Mammary Gland Transcriptome and Proteome Modifications by Nutrient Restriction in Early Lactation Holstein Cows Challenged with Intra-Mammary Lipopolysaccharide
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Dietary and Inflammatory Challenges Influenced Milk and Blood Composition
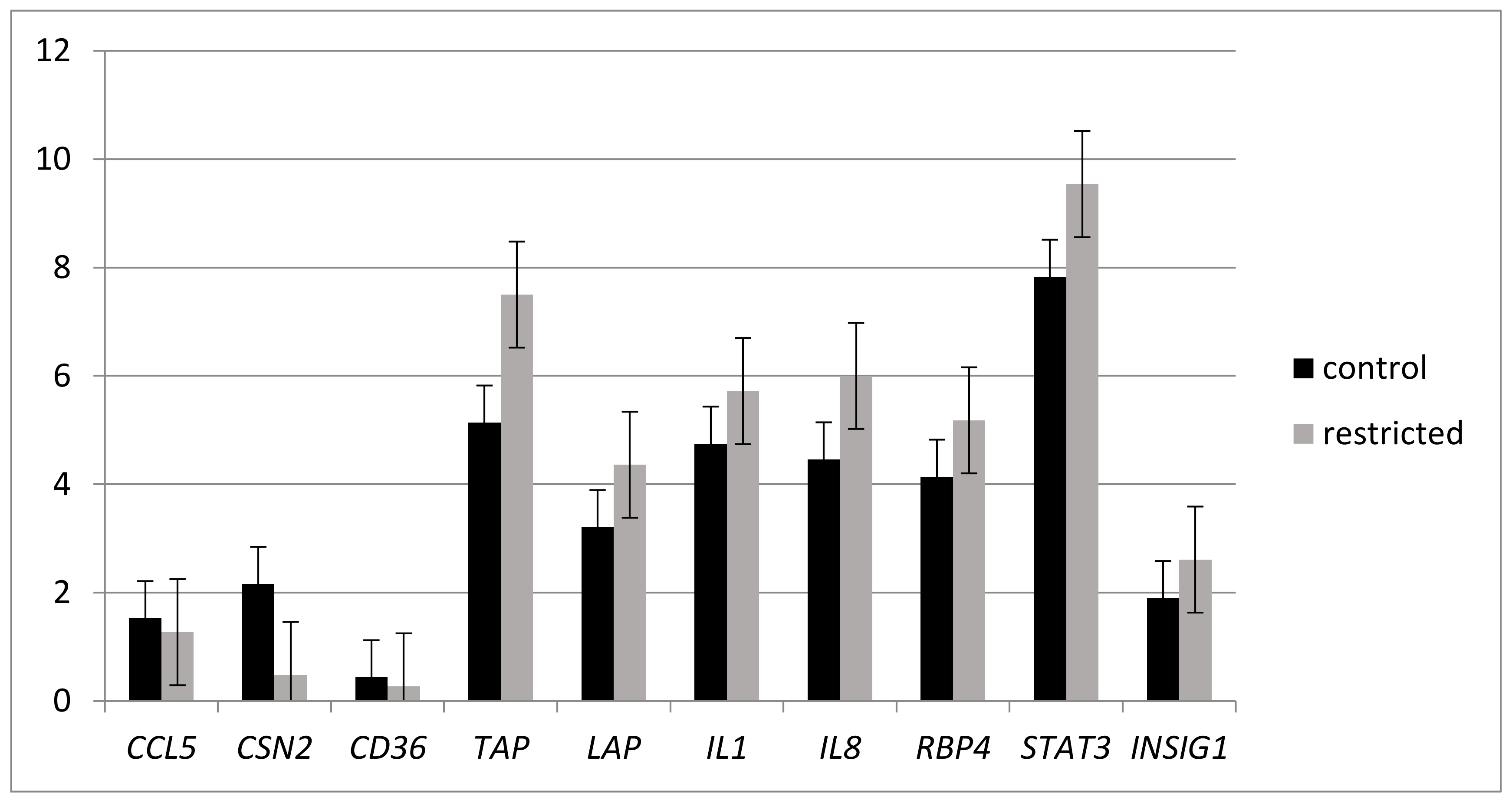
2.2. Effects of Under-nutrition on Expression of Genes Involved in Inflammation Response by RT-qPCR Analysis
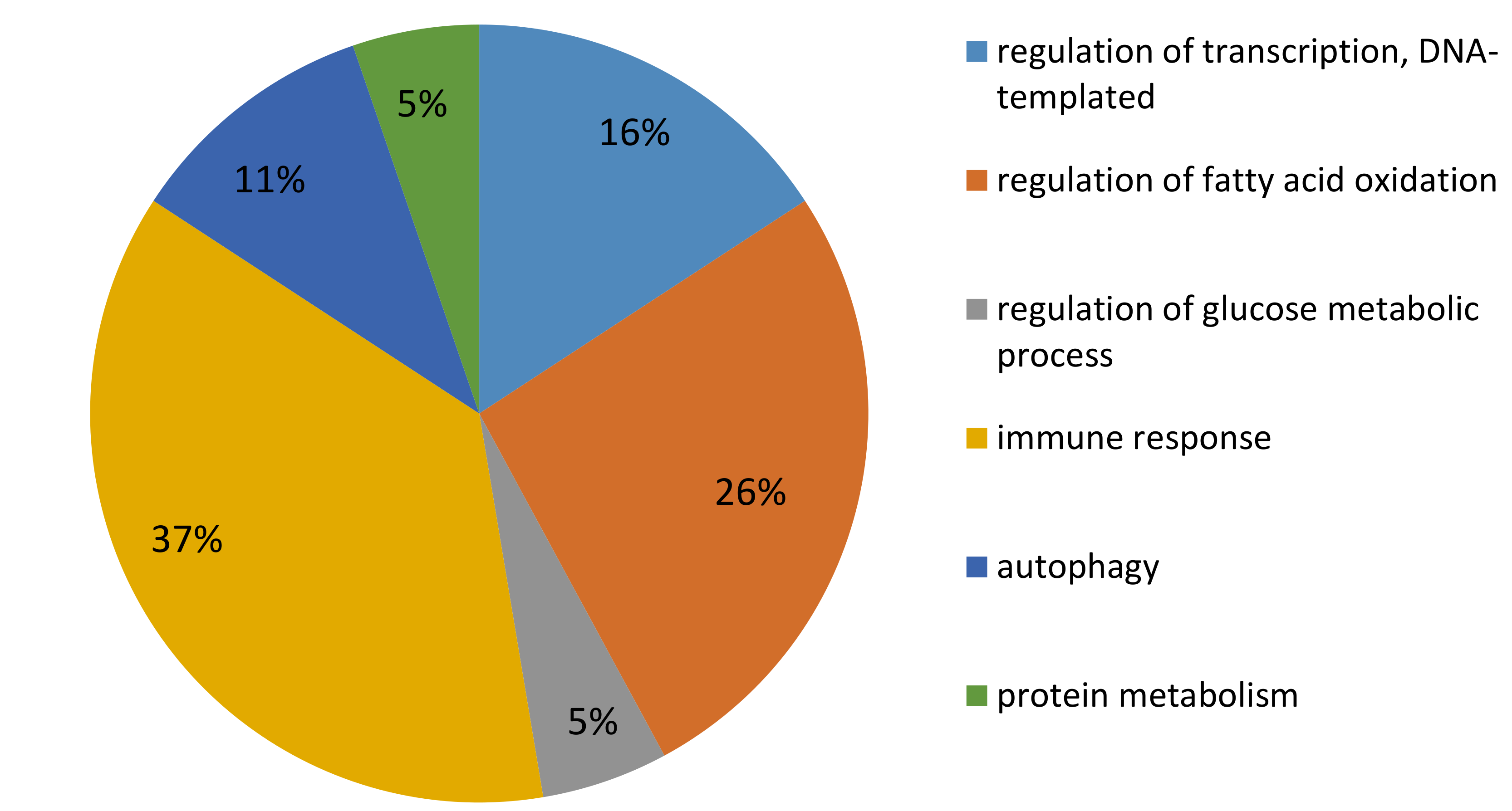
2.3. Microarray Analysis
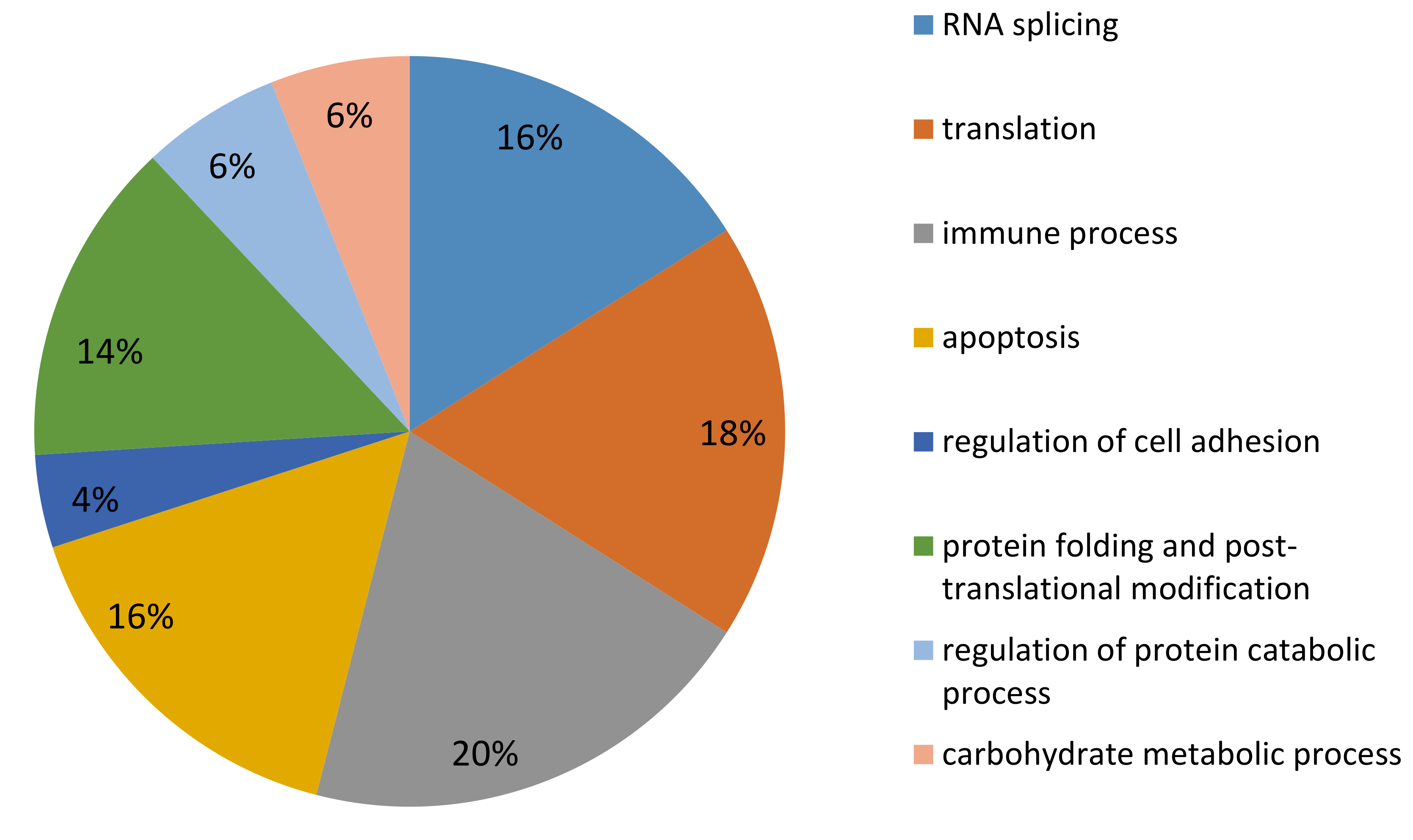
2.4. LC MS/MS Proteomic Analysis
3. Discussion
3.1. Gene Expression Changes at mRNA Level
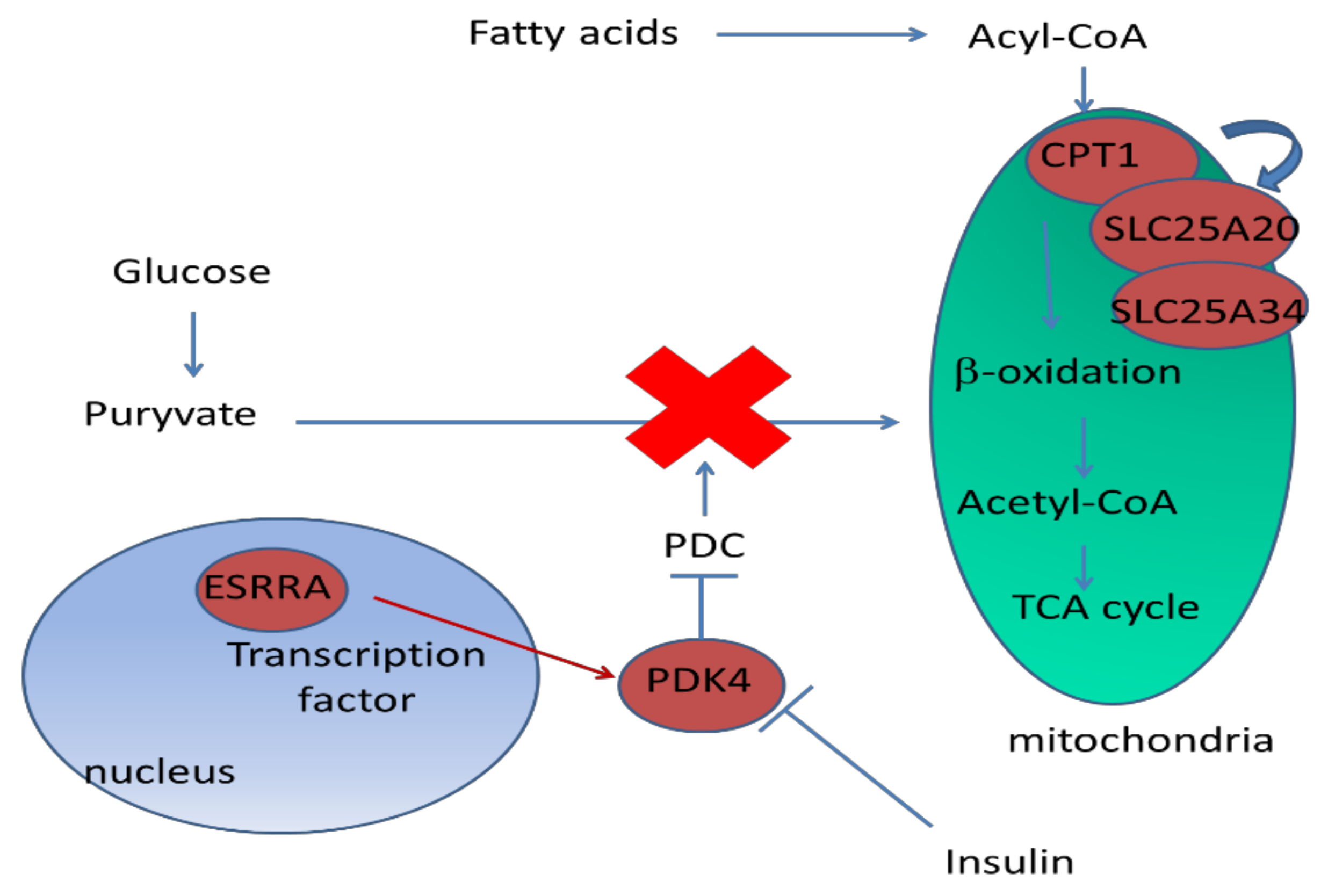
3.1.1. DEG Involved in Metabolism
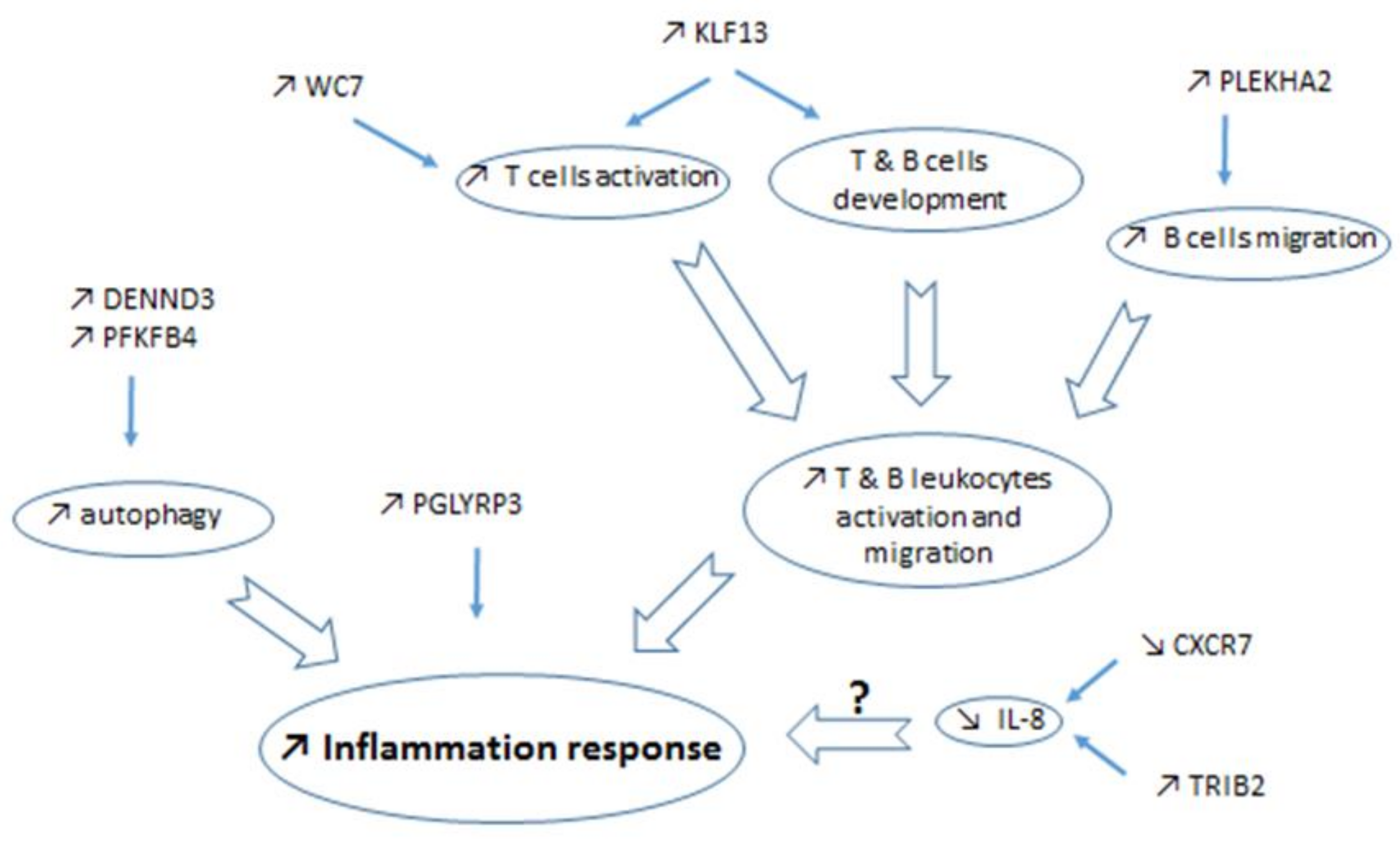
3.1.2. DEG Involved in Immune Response
3.2. Gene Expression at Protein Level
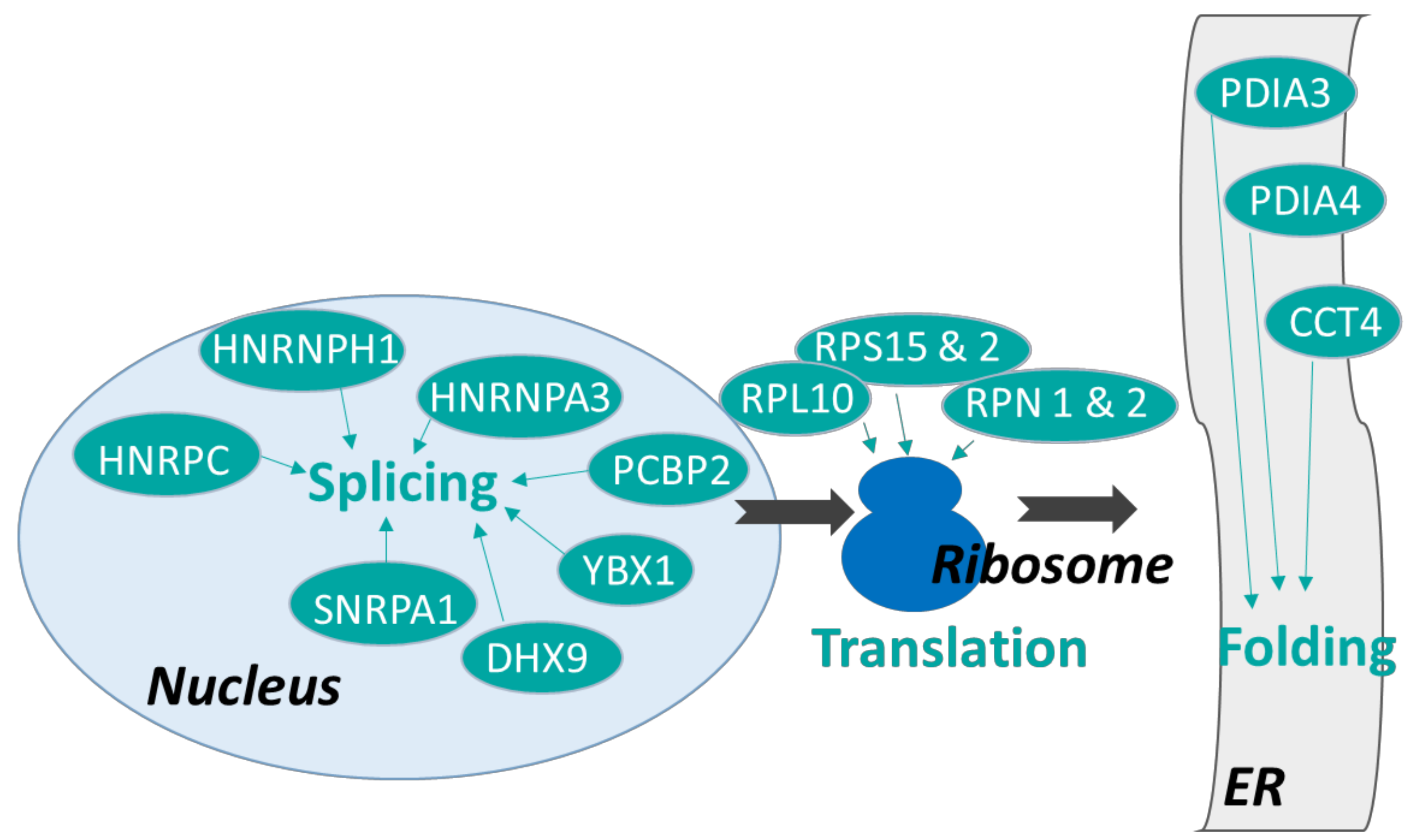
3.2.1. Proteins Involved in Protein Synthesis
3.2.2. DEP Involved in Immune Response
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Ethics Statement, Treatments and Sampling
4.2. RNA Preparation and Analyses
4.3. RT-PCR Analyses
4.4. Microarray Analyses
4.5. Protein Preparation and Analyses
4.6. LC MS/MS Analysis
4.7. Protein Identification and Label-Free Quantitation
5. Conclusion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ollier, S.; Robert-Granié, C.; Bernard, L.; Chilliard, Y.; Leroux, C. Mammary transcriptome analysis of food-deprived lactating goats highlights genes involved in milk secretion and programmed cell death. J. Nutr. 2007, 137, 560–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minuti, A.; Zhou, Z.; Graugnard, D.E.; Rodriguez-Zas, S.L.; Palladino, A.R.; Cardoso, F.C.; Trevisi, E.; Loor, J.J. Acute mammary and liver transcriptome responses after an intramammary Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharide challenge in postpartal dairy cows. Physiol. Rep. 2015, 3, e12388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seegers, H.; Fourichon, C.; Beaudeau, F. Production effects related to mastitis and mastitis economics in dairy cattle herds. Vet. Res. 2003, 34, 475–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthews, K.R.; Almeida, R.A.; Oliver, S.P. Bovine mammary epithelial cell invasion by Streptococcus uberis. Infect. Immun. 1994, 62, 5641–5646. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Almeida, R.A.; Matthews, K.R.; Cifrian, E.; Guidry, A.J.; Oliver, S.P. Staphylococcus aureus invasion of bovine mammary epithelial cells. J. Dairy Sci. 1996, 70, 1021–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, T.J.; Lipman, L.J.; Schukken, Y.H.; Gaastra, W.; Brand, A. Epidemiological characteristics of bovine clinical mastitis caused by Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli studied by DNA fingerprinting. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1996, 571, 39–42. [Google Scholar]
- Mallard, B.A.; Dekkers, J.C.; Ireland, M.J.; Leslie, K.E.; Sharif, S.; Lacey Vankampen, C.; Wagter, L.; Wilkie, B.N. Alteration in immune responsiveness during the periparturient period and its ramification on dairy cow and calf health. J. Dairy Sci. 1998, 81, 585–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sordillo, L.M.; Raphael, W. Significance of Metabolic Stress, Lipid Mobilization, and Inflammation on Transition Cow Disorders. Vet. Clin. Food Anim. 2013, 29, 267–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suriyasathaporn, W.; Heuer, C.; Noordhuizen-Stassen, E.N.; Schukken, Y.H. Hyperketonemia and the impairment of udder defense: A review. Vet. Res. 2000, 31, 397–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shuster, D.E.; Lee, E.; Kehrli, M.E. Bacterial growth, inflammatory cytokine production, and neutrophil recruitment during coliform mastitis in cows within ten days after calving, compared with cows at midlactation. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1996, 57, 1569–1575. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bruckmaier, R.M. Gene expression of factors related to the immune reaction in response to intramammary Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharide challenge. J. Dairy Res. 2005, 72, 120–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moyes, K.M.; Drackley, J.K.; Salak-Johnson, J.L.; Morin, D.E.; Hope, J.C.; Loor, J.J. Dietary-induced negative energy balance has minimal effects on innate immunity during a Streptococcus uberis mastitis challenge in dairy cows during midlactation. J. Dairy Sci. 2009, 929, 4301–4316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perkins, K.H.; VandeHaar, M.J.; Burton, J.L.; Liesman, J.S.; Erskine, R.J.; Elsasser, T.H. Clinical Responses to Intramammary Endotoxin Infusion in Dairy Cows Subjected to Feed Restriction. J. Dairy Sci. 2002, 85, 1724–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sordillo, L.M.; Shafer-Weaver, K.; DeRosa, D. Immunobiology of the mammary gland. J. Dairy Sci. 1997, 808, 1851–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldron, M.R.; Kulick, A.E.; Bell, A.W.; Overton, T.R. Acute Experimental Mastitis Is Not Causal Toward the Development of Energy-Related Metabolic Disorders in Early Postpartum Dairy Cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2006, 89, 596–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaldi, M.; Li, R.W.; Capuco, A.V. Mastitis associated transcriptomic disruptions in cattle. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2010, 138, 267–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loor, J.J.; Moyes, K.M.; Bionaz, M. Functional adaptations of the transcriptome to mastitis-causing pathogens: The mammary gland and beyond. J. Mammary Gland Biol. Neoplasia 2011, 16, 305–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buitenhuis, B.; Røntved, C.M.; Edwards, S.M.; Ingvartsen, K.L.; Sørensen, P. In depth analysis of genes and pathways of the mammary gland involved in the pathogenesis of bovine Escherichia coli-mastitis. BMC Genom. 2011, 12, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitterhuemer, S.; Petzl, W.; Krebs, S.; Mehne, D.; Klanner, A.; Wolf, E.; Zerbe, H.; Blum, H. Escherichia coli infection induces distinct local and systemic transcriptome responses in the mammary gland. BMC Genom. 2010, 11, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Günther, J.; Koczan, D.; Yang, W.; Nurnberg, G.; Repsilber, D.; Schuberth, H.J.; Park, Z.; Maqbool, N.; Molenaar, A.; Seyfert, H.M. Assessment of the immune capacity of mammary epithelial cells: Comparison with mammary tissue after challenge with Escherichia coli. Vet. Res. 2009, 40, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Günther, J.; Esch, K.; Poschadel, N.; Petzl, W.; Zerbe, H.; Mitterhuemer, S.; Blum, H.; Seyfert, H.M. Comparative kinetics of Escherichia coli- and Staphylococcus aureus-specific activation of key immune pathways in mammary epithelial cells demonstrates that S. aureus elicits a delayed response dominated by interleukin-6 IL-6) but not by IL-1A or tumor necrosis factor alpha. Infect. Immun. 2011, 79, 695–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griesbeck-Zilch, B.; Meyer, H.H.D.; Kuhn, C.; Schwerin, M.; Wellnitz, O. Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli cause deviating expression profiles of cytokines and lactoferrin messenger ribonucleic acid in mammary epithelial cells. J. Dairy Sci. 2008, 91, 2215–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hogarth, C.J.; Fitzpatrick, J.L.; Nolan, A.M.; Young, F.J.; Pitt, A.; Eckersall, P.D. Differential protein composition of bovine whey: A comparison of whey from healthy animals and from those with clinical mastitis. Proteomics 2004, 4, 2094–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boehmer, J.L.; Bannerman, D.D.; Shefcheck, K.; Ward, J.L. Proteomic analysis of differentially expressed proteins in bovine milk during experimentally induced Escherichia colimastitis. J. Dairy Sci. 2008, 91, 4206–4218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pires, J.; Pawlowski, K.; Rouel, J.; Delavaud, C.; Foucras, G.; Rainard, P.; Germon, P.; Leroux, C. Undernutrition modifies metabolic responses to intramammary lipopolysaccharide but has limited effects on inflammation indicators in early lactation cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rainard, P.; Riollet, C. Innate immunity of the bovine mammary gland. Vet. Res. 2006, 37, 369–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atabai, K.; Sheppard, D.; Werb, Z. Roles of the Innate Immune System in Mammary Gland Remodeling During Involution. J. Mammary Gland Biol. Neoplasia 2007, 121, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, K.; Watson, C.J. The spectrum of STAT functions in mammary gland development. Jak-stat 2012, 13, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Meza, J.E.; Gutiérrez-Barroso, A.; Ochoa-Zarzosa, A. Expression of tracheal antimicrobial peptide in bovine mammary epithelial cells. Res. Vet. Sci. 2009, 87, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yarus, S.; Rosen, J.M.; Cole, A.M.; Diamond, G. Production of active bovine tracheal antimicrobial peptide in milk of transgenic mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 14118–14121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moyes, K.M.; Sørensen, P.; Bionaz, M. The Impact of Intramammary Escherichia coli Challenge on Liver and Mammary Transcriptome and Cross-Talk in Dairy Cows during Early Lactation Using RNAseq. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0157480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Priestman, D.A.; Mistry, S.C.; Halsall, A.; Randle, P.J. Role of protein synthesis and of fatty acid metabolism in the longer-term regulation of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase. Biochem. J. 1994, 300, 659–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibeagha-Awemu, E.M.; Li, R.; Ammah, A.A.; Dudemaine, P.L.; Bissonnette, N.; Benchaar, C.; Zhao, X. Transcriptome adaptation of the bovine mammary gland to diets rich in unsaturated fatty acidFAs shows greater impact of linseed oil over safflower oil on gene expression and metabolic pathways. BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouvier-Muller, J.; Allain, C.; Tabouret, G.; Enjalbert, F.; Portes, D.; Noirot, C.; Rupp, R.; Foucras, G. Whole blood transcriptome analysis reveals potential competition in metabolic pathways between negative energy balance and response to inflammatory challenge. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, E.J.; Kim, D.K.; Lee, J.M.; Park, S.B.; Lee, I.K.; Harris, R.A.; Lee, M.O.; Choi, H.S. Hypoxia Induces PDK4 Gene Expression through Induction of the Orphan Nuclear Receptor ERRc. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e46324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, B.B.; Wolfe, R.R. Regulation of fatty acid oxidation in skeletal muscle. Annu Rev. Nutr. 1999, 19, 463–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbar, H.; Bionaz, M.; Carlson, D.B.; Rodriguez-Zas, S.L.; Everts, R.E.; Lewin, H.A.; Drackley, J.K.; Loor, J.J. Feed restriction, but not L-carnitine infusion, alters the liver transcriptome by inhibiting sterol synthesis and mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation and increasing gluconeogenesis in mid-lactation dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2013, 96, 2201–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drackley, J.K. Biology of dairy cows during the transition period: The final frontier? J. Dairy Sci. 1999, 82, 2259–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmieri, F. The mitochondrial transporter family SLC25: Identification, properties and physiopathology. Mol. Asp. Med. 2013, 34, 465–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moyes, K.M.; Drackley, J.D.; Morin, D.E.; Rodriguez-Zas, S.L.; Everts, R.E.; Lewin, H.A.; Loor, J.J. Predisposition of cows to mastitis in non-infected mammary glands: Effects of dietary-induced negative energy balance during mid-lactation on immune-related genes. Funct. Integr. Genom. 2011, 11, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashyap, D.R.; Rompca, A.; Gaballa, A.; Helmann, J.D.; Chan, J.; Chang, C.J.; Hozo, I.; Gupta, D.; Dziarski, R. Peptidoglycan Recognition Proteins Kill Bacteria by Inducing Oxidative, Thiol, and Metal Stress. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohtsuka, H.; Koiwa, M.; Fukuda, S.; Satoh, Y.; Hayashi, T.; Hoshi, F.; Yoshino, T.; Kawamura, S. Changes in peripheral leukocyte subsets in dairy cows with inflammatory diseases after calving. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2004, 66, 905–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Hou, S.; Wu, X.; Nandagopal, S.; Lin, F.; Kung, S.; Marshall, A.J. The Tandem PH Domain-Containing Protein 2 (TAPP2) Regulates Chemokine-Induced Cytoskeletal; Reorganization and Malignant B Cell Migration. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.W.; Paape, M.J.; Elsasser, T.H.; Zhao, X. Elevated milk soluble CD14 in bovine mammary glands challenged with Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharide. J. Dairy Sci. 2003, 86, 2382–2389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bannerman, D.D.; Paape, M.J.; Hare, W.R.; Sohn, E.J. Increased levels of LPS-binding protein in bovine blood and milk following bacterial lipopolysaccharide challenge. J. Dairy Sci. 2003, 86, 3128–3137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.P.; Tang, Y.H.; Smith, R. Functional diversity of the hnRNPs: Past, present and perspectives. Biochem. J. 2010, 430, 379–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geuens, T.; Bouhy, D.; Timmerman, V. The hnRNP family: Insights into their role in health and disease. Hum. Genet. 2016, 135, 851–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raffetseder, U.; Liehn, E.A.; Weber, C.; Mertens, P.R. Role of cold shock Y-box protein-1 in inflammation, atherosclerosis and organ transplant rejection. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2012, 91, 567–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apostolidis, S.A.; Rodríguez-Rodríguez, N.; Suárez-Fueyo, A.; Dioufa, N.; Ozcan, E.; Crispín, J.C.; Tsokos, M.G.; Tsokos, G.C. Phosphatase PP2A is requisite for the function of regulatory T cells. Nat. Immunol. 2016, 17, 556–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhavsar, R.B.; Makley, L.N.; Tsonis, P.A. The other lives of ribosomal proteins. Hum. Genom. 2010, 4, 327–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schachtera, H.; Freeze, H.H. Glycosylation diseases: Quo vadis? Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2009, 1792, 925–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palorini, R.; Cammarata, F.P.; Balestrieri, C.; Monestiroli, A.; Vasso, M.; Gelfi, C.; Alberghina, L.; Chiaradonna, F. Glucose starvation induces cell death in K-ras-transformed cells by interfering with the hexosamine biosynthesis pathway and activating the unfolded protein response. Cell Death Dis. 2013, 4, 732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alanen, H.I.; Salo, K.E.; Pirneskoski, A.; Ruddock, L.W. pH dependence of the peptide thiol-disulfide oxidase activity of six members of the human protein disulfide isomerase family. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2006, 83, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galligan, J.J.; Petersen, D.R. The human protein disulfide isomerase gene family. Hum. Genom. 2012, 6, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grootjans, J.; Kaser, A.; Kaufman, R.J.; Blumberg, R.S. The unfolded protein response in immunity and inflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16, 469–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garbi, N.; Tanaka, S.; Momburg, F.; Hammerling, G.J. Impaired assembly of the major histocompatibility complex class I peptide-loading complex in mice deficient in the oxidoreductase ERp57. Nat. Immunol. 2006, 7, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lilie, H.; McLaughlin, S.; Freedman, R.; Buchner, J. Influence of protein disulfide isomerase PDI) on antibody folding in vitro. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 14290–14296. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bregier, C.; Kupikowska, B.; Fabczak, H.; Fabczak, S. CCT chaperonins and their cochaperons. Postepy Biochem. 2008, 54, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Carneiro, P.; Peters, L.C.; Vorraro, F.; Borrego, A.; Ribeiro, O.G.; Starobinas, N.; Jensen, J.R.; Cabrera, W.H.K.; Ibanez, O.M.; De Franco, M. Gene expression profiles of bone marrow cells from mice phenotype-selected for maximal or minimal acute inflammations: Searching for genes in acute inflammation modifier loci. Immunology 2009, 128, 562–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horvath, A.J.; Irving, J.A.; Rossjohn, J.; Law, R.H.; Bottomley, S.P.; Quinsey, N.S.; Pike, R.N.; Coughlin, P.B.; Whisstock, J.C. The murine orthologue of human antichymotrypsin: A structural paradigm for clade A3 serpins. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 43168–43178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nomura, K.; Kanegane, H.; Karasuyama, H.; Tsukada, S.; Agematsu, K.; Murakami, G.; Sakazume, S.; Sako, M.; Tanaka, R.; Kuniya, Y.; et al. Genetic defect in human X-linked agammaglobulinemia impedes a maturational evolution of pro-B cells into a later stage of pre-B cells in the B-cell differentiation pathway. Blood 2000, 96, 610–617. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bernard, L.; Richard, C.; Gelin, V.; Leroux, C.; Heyman, Y. Milk fatty acid composition and mammary lipogenic genes expression in bovine cloned and control cattle. Livest. Sci. 2015, 176, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnet, M.; Bernard, L.; Bes, S.; Leroux, C. Selection of reference genes for quantitative real-time PCR normalisation in adipose tissue, muscle, liver and MG from ruminants. Animal 2013, 7, 1344–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magee, P.; Pearson, S.; Whittingham-Dowd, J.; Allen, J. PPARgamma as a molecular target of EPA anti-inflammatory activity during TNF-alpha-impaired skeletal muscle cell differentiation. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2012, 23, 1440–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaros, L.G.; Bricarello, P.A.; Amarante, A.F.T.; Coutinho, L.L. Quantification of bovine cytokine expression using real-time RT-PCR methodology. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2007, 30, 575–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swanson, K.; Gorodetsky, S.; Good, L.; Davis, S.; Musgrave, D.; Stelwagen, K.; Farr, V.; Molenaar, A. Expression of a beta-defensin mRNA, lingual antimicrobial peptide, in bovine mammary epithelial tissue is induced by mastitis. Infect. Immun. 2004, 72, 7311–7314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.W.; Wang, S.S.; Wu, D.C.; Lin, Y.C.; Ku, C.C.; Wu, C.C.; Chai, C.Y.; Lee, J.N.; Tsai, E.M.; Lin, C.L.; et al. Androgen receptor-mediated apoptosis in bovine testicular induced pluripotent stem cells in response to phthalate esters. Cell Death & Dis. 2013, 4, e907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leroux, C.; Bernard, L.; Faulconnier, Y.; Rouel, J.; de la Foye, A.; Domagalski, J.; Chilliard, Y. Bovine Mammary Nutrigenomics and Changes in the Milk Composition due to Rapeseed or Sunflower Oil Supplementation of High-Forage or High-Concentrate Diets. J. Nutr. Nutr. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westfall, P.H.; Zaykin, D.V.; Young, S.S. Multiple tests for genetic effects in association studies. In Biostatistical Methods (Methods in Molecular Biology); Looney, S., Ed.; Humana Press: Toloway, NJ, USA, 2001; pp. 143–168. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, P.D.; Campbell, M.J.; Kejariwal, A.; Mi, H.; Karlak, B.; Daverman, R.; Diemer, K.; Muruganujan, A.; Narechania, A. PANTHER: A library of protein families and subfamilies indexed by function. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2129–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The UniProt Consortium. UniProt: The universal protein knowledgebase. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D158–D169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Gene Symbol | Accession Number | Gene Name | Fold Change |
|---|---|---|---|
| PDK4 | NM_001101883.1 | [Pyruvate Dehydrogenase (Acetyl-Transferring)] Kinase Isozyme 4, Mitochondrial | 6.80 |
| SLC25A34 | NM_001034497.2 | Solute Carrier Family 25 Member 34 | 4.63 |
| PGLYRP3 | XM_010826801.2 | Peptidoglycan Recognition Protein 3 | 3.31 |
| CPT1A | NM_001304989.1 | Carnitine O-Palmitoyltransferase 1 | 2.77 |
| NEFL | NM_174121.1 | Neurofilament Light Polypeptide | 2.76 |
| KNTC1 | NM_001192091. | Kinetochore-associated protein 1 | 2.58 |
| MBP | NM_001206674.1 | Myelin basic protein | 2.37 |
| DENND3 | XM_010822660.2 | DENN domain-containing protein 3 | 2.33 |
| TFAP2D | NM_001192329.1 | Transcription factor AP-2-delta | 2.29 |
| PFKFB4 | NM_001192835.1 | 6-Phosphofructo-2-kinase/Fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase 4 | 2.04 |
| TRIB2 | NM_178317.3 | Tribbles homolog 2 | 2.03 |
| WC-7 | NM_001281912.1 | WC1 isolate CH149 | 1.85 |
| TMEM50B | NM_001034786.2 | Transmembrane protein 50B | 1.78 |
| ALAD | NM_001014895.1 | Delta-aminolevulinic acid dehydratase | 1.77 |
| LOC517144 | XM_002699133.1 | Putative olfactory receptor 10D3 | 1.74 |
| ESRRA | NM_001191373.2 | Steroid hormone receptor ERR1 | 1.73 |
| SLC25A20 | NM_001077936.2 | Mitochondrial carnitine/Acylcarnitine carrier protein | 1.70 |
| PLEKHA2 | NM_001035383.1 | Pleckstrin homology domain-containing family A member 2 | 1.69 |
| KLF13 | NM_001083533.1 | Krueppel-like factor 13 | 1.67 |
| ARMC1 | NM_001015594.2 | Armadillo repeat-containing protein 1 | −1.43 |
| RPL-37A | NM_001035008.2 | Similar to 60S ribosomal protein L37a | −1.76 |
| BBS9 | NM_001192853.1 | Protein PTHB1 / Bardet-bield syndrom 9 | −1.79 |
| SLC9A7 | XM_015470441.1 | Sodium/Hydrogen exchanger 7 | −1.99 |
| CXCR7 | NM_001098381.2 | Atypical chemokine receptor 3 | −2.10 |
| OOEP | NM_001077869.2 | Oocyte-expressed protein homolog | −2.52 |
| Gene Symbol | Accession Number | Protein Name | Fold Change |
|---|---|---|---|
| Unknown | F1MLW8_BOVIN | Uncharacterized protein / Immunoglobulin light chain, lambda | 5.5 |
| SERPINA3 | G8JKW7_BOVIN | Uncharacterized protein | 2.4 |
| SERPINA3-5 | SPA35_BOVIN | Serpin A3-5 | 2.0 |
| Unknown | Q1RMN8 | TREMBL:Q1RMN8 (Bos taurus) Similar to Immunoglobulin lambda-like polypeptide 1 | 1.9 |
| ALDH18A1 | Q2KJH7_BOVIN | Aldehyde dehydrogenase 18 family, member A1 | 1.7 |
| Unknown | F1MH40_BOVIN | Uncharacterized protein | 1.5 |
| HBA | HBA_BOVIN | Hemoglobin subunit alpha | 1.3 |
| HBB | HBB_BOVIN | Hemoglobin subunit beta | 1.3 |
| PCBP2 | Q3SYT9_BOVIN | Poly(RC) binding protein 2 | 1.2 |
| ARPC2 | ARPC2_BOVIN | Actin-related protein 2/3 complex subunit 2 | 1.1 |
| CCT4 | TCPD_BOVIN | T-complex protein 1 subunit delta | −1.2 |
| DDX17 | A7E307_BOVIN | DDX17 protein | −1.2 |
| GANAB | F1N6Y1_BOVIN | Uncharacterized protein | −1.2 |
| HNRNPH1 | E1BF20_BOVIN | Uncharacterized protein | −1.2 |
| HNRPC | Q3SX47_BOVIN | Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein C (C1/C2) | −1.2 |
| LMAN2 | A6QP36_BOVIN | LMAN2 protein | −1.2 |
| NACA | NACA_BOVIN | Nascent polypeptide-associated complex subunit alpha | −1.2 |
| PDIA4 | PDIA4_BOVIN | Protein disulfide-isomerase A4 | −1.2 |
| PPP2CA | PP2AA_BOVIN | Serine/threonine-protein phosphatase 2A catalytic subunit alpha isoform | −1.2 |
| PSMA3 | PSA3_BOVIN | Proteasome subunit alpha type-3 | −1.2 |
| RPS2 | RS2_BOVIN | 40S ribosomal protein S2 | −1.2 |
| RPS27A | RS27A_BOVIN | Ubiquitin-40S ribosomal protein S27a | −1.2 |
| HNRNPA3 | E1BEG2_BOVIN | Uncharacterized protein | −1.1 |
| PDIA3 | PDIA3_BOVIN | Protein disulfide-isomerase A3 | −1.1 |
| PRKCDBP | PRDBP_BOVIN | Protein kinase C delta-binding protein | −1.1 |
| ACTR1A | F2Z4F0_BOVIN | Uncharacterized protein | −1.3 |
| DHX9 | DHX9_BOVIN | ATP-dependent RNA helicase A | −1.3 |
| GNB1 | GBB1_BOVIN | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(I)/G(S)/G(T) subunit beta-1 | −1.3 |
| KIF5B | F1N1G7_BOVIN | Kinesin-like protein | −1.3 |
| PLBD2 | PLBL2_BOVIN | Putative phospholipase B-like 2 | −1.3 |
| RPN1 | A3KN04_BOVIN | Dolichyl-diphosphooligosaccharide--protein glycosyltransferase subunit 1 | −1.3 |
| SNRPA1 | A6H788_BOVIN | SNRPA1 protein | −1.3 |
| Unknown | F6PWD5_BOVIN | Uncharacterized protein (Fragment) | −1.3 |
| CAPZA2 | CAZA2_BOVIN | F-actin-capping protein subunit alpha-2 | −1.4 |
| FARSB | A8E4P2_BOVIN | FARSB protein | −1.4 |
| HSPA4 | E1BBY7_BOVIN | Uncharacterized protein | -1.4 |
| PAPSS1 | Q3T0J0_BOVIN | 3′-phosphoadenosine 5′-phosphosulfate synthase 1 | −1.4 |
| PPIB | PPIB_BOVIN | Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase B | −1.4 |
| PSMD2 | PSMD2_BOVIN | 26S proteasome non-ATPase regulatory subunit 2 | −1.4 |
| RPS15 | RS15_BOVIN | 40S ribosomal protein S15 | −1.4 |
| STAT5A | STA5A_BOVIN | Signal transducer and activator of transcription 5A | −1.4 |
| CASP6 | CASP6_BOVIN | Caspase-6 | −1.5 |
| RPN2 | RPN2_BOVIN | Dolichyl-diphosphooligosaccharide-protein glycosyltransferase subunit 2 | −1.5 |
| NIPSNAP3A | G3X6L8_BOVIN | Uncharacterized protein | −1.6 |
| EIF3H | EIF3H_BOVIN | Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 3 subunit H | −1.7 |
| YBX1 | YBOX1_BOVIN | Nuclease-sensitive element-binding protein 1 | −1.7 |
| COPS7A | F6QE33_BOVIN | Uncharacterized protein | −1.8 |
| PDLIM5 | G3MY19_BOVIN | Uncharacterized protein | −1.8 |
| MYBBP1A | E1BKX3_BOVIN | Uncharacterized protein | −1.9 |
| RPL10 | RL10_BOVIN | 60S ribosomal protein L10 | −1.9 |
| EEA1 | F1MN61_BOVIN | Uncharacterized protein (Fragment) | −2.0 |
| ARPC1B | ARC1B_BOVIN | Actin-related protein 2/3 complex subunit 1B | −2.2 |
| C789567 | A6H7H3_BOVIN | LOC789567 | −2.5 |
| Gene Symbol | Primers Pair | Amplicon Size (bp) | T °C annealing | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CCL5 | AGC AGT TGT CTT TAT CAC CAG GA | 87 | 60 | [65] |
| TCC AAA GCG TTG ATG TAC TCT C | ||||
| CD 36 | ACA GAT GTG GCT TGA GCG TG | 186 | 58 | [63] |
| ACT GGG TCT GTG TTT TGC AGG | ||||
| CSN2 | CTC AAA CCC CTG TGG TGG TG | 332 | 60 | [1] |
| AAA GGC CTG GAT GGG CAT AT | ||||
| IL1 | GAA TGG AAA CCC TCT CTC CC | 104 | 62 | this article |
| GCT GCA GCT ACA TTC TTC CC | ||||
| IL8 | TGG GCC ACA CTG TGA AAA T | 138 | 62 | [66] |
| TCA TGG ATC TTG CTT CTC AGC | ||||
| LAP | GAA ATT CTC AAA GCT GCC GTA | 114 | 60 | [67] |
| TCC TCC TGC AGC ATT TTA CTT | ||||
| RBP4 | CAA CGG TTA CTG TGA TGG | 98 | 60 | this article |
| GAG GCT GAG TAA GGT TAA TG | ||||
| STAT3 | GTC TAA CAA TGG CAG CCT CTC AGC | 405 | 60 | [68] |
| AAG AGT TTC TCC GCC AGC GTC | ||||
| TAP | GCC AGC ATG AGG CTC CAT | 166 | 60 | [29] |
| AAC AGG TGC CAA TCT GT | ||||
| INSIG1 | CTA GCC TCG AAC TAA AGC CTG ACT | 101 | 59 | [69] |
| TTC CTG TCT CAC CAC ACT TCA TCT | ||||
| Housekeeping genes | ||||
| UXT | TGT GGC CCT TGG ATA TGG TT | 101 | 60 | [63] |
| GGT TGT CGC TGA GCT CTG TG | ||||
| EIF3K | CCA GGC CCA CCA AGA AGA A | 125 | 60 | [63] |
| TTA TAC CTT CCA GGA GGT CCA TGT | ||||
| CLN3 | TTC TGA CTC CTT GGG ACA CA | 62 | 62 | [63] |
| CAA CCT GCC CAC CTA TCA GT | ||||
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pawłowski, K.; Pires, J.A.A.; Faulconnier, Y.; Chambon, C.; Germon, P.; Boby, C.; Leroux, C. Mammary Gland Transcriptome and Proteome Modifications by Nutrient Restriction in Early Lactation Holstein Cows Challenged with Intra-Mammary Lipopolysaccharide. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1156. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20051156
Pawłowski K, Pires JAA, Faulconnier Y, Chambon C, Germon P, Boby C, Leroux C. Mammary Gland Transcriptome and Proteome Modifications by Nutrient Restriction in Early Lactation Holstein Cows Challenged with Intra-Mammary Lipopolysaccharide. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(5):1156. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20051156
Chicago/Turabian StylePawłowski, Karol, José A. A. Pires, Yannick Faulconnier, Christophe Chambon, Pierre Germon, Céline Boby, and Christine Leroux. 2019. "Mammary Gland Transcriptome and Proteome Modifications by Nutrient Restriction in Early Lactation Holstein Cows Challenged with Intra-Mammary Lipopolysaccharide" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 5: 1156. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20051156
APA StylePawłowski, K., Pires, J. A. A., Faulconnier, Y., Chambon, C., Germon, P., Boby, C., & Leroux, C. (2019). Mammary Gland Transcriptome and Proteome Modifications by Nutrient Restriction in Early Lactation Holstein Cows Challenged with Intra-Mammary Lipopolysaccharide. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(5), 1156. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20051156





