Swelling of Homogeneous Alginate Gels with Multi-Stimuli Sensitivity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
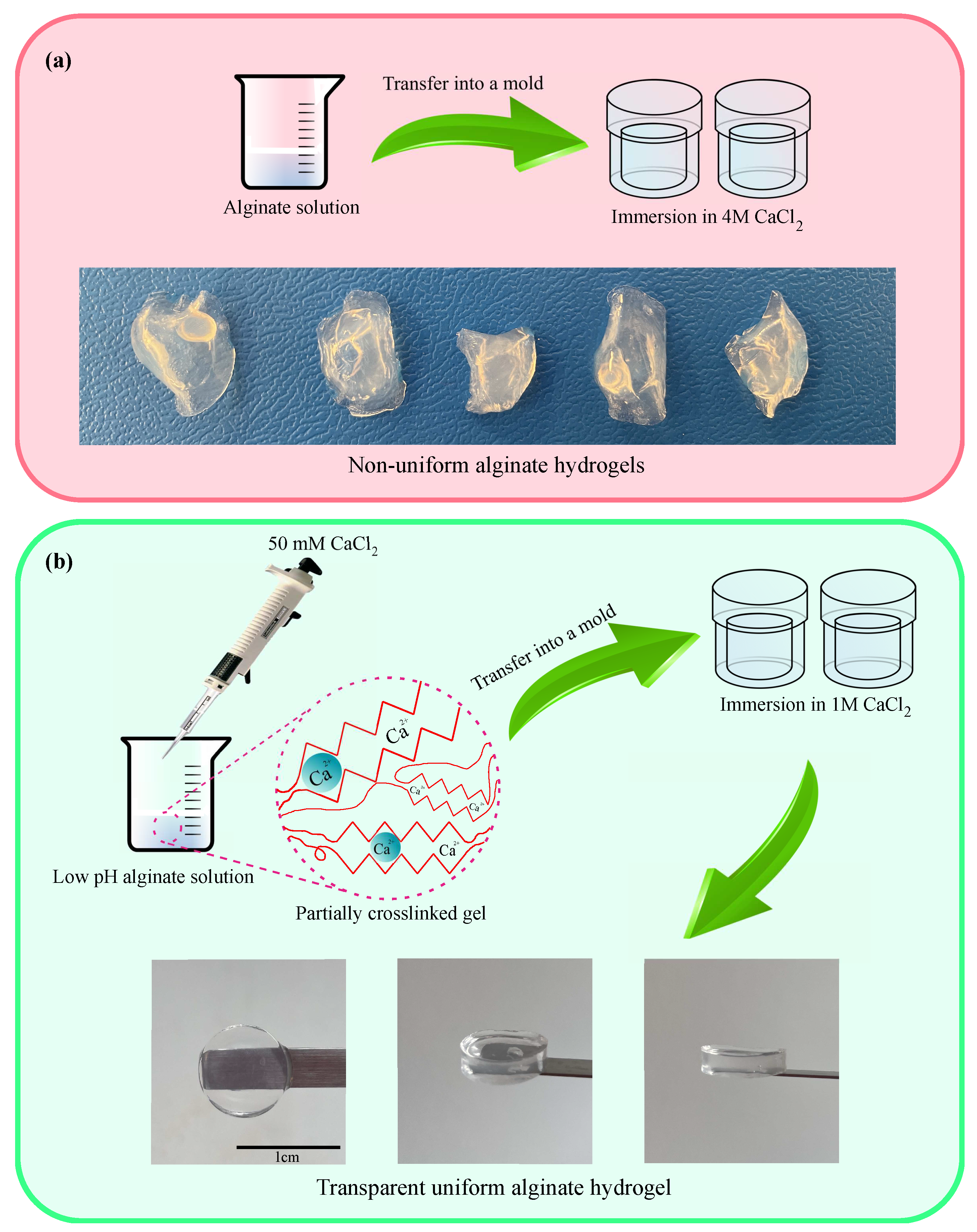
2.2. Preparation of Hydrogels
2.3. Swelling Tests
3. Results and Discussion
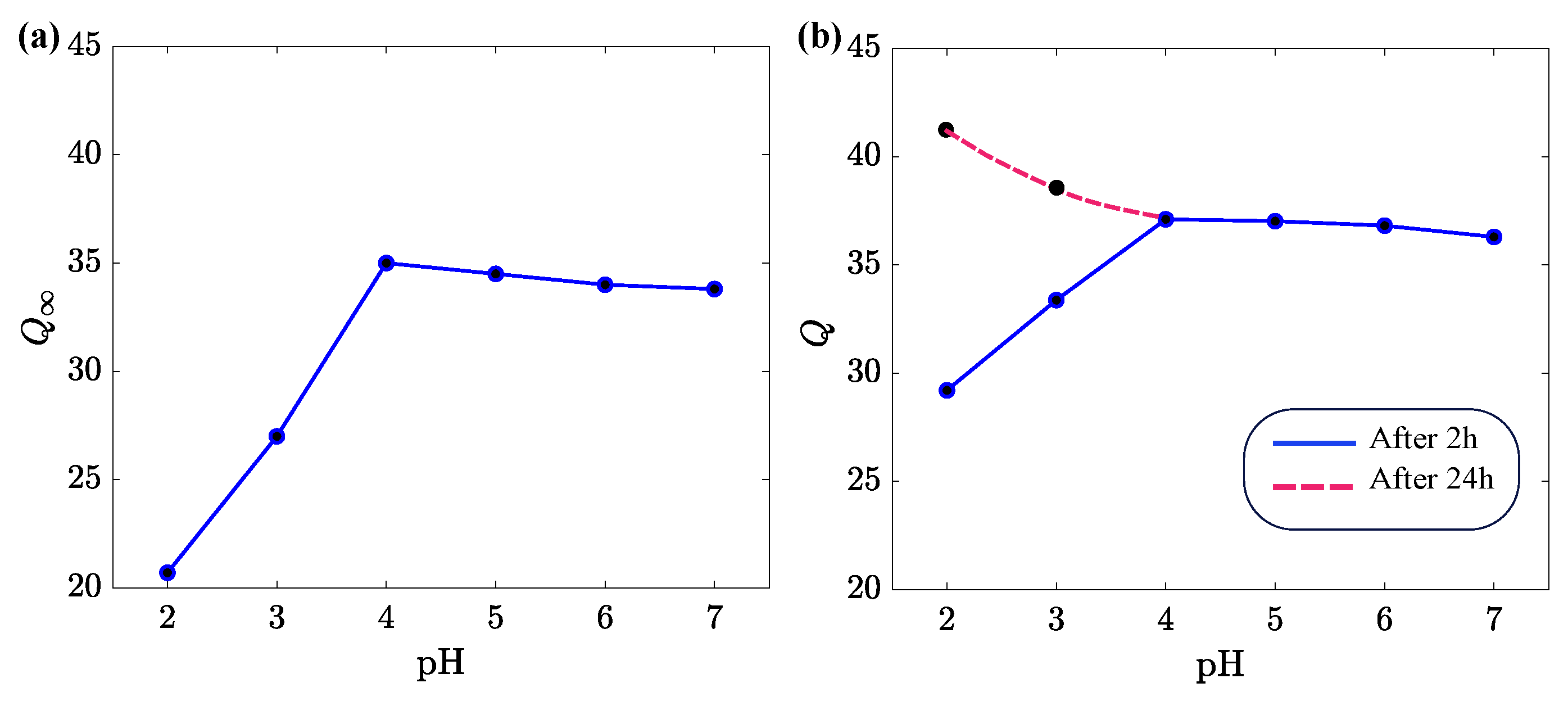
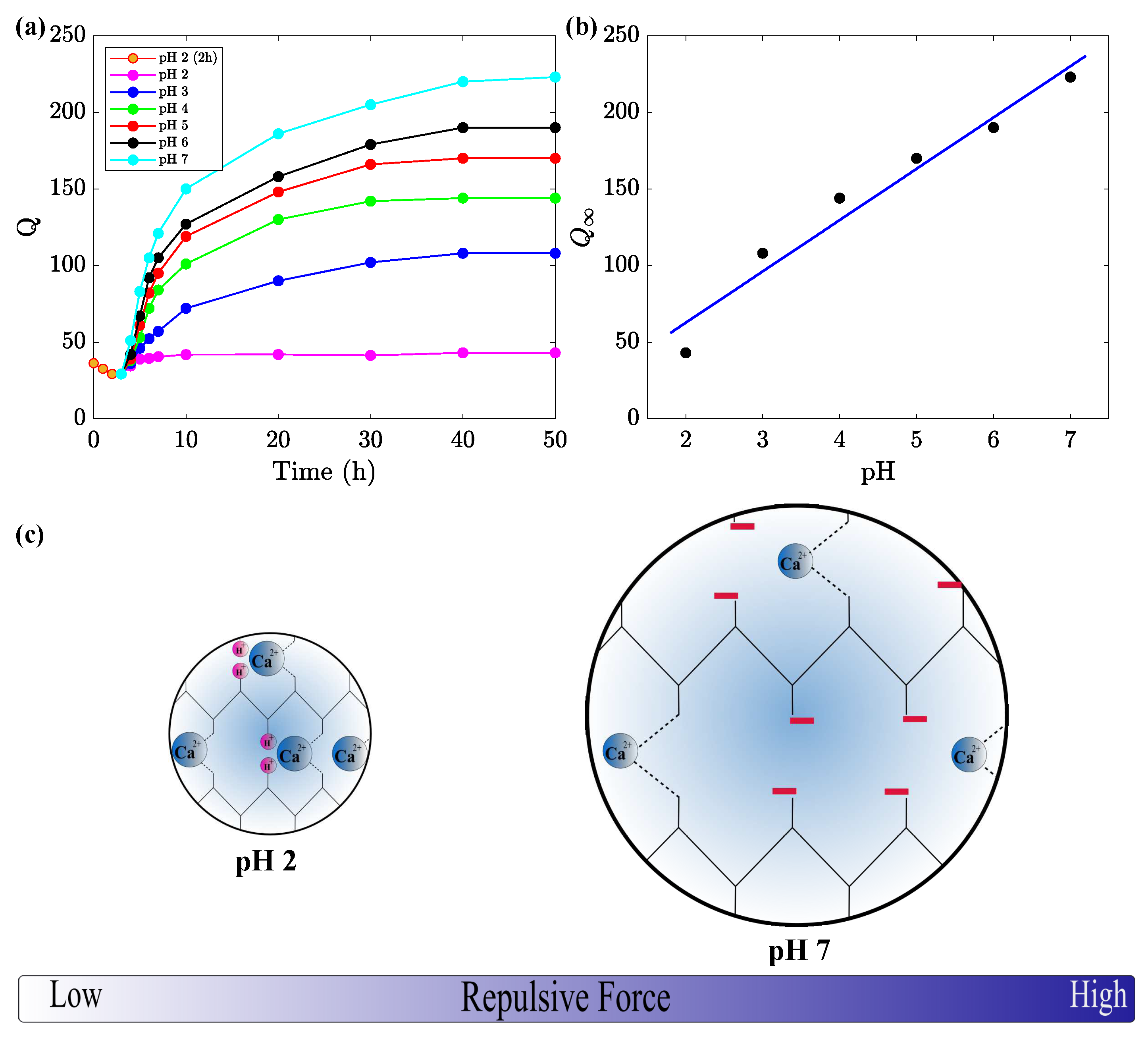
3.1. Swelling of Alginate Gels in Solutions with Various pH
3.2. The Effects of pH on Shrinkage and Re-Swelling of Alginate Gels
3.3. The Effect of Ionic Strength on Swelling of Alginate Gels
3.4. The Effect of Temperature on Swelling of Alginate Gels
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, K.Y.; Mooney, D.J. Alginate: Properties and biomedical applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2012, 37, 106–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurtado, A.; Aljabali, A.A.A.; Mishra, V.; Tambuwala, M.M.; Serrano-Aroca, A. Alginate: Enhancement strategies for advanced applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, C.; Lu, W.; Mata, A.; Nishinari, K.; Fang, Y. Ions-induced gelation of alginate: Mechanisms and applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 177, 578–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grant, G.T.; Morris, E.R.; Rees, D.A.; Smith, P.J.C.; Thom, D. Biological interactions between polysaccharides and divalent cations: The egg-box model. FEBS Lett. 1973, 32, 195–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braccini, I.; Perez, S. Molecular Basis of Ca2+-induced gelation in alginates and pectins: The egg-box model revisited. Biomacromolecules 2001, 2, 1089–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Tan, H. Alginate-based biomaterials for regenerative medicine applications. Materials 2013, 6, 1285–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Axpe, E.; Oyen, M.L. Applications of alginate-based bioinks in 3D bioprinting. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abasalizadeh, F.; Moghaddam, S.V.; Alizadeh, E.; Kashani, E.; Fazljou, S.M.B.; Torbati, M.; Akbarzadeh, A. Alginate-based hydrogels as drug delivery vehicles in cancer treatment and their applications in wound dressing and 3D bioprinting. J. Biol. Eng. 2020, 14, 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Veronica, N.; Heng, P.W.S.; Liew, C.V. Alginate-based matrix tablets for drug delivery. Expert Opin. Drug. Deliv. 2023, 20, 115–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elosegui-Artola, A.; Gupta, A.; Najibi, A.J.; Seo, B.R.; Garry, R.; Tringides, C.M.; de Lazaro, I.; Darnell, M.; Gu, W.; Zhou, Q.; et al. Matrix viscoelasticity controls spatiotemporal tissue organization. Nat. Mater. 2023, 22, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, K.; An, Q.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Y. Recent development of alginate-based materials and their versatile functions in biomedicine, flexible electronics, and environmental uses. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 7, 1302–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skjak-Braek, G.; Grasdalen, H.; Smidsrod, O. Inhomogeneous polysaccharide ionic gels. Carbohydr. Polym. 1989, 10, 31–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, C.K.; Ma, P.X. Ionically crosslinked alginate hydrogels as scaffolds for tissue engineering: Part 1. Structure, gelation rate and mechanical properties. Biomaterials 2001, 22, 511–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Illeperuma, W.R.K.; Suo, Z.; Vlassak, J.J. Hybrid hydrogels with extremely high stiffness and toughness. ACS Macro Lett. 2014, 3, 520–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.D.; Yu, W.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xue, W.M.; Yu, W.T.; Xiong, Y.; Ma, X.J.; Chen, Y.; Yuan, Q. Characterization of structure and diffusion behaviour of Ca-alginate beads prepared with external or internal calcium sources. J. Microencapsul. 2002, 19, 775–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paques, J.P.; van der Linden, E.; van Rijna, C.J.M.; Sagis, L.M.C. Preparation methods of alginate nanoparticles. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 209, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, M.; Abrahim, B.; Veiga, F.; Seica, R.; Cabral, L.M.; Arnaud, P.; Andrade, J.C.; Ribeiro, A.J. Preparation methods and applications behind alginate-based particles. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2017, 14, 769–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maity, C.; Das, N. Alginate-based smart materials and their application: Recent advances and perspectives. Top. Curr. Chem. 2022, 380, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Zhou, H.; Wu, H.; Chen, R.; Guo, S. Preparation of alginate hydrogels through solution extrusion and the release behavior of different drugs. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2016, 27, 1808–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Liu, H.; Qu, X.; Lei, M.; Zhang, C.; Hong, H.; Payne, G.F.; Liu, C. Electrical signals triggered controllable formation of calcium-alginate film for wound treatment. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2017, 28, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javvaji, V.; Baradwaj, A.G.; Payne, G.F.; Raghavan, S.R. Light-activated ionic gelation of common biopolymers. Langmuir 2011, 27, 12591–12596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.D.; Bao, D.C.; Xue, W.M.; Xiong, Y.; Yu, W.T.; Yu, X.J.; Ma, X.J.; Yuan, Q. Preparation of uniform calcium alginate gel beads by membrane emulsification coupled with internal gelation. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2003, 87, 848–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jejurikar, A.; Lawrie, G.; Martin, D.; Grondahl, L. A novel strategy for preparing mechanically robust ionically cross-linked alginate hydrogels. Biomed. Mater. 2011, 6, 025010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, B.Y.; Kim, J. Controlled remodeling of hydrogel networks and subsequent crosslinking: A strategy for preparation of alginate hydrogels with ultrahigh density and enhanced mechanical properties. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2015, 216, 914–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazur, J.; Detsch, R.; Karakaya, E.; Kaschta, J.; Tessmar, J.; Schneidereit, D.; Friedrich, O.; Schubert, D.W.; Boccaccini, A.R. Improving alginate printability for biofabrication: Establishment of a universal and homogeneous pre-crosslinking technique. Biofabrication 2020, 12, 045004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamandia, Z.; Zohurian-Mehr, M.J.; Kabiri, K.; Jamshidi, A.; Mobedi, H. pH-sensitive IPN hydrogel beads of carrageenan-alginate for controlled drug delivery. J. Bioact. Compat. Polym. 2007, 22, 342–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, G.; Lin, Q.; Fan, J. pH- and electro-response characteristics of bacterial cellulose nanofiber/sodium alginate hybrid hydrogels for dual controlled drug delivery. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 47056–47065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sariyer, S.; Duranoglu, D.; Dogan, O.; Kucuk, I. pH-responsive double network alginate/kappa-carrageenan hydrogel beads for controlled protein release: Effect of pH and crosslinking agent. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 56, 101551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postolovic, K.S.; Antonijevic, M.D.; Ljujic, B.; Miletic Kovacevic, M.; Gazdic Jankovic, M.; Stanic, Z.D. pH-responsive hydrogel beads based on alginate, κ-carrageenan and poloxamer for enhanced curcumin, natural bioactive compound, encapsulation and controlled release efficiency. Molecules 2022, 27, 4045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Yu, Z.; Liu, Q.; Liu, K.; Li, M.; Wang, D. Hydrogel degradation triggered by pH for the smart release of antibiotics to combat bacterial infection. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 432–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Hurren, C.; Lu, Z.; Wang, D. pH-Sensitive alginate hydrogel for synergistic anti-infection. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 222, 1723–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhail, M.; Ullah, H.; Vu, Q.L.; Khan, A.; Tsai, M.-J.; Wu, P.-C. Preparation of pH-responsive hydrogels based on chondroitin sulfate/alginate for oral drug delivery. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, B.T.; Long, M.; Piper, J.W.; Yago, T.; McEver, R.P.; Zhu, C. Direct observation of catch bonds involving cell-adhesion molecules. Nature 2003, 423, 190–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulla, Y.; Avellaneda, M.J.; Roland, A.; Baldauf, L.; Jung, W.; Kim, T.; Tans, S.J.; Koenderink, G.H. Weak catch bonds make strong networks. Nat. Mater. 2022, 21, 1019–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakrabarti, S.; Hinczewski, M.; Thirumalai, D. Phenomenological and microscopic theories for catch bonds. J. Struct. Biol. 2017, 197, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, R.T.; Boulatov, R. The many flavours of mechanochemistry and its plausible conceptual underpinnings. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2021, 5, 148–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyer, B.V.S.; Yashin, V.V.; Balazs, A.C. Harnessing biomimetic catch bonds to create mechanically robust nanoparticle networks. Polymer 2015, 69, 310–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbanga, B.L.; Iyer, B.V.S.; Yashin, V.V.; Balazs, A.C. Tuning the mechanical properties of polymer-grafed nanoparticle networks through the use of biomimetic catch bonds. Macromolecules 2016, 49, 1353–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dansuk, K.C.; Keten, S. Self-strengthening biphasic nanoparticle assemblies with intrinsic catch bonds. Nat. Comm. 2021, 12, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Duan, X.; Su, X.; Tian, Z.; Jiang, A.; Wan, Z.; Wang, H.; Wei, P.; Zhao, B.; Liu, X.; et al. Catch bond-inspired hydrogels with repeatable and loading rate-sensitive specific adhesion. Bioact. Mater. 2023, 21, 566–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khare, A.R.; Peppas, N.A. Swelling/deswelling of anionic copolymer gels. Biomaterials 1995, 16, 559–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drozdov, A.D.; Christiansen, J.d.C. Swelling of pH-sensitive hydrogels. Phys. Rev. E 2015, 91, 022305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doumeche, B.; Kuppers, M.; Stapf, S.; Blumich, B.; Hartmeier, W.; Ansorge-Schumacher, M.B. New approaches to the visualization, quantification and explanation of acid-induced water loss from Ca-alginate hydrogel beads. J. Microencapsul. 2004, 21, 565–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumberger, T.; Ronsin, O. Cooperative effect of stress and ion displacement on the dynamics of cross-link unzipping and rupture of alginate gels. Biomacromolecules 2010, 11, 1571–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, L.; Jiang, M.; Dong, X.; Bai, X.; Tong, J.; Zhou, J. Controlled mechanical and swelling properties of poly(vinyl alcohol)/sodium alginate blend hydrogels prepared by freeze-thaw followed by Ca2+ crosslinking. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 124, 823–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donati, I.; Holtan, S.; Morch, Y.A.; Borgogna, M.; Dentini, M.; Skjak-Braek, G. New hypothesis on the role of alternating sequences in calcium-alginate gels. Biomacromolecules 2005, 6, 1031–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinsen, A.; Skjak-Braek, G.; Smidsrod, O. Alginate as immobilization material: I. Correlation between chemical and physical properties of alginate gel beads. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1989, 33, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajpai, S.; Sharma, S. Investigation of swelling/degradation behaviour of alginate beads crosslinked with Ca2+ and Ba2+ ions. React. Funct. Polym. 2004, 59, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messing, R.; Schmidt, A.M. Perspectives for the mechanical manipulation of hybrid hydrogels. Polym. Chem. 2011, 2, 18–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drozdov, A.D.; deClaville Christiansen, J. Modeling the effects of pH and ionic strength on swelling of polyelectrolyte gels. J. Chem. Phys. 2015, 142, 114904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drozdov, A.D.; deClaville Christiansen, J. Modeling the effects of pH and ionic strength on swelling of anionic polyelectrolyte gels. Model. Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2015, 23, 055005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golmohamadi, M.; Wilkinson, K.J. Diffusion of ions in a calcium alginate hydrogel – structure is the primary factor controlling diffusion. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 94, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Huang, C.; Jin, X. Influence of K+ and Na+ ions on the degradation of wet-spun alginate fibers for tissue engineering. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2017, 134, 44396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, L.; Wu, P.Y. Exploring the hydrogen-bond structures in sodium alginate through two-dimensional correlation infrared spectroscopy. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 205, 420–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Cheng, J.; Ao, Q. Preparation of alginate-based biomaterials and their applications in biomedicine. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.J.; Srebnik, S.; Rojas, O.J. Revisiting cation complexation and hydrogen bonding of single-chain polyguluronate alginate. Biomacromolecules 2021, 22, 4027–4036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.J.; Srebnik, S.; Rojas, O.J. Competing effects of hydration and cation complexation in single-chain alginate. Biomacromolecules 2022, 23, 1949–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.S.; McKay, G. A comparison of chemisorption kinetic models applied to pollutant removal on various sorbents. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 1998, 76, 332–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schott, H. Swelling kinetics of polymers. J. Macromol. Sci. Part B 2006, 31, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peppas, N.A.; Narasimhan, B. Mathematical models in drug delivery: How modeling has shaped the way we design new drug delivery systems. J. Control. Release 2014, 190, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caccavo, D. An overview on the mathematical modeling of hydrogels behavior for drug delivery systems. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 560, 175–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amsden, B. Solute diffusion within hydrogels. Mechanisms and models. Macromolecules 1998, 31, 8382–8395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drozdov, A.D.; Papadimitriou, A.A.; Liely, J.H.M.; Sanporean, C.-G. Constitutive equations for the kinetics of swelling of hydrogels. Mech. Mater. 2016, 102, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drozdov, A.D. Mechanical behavior of temperature-sensitive gels under equilibrium and transient swelling. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 2018, 128, 79–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Malektaj, H.; Drozdov, A.D.; deClaville Christiansen, J. Swelling of Homogeneous Alginate Gels with Multi-Stimuli Sensitivity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5064. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24065064
Malektaj H, Drozdov AD, deClaville Christiansen J. Swelling of Homogeneous Alginate Gels with Multi-Stimuli Sensitivity. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(6):5064. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24065064
Chicago/Turabian StyleMalektaj, Haniyeh, Aleksey D. Drozdov, and Jesper deClaville Christiansen. 2023. "Swelling of Homogeneous Alginate Gels with Multi-Stimuli Sensitivity" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 6: 5064. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24065064
APA StyleMalektaj, H., Drozdov, A. D., & deClaville Christiansen, J. (2023). Swelling of Homogeneous Alginate Gels with Multi-Stimuli Sensitivity. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(6), 5064. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24065064







