Mutational Analysis of the Nsa2 N-Terminus Reveals Its Essential Role in Ribosomal 60S Subunit Assembly
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
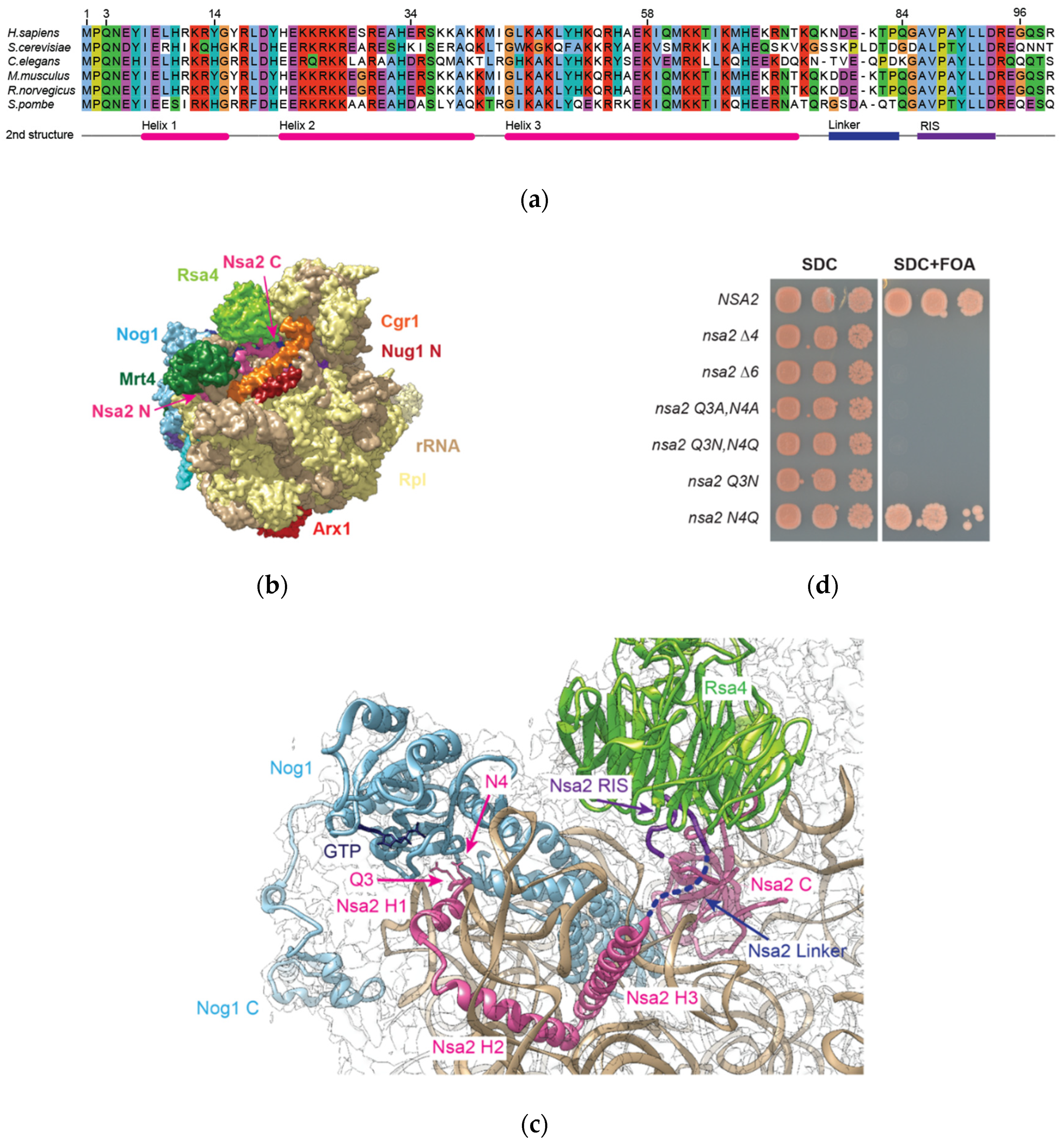
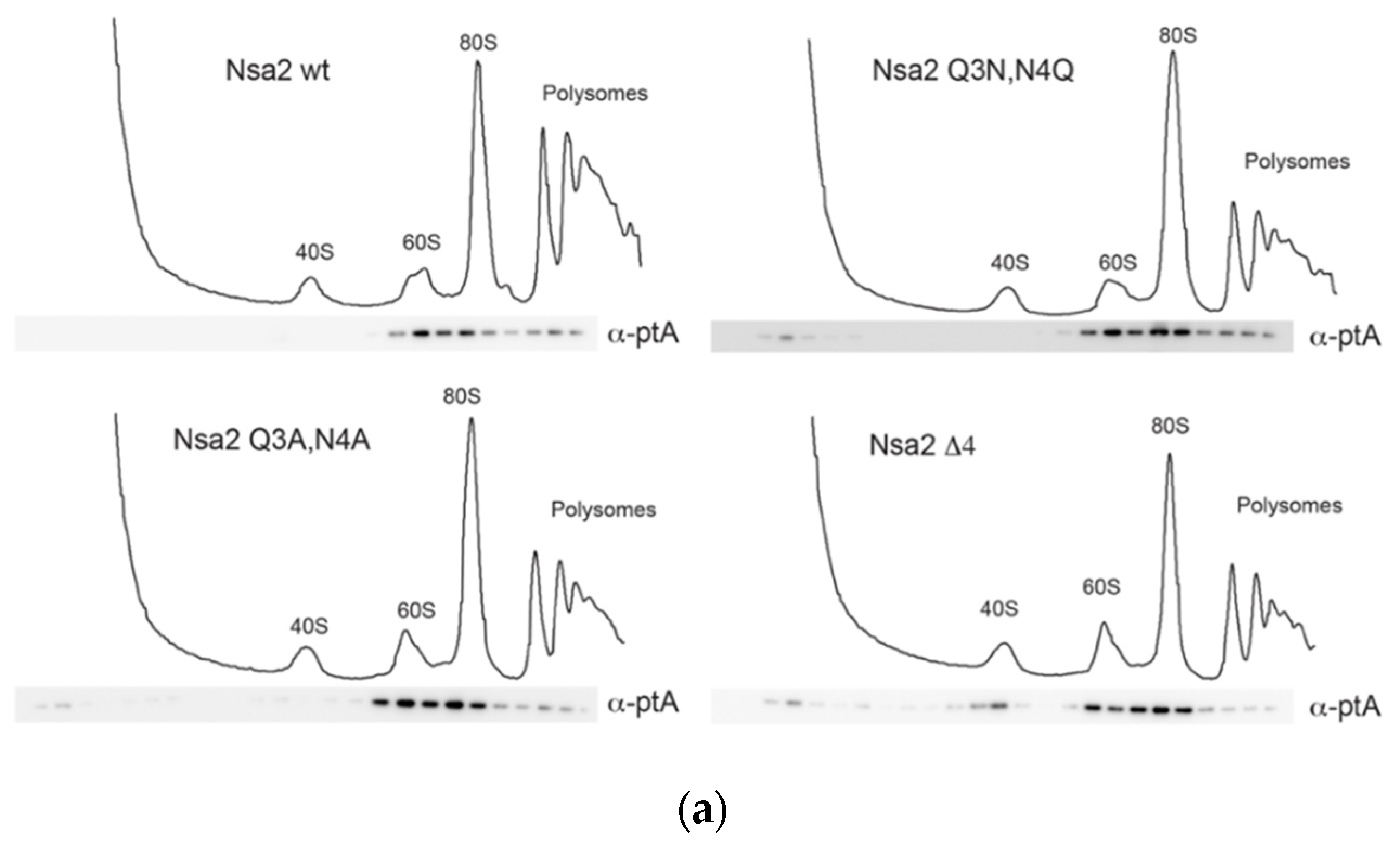
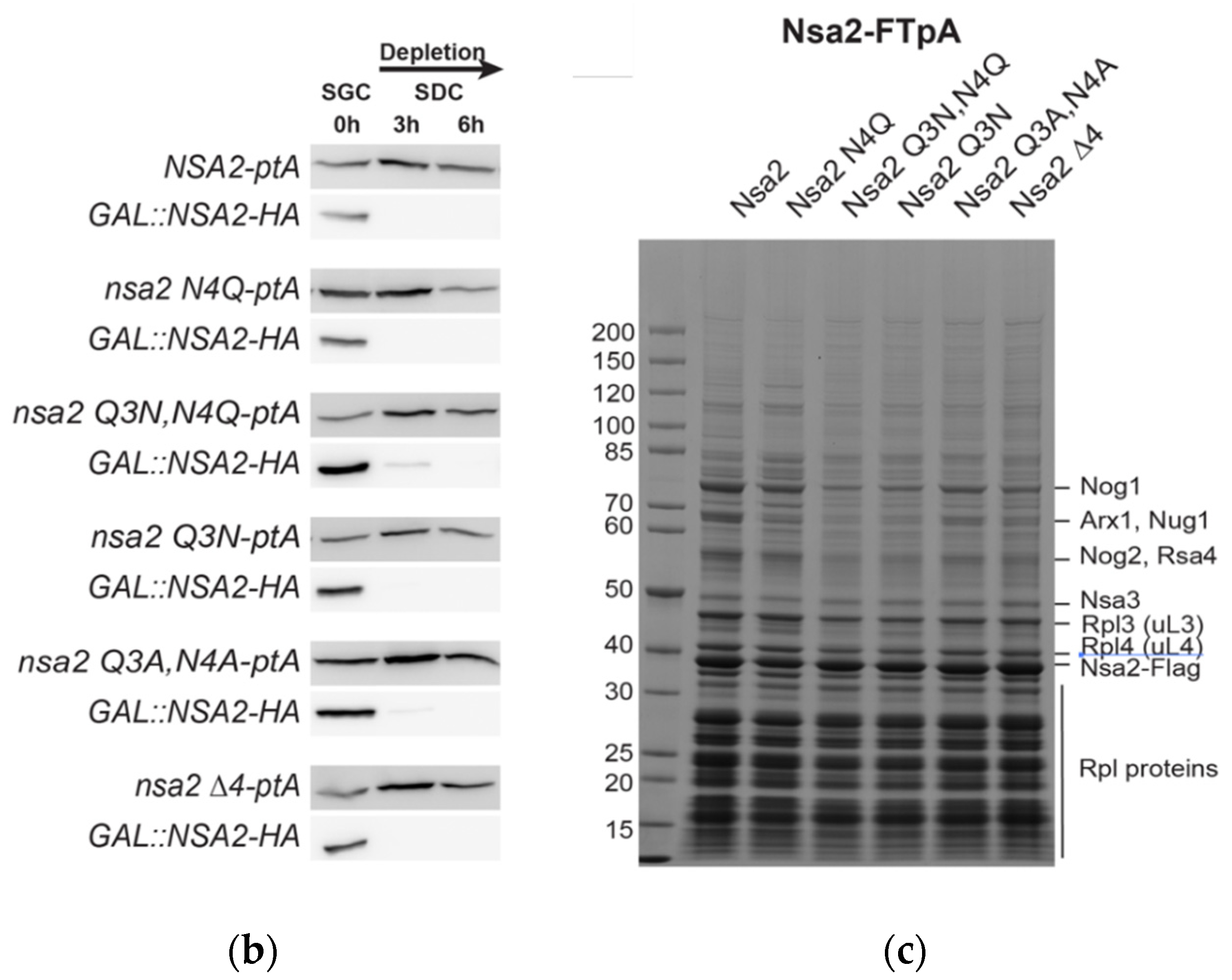
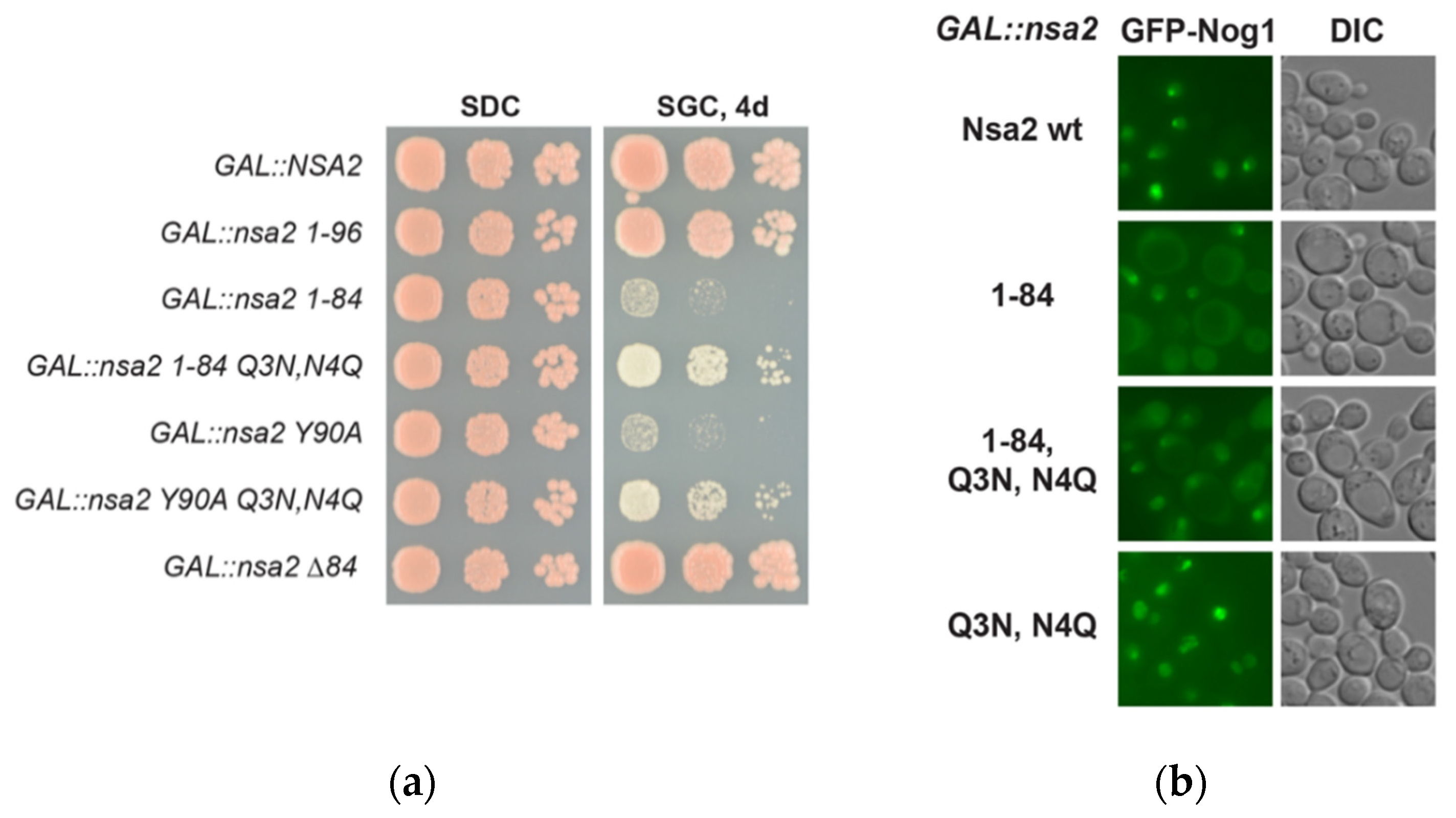
2.1. Nsa2 Q3 Residue Contacting the Catalytic Center of the Nog1 GTPase is Crucial for 60S Biogenesis
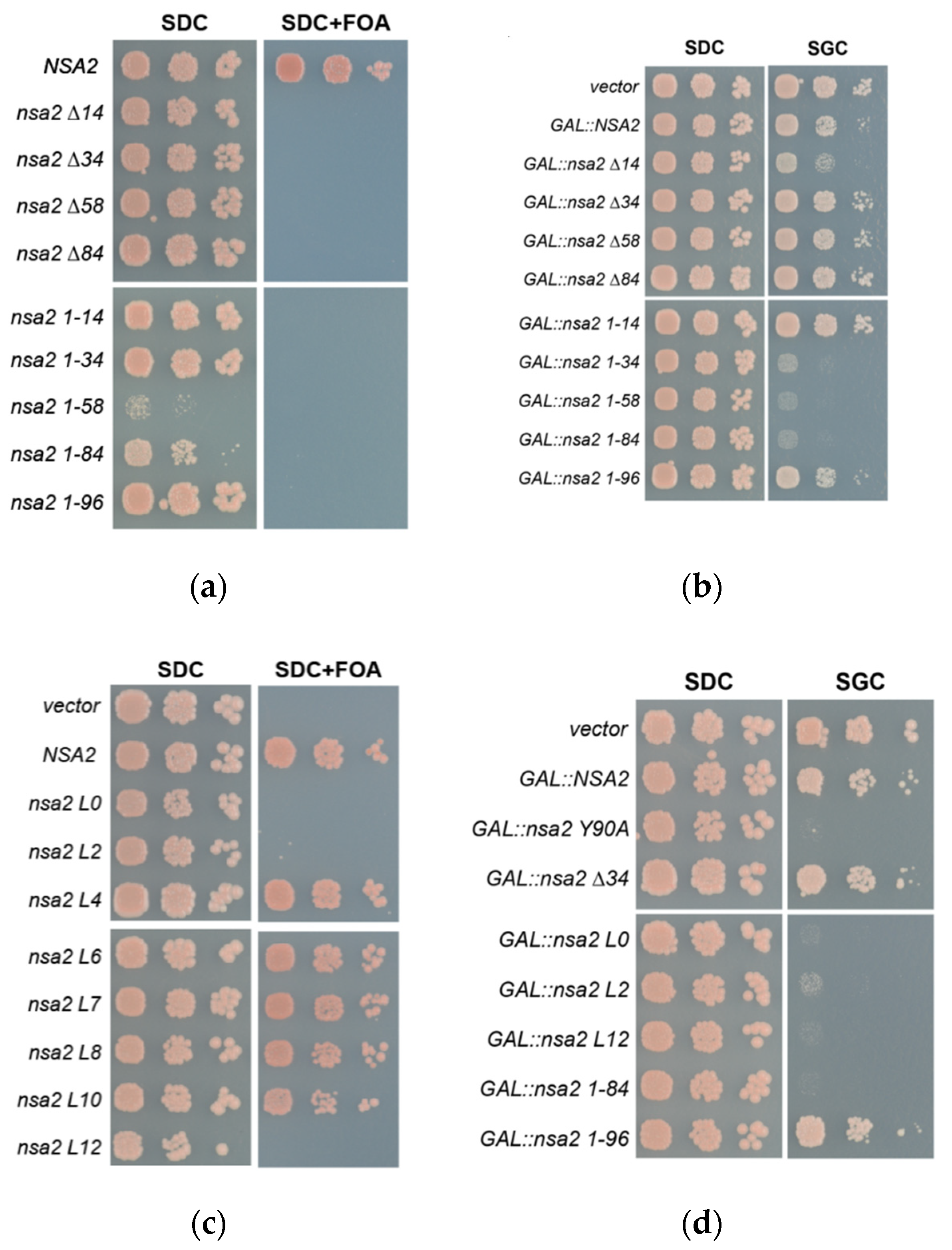
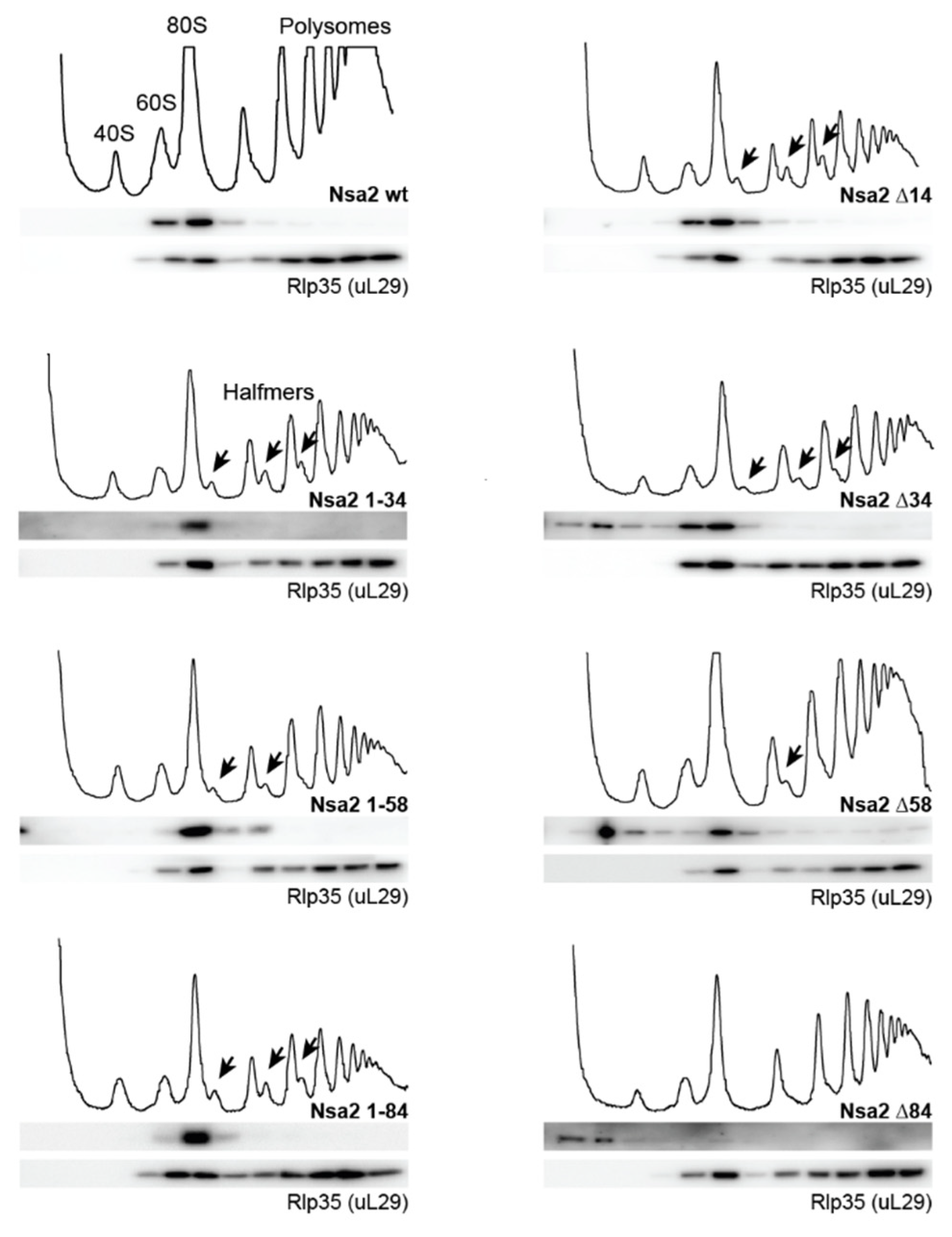
2.2. Overexpression of the Nsa2 N-Terminus Blocks 60S Biogenesis
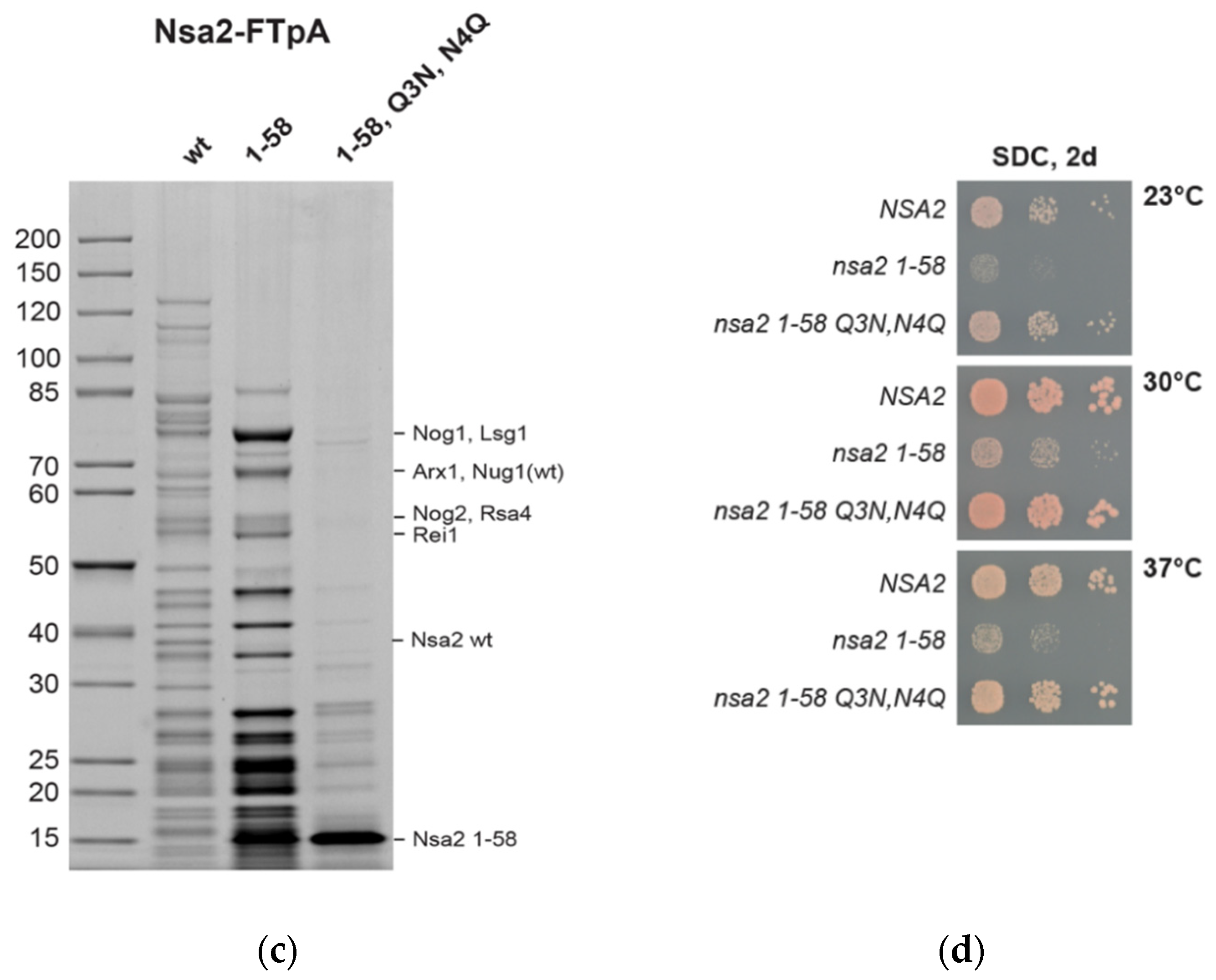
2.3. The Linker between Nsa2 N-Terminus and the Rsa4 Interaction Sequence is Critical for 60S Assembly
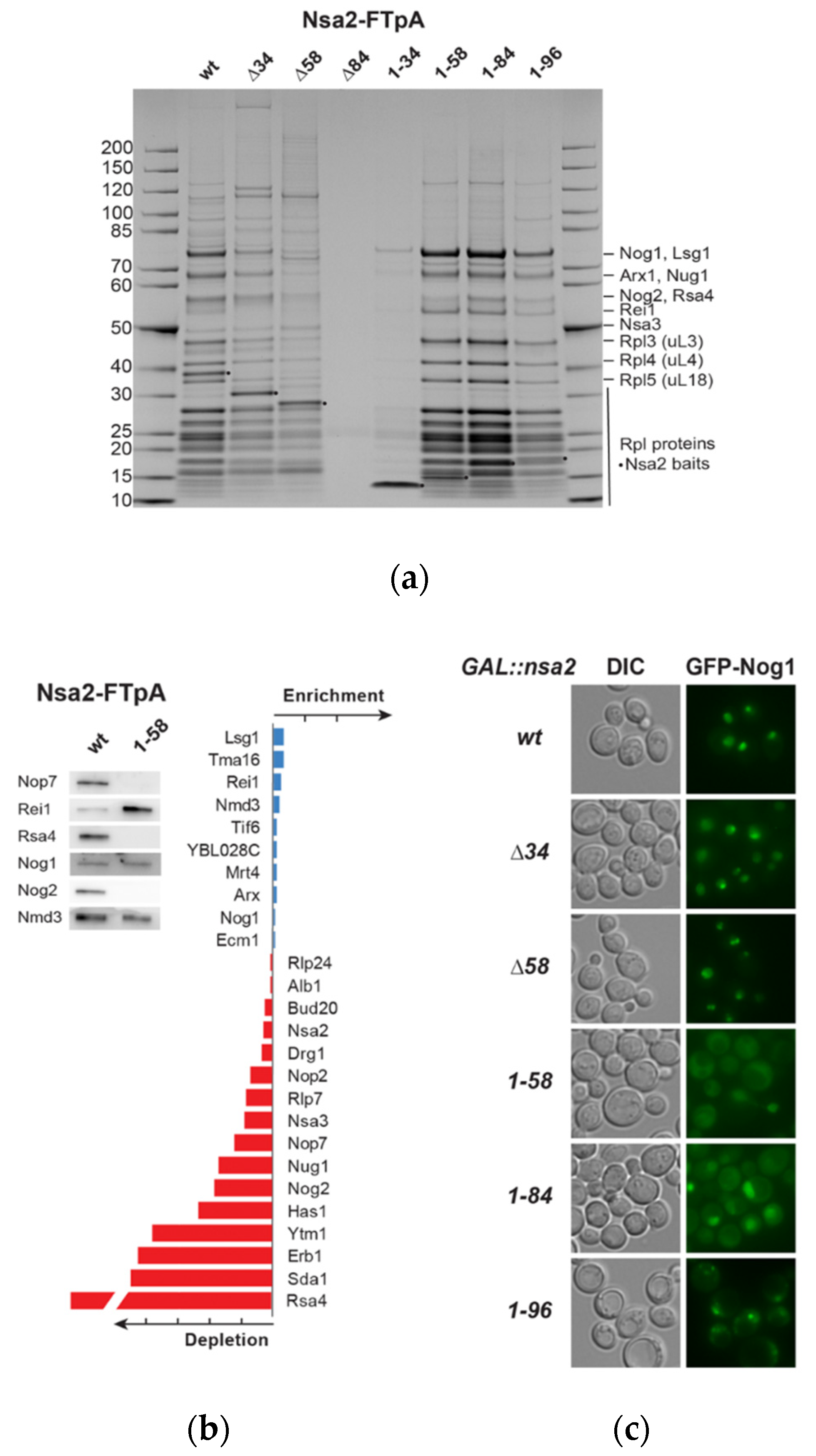
2.4. The Nsa2 N-Terminus is Responsible for its Recruitment to Pre-Ribosomes
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Affinity Purification
4.2. Live Cell Imaging
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ptA | ProteinA |
| FtpA | Flag-TEV-proteinA |
| RIS | Rsa4 interacting sequence |
| LD | linear dichroism |
| PTC | Peptidyl tranferase center |
| SRL | Sarcin–Ricin-loop |
References
- Bassler, J.; Hurt, E. Eukaryotic ribosome assembly. Ann. Rev. Biochem. 2018, 88, 281–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pena, C.; Hurt, E.; Panse, V.G. Eukaryotic ribosome assembly, transport and quality control. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2017, 24, 689–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klinge, S.; Woolford, J.L., Jr. Ribosome assembly coming into focus. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 20, 116–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kater, L.; Thoms, M.; Barrio-Garcia, C.; Cheng, J.; Ismail, S.; Ahmed, Y.L.; Bange, G.; Kressler, D.; Berninghausen, O.; Sinning, I.; et al. Visualizing the assembly pathway of nucleolar pre-60S ribosomes. Cell 2017, 171, 1599–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanghai, Z.A.; Miller, L.; Molloy, K.R.; Barandun, J.; Hunziker, M.; Chaker-Margot, M.; Wang, J.; Chait, B.T.; Klinge, S. Modular assembly of the nucleolar pre-60S ribosomal subunit. Nature 2018, 556, 126–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, D.; Zhu, X.; Zheng, S.; Tan, D.; Dong, M.Q.; Ye, K. Cryo-EM structure of an early precursor of large ribosomal subunit reveals a half-assembled intermediate. Protein Cell 2019, 10, 120–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasse, L.; Flemming, D.; Hurt, E. Coordinated ribosomal ITS2 RNA processing by the Las1 complex integrating endonuclease, polynucleotide kinase, and exonuclease activities. Mol. Cell 2015, 60, 808–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuller, J.M.; Falk, S.; Fromm, L.; Hurt, E.; Conti, E. Structure of the nuclear exosome captured on a maturing preribosome. Science 2018, 360, 219–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fromm, L.; Falk, S.; Flemming, D.; Schuller, J.M.; Thoms, M.; Conti, E.; Hurt, E. Reconstitution of the complete pathway of ITS2 processing at the pre-ribosome. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schillewaert, S.; Wacheul, L.; Lhomme, F.; Lafontaine, D.L. The evolutionarily conserved protein Las1 is required for pre-rRNA processing at both ends of ITS2. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2012, 32, 430–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castle, C.D.; Sardana, R.; Dandekar, V.; Borgianini, V.; Johnson, A.W.; Denicourt, C. Las1 interacts with Grc3 polynucleotide kinase and is required for ribosome synthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 1135–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Harnpicharnchai, P.; Jakovljevic, J.; Tang, L.; Guo, Y.; Oeffinger, M.; Rout, M.P.; Hiley, S.L.; Hughes, T.; Woolford, J.L., Jr. Assembly factors Rpf2 and Rrs1 recruit 5S rRNA and ribosomal proteins rpL5 and rpL11 into nascent ribosomes. Genes Dev. 2007, 21, 2580–2592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madru, C.; Lebaron, S.; Blaud, M.; Delbos, L.; Pipoli, J.; Pasmant, E.; Rety, S.; Leulliot, N. Chaperoning 5S RNA assembly. Genes Dev. 2015, 29, 1432–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leidig, C.; Thoms, M.; Holdermann, I.; Bradatsch, B.; Berninghausen, O.; Bange, G.; Sinning, I.; Hurt, E.; Beckmann, R. 60S ribosome biogenesis requires rotation of the 5S ribonucleoprotein particle. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrio-Garcia, C.; Thoms, M.; Flemming, D.; Kater, L.; Berninghausen, O.; Bassler, J.; Beckmann, R.; Hurt, E. Architecture of the Rix1-Rea1 checkpoint machinery during pre-60S-ribosome remodeling. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2016, 23, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassler, J.; Paternoga, H.; Holdermann, I.; Thoms, M.; Granneman, S.; Barrio-Garcia, C.; Nyarko, A.; Stier, G.; Clark, S.A.; Schraivogel, D.; et al. A network of assembly factors is involved in remodeling rRNA elements during preribosome maturation. J. Cell Biol. 2014, 207, 481–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulbrich, C.; Diepholz, M.; Bassler, J.; Kressler, D.; Pertschy, B.; Galani, K.; Böttcher, B.; Hurt, E. Mechanochemical removal of ribosome biogenesis factors from nascent 60S ribosomal subunit. Cell 2009, 138, 911–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuo, Y.; Granneman, S.; Thoms, M.; Manikas, R.G.; Tollervey, D.; Hurt, E. Coupled GTPase and remodelling ATPase activities form a checkpoint for ribosome export. Nature 2014, 505, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trotta, C.R.; Lund, E.; Kahan, L.; Johnson, A.W.; Dahlberg, J.E. Coordinated nuclear export of 60S ribosomal subunits and NMD3 in vertebrates. EMBO J. 2003, 22, 2841–2851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadal, O.; Strauss, D.; Kessl, J.; Trumpower, B.; Tollervey, D.; Hurt, E. Nuclear export of 60S ribosomal subunits depends on Xpo1p and requires a NES-containing factor Nmd3p that associates with the large subunit protein Rpl10p. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2001, 21, 3405–3415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, J.H.N.; Kallstrom, G.; Johnson, A.W. Nmd3p is a Crm1p-dependent adapter protein for nuclear export of the large ribosomal subunit. J. Cell Biol. 2000, 151, 1057–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Musalgaonkar, S.; Johnson, A.W.; Taylor, D.W. Tightly-orchestrated rearrangements govern catalytic center assembly of the ribosome. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kater, L.; Mitterer, V.; Thoms, M.; Cheng, J.; Berninghausen, O.; Beckmann, R.; Hurt, E. Construction of the central protuberance and L1 stalk during 60S subunit biogenesis. Mol. Cell 2020, 79, 615–628.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klingauf-Nerurkar, P.; Gillet, L.C.; Portugal-Calisto, D.; Oborska-Oplova, M.; Jager, M.; Schubert, O.T.; Pisano, A.; Pena, C.; Rao, S.; Altvater, M.; et al. The GTPase Nog1 co-ordinates the assembly, maturation and quality control of distant ribosomal functional centers. eLife 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kappel, L.; Loibl, M.; Zisser, G.; Klein, I.; Fruhmann, G.; Gruber, C.; Unterweger, S.; Rechberger, G.; Pertschy, B.; Bergler, H. Rlp24 activates the AAA-ATPase Drg1 to initiate cytoplasmic pre-60S maturation. J. Cell Biol. 2012, 199, 771–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pertschy, B.; Saveanu, C.; Zisser, G.; Lebreton, A.; Tengg, M.; Jacquier, A.; Liebminger, E.; Nobis, B.; Kappel, L.; van der Klei, I.; et al. Cytoplasmic recycling of 60S preribosomal factors depends on the AAA protein Drg1. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2007, 27, 6581–6592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malyutin, A.G.; Musalgaonkar, S.; Patchett, S.; Frank, J.; Johnson, A.W. Nmd3 is a structural mimic of eIF5A, and activates the cpGTPase Lsg1 during 60S ribosome biogenesis. EMBO J. 2017, 36, 854–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weis, F.; Giudice, E.; Churcher, M.; Jin, L.; Hilcenko, C.; Wong, C.C.; Traynor, D.; Kay, R.R.; Warren, A.J. Mechanism of eIF6 release from the nascent 60S ribosomal subunit. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2015, 22, 914–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, A.; Pech, M.; Thoms, M.; Beckmann, R.; Hurt, E. Ribosome-stalk biogenesis is coupled with recruitment of nuclear-export factor to the nascent 60S subunit. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2016, 23, 1074–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, K.-Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, F.; Marcotte, E.; Johnson, A.W. Ribosome stalk assembly requires the dual specificity phosphatase Yvh1 for the exchange of Mrt4 with P0. J. Cell Biol. 2009, 186, 849–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemmler, S.; Occhipinti, L.; Veisu, M.; Panse, V.G. Yvh1 is required for a late maturation step in the 60S biogenesis pathway. J. Cell Biol. 2009, 186, 863–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebreton, A.; Saveanu, C.; Decourty, L.; Jacquier, A.; Fromont-Racine, M. Nsa2 is an unstable, conserved factor required for the maturation of 27 SB pre-rRNAs. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 27099–27108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Song, A.P.; Zhao, F.; Hu, Y.M.; Hua, M. A novel human TINP1 gene promotes cell proliferation through inhibition of p53 and p21 expression. Oncol. Rep. 2013, 30, 1848–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelava, A.; Schneider, C.; Watkins, N.J. The importance of ribosome production, and the 5S RNP-MDM2 pathway, in health and disease. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2016, 44, 1086–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bursac, S.; Brdovcak, M.C.; Donati, G.; Volarevic, S. Activation of the tumor suppressor p53 upon impairment of ribosome biogenesis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1842, 817–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Tutuncuoglu, B.; Yan, K.; Brown, H.; Zhang, Y.; Tan, D.; Gamalinda, M.; Yuan, Y.; Li, Z.; Jakovljevic, J.; et al. Diverse roles of assembly factors revealed by structures of late nuclear pre-60S ribosomes. Nature 2016, 534, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madeira, F.; Park, Y.M.; Lee, J.; Buso, N.; Gur, T.; Madhusoodanan, N.; Basutkar, P.; Tivey, A.R.N.; Potter, S.C.; Finn, R.D.; et al. The EMBL-EBI search and sequence analysis tools APIs in 2019. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W636–W641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waterhouse, A.M.; Procter, J.B.; Martin, D.M.; Clamp, M.; Barton, G.J. Jalview Version 2—A multiple sequence alignment editor and analysis workbench. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1189–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersen, E.F.; Goddard, T.D.; Huang, C.C.; Couch, G.S.; Greenblatt, D.M.; Meng, E.C.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF Chimera—A visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1605–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassler, J.; Kallas, M.; Ulbrich, C.; Thoms, M.; Pertschy, B.; Hurt, E. The AAA-ATPase Rea1 drives removal of biogenesis factors during multiple stages of 60S ribosome assembly. Mol. Cell 2010, 38, 712–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Hung, N.J.; Johnson, A.W. Nuclear recycling of the pre-60S ribosomal subunit-associated factor Arx1 depends on Rei1 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2006, 26, 3718–3727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nissan, T.A.; Bassler, J.; Petfalski, E.; Tollervey, D.; Hurt, E.C. 60S pre-ribosome formation viewed from assembly in the nucleolus until export to the cytoplasm. EMBO J. 2002, 21, 5539–5547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lapik, Y.R.; Misra, J.M.; Lau, L.F.; Pestov, D.G. Restricting conformational flexibility of the switch II region creates a dominant-inhibitory phenotype in Obg GTPase Nog1. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2007, 27, 7735–7744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Thomas, B.J.; Rothstein, R. Elevated recombination rates in transcriptionally active DNA. Cell 1989, 56, 619–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janke, C.; Magiera, M.M.; Rathfelder, N.; Taxis, C.; Reber, S.; Maekawa, H.; Moreno-Borchart, A.; Doenges, G.; Schwob, E.; Schiebel, E.; et al. A versatile toolbox for PCR-based tagging of yeast genes: New fluorescent proteins, more markers and promoter substitution cassettes. Yeast 2004, 21, 947–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassler, J.; Grandi, P.; Gadal, O.; Leßmann, T.; Tollervey, D.; Lechner, J.; Hurt, E.C. Identification of a 60S pre-ribosomal particle that is closely linked to nuclear export. Mol. Cell 2001, 8, 517–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, S.; Pool, M.; Seedorf, M. Scp160p, an RNA-binding, polysome-associated protein, localizes to the endoplasmic reticulum of Saccharomyces cerevisiae in a microtubule-dependent manner. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 15905–15912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebreton, A.; Saveanu, C.; Decourty, L.; Rain, J.C.; Jacquier, A.; Fromont-Racine, M. A functional network involved in the recycling of nucleocytoplasmic pre-60S factors. J. Cell Biol. 2006, 173, 349–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Cruz, J.; Sanz-Martinez, E.; Remacha, M. The essential WD-repeat protein Rsa4p is required for rRNA processing and intra-nuclear transport of 60S ribosomal subunits. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, 5728–5739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saveanu, C.; Namane, A.; Gleizes, P.E.; Lebreton, A.; Rousselle, J.C.; Noaillac-Depeyre, J.; Gas, N.; Jacquier, A.; Fromont-Racine, M. Sequential protein association with nascent 60S ribosomal particles. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2003, 23, 4449–4460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, J.; Mann, M. MaxQuant enables high peptide identification rates, individualized p.p.b.-range mass accuracies and proteome-wide protein quantification. Nat. Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 1367–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sturm, M.; Cheng, J.; Bassler, J.; Beckmann, R.; Hurt, E. Interdependent action of KH domain proteins Krr1 and Dim2 drive the 40S platform assembly. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bassler, J.; Kallas, M.; Hurt, E. The Nug1 GTPase reveals an N-terminal RNA-binding domain that is essential for association with 60 S pre-ribosomal particles. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 24737–24744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Paternoga, H.; Früh, A.; Kunze, R.; Bradatsch, B.; Baßler, J.; Hurt, E. Mutational Analysis of the Nsa2 N-Terminus Reveals Its Essential Role in Ribosomal 60S Subunit Assembly. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9108. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21239108
Paternoga H, Früh A, Kunze R, Bradatsch B, Baßler J, Hurt E. Mutational Analysis of the Nsa2 N-Terminus Reveals Its Essential Role in Ribosomal 60S Subunit Assembly. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(23):9108. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21239108
Chicago/Turabian StylePaternoga, Helge, Alexander Früh, Ruth Kunze, Bettina Bradatsch, Jochen Baßler, and Ed Hurt. 2020. "Mutational Analysis of the Nsa2 N-Terminus Reveals Its Essential Role in Ribosomal 60S Subunit Assembly" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 23: 9108. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21239108
APA StylePaternoga, H., Früh, A., Kunze, R., Bradatsch, B., Baßler, J., & Hurt, E. (2020). Mutational Analysis of the Nsa2 N-Terminus Reveals Its Essential Role in Ribosomal 60S Subunit Assembly. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(23), 9108. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21239108




