Nano-Zn Increased Zn Accumulation and Triglyceride Content by Up-Regulating Lipogenesis in Freshwater Teleost, Yellow Catfish Pelteobagrus fulvidraco
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Growth Performance, Feed Utilization, and Morphological Parameters
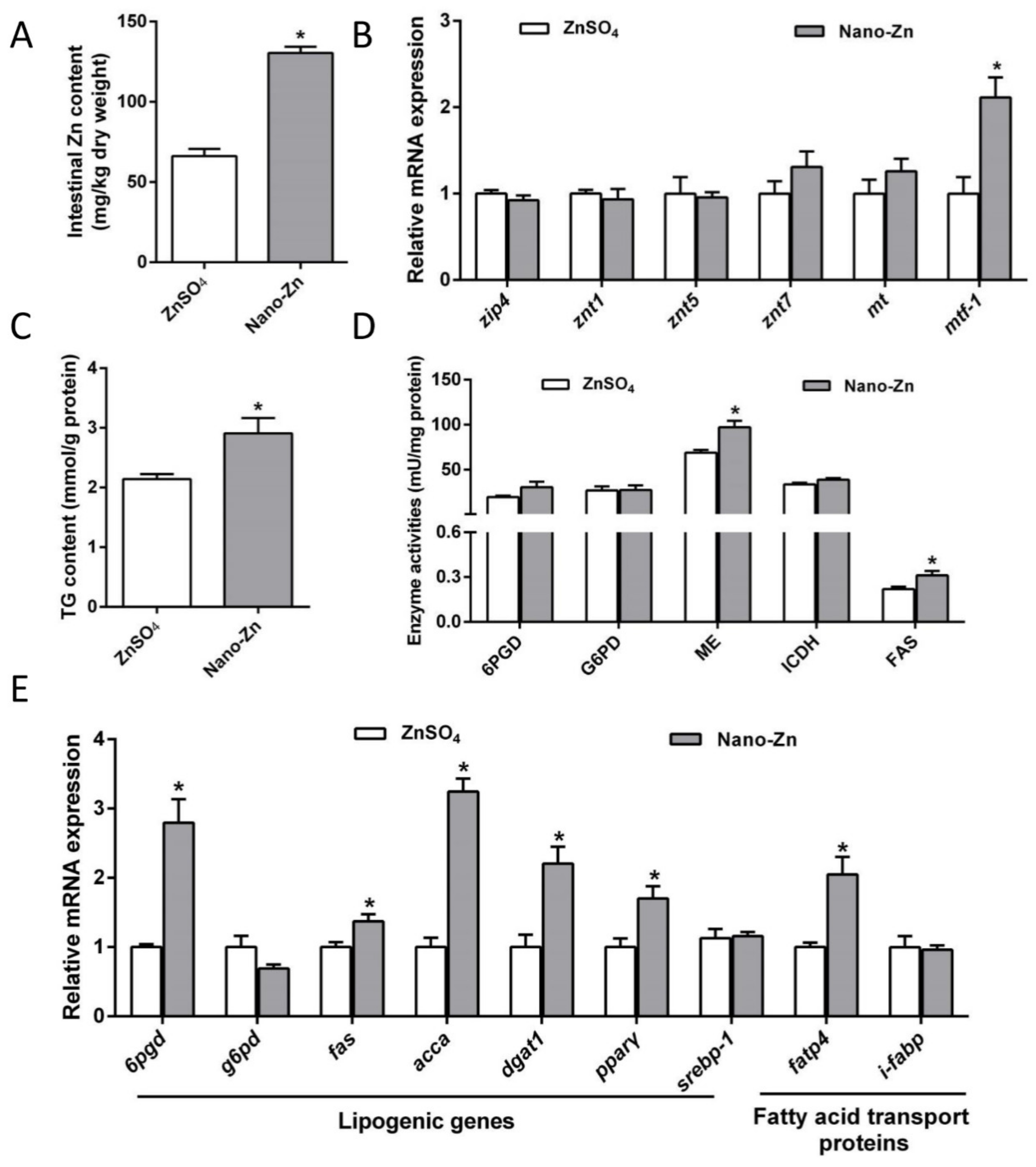
2.2. Zn Accumulation, Zn Absorption, and Lipid Metabolism in the Intestine
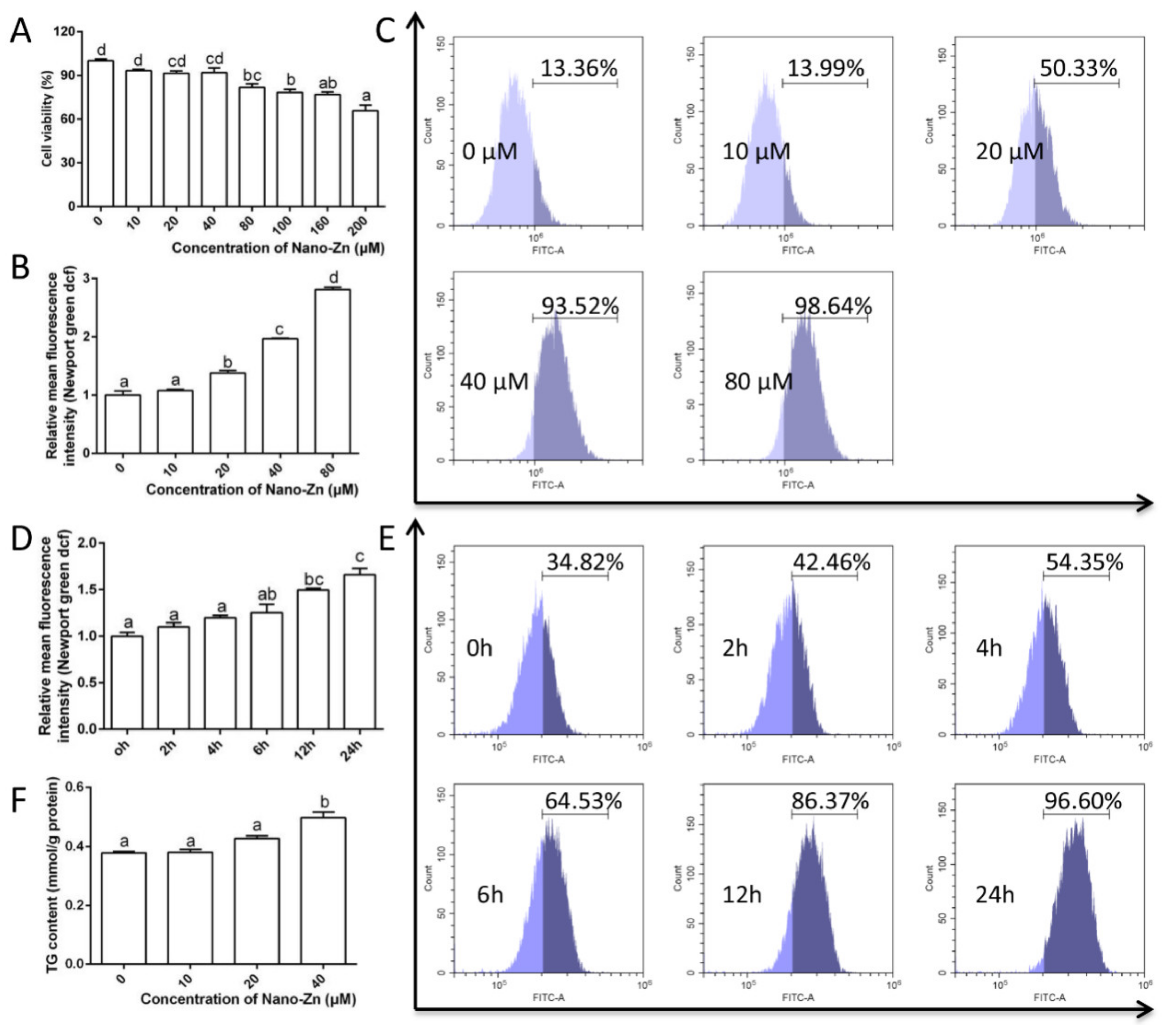
2.3. Intestinal Epithelial Cells Absorb Nano-Zn via Clathrin Pathway
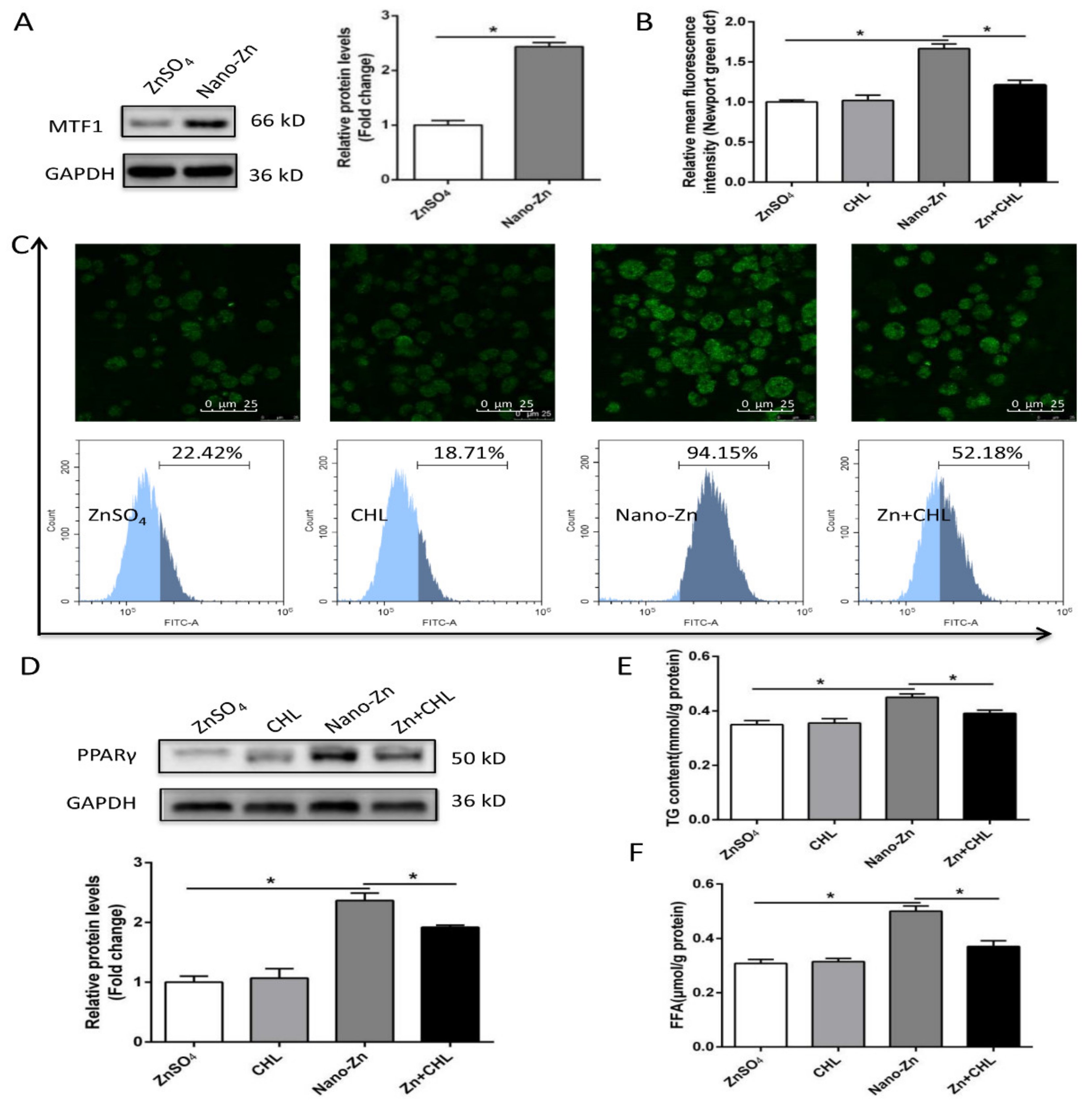
2.4. Higher TG Accumulation in Nano-Zn Group Than in Znso4 Group was Attributable to the Nano-Zn-Induced Activation of PPARγ
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Expt. 1: In Vivo Study
4.2. Expt. 2: In Vitro Study
4.3. Cell Viability, TG Content, and Enzymatic Activity Assays
4.4. Real-Time Quantitative PCR (qPCR)
4.5. Immunoblotting Analysis
4.6. Zn2+ Measurement
4.7. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 6PGD | 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase |
| ACC | acetyl-CoA carboxylase |
| ANOVA | one-way analysis of variance |
| CF | condition factor |
| DGAT | diacylglycerol acyltransferase |
| FAS | fatty acid synthase |
| FATP4 | fatty acid transport protein 4 |
| FCR | feed conversion rate |
| FFA | free fatty acid |
| FI | feed intake |
| G6PD | glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase |
| ICDH | isocitrate dehydrogenase |
| I-FABP | intestine fatty acid binding protein |
| ISI | intestinal somatic index |
| ME | malic enzyme |
| MS-222 | tricaine methanesulfonate |
| MT | metallothionein |
| MTF-1 | metal response element-binding transcription factor-1 |
| NaN3 | sodium azide |
| PPAR | peroxisome proliferator activated receptor |
| SEM | standard error of mean |
| SGR | specific growth rate |
| SREBP | sterol regulatory element-binding protein |
| TG | triglyceride |
| TPEN | N,N,N′,N′-tetrakis (2-pyridylmethyl) ethylenediamine |
| VSI | viscerosomatic index |
| WG | weight gain |
| ZIP | ZRT, IRT-like protein |
| ZnT | zinc transporter |
| Zn | zinc |
| ZnSO4 | zinc sulfate |
| Nano-Zn | zinc nanoparticles |
References
- Watanabe, T.; Kiron, V.; Satoh, S.; Wilson, R.P.; Wee, K.L. Trace minerals in fish nutrition. Aquaculture 1997, 151, 185–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bury, N.R.; Walker, P.A.; Glover, C.N. Nutritive metal uptake in teleost fish. J. Exp. Biol. 2003, 206, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kambe, T.; Tsuji, T.; Hashimoto, A.; Itsumura, N. The physiological, biochemical, and molecular roles of zinc transporters in zinc homeostasis and metabolism. Physiol. Rev. 2015, 95, 749–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.H.; Luo, Z.; Wei, C.C.; Li, D.D.; Pan, Y.X. Six indicator genes for zinc (Zn) homeostasis in freshwater teleost yellow catfish Pelteobagrus fulvidraco: molecular characterization, mRNA tissue expression and transcriptional changes to Zn exposure. Biometals 2018, 31, 527–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmiter, R.D.; Findley, S.D. Cloning and functional characterization of a mammalian zinc transporter that confers resistance to zinc. EMBO J. 1995, 14, 639–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishihara, K.; Yamazaki, T.; Ishida, Y.; Suzuki, T.; Oda, K.; Nagao, M.; Yamaguchi-Iwai, Y.; Kambe, T. Zinc transport complexes contribute to the homeostasis maintenance of secretory pathway function in vertebrate cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 17743–17750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Tan, X.Y.; Zheng, J.L.; Chen, Q.L.; Liu, C.X. Quantitative dietary zinc requirement of juvenile yellow catfish Pelteobagrus fulvidraco, and effects on hepatic intermediary metabolism and antioxidant responses. Aquac. 2011, 319, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olechnowicz, J.; Tinkov, A.; Skalny, A.; Suliburska, J. Zinc status is associated with inflammation, oxidative stress, lipid and glucose metabolism. J. Physiol. Sci. 2018, 68, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.L.; Luo, Z.; Hu, W.; Liu, C.X.; Chen, Q.L.; Zhu, Q.L.; Gong, Y. Different effects of dietary Zn deficiency and excess on lipid metabolism in yellow catfish Pelteobagrus fulvidraco. Aquaculture 2015, 435, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chithrani, B.D.; Chan, W.C.W. Elucidating the mechanism of cellular uptake and removal of protein-coated gold nanoparticles of different sizes and shapes. Nano Lett. 2007, 7, 1542–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.Y.; Tan, S.X.; Xiao, X.Y.; Qiu, X.S.; Pan, J.Q.; Tang, Z.X. Effects of dietary zinc oxide nanoparticles on growth performance and antioxidant status in broilers. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2014, 160, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faiz, H.; Zuberi, A.; Nazir, S.; Rauf, M.; Younus, N. Zinc oxide, zinc sulfate and zinc oxide nanoparticles as source of dietary zinc: comparative effects on growth and hematological indices of juvenile grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idela). Int. J. Agric. Biol. 2015, 17, 568–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Award, A.; Zaglool, A.W.; Ahmed, S.A.A.; Khalil, S.R. Transcriptomic profile change, immunological response and disease resistance of Oreochromis niloticus fed with conventional and Nano-Zinc oxide dietary supplements. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 93, 336–343. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, J.M.; Choi, S.J.; Kim, S.T.; Choy, J.H. Cellular uptake mechanism of an inorganic nanovehicle and its drug conjugates: enhanced efficacy due to clathrin-mediated endocytosis. Bioconjugate Chem. 2006, 17, 1411–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conner, S.D.; Schmid, S.L. Regulated portals of entry into the cell. Nature 2003, 422, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lina, T.; Jianyang, J.; Fenghua, Z.; Huiying, R.; Wenli, L. Effect of nano-zinc oxide on the production and dressing performance of broiler. Chin. Agricult. Sci. Bull. 2009, 25, 1–5, (in Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, A.; Swain, R.K.; Mishra, S.K.; Panda, N.; Sethy, K. Growth performance and serum biochemical parameters as affected by nano zinc supplementation in layer chicks. Ind J. Anim. Nutr. 2014, 31, 384–388. [Google Scholar]
- Horký, P.; Skalickova, S.; Urbankova, L.; Baholet, D.; Kociova, S.; Richtera, L.; Kabourkova, E.; Lacková, Z.; Cernei, N.; Gagic, M.; et al. Zinc phosphate-based nanoparticles as a novel antibacterial agent: in vivo study on rats after dietary exposure. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2019, 10, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.H.; Hogstrand, C.; Luo, Z.; Zhang, D.G.; Ling, S.C.; Wu, K. Dietary zinc addition influenced zinc and lipid deposition in the fore-and mid-intestine of juvenile yellow catfish Pelteobagrus fulvidraco. Br. J. Nutr. 2017, 118, 570–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, A.; Wang, W.X. Evaluation of nano-ZnOs as a novel Zn source for marine fish: importance of digestive physiology. Nanotoxicology 2017, 11, 1026–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matito, E.; Putz, M.V. New link between conceptual density functional theory and electron delocalization. J. Phys. Chem. A 2011, 115, 12459–12462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Putz, M.V.; Chattaraj, P.K. Electrophilicity kernel and its hierarchy through softness in concenptual density functional theory. Int. J. Quant. Chem. 2013, 113, 2163–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydemir, T.B.; Blanchard, R.K.; Cousins, R.J. Zinc supplementation of young men alters metallothionein, zinc transporter, and cytokine gene expression in leukocyte populations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 1699–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Qin, H.; Guo, J. Cooperation of metallothionein and zinc transporters for regulating zinc homeostasis in human intestinal Caco-2 cells. Nutr. Res. 2008, 28, 406–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirschke, C.P.; Huang, L. ZnT7, a novel mammalian zinc transporter, accumulates zinc in the Golgi apparatus. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 4096–4102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mann, S.K.; Czuba, E.; Selby, L.I.; Such, G.K.; Johnston, A.P.R. Quantifying nanoparticle internalization using a high throughput internalization assay. Pharm. Res. 2016, 33, 2421–2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yumoto, R.; Nishikawa, H.; Okamoto, M.; Katayama, H.; Nagai, J.; Takano, M. Clathrin-mediated endocytosis of FITC-albumin in alveolar type II epithelial cell line RLE-6TN. Am. J. Physiol. 2006, 290, 946–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranasinghe, P.; Wathurapatha, W.S.; Ishara, M.H.; Jayawardana, R.; Galappatthy, P.; Katulanda, P.; Constantine, G.R. Effects of zinc supplementation on serum lipids: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutr. Metab. (Lond.) 2015, 12, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.C.; Luo, Z.; Hogstrand, C.; Xu, Y.H.; Wu, L.X.; Chen, G.H.; Pan, Y.X.; Song, Y.F. Zinc reduces hepatic lipid deposition and activates lipophagy via Zn2+/MTF-1/PPARα and Ca2+/CaMKKβ/AMPK pathways. FASEB J. 2018, 32, 6666–6680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.F.; Hogstrand, C.; Wei, C.C.; Wu, K.; Pan, Y.X.; Luo, Z. Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress and cAMP/PKA pathway mediated Zn-induced hepatic lipolysis. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 228, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, E.D.; Sarraf, P.; Troy, A.E.; Bradwin, G.; Moore, K.; Milstone, D.S.; Spiegelman, B.M.; Mortensen, R.M. PPARγ is required for the differentiation of adipose tissue in vivo and in vitro. Mol. Cell. 1999, 4, 611–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, H.W.; You, H.M.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Y.L.; Meng, X.M.; Ma, T.T.; Huang, C.; Li, J. 4-methylcoumarin-[5,6-g]-hesperetin attenuates inflammatory responses in alcoholic hepatitis through PPAR-γ activation. Toxicol. 2019, 421, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Kim, D.S.; Kang, S. Vitamin D deficiency impairs glucose-stimulated insulin secretion and increases insulin resistance by reducing PPAR-γ expression in nonobese type 2 diabetic rats. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2016, 27, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, X.; Bian, F.; Wu, P.; Xing, S.; Xu, G.; Li, W.; Chi, J.; Ouyang, C.; Zheng, T.; et al. TNF-a promotes early atherosclerosis by increasing transcytosis of LDL across endothelial cells: crosstalk between NF-kB and PPAR-γ. J. Mol. Cell Cardiol. 2014, 72, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tontonoz, P.; Hu, E.; Spiegelman, B.M. Stimulation of adipogenesis in fibroblasts by PPAR[gamma] 2, a lipid-activated transcription factor. Cell 1994, 79, 1147–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.L.; Luo, Z.; Liu, C.X.; Chen, Q.L.; Zhu, Q.L.; Gong, Y. Differential effects of acute and chronic zinc (Zn) exposure on hepatic lipid deposition and metabolism in yellow catfish Pelteobagrus fulvidraco. Aquat. Toxicol. 2013, 132–133, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Luo, Z.; Hogstrand, C.; Chen, G.H.; Wei, C.C.; Li, D.D. Zn stimulates the phospholipids biosynthesis via the pathways of oxidative and endoplasmic reticulum stress in the intestine of freshwater teleost yellow catfish. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 9206–9214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khurana, R.K.; Kumar, R.; Gaspar, B.L.; Welsby, G.; Welsby, P.; Kesharwani, P.; Katare, O.P.; Singh, K.K.; Singh, B. Clathrin-mediated endocytic uptake of PUFA enriched self-nanoemulsifying lipidic systems (SNELS) of an anticancer drug against triple negative cancer and DMBA induced preclinical tumor model. Materials Sci. Engin. C 2018, 91, 645–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, D.; Donaldson, J.G. Search for inhibitors of endocytosis: Intended specificity and unintended consequences. Cell. Logist. 2012, 2, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandesompele, J.; De Preter, K.; Pattyn, F.; Poppe, B.; Van Roy, N.; De Paepe, A.; Speleman, F. Accurate normalization of real-time quantitative RT-PCR data by genometric averaging of multiple internal control genes. Genome Biol. 2002, 3, research0034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ling, S.-C.; Zhuo, M.-Q.; Zhang, D.-G.; Cui, H.-Y.; Luo, Z. Nano-Zn Increased Zn Accumulation and Triglyceride Content by Up-Regulating Lipogenesis in Freshwater Teleost, Yellow Catfish Pelteobagrus fulvidraco. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1615. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21051615
Ling S-C, Zhuo M-Q, Zhang D-G, Cui H-Y, Luo Z. Nano-Zn Increased Zn Accumulation and Triglyceride Content by Up-Regulating Lipogenesis in Freshwater Teleost, Yellow Catfish Pelteobagrus fulvidraco. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(5):1615. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21051615
Chicago/Turabian StyleLing, Shi-Cheng, Mei-Qin Zhuo, Dian-Guang Zhang, Heng-Yang Cui, and Zhi Luo. 2020. "Nano-Zn Increased Zn Accumulation and Triglyceride Content by Up-Regulating Lipogenesis in Freshwater Teleost, Yellow Catfish Pelteobagrus fulvidraco" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 5: 1615. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21051615
APA StyleLing, S.-C., Zhuo, M.-Q., Zhang, D.-G., Cui, H.-Y., & Luo, Z. (2020). Nano-Zn Increased Zn Accumulation and Triglyceride Content by Up-Regulating Lipogenesis in Freshwater Teleost, Yellow Catfish Pelteobagrus fulvidraco. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(5), 1615. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21051615





