The SWI/SNF ATP-Dependent Chromatin Remodeling Complex in Arabidopsis Responds to Environmental Changes in Temperature-Dependent Manner
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Lower Temperature Alleviates Phenotypic Defects Caused by Mutations of the SWI3C Core Subunit Gene of Arabidopsis SWI/SNF CRC
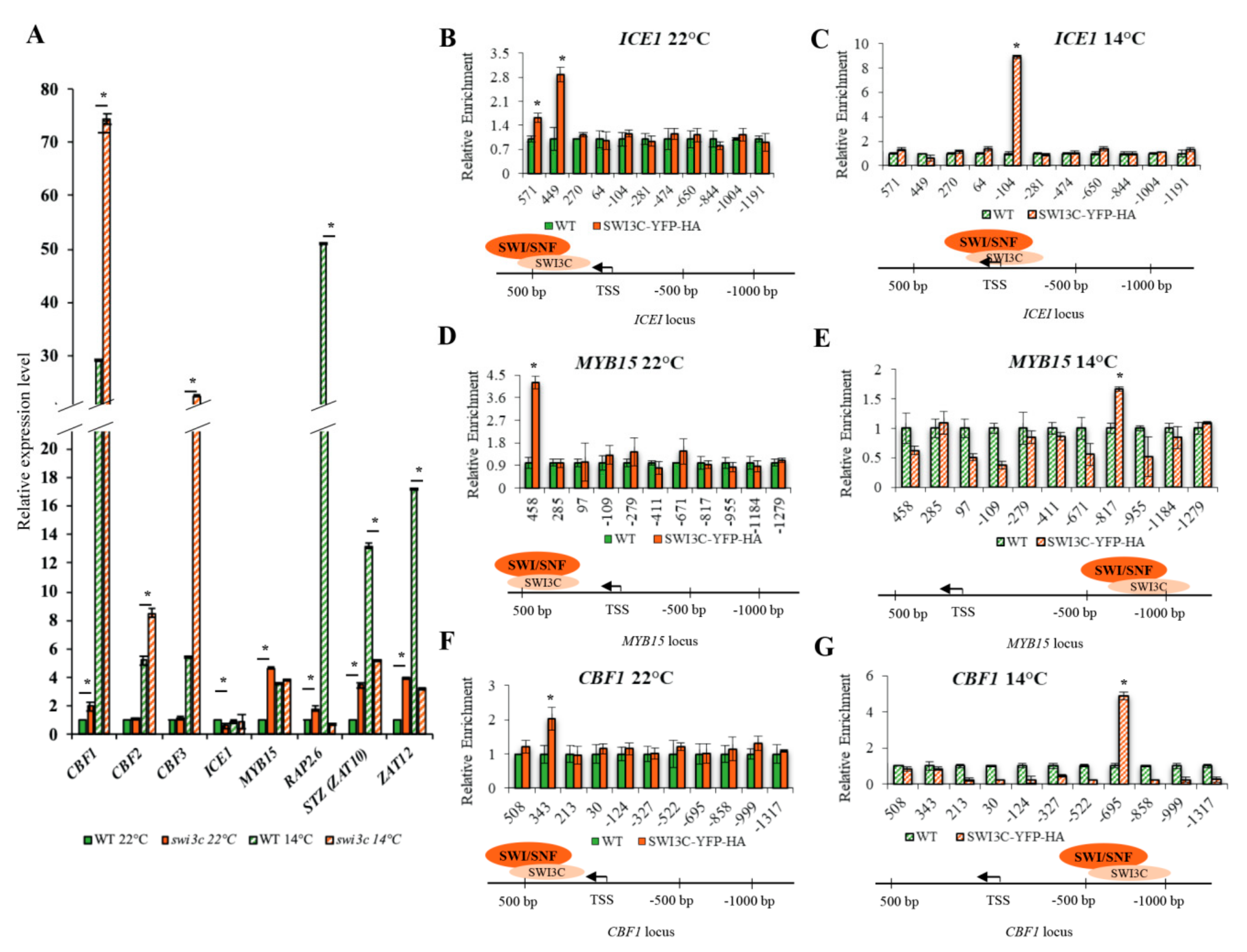
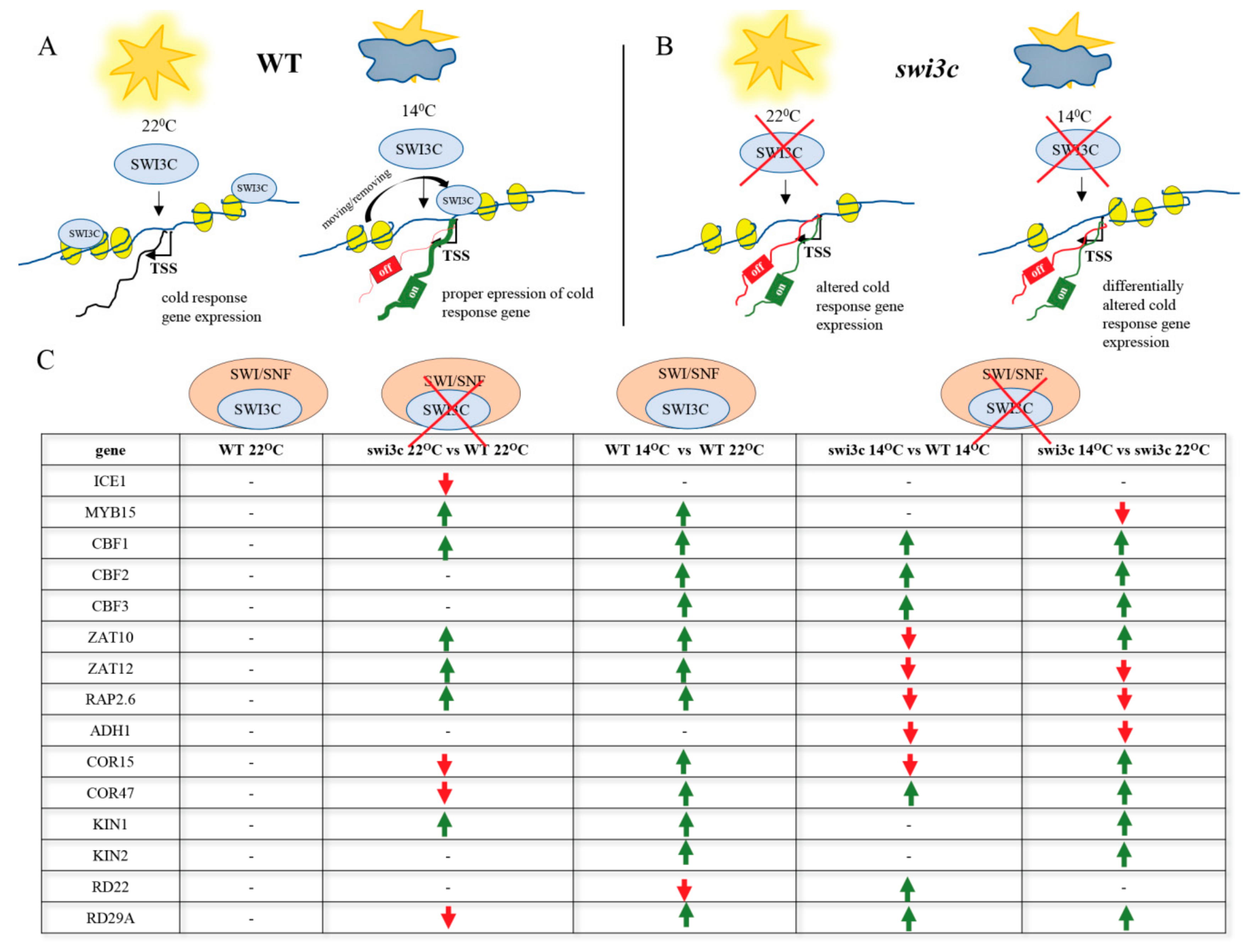
2.2. Genes Involved in Low Temperature Responses Show Altered Expression in the Swi3c Mutant
2.3. Temperature-Dependent Shift of Localization of SWI3C-Containing SWI/SNF CRCs in the 5′-UTR Regions of ICE1, MYB15 and CBF1 Genes
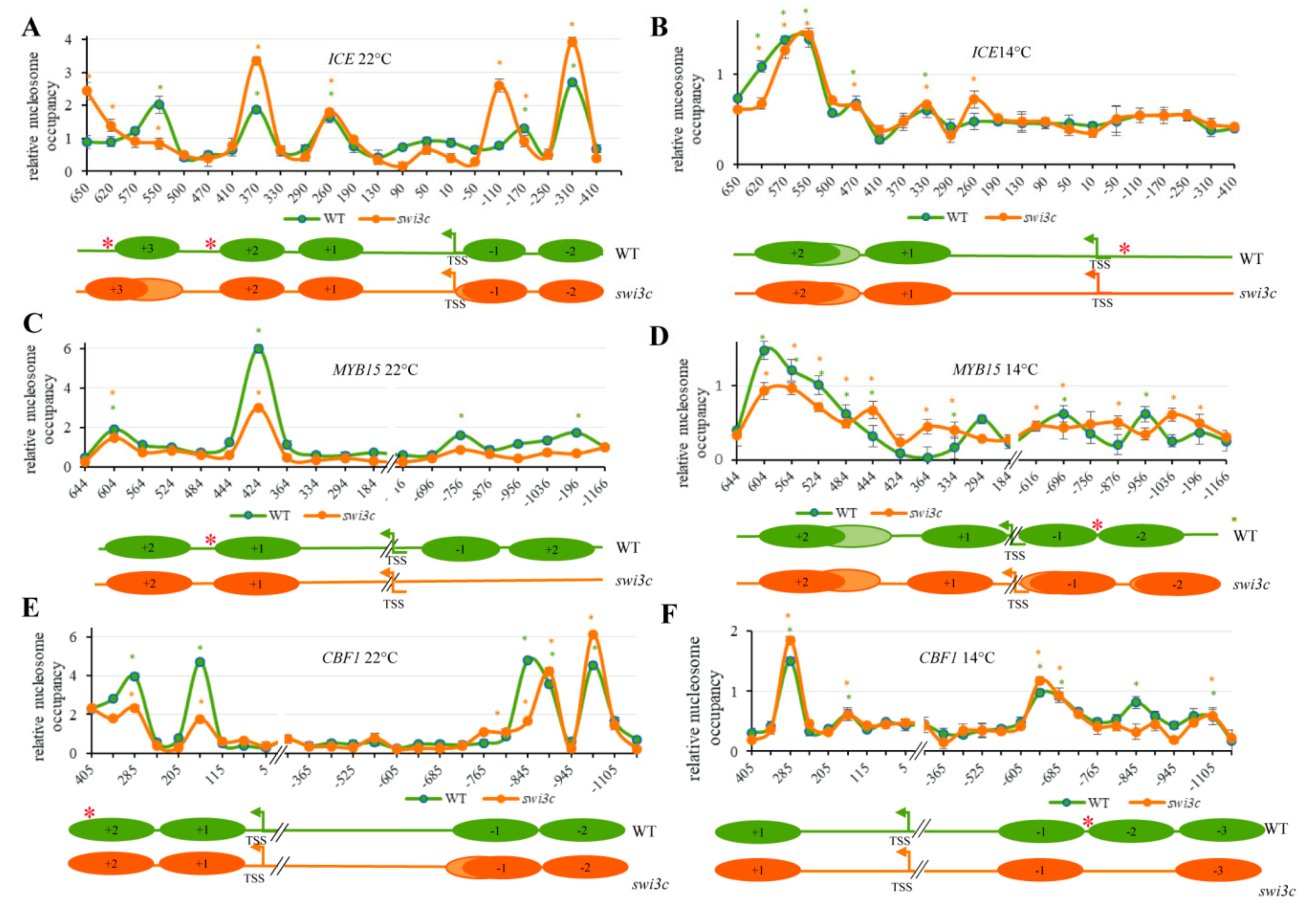
2.4. The Swi3c Mutation Changes Nucleosome Positioning on the ICE1, MYB15 and CBF1 Loci
2.5. Genetic Interactions Between SWI3C and ICE1
2.6. Inactivation of SWI3C Alters the Expression of Cold-Responsive (COR) Genes
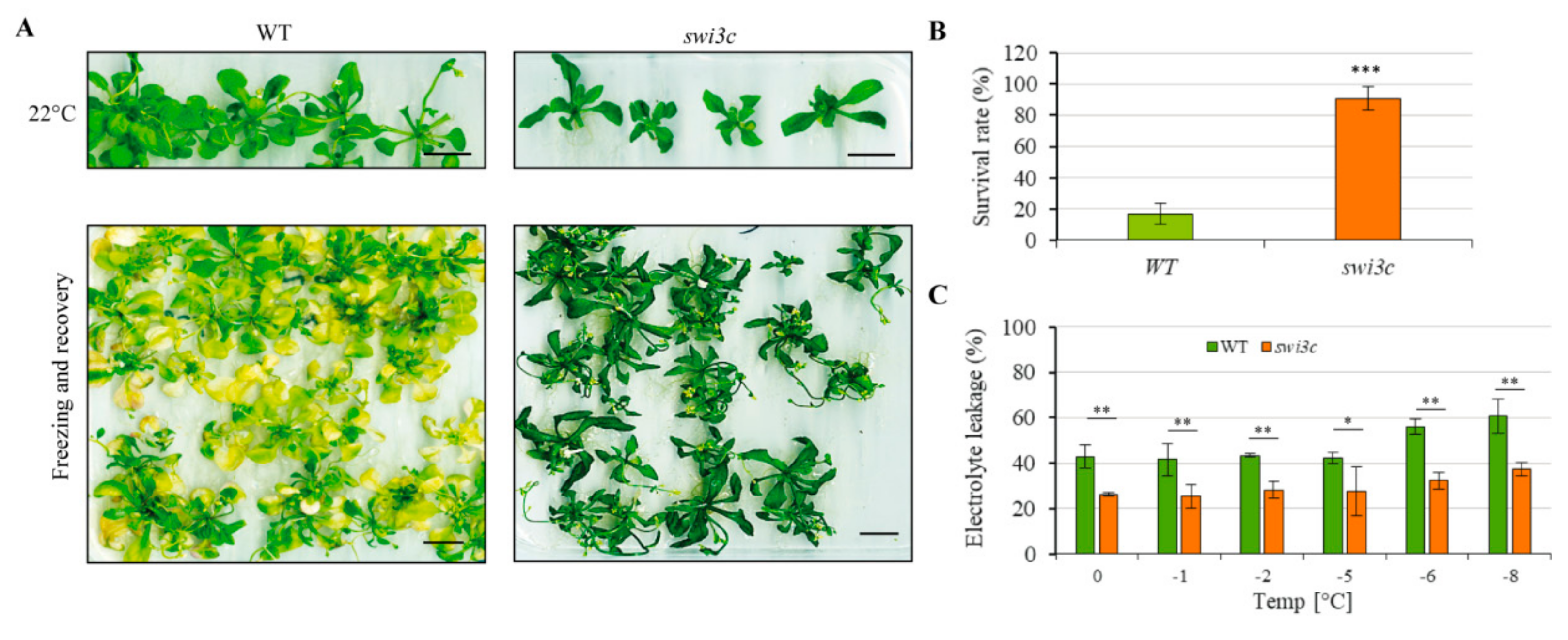
2.7. Swi3c Mutant Exhibits Enhanced Freezing Tolerance
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Lines and Growth Conditions
4.2. Construction of Genetically Complemented Plants by Expression of YFP-HA Tagged SWI3C Protein
4.3. RNA Extraction and qRT-PCR Analysis
4.4. Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIP)
4.5. Mapping of Nucleosome Locations Using MNase Protection Assay
4.6. Microscopic Analyses
4.7. Freezing Tolerance Assay
4.8. Bioinformatic Analysis of Cis-Regulatory Elements
4.9. Statistical Analyses
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sarnowska, E.; Gratkowska, D.M.; Sacharowski, S.P.; Cwiek, P.; Tohge, T.; Fernie, A.R.; Siedlecki, J.A.; Koncz, C.; Sarnowski, T.J. The Role of SWI/SNF Chromatin Remodeling Complexes in Hormone Crosstalk. Trends Plant. Sci. 2016, 21, 594–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phelan, M.L.; Sif, S.; Narlikar, G.J.; Kingston, R.E. Reconstitution of a core chromatin remodeling complex from SWI/SNF subunits. Mol. Cell 1999, 3, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrona, S. The Arabidopsis thaliana SNF2 homolog AtBRM controls shoot development and flowering. Development 2004, 131, 4965–4975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mlynárová, L.; Nap, J.P.; Bisseling, T. The SWI/SNF chromatin-remodeling gene AtCHR12 mediates temporary growth arrest in Arabidopsis thaliana upon perceiving environmental stress. Plant. J. 2007, 51, 874–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sang, Y.; Silva-Ortega, C.O.; Wu, S.; Yamaguchi, N.; Wu, M.F.; Pfluger, J.; Gillmor, C.S.; Gallagher, K.L.; Wagner, D. Mutations in two non-canonical Arabidopsis SWI2/SNF2 chromatin remodeling ATPases cause embryogenesis and stem cell maintenance defects. Plant. J. 2012, 72, 1000–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, D.; Meyerowitz, E.M. SPLAYED, a novel SWI/SNF ATPase homolog, controls reproductive development in Arabidopsis. Curr. Biol. 2002, 12, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brzeski, J.; Podstolski, W.; Olczak, K.; Jerzmanowski, A. Identification and analysis of the Arabidopsis thaliana BSH gene, a member of the SNF5 gene family. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999, 27, 2393–2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarnowski, T.J.; Ríos, G.; Jásik, J.; Swiezewski, S.; Kaczanowski, S.; Li, Y.; Kwiatkowska, A.; Pawlikowska, K.; Koźbiał, M.; Koźbiał, P.; et al. SWI3 subunits of putative SWI/SNF chromatin-remodeling complexes play distinct roles during Arabidopsis development. Plant. Cell 2005, 17, 2454–2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezhani, S.; Winter, C.; Hershman, S.; Wagner, J.D.; Kennedy, J.F.; Kwon, C.S.; Pfluger, J.; Su, Y.; Wagner, D. Unique, Shared, and Redundant Roles for the Arabidopsis SWI/SNF Chromatin Remodeling ATPases BRAHMA and SPLAYED. Plant. Cell 2007, 19, 403–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vercruyssen, L.; Verkest, A.; Gonzalez, N.; Heyndrickx, K.S.; Eeckhout, D.; Han, S.-K.; Jegu, T.; Archacki, R.; Van Leene, J.; Andriankaja, M.; et al. ANGUSTIFOLIA3 Binds to SWI/SNF Chromatin Remodeling Complexes to Regulate Transcription during Arabidopsis Leaf Development. Plant. Cell 2014, 26, 210–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacharowski, S.P.; Gratkowska, D.M.; Sarnowska, E.A.; Kondrak, P.; Jancewicz, I.; Porri, A.; Bucior, E.; Rolicka, A.T.; Franzen, R.; Kowalczyk, J.; et al. SWP73 subunits of arabidopsis SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling complexes play distinct roles in leaf and flower development. Plant. Cell 2015, 27, 1889–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarnowska, E.A.; Rolicka, A.T.; Bucior, E.; Cwiek, P.; Tohge, T.; Fernie, A.R.; Jikumaru, Y.; Kamiya, Y.; Franzen, R.; Schmelzer, E.; et al. DELLA-Interacting SWI3C Core Subunit of Switch/Sucrose Nonfermenting Chromatin Remodeling Complex Modulates Gibberellin Responses and Hormonal Cross Talk in Arabidopsis. Plant. Physiol. 2013, 163, 305–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cairns, B.R.; Levinson, R.S.; Yamamoto, K.R.; Kornberg, R.D. Essential role of Swp73p in the function of yeast SWI/SNF complex. Genes Dev. 1996, 10, 2131–2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buszewicz, D.; Archacki, R.; Palusiński, A.; Kotliński, M.; Fogtman, A.; Iwanicka-Nowicka, R.; Sosnowska, K.; Kuciński, J.; Pupel, P.; Olędzki, J.; et al. HD2C histone deacetylase and a SWI/SNF chromatin remodelling complex interact and both are involved in mediating the heat stress response in Arabidopsis. Plant. Cell Environ. 2016, 39, 2108–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinnusamy, V.; Ohta, M.; Kanrar, S.; Lee, B.H.; Hong, X.; Agarwal, M.; Zhu, J.K. ICE1: A regulator of cold-induced transcriptome and freezing tolerance in arabidopsis. Genes Dev. 2003, 17, 1043–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockinger, E.J.; Gilmour, S.J.; Thomashow, M.F. Arabidopsis thaliana CBF1 encodes an AP2 domain-containing transcriptional activator that binds to the C-repeat/DRE, a cis-acting DNA regulatory element that stimulates transcription in response to low temperature and water deficit. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 1035–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Kasuga, M.; Sakuma, Y.; Abe, H.; Miura, S.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K.; Shinozaki, K. Two transcription factors, DREB1 and DREB2, with an EREBP/AP2 DNA binding domain separate two cellular signal transduction pathways in drought- and low-temperature-responsive gene expression, respectively, in Arabidopsis. Plant. Cell 1998, 10, 1391–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.-H.; Agarwal, M.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, Q.; Zhu, J.-K. The negative regulator of plant cold responses, HOS1, is a RING E3 ligase that mediates the ubiquitination and degradation of ICE1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 8281–8286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, S.; Thomashow, M.F. Arabidopsis Transcriptome Profiling Indicates That Multiple Regulatory Pathways Are Activated during Cold Acclimation in Addition to the CBF Cold Response Pathway. Plant. Cell 2002, 14, 1675–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, M.; Hao, Y.; Kapoor, A.; Dong, C.H.; Fujii, H.; Zheng, X.; Zhu, J.K. A R2R3 type MYB transcription factor is involved in the cold regulation of CBF genes and in acquired freezing tolerance. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 37636–37645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, S.G.; Cook, D.; Thomashow, M.F. Low temperature induction of Arabidopsis CBF1, 2, and 3 is gated by the circadian clock. Plant. Physiol. 2005, 137, 961–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinnusamy, V.; Zhu, J.; Zhu, J.K. Cold stress regulation of gene expression in plants. Trends Plant. Sci. 2007, 12, 444–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Earley, K.W.; Haag, J.R.; Pontes, O.; Opper, K.; Juehne, T.; Song, K.; Pikaard, C.S. Gateway-compatible vectors for plant functional genomics and proteomics. Plant. J. 2006, 45, 616–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyes, D.C.; Zayed, A.M.; Ascenzi, R.; McCaskill, A.J.; Hoffman, N.E.; Davis, K.R.; Görlach, J. Growth Stage–Based Phenotypic Analysis of Arabidopsis. Plant. Cell 2001, 13, 1499–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, T.L.; Elkan, C. Fitting a mixture model by expectation maximization to discover motifs in biopolymers. Proc. Int. Conf. Intell. Syst. Mol. Biol. 1994, 2, 28–36. [Google Scholar]
- Stracke, R.; Werber, M.; Weisshaar, B. The R2R3-MYB gene family in Arabidopsis thaliana. Curr. Opin. Plant. Biol. 2001, 4, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riechmann, J.L.; Heard, J.; Martin, G.; Reuber, L.; Jiang, C.Z.; Keddie, J.; Adam, L.; Pineda, O.; Ratcliffe, O.J.; Samaha, R.R.; et al. Arabidopsis transcription factors: Genome-wide comparative analysis among eukaryotes. Science 2000, 290, 2105–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson, M.E. Identification of Promoter Motifs Involved in the Network of Phytochrome A-Regulated Gene Expression by Combined Analysis of Genomic Sequence and Microarray Data. Plant. Physiol. 2003, 133, 1605–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.-F.; Sang, Y.; Bezhani, S.; Yamaguchi, N.; Han, S.-K.; Li, Z.; Su, Y.; Slewinski, T.L.; Wagner, D. SWI2/SNF2 chromatin remodeling ATPases overcome polycomb repression and control floral organ identity with the LEAFY and SEPALLATA3 transcription factors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 3576–3581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubos, C.; Stracke, R.; Grotewold, E.; Weisshaar, B.; Martin, C.; Lepiniec, L. MYB transcription factors in Arabidopsis. Trends Plant. Sci. 2010, 15, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomashow, M.F. PLANT COLD ACCLIMATION: Freezing Tolerance Genes and Regulatory Mechanisms. Annu. Rev. Plant. Physiol. Plant. Mol. Biol. 1999, 50, 571–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Y.; Ding, Y.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, X.; Gong, Z.; Yang, S. The cbfs triple mutants reveal the essential functions of CBFs in cold acclimation and allow the definition of CBF regulons in Arabidopsis. New Phytol. 2016, 212, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Lee, C.M.; Doherty, C.J.; Gilmour, S.J.; Kim, Y.; Thomashow, M.F. Regulation of the Arabidopsis CBF regulon by a complex low-temperature regulatory network. Plant. J. 2015, 82, 193–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.; Zhang, Z.; Xie, S.; Si, T.; Li, Y.; Zhu, J.-K. Mutational Evidence for the Critical Role of CBF Genes in Cold Acclimation in Arabidopsis. Plant. Physiol. 2016, 171, 2744–2759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlichting, C.D.; Wund, M.A. Phenotypic plasticity and epigenetic marking: An assessment of evidence for genetic accommodation. Evolution (N. Y). 2014, 68, 656–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinnusamy, V.; Zhu, J.K.; Sunkar, R. Gene regulation during cold stress acclimation in plants. Methods Mol. Biol. 2010, 639, 39–55. [Google Scholar]
- Siddiqua, M.; Nassuth, A. Vitis CBF1 and Vitis CBF4 differ in their effect on Arabidopsis abiotic stress tolerance, development and gene expression. Plant. Cell Environ. 2011, 34, 1345–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Fowler, S.G.; Cheng, H.; Lou, Y.; Rhee, S.Y.; Stockinger, E.J.; Thomashow, M.F. Freezing-sensitive tomato has a functional CBF cold response pathway, but a CBF regulon that differs from that of freezing-tolerant Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2004, 39, 905–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannah, M.A. Natural Genetic Variation of Freezing Tolerance in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2006, 142, 98–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaskiewicz, M.; Conrath, U.; Peterhälnsel, C. Chromatin modification acts as a memory for systemic acquired resistance in the plant stress response. EMBO Rep. 2011, 12, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.V.; Wigge, P.A. H2A.Z-Containing Nucleosomes Mediate the Thermosensory Response in Arabidopsis. Cell 2010, 140, 136–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Lim, C.J.; Shen, M.; Park, H.J.; Cha, J.-Y.; Iniesto, E.; Rubio, V.; Mengiste, T.; Zhu, J.-K.; Bressan, R.A.; et al. Epigenetic switch from repressive to permissive chromatin in response to cold stress. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E5400–E5409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilmour, S.J.; Zarka, D.G.; Stockinger, E.J.; Salazar, M.P.; Houghton, J.M.; Thomashow, M.F. Low temperature regulation of the Arabidopsis CBF family of AP2 transcriptional activators as an early step in cold-induced COR gene expression. Plant J. 1998, 16, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Euskirchen, G.M.; Auerbach, R.K.; Davidov, E.; Gianoulis, T.A.; Zhong, G.; Rozowsky, J.; Bhardwaj, N.; Gerstein, M.B.; Snyder, M. Diverse roles and interactions of the SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling complex revealed using global approaches. PLoS Genet. 2011, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archacki, R.; Yatusevich, R.; Buszewicz, D.; Krzyczmonik, K.; Patryn, J.; Iwanicka-Nowicka, R.; Biecek, P.; Wilczynski, B.; Koblowska, M.; Jerzmanowski, A.; et al. Arabidopsis SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling complex binds both promoters and terminators to regulate gene expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 45, 3116–3129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jordán-Pla, A.; Yu, S.; Waldholm, J.; Källman, T.; Östlund Farrants, A.K.; Visa, N. SWI/SNF regulates half of its targets without the need for ATP-driven nucleosome remodeling by Brahma. BMC Genomics 2018, 19, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lake, R.J.; Boetefuer, E.L.; Tsai, P.F.; Jeong, J.; Choi, I.; Won, K.J.; Fan, H.Y. The Sequence-Specific Transcription Factor c-Jun Targets Cockayne Syndrome Protein B to Regulate Transcription and Chromatin Structure. PLoS Genet. 2014, 10, e1004284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zha, P.; Lin, R. The SWI2/SNF2 Chromatin-Remodeling ATPase BRAHMA Regulates Chlorophyll Biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. Mol. Plant. 2017, 10, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, D.; Liu, M.; Chen, H.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Yang, S.; Zhou, M.; Lin, J. INDUCER OF CBF EXPRESSION 1 is a male fertility regulator impacting anther dehydration in Arabidopsis. PLOS Genet. 2018, 14, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, J.M.; Stepanova, A.N.; Leisse, T.J.; Kim, C.J.; Chen, H.; Shinn, P.; Stevenson, D.K.; Zimmerman, J.; Barajas, P.; Cheuk, R.; et al. Genome-wide insertional mutagenesis of Arabidopsis thaliana. Science (80-. ) 2003, 301, 653–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koncz, C.; Schell, J. The promoter of TL-DNA gene 5 controls the tissue-specific expression of chimaeric genes carried by a novel type of Agrobacterium binary vector. Mol. Gen. Genet. MGG 1986, 204, 383–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, A.M.; Hall, A.; Millar, A.J.; Darrah, C.; Davis, S.J. Protocol: Streamlined sub-protocols for floral-dip transformation and selection of transformants in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant. Methods 2009, 5, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmittgen, T.D.; Livak, K.J. Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative CT method. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 1101–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saleh, A.; Alvarez-Venegas, R.; Avramova, Z. An efficient chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) protocol for studying histone modifications in Arabidopsis plants. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 1018–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pastore, J.J.; Limpuangthip, A.; Yamaguchi, N.; Wu, M.F.; Sang, Y.; Han, S.K.; Malaspina, L.; Chavdaroff, N.; Yamaguchi, A.; Wagner, D. LATE MERISTEM IDENTITY2 acts together with LEAFY to activate APETALA1. Development 2011, 138, 3189–3198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyes, D.C. Growth Stage-Based Phenotypic Analysis of Arabidopsis: A Model for High Throughput Functional Genomics in Plants. Plant. Cell 2001, 13, 1499–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Rowley, M.J.; Böhmdorfer, G.; Wierzbicki, A.T. A SWI/SNF Chromatin-Remodeling Complex Acts in Noncoding RNA-Mediated Transcriptional Silencing. Mol. Cell 2013, 49, 298–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Xiong, L.; Ishitani, M.; Zhu, J.-K. An Arabidopsis mutation in translation elongation factor 2 causes superinduction of CBF/DREB1 transcription factor genes but blocks the induction of their downstream targets under low temperatures. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 7786–7791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buske, F.A.; Bodén, M.; Bauer, D.C.; Bailey, T.L. Assigning roles to DNA regulatory motifs using comparative genomics. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 860–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palaniswamy, S.K.; James, S.; Sun, H.; Lamb, R.S.; Davuluri, R.V.; Grotewold, E. AGRIS and AtRegNet. A Platform to Link cis-Regulatory Elements and Transcription Factors into Regulatory Networks. PLANT Physiol. 2006, 140, 818–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davuluri, R.V.; Sun, H.; Palaniswamy, S.K.; Matthews, N.; Molina, C.; Kurtz, M.; Grotewold, E. AGRIS: Arabidopsis Gene Regulatory Information Server, an information resource of Arabidopsis cis-regulatory elements and transcription factors. BMC Bioinformatics 2003, 4, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yilmaz, A.; Mejia-Guerra, M.K.; Kurz, K.; Liang, X.; Welch, L.; Grotewold, E. AGRIS: The arabidopsis gene regulatory information server, an update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, 1118–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
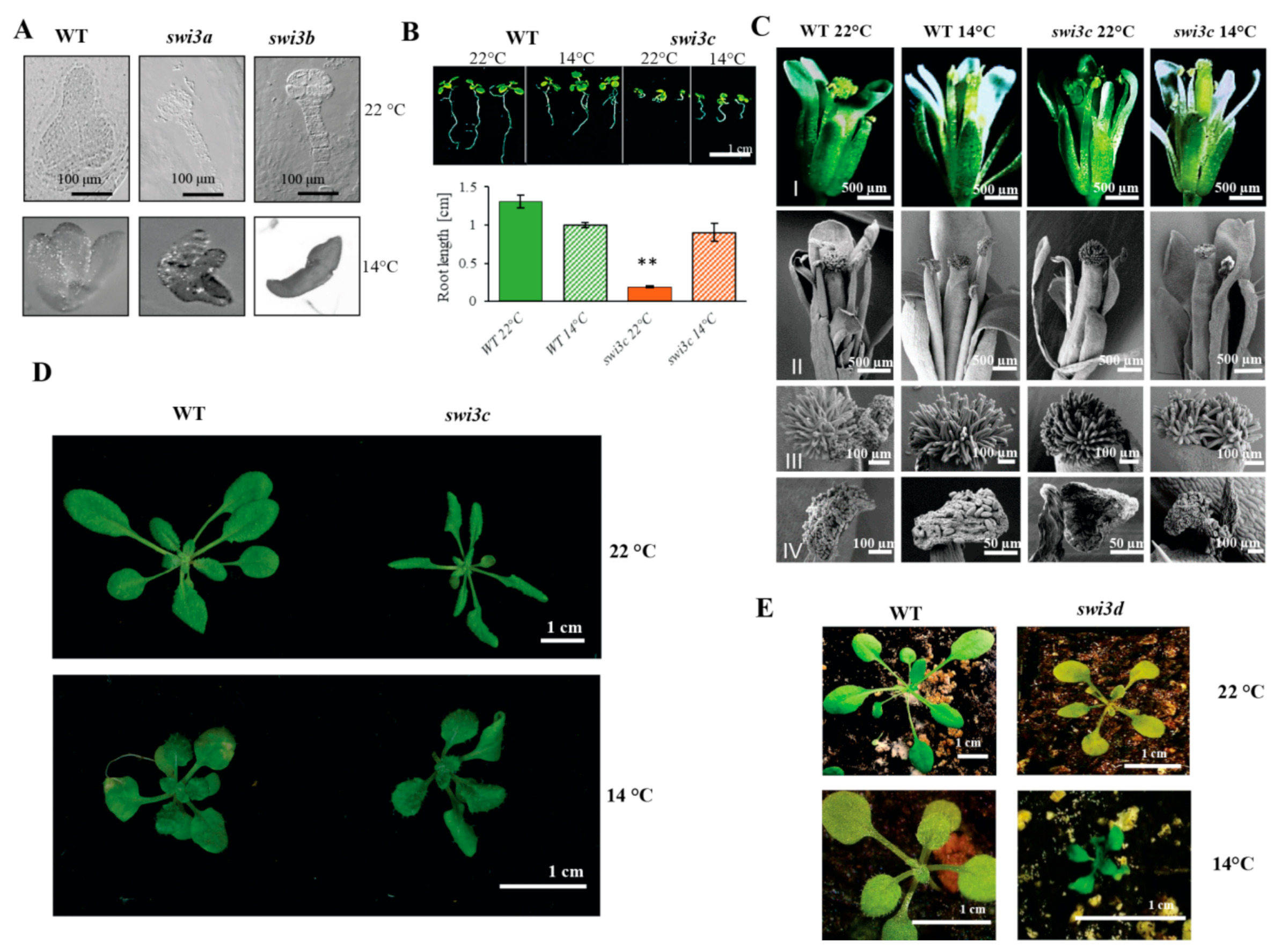
| Number of Analyzed Seeds | Embryo Lethality [%] | Gametophyte Lethality [%] | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 14 °C | WT | 265 | 0 | 0 |
| swi3a/+ | 350 | 6.29 | 0 | |
| swi3b/+ | 502 | 0.80 | 11.95 | |
| 22 °C | WT | 263 | 0 | 0 |
| swi3a/+ | 310 | 24.84 | 0 | |
| swi3b/+ | 244 | 14.75 | 34.43 | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gratkowska-Zmuda, D.M.; Kubala, S.; Sarnowska, E.; Cwiek, P.; Oksinska, P.; Steciuk, J.; Rolicka, A.T.; Zaborowska, M.; Bucior, E.; Maassen, A.; et al. The SWI/SNF ATP-Dependent Chromatin Remodeling Complex in Arabidopsis Responds to Environmental Changes in Temperature-Dependent Manner. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 762. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21030762
Gratkowska-Zmuda DM, Kubala S, Sarnowska E, Cwiek P, Oksinska P, Steciuk J, Rolicka AT, Zaborowska M, Bucior E, Maassen A, et al. The SWI/SNF ATP-Dependent Chromatin Remodeling Complex in Arabidopsis Responds to Environmental Changes in Temperature-Dependent Manner. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(3):762. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21030762
Chicago/Turabian StyleGratkowska-Zmuda, Dominika M., Szymon Kubala, Elzbieta Sarnowska, Pawel Cwiek, Paulina Oksinska, Jaroslaw Steciuk, Anna T. Rolicka, Magdalena Zaborowska, Ernest Bucior, Anna Maassen, and et al. 2020. "The SWI/SNF ATP-Dependent Chromatin Remodeling Complex in Arabidopsis Responds to Environmental Changes in Temperature-Dependent Manner" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 3: 762. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21030762
APA StyleGratkowska-Zmuda, D. M., Kubala, S., Sarnowska, E., Cwiek, P., Oksinska, P., Steciuk, J., Rolicka, A. T., Zaborowska, M., Bucior, E., Maassen, A., Franzen, R., Koncz, C., & Sarnowski, T. J. (2020). The SWI/SNF ATP-Dependent Chromatin Remodeling Complex in Arabidopsis Responds to Environmental Changes in Temperature-Dependent Manner. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(3), 762. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21030762






