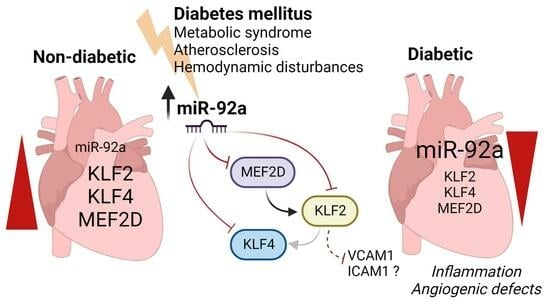
Dysregulation of Krüppel-like Factor 2 and Myocyte Enhancer Factor 2D Drive Cardiac Microvascular Inflammation and Dysfunction in Diabetes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
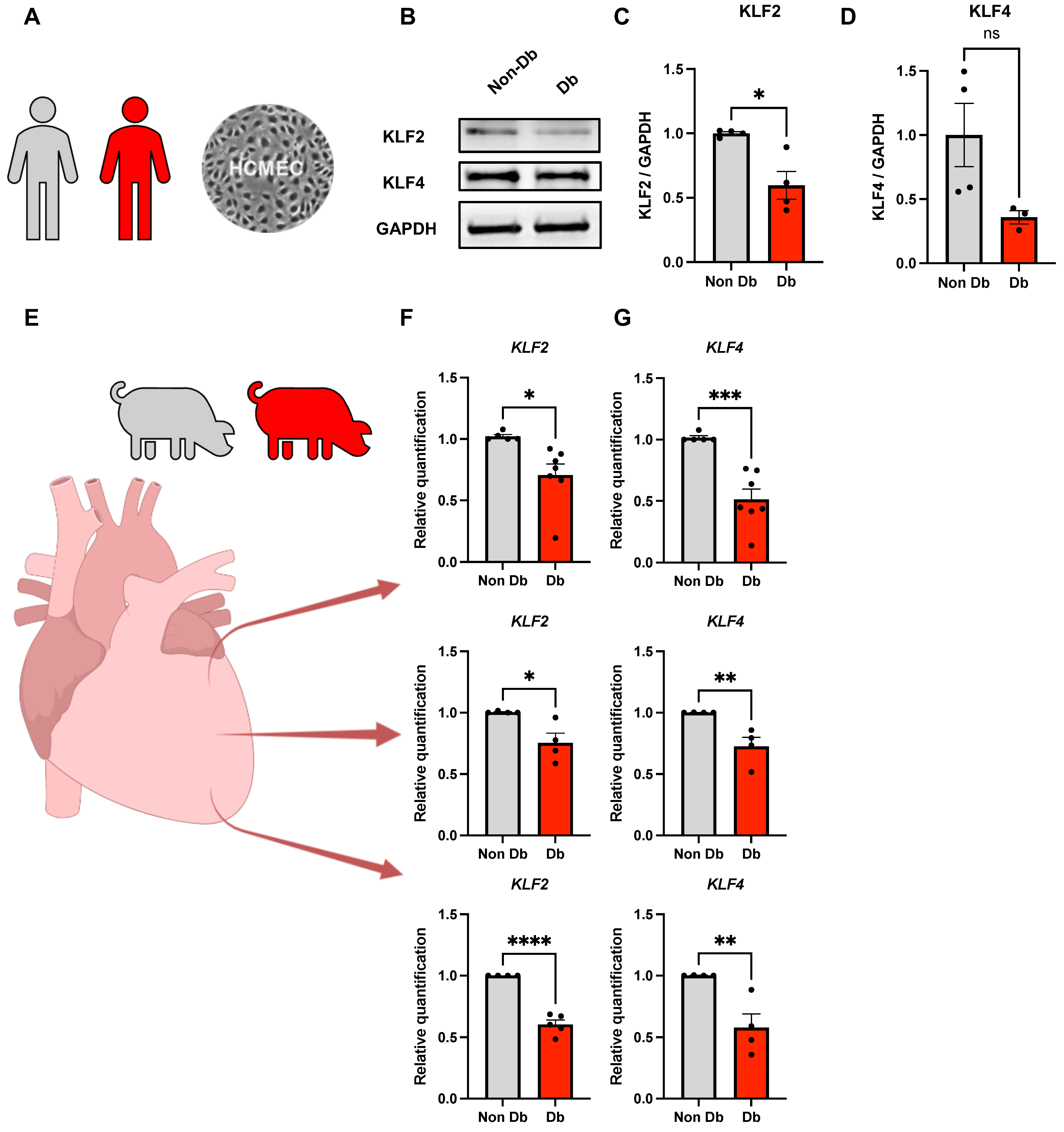
2.1. Expression of KLF2 and KLF4 in Diabetic HCMECs and Porcine Heart Tissue
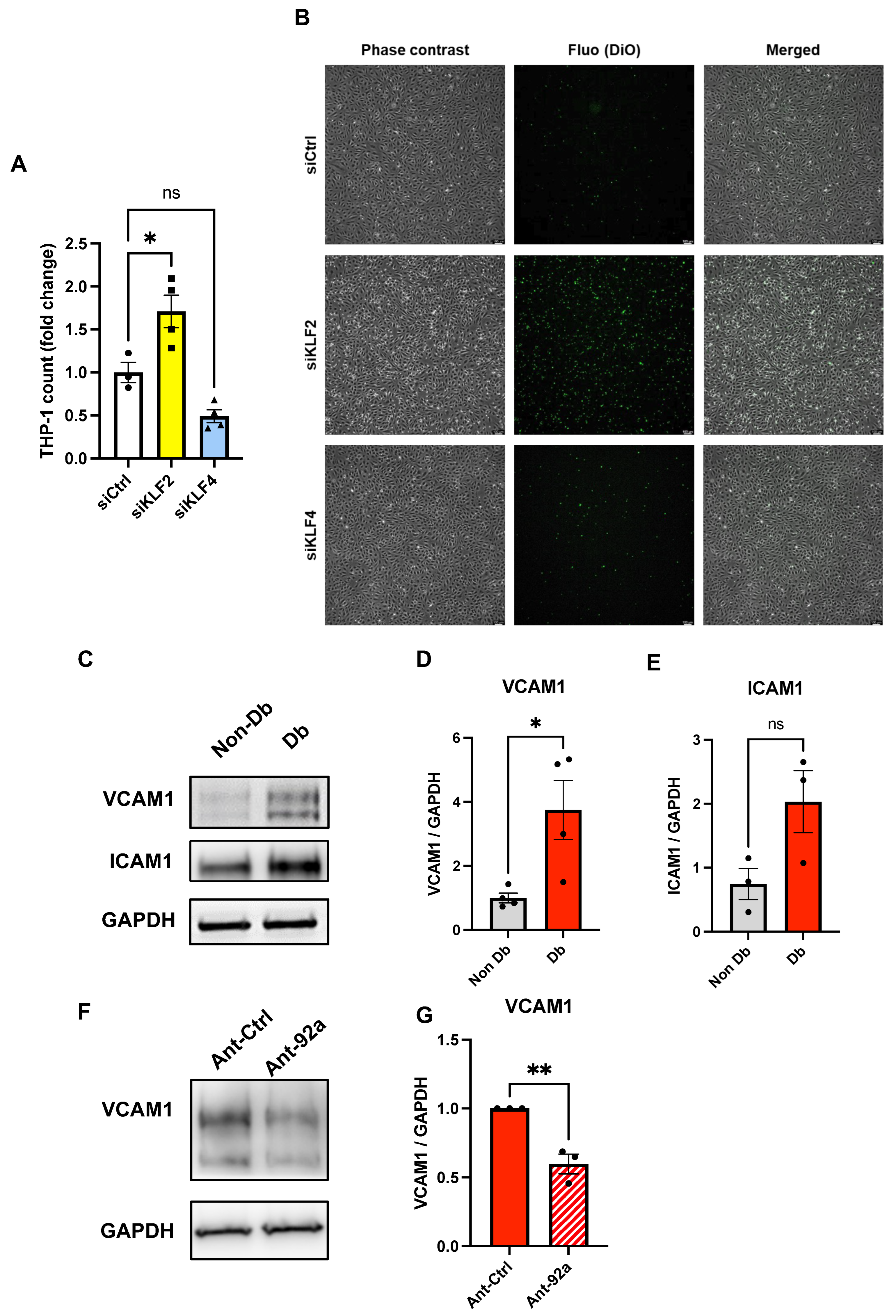
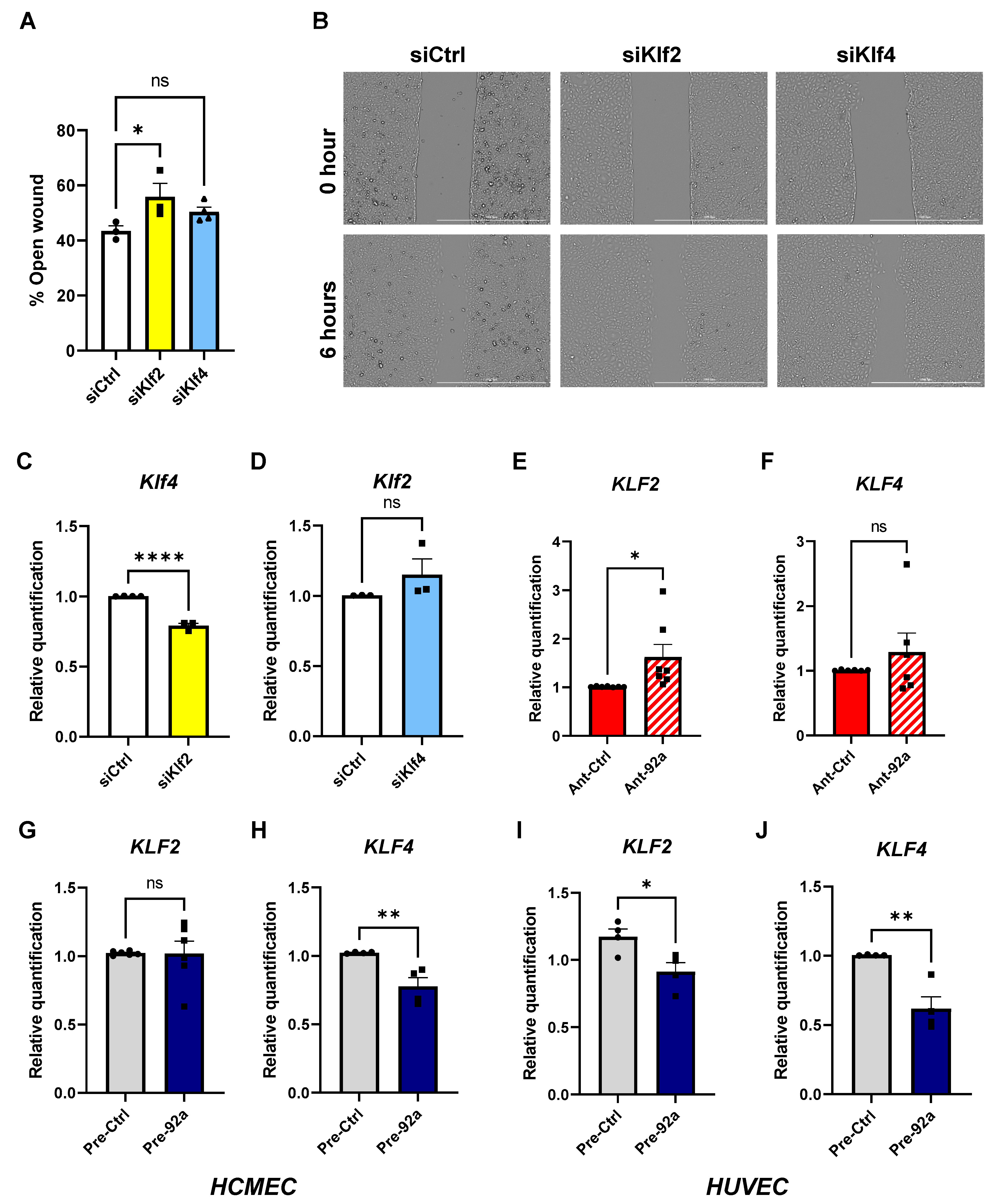
2.2. Endothelial Inflammatory Phenotype Driven by KLF2 Ablation
2.3. The Role of miR-92a in Expression and Regulation of KLF2 and KLF4 in Endothelial Cells
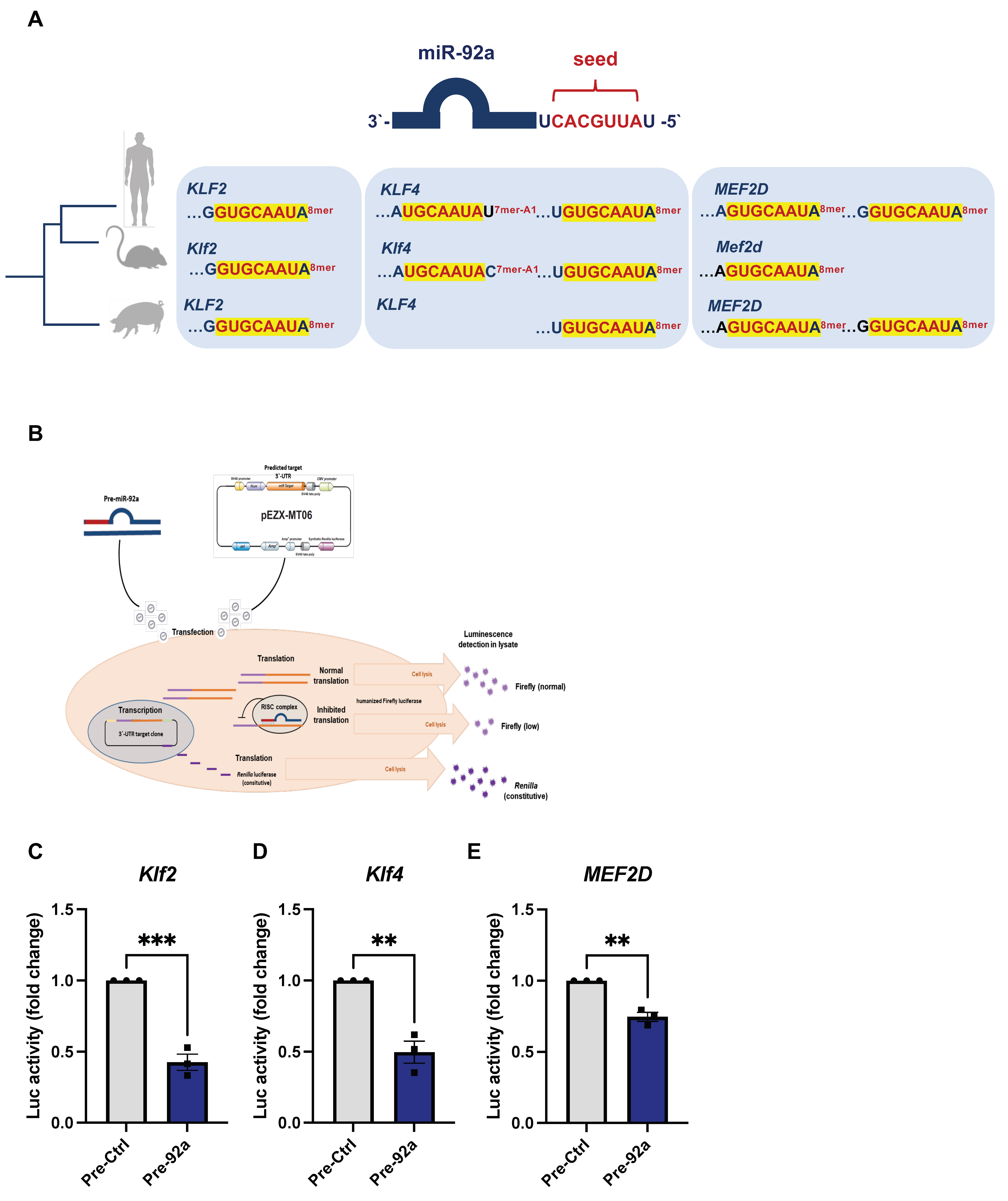
2.4. Direct Targeting of KLF2, KLF4, and MEF2D by miR-92a
2.5. MEF2D as miR-92a Target Dysregulated in Diabetes
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. EC Culture
4.2. Transfection
4.3. Wound Healing
4.4. Flow Chamber Assay
4.5. Western Blot
4.6. Quantitative PCR
4.7. ImageJ Analysis
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sarwar, N.; Gao, P.; Seshasai, S.R.; Gobin, R.; Kaptoge, S.; Di Angelantonio, E.; Ingelsson, E.; Lawlor, D.A.; Selvin, E.; Stampfer, M.; et al. Diabetes mellitus, fasting blood glucose concentration, and risk of vascular disease: A collaborative meta-analysis of 102 prospective studies. Lancet 2010, 375, 2215–2222. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Assar, M.E.; Angulo, J.; Rodríguez-Mañas, L. Diabetes and ageing-induced vascular inflammation. J. Physiol. 2016, 594, 2125–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinkel, R.; Howe, A.; Renner, S.; Ng, J.; Lee, S.; Klett, K.; Kaczmarek, V.; Moretti, A.; Laugwitz, K.L.; Skroblin, P.; et al. Diabetes Mellitus-Induced Microvascular Destabilization in the Myocardium. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2017, 69, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samak, M.; Kaltenborn, D.; Kues, A.; Le Noble, F.; Hinkel, R.; Germena, G. Micro-RNA 92a as a Therapeutic Target for Cardiac Microvascular Dysfunction in Diabetes. Biomedicines 2021, 10, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pechlivani, N.; Ajjan, R.A. Thrombosis and Vascular Inflammation in Diabetes: Mechanisms and Potential Therapeutic Targets. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2018, 5, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkins, G.B.; Jain, M.K. Role of Krüppel-like transcription factors in endothelial biology. Circ. Res. 2007, 100, 1686–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, T.; Aizawa, K.; Matsumura, T.; Nagai, R. Vascular implications of the Krüppel-like family of transcription factors. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2005, 25, 1135–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botella, L.M.; Sánchez-Elsner, T.; Sanz-Rodriguez, F.; Kojima, S.; Shimada, J.; Guerrero-Esteo, M.; Cooreman, M.P.; Ratziu, V.; Langa, C.; Vary, C.P.; et al. Transcriptional activation of endoglin and transforming growth factor-beta signaling components by cooperative interaction between Sp1 and KLF6: Their potential role in the response to vascular injury. Blood 2002, 100, 4001–4010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweet, D.R.; Fan, L.; Hsieh, P.N.; Jain, M.K. Krüppel-Like Factors in Vascular Inflammation: Mechanistic Insights and Therapeutic Potential. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2018, 5, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkins, G.B.; Wang, Y.; Mahabeleshwar, G.H.; Shi, H.; Gao, H.; Kawanami, D.; Natesan, V.; Lin, Z.; Simon, D.I.; Jain, M.K. Hemizygous deficiency of Krüppel-like factor 2 augments experimental atherosclerosis. Circ. Res. 2008, 103, 690–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, G.; Hamik, A.; Nayak, L.; Tian, H.; Shi, H.; Lu, Y.; Sharma, N.; Liao, X.; Hale, A.; Boerboom, L.; et al. Endothelial Kruppel-like factor 4 protects against atherothrombosis in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 4727–4731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dekker, R.J.; van Soest, S.; Fontijn, R.D.; Salamanca, S.; de Groot, P.G.; VanBavel, E.; Pannekoek, H.; Horrevoets, A.J. Prolonged fluid shear stress induces a distinct set of endothelial cell genes, most specifically lung Krüppel-like factor (KLF2). Blood 2002, 100, 1689–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Thienen, J.V.; Fledderus, J.O.; Dekker, R.J.; Rohlena, J.; van Ijzendoorn, G.A.; Kootstra, N.A.; Pannekoek, H.; Horrevoets, A.J. Shear stress sustains atheroprotective endothelial KLF2 expression more potently than statins through mRNA stabilization. Cardiovasc. Res. 2006, 72, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; Xiao, H.; Laguna-Fernandez, A.; Villarreal, G., Jr.; Wang, K.C.; Geary, G.G.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, W.C.; Huang, H.D.; Zhou, J.; et al. Flow-Dependent Regulation of Kruppel-Like Factor 2 Is Mediated by MicroRNA-92a. Circulation 2011, 124, 633–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.Z.; Jiménez, J.M.; Ou, K.; McCormick, M.E.; Zhang, L.D.; Davies, P.F. Hemodynamic disturbed flow induces differential DNA methylation of endothelial Kruppel-Like Factor 4 promoter in vitro and in vivo. Circ. Res. 2014, 115, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmar, K.M.; Larman, H.B.; Dai, G.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, E.T.; Moorthy, S.N.; Kratz, J.R.; Lin, Z.; Jain, M.K.; Gimbrone, M.A., Jr.; et al. Integration of flow-dependent endothelial phenotypes by Kruppel-like factor 2. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pon, J.R.; Marra, M.A. MEF2 transcription factors: Developmental regulators and emerging cancer genes. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 2297–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Gao, B.; Ponnusamy, M.; Lin, Z.; Liu, J. MEF2 signaling and human diseases. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 112152–112165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potthoff, M.J.; Olson, E.N. MEF2: A central regulator of diverse developmental programs. Development 2007, 134, 4131–4140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornwell, J.D.; McDermott, J.C. MEF2 in cardiac hypertrophy in response to hypertension. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.W.; Martino, N.; Gerlach, B.D.; Lamar, J.M.; Vincent, P.A.; Adam, A.P.; Schwarz, J.J. MEF2 (Myocyte Enhancer Factor 2) Is Essential for Endothelial Homeostasis and the Atheroprotective Gene Expression Program. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2021, 41, 1105–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maejima, T.; Inoue, T.; Kanki, Y.; Kohro, T.; Li, G.; Ohta, Y.; Kimura, H.; Kobayashi, M.; Taguchi, A.; Tsutsumi, S.; et al. Direct evidence for pitavastatin induced chromatin structure change in the KLF4 gene in endothelial cells. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e96005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sen-Banerjee, S.; Mir, S.; Lin, Z.; Hamik, A.; Atkins, G.B.; Das, H.; Banerjee, P.; Kumar, A.; Jain, M.K. Kruppel-like factor 2 as a novel mediator of statin effects in endothelial cells. Circulation 2005, 112, 720–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonauer, A.; Dimmeler, S. The microRNA-17-92 cluster: Still a miRacle? Cell Cycle 2009, 8, 3866–3873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonauer, A.; Carmona, G.; Iwasaki, M.; Mione, M.; Koyanagi, M.; Fischer, A.; Burchfield, J.; Fox, H.; Doebele, C.; Ohtani, K.; et al. MicroRNA-92a controls angiogenesis and functional recovery of ischemic tissues in mice. Science 2009, 324, 1710–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinkel, R.; Penzkofer, D.; Zuhlke, S.; Fischer, A.; Husada, W.; Xu, Q.F.; Baloch, E.; van Rooij, E.; Zeiher, A.M.; Kupatt, C.; et al. Inhibition of microRNA-92a protects against ischemia/reperfusion injury in a large-animal model. Circulation 2013, 128, 1066–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radmanesh, F.; Sadeghi Abandansari, H.; Ghanian, M.H.; Pahlavan, S.; Varzideh, F.; Yakhkeshi, S.; Alikhani, M.; Moradi, S.; Braun, T.; Baharvand, H. Hydrogel-mediated delivery of microRNA-92a inhibitor polyplex nanoparticles induces localized angiogenesis. Angiogenesis 2021, 24, 657–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrigendum to: 2019 ESC Guidelines on diabetes, pre-diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases developed in collaboration with the EASD. Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 4317. [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Zhang, C.L.; Gou, L.; He, L.; Gong, Y.Y.; Qu, D.; Zhao, L.; Jin, N.; Chan, T.F.; Wang, L.; et al. Endothelial TFEB (Transcription Factor EB) Restrains IKK (IκB Kinase)-p65 Pathway to Attenuate Vascular Inflammation in Diabetic db/db Mice. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2019, 39, 719–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiplunkar, A.R.; Curtis, B.C.; Eades, G.L.; Kane, M.S.; Fox, S.J.; Haar, J.L.; Lloyd, J.A. The Krüppel-like factor 2 and Krüppel-like factor 4 genes interact to maintain endothelial integrity in mouse embryonic vasculogenesis. BMC Dev. Biol. 2013, 13, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweet, D.R.; Lam, C.; Jain, M.K. Evolutionary Protection of Krüppel-Like Factors 2 and 4 in the Development of the Mature Hemovascular System. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 645719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Angelantonio, E.; Kaptoge, S.; Wormser, D.; Willeit, P.; Butterworth, A.S.; Bansal, N.; O’Keeffe, L.M.; Gao, P.; Wood, A.M.; Burgess, S.; et al. Association of Cardiometabolic Multimorbidity With Mortality. JAMA 2015, 314, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nedosugova, L.V.; Markina, Y.V.; Bochkareva, L.A.; Kuzina, I.A.; Petunina, N.A.; Yudina, I.Y.; Kirichenko, T.V. Inflammatory Mechanisms of Diabetes and Its Vascular Complications. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brownlee, M. The pathobiology of diabetic complications: A unifying mechanism. Diabetes 2005, 54, 1615–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbas, A.; Grant, P.J.; Kearney, M.T. Role of IGF-1 in glucose regulation and cardiovascular disease. Expert Rev. Cardiovasc. Ther. 2008, 6, 1135–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wani, M.A.; Means, R.T., Jr.; Lingrel, J.B. Loss of LKLF function results in embryonic lethality in mice. Transgenic. Res. 1998, 7, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sangwung, P.; Zhou, G.; Nayak, L.; Chan, E.R.; Kumar, S.; Kang, D.W.; Zhang, R.; Liao, X.; Lu, Y.; Sugi, K.; et al. KLF2 and KLF4 control endothelial identity and vascular integrity. JCI Insight 2017, 2, e91700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SenBanerjee, S.; Lin, Z.; Atkins, G.B.; Greif, D.M.; Rao, R.M.; Kumar, A.; Feinberg, M.W.; Chen, Z.; Simon, D.I.; Luscinskas, F.W.; et al. KLF2 Is a novel transcriptional regulator of endothelial proinflammatory activation. J. Exp. Med. 2004, 199, 1305–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Lin, Z.; SenBanerjee, S.; Jain, M.K. Tumor necrosis factor alpha-mediated reduction of KLF2 is due to inhibition of MEF2 by NF-kappaB and histone deacetylases. Mol. Cell Biol. 2005, 25, 5893–5903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacilotto, N.; Chouliaras, K.M.; Nikitenko, L.L.; Lu, Y.W.; Fritzsche, M.; Wallace, M.D.; Nornes, S.; García-Moreno, F.; Payne, S.; Bridges, E.; et al. MEF2 transcription factors are key regulators of sprouting angiogenesis. Genes Dev. 2016, 30, 2297–2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laggerbauer, B.; Engelhardt, S. MicroRNAs as therapeutic targets in cardiovascular disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2022, 132, e159179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abplanalp, W.T.; Fischer, A.; John, D.; Zeiher, A.M.; Gosgnach, W.; Darville, H.; Montgomery, R.; Pestano, L.; Allée, G.; Paty, I.; et al. Efficiency and Target Derepression of Anti-miR-92a: Results of a First in Human Study. Nucleic Acid Ther. 2020, 30, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stachel, G.; Trenkwalder, T.; Gotz, F.; El Aouni, C.; Muenchmeier, N.; Pfosser, A.; Nussbaum, C.; Sperandio, M.; Hatzopoulos, A.K.; Hinkel, R.; et al. SDF-1 fused to a fractalkine stalk and a GPI anchor enables functional neovascularization. Stem Cells 2013, 31, 1795–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Støy, J.; Edghill, E.L.; Flanagan, S.E.; Ye, H.; Paz, V.P.; Pluzhnikov, A.; Below, J.E.; Hayes, M.G.; Cox, N.J.; Lipkind, G.M.; et al. Insulin gene mutations as a cause of permanent neonatal diabetes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 15040–15044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renner, S.; Braun-Reichhart, C.; Blutke, A.; Herbach, N.; Emrich, D.; Streckel, E.; Wünsch, A.; Kessler, B.; Kurome, M.; Bähr, A.; et al. Permanent neonatal diabetes in INS(C94Y) transgenic pigs. Diabetes 2013, 62, 1505–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loyer, X.; Potteaux, S.; Vion, A.C.; Guérin, C.L.; Boulkroun, S.; Rautou, P.E.; Ramkhelawon, B.; Esposito, B.; Dalloz, M.; Paul, J.L.; et al. Inhibition of microRNA-92a prevents endothelial dysfunction and atherosclerosis in mice. Circ. Res. 2014, 114, 434–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, J.M.; Penzkofer, D.; Teske, R.; Dutzmann, J.; Koch, A.; Bielenberg, W.; Bonauer, A.; Boon, R.A.; Fischer, A.; Bauersachs, J.; et al. Inhibition of miR-92a improves re-endothelialization and prevents neointima formation following vascular injury. Cardiovasc. Res. 2014, 103, 564–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Target mRNA | Match Position | Site Type | Site Context Score |
|---|---|---|---|
| Homo sapiens-KLF2 | 242–249 | 8mer | −0.50 |
| Homo sapiens-KLF4 | 362–368 | 7mer-A1 | −0.06 |
| 674–681 | 8mer | −0.41 | |
| Homo sapiens-MEF2D | 858–865 | 8mer | −0.28 |
| 2814–2821 | 8mer | −0.09 | |
| Mus musculus-Klf2 | 214–221 | 8mer | −0.57 |
| Mus musculus-Klf4 | 433–439 | 7mer-A1 | −0.10 |
| 751–758 | 8mer | −0.36 | |
| Mus musculus-Mef2d | 1057–1064 | 8mer | −0.24 |
| Sus scrofa-KLF2 | NA | 8mer | NA |
| Sus scrofa-KLF4 | NA | 8mer | NA |
| Sus scrofa-MEF2D | NA | 8mer | NA |
| 8mer |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Samak, M.; Kues, A.; Kaltenborn, D.; Klösener, L.; Mietsch, M.; Germena, G.; Hinkel, R. Dysregulation of Krüppel-like Factor 2 and Myocyte Enhancer Factor 2D Drive Cardiac Microvascular Inflammation and Dysfunction in Diabetes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2482. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24032482
Samak M, Kues A, Kaltenborn D, Klösener L, Mietsch M, Germena G, Hinkel R. Dysregulation of Krüppel-like Factor 2 and Myocyte Enhancer Factor 2D Drive Cardiac Microvascular Inflammation and Dysfunction in Diabetes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(3):2482. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24032482
Chicago/Turabian StyleSamak, Mostafa, Andreas Kues, Diana Kaltenborn, Lina Klösener, Matthias Mietsch, Giulia Germena, and Rabea Hinkel. 2023. "Dysregulation of Krüppel-like Factor 2 and Myocyte Enhancer Factor 2D Drive Cardiac Microvascular Inflammation and Dysfunction in Diabetes" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 3: 2482. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24032482
APA StyleSamak, M., Kues, A., Kaltenborn, D., Klösener, L., Mietsch, M., Germena, G., & Hinkel, R. (2023). Dysregulation of Krüppel-like Factor 2 and Myocyte Enhancer Factor 2D Drive Cardiac Microvascular Inflammation and Dysfunction in Diabetes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(3), 2482. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24032482