Structure, Function, and Regulation of the Essential Virulence Factor Capsular Polysaccharide of Vibrio vulnificus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Identification of the V. vulnificus Capsule and Its Correlation with Virulence
3. CPS Composition and Structure
4. Further Insights Regarding CPS Functions That Contribute to Virulence
5. CPS Genetics and Biosynthesis
6. CPS Phase Variation
7. Other Regulation of CPS
8. Concluding Remarks
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CPS | Capsular polysaccharide |
| LPS | Lipopolysaccharide |
| NHS | Normal human serum |
| NMR | Nuclear magnetic resonance |
| HPAEC | High performance anion-exchange chromatography |
| TNF-α | Tumor necrosis factor alpha |
| IL | Interleukin |
| Und-P | Undecaprenyl phosphate |
References
- Oliver, J.D. Vibrio vulnificus: Death on the half shell. A personal journey with the pathogen and its ecology. Microb. Ecol. 2013, 65, 793–799. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Horseman, M.A.; Surani, S. A comprehensive review of Vibrio vulnificus: An important cause of severe sepsis and skin and soft-tissue infection. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2011, 15, e157–e166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, M.K.; Oliver, J.D. Vibrio vulnificus: Disease and pathogenesis. Infect. Immun. 2009, 77, 1723–1733. [Google Scholar]
- Oliver, J.D. Wound infections caused by Vibrio vulnificus and other marine bacteria. Epidemiol. Infect. 2005, 133, 383–391. [Google Scholar]
- Gulig, P.A.; Bourdage, K.L.; Starks, A.M. Molecular Pathogenesis of Vibrio vulnificus. J. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 118–131. [Google Scholar]
- Kreger, A.; DeChatelet, L.; Shirley, P. Interaction of Vibrio vulnificus with human polymorphonuclear leukocytes: Association of virulence with resistance to phagocytosis. J. Infect. Dis. 1981, 144, 244–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreger, A.S.; Gray, L.D.; Testa, J. Protection of mice against Vibrio vulnificus disease by vaccination with surface antigen preparations and anti-surface antigen antisera. Infect. Immun. 1984, 45, 537–543. [Google Scholar]
- Amako, K.; Okada, K.; Miake, S. Evidence for the presence of a capsule in Vibrio vulnificus. J. Gen. Microbiol. 1984, 130, 2741–2743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, S.; Ogawa, M.; Mizuguchi, Y. Relation of capsular materials and colony opacity to virulence of Vibrio vulnificus. Infect. Immun. 1985, 47, 446–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, L.M.; White, V.K.; Zane, S.F.; Oliver, J.D. Correlation between virulence and colony morphology in Vibrio vulnificus. Infect. Immun. 1987, 55, 269–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, A.C.; Simpson, L.M.; Oliver, J.D.; Morris, J.G., Jr. Phenotypic evaluation of acapsular transposon mutants of Vibrio vulnificus. Infect. Immun. 1990, 58, 1769–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, A.B.; Siebeling, R.J. Identification of genetic loci required for capsular expression in Vibrio vulnificus. Infect. Immun. 2003, 71, 1091–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Yamazaki, K.; Kashimoto, T.; Morita, M.; Kado, T.; Matsuda, K.; Yamasaki, M.; Ueno, S. Identification of in vivo Essential Genes of Vibrio vulnificus for Establishment of Wound Infection by Signature-Tagged Mutagenesis. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuppardo, A.B.; Siebeling, R.J. An epimerase gene essential for capsule synthesis in Vibrio vulnificus. Infect. Immun. 1998, 66, 2601–2606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, G.P.; Hayat, U.; Abeygunawardana, C.; Fox, C.; Wright, A.C.; Maneval, D.R., Jr.; Bush, C.A.; Morris, J.G., Jr. Purification and determination of the structure of capsular polysaccharide of Vibrio vulnificus MO6-24. J. Bacteriol. 1992, 174, 2620–2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, G.P.; Hayat, U.; Bush, C.A.; Morris, J.G., Jr. Capsular polysaccharide structure of a clinical isolate of Vibrio vulnificus strain BO62316 determined by heteronuclear NMR spectroscopy and high-performance anion-exchange chromatography. Anal. Biochem. 1993, 214, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunawardena, S.; Reddy, G.P.; Wang, Y.; Kolli, V.S.; Orlando, R.; Morris, J.G.; Bush, C.A. Structure of a muramic acid containing capsular polysaccharide from the pathogenic strain of Vibrio vulnificus ATCC 27562. Carbohydr. Res. 1998, 309, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonson, J.G.; Siebeling, R.J. Immunogenicity of Vibrio vulnificus capsular polysaccharides and polysaccharide-protein conjugates. Infect. Immun. 1993, 61, 2053–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayat, U.; Reddy, G.P.; Bush, C.A.; Johnson, J.A.; Wright, A.C.; Morris, J.G., Jr. Capsular types of Vibrio vulnificus: An analysis of strains from clinical and environmental sources. J. Infect. Dis. 1993, 168, 758–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bush, C.A.; Patel, P.; Gunawardena, S.; Powell, J.; Joseph, A.; Johnson, J.A.; Morris, J.G. Classification of Vibrio vulnificus strains by the carbohydrate composition of their capsular polysaccharides. Anal. Biochem. 1997, 250, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.E.; Calia, F.M.; Musher, D.M.; Goree, A. Resistance of Vibrio vulnificus to serum bactericidal and opsonizing factors: Relation to virulence in suckling mice and humans. J. Infect. Dis. 1984, 150, 413–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamplin, M.L.; Specter, S.; Rodrick, G.E.; Friedman, H. Vibrio vulnificus resists phagocytosis in the absence of serum opsonins. Infect. Immun. 1985, 49, 715–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamplin, M.L.; Specter, S.; Rodrick, G.E.; Friedman, H. Differential complement activation and susceptibility to human serum bactericidal action by Vibrio species. Infect. Immun. 1983, 42, 1187–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, T.C.; Ayrapetyan, M.; Ryan, H.; Oliver, J.D. Serum survival of Vibrio vulnificus: Role of genotype, capsule, complement, clinical origin, and in situ incubation. Pathogens 2014, 3, 822–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, T.; Kawai, T. Toll-like receptor signaling pathways. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powell, J.L.; Wright, A.C.; Wasserman, S.S.; Hone, D.M.; Morris, J.G., Jr. Release of tumor necrosis factor alpha in response to Vibrio vulnificus capsular polysaccharide in in vivo and in vitro models. Infect. Immun. 1997, 65, 3713–3718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, B.C.; Kim, M.S.; Choi, S.H.; Kim, T.S. Involvement of capsular polysaccharide via a TLR2/NF-kappaB pathway in Vibrio vulnificus-induced IL-8 secretion of human intestinal epithelial cells. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2010, 25, 581–591. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hampton, C.M.; Guerrero-Ferreira, R.C.; Storms, R.E.; Taylor, J.V.; Yi, H.; Gulig, P.A.; Wright, E.R. The Opportunistic Pathogen Vibrio vulnificus Produces Outer Membrane Vesicles in a Spatially Distinct Manner Related to Capsular Polysaccharide. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.R.; Kim, B.U.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, C.M.; Na, H.S.; Koh, J.T.; Choy, H.E.; Rhee, J.H.; Lee, S.E. Outer membrane vesicles of Vibrio vulnificus deliver cytolysin-hemolysin VvhA into epithelial cells to induce cytotoxicity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 399, 607–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitfield, C. Biosynthesis and assembly of capsular polysaccharides in Escherichia coli. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2006, 75, 39–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitfield, C.; Paiment, A. Biosynthesis and assembly of Group 1 capsular polysaccharides in Escherichia coli and related extracellular polysaccharides in other bacteria. Carbohydr. Res. 2003, 338, 2491–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatzidaki-Livanis, M.; Jones, M.K.; Wright, A.C. Genetic variation in the Vibrio vulnificus group 1 capsular polysaccharide operon. J. Bacteriol. 2006, 188, 1987–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, A.C.; Powell, J.L.; Kaper, J.B.; Morris, J.G., Jr. Identification of a group 1-like capsular polysaccharide operon for Vibrio vulnificus. Infect. Immun. 2001, 69, 6893–6901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakhamchik, A.; Wilde, C.; Chong, H.; Rowe-Magnus, D.A. Evidence for the horizontal transfer of an unusual capsular polysaccharide biosynthesis locus in marine bacteria. Infect. Immun. 2010, 78, 5214–5222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Nakhamchik, A.; Wilde, C.; Rowe-Magnus, D.A. Identification of a Wzy polymerase required for group IV capsular polysaccharide and lipopolysaccharide biosynthesis in Vibrio vulnificus. Infect. Immun. 2007, 75, 5550–5558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neiman, J.; Guo, Y.; Rowe-Magnus, D.A. Chitin-induced carbotype conversion in Vibrio vulnificus. Infect. Immun. 2011, 79, 3195–3203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, M.L.; Landgraf, M. Virulence factors and pathogenicity of Vibrio vulnificus strains isolated from seafood. J. Appl. Microbiol. 1998, 84, 747–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.M.; Jeong, K.C.; Rhee, J.H.; Choi, S.H. Thermal-death times of opaque and translucent morphotypes of Vibrio vulnificus. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1997, 63, 3308–3310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosche, T.M.; Smith, B.; Oliver, J.D. Evidence for an intermediate colony morphology of Vibrio vulnificus. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 4356–4359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilton, T.; Rosche, T.; Froelich, B.; Smith, B.; Oliver, J. Capsular polysaccharide phase variation in Vibrio vulnificus. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 6986–6993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosche, T.M.; Yano, Y.; Oliver, J.D. A rapid and simple PCR analysis indicates there are two subgroups of Vibrio vulnificus which correlate with clinical or environmental isolation. Microbiol. Immunol. 2005, 49, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phippen, B.L.; Oliver, J.D. Role of anaerobiosis in capsule production and biofilm formation in Vibrio vulnificus. Infect. Immun. 2015, 83, 551–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrison-Schilling, K.L.; Grau, B.L.; McCarter, K.S.; Olivier, B.J.; Comeaux, N.E.; Pettis, G.S. Calcium promotes exopolysaccharide phase variation and biofilm formation of the resulting phase variants in the human pathogen Vibrio vulnificus. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 13, 643–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaluskar, Z.M.; Garrison-Schilling, K.L.; McCarter, K.S.; Lambert, B.; Simar, S.R.; Pettis, G.S. Manganese is an additional cation that enhances colonial phase variation of Vibrio vulnificus. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2015, 7, 789–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, M.; Tucker, M.S.; Gulig, P.A.; Wright, A.C. Phase variation, capsular polysaccharide, pilus and flagella contribute to uptake of Vibrio vulnificus by the Eastern oyster (Crassostrea virginica). Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 11, 1934–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris-Young, L.; Tamplin, M.L.; Fisher, W.S.; Mason, J.W. Effects of Physicochemical Factors and Bacterial Colony Morphotype on Association of Vibrio vulnificus with Hemocytes of Crassostrea virginica. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1993, 59, 1012–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heeb, S.; Haas, D. Regulatory roles of the GacS/GacA two-component system in plant-associated and other gram-negative bacteria. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2001, 14, 1351–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauthier, J.D.; Jones, M.K.; Thiaville, P.; Joseph, J.L.; Swain, R.A.; Krediet, C.J.; Gulig, P.A.; Teplitski, M.; Wright, A.C. Role of GacA in virulence of Vibrio vulnificus. Microbiology 2010, 156, 3722–3733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, R.N.; Gulig, P.A. Roles of RseB, sigmaE, and DegP in virulence and phase variation of colony morphotype of Vibrio vulnificus. Infect. Immun. 2009, 77, 3768–3781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeAngelis, C.M.; Saul-McBeth, J.; Matson, J.S. Vibrio responses to extracytoplasmic stress. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2018, 10, 511–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, A.C.; Powell, J.L.; Tanner, M.K.; Ensor, L.A.; Karpas, A.B.; Morris, J.G., Jr.; Sztein, M.B. Differential expression of Vibrio vulnificus capsular polysaccharide. Infect. Immun. 1999, 67, 2250–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrison-Schilling, K.L.; Kaluskar, Z.M.; Lambert, B.; Pettis, G.S. Genetic analysis and prevalence studies of the brp exopolysaccharide locus of Vibrio vulnificus. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e100890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Rowe-Magnus, D.A. Identification of a c-di-GMP-regulated polysaccharide locus governing stress resistance and biofilm and rugose colony formation in Vibrio vulnificus. Infect. Immun. 2010, 78, 1390–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joseph, L.A.; Wright, A.C. Expression of Vibrio vulnificus capsular polysaccharide inhibits biofilm formation. J. Bacteriol. 2004, 186, 889–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.J.; Kim, J.A.; Hwang, W.; Park, S.J.; Lee, K.H. Role of capsular polysaccharide (CPS) in biofilm formation and regulation of CPS production by quorum-sensing in Vibrio vulnificus. Mol. Microbiol. 2013, 90, 841–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.J.; Jung, Y.C.; Park, S.J.; Lee, K.H. Role of Heat Shock Proteases in Quorum-Sensing-Mediated Regulation of Biofilm Formation by Vibrio Species. MBio 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, M.J.; Hughes, C.; Koronakis, V. RfaH and the ops element, components of a novel system controlling bacterial transcription elongation. Mol. Microbiol. 1997, 26, 845–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakhnin, A.V.; Babitzke, P. NusG/Spt5: Are there common functions of this ubiquitous transcription elongation factor? Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2014, 18, 68–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrett, S.B.; Garrison-Schilling, K.L.; Cooke, J.T.; Pettis, G.S. Capsular polysaccharide production and serum survival of Vibrio vulnificus are dependent on antitermination control by RfaH. FEBS Lett. 2016, 590, 4564–4572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
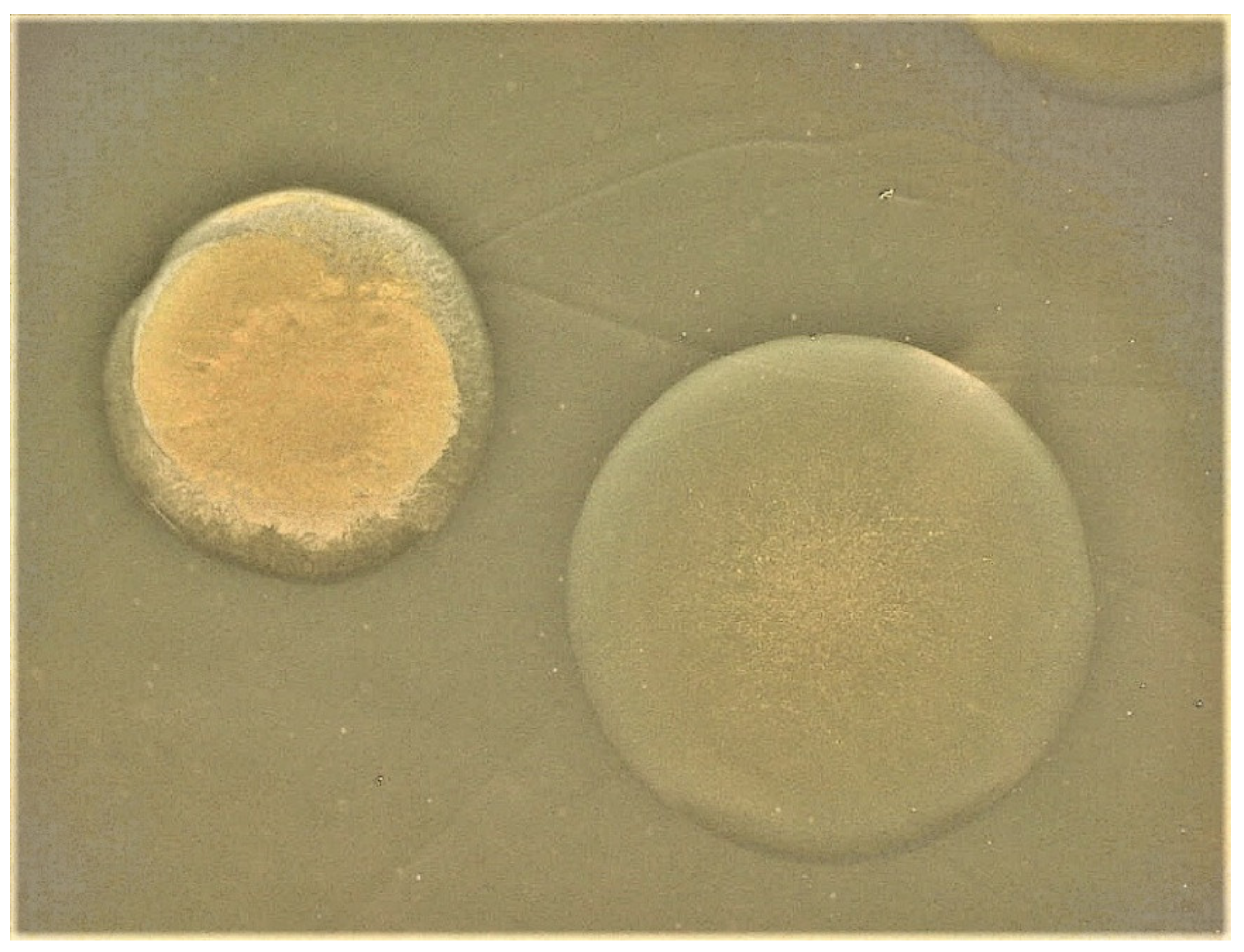
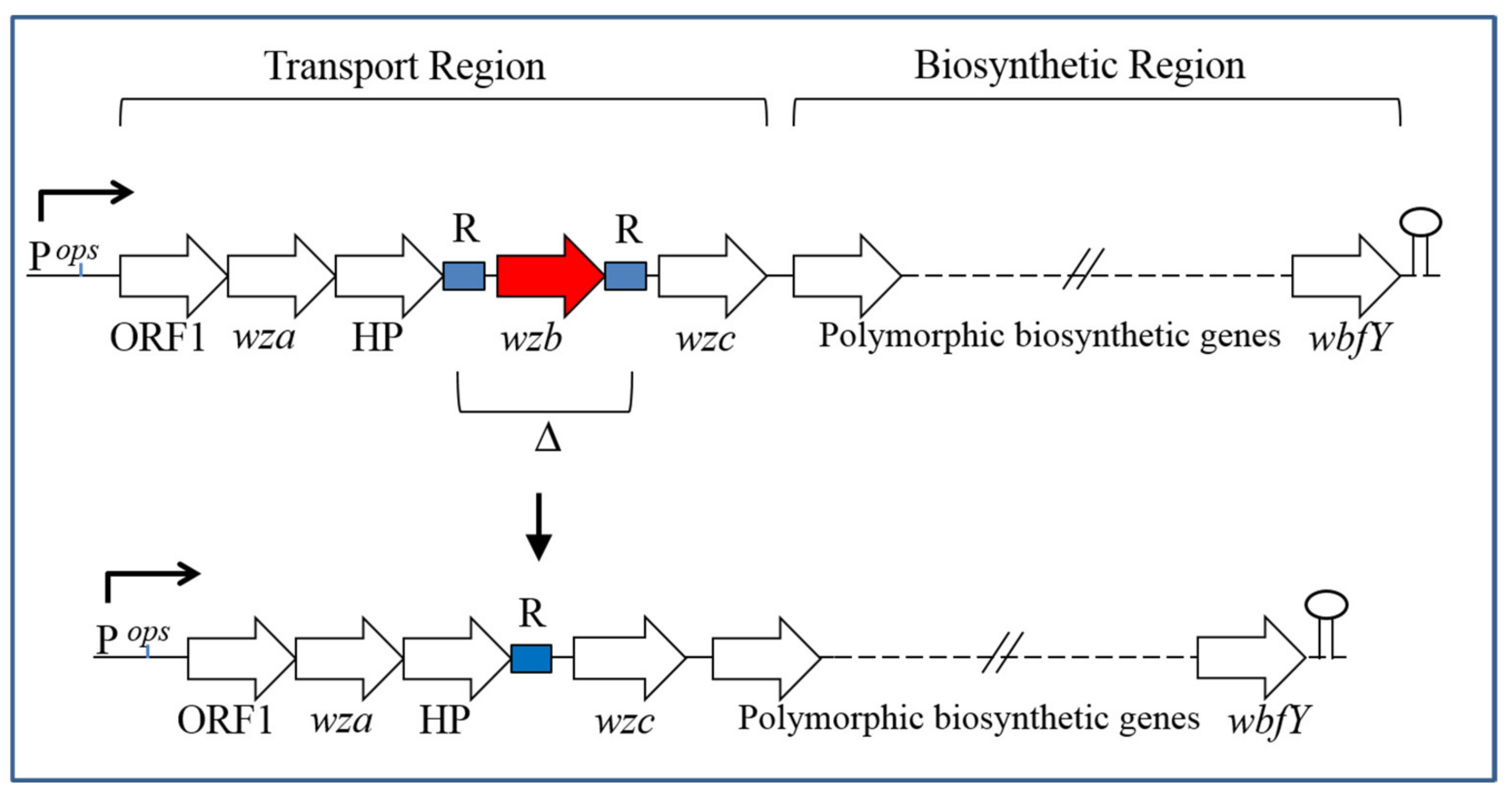
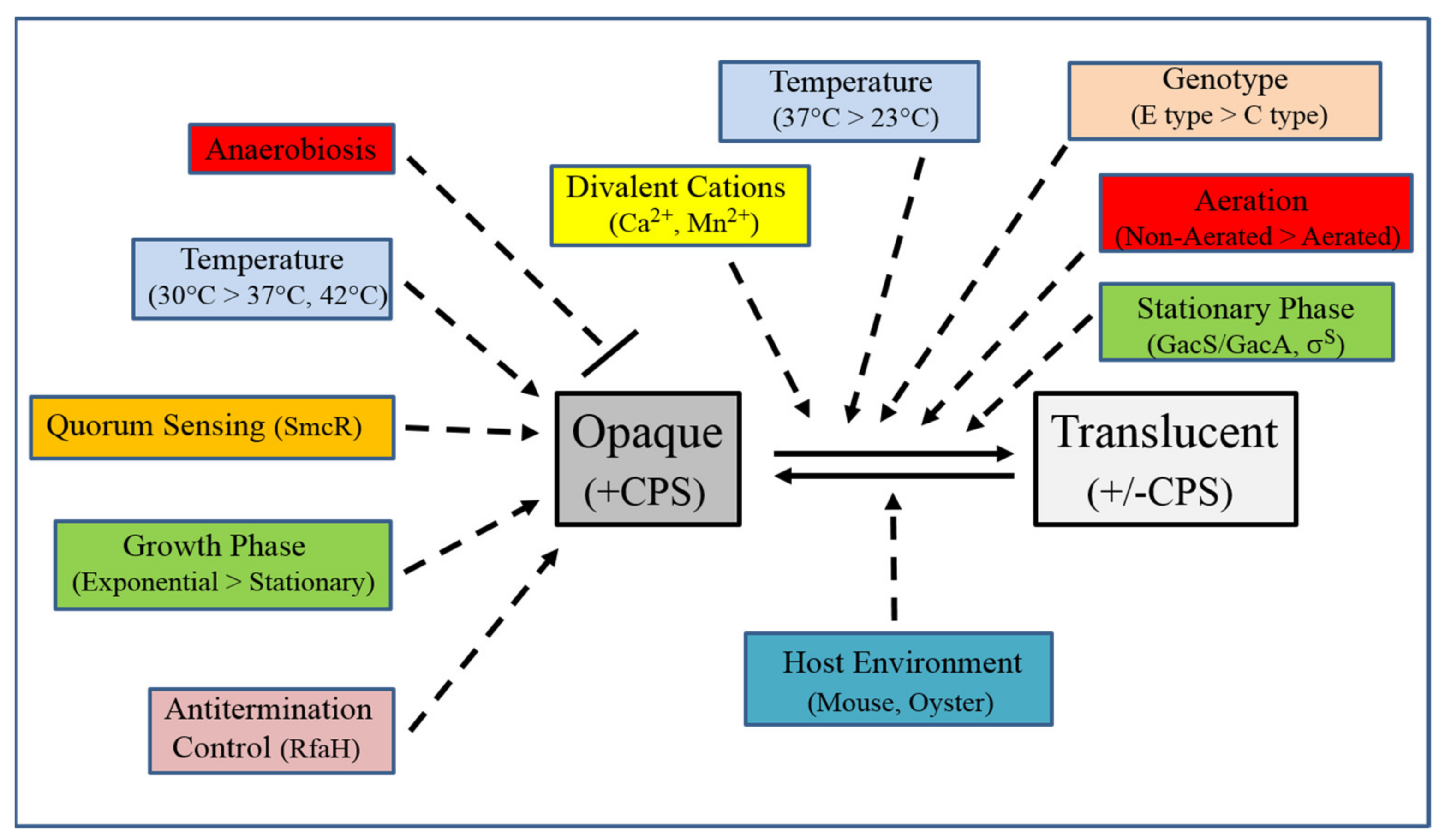
| Strain | Source | CPS Phenotype | CPS Group |
|---|---|---|---|
| ATCC275621 | Clinical | Opaque | 4 |
| FCC | Clinical | Opaque2 | N.D.3 |
| MO6-24/O | Clinical | Opaque | 1 |
| MO6-24/T | Phase variant of MO6-24/O | Translucent | 1 |
| BO62316 | Clinical | Opaque | N.D. |
| C7184 | Clinical | Opaque | N.D. |
| 1003(O) | Clinical | Opaque | N.D. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pettis, G.S.; Mukerji, A.S. Structure, Function, and Regulation of the Essential Virulence Factor Capsular Polysaccharide of Vibrio vulnificus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3259. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21093259
Pettis GS, Mukerji AS. Structure, Function, and Regulation of the Essential Virulence Factor Capsular Polysaccharide of Vibrio vulnificus. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(9):3259. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21093259
Chicago/Turabian StylePettis, Gregg S., and Aheli S. Mukerji. 2020. "Structure, Function, and Regulation of the Essential Virulence Factor Capsular Polysaccharide of Vibrio vulnificus" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 9: 3259. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21093259
APA StylePettis, G. S., & Mukerji, A. S. (2020). Structure, Function, and Regulation of the Essential Virulence Factor Capsular Polysaccharide of Vibrio vulnificus. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(9), 3259. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21093259





