Abstract
For pathogens identification, the PCR test is a widely used method, which requires the isolation of nucleic acids from different samples. This extraction can be based on the principle of magnetic separation. In our work, amine-functionalized magnesium ferrite nanoparticles were synthesized for this application by the coprecipitation of ethanolamine in ethylene glycol from Mg(II) and Fe(II) precursors. The conventional synthesis method involves a reaction time of 12 h (MgFe2O4-H&R MNP); however, in our modified method, the reaction time could be significantly reduced to only 4 min by microwave-assisted synthesis (MgFe2O4-MW MNP). A comparison was made between the amine-functionalized MgFe2O4 samples prepared by two methods in terms of the DNA-binding capacity. The experimental results showed that the two types of amine-functionalized magnesium ferrite magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs) were equally effective in terms of their DNA extraction yield. Moreover, by using a few minutes-long microwave synthesis, we obtained the same quality magnesium ferrite particles as those made through the long and energy-intensive 12-h production method. This advancement has the potential to improve and expedite pathogen identification processes, helping to better prevent the spread of epidemics.
1. Introduction
Nanomaterials are continuously increasing in popularity for their advantageous properties in catalysis [1], carbon dioxide sequestration [2,3,4] and biological applications [5]. Among the various nanomaterials, magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs) are used for biological applications, such as magnetic resonance imaging [6], hyperthermia treatment [7], drug delivery [8] or the isolation of macromolecules [9], like deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). Some of the advantageous properties of the magnetic nanomaterials in these applications are biocompatibility, low or zero toxicity, cost-effectiveness, superparamagnetic properties, a high binding capacity and straightforward synthesis [10]. Generally, DNA isolation can be achieved by liquid–liquid phase extraction methods, like alkaline lysis and phenol-chloroform extraction, or with solid–liquid phase extraction, such as silica cartridge-based or magnetic nanoparticle-based isolation [11]. In the case of purification and separation techniques, MNPs are more frequently utilized due to the cost-effective nature of the method, its practicality, and lower toxicity compared to conventional isolation methods [12,13].
From the vast available literature, some are especially important for our research on DNA isolation using magnetic nanoparticles. For example, Prodělalová et al. [14] used cobalt ferrite MNPs for genomic DNA isolation from different dairy products. Modified MNPs were also used for nucleic acid isolation applications [15], where the Al3+- and iminodiacetic acid-modified surfaces of ferrite nanoparticles have an increased affinity to DNA. Other approaches like silica- or amine-functionalized MNPs have also been developed and demonstrated that these MNPs are also good solid-phase candidates in the extraction of plasmid or genomic DNA [9,16,17,18,19]. In the case of iron oxide MNPs, it has been observed that a higher density of amino groups on the particle surface leads to improved DNA-binding efficiency [20,21]. On the other hand, numerous papers describe that amino-modified magnetic materials can adsorb DNA molecules at low salinity or neutral pH conditions [22,23,24,25,26].
Plasmid DNA (pDNA) is an extrachromosomal, circular, double-stranded DNA molecule, usually found in a small nucleic acid compartment in bacterial, archaeal or some eukaryotic organisms. The chemical composition of the plasmids does not differ from the genomic DNA [27]; therefore, plasmids are often used as a tool for molecular cloning and gene delivery systems. For such downstream applications, the quantity and quality of the purified pDNA must be determined and meet some criteria. The absorbance ratio measured at 260 nm and 280 nm is used to assess the purity (quality) of the isolated DNA, and according to the literature, a ratio of 1.7–2.0 is accepted as a pure DNA solution. A considerably lower ratio (below 1.6) may indicate contamination with protein, phenol or other reagents that absorb at 280 nm and can negatively affect further processes. On the other hand, the presence of RNA can lead to an increase in the ratio value [28]. Generally, the DNA isolation methods that provide high quality and an adequate quantity of the extracted plasmid or genomic DNA are at the center of specific scientific interest.
Nanoparticles that are used in molecular biological or bioanalytical separation processes have superparamagnetic properties (e.g., magnetite, maghemite and alkaline earth or transition metal ferrites). These ferrites are spinel-type metal oxides with the chemical composition MFe2O4, where M denotes divalent metal ions [29], such as Mn2+, Ni2+, Co2+, Mg2+, Zn2+ and Cd2+ [7,30]. These ferrite nanoparticles may differ not only in their composition but also in their preparation techniques and the corresponding synthesis time.
In the literature, there are examples of longer and energetically less efficient methods, as well as protocols that propose shorter synthesis times to produce magnetic nanoparticles. Chattharika et al. reported a 12-h coprecipitation synthesis method (abbreviated as H&R due to its heating and refluxing steps) for amine-functionalized magnesium ferrite magnetic nanoparticle (MgFe2O4 MNP) preparation and characterized its adsorption properties using Congo red [31]. Vishwas et al. published a 4-h coprecipitation protocol for cobalt ferrite nanoparticles used in photocatalysis [32]. Yadav and co-workers have described a simple 60-min-long sonochemical method for the synthesis of gadolinium-doped cobalt ferrite nanoparticles [33]. Compared to these procedures, microwave-assisted synthesis (MW) can be an even faster way to produce large amounts of magnetic nanoparticles. The advantages of MW synthesis include fast volume heating, high reaction rates, size and shape control by adjusting the reaction parameters and energy efficiency. Moreover, MW synthesis enables homogenous heating, minimizing the thermal gradients and providing uniform nucleation and growth conditions, resulting in magnetic nanoparticles with a consistent size distribution [34]. For example, Ayyıldız and co-workers applied MW synthesis for 35 min to prepare cobalt ferrite nanoparticles, which were then used to extract Pb ions in rooibos (Aspalathus linearis) tea [35], while Abhishek et al. produced titanium ferrite MNPs with a 15-min MW synthesis. They found that varying the synthesis time could improve the magnetic properties of the particles [36].
Based on the literature examples, the aim of our work was to prepare amine-functionalized magnesium ferrite nanoparticles by using both the classical 12-h coprecipitation method (MgFe2O4-H&R MNP) and 4-min microwave treatment (MgFe2O4-MW MNP). The physicochemical properties of the resulting particles (such as particle morphology, specific surface area, size, phase composition, surface polarity and dispersibility) were characterized by high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM), selected area diffraction (SAED), X-ray powder diffraction (XRD), Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) and laser-Doppler electrophoresis (zeta potential) measurements. The DNA-binding ability was also investigated; to the best of our current scientific knowledge, magnesium ferrite magnetic nanoparticles have not been used for DNA isolation before. The DNA-binding ability and DNA-binding efficiency of the synthesized MNP samples were compared, and the isolation efficiency and isolated pDNA were tested using molecular biological downstream processes. The DNA extraction efficiency was also compared to that of a commercially available MNP-based isolation kit in terms of the DNA yield capacity.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Surface Area Measurements
A basic feature of the MNPs in DNA isolation applications is that the DNA reversibly adsorbs to the surface of amine-functionalized MNPs, where the specific surface area (SSA) has a crucial role. Thus, CO2 adsorption–desorption measurements were carried out at 273 K based on the Dubinin–Astakhov (DA) method to determine the SSA. The surface areas were 86.3 m2 g−1 (MgFe2O4-MW) and 54.4 m2 g−1 (MgFe2O4-H&R)—the difference reflecting the importance of the synthesis route. MgFe2O4 samples with similar specific surface areas (SABET: 47 m2 g−1 and 56.5 m2 g−1) were reported previously using a coprecipitation method by applying long-time reflux [31,37].
2.2. Particle Size Distribution
An increased SSA can be obtained by using ultrafine particle sizes, highlighting the importance of nanoparticles since the quantity of anchored DNA depends on the accessible surface area of the adsorbent [38]. In this sense, the determination of the particle size distribution is important, and it was acquired from HRTEM images of the amine-functionalized MgFe2O4 samples using ImageJ image analyser software (Figure 1A,B,D,E). Based on the particle diameters, size distribution histograms were built and compared with other magnesium ferrites prepared by different methods. In the case of all the samples acquired from the HRTEM images, similar spherical ferrite nanoparticles were visible despite the different synthesis methods (Figure 1 A,B,D,E). These aggregated spheres build up from individual 4–8 nm sized nanoparticles (SI Figure 1A,B).
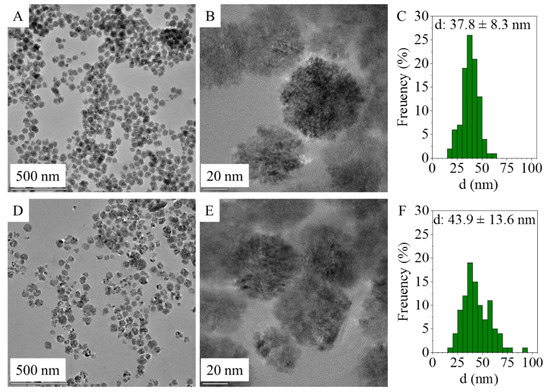
Figure 1.
HRTEM images of the MgFe2O4-H&R (A,B) and MgFe2O4-MW (D,E) and particle size distribution of MgFe2O4-H&R (C) and MgFe2O4-MW (F).
The average particle size of the MgFe2O4-MW spheres (aggregates) is 43.9 ± 13.6 nm and is in a wide distribution range (Table 1) based on the standard deviation and while considering the interquartile range. A similar distribution was observed in the case of the amine-functionalized MgFe2O4-H&R nanoparticles, where the average particle size was 37.8 ± 8.3 nm (Figure 1C,F). During the synthesis of the amine-functionalized MgFe2O4-MW nanospheres, higher diameters developed: 43.9 ± 13.6 nm (Table 1 and Figure 1F). A total of 10% of the MgFe2O4-MW MNPs had sizes exceeding 61.8 nm, while 10% of the MgFe2O4-H&R MNPs were larger than 47.3 nm. In the case of the two ferrite samples, the mean particle sizes are quite close to the corresponding median values, which is a characteristic of the normal distribution.

Table 1.
Size analysis results of the two types of magnesium ferrite nanospheres that were synthesized using 4-min microwave irradiation (MW) or 12-h heating and refluxing (H&R).
2.3. XRD Characterization of Amine-Functionalized Magnesium Ferrite Nanoparticles
The individual nanospheres in both types of amine-functionalized MgFe2O4 MNP samples were examined by selected area diffraction (SAED) during the HRTEM analysis, and the measured d-spacings were matched with the d-values in the diffraction databases (Figure 2A,B). After identifying the individual particles, it was necessary to examine both types of nanopowder samples using the X-ray powder diffraction (XRD) method. XRD is the only reliable technique for the bulk-phase identification, quantification and size-shape characterization required for our samples, especially since non-ferrite phases might occur in the samples as technological residues. The XRD pattern of the samples (Figure 2C) revealed peaks of only magnesium ferrite, located at (2Th/hkl) 18.2°/(111), 30.1°/(220), 35.4°/(311), 43.1°/(400), 53.4°/(422), 56.9°/(511) and 62.6°/(440), matching the PDF 36–0398 card. Other phases as residue were not detected; therefore, it can be stated that the two proposed synthesis methods are equally suitable for obtaining pure spinel-phase MNPs.
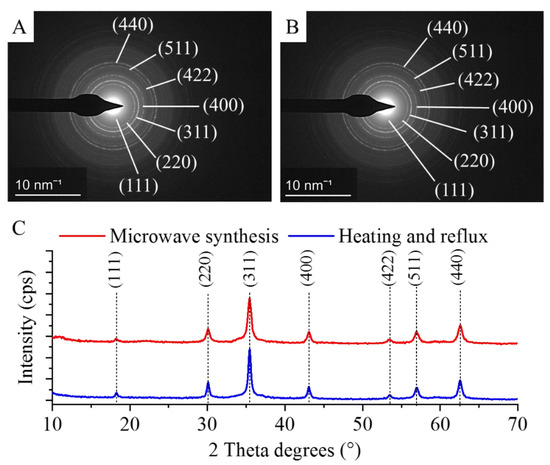
Figure 2.
SAED image of the MgFe2O4-H&R (A) and MgFe2O4-MW (B) particles and X-ray powder diffraction of the MgFe2O4-H&R and MgFe2O4-MW nanopowders (C).
2.4. FTIR Measurements
The identification of surface functional groups—best detected by FTIR measurements—is very important regarding the dispersibility of MNPs in polar solvents. Two characteristic bands are observed at the 564 cm−1 and 621 cm−1 wavenumbers, which are assigned to the intrinsic stretching vibration modes of the metal–oxygen bonds at the octahedral and tetrahedral sites [39] (Figure 3A). Other bands found on the recorded spectra are at 876 cm−1 and 1052 cm−1, assigned to the νC–O and the νC-N vibrations, which originate from the hydroxyl and carboxyl groups, where the νC-N vibrations developed with the presence of amine functional groups. Other absorption bands are found at 1365 cm−1, ascribed to the C–O vibrations and the C–N stretching vibrations, respectively. The stretching vibration band of the N–H bonds overlaps with the vibration band of the -OH groups. Another band was identified as a carbon-related bond at the 1610 cm−1 wavenumber, belonging to the βN–H (bending vibration mode) of the free amine functional groups. The symmetric and asymmetric stretching vibration of the aliphatic and aromatic C–H bonds resulted in absorption at 2870 cm−1 and 2941 cm−1, which can be explained by the adsorbed organic molecules (EG and EA) on the surface [40,41]. The stretching vibration bands of the hydroxyl and amine groups overlap and result in a broad region at 3420 cm−1 and 3617 cm−1. Zeta potential (ZP) measurements were carried out at an ambient pH in distilled water (pH: 6). The surface hydroxyl groups are partially found in a deprotonated form, resulting in negative ZPs (-5.6 ± 4.3 mV and -8.5 ± 4.5 mV). Next to the -OH groups, -NH2 functional groups are found on the nanoparticles, which can become protonated when the pH decreases, leading to the appearance of positive charges (-NH3+). Due to the positive charges formed as a result of the protonation of the amine groups, negatively charged DNA can form an electrostatic interaction with the magnetic nanoparticles. By increasing the pH (adding an elution buffer), the positive charges on the surface can be reduced. Then, the deprotonation of the -OH groups result in a negative ZP, thus eliminating the electrostatic interaction between the DNA and nanoparticles. We must also take into account that other interactions can develop between DNA and ferrite nanoparticles. In addition to the electrostatic interactions, other adsorption mechanisms can also take place, as the nitrogen-containing bases in DNA can strongly coordinate with the surface of the metal oxide, i.e., the Fe3O4 surface [42]. Owing to this, the magnetic nanoparticles can be coprecipitated by DNA molecules.
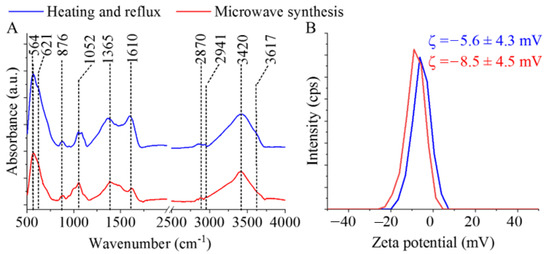
Figure 3.
FTIR spectra of the MgFe2O4-H&R and MgFe2O4-MW (A), as well as zeta potential distribution diagrams and average zeta potential values of these ferrites (B).
Due to the surface hydroxyl and amine functional groups, hydrogen bonds can be formed between the nanoparticles and DNA molecules [43,44]. Such interaction sites enable the DNA to bind reversibly to the magnetic nanoparticles during the extraction process, and thus, by changing the buffer medium, it can be easily separated from the unwanted cell-forming macromolecules [43,44].
2.5. Magnetization Measurements
The magnetization curve of the amine-functionalized MgFe2O4 samples was measured at room temperature using a vibrating-sample magnetometer (VSM). The magnetic saturation (Ms) reached 36 emu/g in the case of MgFe2O4-H&R, as shown in Figure 4A. A lower Ms value (21 emu/g) was measured in the MgFe2O4-MW sample (Figure 4B). For the MgFe2O4 nanoparticles, similar Ms values (between 12 and 32 emu/g) to our results have been reported in other works of literature [45,46,47].
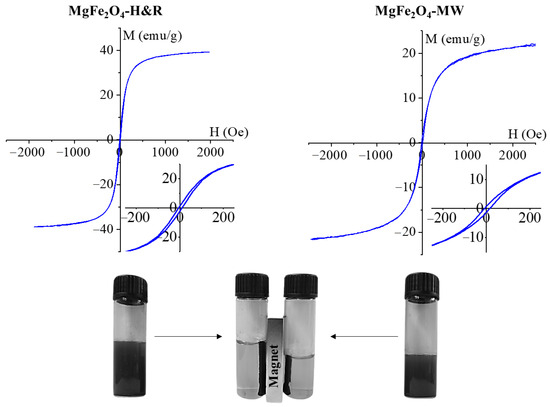
Figure 4.
Magnetization curves of the MgFe2O4-H&R and MgFe2O4-MW samples, with the narrow hysteresis loops in higher scale resolution (insets). The photo at the bottom demonstrates the dispersibility in a polar solvent and the magnetic separability of the ferrite nanoparticles.
The magnetization curve shows a narrow hysteresis loop with low coercivity (Hc) and low remanent magnetization (Mr), as seen in the inset of Figure 4. The values of Hc and Mr were 12 Oe and 1.3 emu/g (MgFe2O4-H&R), as well as 18 Oe and 2.5 emu/g (MgFe2O4-MW). These are relatively small values that indicate the soft magnetic nature of the synthesized particles at room temperature [48]. Narrow hysteresis loops also indicate that the prepared samples can be easily demagnetized as well.
2.6. pDNA Isolation with Amine-Functionalized Magnesium Ferrite Nanoparticles
The Escherichia coli (E. coli) bacterium was used as a model organism to provide pDNA for the study of reversible DNA-binding properties of the tested MNPs. The isolation procedure is described in Section 3.5. and was performed at least 3 times with the MgFe2O4-H&R MNPs, as well as with the MgFe2O4-MW MNPs. All our tests have proved that the MNPs reversibly bind DNA molecules and are able to extract DNA from crude cell lysates. DNA concentrations and the purity of the isolated solutions were determined with micro-volume UV-VIS spectrophotometry.
Both MNPs (MgFe2O4-H&R MNP and MgFe2O4-MW MNP) provided similar DNA isolation yields. The mean DNA concentrations isolated with the MgFe2O4-H&R MNP were 500.83 ± 250.37 µg/mL in the first elution (E1) and 141.13 ± 87.21 µg/mL in the second elution fraction (E2), while in the case of the MgFe2O4-MW MNP, the isolated DNA yields were 416.80 ± 285.35 µg/mL (E1) and 180.13 ± 16.97 µg/mL (E2), respectively. The appropriate purity values (A260nm/A280nm) were as follows: 1.93 for E1 and 1.83 for E2 in the case of the MgFe2O4-H&R MNP-isolated pDNA, and 1.92 (E1) and 1.95 (E2) for the MgFe2O4-MW MNP pDNA isolation. These values show that the pDNA extracted with the help of both types of amine-functionalized magnesium ferrite nanoparticles can be considered pure, as the values are in the range of 1.7–2.0 [28].
Figure 5 shows the agarose gel electrophoresis results of the multiple DNA isolations, where columns 1 and 2 stand for the elution fractions isolated with the MgFe2O4-MW MNP, while columns 7 and 8 are the elution fractions isolated with the MgFe2O4-H&R MNP. Additional fluorescent bands (e.g., in columns 1, 2 and 7) show different pDNA conformations [49]. The mean DNA quantity of these samples (where the binding buffer contained NaCl and elution buffer contained only Tris-HCl) were the following: 51.36 µg for the MgFe2O4-H&R MNP and 47.75 µg for the MgFe2O4-MW MNP. Smeared bands were found in the case of the MgFe2O4-H&R MNP gel experiment (Figure 5), which may originate from the residual contamination of the buffers used during isolation. In contrast to this, the isolation performed using the MgFe2O4-MW MNP resulted in well-defined bands. In addition, it was here that the purity values were also in the required range, with values of 1.92 in E1 and 1.95 in E2. These facts confirm that the quality of the isolated pDNA is already good when using the MgFe2O4-MW MNP. To further improve the quality of the purified DNA, the composition of the binding and elution buffers was modified, and the corresponding results for the MgFe2O4-MW MNP are shown in columns 3–6 of Figure 5. The same strategy was applied to eliminate the previously identified faint band from the MgFe2O4-H&R MNP isolation as well, and columns 9–12 represent the isolations performed using the MgFe2O4-H&R MNP using the PB, Tris-HCl and NaCl buffers for better isolation.
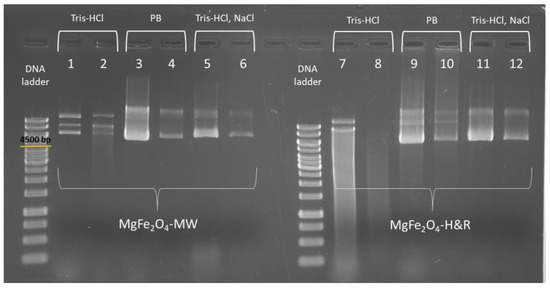
Figure 5.
Agarose gel electrophoresis picture of the DNA samples isolated with magnesium ferrite magnetic nanoparticles, differing in the elution buffer. pDNA extracted with MgFe2O4-MW and MgFe2O4-H&R MNPs are shown in columns 1–2 and 7–8 containing the first (1 and 7) and second elutions (2 and 8) performed with Tris-HCl (pH 7.0) buffer. Columns 3, 9, 4 and 10 stand for the first and second elutions obtained with phosphate buffer (PB, pH 8.0), while columns 5, 11, 6 and 12 show the first and second elutions using Tris-HCl (pH 8.5) buffer containing 800 mM of NaCl.
As seen in Figure 5 (columns 3–4 and 9–10), using 0.1 M potassium phosphate (pH 8.0) as the elution buffer, the DNA desorption from the MNPs (elution step) was successful. This indicates that the negatively charged DNA molecules could be replaced with phosphate ions on the surface of positively charged ferrite MNPs [50]. Xu et al. [18] reported that decreasing the NaCl concentration in the binding buffer and increasing it in the elution buffer can increase the yield of DNA extraction. Based on this, we performed the extraction protocol by removing the NaCl from the binding buffer and adding it to the Tris-HCl elution buffer (final concentrations: Tris-HCl 10 mM (pH 8.5), NaCl 800 mM). These modified buffers resulted in well-defined bands in the gel electrophoresis experiment, as seen clearly from columns 5–6 and 11–12 of Figure 5.
The DNA yields obtained using different elution buffers are shown in Figure 6. Such column representations of the isolation efficiency of MgFe2O4-H&R MNP clearly show a maximum in the DNA yield when the phosphate buffer (PB) was used as the elution solution (107.27 µg of DNA extracted), while when applying the NaCl-containing elution buffer (Tris-HCl and NaCl, seen in the last two columns in Figure 6), the amount of extracted DNA slightly decreased (40.42 µg in the case of MgFe2O4-H&R and 47.57 µg for the MgFe2O4-MW MNP isolations). This may occur due to the fact that when DNA binds to the surface of the used amine-functionalized MgFe2O4 MNPs in low- or no-salt-containing binding buffers, DNA molecules have an elongated coil conformation [48]. This molecular state allows all accessible phosphate groups along the DNA backbone to bind to the positively charged nanomaterials, leading to fewer DNA molecules interacting with the surface of the MNPs. However, using higher salt concentrations during DNA–MNP binding (when the binding buffer contains NaCl and the elution buffer is only Tris-HCl or phosphate buffer), cations reduce the repulsion between the DNA strands, leading to a compact and bent globular state of the DNA molecule. This means that the DNA loading capacity of MNPs expands in high-salt-concentration binding circumstances because the condensed shape of the DNA molecule reduces the number of electrostatic contact points between the DNA and MNP [50].
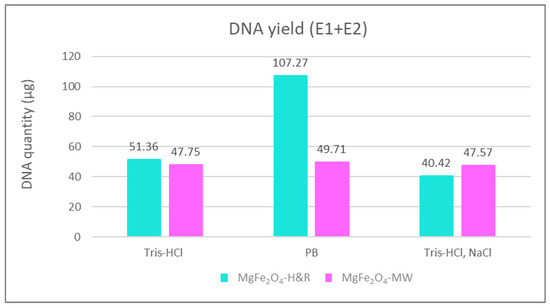
Figure 6.
Comparison of the quantity of isolated DNA summarized from the first (E1) and second (E2) elution steps with 3 different elution buffers. DNA purity of the samples (A260nm/A280nm value): Tris-HCl as elution buffer with MgFe2O4-MW (1.94), with MgFe2O4-H&R (1.88); phosphate buffer as elution buffer with MgFe2O4-MW (1.79), with MgFe2O4-H&R (1.88); NaCl containing Tris-HCl elution buffer with MgFe2O4-MW (2.07), with MgFe2O4-H&R (2.05). E1 + E2 = sum of the DNA quantity extracted from the first (E1) and second (E2) elution steps; PB = phosphate buffer.
These experiments highlight the importance of selecting the right buffer combinations for efficient DNA isolation while maintaining DNA quality and integrity, which is crucial for reliable results.
The DNA isolation efficiency of extraction methods using MgFe2O4-H&R and MgFe2O4-MW MNPs was compared to that of a commercially available magnetic particle-based kit. Specifically, we tested the Mag-Bind Ultra-Pure Plasmid DNA 96 Kit from Omega Bio-Tek, which is designed to isolate approximately 50 µg of high-copy-number pDNA. Our results, as presented in Figure 6, showed that the DNA yield obtained with amine-functionalized magnesium ferrite MNPs was at least as high as the kit manufacturer’s guarantee, even for low-copy-number pBAD plasmid DNA. With MgFe2O4-MW MNPs, we achieved a yield of 47.75 µg of DNA with Tris-HCl elution, 49.71 µg with phosphate buffer and 47.57 µg with Tris-HCl+NaCl elution. For the MgFe2O4-H&R MNPs, we obtained 51.36 µg of DNA with Tris-HCl elution, 107.24 µg with phosphate buffer and 40.42 µg with Tris-HCl+NaCl elution. These findings confirm the suitability of the synthesized nanoparticles for successful DNA isolation experiments.
DNA purity is an equally important feature of the DNA isolation protocol; therefore, the absorbance values were also measured at 260 nm and 280 nm in all cases. Their ratios, the A260nm/A280nm values, were within the appropriate range (specific data can be found in the caption of Figure 6), indicating that the purity of the isolated DNA meets the target values. Therefore, despite the slight decrease in the purity observed with NaCl-containing elution buffer (A260nm/A280nm: 2.05 for the MgFe2O4-H&R MNP and 2.07 for the MgFe2O4-MW MNP), the A260nm/A280nm ratios fall within the range found in the previous literature, still indicating insignificant levels of contamination [51,52] and reinforcing the overall suitability of our isolation protocol.
2.7. Restriction Digestion of the Extracted pDNA
To test that the isolated DNA can be a good template for restriction digestion and thus for molecular cloning processes, several different reactions were performed using restriction enzymes from the ThermoFisher Scientific company (Figure 7). In all restriction reactions, pDNA (namely the pBAD24), isolated both with MgFe2O4-H&R and MgFe2O4-MW MNPs, was used as a template. The aim of this test was to compare the performance of the templates obtained from the isolation procedures with the MNPs produced by 12-h (H&R) and 4-min (MW) treatments in various digestion reactions. Additionally, we wanted to investigate if there was a difference in the digestion efficiency depending on the elution buffer in which the template pDNA was placed (Tris-HCl only, PB, or Tris-HCl+NaCl).
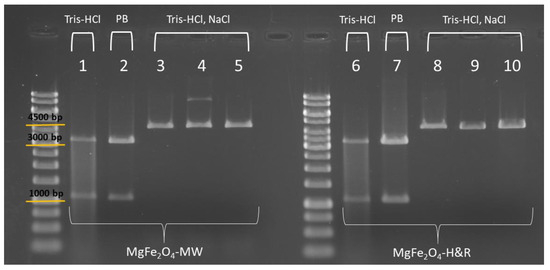
Figure 7.
Agarose gel electrophoresis picture of the DNA fragments digested with restriction endonucleases. In the first part of the picture, the isolates of the MgFe2O4-MW sample are shown, and in the second part, the isolates of the MgFe2O4-H&R sample (PB = phosphate buffer). In fast digest reactions, two enzymes were used having a single recognition site on the pDNA (1, 2 and 6, 7), while in overnight digestions, one type of linearizing enzyme was used (3, 4, 5 and 8, 9, 10).
First, the pDNA samples eluted in Tris-HCl and in phosphate buffer were used as templates in the fast digest reactions. Fast HindIII and Fast VspI (AseI) endonucleases are specific to pBAD24 plasmid DNA, each making a single cut on the double-stranded pDNA. Using them together in the same digestion reaction, two DNA fragments can be obtained (3407 bp (base pair) and 1135 bp, shown in columns 1–2 and 6–7 of Figure 7).
The DNA templates eluted with NaCl-containing buffer (columns denoted as Tris-HCl, NaCl in Figure 7) were investigated in overnight digestions, where conventional restriction digestion buffers can be used. In this case, our aim was to test if extra salt has any effect on the reaction itself since some restriction buffers already contain NaCl (e.g., Red and Orange buffer, according to the manufacturer’s description). Figure 7 also shows the results of the overnight digestions with ClaI (Bsu15I) endonuclease in Tango buffer (columns 3 and 8), HindIII in Red buffer (columns 4 and 9) and VspI (AseI) in Orange buffer (columns 5 and 10). These digestions resulted in a single fragment (linearized pBAD24 plasmid of 4542 bp length), as these enzymes have only one recognition site on pBAD24 (Figure 7, columns 3, 4 and 5: elution fractions of the MgFe2O4-MW MNP isolations; columns 8, 9 and 10: elution fractions of the MgFe2O4-H&R MNP isolations). Comparing the agarose gel images of different restriction reactions (where the pDNA in different elution buffers was used as the template), we observed that when using Tris-HCl as the elution buffer (for both the MgFe2O4-MW and MgFe2O4-H&R MNP isolations, denoted as columns 1 and 6 in Figure 7), faint restriction fragments were noticeable. However, when digesting the pDNA in the phosphate buffered (PB column) or NaCl-containing elution buffer (Tris-HCl, NaCl columns in Figure 7), the appearance of the fragments on the gel matched the expectations for the restriction digestion results. The presence of additional salts during overnight digestion with the Red or Orange buffers (Figure 7, columns 4, 5, 9, 10) did not negatively impact the restriction reaction. The fluorescent DNA bands appeared at the appropriate height (in line with the 4500 bp marker band) and displayed the expected appearance on the agarose gel.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
The amine-functionalized magnesium ferrite nanoparticles were synthesized from magnesium nitrate hexahydrate, Mg(NO3)2∙6 H2O, MW: 290.79 g/mol (ThermoFisher GmbH, D-76870 Kandel, Germany) and iron(III) nitrate nonahydrate, Fe(NO3)3∙9 H2O, MW: 404.00 g/mol (VWR Int. LtD., B-3001 Leuven, Belgium). Ethylene glycol (EG), HOCH2CH2OH (VWR Int. Ltd., F-94126 Fontenay-sous-Bois, France), was used as the dispersion medium. For the coprecipitation and functionalization of the ferrites, ethanolamine (EA), NH2CH2OH (Merck KGaA, D-64271 Darmstadt, Germany), and sodium acetate, CH3COONa (ThermoFisher GmbH, D-76870 Kandel, Germany), were used.
The following materials and chemicals were used to maintain the bacterial cell culture and for the plasmid DNA isolation assays with magnetic nanoparticles: tryptone and yeast extract (Neogen Culture Media, Lansing, MI, USA); sodium chloride, bacteriological agar and polyethylene glycol 1450 and 6000 (VWR International, Leuven, Belgium); ampicillin sodium salt (Alfa Aesar, Kandel, Germany); Plasmid Purification Midi Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany); tris hydrochloride salt and bromophenol blue sodium salt (VWR International, Solon, OH, USA); ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid disodium salt (Sigma-Aldrich, Louis, MO, USA); 96% ethanol and glycerol (VWR International, Fontenay-sous-Bois, France); Tween 20, Gel Red nucleic acid gel stain and agarose (Merck Millipore, Billerica, MA, USA); 1 kb DNA ladder (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA).
3.2. Synthesis of the Amine-Functionalized MgFe2O4-H&R by Coprecipitation with 12-h Refluxing
Synthesis of the MgFe2O4-H&R sample was based on the method of Nonkumwong et al. [31]. In the first step, 1.23 g (15 mmol) of sodium acetate was dissolved in EG (10 mL) and heated to 100 °C during continuous stirring and refluxing for 15 min. A total of 0.2564 g (1 mmol) of magnesium nitrate hexahydrate and 0.8080 g (2 mmol) of iron(III) nitrate nonahydrate were dissolved in 5 mL of EG and then added to the preheated sodium acetate solution. The mixture was stirred for 30 min, then ethanolamine (3.5 mL) was added. The mixture was heated to 200 °C and kept for 12 h in a system with stirring and refluxing. This high viscosity dispersion was cooled down to room temperature; then, it was separated by centrifuging (4200 rpm, 10 min). The solid phase was washed with distilled water several times, and the ferrite was easily separated from the aqueous medium with a magnet. Finally, the ferrite was rinsed with absolute ethanol and dried by lyophilisation.
3.3. Synthesis of the Amine-Functionalized MgFe2O4-MW by Microwave Irradiation-Assisted Coprecipitation
The 12-h heating and refluxing coprecipitation is a protracted and energy-consuming synthesis method. Thus, microwave synthesis was applied for the preparation of amine-functionalized magnesium ferrite. As a result, we significantly shortened the synthesis time to only 4 min from 12 h. During the experiment, the above-mentioned quantities of the metal precursors, sodium acetate, EG and EA, were measured in a PTFE digestion tube (volume: 50 mL). The reaction mixture was treated at 200 °C (350 W) for 4 min at atmospheric pressure in a CEM MDS 81 D microwave digestion instrument. After cooling, the MgFe2O4-MW sample was separated from the dispersion medium and was washed with distilled water.
3.4. Characterization Techniques
High-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM, Talos F200X G2 electron microscope with field emission electron gun, X-FEG, accelerating voltage: 20-200 kV, ThermoScientific, Waltham, MA, USA) was used for the characterization of the particle size and morphology of ferrite samples. For the imaging and electron diffraction, the SmartCam digital search camera (Ceta 16 Mpixel, 4k x 4k CMOS camera, Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) was applied with a high-angle annular dark-field (HAADF) detector. During the sample preparation, the aqueous dispersion of the nanoparticles was dropped onto 300 mesh copper grids (Ted Pella Inc., 4595 Redding, CA 96003, USA). For the quantitative analysis of the magnesium ferrite, the X-ray diffraction (XRD) technique and the Rietveld refinement method were used. For the measurements, a Bruker D8 diffractometer (Cu-Kα source) in parallel beam geometry (Göbel mirror) with a Vantec detector was used. The functional groups on the surface of the amine-functionalized ferrite nanoparticles were identified with Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) using a Bruker Vertex 70 spectroscope. The measurements were carried out in transmission mode (10 mg of the ferrite sample was pelletized with 250 mg of potassium bromide). The zeta potential of the MgFe2O4 nanoparticles was examined based on the electrophoretic mobility measurements by applying laser-Doppler electrophoresis with the Malvern Zetasizer Nano ZS equipment (Malvern Panalytical, Malvern, UK). The specific surface area of the samples was measured by CO2 adsorption–desorption experiments at 273 K by using a Micromeritics ASAP 2020 sorptometer and the Dubinin–Astakhov (DA) method. The magnetic characterization of ferrite nanoparticles was carried out with a self-developed (University of Debrecen) vibrating-sample magnetometer system based on a water-cooled Weiss-type electromagnet. The powder samples were pelletized for the measurements with a typical mass of 20 mg. The magnetization (M) was measured as a function of the magnetic field (H) up to a 10,000 Oe field strength at room temperature.
3.5. pDNA Isolation with Magnesium Ferrite Magnetic Nanoparticles
The pDNA isolation procedure was carried out based on the protocol developed in our previous research on the use of manganese ferrite magnetic nanoparticles in DNA isolation applications [53]. An E. coli bacterial cell suspension was used for the isolation of a low-copy-number plasmid DNA called pBAD24. A total of 5 mL of the cells grown in the Luria–Bertani (LB) medium (10 g of tryptone, 10 g of NaCl and 5 g of yeast extract dissolved in 1000 mL of ultrapure water) was centrifuged for 5 min on 6000×g. After decanting the supernatant, cell lysis was carried out by following the Qiagen manufacturer’s recommendations (QIAGEN Plasmid Purification Handbook) using the solutions (P1, P2, P3) prepared as described in the composition description of the QIAGEN Plasmid Purification Midi Kit. In these steps, the macromolecules are precipitated on an alkaline pH value, but by neutralizing the pH, the pDNA is renaturated in the solution. To separate the irreversibly denaturated cell debris and the solution containing the pDNA, a centrifugation step is required (14,500× g, 10 min (Mega Star 1.6R centrifuge (VWR International, Leuven, Belgium))). The supernatant fraction was separated. To test the DNA-binding capacity of the amine-functionalized nanoparticles, the separated supernatant was mixed in an Eppendorf tube with 600 µL of 2.3 mg/mL MgFe2O4 MNPs dispersed in binding buffer (2.5 M NaCl; 1 M Tris-HCl, pH 8.0; 0.5 M EDTA, 20% (w/v) polyethylene glycol 6000 and 0.05% Tween 20). From this step, the isolation procedure was carried out using a slightly modified version of a protocol from the literature [54]. The DNA–MNP complexes were formed while flipping the Eppendorf tube upside down for 10 min. The cell lysate–MNP complex was incubated at room temperature on a magnetic stand so that the supernatant could be isolated and pipetted into a new tube without disturbing the pellet (DNA–MNP complexes). This was followed by three washing steps with wash buffer containing 1 M Tris-HCl at a pH of 7.5 and 96% ethanol. First, 1000 µL of washing buffer was used, and the dispersion was vortexed and incubated on the magnetic stand for 2 min. The second washing step was shorter, with the same buffer volume; however, this was without vortexing and only 30 s of incubation time. The last step was carried out with 500 µL of washing solution, in which the sample was vortexed and a 2-min incubation was performed on the magnetic stand. To remove the excess ethanol, a short centrifugation step was implemented. This was followed by the incubation of the sample at 37℃ with the tube opened to dry out the magnetic nanoparticles. This is a crucial step that needs to be monitored because an overlong incubation can damage the DNA molecules. Eluting the pDNA from the MNPs is the last phase of the protocol. The DNA–MNP complexes were resuspended in 80 µL of elution buffer (10 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.0). After a 10-min incubation at 37℃ and 5 min on the magnetic stand, the extracted pDNA was separated from the magnetic nanoparticles. To increase the amount of purified DNA, additional elution steps were implemented.
3.6. Gel Electrophoresis
Agarose gel electrophoresis was performed with a Mini-Sub Cell GT horizontal agarose gel electrophoresis system (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Hercules, CA, USA) to confirm the success of the MNP-based DNA extraction. We used 0.75 cm thick 1.0 w/v% and 0.8 w/v% agarose gels (1 g or 0.8 g of agarose powder, 100 mL of Tris-Acetate-EDTA buffer (TAE; 40 mM Tris-base, 20 mM acetic acid, 1 mM EDTA)) [55]. TAE buffer was also used as a running buffer for the electrophoresis. To provide the essential density for loading the sample into the agarose gel well and to monitor the process, the 6x gel loading dye solution (1 part DNA loading dye and 5 parts isolated DNA sample) was used (30 v/v% glycerol, 0.25 w/v% bromophenol blue dye, and ultrapure water) [55]. The electrophoresis was run for 40 min at 90 V, or in the case of smaller fragments (e.g., ~1100 bp), for 2 h at 30 V.
3.7. Quantification of pDNA and Restriction Endonuclease Reactions
The DNA concentration measurements were performed on a NanoDrop One Microvolume UV-Vis spectrophotometer (ThermoFisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). The purity of extracted DNA can be characterized by measuring the absorbance ratio of the 260 and 280 nm wavelengths. For pure DNA solutions, this value should be between 1.7 and 2.0 [28].
The good purity of DNA can also be shown using the purified pDNA in restriction digestion reactions [56]. Different restriction enzymes specific for the pBAD24 plasmid DNA were used to perform fast digestion or overnight digestion reactions. The amount of pDNA used in the restriction reaction was determined from the fluorescence intensity of the sample on the agarose gel and the concentration values obtained from the NanoDrop measurements (varying from 0.5 to 3.5 µg of DNA). The restriction enzyme reaction consisted of 1 µL of Fast Digest or conventional restriction enzyme(s), 2 µL of 10x buffer (Fast Digest, Red, Orange or Tango buffer) and dH2O (the final volume of the reaction was 20 µL in all cases). Fast digestion with HindIII and VspI (AseI) endonucleases lasted 10 min at 37 °C, while the inactivation was performed in a 65 °C thermoblock (MultiTherm Shaker (Benchmark Scientific, Edison, NJ, USA)) for 10 min. All the overnight digestions were performed in an incubator (Nuve EN 055 (Nuve Laboratory & Sterilization Technology, Ankara, Turkey)) at 37 °C. The inactivation temperatures differ with enzymes: ClaI (Bsu15I) and VspI (AseI): 65 °C, 20 min; HindIII: 80 °C, 20 min.
4. Conclusions
According to the literature, magnesium ferrite magnetic nanoparticles have not been previously investigated using DNA isolation applications. Therefore, in this study, amine-functionalized magnesium ferrite nanoparticles were prepared for application in nucleic acid isolation processes by the coprecipitation synthesis method.
The conventional method involves a 12-h refluxing step (H&R), which is a time- and energy-consuming process; however, this could be shortened to 4 min by using microwave (MW) synthesis, thus offering a faster, more energy-efficient and more effective solution for the synthesis of amine-functionalized MgFe2O4 particles. Comparing the two above-mentioned synthesis methods, the magnesium ferrite nanoparticles (MgFe2O4-H&R MNP and MgFe2O4-MW MNP) showed no significant differences in terms of the crystalline phases, particle morphology, average particle sizes and zeta potentials. Both samples were well-dispersible in aqueous media and were easily demagnetized. These results indicate that both sets of nanoparticles have negatively charged surfaces, suggesting a consistent and comparable surface chemistry.
The two types of MNP samples were compared not only in terms of their physicochemical properties but also in terms of their applicability in DNA purification procedures. Using our former protocol, pDNA from bacterial cells was successfully isolated using both the amine-functionalized MgFe2O4-H&R and MgFe2O4-MW MNPs. The DNA quantity values obtained (51.36 µg for the MgFe2O4-H&R MNP and 47.75 µg for the MgFe2O4-MW MNP) and the results of restriction digestion confirm the successful isolation. We could conclude that using amine-functionalized MgFe2O4-H&R or MgFe2O4-MW MNPs as solid-phase extraction tools provides a DNA yield as good as the yield of commercially available MNP-based pDNA isolation kits [57]. Based on the obtained results in DNA yield, quality and usability in restriction digestion reactions, the nanoparticles synthesized with the shortened procedure (4-min MW synthesis) are as efficient as those produced with the conventional long-term (12-h H&R) procedure. Hence, we propose a new synthesis method for producing good-quality magnesium ferrite particles and a protocol using these MgFe2O4-MW MNPs as a solid-phase pDNA extraction tool and method for further molecular biological applications.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Á.M.I., T.B.G., E.S.-D. and L.V.; methodology Á.M.I., L.H., F.K., T.B.G., E.S. and E.S.-D.; validation, E.S.-D. and L.V.; investigation, T.B.G. and E.S.-D.; resources, Á.M.I., E.S. and L.V.; data curation, T.B.G., E.S.-D. and L.V.; writing—original draft preparation, Á.M.I., T.B.G., E.S.-D. and L.V.; writing—review and editing, T.B.G., E.S.-D. and L.V.; supervision, E.S.-D. and L.V.; funding acquisition, B.V. and C.V. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the European Union and the Hungarian State, co-financed by the European Regional Development Fund in the framework of the GINOP-2.3.4-15-2016-00004 project, aimed to promote cooperation between higher education and industry. This was also supported by the ÚNKP-22-3 New National Excellence Program of the Ministry for Innovation and Technology from the Source of the National Research, Development and Innovation Fund.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data are available upon request from the corresponding authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Hajdu, V.; Sikora, E.; Kristály, F.; Muránszky, G.; Fiser, B.; Viskolcz, B.; Nagy, M.; Vanyorek, L. Palladium Decorated, Amine Functionalized Ni-, Cd- and Co-Ferrite Nanospheres as Novel and Effective Catalysts for 2,4-Dinitrotoluene Hydrogenation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 13197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreeva, N.A.; Chaban, V.V. Electronic and Thermodynamic Properties of the Amino- and Carboxamido-Functionalized C-60-Based Fullerenes: Towards Non-Volatile Carbon Dioxide Scavengers. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2017, 116, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreeva, N.A.; Chaban, V.V. Amino-Functionalized Ionic Liquids as Carbon Dioxide Scavengers. Ab Initio Thermodynamics for Chemisorption. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2016, 103, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaban, V.V.; Andreeva, N.A. Extensively Amino-Functionalized Graphene Captures Carbon Dioxide. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2022, 24, 25801–25815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sowmiya, P.; Dhas, T.S.; Inbakandan, D.; Anandakumar, N.; Nalini, S.; Suganya, K.S.U.; Remya, R.R.; Karthick, V.; Kumar, C.M.V. Optically Active Organic and Inorganic Nanomaterials for Biological Imaging Applications: A Review. Micron 2023, 172, 103486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalaiselvan, C.R.; Thorat, N.D.; Sahu, N.K. Carboxylated PEG-Functionalized MnFe2O4Nanocubes Synthesized in a Mixed Solvent: Morphology, Magnetic Properties, and Biomedical Applications. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 5266–5275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manohar, A.; Vijayakanth, V.; Vattikuti, S.V.P.; Kim, K.H. A Mini-Review on AFe2O4 (A = Zn, Mg, Mn, Co, Cu, and Ni) Nanoparticles: Photocatalytic, Magnetic Hyperthermia and Cytotoxicity Study. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2022, 286, 126117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tietze, R.; Zaloga, J.; Unterweger, H.; Lyer, S.; Friedrich, R.P.; Janko, C.; Pöttler, M.; Dürr, S.; Alexiou, C. Magnetic Nanoparticle-Based Drug Delivery for Cancer Therapy. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 468, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Q.; Guan, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, G.; Yang, Y.; Guo, C. A New Method of Synthesis Well-Dispersion and Dense Fe3O4@SiO2 Magnetic Nanoparticles for DNA Extraction. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2019, 715, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yıldırım, E.; Arıkan, B.; Yücel, O.; Çakır, O.; Kara, N.T.; İyim, T.B.; Gürdağ, G.; Emik, S. Synthesis and Characterization of Amino Functional Poly(Acrylamide) Coated Fe3O4 Nanoparticles and Investigation of Their Potential Usage in DNA Isolation. Chem. Pap. 2022, 76, 5747–5759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.C.; Yiap, B.C. DNA, RNA, and Protein Extraction: The Past and the Present. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2009, 2009, 574398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Han, X.; Li, Z.; Chen, X.; Hou, Y.; Gai, L.; Li, D.; Lu, X.; Fu, T. Superparamagnetic Core–Shell Structured Microspheres Carrying Carboxyl Groups as Adsorbents for Purification of Genomic DNA. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2012, 401, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Je, H.H.; Noh, S.; Hong, S.G.; Ju, Y.; Kim, J.; Hwang, D.S. Cellulose Nanofibers for Magnetically-Separable and Highly Loaded Enzyme Immobilization. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 323, 425–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prodělalová, J.; Rittich, B.; Španová, A.; Petrová, K.; Beneš, M.J. Isolation of Genomic DNA Using Magnetic Cobalt Ferrite and Silica Particles. J. Chromatogr. A 2004, 1056, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Zheng, Z.; Liu, C.; Yang, W. Synthesis of Magnetic Fe3O4@Al3+ Particles and Its Application in DNA Extraction. Int. J. 2022, 41, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comanescu, C. Magnetic Nanoparticles: Current Advances in Nanomedicine, Drug Delivery and MRI. Chemistry 2022, 4, 872–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Roncancio, D.; Suo, Y.; Shao, Y.; Zhang, D.; Zhou, C. A Method Based on Amino-Modified Magnetic Nanoparticles to Extract DNA for PCR-Based Analysis. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 179, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Chen, D.; Yang, Y.; Gong, H.; Gao, W.; Xiao, H. A One Step Method for Isolation of Genomic DNA Using Multi-Amino Modified Magnetic Nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 3324–3332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.S.; An, G.S. Preparation of Dual-Layered Core–Shell Fe3O4@SiO2 Nanoparticles and Their Properties of Plasmid DNA Purification. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 3422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoza, B.; Matsumoto, M.; Matsunaga, T. DNA Extraction Using Modified Bacterial Magnetic Particles in the Presence of Amino Silane Compound. J. Biotechnol. 2002, 94, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hikosaka, R.; Nagata, F.; Tomita, M.; Kato, K. Adsorption and Desorption Characteristics of DNA onto the Surface of Amino Functional Mesoporous Silica with Various Particle Morphologies. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2016, 140, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, W.; Wei, W.; Li, J.; Qi, X.; Zuo, G.; Chen, Q.; Pan, X.; Dong, W. Amine-Functionalized Magnetic Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for DNA Separation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 387, 1116–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Elaissari, A. Temperature and Magnetic Dual Responsive Microparticles for DNA Separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2011, 81, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosa-Acosta, J.R.; Silva, J.A.; Fernández-Izquierdo, L.; Díaz-Castañón, S.; Ortiz, M.; Zuaznabar-Gardona, J.C.; Díaz-García, A.M. Iron Oxide Nanoparticles (IONPs) with Potential Applications in Plasmid DNA Isolation. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2018, 545, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ma, X.; Ding, C.; Jia, L. PH-Responsive Deoxyribonucleic Acid Capture/Release by Polydopamine Functionalized Magnetic Nanoparticles. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 862, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoza, B.; Arakaki, A.; Matsunaga, T. DNA Extraction Using Bacterial Magnetic Particles Modified with Hyperbranched Polyamidoamine Dendrimer. J. Biotechnol. 2003, 101, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonheim, T.C.; Bøgwald, J.; Dalmo, R.A. What Happens to the DNA Vaccine in Fish? A Review of Current Knowledge. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2008, 25, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucena-Aguilar, G.; Sánchez-López, A.M.; Barberán-Aceituno, C.; Carrillo-Ávila, J.A.; López-Guerrero, J.A.; Aguilar-Quesada, R. DNA Source Selection for Downstream Applications Based on DNA Quality Indicators Analysis. Biopreserv. Biobank. 2016, 14, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kefeni, K.K.; Mamba, B.B. Photocatalytic Application of Spinel Ferrite Nanoparticles and Nanocomposites in Wastewater Treatment: Review. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2020, 23, e00140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salih, S.J.; Mahmood, W.M. Review on Magnetic Spinel Ferrite (MFe2O4) Nanoparticles: From Synthesis to Application. Heliyon 2023, 9, e16601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoopngan, C.; Nonkumwong, J.; Phumying, S.; Promjantuek, W.; Maensiri, S.; Noisa, P.; Pinitsoontorn, S.; Ananta, S.; Srisombat, L. Amine-Functionalized and Hydroxyl-Functionalized Magnesium Ferrite Nanoparticles for Congo Red Adsorption. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2019, 2, 5329–5341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishwas, M.; Venkatesha Babu, K.R.; Arjuna Gowda, K.V.; Babu Gandla, S. Synthesis, Characterization and Photo-Catalytic Activity of Magnetic CoFe2O4 Nanoparticles Prepared by Temperature Controlled Co-Precipitation Method. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 68, 497–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, R.S.; Kuřitka, I.; Vilcakova, J.; Havlica, J.; Kalina, L.; Urbánek, P.; Machovsky, M.; Skoda, D.; Masař, M.; Holek, M. Sonochemical Synthesis of Gd3+ Doped CoFe2O4 Spinel Ferrite Nanoparticles and Its Physical Properties. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2018, 40, 773–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, T.A.; Majeed, S.; Nayak, A.; Bhushan, B. Principles and Advantages of Microwave-Assisted Methods for the Synthesis of Nanomaterials for Water Purification. In Advanced Nanomaterials for Water Engineering, Treatment, and Hydraulics; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2017; pp. 40–57. ISBN 9781522521372. [Google Scholar]
- Ayyıldız, M.F.; Karaman, D.N.; Kartoğlu, B.; Şaylan, M.; Chormey, D.S.; Bakırdere, S. A Simple Microwave-Assisted Synthesis of Cobalt Ferrite Nanoparticles and Its Application for the Determination of Lead Ions in Rooibos (Aspalathus Linearis) Tea. Food Chem. 2023, 429, 136862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, A.; Bhardwaj, A.K.; Singh, S.C.; Uttam, K.N.; Gautam, N.; Himanshu, A.K.; Shah, J.; Kotnala, R.K.; Gopal, R. Microwave Assisted Scalable Synthesis of Titanium Ferrite Nanomaterials. J. Appl. Phys. 2018, 123, 161411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nonkumwong, J.; Ananta, S.; Srisombat, L. Effective Removal of Lead(II) from Wastewater by Amine-Functionalized Magnesium Ferrite Nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 47382–47393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issa, B.; Obaidat, I.M.; Albiss, B.A.; Haik, Y. Magnetic Nanoparticles: Surface Effects and Properties Related to Biomedicine Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 21266–21305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, B.; Zhang, Y.W.; Liao, C.S.; Yan, C.H.; Chen, L.Y.; Wang, S.Y. Rare-Earth-Mediated Magnetism and Magneto-Optical Kerr Effects in Nanocrystalline CoFeMn0.9RE0.1O4 Thin Films. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2004, 280, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruce, I.J.; Taylor, J.; Todd, M.; Davies, M.J.; Borioni, E.; Sangregorio, C.; Sen, T. Synthesis, Characterisation and Application of Silica-Magnetite Nanocomposites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2004, 284, 145–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Su, W.; Tan, M. Endogenous Fluorescence Carbon Dots Derived from Food Items. Innovation 2020, 1, 100009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Chen, H.; Bao, H.; Gao, M. One-Pot Reaction to Synthesize Water-Soluble Magnetite Nanocrystals. Chem. Mater. 2004, 16, 1391–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pershina, A.G.; Sazonov, A.E.; Filimonov, V.D. Magnetic Nanoparticles–DNA Interactions: Design and Applications of Nanobiohybrid Systems. Russ. Chem. Rev. 2014, 83, 299–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; He, Z.; Liu, H.; Xu, Y.; Huang, H.; Yang, G.; Xiao, Z.; Li, S.; Liu, H.; Deng, Y.; et al. Application of Magnetic Nanoparticles in Nucleic Acid Detection. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2020, 18, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aslibeiki, B.; Varvaro, G.; Peddis, D.; Kameli, P. Particle Size, Spin Wave and Surface Effects on Magnetic Properties of MgFe2O4 Nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2017, 422, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, J.C.R.; Araujo-Barbosa, S.; Souza, A.L.R.; Iglesias, C.A.M.; Xavier, J.; Souza, P.B.; Plá Cid, C.C.; Azevedo, S.; da Silva, R.B.; Correa, M.A.; et al. Tuning Structural, Magnetic, Electrical, and Dielectric Properties of MgFe2O4 Synthesized by Sol-Gel Followed by Heat Treatment. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2021, 154, 110051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, M.Z.; Salker, A.V. Tailoring the Super-Paramagnetic Nature of MgFe2O4 Nanoparticles by In3+ Incorporation. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2016, 211, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naaz, F.; Dubey, H.K.; Kumari, C.; Lahiri, P. Structural and Magnetic Properties of MgFe2O4 Nanopowder Synthesized via Co-Precipitation Route. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hintermann, G.; Fischer, H.M.; Crameri, R.; Hütter, R. Simple Procedure for Distinguishing CCC, OC, and L Forms of Plasmid DNA by Agarose Gel Electrophoresis. Plasmid 1981, 5, 371–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Guo, M.; Bennett, J.C.; Li, X.; Tian, H.; Oakes, K.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, Q.; et al. Promoting DNA Loading on Magnetic Nanoparticles Using a DNA Condensation Strategy. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2015, 125, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Latif, A.; Osman, G. Comparison of Three Genomic DNA Extraction Methods to Obtain High DNA Quality from Maize. Plant Methods 2017, 13, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pervaiz, Z.H.; Turi, N.A.; Khaliq, I.; Rabbani, M.A.; Malik, S.A. Methodology: A Modified Method for High-Quality DNA Extraction for Molecular Analysis in Cereal Plants. Genet. Mol. Res. 2011, 10, 1669–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerzsenyi, T.B.; Ilosvai, Á.M.; Szilágyi, G.; Szőri, M.; Váradi, C.; Viskolcz, B.; Vanyorek, L.; Szőri-Dorogházi, E. A Simplified and Efficient Method for Production of Manganese Ferrite Magnetic Nanoparticles and Their Application in DNA Isolation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Treitli, S.C. BOMB Plasmid DNA Extraction Using Sera-Mag Carboxylated Beads, in Protocol 5.3. Doctoral Dissertation, Louisiana State University, Baton Rouge, LA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Surzycki, S. (Ed.) Agarose Gel Electrophoresis of DNA. In Basic Techniques in Molecular Biology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Oakes, C.C.; La Salle, S.; Trasler, J.M.; Robaire, B. Restriction Digestion and Real-Time PCR (QAMP). Methods Mol. Biol. 2009, 507, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mag-Bind® Ultra-Pure Plasmid DNA 96 Kit | Omega Bio-tek, (n.d.). Available online: https://www.omegabiotek.com/product/mag-bind-ultra-pure-plasmid-dna-kit/?cn-reloaded=1 (accessed on 13 September 2023).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).