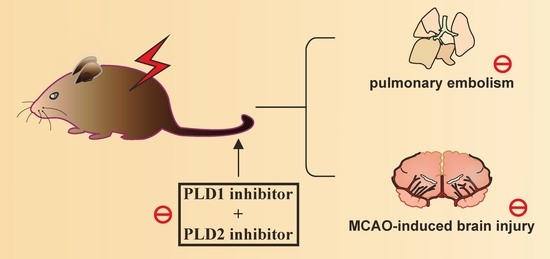
Phospholipase D1 and D2 Synergistically Regulate Thrombus Formation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
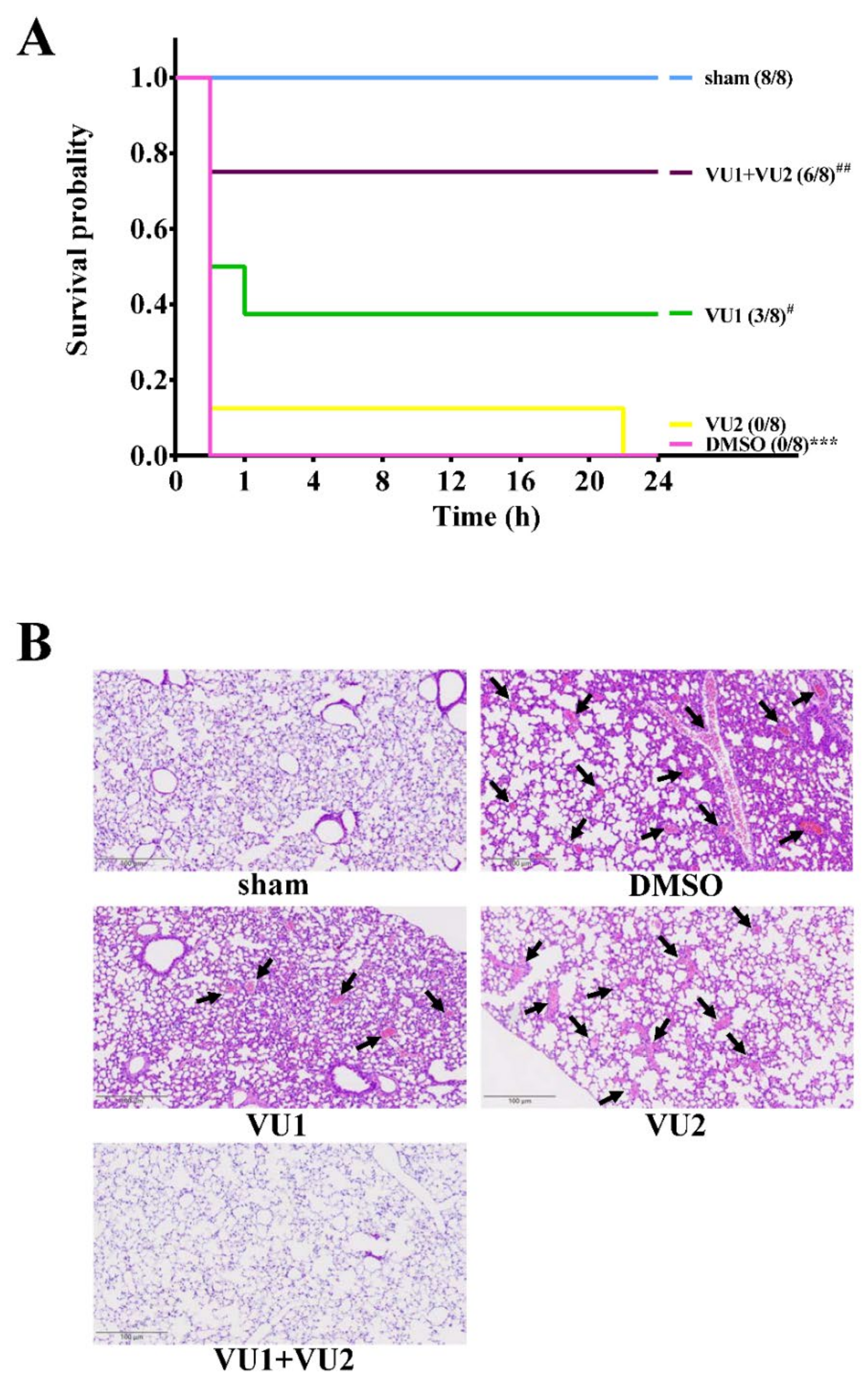
2.1. Effects of the PLD1 and PLD2 Inhibitors in Adenosine 5′-Diphosphate (ADP)-Induced Acute Pulmonary Thrombosis in Mice
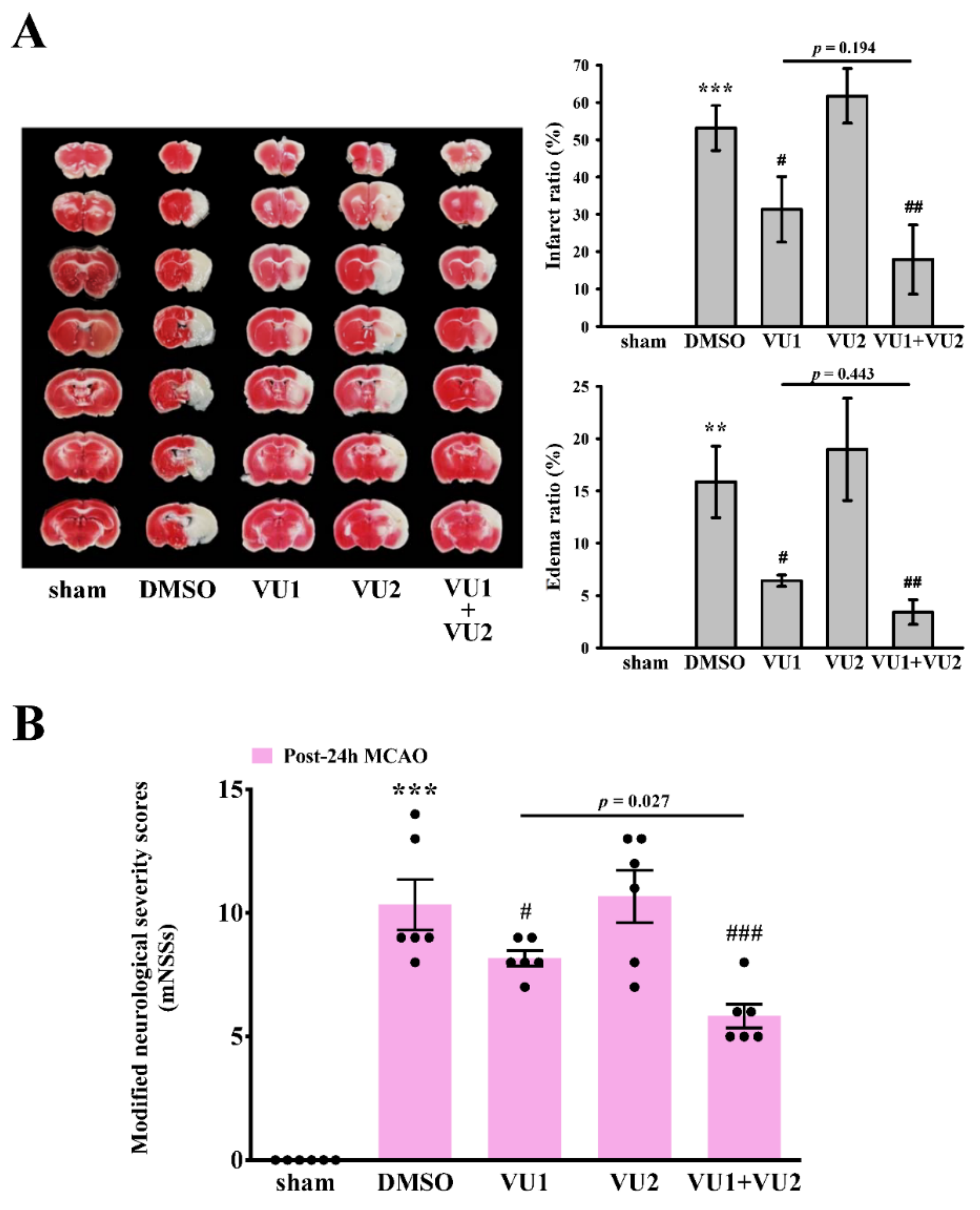
2.2. Effects of PLD1 and PLD2 Inhibitors on Transient MCAO-Induced Brain Injury
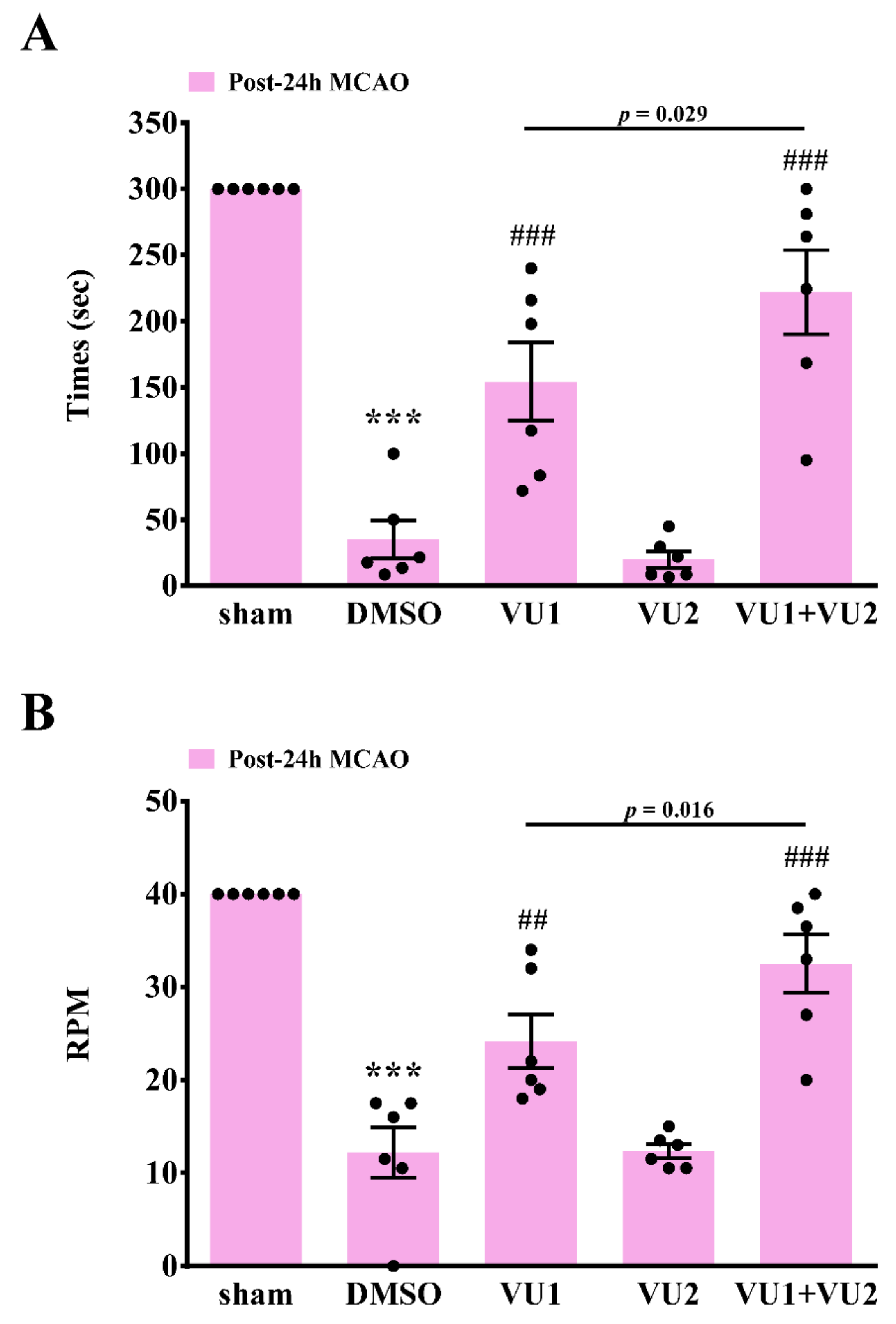
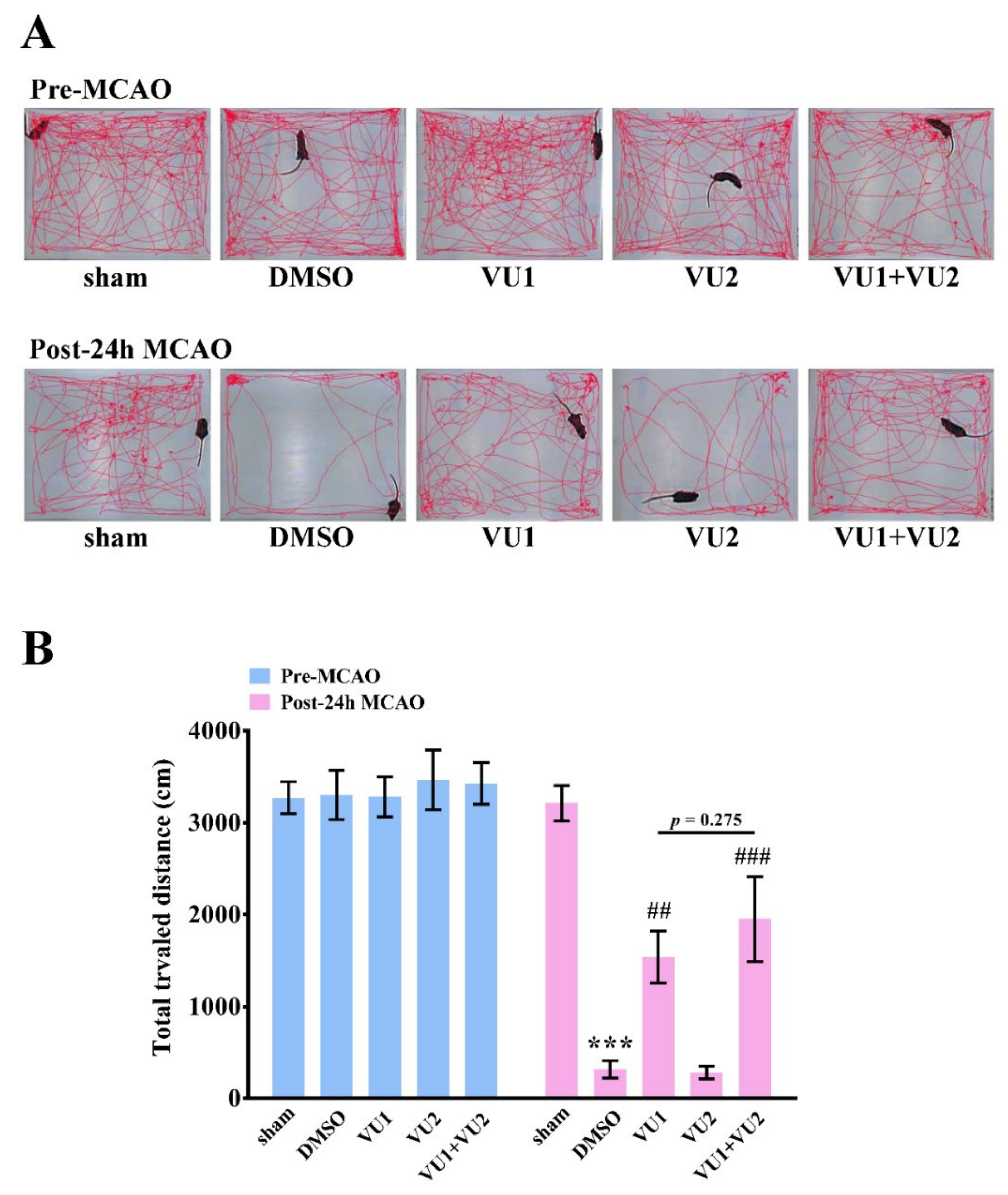
2.3. Effects of PLD1 and PLD2 Inhibitors on Neurobehavioral Function after Transient MCAO
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Animals
4.3. Acute Pulmonary Thrombosis Induced by ADP in Mice
4.4. Transient MCAO-Induced Brain Injury in Mice
4.5. Modified Neurological Severity Scores
4.6. Rotarod Test
4.7. Open-Field Test
4.8. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PLD | Phospholipase D |
| FeCl3 | Ferric chloride |
| FIPI | 5-fluoro-2-indolyl des-chlorohalopemide |
| MCA | Middle cerebral artery |
| MCAO | Middle cerebral artery occlusion |
| ADP | Adenosine 5′-diphosphate |
| TTC | 2,3,5-triphenyltetrazolium chloride |
| DMSO | Dimethyl sulphoxide |
| HE | Hematoxylin-eosin |
| mNSSs | Modified neurological severity scores |
| rpm | Revolutions per min |
References
- McFadyen, J.D.; Schaff, M.; Peter, K. Current and future antiplatelet therapies: Emphasis on preserving haemostasis. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2018, 15, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballini, A.; Scacco, S.; Coletti, D.; Pluchino, S.; Tatullo, M. Mesenchymal Stem Cells as Promoters, Enhancers, and Playmakers of the Translational Regenerative Medicine. Stem. Cells Int. 2017, 2017, 3292810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballini, A.; Cantore, S.; Scacco, S.; Coletti, D.; Tatullo, M. Mesenchymal Stem Cells as Promoters, Enhancers, and Playmakers of the Translational Regenerative Medicine. Stem. Cells Int. 2018, 2018, 6927401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tobin, M.K.; Stephen, T.K.L.; Lopez, K.L.; Pergande, M.R.; Bartholomew, A.M.; Cologna, S.M.; Lazarov, O. Activated Mesenchymal Stem Cells Induce Recovery Following Stroke Via Regulation of Inflammation and Oligodendrogenesis. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2020, 9, e013583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, R.K.; Frohman, M.A. Physiological and pathophysiological roles for phospholipase D. J. Lipid. Res. 2015, 56, 2229–2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvers, M.; Stegner, D.; Hagedorn, I.; Kleinschnitz, C.; Braun, A.; Kuijpers, M.E.; Boesl, M.; Chen, Q.; Heemskerk, J.W.; Stoll, G.; et al. Impaired alpha(IIb)beta(3) integrin activation and shear-dependent thrombus formation in mice lacking phospholipase D1. Sci. Signal. 2010, 3, ra1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thielmann, I.; Stegner, D.; Kraft, P.; Hagedorn, I.; Krohne, G.; Kleinschnitz, C.; Stoll, G.; Nieswandt, B. Redundant functions of phospholipases D1 and D2 in platelet alpha-granule release. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2012, 10, 2361–2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stegner, D.; Thielmann, I.; Kraft, P.; Frohman, M.A.; Stoll, G.; Nieswandt, B. Pharmacological inhibition of phospholipase D protects mice from occlusive thrombus formation and ischemic stroke--brief report. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2013, 33, 2212–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.J.; Chung, C.L.; Chen, R.J.; Huang, L.T.; Lien, L.M.; Chang, C.C.; Lin, K.H.; Sheu, J.R. An Antithrombotic Strategy by Targeting Phospholipase D in Human Platelets. J. Clin. Med. 2018, 7, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, S.P.; Dunnett, S.B. Tests to assess motor phenotype in mice: A user’s guide. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2009, 10, 519–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balkaya, M.; Krober, J.M.; Rex, A.; Endres, M. Assessing post-stroke behavior in mouse models of focal ischemia. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2013, 33, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frohman, M.A. The phospholipase D superfamily as therapeutic targets. Trends. Pharmacol. Sci. 2015, 36, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruntz, R.C.; Taylor, H.E.; Lindsley, C.W.; Brown, H.A. Phospholipase D2 mediates survival signaling through direct regulation of Akt in glioblastoma cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 600–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fite, K.; Gomez-Cambronero, J. Down-regulation of MicroRNAs (MiRs) 203, 887, 3619 and 182 Prevents Vimentin-triggered, Phospholipase D (PLD)-mediated Cancer Cell Invasion. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 719–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.W.; Choi, C.Y.; Cho, Y.H.; Tian, H.; Di Paolo, G.; Choi, K.Y.; Min do, S. Targeting phospholipase D1 attenuates intestinal tumorigenesis by controlling beta-catenin signaling in cancer-initiating cells. J. Exp. Med. 2015, 212, 1219–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, T.G.; Chan, R.B.; Tian, H.; Laredo, M.; Shui, G.; Staniszewski, A.; Zhang, H.; Wang, L.; Kim, T.W.; Duff, K.E.; et al. Phospholipase d2 ablation ameliorates Alzheimer’s disease-linked synaptic dysfunction and cognitive deficits. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 16419–16428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klier, M.; Gowert, N.S.; Jackel, S.; Reinhardt, C.; Elvers, M. Phospholipase D1 is a regulator of platelet-mediated inflammation. Cell Signal. 2017, 38, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbahn, M.A.; Kaup, S.C.; Reusswig, F.; Kruger, I.; Spelleken, M.; Jurk, K.; Klier, M.; Lang, P.A.; Elvers, M. Phospholipase D1 regulation of TNF-alpha protects against responses to LPS. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.K.; Kim, Y.S.; Bae, G.H.; Lee, H.Y.; Bae, Y.S. VU0155069 inhibits inflammasome activation independent of phospholipase D1 activity. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 14349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mestas, J.; Hughes, C.C. Of mice and not men: Differences between mouse and human immunology. J. Immunol. 2004, 172, 2731–2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nylander, S.; Mattsson, C.; Lindahl, T.L. Characterisation of species differences in the platelet ADP and thrombin response. Thromb Res. 2006, 117, 543–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iyer, S.S.; Barton, J.A.; Bourgoin, S.; Kusner, D.J. Phospholipases D1 and D2 coordinately regulate macrophage phagocytosis. J. Immunol. 2004, 173, 2615–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henkels, K.M.; Boivin, G.P.; Dudley, E.S.; Berberich, S.J.; Gomez-Cambronero, J. Phospholipase D (PLD) drives cell invasion, tumor growth and metastasis in a human breast cancer xenograph model. Oncogene 2013, 32, 5551–5562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.W.; Lee, B.H.; Suh, Y.A.; Choi, Y.S.; Jang, S.J.; Kim, Y.M.; Choi, K.Y.; Min, D.S. Phospholipase D1 Inhibition Linked to Upregulation of ICAT Blocks Colorectal Cancer Growth Hyperactivated by Wnt/beta-Catenin and PI3K/Akt Signaling. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 7340–7350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, X.; Sun, Z.; Chu, C.; Boltze, J.; Li, S. Dental Pulp Stem Cells: An Attractive Alternative for Cell Therapy in Ischemic Stroke. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marrazzo, P.; Paduano, F.; Palmieri, F.; Marrelli, M.; Tatullo, M. Highly Efficient In Vitro Reparative Behaviour of Dental Pulp Stem Cells Cultured with Standardised Platelet Lysate Supplementation. Stem. Cells Int. 2016, 2016, 7230987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reagan-Shaw, S.; Nihal, M.; Ahmad, N. Dose translation from animal to human studies revisited. FASEB J. 2008, 22, 659–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lien, L.M.; Lin, K.H.; Huang, L.T.; Tseng, M.F.; Chiu, H.C.; Chen, R.J.; Lu, W.J. Licochalcone A Prevents Platelet Activation and Thrombus Formation through the Inhibition of PLCgamma2-PKC, Akt, and MAPK Pathways. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, M.; Pan, J.; Wang, L.; Zhou, P.; Song, Y.; Wang, S.; Jiang, L.; Geng, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; et al. MicroRNA-126 Regulates Angiogenesis and Neurogenesis in a Mouse Model of Focal Cerebral Ischemia. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids. 2019, 16, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheu, J.R.; Chen, Z.C.; Jayakumar, T.; Chou, D.S.; Yen, T.L.; Lee, H.N.; Pan, S.H.; Hsia, C.H.; Yang, C.H.; Hsieh, C.Y. A novel indication of platonin, a therapeutic immunomodulating medicine, on neuroprotection against ischemic stroke in mice. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheu, J.R.; Hsieh, C.Y.; Jayakumar, T.; Tseng, M.F.; Lee, H.N.; Huang, S.W.; Manubolu, M.; Yang, C.H. A Critical Period for the Development of Schizophrenia-Like Pathology by Aberrant Postnatal Neurogenesis. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lien, L.-M.; Lu, W.-J.; Chen, T.-Y.; Lee, T.-Y.; Wang, H.-H.; Peng, H.-Y.; Chen, R.-J.; Lin, K.-H. Phospholipase D1 and D2 Synergistically Regulate Thrombus Formation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6954. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21186954
Lien L-M, Lu W-J, Chen T-Y, Lee T-Y, Wang H-H, Peng H-Y, Chen R-J, Lin K-H. Phospholipase D1 and D2 Synergistically Regulate Thrombus Formation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(18):6954. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21186954
Chicago/Turabian StyleLien, Li-Ming, Wan-Jung Lu, Ting-Yu Chen, Tzu-Yin Lee, Hsueh-Hsiao Wang, Hsien-Yu Peng, Ray-Jade Chen, and Kuan-Hung Lin. 2020. "Phospholipase D1 and D2 Synergistically Regulate Thrombus Formation" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 18: 6954. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21186954
APA StyleLien, L.-M., Lu, W.-J., Chen, T.-Y., Lee, T.-Y., Wang, H.-H., Peng, H.-Y., Chen, R.-J., & Lin, K.-H. (2020). Phospholipase D1 and D2 Synergistically Regulate Thrombus Formation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(18), 6954. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21186954