Relationship Between Obesity and Depression Considering the Inflammatory Theory
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
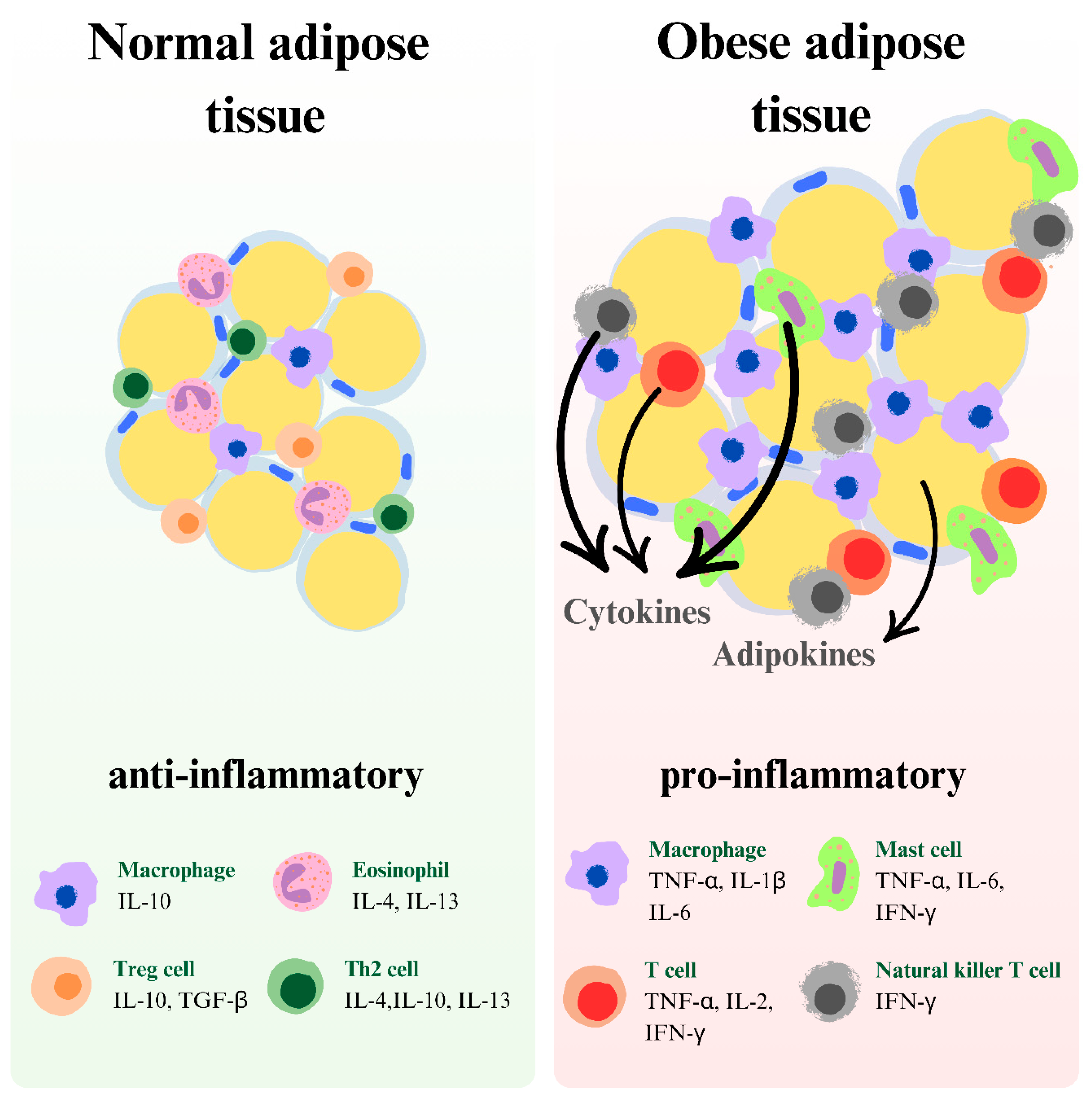
3. Obesity: Causes and Link to Depression
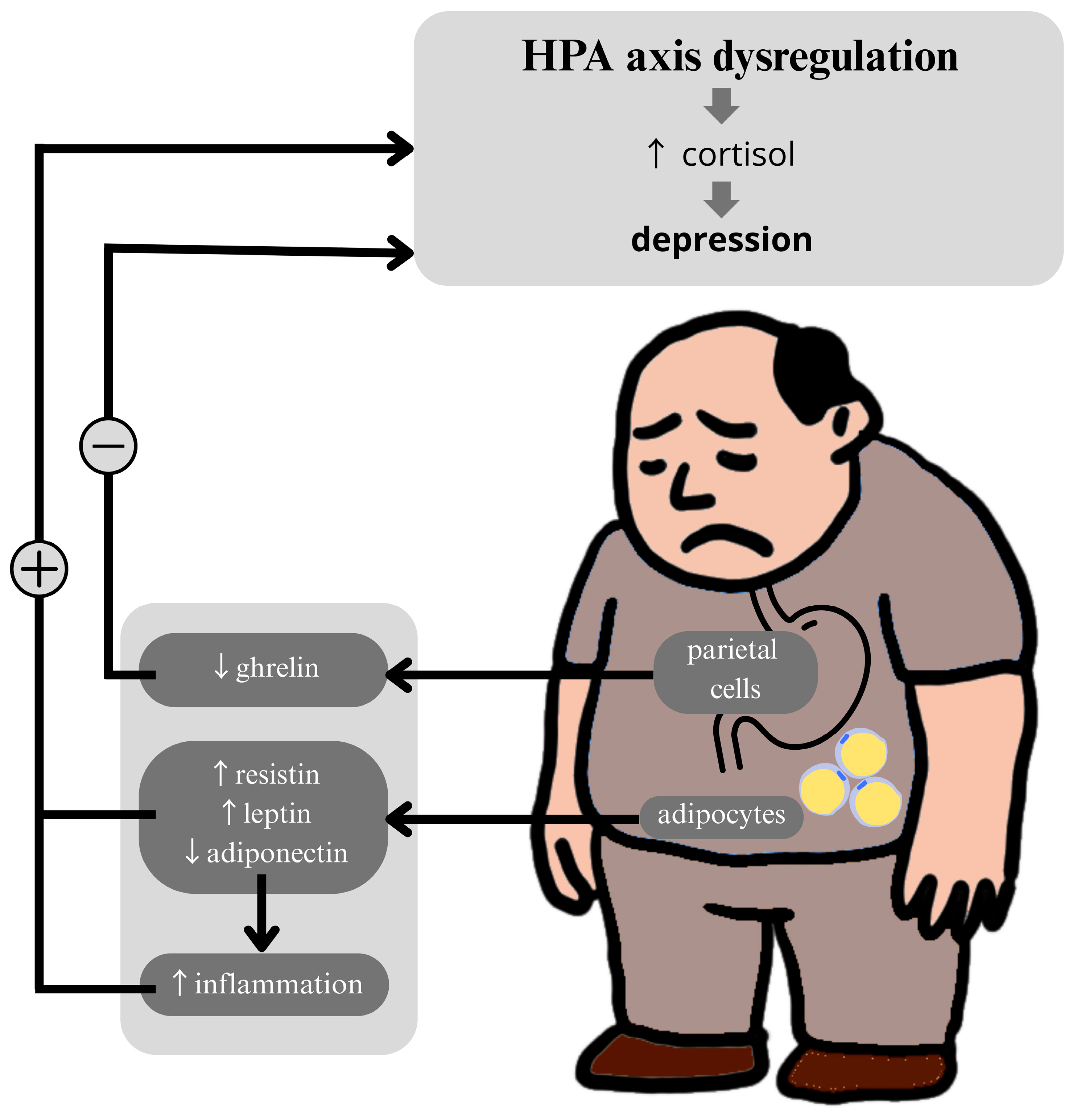
4. Metabolic Biomarkers and the HPA Axis
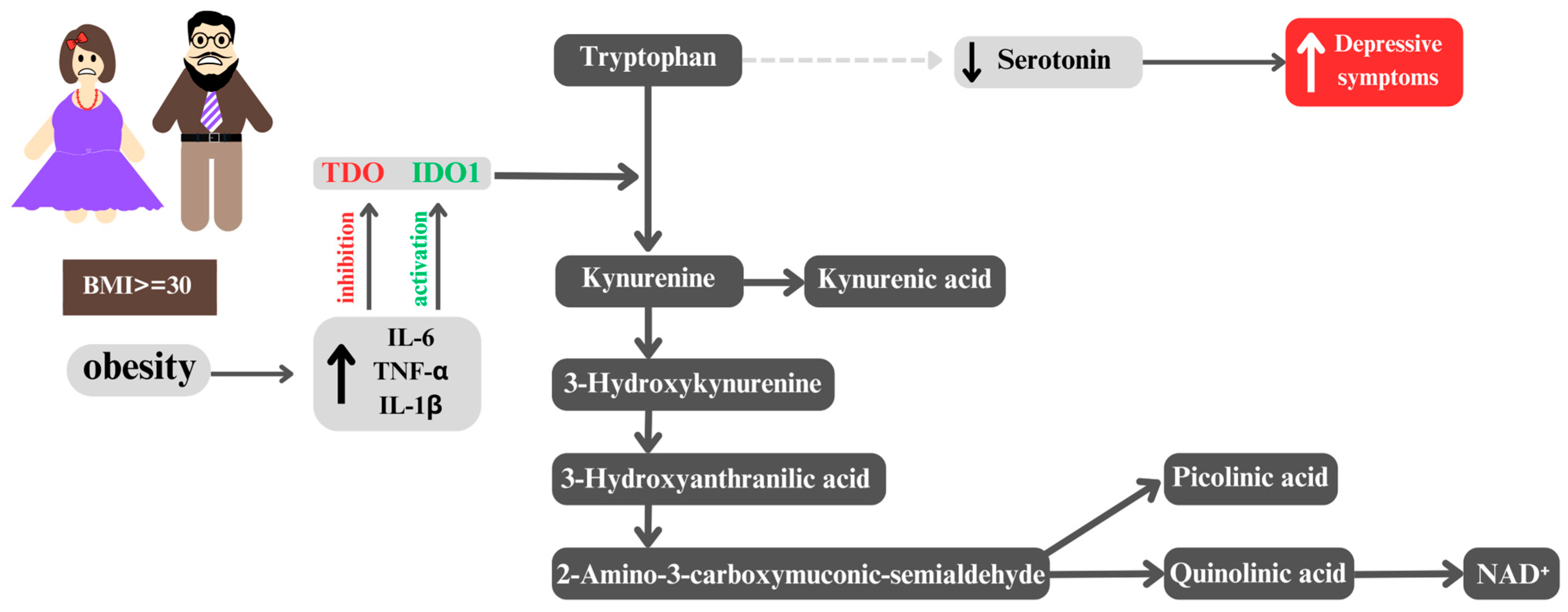
5. From Obesity to Depression: The Role of the Kynurenine Pathway
6. Metabolic Biomarkers of Depression and Obesity
6.1. Leptin
6.2. Adiponectin
6.3. Resistin
6.4. Fetuin-A
6.5. Ghrelin
6.6. Fibroblast Growth Factor 1
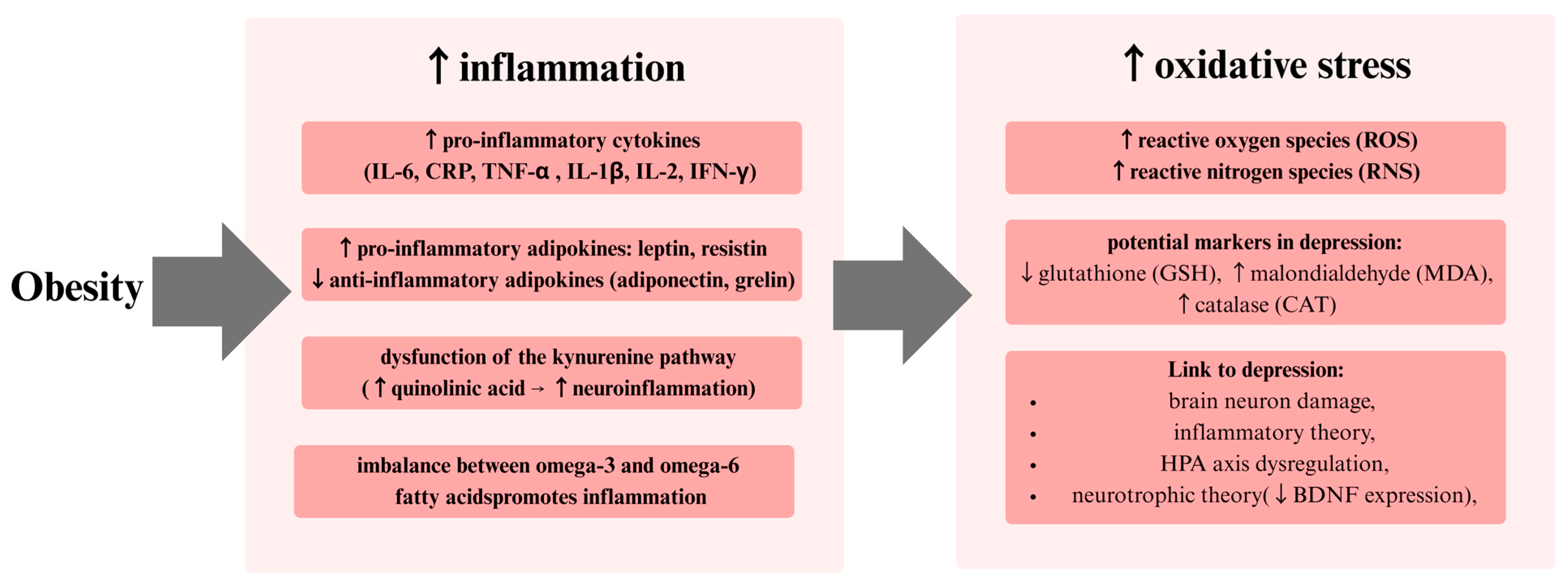
7. Inflammatory Model of Depression
8. Oxidative Stress
9. Fatty Acids and Cholesterol
10. GABAergic System
11. Limitations
12. Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ng, M.; Gakidou, E.; Lo, J.; Abate, Y.H.; Abbafati, C.; Abbas, N.; Abbasian, M.; Abd ElHafeez, S.; Abdel-Rahman, W.M.; Abd-Elsalam, S.; et al. Global, Regional, and National Prevalence of Adult Overweight and Obesity, 1990–2021, with Forecasts to 2050: A Forecasting Study for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet 2025, 405, 813–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobson, K.G.; Vigod, S.N.; Mustard, C.; Smith, P.M. Trends in the Prevalence of Depression and Anxiety Disorders among Canadian Working-Age Adults between 2000 and 2016. Health Rep. 2020, 31, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira-Miranda, E.; Costa, P.R.F.; Queiroz, V.A.O.; Pereira-Santos, M.; Santana, M.L.P. Overweight and Obesity Associated with Higher Depression Prevalence in Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2017, 36, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bains, N.; Abdijadid, S. Major Depressive Disorder. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Christoffel, D.J.; Golden, S.A.; Russo, S.J. Structural and Synaptic Plasticity in Stress-Related Disorders. Rev. Neurosci. 2011, 22, 535–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amerikanou, C.; Valsamidou, E.; Kleftaki, S.A.; Gioxari, A.; Koutoulogenis, K.; Aroutiounova, M.; Stergiou, I.; Kaliora, A.C. Peripheral Inflammation Is Linked with Emotion and Mental Health in People with Obesity. A “Head to Toe” Observational Study. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1197648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelton, R.C.; Miller, A.H. Inflammation in Depression: Is Adiposity a Cause? Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 2011, 13, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gałecki, P.; Talarowska, M. Inflammatory Theory of Depression. Psychiatr. Pol. 2018, 52, 437–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Obesity and Overweight. WHO Fact Sheets 2024. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight (accessed on 18 April 2025).
- Sweatt, K.; Garvey, W.T.; Martins, C. Strengths and Limitations of BMI in the Diagnosis of Obesity: What is the Path Forward? Curr. Obes. Rep. 2024, 13, 584–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westbury, S.; Oyebode, O.; van Rens, T.; Barber, T.M. Obesity Stigma: Causes, Consequences, and Potential Solutions. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2023, 12, 10–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, S.M.; Aronne, L.J. Causes of obesity. Abdom. Radiol. 2012, 37, 730–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redinger, R.N. The Prevalence and Etiology of Nongenetic Obesity and Associated Disorders. South. Med. J. 2008, 101, 395–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinlen, D.; Cody, D.; O’Shea, D. Complications of obesity. QJM Int. J. Med. 2018, 111, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.Y. The Leptin Hypothesis of Depression: A Potential Link between Mood Disorders and Obesity? Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2007, 7, 648–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papargyri, P.; Zapanti, E.; Salakos, N.; Papargyris, L.; Bargiota, A.; Mastorakos, G. Links between HPA Axis and Adipokines: Clinical Implications in Paradigms of Stress-Related Disorders. Expert Rev. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 13, 317–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Guo, M.; Zhang, D.; Cheng, S.Y.; Liu, M.; Ding, J.; Scherer, P.E.; Liu, F.; Lu, X.Y. Adiponectin Is Critical in Determining Susceptibility to Depressive Behaviors and Has Antidepressant-like Activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 12248–12253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber-Hamann, B.; Kratzsch, J.; Kopf, D.; Lederbogen, F.; Gilles, M.; Heuser, I.; Deuschle, M. Resistin and Adiponectin in Major Depression: The Association with Free Cortisol and Effects of Antidepressant Treatment. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2007, 41, 344–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giordano, R.; Picu, A.; Broglio, F.; Bonelli, L.; Baldi, M.; Berardelli, R.; Ghigo, E.; Arvat, E. Ghrelin, Hypothalamus-Pituitary-Adrenal (HPA) Axis and Cushing’s Syndrome. Pituitary 2004, 7, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Loenen, M.R.; Geenen, B.; Arnoldussen, I.A.C.; Kiliaan, A.J. Ghrelin as a Prominent Endocrine Factor in Stress-Induced Obesity. Nutr. Neurosci. 2022, 25, 1413–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceruso, A.; Martínez-Cengotitabengoa, M.; Peters-Corbett, A.; Diaz-Gutierrez, M.J. Alterations of the HPA Axis Observed in Patients with Major Depressive Disorder and Their Relation to Early Life Stress: A Systematic Review. Neuropsychobiology 2020, 79, 417–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillespie, C.F.; Nemeroff, C.B. Hypercortisolemia and Depression. Psychosom. Med. 2005, 67 (Suppl. 1), S26–S28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juruena, M.F.; Bocharova, M.; Agustini, B.; Young, A.H. Atypical Depression and Non-Atypical Depression: Is HPA Axis Function a Biomarker? A Systematic Review. J. Affect. Disord. 2018, 233, 45–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Ren, Y.M.; Guo, Y.X.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Sui, H.; Zhang, H.Y. The Effects of Baicalin in Depression: Preclinical Evidence Construction Based on Meta-Analysis. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1425094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.; Yu, M.; Han, N.; Zhu, M.; Li, X.; Zhou, J. Antidepressant Effects of Esketamine via the BDNF/AKT/mTOR Pathway in Mice with Postpartum Depression and Their Offspring. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2024, 132, 110992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.; Zhong, L.; Zhu, C.; Zhao, H.; Zhao, F.; Cui, R.; Gao, S.; Li, B. Role of Leptin in Mood Disorder and Neurodegenerative Disease. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloemer, J.; Pinky, P.D.; Govindarajulu, M.; Hong, H.; Judd, R.; Amin, R.H.; Moore, T.; Dhanasekaran, M.; Reed, M.N.; Suppiramaniam, V. Role of Adiponectin in Central Nervous System Disorders. Neural Plast. 2018, 2018, 4593530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tilg, H.; Wolf, A.M. Adiponectin: A Key Fat-Derived Molecule Regulating Inflammation. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2005, 9, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanchanatawan, B.; Sirivichayakul, S.; Thika, S.; Ruxrungtham, K.; Carvalho, A.F.; Geffard, M.; Anderson, G.; Noto, C.; Ivanova, R.; Maes, M. Physio-Somatic Symptoms in Schizophrenia: Association with Depression, Anxiety, Neurocognitive Deficits and the Tryptophan Catabolite Pathway. Metab. Brain Dis. 2017, 32, 1003–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasayama, D.; Hori, H.; Nakamura, S.; Yamamoto, N.; Hattori, K.; Teraishi, T.; Ota, M.; Kunugi, H. Increased Protein and mRNA Expression of Resistin after Dexamethasone Administration. Horm. Metab. Res. 2015, 47, 433–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, K.; Emoto, M.; Inaba, M. Fetuin-A: A Multifunctional Protein. Recent Pat. Endocr. Metab. Immune Drug Discov. 2011, 5, 124–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Fu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Weng, S.; Liu, D.; Cui, D.; Yu, S.; Liu, X.; Jiang, K.; Dong, Y. Chronic Mild Restraint Stress Rats Decreased CMKLR1 Expression in Distinct Brain Region. Neurosci. Lett. 2012, 524, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanelli, G.; Benedetti, F.; Wang, S.M.; Lee, S.J.; Jun, T.Y.; Masand, P.S.; Patkar, A.A.; Han, C.; Serretti, A.; Pae, C.U.; et al. Reduced Plasma Fetuin-A Is a Promising Biomarker of Depression in the Elderly. Eur. Arch. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2020, 270, 901–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, H.; Han, C.; Kim, B. Can Obesity Cause Depression? A Pseudo-Panel Analysis. J. Prev. Med. Public Health 2017, 50, 262–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuller, N.R.; Burns, J.; Sainsbury, A.; Horsfield, S.; da Luz, F.; Zhang, S.; Denyer, G.; Markovic, T.P.; Caterson, I.D. Examining the Association between Depression and Obesity during a Weight Management Programme. Clin. Obes. 2017, 7, 354–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luppino, F.S.; de Wit, L.M.; Bouvy, P.F.; Stijnen, T.; Cuijpers, P.; Penninx, B.W.; Zitman, F.G. Overweight, Obesity, and Depression: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Longitudinal Studies. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2010, 67, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Lima, J.; Leite, J.A.; Basso, P.J.; Ghirotto, B.; Martins da Silva, E.; Menezes-Silva, L.; Hiyane, M.I.; Goes, C.P.; Coutinho, L.L.; de Andrade Oliveira, V.; et al. Sirtuin 1 Regulates the Phenotype and Functions of Dendritic Cells through Ido1 Pathway in Obesity. Cell Death Dis. 2024, 15, 757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.N.; Peng, Y.L.; Liu, L.; Wu, T.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Lian, Y.J.; Yang, Y.Y.; Kelley, K.W.; Jiang, C.L.; Wang, Y.X. TNFα Mediates Stress-Induced Depression by Upregulating Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase in a Mouse Model of Unpredictable Chronic Mild Stress. Eur. Cytokine Netw. 2015, 26, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maes, M.; Mihaylova, I.; Ruyter, M.D.; Kubera, M.; Bosmans, E. The Immune Effects of TRYCATs (Tryptophan Catabolites along the IDO Pathway): Relevance for Depression—And Other Conditions Characterized by Tryptophan Depletion Induced by Inflammation. Neuro Endocrinol. Lett 2007, 28, 826–831. [Google Scholar]
- Myint, A.M.; Kim, Y.K. Cytokine-Serotonin Interaction through IDO: A Neurodegeneration Hypothesis of Depression. Med. Hypotheses 2003, 61, 519–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakash, J.B.; Byrne, G.I.; Lichtman, A.; Libby, P. Cytokines Induce Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase Expression in Human Atheroma-Asociated Cells: Implications for Persistent Chlamydophila pneumoniae Infection. Infect. Immun. 2002, 70, 3959–3961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comai, S.; Bertazzo, A.; Brughera, M.; Crotti, S. Tryptophan in Health and Disease. Adv. Clin. Chem. 2020, 95, 165–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastis, I.; Santos, M.G.; Paruchuri, A. Exploring the Role of Inflammation in Major Depressive Disorder: Beyond the Monoamine Hypothesis. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1282242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Achtyes, E.; Keaton, S.A.; Smart, L.; Burmeister, A.R.; Heilman, P.L.; Krzyzanowski, S.; Nagalla, M.; Guillemin, G.J.; Escobar Galvis, M.L.; Lim, C.K.; et al. Inflammation and Kynurenine Pathway Dysregulation in Post-Partum Women with Severe and Suicidal Depression. Brain Behav. Immun. 2020, 83, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubacka, J.; Staniszewska, M.; Sadok, I.; Sypniewska, G.; Stefanska, A. The Kynurenine Pathway in Obese Middle-Aged Women with Normoglycemia and Type 2 Diabetes. Metabolites 2022, 12, 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engin, A.B.; Engin, A. Tryptophan Metabolism in Obesity: The Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase-1 Activity and Therapeutic Options. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2024, 1460, 629–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, J.C.; Lawson, M.A.; André, C.; Moreau, M.; Lestage, J.; Castanon, N.; Kelley, K.W.; Dantzer, R. Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Depressive-like Behavior Is Mediated by Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase Activation in Mice. Mol. Psychiatry 2009, 14, 511–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, H.; Ozaki, N.; Sawada, M.; Isobe, K.; Ohta, T.; Nagatsu, T. A Link between Stress and Depression: Shifts in the Balance between the Kynurenine and Serotonin Pathways of Tryptophan Metabolism and the Etiology and Pathophysiology of Depression. Stress 2008, 11, 198–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Chang, R.; Zou, J.; Tan, S.; Huang, Z. The Role and Mechanism of Tryptophan-Kynurenine Metabolic Pathway in Depression. Rev. Neurosci. 2023, 34, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kupjetz, M.; Patt, N.; Joisten, N.; Ueland, P.M.; McCann, A.; Gonzenbach, R.; Bansi, J.; Zimmer, P. The Serum Kynurenine Pathway Metabolic Profile Is Associated with Overweight and Obesity in Multiple Sclerosis. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2023, 72, 104592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Wang, N.; Zhang, X.; Han, X.; Zhai, X.; Lu, Y. IDO and TDO as a Potential Therapeutic Target in Different Types of Depression. Metab. Brain Dis. 2018, 33, 1787–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, I.; Cussotto, S.; Anesi, A.; Dexpert, S.; Aubert, A.; Aouizerate, B.; Beau, C.; Forestier, D.; Ledaguenel, P.; Magne, E.; et al. Association between the Indole Pathway of Tryptophan Metabolism and Subclinical Depressive Symptoms in Obesity: A Preliminary Study. Int. J. Obes. 2022, 46, 885–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, M.K.; Leboyer, M.; Pariante, C.M.; Miller, A.H. Should Inflammation Be a Specifier for Major Depression in the DSM-6? JAMA Psychiatry 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arteaga-Henríquez, G.; Simon, M.S.; Burger, B.; Weidinger, E.; Wijkhuijs, A.; Arolt, V.; Birkenhager, T.K.; Musil, R.; Müller, N.; Drexhage, H.A. Low-Grade Inflammation as a Predictor of Antidepressant and Anti-Inflammatory Therapy Response in MDD Patients: A Systematic Review of the Literature in Combination With an Analysis of Experimental Data Collected in the EU-MOODINFLAME Consortium. Front. Psychiatry 2019, 10, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucido, M.J.; Bekhbat, M.; Goldsmith, D.R.; Treadway, M.T.; Haroon, E.; Felger, J.C.; Miller, A.H. Aiding and Abetting Anhedonia: Impact of Inflammation on the Brain and Pharmacological Implications. Pharmacol. Rev. 2021, 73, 1084–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasshauer, M.; Blüher, M. Adipokines in Health and Disease. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2015, 36, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Małujło-Balcerska, E.; Pietras, T. Adipocytokines Levels as Potential Biomarkers for Discriminating Patients with a Diagnosis of Depressive Disorder from Healthy Controls. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2024, 171, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zorena, K.; Jachimowicz-Duda, O.; Ślęzak, D.; Robakowska, M.; Mrugacz, M. Adipokines and Obesity. Potential Link to Metabolic Disorders and Chronic Complications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, A.F.; Rocha, D.Q.; McIntyre, R.S.; Mesquita, L.M.; Köhler, C.A.; Hyphantis, T.N.; Sales, P.M.; Machado-Vieira, R.; Berk, M. Adipokines as Emerging Depression Biomarkers: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2014, 59, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, K.; Fuster, J.J.; Walsh, K. Adipokines: A Link between Obesity and Cardiovascular Disease. J. Cardiol. 2014, 63, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diniz, B.S.; Teixeira, A.L.; Campos, A.C.; Miranda, A.S.; Rocha, N.P.; Talib, L.L.; Gattaz, W.F.; Forlenza, O.V. Reduced Serum Levels of Adiponectin in Elderly Patients with Major Depression. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2012, 46, 1081–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milaneschi, Y.; Lamers, F.; Bot, M.; Drent, M.L.; Penninx, B.W. Leptin Dysregulation Is Specifically Associated With Major Depression With Atypical Features: Evidence for a Mechanism Connecting Obesity and Depression. Biol. Psychiatry 2017, 81, 807–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obradovic, M.; Sudar-Milovanovic, E.; Soskic, S.; Essack, M.; Arya, S.; Stewart, A.J.; Gojobori, T.; Isenovic, E.R. Leptin and Obesity: Role and Clinical Implication. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 585887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burrows, K.; Figueroa-Hall, L.K.; Stewart, J.L.; Alarbi, A.M.; Kuplicki, R.; Hannafon, B.N.; Tan, C.; Risbrough, V.B.; McKinney, B.A.; Ramesh, R.; et al. Exploring the Role of Neuronal-Enriched Extracellular Vesicle miR-93 and Interoception in Major Depressive Disorder. Transl. Psychiatry 2024, 14, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esel, E.; Ozsoy, S.; Tutus, A.; Sofuoglu, S.; Kartalci, S.; Bayram, F.; Kokbudak, Z.; Kula, M. Effects of Antidepressant Treatment and of Gender on Serum Leptin Levels in Patients with Major Depression. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2005, 29, 565–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinen, D.; Heissel, A.; Heinzel, S.; Fydrich, T.; Ströhle, A.; Rapp, M.A.; Vogel, H. Effect of Acute and Long-Term Exercise on Leptin Levels in Depressed Outpatients. BMC Public Health 2023, 23, 2509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohan, M.; Qusar, M.M.A.S.; Shahriar, M.; Islam, S.M.A.; Bhuiyan, M.A.; Islam, M.R. Association of Reduced Serum EGF and Leptin Levels with the Pathophysiology of Major Depressive Disorder: A Case-Control Study. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0288159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milaneschi, Y.; Sutin, A.R.; Terracciano, A.; Canepa, M.; Gravenstein, K.S.; Egan, J.M.; Vogelzangs, N.; Guralnik, J.M.; Bandinelli, S.; Penninx, B.W.; et al. The Association between Leptin and Depressive Symptoms Is Modulated by Abdominal Adiposity. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2014, 42, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łojko, D.; Rybakowski, J.K. Atypical Depression: Current Perspectives. Neuropsychiatr. Treat. 2017, 13, 2447–2456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Munshi, S.; Burrows, K.; Kuplicki, R.; Figueroa-Hall, L.K.; Aupperle, R.L.; Khalsa, S.S.; Teague, T.K.; Taki, Y.; Paulus, M.P.; et al. Leptin’s Inverse Association With Brain Morphology and Depressive Symptoms: A Discovery and Confirmatory Study Across 2 Independent Samples. Biol. Psychiatry Cogn. Neurosci. Neuroimaging 2024, 9, 714–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Lobo, A.M.; Donato, J. The Role of Leptin in Health and Disease. Temperature 2017, 4, 258–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansar, W.; Ghosh, S. Inflammation and Inflammatory Diseases, Markers, and Mediators: Role of CRP in Some Inflammatory Diseases. In Biology of C Reactive Protein in Health and Disease; Ansar, W., Ghosh, S., Eds.; Springer: New Delhi, India, 2016; pp. 67–107. ISBN 978-81-322-2680-2. [Google Scholar]
- Burrows, K.; McNaughton, B.A.; Figueroa-Hall, L.K.; Spechler, P.A.; Kuplicki, R.; Victor, T.A.; Aupperle, R.; Khalsa, S.S.; Savitz, J.B.; Teague, T.K.; et al. Elevated Serum Leptin Is Associated with Attenuated Reward Anticipation in Major Depressive Disorder Independent of Peripheral C-Reactive Protein Levels. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 11313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotlib, I.H.; Hamilton, J.P.; Cooney, R.E.; Singh, M.K.; Henry, M.L.; Joormann, J. Neural Processing of Reward and Loss in Girls at Risk for Major Depression. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2010, 67, 380–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Fruyt, J.; Sabbe, B.; Demyttenaere, K. Anhedonia in Depressive Disorder: A Narrative Review. Psychopathology 2020, 53, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabrese, J.R.; Fava, M.; Garibaldi, G.; Grunze, H.; Krystal, A.D.; Laughren, T.; Macfadden, W.; Marin, R.; Nierenberg, A.A.; Tohen, M. Methodological Approaches and Magnitude of the Clinical Unmet Need Associated with Amotivation in Mood Disorders. J. Affect. Disord. 2014, 168, 439–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, N.; Katsuura, G.; Ochi, Y.; Ebihara, K.; Kusakabe, T.; Hosoda, K.; Nakao, K. Impaired CNS Leptin Action Is Implicated in Depression Associated with Obesity. Endocrinology 2011, 152, 2634–2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stern, N.; Osher, E.; Greenman, Y. Hypoadiponectinemia as a Marker of Adipocyte Dysfunction -- Part I: The Biology of Adiponectin. J. Cardiometab. Syndr. 2007, 2, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Shin, H.J.; Ding, E.L.; van Dam, R.M. Adiponectin Levels and Risk of Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. JAMA 2009, 302, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, S.; Islam, T.; Nahar, Z.; Shahriar, M.; Islam, S.M.A.; Bhuiyan, M.A.; Islam, M.R. Altered Serum Adiponectin and Interleukin-8 Levels Are Associated in the Pathophysiology of Major Depressive Disorder: A Case-Control Study. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0276619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pannacciulli, N.; Le, D.S.; Chen, K.; Reiman, E.M.; Krakoff, J. Relationships between Plasma Leptin Concentrations and Human Brain Structure: A Voxel-Based Morphometric Study. Neurosci. Lett. 2007, 412, 248–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, T.S.; Sattar, N.; Lean, M. ABC of Obesity. Assessment of Obesity and Its Clinical Implications. BMJ 2006, 333, 695–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuong, E.; Nothling, J.; Lombard, C.; Jewkes, R.; Peer, N.; Abrahams, N.; Seedat, S. Peripheral Adiponectin Levels in Anxiety, Mood, Trauma- and Stressor-Related Disorders: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Affect. Disord. 2020, 260, 372–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonard, B.E.; Wegener, G. Inflammation, Insulin Resistance and Neuroprogression in Depression. Acta Neuropsychiatr. 2020, 32, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machado-Vieira, R.; Gold, P.W.; Luckenbaugh, D.A.; Ballard, E.D.; Richards, E.M.; Henter, I.D.; De Sousa, R.T.; Niciu, M.J.; Yuan, P.; Zarate, C.A. The Role of Adipokines in the Rapid Antidepressant Effects of Ketamine. Mol. Psychiatry 2017, 22, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, Y.J.; Hsieh, C.H.; Chen, Y.J.; Pei, D.; Kuo, S.W.; Shen, D.C.; Sheu, W.H.; Chen, Y.C. Insulin Sensitivity, Proinflammatory Markers and Adiponectin in Young Males with Different Subtypes of Depressive Disorder. Clin. Endocrinol. 2007, 67, 784–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantuzzi, G. Adiponectin in Inflammatory and Immune-Mediated Diseases. Cytokine 2013, 64, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghadge, A.A.; Khaire, A.A.; Kuvalekar, A.A. Adiponectin: A Potential Therapeutic Target for Metabolic Syndrome. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2018, 39, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, H.G.; Min, B.J.; Lim, S.; Kim, T.H.; Lee, J.J.; Park, J.H.; Lee, S.B.; Han, J.W.; Choi, S.H.; Park, Y.J.; et al. Plasma adiponectin elevation in elderly individuals with subsyndromal depression. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2012, 37, 948–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Dong, X.; Chen, J. Adiponectin and Depression: A Meta-Analysis. Biomed. Rep. 2015, 3, 38–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Permoda-Pachuta, A.; Malewska-Kasprzak, M.; Skibińska, M.; Rzepski, K.; Dmitrzak-Węglarz, M. Changes in Adipokine, Resitin, and BDNF Concentrations in Treatment-Resistant Depression after Electroconvulsive Therapy. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedetti, F.; Branchi, I.; Poletti, S.; Lorenzi, C.; Bigai, G.; Colombo, C.; Zanardi, R. Adiponectin Predicts Poor Response to Antidepressant Drugs in Major Depressive Disorder. Hum. Psychopharmacol. 2021, 36, e2793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Lu, E.; Deng, L.; Zhu, Y.; Lu, X.; Li, X.; Li, F.; Yan, Y.; Han, J.Y.; Li, Y.; et al. Immunological Roles for Resistin and Related Adipokines in Obesity-Associated Tumors. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 142, 112911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, D.; Kant, S.; Pandey, S.; Ehtesham, N.Z. Resistin in Metabolism, Inflammation, and Disease. FEBS J. 2020, 287, 3141–3149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lasserre, A.M.; Glaus, J.; Vandeleur, C.L.; Marques-Vidal, P.; Vaucher, J.; Bastardot, F.; Waeber, G.; Vollenweider, P.; Preisig, M. Depression With Atypical Features and Increase in Obesity, Body Mass Index, Waist Circumference, and Fat Mass. JAMA Psychiatry 2014, 71, 880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konuk, N.; Tekin, I.O.; Ozturk, U.; Atik, L.; Atasoy, N.; Bektas, S.; Erdogan, A. Plasma Levels of Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha and Interleukin-6 in Obsessive Compulsive Disorder. Mediat. Inflamm. 2007, 2007, 65704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirci, S.; Aynalı, A.; Demirci, K.; Arıdoğan, B.C. The Serum Levels of Resistin and Its Relationship with Other Proinflammatory Cytokines in Patients with Alzheimer’s Disease. Clin. Psychopharmacol. Neurosci. 2017, 15, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunetti, L.; Orlando, G.; Recinella, L.; Michelotto, B.; Ferrante, C.; Vacca, M. Resistin, but Not Adiponectin, Inhibits Dopamine and Norepinephrine Release in the Hypothalamus. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2004, 493, 41–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehto, S.M.; Huotari, A.; Niskanen, L.; Tolmunen, T.; Koivumaa-Honkanen, H.; Honkalampi, K.; Ruotsalainen, H.; Herzig, K.H.; Viinamäki, H.; Hintikka, J. Serum Adiponectin and Resistin Levels in Major Depressive Disorder. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 2010, 121, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeugmann, S.; Quante, A.; Heuser, I.; Schwarzer, R.; Anghelescu, I. Inflammatory Biomarkers in 70 Depressed Inpatients with and without the Metabolic Syndrome. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2010, 71, 1007–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Degawa-Yamauchi, M.; Bovenkerk, J.E.; Juliar, B.E.; Watson, W.; Kerr, K.; Jones, R.; Zhu, Q.; Considine, R.V. Serum Resistin (FIZZ3) Protein Is Increased in Obese Humans. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 88, 5452–5455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owecki, M.; Miczke, A.; Nikisch, E.; Pupek-Musialik, D.; Sowiński, J. Serum Resistin Concentrations Are Higher in Human Obesity but Independent from Insulin Resistance. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2011, 119, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Way, J.M.; Görgün, C.Z.; Tong, Q.; Uysal, K.T.; Brown, K.K.; Harrington, W.W.; Oliver, W.R.; Willson, T.M.; Kliewer, S.A.; Hotamisligil, G.S. Adipose Tissue Resistin Expression Is Severely Suppressed in Obesity and Stimulated by Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor Gamma Agonists. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 25651–25653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, S.; Shanta, A.A.; Daria, S.; Nahar, Z.; Shahriar, M.; Qusar, M.S.; Islam, S.M.A.; Bhuiyan, M.A.; Islam, M.R. Increased Serum Resistin but Not G-CSF Levels Are Associated in the Pathophysiology of Major Depressive Disorder: Findings from a Case-Control Study. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0264404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Ayadhi, L.Y.; Alghamdi, F.A.; Altamimi, L.A.; Alsughayer, L.Y.; Alhowikan, A.M.; Halepoto, D.M. The Possible Link between Fetuin-A Protein and Neuro-Inflammation in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder. Pak. J. Med. Sci. 2021, 37, 1166–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Li, W.; Zhu, S.; Li, J.; D’Amore, J.; Ward, M.F.; Yang, H.; Wu, R.; Jahnen-Dechent, W.; Tracey, K.J.; et al. Peripheral Administration of Fetuin-A Attenuates Early Cerebral Ischemic Injury in Rats. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2010, 30, 493–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trepanowski, J.F.; Mey, J.; Varady, K.A. Fetuin-A: A Novel Link between Obesity and Related Complications. Int. J. Obes. 2015, 39, 734–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laughlin, G.A.; Barrett-Connor, E.; Cummins, K.M.; Daniels, L.B.; Wassel, C.L.; Ix, J.H. Sex-Specific Association of Fetuin-A with Type 2 Diabetes in Older Community-Dwelling Adults: The Rancho Bernardo Study. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 1994–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ix, J.H.; Wassel, C.L.; Kanaya, A.M.; Vittinghoff, E.; Johnson, K.C.; Koster, A.; Cauley, J.A.; Harris, T.B.; Cummings, S.R.; Shlipak, M.G.; et al. Fetuin-A and Incident Diabetes Mellitus in Older Persons. JAMA 2008, 300, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vörös, K.; Gráf, L.; Prohászka, Z.; Szenthe, P.; Kaszás, E.; Böröcz, Z.; Cseh, K.; Kalabay, L. Serum Fetuin-A in Metabolic and Inflammatory Pathways in Patients with Myocardial Infarction. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 41, 703–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makris, M.C.; Alexandrou, A.; Papatsoutsos, E.G.; Malietzis, G.; Tsilimigras, D.I.; Guerron, A.D.; Moris, D. Ghrelin and Obesity: Identifying Gaps and Dispelling Myths. A Reappraisal. In Vivo 2017, 31, 1047–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radziszewska, M.; Ostrowska, L.; Smarkusz-Zarzecka, J. The Impact of Gastrointestinal Hormones on Human Adipose Tissue Function. Nutrients 2024, 16, 3245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueiras, R. MECHANISMS IN ENDOCRINOLOGY: The Gut-Brain Axis: Regulating Energy Balance Independent of Food Intake. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2021, 185, R75–R91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abizaid, A.; Horvath, T.L. Ghrelin and the Central Regulation of Feeding and Energy Balance. Indian J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 16, S617–S626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozsoy, S.; Besirli, A.; Abdulrezzak, U.; Basturk, M. Serum Ghrelin and Leptin Levels in Patients with Depression and the Effects of Treatment. Psychiatry Investig. 2014, 11, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurt, E.; Guler, O.; Serteser, M.; Cansel, N.; Ozbulut, O.; Altinbaş, K.; Alataş, G.; Savaş, H.; Gecici, O. The Effects of Electroconvulsive Therapy on Ghrelin, Leptin and Cholesterol Levels in Patients with Mood Disorders. Neurosci. Lett. 2007, 426, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kluge, M.; Schussler, P.; Schmid, D.; Uhr, M.; Kleyer, S.; Yassouridis, A.; Steiger, A. Ghrelin Plasma Levels Are Not Altered in Major Depression. Neuropsychobiology 2009, 59, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuo, K.; Nakano, M.; Nakashima, M.; Watanuki, T.; Egashira, K.; Matsubara, T.; Watanabe, Y. Neural Correlates of Plasma Acylated Ghrelin Level in Individuals with Major Depressive Disorder. Brain Res. 2012, 1473, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sempach, L.; Doll, J.P.K.; Limbach, V.; Marzetta, F.; Schaub, A.C.; Schneider, E.; Kettelhack, C.; Mählmann, L.; Schweinfurth-Keck, N.; Ibberson, M.; et al. Examining Immune-Inflammatory Mechanisms of Probiotic Supplementation in Depression: Secondary Findings from a Randomized Clinical Trial. Transl. Psychiatry 2024, 14, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, R.; Dong, W.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, F.; Marini, C.P.; Ravikumar, T.S.; Wang, P. Ghrelin Attenuates Sepsis-Induced Acute Lung Injury and Mortality in Rats. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2007, 176, 805–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixit, V.D.; Schaffer, E.M.; Pyle, R.S.; Collins, G.D.; Sakthivel, S.K.; Palaniappan, R.; Lillard, J.W.; Taub, D.D. Ghrelin Inhibits Leptin- and Activation-Induced Proinflammatory Cytokine Expression by Human Monocytes and T Cells. J. Clin. Investig. 2004, 114, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monti, V.; Carlson, J.J.; Hunt, S.C.; Adams, T.D. Relationship of Ghrelin and Leptin Hormones with Body Mass Index and Waist Circumference in a Random Sample of Adults. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2006, 106, 822–828; quiz 829–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morin, V.; Hozer, F.; Costemale-Lacoste, J.F. The Effects of Ghrelin on Sleep, Appetite, and Memory, and Its Possible Role in Depression: A Review of the Literature. Encephale 2018, 44, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atescelik, M.; Yilmaz, M.; Korkmaz, S.; Goktekin, M.C.; Gurger, M.; Ilhan, N. The Relationship between Ghrelin and Copeptin Levels, and Anxiety and Depression Levels in Suicide Attempts. Clin. Psychopharmacol. Neurosci. 2017, 15, 256–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Štorkánová, H.; Oreská, S.; Špiritović, M.; Heřmánková, B.; Bubová, K.; Komarc, M.; Pavelka, K.; Vencovský, J.; Distler, J.H.W.; Šenolt, L.; et al. Plasma Hsp90 Levels in Patients with Systemic Sclerosis and Relation to Lung and Skin Involvement: A Cross-Sectional and Longitudinal Study. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beurel, E.; Toups, M.; Nemeroff, C.B. The Bidirectional Relationship of Depression and Inflammation: Double Trouble. Neuron 2020, 107, 234–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, A.; Tam, W.W.; Zhang, M.W.; Ho, C.S.; Husain, S.F.; McIntyre, R.S.; Ho, R.C. IL-1β, IL-6, TNF- α and CRP in Elderly Patients with Depression or Alzheimer’s Disease: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 12050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, R.; Emon, M.P.Z.; Shahriar, M.; Nahar, Z.; Islam, S.M.A.; Bhuiyan, M.A.; Islam, S.N.; Islam, M.R. Higher Levels of Serum IL-1β and TNF-α Are Associated with an Increased Probability of Major Depressive Disorder. Psychiatry Res. 2021, 295, 113568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawar, G.R.; Agrawal, Y.O.; Nakhate, K.T.; Patil, C.R.; Sharma, C.; Ojha, S.; Mahajan, U.B.; Goyal, S.N. Ghrelin Alleviates Depression-like Behaviour in Rats Subjected to High-Fat Diet and Diurnal Rhythm Disturbance. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2022, 14, 7098–7108. [Google Scholar]
- Ishitobi, Y.; Kohno, K.; Kanehisa, M.; Inoue, A.; Imanaga, J.; Maruyama, Y.; Ninomiya, T.; Higuma, H.; Okamoto, S.; Tanaka, Y.; et al. Serum Ghrelin Levels and the Effects of Antidepressants in Major Depressive Disorder and Panic Disorder. Neuropsychobiology 2012, 66, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sancar, G.; Liu, S.; Gasser, E.; Alvarez, J.G.; Moutos, C.; Kim, K.; van Zutphen, T.; Wang, Y.; Huddy, T.F.; Ross, B.; et al. FGF1 and insulin control lipolysis by convergent pathways. Cell Metab. 2022, 34, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nies, V.J.M.; Struik, D.; Liu, S.; Liu, W.; Kruit, J.K.; Downes, M.; van Zutphen, T.; Verkade, H.J.; Evans, R.M.; Jonker, J.W. Autocrine FGF1 signaling promotes glucose uptake in adipocytes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2122382119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.; Deng, S.; Zhang, M.R.; Tang, M.M. Fibroblast Growth Factors in Depression. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, C.Y.; Hsu, Y.C.; Liu, J.W.; Lee, D.C.; Chung, Y.F.; Chiu, I.M. The mood stabilizer valproate activates human FGF 1 gene promoter through inhibiting HDAC and GSK-3 activities. J. Neurochem. 2013, 126, 4–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matia-Garcia, I.; Vadillo, E.; Pelayo, R.; Muñoz-Valle, J.F.; García-Chagollán, M.; Loaeza-Loaeza, J.; Vences-Velázquez, A.; Salgado-Goytia, L.; García-Arellano, S.; Parra-Rojas, I. Th1/Th2 Balance in Young Subjects: Relationship with Cytokine Levels and Metabolic Profile. J. Inflamm. Res. 2021, 14, 6587–6600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romagnani, S. Th1/Th2 Cells. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 1999, 5, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romagnani, S. Understanding the Role of Th1/Th2 Cells in Infection. Trends Microbiol. 1996, 4, 470–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacifico, L.; Di Renzo, L.; Anania, C.; Osborn, J.F.; Ippoliti, F.; Schiavo, E.; Chiesa, C. Increased T-Helper Interferon-Gamma-Secreting Cells in Obese Children. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2006, 154, 691–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damsker, J.M.; Hansen, A.M.; Caspi, R.R. Th1 and Th17 Cells: Adversaries and Collaborators. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2010, 1183, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Rourke, R.W.; Metcalf, M.D.; White, A.E.; Madala, A.; Winters, B.R.; Maizlin, I.I.; Jobe, B.A.; Roberts, C.T.; Slifka, M.K.; Marks, D.L. Depot-Specific Differences in Inflammatory Mediators and a Role for NK Cells and IFN-Gamma in Inflammation in Human Adipose Tissue. Int. J. Obes. 2009, 33, 978–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Garra, A.; Murphy, K. Role of Cytokines in Development of Th1 and Th2 Cells. In Th1 and Th2 Cells in Health and Disease; Romagnani, S., Ed.; S. Karger AG: Basel, Switzerland, 1996; Volume 63, ISBN 978-3-8055-6241-6. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, C.; Lichtenauer, M.; Strodthoff, D.; Winkels, H.; Wernly, B.; Bürger, C.; Kamchybekov, U.; Lutgens, E.; Figulla, H.R.; Gerdes, N. Alterations in Systemic Levels of Th1, Th2, and Th17 Cytokines in Overweight Adolescents and Obese Mice. Pediatr. Diabetes 2017, 18, 714–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surendar, J.; Mohan, V.; Rao, M.M.; Babu, S.; Aravindhan, V. Increased Levels of Both Th1 and Th2 Cytokines in Subjects with Metabolic Syndrome (CURES-103). Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2011, 13, 477–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, A.D.; Manson, J.E.; Rifai, N.; Buring, J.E.; Ridker, P.M. C-Reactive Protein, Interleukin 6, and Risk of Developing Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. JAMA 2001, 286, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Hu, Z.; Yang, S.; Sun, L.; Yu, Z.; Wang, G. Role of Adaptive and Innate Immunity in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. J. Diabetes Res. 2018, 2018, 7457269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calder, P.C.; Ahluwalia, N.; Brouns, F.; Buetler, T.; Clement, K.; Cunningham, K.; Esposito, K.; Jönsson, L.S.; Kolb, H.; Lansink, M.; et al. Dietary Factors and Low-Grade Inflammation in Relation to Overweight and Obesity. Br. J. Nutr. 2011, 106 (Suppl. 3), S5–S78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sell, H.; Eckel, J. Adipose Tissue Inflammation: Novel Insight into the Role of Macrophages and Lymphocytes. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2010, 13, 366–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Carli, M.; D’Elios, M.M.; Zancuoghi, G.; Romagnani, S.; Del Prete, G. Human Th1 and Th2 Cells: Functional Properties, Regulation of Development and Role in Autoimmunity. Autoimmunity 1994, 18, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dantzer, R.; O’Connor, J.C.; Freund, G.G.; Johnson, R.W.; Kelley, K.W. From Inflammation to Sickness and Depression: When the Immune System Subjugates the Brain. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2008, 9, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAfoose, J.; Baune, B.T. Evidence for a Cytokine Model of Cognitive Function. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2009, 33, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, A.H.; Maletic, V.; Raison, C.L. Inflammation and Its Discontents: The Role of Cytokines in the Pathophysiology of Major Depression. Biol. Psychiatry 2009, 65, 732–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudra Rakshasa-Loots, A.; Vera, J.H.; Laughton, B. Neuroinflammation and Mental Health Outcomes in Adolescents Living with HIV. Curr. Opin. HIV AIDS 2024, 19, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowlati, Y.; Herrmann, N.; Swardfager, W.; Liu, H.; Sham, L.; Reim, E.K.; Lanctôt, K.L. A Meta-Analysis of Cytokines in Major Depression. Biol. Psychiatry 2010, 67, 446–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slavich, G.M.; Sacher, J. Stress, Sex Hormones, Inflammation, and Major Depressive Disorder: Extending Social Signal Transduction Theory of Depression to Account for Sex Differences in Mood Disorders. Psychopharmacology 2019, 236, 3063–3079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ao, M.; Yang, X.; Wang, S.; Li, M.; Zhang, W.; Ou, Q.; Xu, K.; Sun, D. Relationships between Depression Level and Serum Inflammatory Factors and Thyroxine Levels in Patients with Malignant Bone Tumors Associated with Depression. Hum. Exp. Toxicol 2024, 43, 9603271241293119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lombardi, A.L.; Manfredi, L.; Conversi, D. How Does IL-6 Change after Combined Treatment in MDD Patients? A Systematic Review. Brain Behav. Immun.-Health 2023, 27, 100579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roohi, E.; Jaafari, N.; Hashemian, F. On Inflammatory Hypothesis of Depression: What Is the Role of IL-6 in the Middle of the Chaos? J. Neuroinflammation 2021, 18, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haapakoski, R.; Mathieu, J.; Ebmeier, K.P.; Alenius, H.; Kivimäki, M. Cumulative Meta-Analysis of Interleukins 6 and 1β, Tumour Necrosis Factor α and C-Reactive Protein in Patients with Major Depressive Disorder. Brain. Behav. Immun. 2015, 49, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Ran, M.; Li, H.; Lin, Y.; Ma, K.; Yang, Y.; Fu, X.; Yang, S. New Insight into Neurological Degeneration: Inflammatory Cytokines and Blood–Brain Barrier. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2022, 15, 1013933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della Vecchia, A.; Arone, A.; Piccinni, A.; Mucci, F.; Marazziti, D. GABA System in Depression: Impact on Pathophysiology and Psychopharmacology. Curr. Med. Chem. 2022, 29, 5710–5730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, M.R.; Sohan, M.; Daria, S.; Masud, A.A.; Ahmed, M.U.; Roy, A.; Shahriar, M. Evaluation of Inflammatory Cytokines in Drug-Naïve Major Depressive Disorder: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2023, 37, 3946320231198828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFarland, D.C.; Doherty, M.; Atkinson, T.M.; O’Hanlon, R.; Breitbart, W.; Nelson, C.J.; Miller, A.H. Cancer-Related Inflammation and Depressive Symptoms: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancer 2022, 128, 2504–2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Wijk, I.; Belteczki, Z.; Dome, P. The Role of Oxidative Stress in the Pathomechanism of Major Mood Disorders: A Narrative Review with a Special Focus on Uric Acid. Neuropsychopharmacol. Hung. 2024, 26, 105–124. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Wang, X.; Li, C.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, S.; Xu, S. A Scientometric Analysis of Research on the Role of NMDA Receptor in the Treatment of Depression. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1394730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marseglia, L.; Manti, S.; D’Angelo, G.; Nicotera, A.; Parisi, E.; Di Rosa, G.; Gitto, E.; Arrigo, T. Oxidative Stress in Obesity: A Critical Component in Human Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 16, 378–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cecerska-Heryć, E.; Polikowska, A.; Serwin, N.; Roszak, M.; Grygorcewicz, B.; Heryć, R.; Michalczyk, A.; Dołęgowska, B. Importance of Oxidative Stress in the Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Monitoring of Patients with Neuropsychiatric Disorders, a Review. Neurochem. Int. 2022, 153, 105269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jelinek, M.; Jurajda, M.; Duris, K. Oxidative Stress in the Brain: Basic Concepts and Treatment Strategies in Stroke. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winiarska-Mieczan, A.; Kwiecień, M.; Jachimowicz-Rogowska, K.; Donaldson, J.; Tomaszewska, E.; Baranowska-Wójcik, E. Anti-Inflammatory, Antioxidant, and Neuroprotective Effects of Polyphenols-Polyphenols as an Element of Diet Therapy in Depressive Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrne, J.F.; Healy, C.; Mongan, D.; Susai, S.R.; Zammit, S.; Föcking, M.; Cannon, M.; Cotter, D.R. Transdiagnostic Inflammatory Subgroups among Psychiatric Disorders and Their Relevance to Role Functioning: A Nested Case-Control Study of the ALSPAC Cohort. Transl. Psychiatry 2022, 12, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsubaie, N.; Al-Kuraishy, H.M.; Al-Gareeb, A.I.; Alharbi, B.; De Waard, M.; Sabatier, J.M.; Saad, H.M.; Batiha, G.E. Statins Use in Alzheimer Disease: Bane or Boon from Frantic Search and Narrative Review. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batiha, G.E.; Al-Kuraishy, H.M.; Al-Gareeb, A.I.; Elekhnawy, E. SIRT1 Pathway in Parkinson’s Disease: A Faraway Snapshot but so Close. Inflammopharmacology 2023, 31, 37–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Dong, L.; Pan, D.; Xu, D.; Lu, Y.; Yin, S.; Wang, S.; Xia, H.; Liao, W.; Sun, G. Effect of High Ratio of N-6/n-3 PUFAs on Depression: A Meta-Analysis of Prospective Studies. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 889576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laederach-Hofmann, K.; Kupferschmid, S.; Mussgay, L. Links between Body Mass Index, Total Body Fat, Cholesterol, High-Density Lipoprotein, and Insulin Sensitivity in Patients with Obesity Related to Depression, Anger, and Anxiety. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2002, 32, 58–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ait Tayeb, A.E.K.; Poinsignon, V.; Chappell, K.; Bouligand, J.; Becquemont, L.; Verstuyft, C. Major Depressive Disorder and Oxidative Stress: A Review of Peripheral and Genetic Biomarkers According to Clinical Characteristics and Disease Stages. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, N.; Lei, M.; Chen, Y.; Tian, S.; Li, C.; Zhang, B. How Oxidative Stress Induces Depression? ASN Neuro 2023, 15, 17590914231181037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Correia, A.S.; Cardoso, A.; Vale, N. Oxidative Stress in Depression: The Link with the Stress Response, Neuroinflammation, Serotonin, Neurogenesis and Synaptic Plasticity. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanaeifar, F.; Pourranjbar, S.; Pourranjbar, M.; Ramezani, S.; Mehr, S.R.; Wadan, A.S.; Khazeifard, F. Beneficial Effects of Physical Exercise on Cognitive-Behavioral Impairments and Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Alteration in the Limbic System Induced by Neurodegeneration. Exp. Gerontol. 2024, 195, 112539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fanelli, G.; Mota, N.R.; Salas-Salvadó, J.; Bulló, M.; Fernandez-Aranda, F.; Camacho-Barcia, L.; Testa, G.; Jiménez-Murcia, S.; Bertaina-Anglade, V.; Franke, B.; et al. The Link between Cognition and Somatic Conditions Related to Insulin Resistance in the UK Biobank Study Cohort: A Systematic Review. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2022, 143, 104927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lievanos-Ruiz, F.J.; Fenton-Navarro, B. Enzymatic Biomarkers of Oxidative Stress in Patients with Depressive Disorders. A Systematic Review. Clin. Biochem. 2024, 130, 110788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niedzielska, E.; Smaga, I.; Gawlik, M.; Moniczewski, A.; Stankowicz, P.; Pera, J.; Filip, M. Oxidative Stress in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 53, 4094–4125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eshkevari, L.; Sales, M.; Collins, C.; Totoraitis, J.; Donohue, L.; Bowman-Dalley, C.; Bregman, B.; Negro, P.; Gordon, S.; Estrada, C. Efficacy of Addition of the Anti-Inflammatory, IV Glutathione to Standard Ketamine IV Therapy in Major Depressive Disorder. Psychiatry Res. 2024, 337, 115949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffy, S.L.; Lagopoulos, J.; Cockayne, N.; Lewis, S.J.; Hickie, I.B.; Hermens, D.F.; Naismith, S.L. The Effect of 12-Wk ω-3 Fatty Acid Supplementation on in Vivo Thalamus Glutathione Concentration in Patients “at Risk” for Major Depression. Nutrition 2015, 31, 1247–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tortosa-Caparrós, E.; Navas-Carrillo, D.; Marín, F.; Orenes-Piñero, E. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Omega 3 and Omega 6 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids in Cardiovascular Disease and Metabolic Syndrome. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 3421–3429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öngöz Dede, F.; Bozkurt Doğan, Ş.; Balli, U.; Avci, B.; Durmuşlar, M.C.; Baratzade, T. Glutathione Levels in Plasma, Saliva and Gingival Crevicular Fluid after Periodontal Therapy in Obese and Normal Weight Individuals. J. Periodontal Res. 2016, 51, 726–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foulds, P.G.; Mitchell, J.D.; Parker, A.; Turner, R.; Green, G.; Diggle, P.; Hasegawa, M.; Taylor, M.; Mann, D.; Allsop, D. Phosphorylated α-Synuclein Can Be Detected in Blood Plasma and Is Potentially a Useful Biomarker for Parkinson’s Disease. FASEB J. 2011, 25, 4127–4137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanescu, C.; Ciobica, A. The Relevance of Oxidative Stress Status in First Episode and Recurrent Depression. J. Affect. Disord. 2012, 143, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camkurt, M.A.; Fındıklı, E.; İzci, F.; Kurutaş, E.B.; Tuman, T.C. Evaluation of Malondialdehyde, Superoxide Dismutase and Catalase Activity and Their Diagnostic Value in Drug Naïve, First Episode, Non-Smoker Major Depression Patients and Healthy Controls. Psychiatry Res. 2016, 238, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, D.; Park, Y. Association between Erythrocyte N-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids and Biomarkers of Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in Patients with and without Depression. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fat. Acids 2013, 89, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szuster-Ciesielska, A.; Słotwińska, M.; Stachura, A.; Marmurowska-Michałowska, H.; Dubas-Slemp, H.; Bojarska-Junak, A.; Kandefer-Szerszeń, M. Accelerated Apoptosis of Blood Leukocytes and Oxidative Stress in Blood of Patients with Major Depression. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2008, 32, 686–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, M.C.; Huang, T.L. Increased Activities of Both Superoxide Dismutase and Catalase Were Indicators of Acute Depressive Episodes in Patients with Major Depressive Disorder. Psychiatry Res. 2016, 235, 38–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajpai, A.; Verma, A.K.; Srivastava, M.; Srivastava, R. Oxidative Stress and Major Depression. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2014, 8, CC04–CC07. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caso, J.R.; MacDowell, K.S.; González-Pinto, A.; García, S.; de Diego-Adeliño, J.; Carceller-Sindreu, M.; Sarramea, F.; Caballero-Villarraso, J.; Gracia-García, P.; De la Cámara, C.; et al. Gut Microbiota, Innate Immune Pathways, and Inflammatory Control Mechanisms in Patients with Major Depressive Disorder. Transl. Psychiatry 2021, 11, 645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Zhao, J.; Ren, W.; Cai, Y.; Wang, Q.; Luan, X.; Zhao, K.; He, J. Malondialdehyde: A Novel Predictive Biomarker for Post-Stroke Depression. J. Affect. Disord. 2017, 220, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Fernández, S.; Gurpegui, M.; Garrote-Rojas, D.; Gutiérrez-Rojas, L.; Carretero, M.D.; Correll, C.U. Oxidative Stress Parameters and Antioxidants in Adults with Unipolar or Bipolar Depression versus Healthy Controls: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Affect. Disord. 2022, 314, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimti, F.H.; Shahbaz, R.; Bhatt, K.; Xiang, A. A Review of New Insights into Existing Major Depressive Disorder Biomarkers. Heliyon 2023, 9, e18909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, M.R.; Ahmed, I.; Moktadir, A.A.; Nahar, Z.; Islam, M.S.; Shahid, S.F.B.; Islam, S.N.; Hasnat, A. Elevated Serum Levels of Malondialdehyde and Cortisol Are Associated with Major Depressive Disorder: A Case-Control Study. SAGE Open Med. 2018, 6, 2050312118773953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotan, V.O.; Sarandol, E.; Kirhan, E.; Ozkaya, G.; Kirli, S. Effects of Long-Term Antidepressant Treatment on Oxidative Status in Major Depressive Disorder: A 24-Week Follow-up Study. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2011, 35, 1284–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarandol, A.; Sarandol, E.; Eker, S.S.; Erdinc, S.; Vatansever, E.; Kirli, S. Major Depressive Disorder Is Accompanied with Oxidative Stress: Short-Term Antidepressant Treatment Does Not Alter Oxidative-Antioxidative Systems. Hum. Psychopharmacol. 2007, 22, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybka, J.; Kędziora-Kornatowska, K.; Banaś-Leżańska, P.; Majsterek, I.; Carvalho, L.A.; Cattaneo, A.; Anacker, C.; Kędziora, J. Interplay between the Pro-Oxidant and Antioxidant Systems and Proinflammatory Cytokine Levels, in Relation to Iron Metabolism and the Erythron in Depression. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2013, 63, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prázný, M.; Skrha, J.; Hilgertová, J. Plasma Malondialdehyde and Obesity: Is There a Relationship? Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 1999, 37, 1129–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Čolak, E.; Pap, D. The Role of Oxidative Stress in the Development of Obesity and Obesity-Related Metabolic Disorders. J. Med. Biochem. 2021, 40, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Fernández, S.; Gurpegui, M.; Garrote-Rojas, D.; Gutiérrez-Rojas, L.; Carretero, M.D.; Correll, C.U. Oxidative Stress Parameters and Antioxidants in Patients with Bipolar Disorder: Results from a Meta-Analysis Comparing Patients, Including Stratification by Polarity and Euthymic Status, with Healthy Controls. Bipolar Disord. 2021, 23, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gałecki, P.; Szemraj, J.; Bieńkiewicz, M.; Florkowski, A.; Gałecka, E. Lipid Peroxidation and Antioxidant Protection in Patients during Acute Depressive Episodes and in Remission after Fluoxetine Treatment. Pharmacol. Rep. 2009, 61, 436–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maes, M.; Mihaylova, I.; Kubera, M.; Uytterhoeven, M.; Vrydags, N.; Bosmans, E. Lower Whole Blood Glutathione Peroxidase (GPX) Activity in Depression, but Not in Myalgic Encephalomyelitis / Chronic Fatigue Syndrome: Another Pathway That May Be Associated with Coronary Artery Disease and Neuroprogression in Depression. Neuro Endocrinol. Lett. 2011, 32, 133–140. [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi, A.; MI, K.; Watai, Y.; KI, T.; Shibata, T.; Uchida, K.; Yamamoto, M. Oxidative and Electrophilic Stresses Activate Nrf2 through Inhibition of Ubiquitination Activity of Keap1. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2006, 26, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Khor, T.O.; Xu, C.; Shen, G.; Jeong, W.S.; Yu, S.; Kong, A.N. Activation of Nrf2-antioxidant signaling attenuates NFκB-inflammatory response and elicits apoptosis. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2008, 76, 1485–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martín-de-Saavedra, M.D.; Budni, J.; Cunha, M.P.; Gómez-Rangel, V.; Lorrio, S.; Del Barrio, L.; Lastres-Becker, I.; Parada, E.; Tordera, R.M.; Rodrigues, A.L.; et al. Nrf2 participates in depressive disorders through an anti-inflammatory mechanism. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2013, 38, 2010–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golden, S.A.; Covington, H.E.; Berton, O.; Russo, S.J. A standardized protocol for repeated social defeat stress in mice. Nat. Protoc. 2011, 6, 1183–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, K. Essential Role of Keap1-Nrf2 Signaling in Mood Disorders: Overview and Future Perspective. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parekh, A.; Smeeth, D.; Milner, Y.; Thuret, S. The Role of Lipid Biomarkers in Major Depression. Healthcare 2017, 5, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milano, W.; Ambrosio, P.; Carizzone, F.; De Biasio, V.; Di Munzio, W.; Foia, M.G.; Capasso, A. Depression and Obesity: Analysis of Common Biomarkers. Diseases 2020, 8, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, P.F.; Joyce, P.R.; Bulik, C.M.; Mulder, R.T.; Oakley-Browne, M. Total Cholesterol and Suicidality in Depression. Biol. Psychiatry 1994, 36, 472–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marion-Letellier, R.; Savoye, G.; Ghosh, S. Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids and Inflammation. IUBMB Life 2015, 67, 659–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simopoulos, A.P. An Increase in the Omega-6/Omega-3 Fatty Acid Ratio Increases the Risk for Obesity. Nutrients 2016, 8, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borsini, A.; Nicolaou, A.; Camacho-Muñoz, D.; Kendall, A.C.; Di Benedetto, M.G.; Giacobbe, J.; Su, K.P.; Pariante, C.M. Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids Protect against Inflammation through Production of LOX and CYP450 Lipid Mediators: Relevance for Major Depression and for Human Hippocampal Neurogenesis. Mol. Psychiatry 2021, 26, 6773–6788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granström, E. The Arachidonic Acid Cascade. The Prostaglandins, Thromboxanes and Leukotrienes. Inflammation 1984, 8, S15–S25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Shaer, A.E.; Buddenbaum, N.; Shaikh, S.R. Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids, Specialized pro-Resolving Mediators, and Targeting Inflammation Resolution in the Age of Precision Nutrition. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2021, 1866, 158936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parletta, N.; Zarnowiecki, D.; Cho, J.; Wilson, A.; Procter, N.; Gordon, A.; Bogomolova, S.; O’Dea, K.; Strachan, J.; Ballestrin, M.; et al. People with Schizophrenia and Depression Have a Low Omega-3 Index. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fat. Acids 2016, 110, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.Y.; Huang, S.Y.; Su, K.P. A Meta-Analytic Review of Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Compositions in Patients with Depression. Biol. Psychiatry 2010, 68, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciesielski, T.H.; Williams, S.M. Low Omega-3 Intake Is Associated with High Rates of Depression and Preterm Birth on the Country Level. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 19749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallahan, B.; Ryan, T.; Hibbeln, J.R.; Murray, I.T.; Glynn, S.; Ramsden, C.E.; SanGiovanni, J.P.; Davis, J.M. Efficacy of Omega-3 Highly Unsaturated Fatty Acids in the Treatment of Depression. Br. J. Psychiatry 2016, 209, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Layé, S.; Nadjar, A.; Joffre, C.; Bazinet, R.P. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Omega-3 Fatty Acids in the Brain: Physiological Mechanisms and Relevance to Pharmacology. Pharmacol. Rev. 2018, 70, 12–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidzan-Wiącek, M.; Tomczyk, M.; Błażek, M.; Mika, A.; Antosiewicz, J. No Effects of Omega-3 Supplementation on Kynurenine Pathway, Inflammation, Depressive Symptoms, and Stress Response in Males: A Placebo-Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2024, 16, 3744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, M.E.; Smesny, S.; Kim, S.W.; Davey, C.G.; Rice, S.; Sarnyai, Z.; Schlögelhofer, M.; Schäfer, M.R.; Berk, M.; McGorry, P.D.; et al. Omega-6 to Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Ratio and Subsequent Mood Disorders in Young People with at-Risk Mental States: A 7-Year Longitudinal Study. Transl. Psychiatry 2017, 7, e1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeagle, P.L. Cholesterol and the Cell Membrane. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA–Rev. Biomembr. 1985, 822, 267–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Shen, W.J.; Azhar, S. Cellular Cholesterol Delivery, Intracellular Processing and Utilization for Biosynthesis of Steroid Hormones. Nutr. Metab. 2010, 7, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saher, G.; Simons, M. Cholesterol and Myelin Biogenesis. Subcell Biochem. 2010, 51, 489–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wysokiński, A.; Strzelecki, D.; Kłoszewska, I. Levels of Triglycerides, Cholesterol, LDL, HDL and Glucose in Patients with Schizophrenia, Unipolar Depression and Bipolar Disorder. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 2015, 9, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Persons, J.E.; Fiedorowicz, J.G. Depression and Serum Low-Density Lipoprotein: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Affect. Disord. 2016, 206, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rina, S.; Martua, L. Overview of HDL, LDL, Triglycerides, and Total Cholesterol in Obese Patients. In Proceedings of the 2nd Syedza Saintika International Conference on Nursing, Midwifery, Medical Laboratory Technology, Public Health, and Health Information Management (SeSICNiMPH 2021), Padang, Indonesia, 23 September 2021; Atlantis Press: Paris, France, 2021; pp. 12–14. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-Pérez, E.J.; Sepúlveda, F.J.; Peters, C.; Bascuñán, D.; Riffo-Lepe, N.O.; González-Sanmiguel, J.; Sánchez, S.A.; Peoples, R.W.; Vicente, B.; Aguayo, L.G. Effect of Cholesterol on Membrane Fluidity and Association of Aβ Oligomers and Subsequent Neuronal Damage: A Double-Edged Sword. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2018, 10, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakao, M.; Yano, E. Relationship between Major Depression and High Serum Cholesterol in Japanese Men. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 2004, 204, 273–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, R.E.; Palinkas, L.A.; Barrett-Connor, E.L.; Wingard, D.L. Plasma Cholesterol and Depressive Symptoms in Older Men. Lancet 1993, 341, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tedders, S.H.; Fokong, K.D.; McKenzie, L.E.; Wesley, C.; Yu, L.; Zhang, J. Low Cholesterol Is Associated with Depression among US Household Population. J. Affect. Disord. 2011, 135, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, C.J.; Musenbichler, C.; Böhm, L.; Färber, K.; Fischer, A.I.; von Nippold, F.; Winkelmann, M.; Richter-Schmidinger, T.; Mühle, C.; Kornhuber, J.; et al. LDL Cholesterol Relates to Depression, Its Severity, and the Prospective Course. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2019, 92, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelberg, H. Low Serum Cholesterol and Suicide. Lancet 1992, 339, 727–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Li, L.; Liu, J.; Huang, Q.; Wang, S.; Shu, Y. Association of Non-HDL-C and Depression: A Cross-Sectional Analysis of the NHANES Data. Front. Psychiatry 2023, 14, 1274648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, G.; Han, Y.; Meng, F.; He, Y.; Srisai, D.; Farias, M.; Dang, M.; Palmiter, R.D.; Xu, Y.; Wu, Q. Reciprocal Control of Obesity and Anxiety-Depressive Disorder via a GABA and Serotonin Neural Circuit. Mol. Psychiatry 2021, 26, 2837–2853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, M.; Maemura, K.; Kanbara, K.; Tamayama, T.; Hayasaki, H. GABA and GABA Receptors in the Central Nervous System and Other Organs. Int. Rev. Cytol. 2002, 213, 1–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, I.; Jo, K.; Shin, K.C.; Kim, J.I.; Ji, Y.; Park, Y.J.; Park, J.; Jeon, Y.G.; Ka, S.; Suk, S.; et al. GABA-Stimulated Adipose-Derived Stem Cells Suppress Subcutaneous Adipose Inflammation in Obesity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 11936–11945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Oh, H.J.; Lee, B.Y. GABA Prevents Age-Related Sarcopenic Obesity in Mice with High-Fat-Diet-Induced Obesity. Cells 2023, 12, 2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueno, H.; Nakazato, M. Mechanistic Relationship between the Vagal Afferent Pathway, Central Nervous System and Peripheral Organs in Appetite Regulation. J. Diabetes Investig. 2016, 7, 812–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geisler, C.E.; Ghimire, S.; Bruggink, S.M.; Miller, K.E.; Weninger, S.N.; Kronenfeld, J.M.; Yoshino, J.; Klein, S.; Duca, F.A.; Renquist, B.J. A Critical Role of Hepatic GABA in the Metabolic Dysfunction and Hyperphagia of Obesity. Cell Rep. 2021, 35, 109301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dantas, W.S.; Zunica, E.R.M.; Heintz, E.C.; Vandanmagsar, B.; Floyd, Z.E.; Yu, Y.; Fujioka, H.; Hoppel, C.L.; Belmont, K.P.; Axelrod, C.L.; et al. Mitochondrial Uncoupling Attenuates Sarcopenic Obesity by Enhancing Skeletal Muscle Mitophagy and Quality Control. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2022, 13, 1821–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Han, H.; Song, G.; Oh, H.J.; Lee, B.Y. Anti-Obesity Effects of GABA in C57BL/6J Mice with High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity and 3T3-L1 Adipocytes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duman, R.S.; Sanacora, G.; Krystal, J.H. Altered Connectivity in Depression: GABA and Glutamate Neurotransmitter Deficits and Reversal by Novel Treatments. Neuron 2019, 102, 75–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fee, C.; Banasr, M.; Sibille, E. Somatostatin-Positive Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid Interneuron Deficits in Depression: Cortical Microcircuit and Therapeutic Perspectives. Biol. Psychiatry 2017, 82, 549–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mann, J.J.; Oquendo, M.A.; Watson, K.T.; Boldrini, M.; Malone, K.M.; Ellis, S.P.; Sullivan, G.; Cooper, T.B.; Xie, S.; Currier, D. Anxiety in Major Depression and Cerebrospinal Fluid Free Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid. Depress. Anxiety 2014, 31, 814–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romeo, B.; Choucha, W.; Fossati, P.; Rotge, J.Y. Meta-Analysis of Central and Peripheral γ-Aminobutyric Acid Levels in Patients with Unipolar and Bipolar Depression. J. Psychiatry Neurosci. 2018, 43, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godfrey, K.E.M.; Gardner, A.C.; Kwon, S.; Chea, W.; Muthukumaraswamy, S.D. Differences in Excitatory and Inhibitory Neurotransmitter Levels between Depressed Patients and Healthy Controls: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2018, 105, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasler, G.; van der Veen, J.W.; Tumonis, T.; Meyers, N.; Shen, J.; Drevets, W.C. Reduced Prefrontal Glutamate/Glutamine and Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid Levels in Major Depression Determined Using Proton Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2007, 64, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, R.B.; Shungu, D.C.; Mao, X.; Nestadt, P.; Kelly, C.; Collins, K.A.; Murrough, J.W.; Charney, D.S.; Mathew, S.J. Amino Acid Neurotransmitters Assessed by Proton Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy: Relationship to Treatment Resistance in Major Depressive Disorder. Biol. Psychiatry 2009, 65, 792–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klumpers, U.M.; Veltman, D.J.; Drent, M.L.; Boellaard, R.; Comans, E.F.; Meynen, G.; Lammertsma, A.A.; Hoogendijk, W.J. Reduced Parahippocampal and Lateral Temporal GABAA-[11C]Flumazenil Binding in Major Depression: Preliminary Results. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2010, 37, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.H.; Dhanaraj, V.; Mackenzie, A.E.; Young, I.M.; Tanglay, O.; Briggs, R.G.; Chakraborty, A.R.; Hormovas, J.; Fonseka, R.D.; Kim, S.J.; et al. Anatomy and White Matter Connections of the Parahippocampal Gyrus. World Neurosurg. 2021, 148, e218–e226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aihara, M.; Ida, I.; Yuuki, N.; Oshima, A.; Kumano, H.; Takahashi, K.; Fukuda, M.; Oriuchi, N.; Endo, K.; Matsuda, H.; et al. HPA Axis Dysfunction in Unmedicated Major Depressive Disorder and Its Normalization by Pharmacotherapy Correlates with Alteration of Neural Activity in Prefrontal Cortex and Limbic/Paralimbic Regions. Psychiatry Res. 2007, 155, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persson, J.; Wall, A.; Weis, J.; Gingnell, M.; Antoni, G.; Lubberink, M.; Bodén, R. Inhibitory and Excitatory Neurotransmitter Systems in Depressed and Healthy: A Positron Emission Tomography and Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Study. Psychiatry Res. Neuroimaging 2021, 315, 111327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattopadhyaya, B.; Di Cristo, G.; Wu, C.Z.; Knott, G.; Kuhlman, S.; Fu, Y.; Palmiter, R.D.; Huang, Z.J. GAD67-Mediated GABA Synthesis and Signaling Regulate Inhibitory Synaptic Innervation in the Visual Cortex. Neuron 2007, 54, 889–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guilloux, J.P.; Douillard-Guilloux, G.; Kota, R.; Wang, X.; Gardier, A.M.; Martinowich, K.; Tseng, G.C.; Lewis, D.A.; Sibille, E. Molecular Evidence for BDNF- and GABA-Related Dysfunctions in the Amygdala of Female Subjects with Major Depression. Mol. Psychiatry 2012, 17, 1130–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilabert-Juan, J.; Varea, E.; Guirado, R.; Blasco-Ibáñez, J.M.; Crespo, C.; Nácher, J. Alterations in the Expression of PSA-NCAM and Synaptic Proteins in the Dorsolateral Prefrontal Cortex of Psychiatric Disorder Patients. Neurosci. Lett. 2012, 530, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibille, E.; Morris, H.M.; Kota, R.S.; Lewis, D.A. GABA-Related Transcripts in the Dorsolateral Prefrontal Cortex in Mood Disorders. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2011, 14, 721–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osaka, H.; Kanazawa, T. Emerging Trends in Antipsychotic and Antidepressant Drug Development: Targeting Nonmonoamine Receptors and Innovative Mechanisms. PCN Rep. 2023, 2, e157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutler, A.J.; Mattingly, G.W.; Kornstein, S.G.; Aaronson, S.T.; Lasser, R.; Zhang, H.; Rana, N.; Brown, C.; Levin, S.; Miller, C.; et al. Long-Term Safety and Efficacy of Initial and Repeat Treatment Courses with Zuranolone in Adult Patients with Major Depressive Disorder: Interim Results From the Open-Label, Phase 3 SHORELINE Study. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2023, 85, 50879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fogaça, M.V.; Duman, R.S. Cortical GABAergic Dysfunction in Stress and Depression: New Insights for Therapeutic Interventions. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2019, 13, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schür, R.R.; Draisma, L.W.; Wijnen, J.P.; Boks, M.P.; Koevoets, M.G.; Joëls, M.; Klomp, D.W.; Kahn, R.S.; Vinkers, C.H. Brain GABA Levels across Psychiatric Disorders: A Systematic Literature Review and Meta-Analysis of (1) H-MRS Studies. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2016, 37, 3337–3352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiapponi, C.; Piras, F.; Caltagirone, C.; Spalletta, G. GABA System in Schizophrenia and Mood Disorders: A Mini Review on Third-Generation Imaging Studies. Front. Psychiatry 2016, 7, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Authors and Year | BMI Differences | Depressive Symptom Severity and Subtype | Key Findings |
|---|---|---|---|
| Milaneschi et al., 2017 [62] | • Current MDD group: mean BMI = 25.8 ± 5.3 kg/m2. • CG: mean BMI = 25.1 ± 4.5 kg/m2. | • Three MDD classes identified based on IDS-SR30: severe typical, severe atypical, and moderate. • Melancholic and atypical subtypes were examined. | • Higher leptin levels were associated with the atypical subtype of MDD. • No association found between leptin and overall MDD diagnosis or melancholic subtype. |
| Burrows et al. (2024) [64] | • MDD group: mean BMI = 30.41 ± 4.61 kg/m2. • CG: mean BMI = 25.1 ± 4.5 kg/m² | • Patients with MDD showed moderate to severe depressive symptoms (assessed using PROMIS Depression Score). • The study did not specify MDD subtypes (e.g., melancholic or atypical). | • Higher serum leptin levels were observed in the MDD group compared to CG. |
| Esel et al. (2005) [65] | • MDD group: mean BMI = 25.68 ± 4.59 kg/m2 (♂ 23.92 ± 3.58; ♀ 26.74 ± 4.88). • CG: mean BMI = 24.49 ± 3.28 kg/m2 (♂ 23.43 ± 3.33; ♀ 26.13 ± 2.56) | • Patients with MDD showed moderate to severe depressive symptoms (assessed using MADRS). • The study did not specify MDD subtypes (e.g., melancholic or atypical). | • Women with MDD had significantly higher leptin levels than healthy women in the CG. • No difference in leptin levels was found between men with MDD and healthy men. |
| Heinen et al. (2023) [66] | • MDD group: mean BMI = 24.7 ± 0.4 kg/m2. • CG: mean BMI = 24.6 ± 0.7 kg/m2. | • Patients with MDD showed moderate depressive symptoms (assessed using BDI-2). • The study did not specify MDD subtypes (e.g., melancholic or atypical). | • No significant differences in leptin levels were found between MDD patients and healthy controls. |
| Sohan et al. (2023) [67] | • MDD group: mean BMI = 23.57 ± 0.308 kg/m2. • CG: mean BMI = 24.45 ± 0.26 kg/m2. | • Patients with MDD showed moderate depressive symptoms (assessed using HAM-D). • The study did not specify MDD subtypes (e.g., melancholic or atypical). | • No significant differences in serum leptin levels were observed between MDD patients and healthy controls. |
| Zhang et al. (2024) [70] | • MDD group: mean BMI = 28.69 ± 5.47 kg/m2 (sample I); 27.16 ± 5.59 kg/m2 (sample II). • CG: BMI = 27.90 ± 5.66 kg/m2 (sample I); 24.86 ± 4.76 kg/m2 (sample II). | • Patients in both samples showed at least moderate, and likely severe, depressive symptoms (assessed using PHQ-9 and PROMIS Depression Score). • The study specifically focused on atypical depressive symptoms, defined as sleep problems, fatigue, and appetite changes. | • Higher leptin levels were correlated with increased severity of atypical depressive symptoms. |
| Metabolic Marker | Mechanism of Action | Marker Level in Obesity | Effect in Obesity | Marker Level in Depression |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Leptin | proinflammatory | ↑ [57,62] | ↑ inflammation | ↑ [64,65,70], no significant difference [67] |
| Adiponectin | anti-inflammatory | ↓ [83] | ↑ inflammation | ↓ [57,80,83,86], no significant difference [59,90], ↑ [87] |
| Resistin | proinflammatory | ↑ [91] | ↑ inflammation | ↑ [18,99,100,101,102,104], ↓ [60,103] |
| Ghrelin | anti-inflammatory | ↓ [122,123] | ↑ inflammation | ↑ [115,116], no significant difference [117,118] |
| Fetuin-A | anti-inflammatory | ↑ [108] | ↓ inflammation | ↑ [57], ↓ [33] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oracz, A.J.; Zwierz, M.; Naumowicz, M.; Suprunowicz, M.; Waszkiewicz, N. Relationship Between Obesity and Depression Considering the Inflammatory Theory. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4966. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26114966
Oracz AJ, Zwierz M, Naumowicz M, Suprunowicz M, Waszkiewicz N. Relationship Between Obesity and Depression Considering the Inflammatory Theory. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(11):4966. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26114966
Chicago/Turabian StyleOracz, Aleksandra Julia, Mateusz Zwierz, Maciej Naumowicz, Maria Suprunowicz, and Napoleon Waszkiewicz. 2025. "Relationship Between Obesity and Depression Considering the Inflammatory Theory" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 11: 4966. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26114966
APA StyleOracz, A. J., Zwierz, M., Naumowicz, M., Suprunowicz, M., & Waszkiewicz, N. (2025). Relationship Between Obesity and Depression Considering the Inflammatory Theory. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(11), 4966. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26114966








