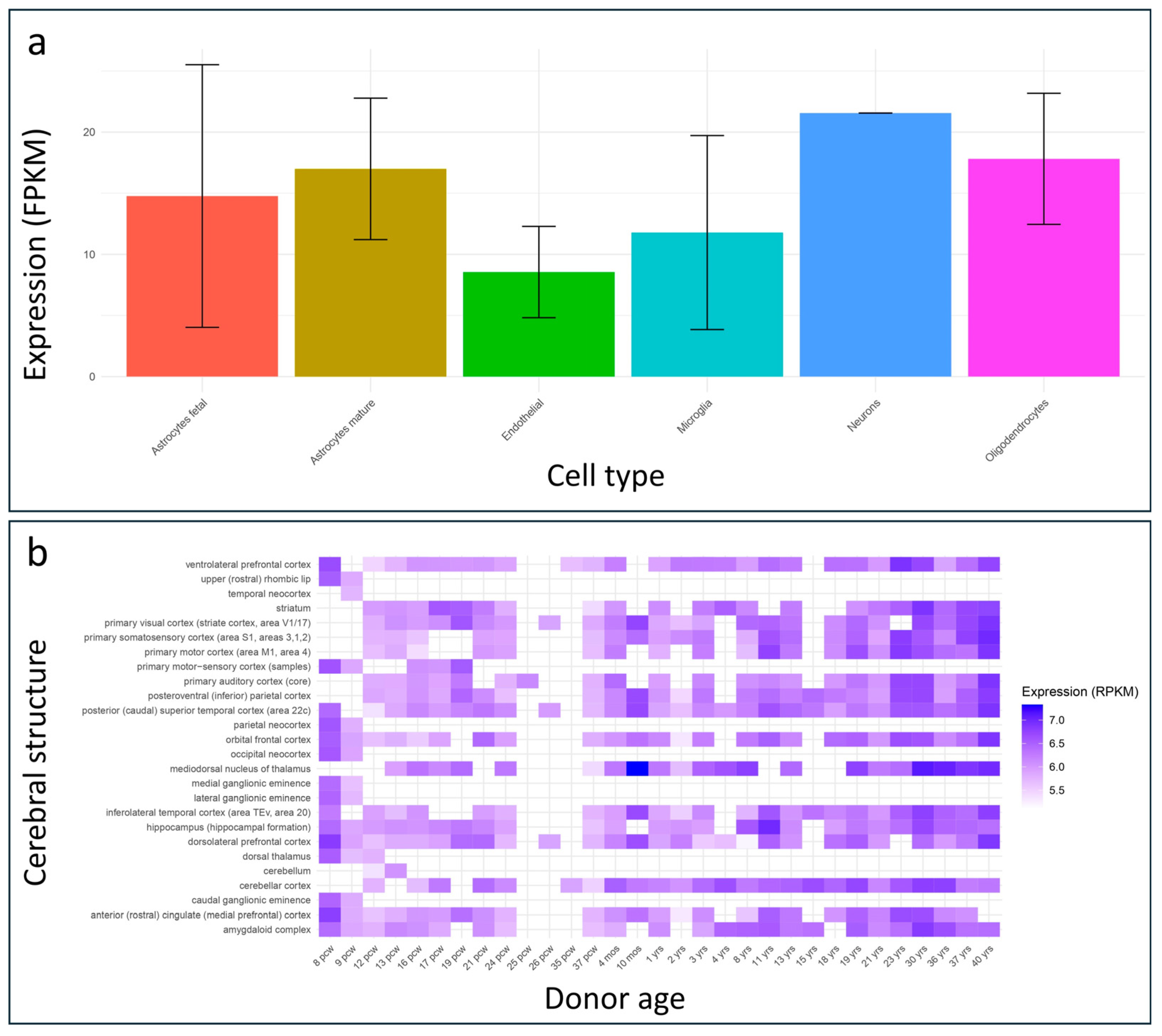
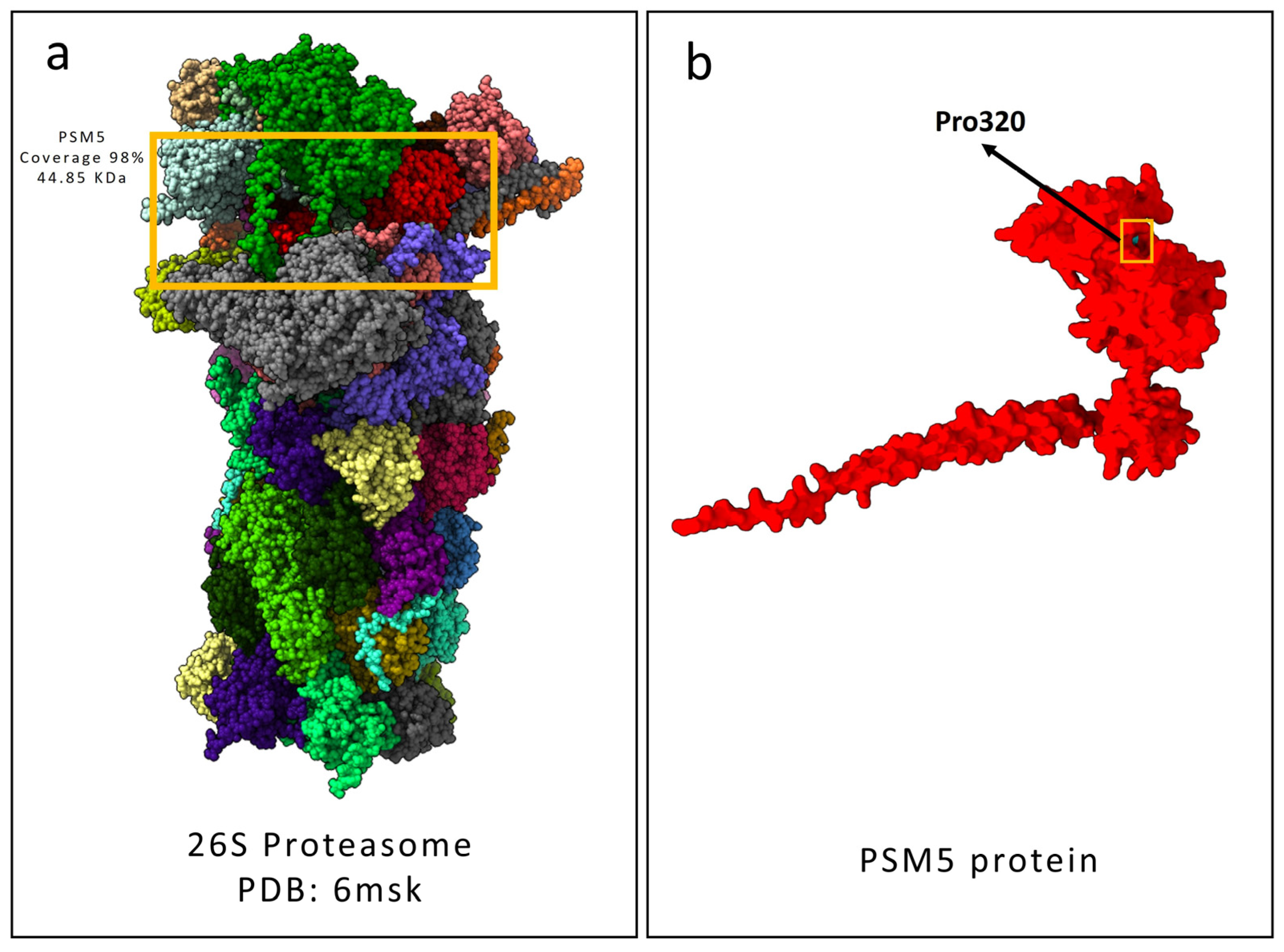
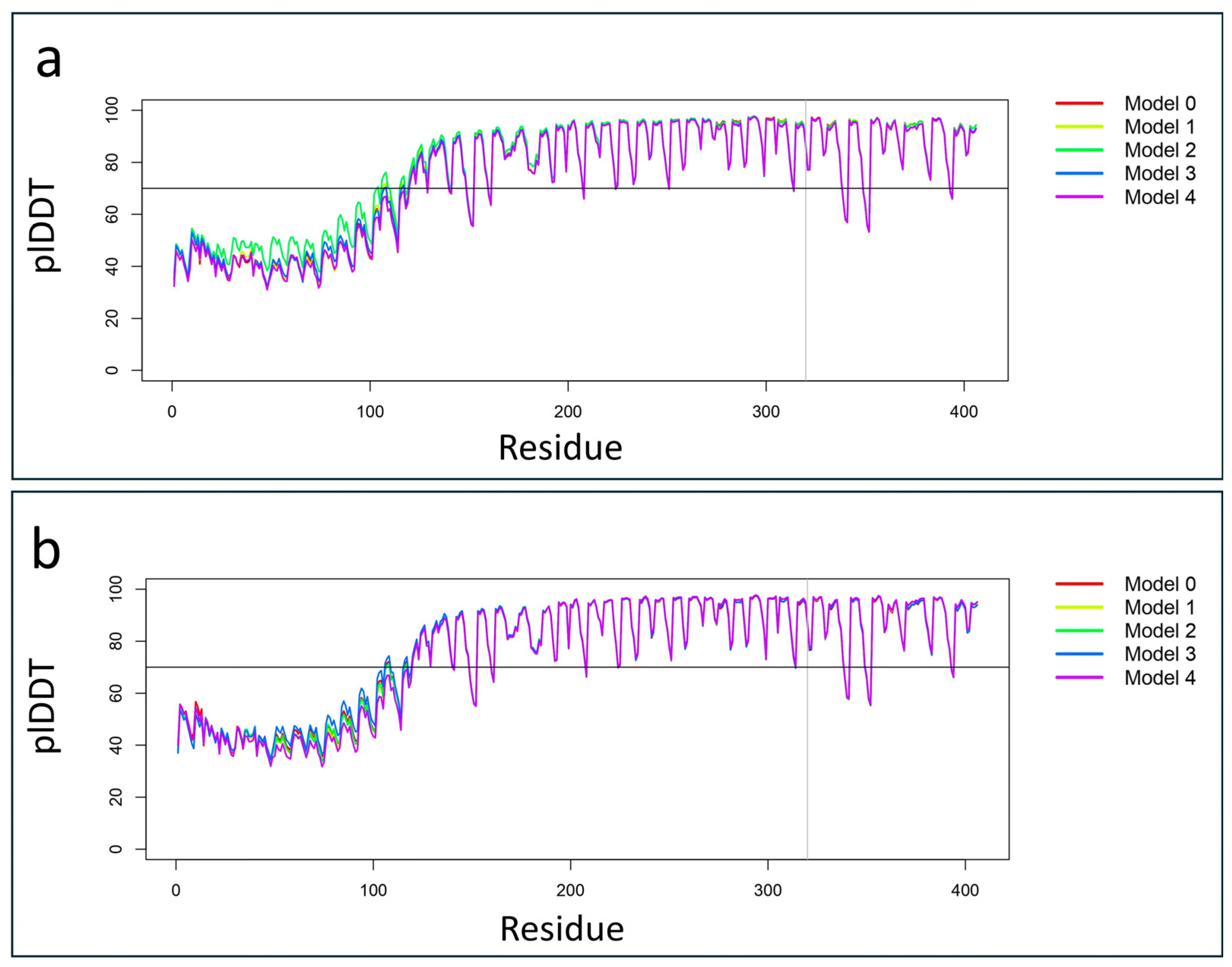
2.3. Protein Structural Prediction
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Library Preparation and WES Analysis
4.2. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACMG | American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics |
| ASD | Autism spectrum disorder |
| IGV | Integrated genomics viewer |
| MAF | Minor allele frequency |
| NGS | Next-generation sequencing |
| SFARI | Simons Foundation Autism Research Initiative |
| VUS | Variant of uncertain significance |
References
- Bard, J.A.M.; Goodall, E.A.; Greene, E.R.; Jonsson, E.; Dong, K.C.; Martin, A. Structure and Function of the 26S Proteasome. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2018, 87, 697–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, M.; Zhao, X.; Sahara, K.; Ohte, Y.; Hirano, Y.; Kaneko, T.; Yashiroda, H.; Murata, S. Assembly Mechanisms of Specialized Core Particles of the Proteasome. Biomolecules 2014, 4, 662–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahu, I.; Glickman, M.H. Proteasome in Action: Substrate Degradation by the 26S Proteasome. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2021, 49, 629–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bedford, L.; Paine, S.; Sheppard, P.W.; Mayer, R.J.; Roelofs, J. Assembly, Structure, and Function of the 26S Proteasome. Trends Cell Biol. 2010, 20, 391–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papendorf, J.J.; Ebstein, F.; Alehashemi, S.; Piotto, D.G.P.; Kozlova, A.; Terreri, M.T.; Shcherbina, A.; Rastegar, A.; Rodrigues, M.; Pereira, R.; et al. Identification of Eight Novel Proteasome Variants in Five Unrelated Cases of Proteasome-Associated Autoinflammatory Syndromes (PRAAS). Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1190104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuinat, S.; Bézieau, S.; Deb, W.; Mercier, S.; Vignard, V.; Isidor, B.; Küry, S.; Ebstein, F. Understanding Neurodevelopmental Proteasomopathies as New Rare Disease Entities: A Review of Current Concepts, Molecular Biomarkers, and Perspectives. Genes Dis. 2024, 11, 101130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Küry, S.; Stanton, J.E.; van Woerden, G.; Hsieh, T.-C.; Rosenfelt, C.; Scott-Boyer, M.P.; Most, V.; Wang, T.; Papendorf, J.J.; de Konink, C.; et al. Unveiling the Crucial Neuronal Role of the Proteasomal ATPase Subunit Gene PSMC5 in Neurodevelopmental Proteasomopathies. medRxiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galperin, E.; Jang, E.R.; Anderson, D.; Jang, H. The (AAA+) ATPases PSMC5 and VCP/P97 Control ERK1/2 Signals Transmitted through the Shoc2 Scaffolding Complex. FASEB J. 2017, 31, 930.1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, E.R.; Jang, H.; Shi, P.; Popa, G.; Jeoung, M.; Galperin, E. Spatial Control of Shoc2 Scaffold-Mediated ERK1/2 Signaling Requires Remodeling Activity of the ATPase PSMC5. J. Cell Sci. 2015, 128, 4428–4441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoyle, J.; Tan, K.H.; Fisher, E.M.C. Localization of Genes Encoding Two Human One-Domain Members of the AAA Family: PSMC5 (the Thyroid Hormone Receptor-Interacting Protein, TRIP1) and PSMC3 (the Tat-Binding Protein, TBP1). Hum. Genet. 1997, 99, 285–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, W.; Bao, K.; Zhou, X.; Deng, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, J.; Lan, X.; Zhao, J.; Lu, D.; Xu, Y.; et al. PSMC5 Regulates Microglial Polarization and Activation in LPS-Induced Cognitive Deficits and Motor Impairments by Interacting with TLR4. J. Neuroinflamm. 2023, 20, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.-Q.; Carmichael, J.; Collins, G.A.; D’Agostino, M.D.; Lessard, M.; Firth, H.V.; Harijan, P.; Fry, A.E.; Dean, J.; Zhang, J.; et al. PSMC5 Insufficiency and P320R Mutation Impair Proteasome Function. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2024, 33, 1506–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferguson, B.R.; Gao, W.-J. Development of Thalamocortical Connections between the Mediodorsal Thalamus and the Prefrontal Cortex and Its Implication in Cognition. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2015, 8, 1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouhaz, Z.; Fleming, H.; Mitchell, A.S. Cognitive Functions and Neurodevelopmental Disorders Involving the Prefrontal Cortex and Mediodorsal Thalamus. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sihn, C.-R.; Cho, S.Y.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, T.R.; Kim, S.H. Mouse Homologue of Yeast Prp19 Interacts with Mouse SUG1, the Regulatory Subunit of 26S Proteasome. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 356, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Wang, Q.; Bayat, A.; Battig, M.R.; Zhou, Y.; Bosch, D.G.M.; van Haaften, G.; Granger, L.; Petersen, A.K.; Pérez-Jurado, L.A.; et al. Spliceosome Malfunction Causes Neurodevelopmental Disorders with Overlapping Features. J. Clin. Investig. 2024, 134, e171235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budny, B.; Szczepanek-Parulska, E.; Zemojtel, T.; Szaflarski, W.; Rydzanicz, M.; Wesoly, J.; Handschuh, L.; Wolinski, K.; Piatek, K.; Niedziela, M.; et al. Mutations in Proteasome-Related Genes Are Associated with Thyroid Hemiagenesis. Endocrine 2017, 56, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnard, J.C.; Williams, A.J.; Rabier, B.; Chassande, O.; Samarut, J.; Cheng, S.; Bassett, J.H.D.; Williams, G.R. Thyroid Hormones Regulate Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor Signaling during Chondrogenesis. Endocrinology 2005, 146, 5568–5580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, D.A.; Harvey, C.B.; Scott, A.J.; O’Shea, P.J.; Barnard, J.C.; Williams, A.J.; Brady, G.; Samarut, J.; Chassande, O.; Williams, G.R. Thyroid Hormone Activates Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor-1 in Bone. Mol. Endocrinol. 2003, 17, 1751–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Shea, P.J.; Guigon, C.J.; Williams, G.R.; Cheng, S. Regulation of Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor-1 (Fgfr1) by Thyroid Hormone: Identification of a Thyroid Hormone Response Element in the Murine Fgfr1 Promoter. Endocrinology 2007, 148, 5966–5976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musumeci, A.; Vinci, M.; Treccarichi, S.; Greco, D.; Rizzo, B.; Gloria, A.; Federico, C.; Saccone, S.; Musumeci, S.A.; Calì, F. Potential Association of the CSMD1 Gene with Moderate Intellectual Disability, Anxiety Disorder, and Obsessive–Compulsive Personality Traits. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richards, S.; Aziz, N.; Bale, S.; Bick, D.; Das, S.; Gastier-Foster, J.; Grody, W.W.; Hegde, M.; Lyon, E.; Spector, E.; et al. Standards and Guidelines for the Interpretation of Sequence Variants: A Joint Consensus Recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet. Med. 2015, 17, 405–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopanos, C.; Tsiolkas, V.; Kouris, A.; Chapple, C.E.; Albarca Aguilera, M.; Meyer, R.; Massouras, A. VarSome: The Human Genomic Variant Search Engine. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 1978–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Tool | Prediction | Score |
|---|---|---|
| BayesDel addAF | Pathogenic Strong | 0.468 |
| MetaRNN | Pathogenic Strong | 0.977 |
| BayesDel noAF | Pathogenic Moderate | 0.434 |
| MetaSVM | Pathogenic Moderate | 0.928 |
| REVEL | Pathogenic Moderate | 0.917 |
| MetaLR | Pathogenic Supporting | 0.835 |
| AlphaMissense | Pathogenic Strong | 0.996 |
| EIGEN | Pathogenic Strong | 1.070 |
| EIGEN PC | Pathogenic Moderate | 0.965 |
| FATHMM-XF | Pathogenic Moderate | 0.963 |
| Mutation assessor | Pathogenic Moderate | 4.180 |
| MutPred | Pathogenic Moderate | 0.858 |
| PrimateAI | Pathogenic Moderate | 0.898 |
| PROVEAN | Pathogenic Moderate | −8.170 |
| FATHMM-MKL | Pathogenic Supporting | 0.992 |
| LIST-S2 | Pathogenic Supporting | 0.979 |
| LRT | Pathogenic Supporting | 0.000 |
| M-CAP | Pathogenic Supporting | 0.583 |
| SIFT | Pathogenic Supporting | 0.000 |
| SIFT4G | Pathogenic Supporting | 0.000 |
| BLOSUM | Uncertain | −5.000 |
| DANN | Uncertain | 0.998 |
| DEOGEN2 | Uncertain | 0.788 |
| FATHMM | Uncertain | −1.650 |
| MutationTaster | Pathogenic | 1.000 |
| MVP | Uncertain | 0.896 |
| Donor Residue | Donor Atom | Acceptor Residue | Acceptor Atom | Distance (Å) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gly17 | N | Gly14 | O | 3.49 |
| Ser26 | OG | Gln22 | O | 3.44 |
| Ser26 | OG | Tyr23 | O | 2.78 |
| Gln40 | N | Asn36 | O | 2.94 |
| Arg49 | NE | Asn50 | OD1 | 3.51 |
| Glu68 | N | Leu65 | O | 3.35 |
| Tyr72 | OH | Asn118 | OD1 | 3.40 |
| Lys101 | N | Asp100 | OD1 | 2.70 |
| Ser120 | OG | Asp119 | OD1 | 3.09 |
| Tyr121 | OH | Glu92 | OE2 | 3.21 |
| His171 | ND1 | Glu173 | OE1 | 2.96 |
| Glu173 | N | Glu173 | OE2 | 2.76 |
| Arg232 | NE | Ala228 | O | 3.35 |
| Gly265 | N | Ser263 | O | 2.78 |
| Ser267 | OG | Gly264 | O | 2.92 |
| Arg297 | NE | Asp299 | OD1 | 3.56 |
| Ser303 | OG | Asp302 | OD1 | 3.56 |
| Leu306 | N | Ser303 | O | 3.22 |
| Arg325 | NH1 | Pro320 | O | 2.93 |
| Asn343 | N | Gln380 | OE1 | 3.00 |
| Ser355 | OG | Glu358 | OE1 | 2.89 |
| Ser400 | OG | Glu396 | O | 2.94 |
| Lys403 | N | Met399 | O | 3.16 |
| Donor Residue | Donor Atom | Acceptor Residue | Acceptor Atom | Distance (Å) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glu13 | N | Leu11 | O | 2.80 |
| Ser18 | OG | Lys15 | O | 3.07 |
| Glu68 | N | Gln64 | O | 3.22 |
| Asn106 | N | Asp104 | OD1 | 3.06 |
| Asn118 | ND2 | Gln69 | OE1 | 3.31 |
| Asn129 | ND2 | Glu240 | OE1 | 2.65 |
| Asp132 | N | Glu233 | OE2 | 3.35 |
| Ser136 | OG | Asp132 | O | 3.45 |
| Val140 | N | Leu137 | O | 3.52 |
| Arg201 | NE | Glu141 | OE2 | 2.99 |
| His241 | ND1 | Met237 | O | 3.06 |
| Asp266 | N | Ser263 | O | 2.90 |
| Val269 | N | Gly265 | O | 3.36 |
| Phe283 | N | Gln279 | O | 3.28 |
| Arg320 | NH2 | Thr194 | O | 2.19 |
| Ala324 | N | Asn321 | OD1 | 2.82 |
| Arg325 | NH1 | Arg320 | O | 2.81 |
| Arg375 | NH1 | His377 | O | 2.92 |
| Asp394 | N | Val390 | O | 3.43 |
| Ser395 | OG | Gln392 | O | 2.68 |
| Ser400 | OG | Lys397 | O | 2.81 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vinci, M.; Musumeci, A.; Papa, C.; Ragalmuto, A.; Saccone, S.; Federico, C.; Greco, D.; Greco, V.; Calì, F.; Treccarichi, S. Strengthening the Role of PSMC5 as a Potential Gene Associated with Neurodevelopmental Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6386. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136386
Vinci M, Musumeci A, Papa C, Ragalmuto A, Saccone S, Federico C, Greco D, Greco V, Calì F, Treccarichi S. Strengthening the Role of PSMC5 as a Potential Gene Associated with Neurodevelopmental Disorders. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(13):6386. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136386
Chicago/Turabian StyleVinci, Mirella, Antonino Musumeci, Carla Papa, Alda Ragalmuto, Salvatore Saccone, Concetta Federico, Donatella Greco, Vittoria Greco, Francesco Calì, and Simone Treccarichi. 2025. "Strengthening the Role of PSMC5 as a Potential Gene Associated with Neurodevelopmental Disorders" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 13: 6386. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136386
APA StyleVinci, M., Musumeci, A., Papa, C., Ragalmuto, A., Saccone, S., Federico, C., Greco, D., Greco, V., Calì, F., & Treccarichi, S. (2025). Strengthening the Role of PSMC5 as a Potential Gene Associated with Neurodevelopmental Disorders. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(13), 6386. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136386








