Muscular and Molecular Pathology Associated with SPATA5 Deficiency in a Child with EHLMRS
Abstract
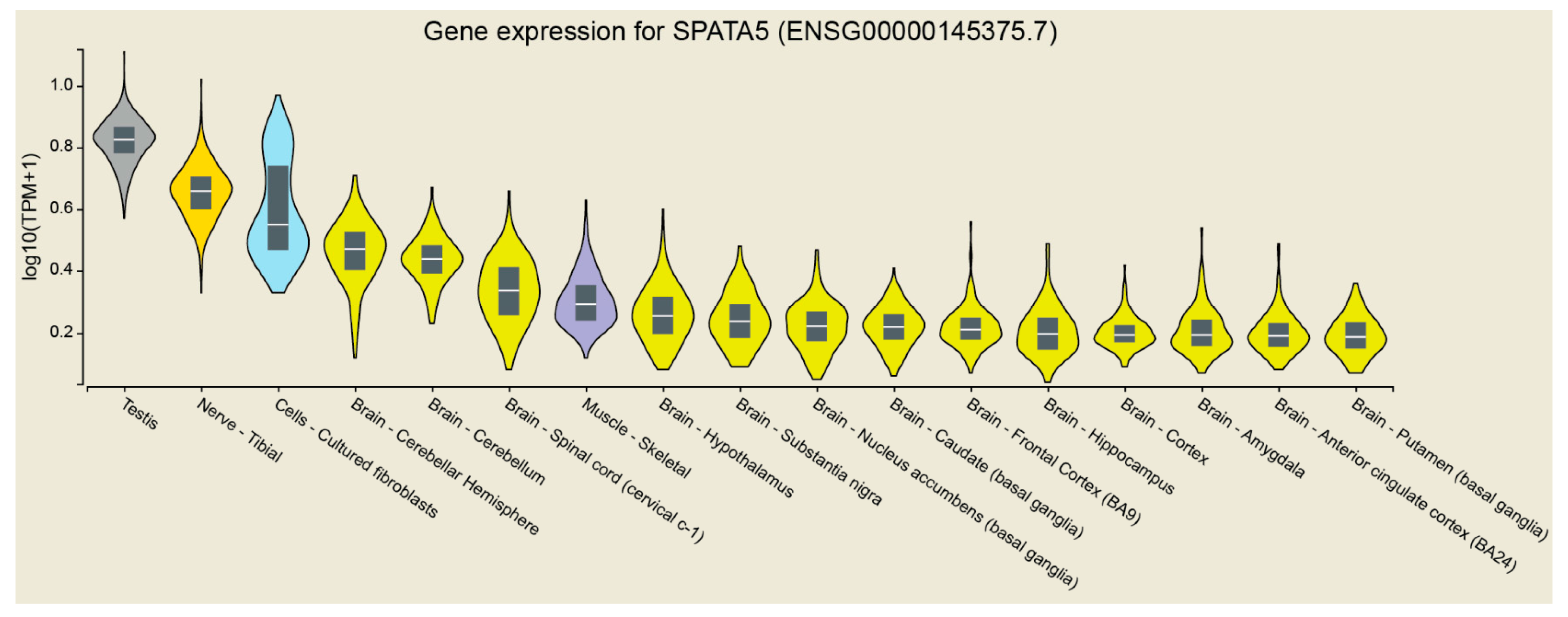
:1. Introduction
2. Results
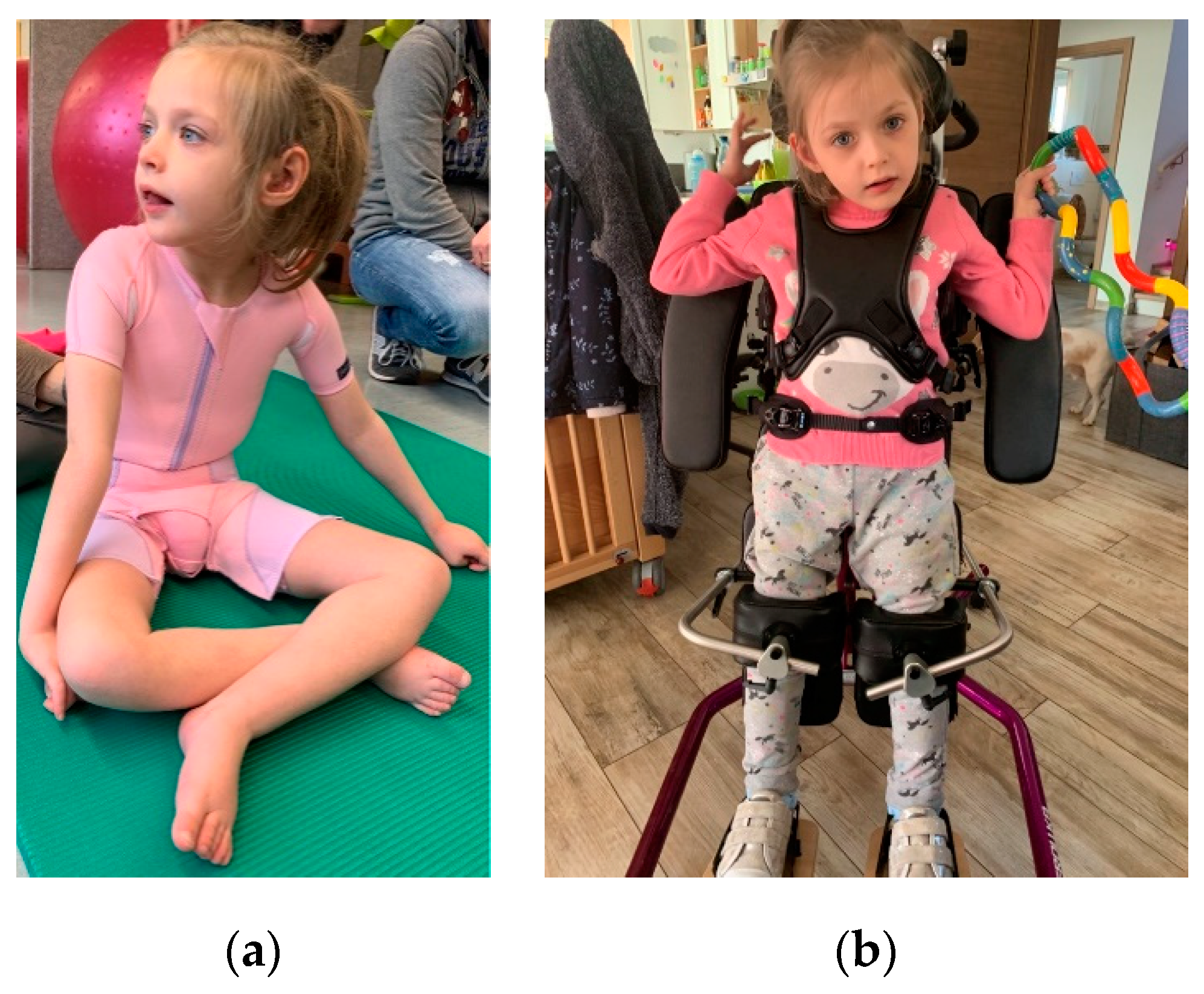
2.1. Clinical Findings
2.2. Genetic Findings
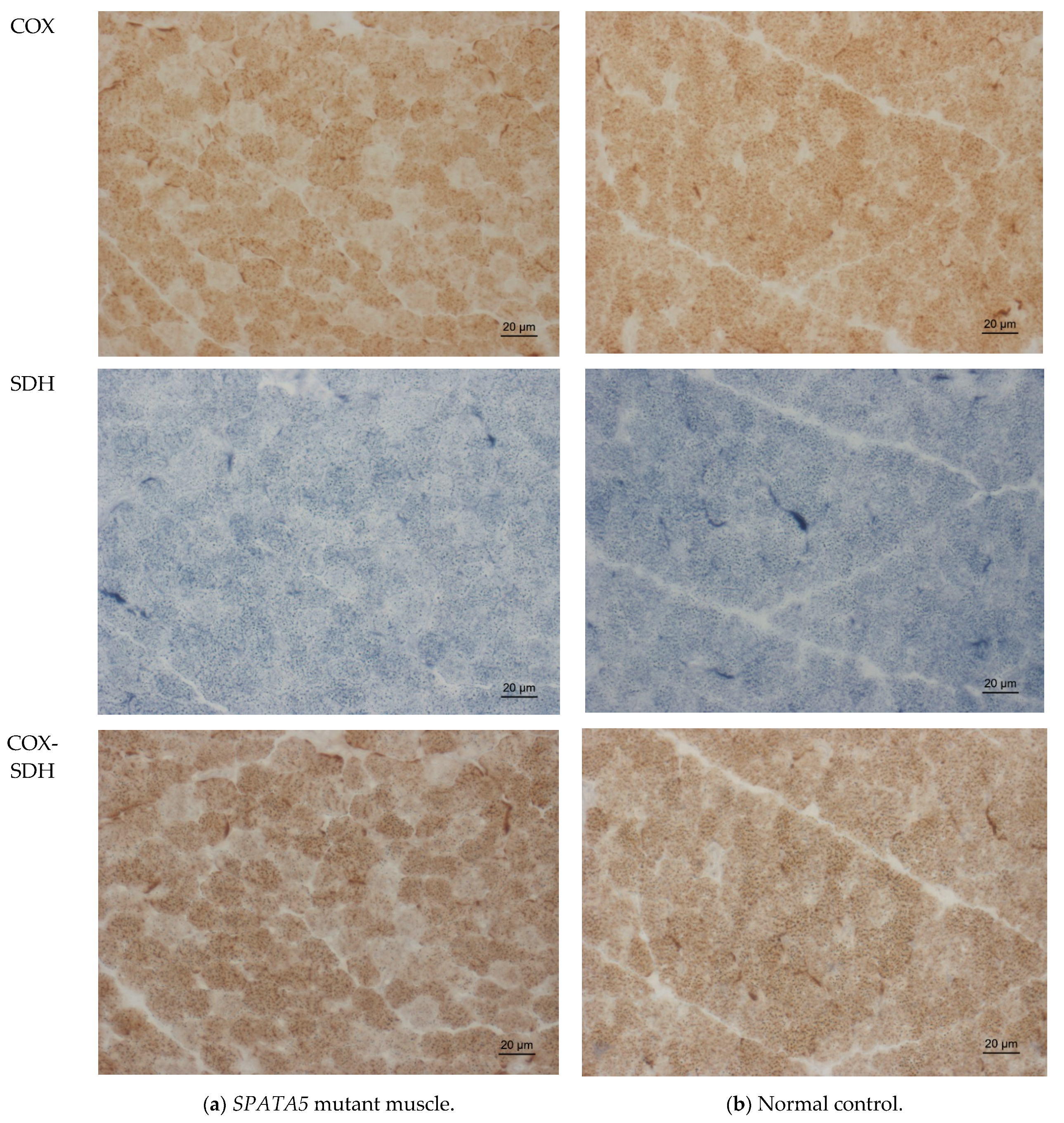
2.3. Muscle Biopsy Findings
2.4. Proteomic Profiling
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Exome-Sequencing
4.2. Histology and Enzyme Histochemistry, Immunohistology
4.3. Human Muscle Preparation for Mass Spectrometry
4.4. DIA-LC-MS/MS Analysis
4.5. Analysis of DIA Data
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data availability statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, Y.; Black, J.; Kisiel, N.; Kulesz-Martin, M.F. SPAF, a new AAA-protein specific to early spermatogenesis and malignant conversion. Oncogene 2000, 19, 1579–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tanaka, A.J.; Cho, M.T.; Millan, F.; Juusola, J.; Retterer, K.; Joshi, C.; Niyazov, D.; Garnica, A.; Gratz, E.; Deardorff, M.; et al. Mutations in SPATA5 Are Associated with Microcephaly, Intellectual Disability, Seizures, and Hearing Loss. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2015, 97, 457–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hawrylycz, M.J.; Lein, E.S.; Guillozet-Bongaarts, A.L.; Shen, E.H.; Ng, L.; Miller, J.A.; Van De Lagemaat, L.N.; Smith, K.A.; Ebbert, A.; Riley, Z.L.; et al. An anatomically comprehensive atlas of the adult human brain transcriptome. Nature 2012, 489, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, J.A.; Ding, S.L.; Sunkin, S.M.; Smith, K.A.; Ng, L.; Szafer, A.; Ebbert, A.; Riley, Z.L.; Royall, J.J.; Aiona, K.; et al. Transcriptional landscape of the prenatal human brain. Nature 2014, 508, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puusepp, S.; Kovacs-Nagy, R.; Alhaddad, B.; Braunisch, M.; Hoffmann, G.F.; Kotzaeridou, U.; Lichvarova, L.; Liiv, M.; Makowski, C.; Mandel, M.; et al. Compound heterozygous SPATA5 variants in four families and functional studies of SPATA5 deficiency. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2018, 26, 407–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Papuc, S.M.; Abela, L.; Steindl, K.; Begemann, A.; Simmons, T.L.; Schmitt, B.; Zweier, M.; Oneda, B.; Socher, E.; Crowther, L.M.; et al. The role of recessive inheritance in early-onset epileptic encephalopathies: A combined whole-exome sequencing and copy number study. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2019, 27, 408–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khurana, S.; Weaver, L.; Miskin, C.; Melvin, J.; Goldenthal, M. Mitochondrial Dysfunction: Consider SPATA5 mutations. Neurology 2019, 92 (Suppl. 15), 4.6-062. [Google Scholar]
- Zanus, C.; Costa, P.; Faletra, F.; Musante, L.; Russo, A.; Grazian, L.; Carrozzi, M. Description of a peculiar alternating ictal electroclinical pattern in a young boy with a novel SPATA5 mutation. Epileptic Disord. 2020, 22, 659–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurata, H.; Terashima, H.; Nakashima, M.; Okazaki, T.; Matsumura, W.; Ohno, K.; Saito, Y.; Maegaki, Y.; Kubota, M.; Nanba, E.; et al. Characterization of SPATA5-related encephalopathy in early childhood. Clin. Genet. 2016, 90, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchert, R.; Nesbitt, A.I.; Tawamie, H.; Krantz, I.D.; Medne, L.; Helbig, I.; Matalon, D.R.; Reis, A.; Santani, A.; Sticht, H.; et al. SPATA5 mutations cause a distinct autosomal recessive phenotype of intellectual disability, hypotonia and hearing loss. Orphanet. J. Rare Dis. 2016, 11, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Szczałuba, K.; Szymańska, K.; Kosińska, J.; Pollak, A.; Murcia, V.; Kędra, A.; Stawiński, P.; Rydzanicz, M.; Demkow, U.; Ploski, R. Isolated Hearing Impairment Caused by SPATA5 Mutations in a Family with Variable Phenotypic Expression. In Respiratory System Diseases Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology; Pokorski, M., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; Volume 980, pp. 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puusepp, S.; Reinson, K.; Pajusalu, S.; Murumets, Ü.; Õiglane-Shlik, E.; Rein, R.; Talvik, I.; Rodenburg, R.J.; Ounap, K. Effectiveness of whole exome sequencing in unsolved patients with a clinical suspicion of a mitochondrial disorder in Estonia. Mol. Genet. Metab. Rep. 2018, 15, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frerman, F.E.; Goodman, S.I. Defects of electron transfer flavoprotein and electron transfer flavoprotein-ubiquinone oxidoreductase: Glutaric acidemia type II. In The Metabolic and Molecular Bases of Inherited Disease, 8th ed.; Scriver, C.R., Beaudet, A.L., Sly, W.S., Valle, D., Eds.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2001; pp. 2357–2365. [Google Scholar]
- Spiekerkoetter, U.; Sun, B.; Khuchua, Z.; Bennett, M.J.; Strauss, A.W. Molecular and phenotypic heterogeneity in mitochondrial trifunctional protein deficiency due to beta-subunit mutations. Hum. Mutat. 2003, 21, 598–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- den Boer, M.E.J.; Dionisi-Vici, C.; Chakrapani, A.; van Thuijl, A.O.J.; Wanders, R.J.A.; Wijburg, F.A. Mitochondrial trifunctional protein deficiency: A severe fatty acid oxidation disorder with cardiac and neurologic involvement. J. Pediat. 2003, 142, 684–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- den Boer, M.E.J.; Wanders, R.J.A.; Morris, A.A.M.; IJlst, L.; Heymans, H.S.A.; Wijburg, F.A. Long-chain 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency: Clinical presentation and follow-up of 50 patients. Pediatrics 2002, 109, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aramaki, S.; Yoshida, I.; Yoshino, M.; Kondo, M.; Sato, Y.; Noda, K.; Jo, R.; Okue, A.; Sai, N.; Yamashita, F. Carbonic anhydrase II deficiency in three unrelated Japanese patients. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 1993, 16, 982–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, M.; Berutti, R.; Lorenz-Depiereux, B.; Graf, E.; Eckstein, G.; Mayr, J.A.; Meitinger, T.; Ahting, U.; Prokisch, H.; Strom, T.M.; et al. Mitochondrial DNA mutation analysis from exome sequencing—A more holistic approach in diagnostics of suspected mitochondrial disease. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2019, 42, 909–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stenton, S.L.; Prokisch, H. Advancing genomic approaches to the molecular diagnosis of mitochondrial disease. Essays Biochem. 2018, 62, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubowitz, V.; Sewry, C.A.; Oldfors, A. Muscle Biopsy. A Practical Approach, 4th ed.; Saunders: London, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Engel, W.K.; Cunningham, G.G. Rapid examination of muscle tissue. An improved trichrome method for fresh-frozen biopsy sections. Neurology 1963, 13, 919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kölbel, H.; Hathazi, D.; Jennings, M.; Horvath, R.; Roos, A.; Schara, U. Identification of Candidate Protein Markers in Skeletal Muscle of Laminin-211-Deficient CMD Type 1A-Patients. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Burkhart, J.M.; Schumbrutzki, C.; Wortelkamp, S.; Sickmann, A.; Zahedi, R.P. Systematic and quantitative comparison of digest efficiency and specificity reveals the impact of trypsin quality on MS-based proteomics. J. Paroteomics 2012, 75, 1454–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| UniProt Entry | Gene Name | Patient vs. Control | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| HMCS2_HUMAN | HMGCS2 | 6.67 | 0.000 |
| SPEB_HUMAN | AGMAT | 2.46 | 0.000 |
| THIM_HUMAN | ACAA2 | 2.38 | 0.000 |
| KAD3_HUMAN | AK3 | 1.98 | 0.001 |
| ATPD_HUMAN | ATP5F1D | 1.98 | 0.003 |
| ETFB_HUMAN | ETFB | 1.95 | 0.000 |
| ECHA_HUMAN | HADHA | 1.91 | 0.000 |
| NDUB6_HUMAN | NDUFB6 | 1.90 | 0.003 |
| COX5B_HUMAN | COX5B | 0.54 | 0.008 |
| CMC1_HUMAN | SLC25A12 | 0.53 | 0.011 |
| ATP5J_HUMAN | ATP5J | 0.52 | 0.009 |
| COX1_HUMAN | MT-CO1 | 0.50 | 0.026 |
| KAD2_HUMAN | AK2 | 0.50 | 0.008 |
| CQ10A_HUMAN | COQ10A | 0.49 | 0.034 |
| HXK1_HUMAN | HK1 | 0.31 | 0.000 |
| Protein | Localization | Gene Name | p-Value 3 | Associated Disease (#OMIM) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PURA1_HUMAN 1 | Cytoplasm | ADSSL1 | 0.000 | # 617030 MYOPATHY, DISTAL, 5; MPD5 |
| LAMA2_HUMAN 1 | Extracellular, basement membrane | LAMA2 | 0.013 | # 607855 MUSCULAR DYSTROPHY, CONGENITAL MEROSIN-DEFICIENT, 1A; MDC1A |
| # 618138 MUSCULAR DYSTROPHY, LIMB-GIRDLE, AUTOSOMAL RECESSIVE 23; LGMDR23 | ||||
| ETFB_HUMAN 1 | Mitochondrion matrix | ETFB | 0.000 | # 231680 GLUTARIC ACIDEMIA IIB, INCLUDED; GA2B, INCLUDED ETFB DEFICIENCY, INCLUDED |
| ECHA_HUMAN 1 | Mitochondrion inner membrane | HADHA | 0.000 | # 609015 MITOCHONDRIAL TRIFUNCTIONAL PROTEIN DEFICIENCY; MTPD |
| # 609016 LONG-CHAIN 3-HYDROXYACYL-CoA DEHYDROGENASE DEFICIENCY | ||||
| # 231680 MULTIPLE ACYL-CoA DEHYDROGENASE DEFICIENCY; MADD | ||||
| CMC1_HUMAN 2 | Mitochondrion inner membrane; multi-pass membrane protein | SLC25A12 | 0.011 | # 612949 DEVELOPMENTAL AND EPILEPTIC ENCEPHALOPATHY 39; DEE39 |
| TELT_HUMAN 2 | Sarcomere | TCAP | 0.004 | # 607487 CARDIOMYOPATHY, FAMILIAL HYPERTROPHIC, 25; CMH25 # 601954 MUSCULAR DYSTROPHY, LIMB-GIRDLE, AUTOSOMAL RECESSIVE 7; LGMDR7 |
| COX1_HUMAN 2 | Mitochondrion inner membrane; multi-pass membrane protein | MT-CO1 | 0.026 | # 535000 LEBER OPTIC ATROPHY |
| # 220110 MITOCHONDRIAL COMPLEX IV DEFICIENCY, NUCLEAR TYPE 1; MC4DN1 | ||||
| # 550500 MYOGLOBINURIA, RECURRENT | ||||
| # 500008 DEAFNESS, NONSYNDROMIC SENSORINEURAL, MITOCHONDRIAL | ||||
| # 114500 COLORECTAL CANCER; CRC | ||||
| HSPB8_HUMAN 2 | Nucleus; cytoplasm | HSPB8 | 0.039 | # 158590 NEURONOPATHY, DISTAL HEREDITARY MOTOR, TYPE IIA; HMN2A |
| # 608673 CHARCOT-MARIE-TOOTH DISEASE, AXONAL, TYPE 2L; CMT2L | ||||
| SPRE_HUMAN 2 | Cytoplasm | SPR | 0.014 | # 612716 DYSTONIA, DOPA-RESPONSIVE, DUE TO SEPIAPTERIN REDUCTASE DEFICIENCY |
| HEM2_HUMAN 2 | Cytosol; extracellular exosome; extracellular region; nucleus; ficolin-1-rich granule lumen; secretory granule lumen | ALAD | 0.031 | # 612740 PORPHYRIA, ACUTE HEPATIC |
| CAH2_HUMAN 2 | Cell membrane; cytoplasm | CA2 | 0.050 | # 259730 OSTEOPETROSIS, AUTOSOMAL RECESSIVE 3; OPTB3 |
| CATD_HUMAN 2 | Lysosome; extracellular space; melanosome | CTSD | 0.003 | # 610127 CEROID LIPOFUSCINOSIS, NEURONAL, 10; CLN10 |
| LDHA_HUMAN 2 | Cytoplasm | LDHA | 0.009 | # 612933 GLYCOGEN STORAGE DISEASE XI; GSD11 |
| HXK1_HUMAN 2 | Cytosol; mitochondrion outer membrane; peripheral membrane protein | HK1 | 0.000 | # 235700 HEMOLYTIC ANEMIA, NONSPHEROCYTIC, DUE TO HEXOKINASE DEFICIENCY |
| # 605285 NEUROPATHY, HEREDITARY MOTOR AND SENSORY, RUSSE TYPE; HMSNR | ||||
| # 617460 RETINITIS PIGMENTOSA 79; RP79 | ||||
| # 618547 NEURODEVELOPMENTAL DISORDER WITH VISUAL DEFECTS AND BRAIN ANOMALIES; NEDVIBA | ||||
| SMPX_HUMAN 2 | Nucleus; costamere; M band—muscle tendon junction | SMPX | 0.036 | # 300066 DEAFNESS, X-LINKED 4; DFNX4 |
| VATA_HUMAN 2 | Cytoplasm | ATP6V1A | 0.006 | # 617403 CUTIS LAXA, AUTOSOMAL RECESSIVE, TYPE IID; ARCL2D |
| # 618012 DEVELOPMENTAL AND EPILEPTIC ENCEPHALOPATHY 93; DEE93 | ||||
| PRPS1_HUMAN 2 | Cytosol; cytoplasm—ribose phosphate diphosphokinase complex | PRPS1 | 0.040 | # 300661 PHOSPHORIBOSYLPYROPHOSPHATE SYNTHETASE SUPERACTIVITY |
| # 311070 CHARCOT-MARIE-TOOTH DISEASE, X-LINKED RECESSIVE, 5; CMTX5 | ||||
| # 301835 ARTS SYNDROME; ARTS | ||||
| # 304500 DEAFNESS, X-LINKED 1; DFNX1 | ||||
| CO5A1_HUMAN 2 | Extracellular matrix | COL5A1 | 0.007 | # 130000 EHLERS-DANLOS SYNDROME, CLASSIC TYPE, 1; EDSCL1 |
| ACY1_HUMAN 2 | Cytoplasm | ACY1 | 0.002 | # 609924 AMINOACYLASE 1 DEFICIENCY; ACY1D |
| Primary Antibody, Clone | Company | Number | Dilution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Caveolin 3, 26/Caveolin3 | BD Transduction Laboratories | 610420 | 1:500 |
| Dystrophin 1, Dy4/6d3 | Novocastra/Leica | NCL-DYS1 | 1:2 |
| Dystrophin 2, Dy8/6c5 | Novocastra/Leica | NCL-DYS2 | 1:10 |
| Dystrophin 3, Dy10/12B2 | Novocastra/Leica | NCL-DYS3 | 1:10 |
| α-Dystroglycan, VIA4-1 | Merck/Upstate | #05-298 | 1:15 |
| β-Dystroglycan, 43DAG1/8D5 | Novocastra/Leica | NCL-b-DG | 1:10 |
| α-Sarcoglycan, Ad1/20A6 | Novocastra/Leica | NCL-a-SARC | 1:50 |
| β-Sarcoglycan, βSarc/5B1 | Novocastra/Leica | NCL-b-SARC | 1:50 |
| γ-Sarcoglycan, 35DAG/21B5 | Novocastra/Leica | NCL-g-SARC | 1:50 |
| δ-Sarcoglycan, 35DAG/21B5 | Novocastra/Leica | NCL-d-SARC | 1:10 |
| Laminin α2 C-term., 5H2 | Merck/Chemicon | MAB1922 | 1:500 |
| Emerin, 4G5 | Novocastra/Leica | NCL-EMERIN | 1:20 |
| Dysferlin, Hamlet 1 | Novocastra/Leica | NCL-HAMLET | 1:5 |
| Collagen 6, VI-26 | Merck/Chemicon | MAB3303 | 1:100 |
| Collagen 6, 3C4 | Merck/Chemicon | MAB1944 | 1:200 |
| Collagen 4, polyclonal | Cedarline | CL50411AP | 1:100 |
| Laminin α5, 4C7 | Merck/Chemicon | MAB1924 | 1:500 |
| DRP 2 (Utrophin), DRP3/20C5 | Novocastra/Leica | NCL-DRP2 | 1:5 |
| Neonatal Myosin, WB-MHCn | Novocastra/Leica | NCL-MHCn | 1:5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Braun, F.; Hentschel, A.; Sickmann, A.; Marteau, T.; Hertel, S.; Förster, F.; Prokisch, H.; Wagner, M.; Wortmann, S.; Della Marina, A.; et al. Muscular and Molecular Pathology Associated with SPATA5 Deficiency in a Child with EHLMRS. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7835. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22157835
Braun F, Hentschel A, Sickmann A, Marteau T, Hertel S, Förster F, Prokisch H, Wagner M, Wortmann S, Della Marina A, et al. Muscular and Molecular Pathology Associated with SPATA5 Deficiency in a Child with EHLMRS. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(15):7835. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22157835
Chicago/Turabian StyleBraun, Frederik, Andreas Hentschel, Albert Sickmann, Theodore Marteau, Swantje Hertel, Fabian Förster, Holger Prokisch, Matias Wagner, Saskia Wortmann, Adela Della Marina, and et al. 2021. "Muscular and Molecular Pathology Associated with SPATA5 Deficiency in a Child with EHLMRS" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 15: 7835. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22157835
APA StyleBraun, F., Hentschel, A., Sickmann, A., Marteau, T., Hertel, S., Förster, F., Prokisch, H., Wagner, M., Wortmann, S., Della Marina, A., Kölbel, H., Roos, A., & Schara-Schmidt, U. (2021). Muscular and Molecular Pathology Associated with SPATA5 Deficiency in a Child with EHLMRS. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(15), 7835. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22157835






