Novel Allosteric Effectors Targeting Human Transcription Factor TEAD
Abstract
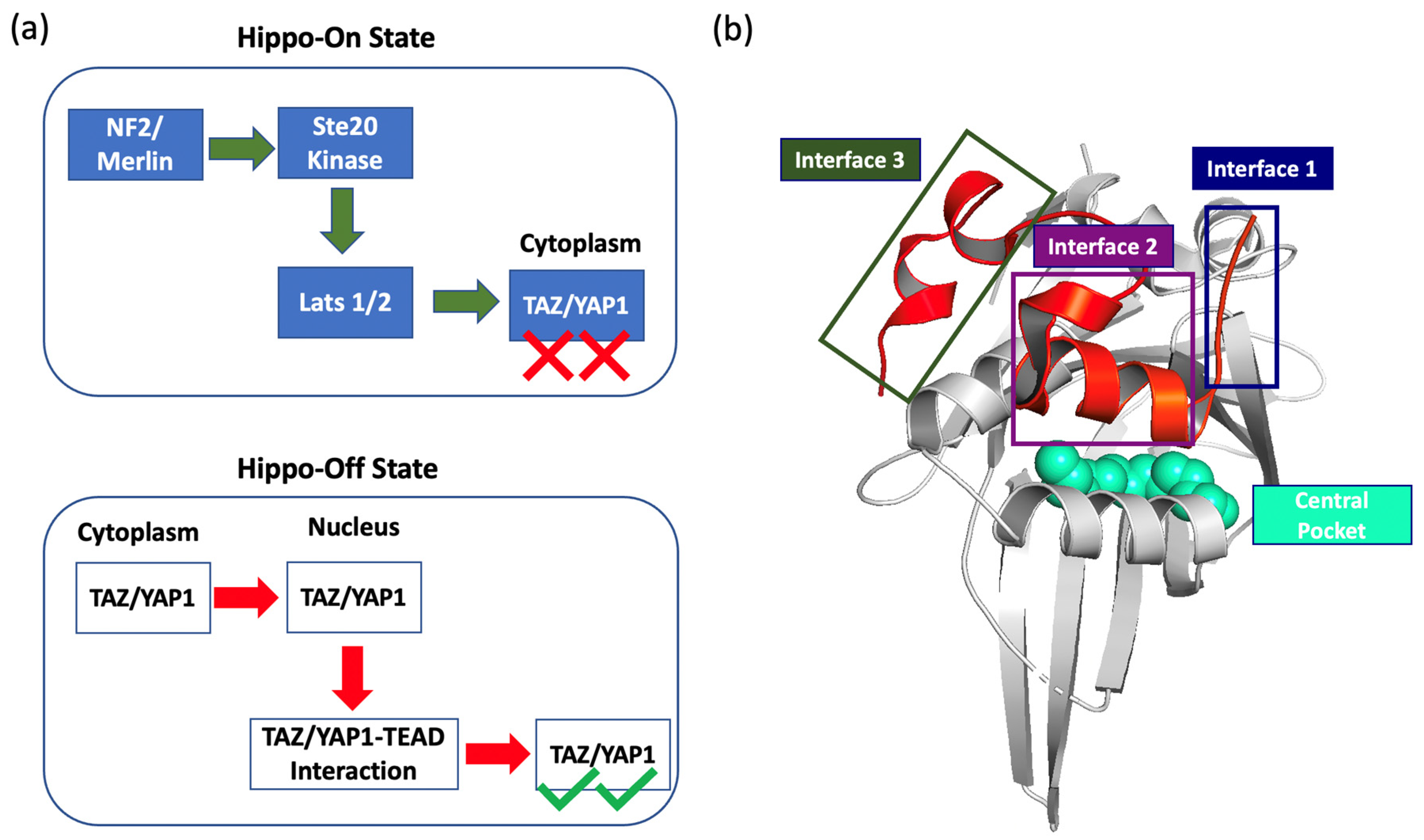
1. Introduction
2. Results
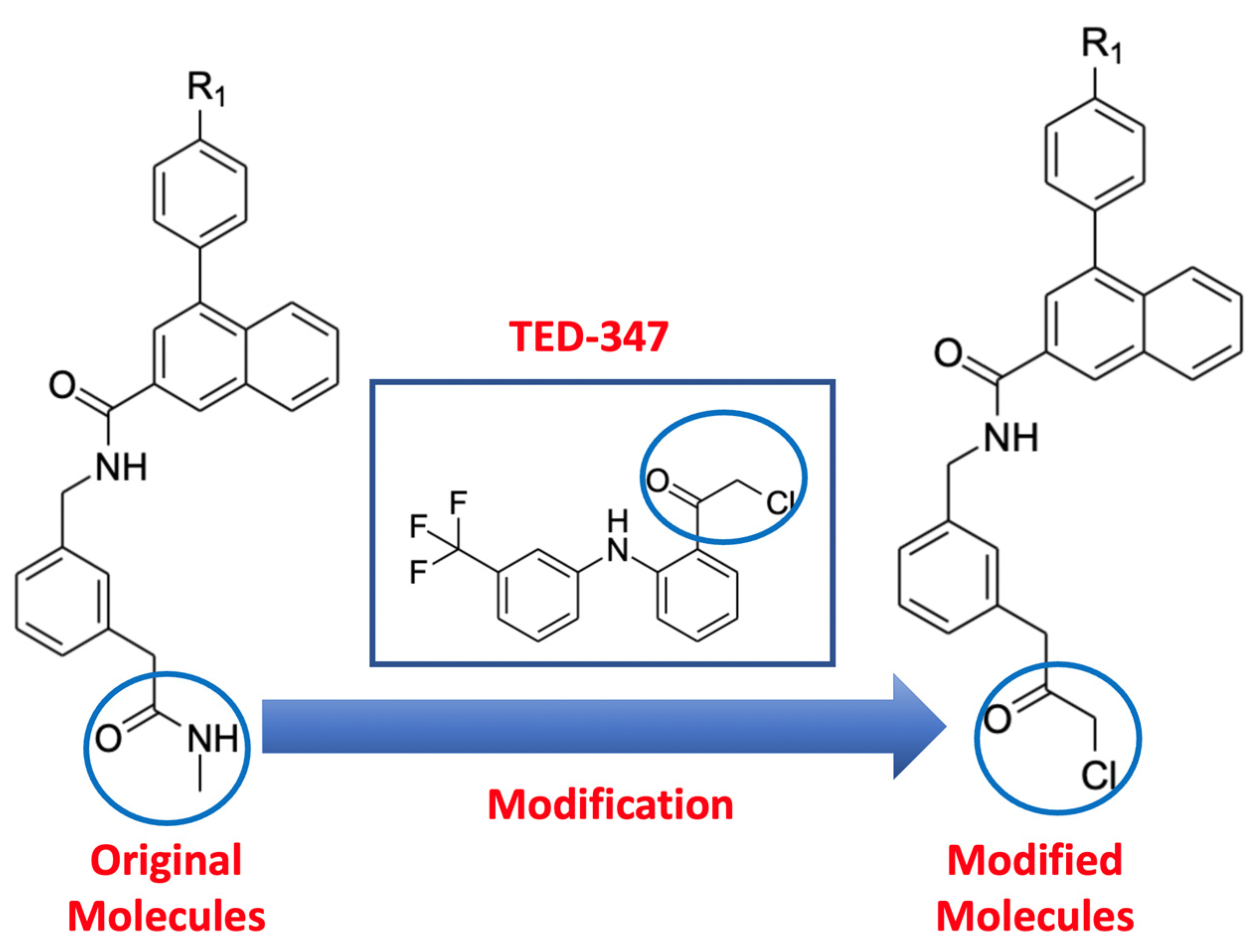
2.1. Molecular Docking of Original and Modified Molecules
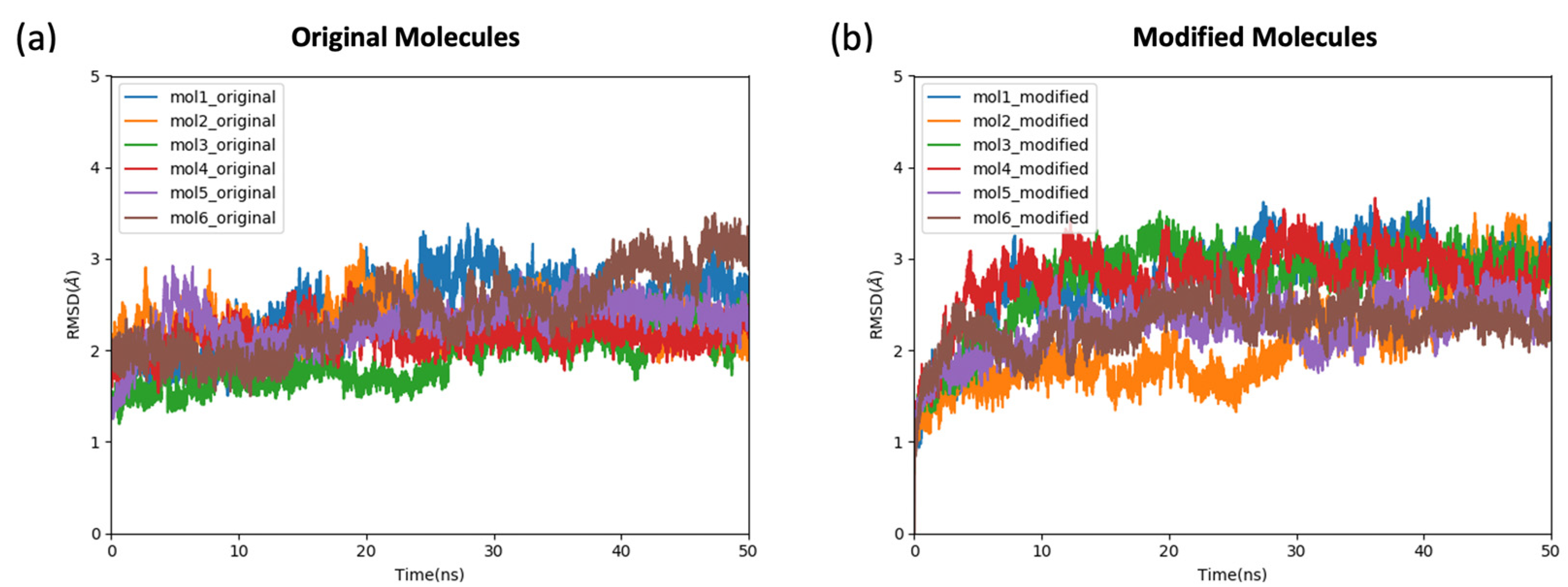
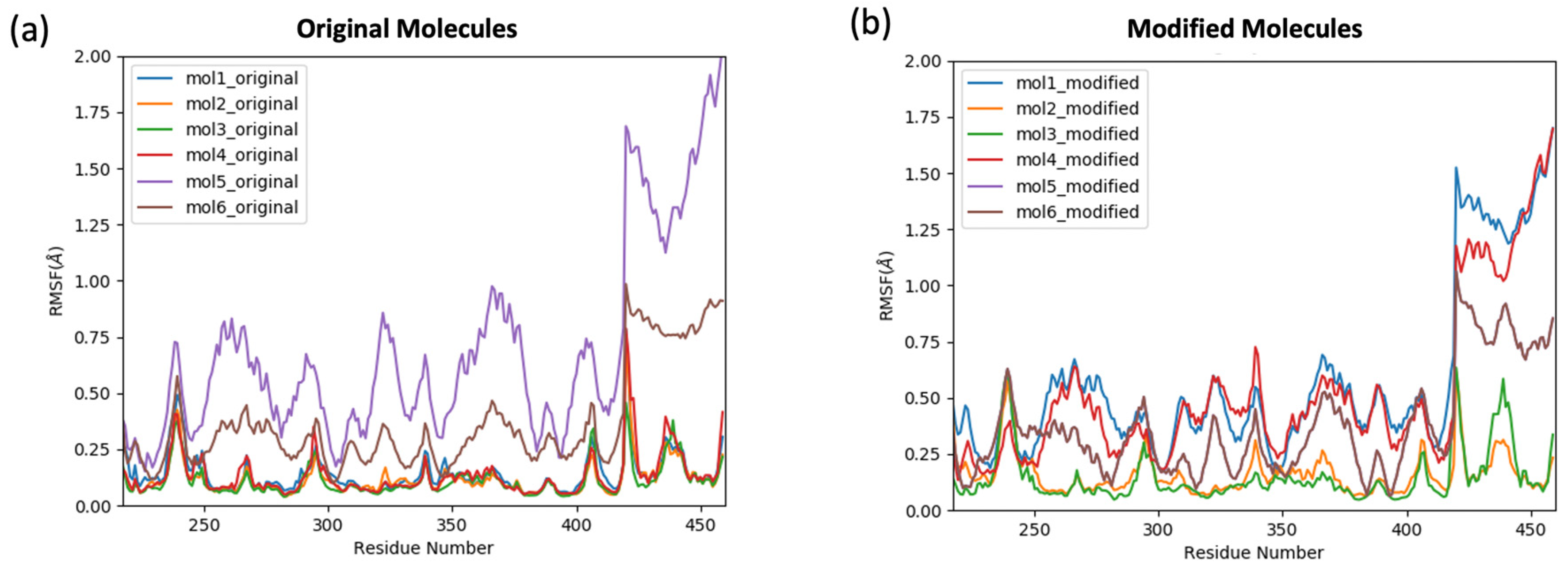
2.2. The Stability and the Binding Affinity of the Original and Modified Ligands
2.3. The Effect of the TEAD4 Ligands on the Conformational Space of the Protein
2.3.1. Time-Independent Component Analysis (t-ICA)
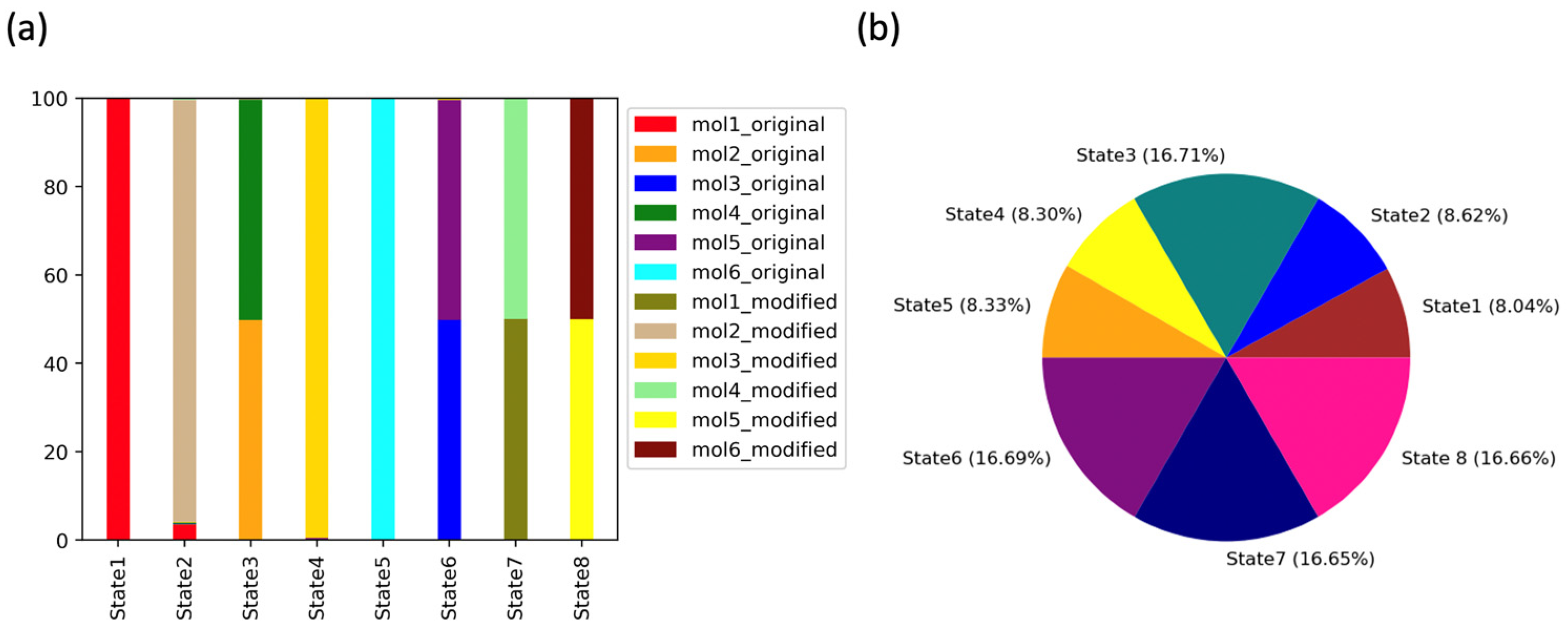
2.3.2. Markov State Model Analysis
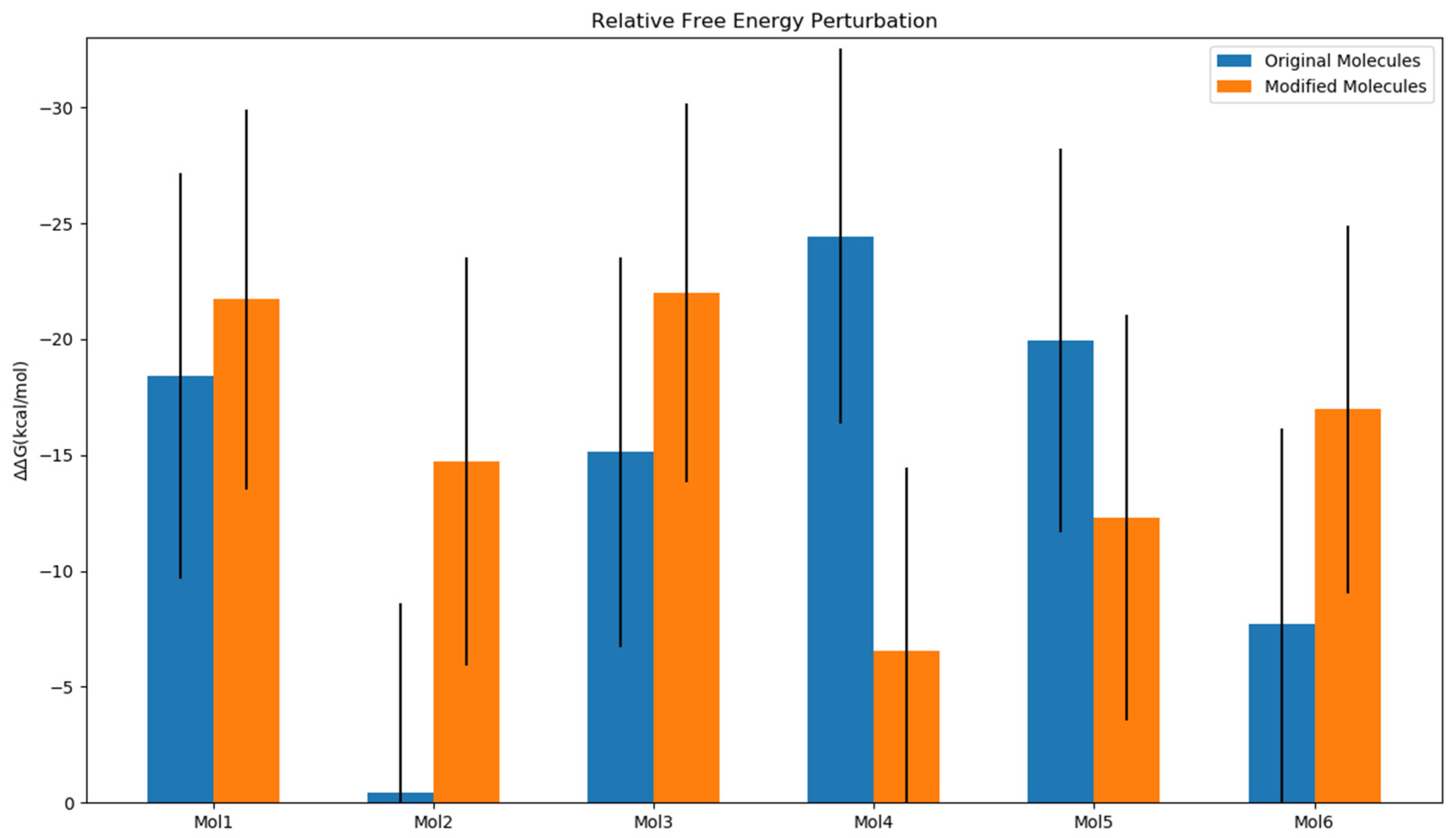
2.4. Impact of Ligands’ Binding on the Relative Free Energy Perturbation
2.5. Formatting of Mathematical Components
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Molecular Docking of Original and Modified Molecules
4.2. Molecular Dynamics Simulations
4.3. MM/GBSA Binding Energy Calculations
4.4. Analysis of Conformational Space
4.4.1. Time-Independent Component Analysis
4.4.2. Markov State Model Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ma, S.; Meng, Z.; Chen, R.; Guan, K.-L. The Hippo pathway: Biology and pathophysiology. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2019, 88, 577–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wackerhage, H.; del Re, D.P.; Judson, R.N.; Sudol, M.; Sadoshima, J. The Hippo signal transduction network in skeletal and cardiac muscle. Sci. Signal. 2014, 7, re4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barry, E.R.; Simov, V.; Valtingojer, I.; Venier, O. Recent therapeutic approaches to modulate the hippo pathway in oncology and regenerative medicine. Cells 2021, 10, 2715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calses, P.C.; Crawford, J.J.; Lill, J.R.; Dey, A. Hippo Pathway in Cancer: Aberrant Regulation and Therapeutic Opportunities. Trends Cancer 2019, 5, 297–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dey, A.; Varelas, X.; Guan, K.-L. Targeting the Hippo pathway in cancer, fibrosis, wound healing and regenerative medicine. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2020, 19, 480–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bum-Erdene, K.; Zhou, D.; Gonzalez-Gutierrez, G.; Ghozayel, M.K.; Si, Y.; Xu, D.; Shannon, H.E.; Bailey, B.J.; Corson, T.W.; Pollok, K.E.; et al. Small-Molecule Covalent Modification of Conserved Cysteine Leads to Allosteric Inhibition of the TEAD⋅Yap Protein-Protein Interaction. Cell Chem. Biol. 2019, 26, 378–389.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pobbati, A.; Han, X.; Hung, A.W.; Weiguang, S.; Huda, N.; Chen, G.-Y.; Kang, C.; Chia, C.S.B.; Luo, X.; Hong, W.; et al. Targeting the central pocket in human transcription factor TEAD as a potential cancer therapeutic strategy. Structure 2015, 23, 2076–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Huang, T.; Cheng, A.S.L.; Yu, J.; Kang, W.; To, K.F. The TEAD family and its oncogenic role in promoting tumorigenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noland, C.L.; Gierke, S.; Schnier, P.D.; Murray, J.; Sandoval, W.N.; Sagolla, M.; Dey, A.; Hannoush, R.N.; Fairbrother, W.J.; Cunningham, C.N. Palmitoylation of TEAD transcription factors is required for their stability and function in Hippo pathway signaling. Structure 2016, 24, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccolo, S.; Dupont, S.; Cordenonsi, M. The biology of YAP/TAZ: Hippo signaling and beyond. Physiol. Rev. 2014, 94, 1287–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huh, H.D.; Kim, D.H.; Jeong, H.-S.; Park, H.W. Regulation of TEAD transcription factors in cancer biology. Cells 2019, 8, 600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanconato, F.; Cordenonsi, M.; Piccolo, S. YAP and TAZ: A signalling hub of the tumour microenvironment. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2019, 19, 454–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AbdelFattah, H.S.; Ibrahim, M.T.; Nasr, M.M.; Nasr Amin, S.N. Cell Signaling in Cancer Microenvironment. Int. J. Adv. Biomed. 2017, 2, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.; Li, Y.; Song, J.; Li, C. Fluorescence polarization assay for the identification and evaluation of inhibitors at YAP–TEAD protein–protein interface 3. Anal. Biochem. 2019, 586, 113413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adihou, H.; Gopalakrishnan, R.; Förster, T.; Guéret, S.M.; Gasper, R.; Geschwindner, S.; García, C.C.; Karatas, H.; Pobbati, A.V.; Vazquez-Chantada, M.; et al. A protein tertiary structure mimetic modulator of the Hippo signalling pathway. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibault, F.; Coevoet, M.; Sturbaut, M.; Farce, A.; Renault, N.; Allemand, F.; Guichou, J.-F.; Drucbert, A.-S.; Foulon, C.; Magnez, R.; et al. Toward the discovery of a novel class of YAP–TEAD interaction inhibitors by virtual screening approach targeting YAP–TEAD protein–protein interface. Cancers 2018, 10, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saunders, J.T.; Holmes, B.; Benavides-Serrato, A.; Kumar, S.; Nishimura, R.N.; Gera, J. Targeting the YAP-TEAD interaction interface for therapeutic intervention in glioblastoma. J. Neurooncol. 2021, 152, 217–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Tao, H.; Xiong, H.; Lian, F.; Gao, J.; Ma, H.; Lu, T.; Zhang, D.; et al. Discovery and biological evaluation of vinylsulfonamide derivatives as highly potent, covalent TEAD autopalmitoylation inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 184, 111767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karatas, H.; Akbarzadeh, M.; Adihou, H.; Hahne, G.; Pobbati, A.V.; Ng, E.Y.; Guéret, S.M.; Sievers, S.; Pahl, A.; Metz, M.; et al. Discovery of Covalent Inhibitors Targeting the Transcriptional Enhanced Associate Domain Central Pocket. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 11972–11989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneda, A.; Seike, T.; Danjo, T.; Nakajima, T.; Otsubo, N.; Yamaguchi, D.; Tsuji, Y.; Hamaguchi, K.; Yasunaga, M.; Nishiya, Y.; et al. The novel potent TEAD inhibitor, K-975, inhibits YAP1/ TAZ-TEAD protein-protein interactions and exerts an anti-tumor effect on malignant pleural mesothelioma. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2020, 10, 4399–4415. Available online: www.ajcr.us/ (accessed on 20 August 2022).
- Kurppa, K.J.; Liu, Y.; To, C.; Zhang, T.; Fan, M.; Vajdi, A.; Knelson, E.H.; Xie, Y.; Lim, K.; Cejas, P.; et al. Treatment-Induced Tumor Dormancy through YAP-Mediated Transcriptional Reprogramming of the Apoptotic Pathway. Cancer Cell 2020, 37, 104–122.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, R.; Kumar, A.; Misra, G. Exploring TEAD2 as a drug target for therapeutic intervention of cancer: A multi-computational case study. Brief. Bioinform. 2021, 22, bbab007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holden, J.K.; Crawford, J.J.; Noland, C.L.; Schmidt, S.; Zbieg, J.R.; Lacap, J.A.; Zang, R.; Miller, G.M.; Zhang, Y.; Beroza, P.; et al. Small Molecule Dysregulation of TEAD Lipidation Induces a Dominant-Negative Inhibition of Hippo Pathway Signaling. Cell Rep. 2020, 31, 107809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pobbati, A.V.; Mejuch, T.; Chakraborty, S.; Karatas, H.; Bharath, S.R.; Guéret, S.M.; Goy, P.-A.; Hahne, G.; Pahl, A.; Sievers, S.; et al. Identification of Quinolinols as Activators of TEAD-Dependent Transcription. ACS Chem. Biol. 2019, 14, 2909–2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Chan, S.W.; Zhang, X.; Walsh, M.; Lim, C.J.; Hong, W.; Song, H. Structural basis of YAP recognition by TEAD4 in the hippo pathway. Genes Dev. 2010, 24, 290–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gironda-Martínez, A.; Donckele, E.J.; Samain, F.; Neri, D. DNA-Encoded chemical libraries: A comprehensive review with succesful stories and future challenges. ACS Pharmacol. Transl. Sci. 2021, 4, 1265–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGann, M. FRED pose prediction and virtual screening accuracy. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2011, 51, 578–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGann, M. FRED and HYBRID docking performance on standardized datasets. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 2012, 26, 897–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, B.P.; Brown, S.P.; Warren, G.L.; Muchmore, S.W. POSIT: Flexible shape-guided docking for pose prediction. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2015, 55, 1771–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husic, B.E.; Pande, V.S. Markov state models: From an art to a science. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 2386–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salentin, S.; Schreiber, S.; Haupt, V.J.; Adasme, M.F.; Schroeder, M. PLIP: Fully automated protein–ligand interaction profiler. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, W443–W447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkins, P.C.D.; Skillman, A.G.; Warren, G.L.; Ellingson, B.A.; Stahl, M.T. Conformer generation with OMEGA: Algorithm and validation using high quality structures from the Protein Databank and Cambridge Structural Database. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2010, 50, 572–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mesrouze, Y.; Meyerhofer, M.; Bokhovchuk, F.; Fontana, P.; Zimmermann, C.; Martin, T.; Delaunay, C.; Izaac, A.; Kallen, J.; Schmelzle, T.; et al. Effect of the acylation of TEAD4 on its interaction with co-activators YAP and TAZ. Protein Sci. 2017, 26, 2399–2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Openeye Scientific Software Inc. OEChem TK; Openeye Scientific Software Inc.: Santa Fe, NM, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Wang, W.; Kollman, P.A.; Case, D.A. Antechamber: An accessory software package for molecular mechanical calculations. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 222, U403. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Wang, W.; Kollman, P.A.; Case, D.A. Automatic atom type and bond type perception in molecular mechanical calculations. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 2006, 25, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, M.T.; Lee, J.; Tao, P. Homology modeling of Forkhead box protein C2: Identification of potential inhibitors using ligand and structure-based virtual screening. Mol. Divers. 2022, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarek Ibrahim, M.; Tao, P. Computational investigation of peptidomimetics as potential inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2022, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, J.A.; Martinez, C.; Kasavajhala, K.; Wickstrom, L.; Hauser, K.E.; Simmerling, C. ff14SB: Improving the accuracy of protein side chain and backbone parameters from ff99SB. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2015, 11, 3696–3713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Case, D.A.; Darden, T.; Cheatham, T.E., III; Simmerling, C.L.; Wang, J.; Duke, R.E.; Luo, R.; Crowley, M.; Walker, R.; Zhang, W.; et al. Amber 10; University of California: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Case, D.A.; Cheatham, T.E., III; Darden, T.; Gohlke, H.; Luo, R.; Merz, K.M., Jr.; Onufriev, A.; Simmerling, C.; Wang, B.; Woods, R.J. The Amber biomolecular simulation programs. J. Comput. Chem. 2005, 26, 1668–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essmann, U.; Perera, L.; Berkowitz, M.L.; Darden, T.; Lee, H.; Pedersen, L.G. A smooth particle mesh Ewald method. J. Chem. Phys. 1995, 103, 8577–8593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Hahn, D.F.; Mobley, D.L. A benchmark of electrostatic method performance in relative binding free energy calculations. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2021, 61, 1048–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Case, D.A.; Aktulga, H.M.; Belfon, K.; Ben-Shalom, I.; Brozell, S.R.; Cerutti, D.S.; Cheatham, T.E., III; Cruzeiro, V.W.D.; Darden, T.A.; Duke, R.E.; et al. Amber 2021; University of California: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, B.R., III; McGee, T.D., Jr.; Swails, J.M.; Homeyer, N.; Gohlke, H.; Roitberg, A.E. MMPBSA. py: An efficient program for end-state free energy calculations. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2012, 8, 3314–3321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breznik, M.; Ge, Y.; Bluck, J.P.; Briem, H.; Hahn, D.F.; Christ, C.D.; Mortier, J.; Mobley, D.L.; Meier, K. Prioritizing Small Sets of Molecules for Synthesis through in-silico Tools: A Comparison of Common Ranking Methods. ChemMedChem 2023, 18, e202200425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Khoury, L.; Santos-Martins, D.; Sasmal, S.; Eberhardt, J.; Bianco, G.; Ambrosio, F.A.; Solis-Vasquez, L.; Koch, A.; Forli, S.; Mobley, D.L. Comparison of affinity ranking using AutoDock-GPU and MM-GBSA scores for BACE-1 inhibitors in the D3R Grand Challenge 4. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 2019, 33, 1011–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrigan, M.P.; Sultan, M.M.; Hernández, C.X.; Husic, B.E.; Eastman, P.; Schwantes, C.R.; Beauchamp, K.A.; McGibbon, R.T.; Pande, V.S. MSMBuilder: Statistical models for biomolecular dynamics. Biophys. J. 2017, 112, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.T.; Trozzi, F.; Tao, P. Dynamics of hydrogen bonds in the secondary structures of allosteric protein Avena Sativa phototropin 1. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2022, 20, 50–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Ligands | R1 a | Chemgauss4 Docking Score (kcal/mol) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Original | Modified | ||
| 1 | 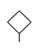 | −9.04 | −8.24 |
| 2 | -SF3 | −8.16 | −8.99 |
| 3 | 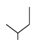 | −9.16 | −9.18 |
| 4 | 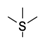 | −7.82 | −8.16 |
| 5 | 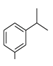 | −9.67 | −10.64 |
| 6 | 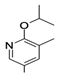 | −7.90 | −8.84 |
| Ligands | R1 a | ΔG (kcal/mol) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Original | Modified | ||
| 1 | 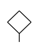 | −62.22 ± 2.94 | −56.90 ± 3.65 |
| 2 | -SF3 | −56.33 ± 3.50 | −49.87 ± 3.17 |
| 3 | 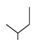 | −65.34 ± 3.13 | −62.73 ± 3.84 |
| 4 | 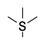 | −57.87 ± 4.97 | −58.18 ± 2.46 |
| 5 |  | −63.99 ± 3.15 | −60.20 ± 2.48 |
| 6 | 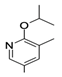 | −60.88 ± 3.40 | −56.07 ± 3.62 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ibrahim, M.T.; Verkhivker, G.M.; Misra, J.; Tao, P. Novel Allosteric Effectors Targeting Human Transcription Factor TEAD. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9009. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24109009
Ibrahim MT, Verkhivker GM, Misra J, Tao P. Novel Allosteric Effectors Targeting Human Transcription Factor TEAD. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(10):9009. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24109009
Chicago/Turabian StyleIbrahim, Mayar Tarek, Gennady M. Verkhivker, Jyoti Misra, and Peng Tao. 2023. "Novel Allosteric Effectors Targeting Human Transcription Factor TEAD" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 10: 9009. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24109009
APA StyleIbrahim, M. T., Verkhivker, G. M., Misra, J., & Tao, P. (2023). Novel Allosteric Effectors Targeting Human Transcription Factor TEAD. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(10), 9009. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24109009








