High Diagnostic Accuracy of RT-QuIC Assay in a Prospective Study of Patients with Suspected sCJD
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. CSF Biomarkers Results and Diagnosis in RPD Patients
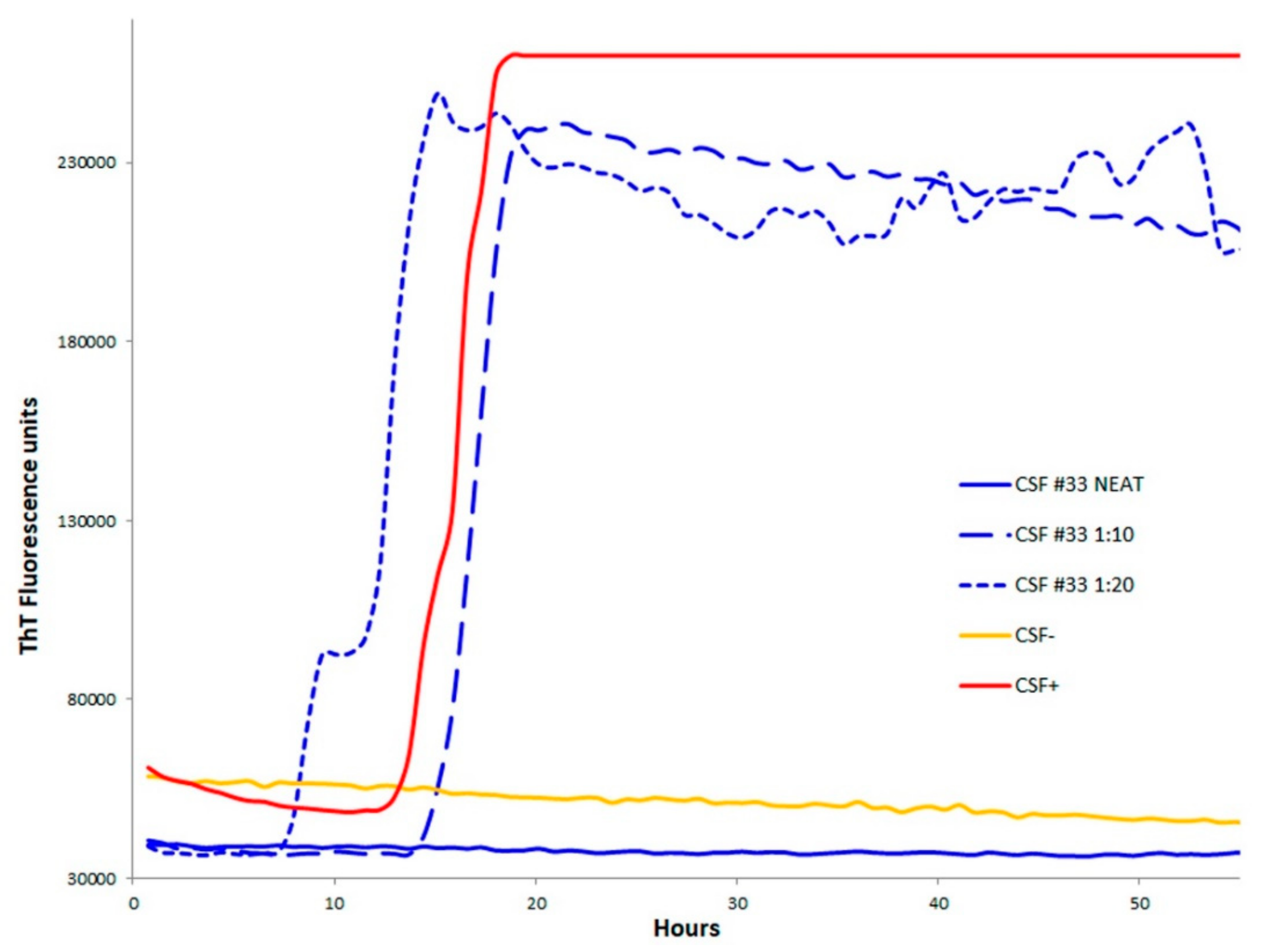
2.2. Diagnostic Accuracy of CSF-RT-QuIC, OM RT-QuIC, and Surrogate Markers in Patients with sCJD Diagnosis
2.3. Atypical CSF Biomarkers in RT-QuIC Positive Samples
2.4. Negative CSF RT-QuIC in Patient with Classical sCJD
2.5. Negative OM RT-QuIC in sCJD
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patients and Samples
4.2. Genetic PRNP Analysis and Codon 129 Determination
4.3. CSF Surrogate Biomarkers Analysis
4.4. RT-QuIC Analysis
4.5. Brain Samples and Proteinase K-Resistant Prion Immunoblot Analysis
4.6. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Geschwind, M.D.; Murray, K. Differential diagnosis with other rapid progressive dementias in human prion diseases. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2018, 153, 371–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Consensus on Criteria for Sporadic CJD; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Otto, M.; Wiltfang, J.; Cepek, L.; Neumann, M.; Mollenhauer, B.; Steinacker, P.; Ciesielczyk, B.; Schulz-Schaeffer, W.; Kretzschmar, H.A.; Poser, S. Tau protein and 14-3-3 protein in the differential diagnosis of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Neurology 2002, 58, 192–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novi, G.; Canosa, A.; Nobili, F.; Bongianni, M.; Zanusso, G.; Balestrino, M.; Roccatagliata, L. Longitudinal brain magnetic resonance imaging and real-time quaking induced conversion analysis in presymptomatic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Eur. J. Neurol. 2018, 25, e127–e128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, A.J.E.; Zanusso, G. Prion protein amplification techniques. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2018, 153, 357–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- THE NATIONAL CJD RESEARCH & SURVEILLANCE UNIT (NCJDRSU). Available online: www.cjd.ed.ac.uk (accessed on 27 January 2020).
- Orrú, C.D.; Bongianni, M.; Tonoli, G.; Ferrari, S.; Hughson, A.G.; Groveman, B.R.; Fiorini, M.; Pocchiari, M.; Monaco, S.; Caughey, B.; et al. A test for Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease using nasal brushings. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 519–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groveman, B.R.; Orrú, C.D.; Hughson, A.G.; Bongianni, M.; Fiorini, M.; Imperiale, D.; Ladogana, A.; Pocchiari, M.; Zanusso, G.; Caughey, B. Extended and direct evaluation of RT-QuIC assays for Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease diagnosis. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2016, 4, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bongianni, M.; Orrù, C.D.; Groveman, B.R.; Sacchetto, L.; Fiorini, M.; Tonoli, G.; Triva, G.; Capaldi, S.; Testi, S.; Ferrari, S.; et al. Diagnosis of Human Prion Disease Using Real-Time Quaking-Induced Conversion Testing of Olfactory Mucosa and Cerebrospinal Fluid Samples. JAMA Neurol. 2017, 74, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanusso, G.; Fiorini, M.; Ferrari, S.; Gajofatto, A.; Cagnin, A.; Galassi, A.; Richelli, S.; Monaco, S. Cerebrospinal fluid markers in sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011, 12, 6281–6292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franceschini, A.; Baiardi, S.; Hughson, A.G.; McKenzie, N.; Moda, F.; Rossi, M.; Capellari, S.; Green, A.; Giaccone, G.; Caughey, B.; et al. High diagnostic value of second generation CSF RT-QuIC across the wide spectrum of CJD prions. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foutz, A.; Appleby, B.S.; Hamlin, C.; Liu, X.; Yang, S.; Cohen, Y.; Chen, W.; Blevins, J.; Fausett, C.; Wang, H.; et al. Diagnostic and prognostic value of human prion detection in cerebrospinal fluid. Ann. Neurol. 2017, 81, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanusso, G.; Fiorini, M.; Farinazzo, A.; Gelati, M.; Benedetti, M.D.; Ferrari, S.; Dalla Libera, A.; Capaldi, S.; Monaco, H.L.; Rizzuto, N.; et al. Phosphorylated 14-3-3zeta protein in the CSF of neuroleptic-treated patients. Neurology. 2005, 64, 1618–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bersano, A.; Fiorini, M.; Allaria, S.; Zanusso, G.; Fasoli, E.; Gelati, M.; Monaco, H.; Squintani, G.; Monaco, S.; Nobile-Orazio, E. Detection of CSF 14-3-3 protein in Guillain-Barré syndrome. Neurology. 2006, 67, 2211–2216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiorini, M.; Zanusso, G.; Baj, A.; Bertolasi, L.; Toniolo, A.; Monaco, S. Post-polio syndrome: Clinical manifestations and cerebrospinal fluid markers. Future Neurol. 2007, 2, 451–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajofatto, A.; Monaco, S.; Fiorini, M.; Zanusso, G.; Vedovello, M.; Rossi, F.; Turatti, M.; Benedetti, M.D. Assessment of outcome predictors in first-episode acute myelitis: A retrospective study of 53 cases. Arch. Neurol. 2010, 67, 724–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorini, M.; Zanusso, G.; Benedetti, M.D.; Righetti, P.G.; Monaco, S. Cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers in clinically isolated syndromes and multiple sclerosis. Proteomics Clin. Appl. 2007, 1, 963–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Süssmuth, S.D.; Reiber, H.; Tumani, H. Tau protein in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF): A blood-CSF barrier related evaluation in patients with various neurological diseases. Neurosci. Lett. 2001, 300, 95–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesse, C.; Rosengren, L.; Vanmechelen, E.; Vanderstichele, H.; Jensen, C.; Davidsson, P.; Blennow, K. Cerebrospinal fluid markers for Alzheimer’s disease evaluated after acute ischemic stroke. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2000, 2, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, S.; Paquet, C.; Malaplate-Armand, C.; Magnin, E.; Schraen, S.; Quillard-Muraine, M.; Bousiges, O.; Delaby, C.; Dumurgier, J.; Hugon, J.; et al. Diagnosis associated with Tau higher than 1200 pg/mL: Insights from the clinical and laboratory practice. Clin. Chim. Acta. 2019, 495, 451–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanier, E.R.; Zoerle, T.; Fiorini, M.; Longhi, L.; Cracco, L.; Bersano, A.; Branca, V.; Benedetti, M.D.; De Simoni, M.G.; Monaco, S.; et al. Heart-fatty acid-binding and tau proteins relate to brain injury severity and long-term outcome in subarachnoid haemorrhage patients. Br. J. Anaesth. 2013, 111, 424–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Properzi, F.; Pocchiari, M. Identification of misfolded proteins in body fluids for the diagnosis of prion diseases. Int. J. Cell. Biol. 2013, 2013, 839329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, P.; Fatima, S.; Ahmad, B.; Khan, R.H. Interactions of thioflavin T with serum albumins: Spectroscopic analyses. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2009, 74, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Medical Association. World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki: Ethical principles for medical research involving human subjects. JAMA 2013, 310, 2191–2194. [Google Scholar]
- Council of Europe. Details of Treaty No. 195. Available online: https://www.coe.int/en/web/conventions/full-list/-/conventions/treaty/195 (accessed on 29 January 2020).
- Tagliapietra, M.; Zanusso, G.; Fiorini, M.; Bonetto, N.; Zarantonello, G.; Zambon, A.; Ermani, M.; Monaco, S.; Manara, R.; Cagnin, A. Accuracy of diagnostic criteria for sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease among rapidly progressive dementia. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2013, 34, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanusso, G.; Fiorini, M.; Ferrari, S.; Meade-White, K.; Barbieri, I.; Brocchi, E.; Ghetti, B.; Monaco, S. Gerstmann-Sträussler-Scheinker disease and “anchorless prion protein” mice share prion conformational properties diverging from sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 4870–4881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Definite sCJD (n = 61) | Probable sCJD (n = 41) | |
|---|---|---|
| Male/female | 31/30 | 23/18 |
| Age, in years (± SD) | 69 (9) * | 66 (8) * |
| Mean disease duration, in months (range) | 5.5 (1–21) * | 7 (2–35) * |
| Mean interval between onset and spinal tap, in months (range) | 3 (1–13) * | 5 (1–14) * |
| Type of PK resistant disase-associated PrP | T.1 n = 42; T.2 n = 16; T.1/2 n = 3 | - |
| Typical EEG | 22/56 | 10/29 |
| Typical MRI | 45/54 ** | 21/31 ** |
| Diagnosis before CSF analysis | Possible CJD n = 12 Probable CJD n = 49 | Possible CJD n = 14 Probable CJD n = 27 |
| Diagnosis after CSF analysis | Possible CJD n = 0 Probable CJD n = 61 | Possible CJD n = 0 Probable CJD n = 41 |
| Clinical Diagnosis | Number of Cases |
|---|---|
| Alzheimer’s disease | 34 |
| Frontotemporal dementia | 5 |
| Lewy body dementia | 3 |
| Other neurodegenerative diseases | 3 * |
| Encephalitis (infectious or autoimmune) | 5 |
| Psychiatric disease | 2 |
| Toxic/metabolic encephalopathies | 5 |
| Vascular dementia | 8 |
| Central Nervous System malignancy | 2 ** |
| Cause unknown (improvement at follow-up) | 4 |
| PrPSc negative (clinical diagnosis at death) | 9 *** |
| Biomarker Result | Definite sCJD (n = 61) | Probable sCJD (n = 41) | Non sCJD (n = 80) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 14-3-3 + | 54 (87%) | 33 (80%) | 43 (54%) |
| Tau >1300 pg/mL | 56 (92%) | 31 (76%) | 24 (30%) |
| CSF RT-QuIC + | 58 (95%) | 40 (98%) | 0 |
| OM RT-QuIC + | 16/17 (94%) | 16/18 (89%) | 0/7 |
| Overall RT-QuIC + | 61 (100%) | 41 (100%) | 0 |
| Patient Code # | 14-3-3 | Tau (pg/mL) | CSF RT-QuIC | OM RT-QuIC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 77 | - | 266 | + | + |
| 80 | - | 193 | + | + |
| 93 | - | 294 | + | + |
| 100 | - | 373 | + | nd |
| 83 | + | 188 | + | nd |
| 4 | - | 1074 | + | nd |
| 14 | - | 806 | + | nd |
| 49 | - | 1088 | + | nd |
| 52 | - | 628 | + | nd |
| 54 | - | 1904 | + | + |
| 57 | - | 699 | + | - |
| 60 | - | 2429 | + | nd |
| 64 | - | 870 | + | nd |
| 92 | - | 1142 | + | nd |
| 95 | - | 562 | + | nd |
| 97 | - | 749 | + | - |
| 62 | + | 1006 | + | nd |
| 74 | + | 1041 | + | nd |
| 96 | + | 1015 | + | - |
| Patient Code # | Duration Month | EEG | MRI | 14-3-3 | Tau (pg/mL) | CSF RT-QuIC | OM RT-QuIC | Final Clinical Diagnosis Codon 129 | Definite Diagnosis PrPSc |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 13 | 2 | + | + | + | >2400 | - | + | Probable sCJD MM | sCJD type1 |
| 33 | 2 | + | + | + | >2400 | - | + | Probable sCJD MM | sCJD type1 |
| 41 | 2.5 | + | + | + | >2400 | - | + | Probable sCJD MM | sCJD type1 |
| 81 | - | nd | + | + | 2101 | - | + | Probable sCJD MM |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fiorini, M.; Iselle, G.; Perra, D.; Bongianni, M.; Capaldi, S.; Sacchetto, L.; Ferrari, S.; Mombello, A.; Vascellari, S.; Testi, S.; et al. High Diagnostic Accuracy of RT-QuIC Assay in a Prospective Study of Patients with Suspected sCJD. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 880. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21030880
Fiorini M, Iselle G, Perra D, Bongianni M, Capaldi S, Sacchetto L, Ferrari S, Mombello A, Vascellari S, Testi S, et al. High Diagnostic Accuracy of RT-QuIC Assay in a Prospective Study of Patients with Suspected sCJD. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(3):880. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21030880
Chicago/Turabian StyleFiorini, Michele, Giorgia Iselle, Daniela Perra, Matilde Bongianni, Stefano Capaldi, Luca Sacchetto, Sergio Ferrari, Aldo Mombello, Sarah Vascellari, Silvia Testi, and et al. 2020. "High Diagnostic Accuracy of RT-QuIC Assay in a Prospective Study of Patients with Suspected sCJD" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 3: 880. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21030880
APA StyleFiorini, M., Iselle, G., Perra, D., Bongianni, M., Capaldi, S., Sacchetto, L., Ferrari, S., Mombello, A., Vascellari, S., Testi, S., Monaco, S., & Zanusso, G. (2020). High Diagnostic Accuracy of RT-QuIC Assay in a Prospective Study of Patients with Suspected sCJD. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(3), 880. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21030880





